#latin linguistics
Text
20 Latin Phrases And Their Italian Equivalents Still In Use Today
Latin: "Carpe Diem" - Seize the day. Italian: "Cogli l'attimo" - Catch the moment.
Latin: "Veni, Vidi, Vici" - I came, I saw, I conquered. Italian: "Venni, Vidi, Vinsi" - I came, I saw, I won.
Latin: "In vino veritas" - In wine, there is truth. Italian: "Nel vino c'è la verità" - In wine, there is truth.
Latin: "Aqua vitae" - Water of life. Italian: "Acqua della vita" - Water of life.
Latin: "Caveat Emptor" - Let the buyer beware. Italian: "Acquirente, attento" - Buyer, be careful.
Latin: "Homo Sapiens" - Wise man. Italian: "Uomo sapiente" - Wise man.
Latin: "Ad Astra" - To the stars. Italian: "Verso le stelle" - Towards the stars.
Latin: "Ars longa, vita brevis" - Art is long, life is short. Italian: "L'arte è lunga, la vita è breve" - Art is long, life is short.
Latin: "Tempus fugit" - Time flies. Italian: "Il tempo vola" - Time flies.
Latin: "Amor Vincit Omnia" - Love conquers all. Italian: "L'amore vince tutto" - Love wins everything.
Latin: "Memento Mori" - Remember that you must die. Italian: "Ricorda che devi morire" - Remember that you have to die.
Latin: "Alea iacta est" - The die is cast. Italian: "Il dado è tratto" - The die is cast.
Latin: "Verbatim" - Word for word. Italian: "Parola per parola" - Word for word.
Latin: "Vox Populi" - Voice of the people. Italian: "Voce del popolo" - Voice of the people.
Latin: "Mea Culpa" - My fault. Italian: "Colpa mia" - My fault.
Latin: "Tabula Rasa" - Clean slate. Italian: "Tavola rasata" - Clean slate.
Latin: "Non sequitur" - It does not follow. Italian: "Non segue" - It doesn't follow.
Latin: "Per se" - By itself. Italian: "Di per sé" - By itself.
Latin: "Status Quo" - The existing state. Italian: "Stato Quo" - The existing state.
Latin: "De facto" - In fact, in reality. Italian: "Di fatto" - In fact.
#latin language#latin linguistics#learning latin#roman#italian language#italian linguistics#italian#latin#learning italian#latin phrases#latin proverbs
93 notes
·
View notes
Text



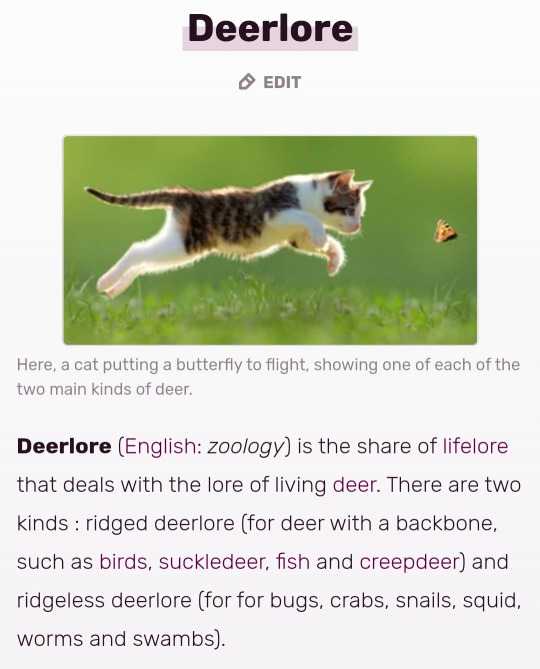
#anglish#deer#english#latin#old english#sorry in advance to aline if this is innacurate in the way pop linguistics often is
50K notes
·
View notes
Text
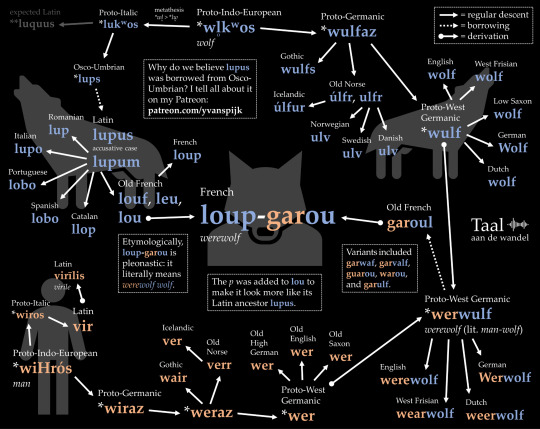
The French word for a werewolf is loup-garou. Etymologically, this compound is pleonastic: garou means 'werewolf' and loup means 'wolf'. It's also hybrid: loup stems from Latin lupus whereas garou was borrowed from West Germanic *werwulf. Click the image for more.
#historical linguistics#linguistics#language#etymology#english#latin#french#old french#proto-germanic#proto-indo-european#proto-italic#proto-west germanic#lingblr#werewolf#werewolves
989 notes
·
View notes
Text
French lessons: ✨Je suis allé en France. C’était bien. J’aime le football. Mon père n’aime pas le football.✨
Latin Lessons: 💀gladiator in viro gladium posuit. multum sanguinis fluxit. Homo mortuus est.💀
#I hate French more than I can express#I went to france. it was good. I like football. my father does not like football.#the gladiator put the sword in the man. a lot of blood flowed. The man died.#Latin lessons#Latin#French#school life#GCSEs#languages#linguistics
463 notes
·
View notes
Text
peninsula
peninsula comes from the Latin paene īnsula, literally ‘almost an island’. How cute is that?

661 notes
·
View notes
Note
I just recently started following you so i don't have the full lore of your murderous gay religiously traumatized doggos, BUT, from my understanding, they are Italian and i don't know what part of Italy they are from, yet i can't help headcanoning Vasco as Tuscan, while Machete is probably from some part of Veneto. And as an Italian who has heard Tuscans and Veneto dialet, well it's an hilarious mental image.
Vasco is indeed Tuscan, Florentine to be specific. He comes from a wealthy and influential noble family that has lived in Florence for centuries. He's proud of his roots, and it's usually easy for strangers to tell where he's from. He's a resonably successful politician and has worked as an ambassador and representative of Florence on numerous occasions.
Machete is originally Sicilian (ironically about as far from Veneto as possible), although he was taken to mainland at young age and has lived in several places since then, before ending up in Rome. The way I see it, he exhibits very little local color, his demeanor and (even though Italian hadn't become a standardized language yet) way of speaking are formal, neutral and scarcely give away any hints about his personal history, at least in the 16th century canon.
#I tend to take the easy way out with the various Italian dialects/languages and temper their effect on how the dog world works#even though to my understanding in reality they differ drastically from each other even today and they aren't always mutually intelligible#especially when you compare northern and southern ones#I know at least Sicilian is so different from modern day Italian it's considered a separate language entirely#it isn't the only one but I'm not a linguist and not even Italian so I'm not really qualified to be explaining any of this to you#main point is that my dogs are well traveled educated and adaptable so I'd like to believe that they manage#otherwise making this whole scenario work would become very complicated#language barriers aplenty#Machete is a fast learner with a natural knack for languages so he absorbs/decodes new ones easily#and I can see him acting as an interpreter if necessary#which is a valuable trait for someone working as the secretary of state I'd imagine#a lot of people he ends up dealing with speak at least passable Latin so at a pinch they might perhaps try switching to that?#Vasco might have a Tuscan flavor but Machete is more of a blank slate (at least in public and at work)#answered#fallenoftheromaempire#feel free to correct me if I've gotten something wrong I'm not an expert and this stuff is complicated for an outsider
196 notes
·
View notes
Text
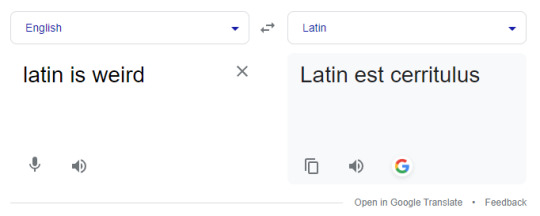
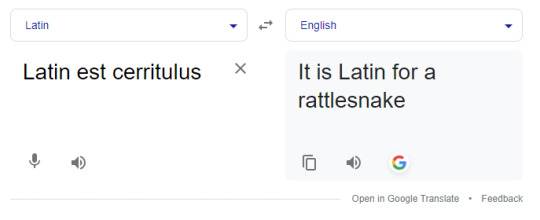
I love latin google translate
191 notes
·
View notes
Text
Because there's an eclipse, in latin class my teacher had us translate all these old Roman dudes thoughts and shit on eclipses and incase you didn't know they filled a basin with oil or tar so they could see the reflection of the eclipse and study it, or just watch it like normal because they were also obsessed like we are
#latin#language#eclipse#school stuff#high schoolers#teenagers#school#high school#rome#philosophy#oil and tar#its cause they wouldnt ripple#learning#learnsomethingneweveryday#linguistics#facts#fun facts#roman dudes#it was called like “questions about nature”#translation#we kinda failed at that part of class tho#solar eclipse
105 notes
·
View notes
Text
I love the latin 4th declension; it truly serves no other purpose than trolling.
"Oh domus ends in -us so it must be 2nd declension masculine"
OBJECTION
domus, domūs, domui, domum, domu, domus, domūs, domuum, domibus, domūs, domibus, domūs also it's feminine
#linguistics#linguistic#languages#shitpost#lingblr#linguist shitpost#latin#classics#classics shitpost#classics memes#latin memes#latin meme#latin shitpost#they also tell you it's only a couple words but don't tell you they're the most important words
78 notes
·
View notes
Text
Strictly speaking, “vriska” is plural; the singular is “vriskum”.
#language#linguistics#word nerdery#media#comics#webcomics#homestuck#spurious latin#this is a serious post
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
How the Renaissance Shaped the Italian Language
The Renaissance, a period of immense cultural, artistic, and intellectual growth in Europe, played a crucial role in the development of the modern Italian language. This era, spanning the 14th to the 17th century, witnessed a revival of interest in the classical art, literature, and learning of ancient Greece and Rome, significantly influencing the evolution of the Italian language.
Dante Alighieri's Contribution:
Dante Alighieri, often referred to as the "Father of the Italian language," was instrumental in establishing the Tuscan dialect as the standard for the Italian language. His most famous work, "The Divine Comedy" ("Divina Commedia"), written in the early 14th century, was one of the first major works of literature written in the vernacular, i.e., the local Tuscan dialect, instead of Latin. Dante's choice of the vernacular over Latin marked a pivotal moment in the development of Italian as a literary language.
Dante's works demonstrated the expressive and aesthetic possibilities of the Italian language, elevating its status and proving it could be used for serious, high literary pursuits, a domain previously reserved for Latin.
Petrarch's Influence:
Francesco Petrarca, known as Petrarch, further solidified the use of the vernacular in literature. He is best known for his Italian sonnet sequences, which focused on themes of love, personal reflection, and the human experience. Petrarch's poetry, particularly his "Canzoniere" (Songbook), greatly influenced Italian literature and language. His refined use of the vernacular and his development of the Italian sonnet format set a standard for lyrical poetry in Italian.
Boccaccio's Contributions:
Giovanni Boccaccio, another key figure of the Italian Renaissance, also contributed significantly to the development of the Italian language. His most famous work, "The Decameron," is a collection of novellas written in the vernacular. It not only had a profound impact on Italian literature but also helped to shape the Italian language by demonstrating its suitability for both serious and more lighthearted, secular topics.
Impact on Standardizing Italian:
The works of these authors were essential in the standardization of the Italian language. Their choice of the Tuscan dialect, particularly that of the Florentine region, as their literary medium contributed to its status as the basis of standard modern Italian.
Legacy and Continued Influence:
The Renaissance's focus on humanism and the return to classical sources also played a role in shaping the Italian language. This period encouraged a deeper exploration of the human condition, emotion, and intellect, aspects that were deeply integrated into the Italian language through literature and art.
In sum, the Renaissance was a period of reawakening that not only rediscovered the riches of classical antiquity but also set the foundation for the development of the modern Italian language. The works of Dante, Petrarch, and Boccaccio were not just literary masterpieces but also linguistic milestones that established the prestige and potential of the Italian vernacular, leading to its evolution into the modern Italian language we know today.
#italian language#learning italian#italian linguistics#renaissance#italian#italian literature#italian culture#romance languages#learning latin#latin linguistics#latin language#roman#italy#italian landscape
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
Daily Etymology #158
Vaccine
The word 'vaccine' originally referred only to cowpox, as it was derived from the Latin vaccinus, meaning related to cows, from vacca meaning cow. This term was initially used to refer to cowpox being used as a method of immunisation to smallpox. When other vaccines were developed, they kept the name of the first vaccine against smallpox, developed by Edward Jenner.
157 notes
·
View notes
Quote
Gretchen: I think the best-known example of do you do the source language versus the target language in terms of plural in English is a certain little creature with eight legs.
Lauren: The octopus.
Gretchen: The octopus.
Lauren: Which I just avoid talking about in the plural at all to save myself a grammatical crisis.
Gretchen: I admit that I have also done this. If you were gonna pluralise “octopus” as if it’s English, it would just be “octopuses.” It’s very easy. But there’s a fairly long-standing tradition in English of when a word is borrowed from Latin to make the plural the actual Latin thing. Because, historically, many English speakers did learn Latin, and so you want to show off your education by using the Latin form even though it’s in English. So, if you’re going to pretend that “octopus” is Latin, then you wanna say, “octopi.” However, there is yet a third complication, which is that “octopus,” in fact, is actually Greek – “octo” meaning “eight” and “pus” meaning “feet. So, Greek does not make these plural by adding I to it. In that case, there has recently become popular a yet even more obscure and yet even more pretentious, to be honest, plural.
Lauren: Is there where you say, “octopodes”?
Gretchen: Well, this is where I used to say, “octopodes.” But I have recently learned that, apparently, it is, for maximum pretentiousness, /aktaˈpodiz/.
Lauren: You’ve out-pretentioused my out-pretentiousness.
Excerpt from Lingthusiasm episode ‘Many ways to talk about many things - Plurals, duals and more’
Listen to the episode, read the full transcript, or check out more links about morphology, syntax, and words.
#Language#linguistics#lingthusiasm#podcasts#quotes#plural#plurals#grammar#words#English#Latin#duals#octopus#octopuses#octopi#octopodes#pronunciation#maximum pretentiouness#morphology#syntax
253 notes
·
View notes
Text
The word for 'I' has many different forms in the Romance languages, such as French je, Italian io, Portuguese eu and Spanish yo. Yet all these forms stem from one Latin word: egō. Here's how egō step by step changed into a selection of its Romance descendants.
People who subscribe to my Patreon get access to extra information further explaining what you see on the infographics and videos. To give you an impression, here's the text that goes with this video.
How did these forms originate?
Latin, Late Latin and Sardinian
Around the second century AD, the [g] sound of Latin egō (as in English go) started to weaken. It became a fricative sound similar to the one in Modern Spanish agua 'water'.
In this form, with only minor vowel changes, it survived until this very day in certain Nuorese dialects of Sardinian: ego. These geographically isolated dialects are known for being the most conservative descendants of Latin. Their most notable trait is the conservation of the Latin [k] and [g] sounds before i and e: Latin centum '100' with [k] became kentu, whereas in Italian it became cento with the [tʃ] sound of English check, and in French, Portuguese and many variaties of Spanish it respectively became cent, cento/cem and ciento/cien with [s].
In a Late Latin text from the 6th century, we encounter egō as eo. By this time, the consonant had been dropped. It's this form that's considered Proto-Romance, i.e. the form that gave birth to all descendants except the form in the Nuorese dialects I discussed above. Eo even remained practically intact in a number of other Nuorese dialects.
Portuguese and Romanian
In Portuguese and Romanian, the -o of eo became w-like: eu. However, the Romanian spelling hides the diphthongisation of [ɛ] to [jɛ], later [je]. Cfr. ferrum > fier, and pellem > piele.
Italian and Neapolitan
In Italian, [ɛ] became [e] and then [i], a sound close to it: io. This sound change didn't only happen in this word: compare mio 'my' (from Old Italian meo) and Dio 'God' (from Deo) with Portuguese meu and Deus. In Neapolitan, the -o weakened and became the schwa sound of English words like roses.
Spanish and French
The form io must have also existed in the distant ancestors of Spanish and French, but there, [i] didn't stop changing: it turned into a [j], its consonantal counterpart. In both languages, this [j] eventually underwent fortition: it became a stronger consonant similar to the one in English joke, which eventually weakened again in Modern French je.
In South American Spanish, interesting things are happening. The sound change that yo pronounced as [ʒo] has undergone in the Rioplatense dialects in Uruguay and the southern part of Argentina is called zheísmo, and what's happening in Buenos Aires and spreading through Argentina is called sheísmo: [ʃo].
#historical linguistics#linguistics#language#etymology#latin#french#spanish#old french#old spanish#romanian#sardinian#portuguese#italian#proto-romance#video#audio#lingblr#late latin
704 notes
·
View notes
Text
god I love to meet people with different cultural backgrounds so much and it feels so good to explore their cultures and customs which makes me wanting to learn a language they speak so bad especially as a someone who is in love with language learning
#culturalexploration#culture#different cultures#foreign languages#langblr#langblog#language learning#english language#language#languages#latin language#aspiring polyglot#polyglot#lingblr#linguistics
134 notes
·
View notes