#less risk averse
Note
Wait, aww does dipper sometimes cook for bill? (Well saying making spicy instant noodles is cooking is a little far fetched but still)
I mean, sometimes!
In the Familiar AU, Dipper and Mabel basically grew up with Stan - and experienced the cooking skills thereof. When faced with choosing a life of glitter in his digestive tract, or earnest but burnt waffles, Dipper figured he might as well learn to cook. He's not winning any culinary awards or anything, but he can follow a recipe and make a decent pasta dish.
Besides. The alternative to Dipper cooking for Bill - is Bill cooking for Dipper. And since Bill's idea of delicacies involve terms like 'unholy abomination', 'unbearably spicy', or 'still squirming', Dipper's more likely than not to shove him out of the kitchen.
They mostly get lot of takeout.
#answers#Technically Bill's the more *skilled* cook. He's super old and eternally knowledgeable and all#Seen everything and learned so much. Probably would watch British Bakeoff while really drunk and make rude commentary#In theory he could make incredible human-edible meals - but where's the fun in that??? They're so BORING#He likes to get Experimental instead!#Good thing Dipper's experienced with less than optimal cooking. He's got a strong stomach#Mostly Bill's uninterested in cooking. When he *does* cook it's best not to ingest the contents unless you're feeling really lucky#So mostly Dipper doesn't#Bill may not *intentionally* poison Dipper - but he's risk-averse#Seriously there's a lot of microwave meals and takeout for these two#Dipper's not gonna spend time to cook when he could be doing other things. Something he takes after Ford in#The upside of Bill having very - shall we say - *expansive* tastes in his dining is that even when Dipper messes up a recipe#Bill eats it without complaint. Maybe some mockery! But not like. Bitching about it.#Dipper just shrugs and is glad the food's not going to waste#Time for instant noodles again#I will add the single exception for Bill's culinary contributions - If Dipper's really sick. Or achingly injured#Bill *might* make a pretty decent soup
65 notes
·
View notes
Note
have you ever given the boy scout flying head?
Not while flying, no. I'm good with death by orgasm but maybe not if it's the first event in a chain reaction that might lead to a crash.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
sometimes i think i'm way too unkind to myself.............
#i'm currently beating myself up over a very small decision i've made recently#at 2am... like i need to sleep but my brain can't stop!!!#i just keep thinking that i could've made a better decision#and whether this decision is really worth it......#and like my mind's always working in resource scarcity mode which is !! crazy!!!! is it bc i'm asian n brought up to be prudent n cautious#ok probably has less to do with me being asian n more being brought up in an environment of risk averseness......#when tbh using more resources to power pursuits shouldn't even be taboo. we should just go for what we want to try as fearlessly as we can..#.. shouldn't we?#my brain knows it but part of me is like 'ack ..... i'm a shitty disorganised thoughtless insane adult'#like there's jsut so much i wanna do with my life and outside of work but i'm just so guilty about pursuing them#like i really wanna make some Big Life decisions. but if i'm here beating myself up over a small one then idk when i'm ever gonna work up-#-the courage to make a Big One#good night i guess#personal#shdkdkmdnskdkfkdkdkd
1 note
·
View note
Text
So Venus is my favorite planet in the solar system - everything about it is just so weird.
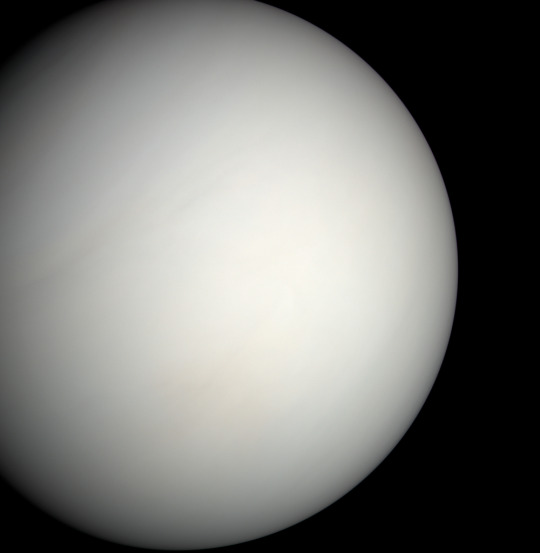

It has this extraordinarily dense atmosphere that by all accounts shouldn't exist - Venus is close enough to the sun (and therefore hot enough) that the atmosphere should have literally evaporated away, just like Mercury's. We think Earth manages to keep its atmosphere by virtue of our magnetic field, but Venus doesn't even have that going for it. While Venus is probably volcanically active, it definitely doesn't have an internal magnetic dynamo, so whatever form of volcanism it has going on is very different from ours. And, it spins backwards! For some reason!!
But, for as many mysteries as Venus has, the United States really hasn't spent much time investigating it. The Soviet Union, on the other hand, sent no less than 16 probes to Venus between 1961 and 1984 as part of the Venera program - most of them looked like this!

The Soviet Union had a very different approach to space than the United States. NASA missions are typically extremely risk averse, and the spacecraft we launch are generally very expensive one-offs that have only one chance to succeed or fail.
It's lead to some really amazing science, but to put it into perspective, the Mars Opportunity rover only had to survive on Mars for 90 days for the mission to be declared a complete success. That thing lasted 15 years. I love the Opportunity rover as much as any self-respecting NASA engineer, but how much extra time and money did we spend that we didn't technically "need" to for it to last 60x longer than required?
Anyway, all to say, the Soviet Union took a more incremental approach, where failures were far less devastating. The Venera 9 through 14 probes were designed to land on the surface of Venus, and survive long enough to take a picture with two cameras - not an easy task, but a fairly straightforward goal compared to NASA standards. They had…mixed results.
Venera 9 managed to take a picture with one camera, but the other one's lens cap didn't deploy.
Venera 10 also managed to take a picture with one camera, but again the other lens cap didn't deploy.
Venera 11 took no pictures - neither lens cap deployed this time.
Venera 12 also took no pictures - because again, neither lens cap deployed.
Lotta problems with lens caps.
For Venera 13 and 14, in addition to the cameras they sent a device to sample the Venusian "soil". Upon landing, the arm was supposed to swing down and analyze the surface it touched - it was a simple mechanism that couldn't be re-deployed or adjusted after the first go.
This time, both lens caps FINALLY ejected perfectly, and we were treated to these marvelous, eerie pictures of the Venus landscape:

However, when the Venera 14 soil sampler arm deployed, instead of sampling the Venus surface, it managed to swing down and land perfectly on….an ejected lens cap.
#space#space history#venus#NASA#Venera#spost#I will talk all day about venus#ask me about venus floating sky cities#unpopular opinion venus > mars#this is probably my favorite space history story#the surface of venus is made of lens caps#don't try to tell me the universe doesn't have a sense of humor#well#I guess its more that people have a sense of humor and we happen to live in the universe
28K notes
·
View notes
Text
Things I've learned from getting covid for the first time in 2023
I wear an N95 in public spaces and I've managed to dodge it for a long time, but I finally got covid for the first time (to my knowledge) in mid-late November 2023. It was a weird experience especially because I feel like it used to be something everyone was talking about and sharing info on, so getting it for the first time now (when people generally seem averse to talking about covid) I found I needed to seek out a lot of info because I wasn't sure what to do. I put so much effort into prevention, I knew less about what to do when you have it. I'm experiencing a rebound right now so I'm currently isolating.
So, I'm making a post in the hopes that if you get covid (it's pretty goddamn hard to avoid right now) this info will be helpful for you. It's a couple things I already knew and several things I learned. One part of it is based on my experience in Minnesota but some other states may have similar programs.
--------
The World Health Organization states you should isolate for 10 days from first having symptoms plus 3 days after the end of symptoms.
--------
At the time of my writing this post, in Minnesota, we have a test to treat program where you can call, report the result of your rapid test (no photo necessary) and be prescribed paxlovid over the phone to pick up from your pharmacy or have delivered to you. It is free and you do not need to have insurance. I found it by googling "Minnesota Test to Treat Covid"
--------
Paxlovid decreases the risk of hospitalization and death, but it's also been shown to decrease the risk of Long Covid. Long Covid can occur even from mild or asymptomatic infections.
--------
Covid rebound commonly occurs 2-8 days after apparent recovery. While many people associate Paxlovid with covid rebound, researchers say there is no strong evidence that Paxlovid causes covid rebound, and rebounds occur in infections that were not treated with Paxlovid as well. I knew rebounds could happen but did not know it could take 8 days. I had mine on day 7 and was completely surprised by it.
--------
If you start experiencing new symptoms or test positive again, the CDC states that you should start your isolation period again at day zero. Covid rebound is still contagious. Personally I'd suggest wearing a high quality respirator around folks for an additional 8-9 days after you start to test negative in case of a rebound.
--------
Positive results on a rapid test can be very faint, but even a very faint line is positive result. Make sure to look at your rapid test result under strong lighting. Also, false negatives are not uncommon. If you have symptoms but test negative taking multiple tests and trying different brands if you have them are not bad ideas. My ihealth tests picked up my covid, my binax now tests did not.
--------
EDIT: I'd highly suggest spending time with friends online if you can, I previously had a link to the NAMI warmline directory in this post but I've since been informed that NAMI is very much funded by pharmaceutical companies and lobbies for policies that take autonomy away from disabled folks, so I've taken that off of here! Sorry, I had no idea, the People's CDC listed them as a resource so I just assumed they were legit! Feel free to reply/reblog this with other warmlines/support resources if you know of them! And please reblog this version!
--------
I know that there is so much we can't control as individuals right now, and that's frightening. All we can do is try our best to reduce harm and to care for each other. I hope this info will be able to help folks.
#covid#covid 19#harm reduction#apparently only 16% of Americans even got their booster#it's wild out there#which makes sense because our public health messaging has been super unhelpful and intentionally shifted the burden#of infection control onto individuals to avoid us holding them accountable because it's politically and economically inconvenient to them
9K notes
·
View notes
Text
Signing up for classes when I'm spiralling like this feels so silly. Like who knows I may be fine in 2 months (anything could happen!) but. Haha.
#I just signed up for the 100 level course because I'm in no state to email the prof for 201 about whether or not I'd qualify#feeling very risk-averse. like if it ends up all being material I've already covered then that just means there'll be less risk of failure#right?#i don't know how to do this#even the thought of being back in a classroom after 5+ years away is like. surreal.
1 note
·
View note
Text
chemistry is so funny to me like yeah tell me more about the absurd and gruesome torment this vanishingly small amount of Stuff could inflict upon me and then EXACTLY how and why, followed by all of the people who have already done it just to check and make sure it still does that
#'this can set concrete on fire' REALLY? YOU PROMISE?#and yet im extremely risk averse in all things. i would run away screaming from all of my favorite chemicals#<- type of guy to have a favorite chemical much less multiple#i dont regret not getting a degree in chem because AHHHHH but i do miss getting to do it in a lab setting#alex lore
1 note
·
View note
Text



here's the reason you procrastinate
based on Fuschia Sirois' research
everyone procrastinate at some point. research suggests that almost 1 in 4 people procrastinate on a fairly regular basis, and the rates are even higher among college and university students ( 50% of them procrastinate regularly and about 85-90% do so occasionally ).
because procrastination is so common we tend not to put too much thought into it, in the end what is the problem? it's just delay.
well, it's not. actually procrastination is harmful delay ( so defined by the researchers ); it is a form of delay which is:
voluntary
unnecessary
involves important tasks which you intended to do
people often underestimate the consequences of procrastination and how debilitating and harmful it can be. if you delay dealing with ( for example ) your academic works, of course you can expect some negative results in that area, but what about the collateral consequences of it?
research has shown that people who have problems with procrastination have low physical and mental health and practice less healthy behaviors. they deal with depression, stress and anxiety.
just think about the enormous amount of stress that procrastination brings: first of all, constantly chasing deadlines. deadlines can nag anyone, even those who don't struggle with delaying, but then it ends, the job is turned in, and everything goes back to normal. for procastinators this is not the case, they will keep putting off important things and will constantly end up with an imminent deadline.
so, if it's so harmful for your health, why do people do it? some people think it's about laziness or poor time managment, but actually:
laziness isn't procrastination. if you're lazy you don't have the energy to do anything, instead procrastinators are always busy with a thousand non-essential tasks to do, in fact they avoid doing one specific task, not every task ( for example if i need to study, but i'm procrastinating it, i end up cleaning my room )
poor time managment it's actually a symptom of procrastination, not a cause.
from a psychological perspective the origins of procrastination are rooted in negative emotions and the urge to cope with them through avoidance. so actually procrastination is about poor mood managment, not poor time managment.
procrastination starts when we have a task that's unpleasant, but we have to do it. and we use procrastination then as a way to get relief from those negative emotions associated with the task, so basically it's not even about avoiding the task, but it's about avoid the negative emotions that we associate with the task.
we need to avoid stress and aversive feeling that come with the task, especially when we don't feel like we can manage those negative emotions at the moment. so we take the task, we put it aside, and it's instant relief. it's fast, it's easy and it works for a little while, then that sense of shame, guilt and self-blame starts to kick in.
so why do we keep procrastinating? for that sense of relief, because that made us feel rewarded and we tend to repeat behaviors that rewarded us. this can easily lead to a cycle of procrastination.
however, the negative thoughts that we have ( "why didn't i start earlier?", "i'm letting myself down" etc. ) don't actually make us take action. they just add layers of layers on pre-existing negativity.
so how do you get out of the procastination cycle?
go back to valuing your task, if it's so important that you do it, remind yourself why you are doing it
remember that we tend to overestimate the discomfort that a given challenge will bring us. probably your task isn't even that time-consuming, unpleasant and frustrating
be compassionate and and forgive yourself, it's an effective strategy to reduce the negative emotions associated with the task. you are not the first nor the last person to procrastinate, we are all human and we all make mistakes. research has shown that doing so reduces the risk of procastination.
hope you enjoyed this little explanation, here's my sources: https://youtu.be/xTEPNxx0MsA
#academia#college#education#note taking#school#student#study aesthetic#study blog#study inspiration#study motivation#study notes#study tips#studyblr#studyinspo#studyspo#chaotic academia#light academia#academic validation#dark academia#uni life#university life#university#motivation#procrastination#why you procrastinate
684 notes
·
View notes
Text
⚣ 5+1: TikTok Trends 🤳🏽


⚣🤳🏽 A/N → I kept seeing all these couple trends on TikTok and it made me think of how Jason would react to these very same trends with his boyfriend...so I wrote it. tee hee
WARNINGS: established relationship | social media trends | relationship goals | fluff/comfort | jason's had enough |
⚣🤳🏽 Summary → Five times Y/N did a social media trend/prank on Jason and the one time the vigilante finally got his boyfriend back.
⚣🤳🏽 Words → 3.7K
REBLOGS & replies are greatly appreciated, please! 💛
⚣ ENJOY 🤳🏽

Social media is an interesting thing with a variety of uses. You could use it to connect with old friends from high school and college, remembering the good ole days. It could be a place to connect with other people in specific communities so individuals could find those they related to and shared similar views and interests with. More than ever, it could be used to spread activism and political messages.
For Y/N L/N, it was a place for him to display his loving and chaotic relationship with his boyfriend Jason Todd.
They both had very different relationships with social media.
Y/N was a whirlwind of hashtags and filters, a living embodiment of the digital age. His phone was an extension of his hand, scrolling through endless videos and GRWMs where they were always running late for whatever they were getting ready for.
The boy took his college studies seriously, but the thought never not crossed his mind that he could become a full-time content creator if he wanted to. Ask any of his friends or especially his boyfriend, the dude was a walking meme who kept hundreds to thousands of reaction pictures and videos on his phone which is something he successfully managed to get his boyfriend addicted to as well.
No seriously, it had gotten so bad that Bruce had to reach out to Y/N to see if he could get Jason to stop or at least delete the photos from his phone. Apparently, in their family group chat, his boyfriend had taken to sending some very targeted and specific images.
It was fine until Bruce said something about Jason being reckless or something and risking lives, and his boyfriend responded with some interesting images and a very petty caption.


Jason: this u?
It was safe to say Bruce was less than amused, though apparently everyone else found it hilarious. But, sadly Y/N had to inform the billionaire that he wouldn’t be able to get his boyfriend to stop even if he tried and that he was also a victim of this new ordeal.
Bruce was confused until Y/N showed him a picture Jason sent him after Y/N refused to come cuddle him because he was studying for a midterm.

Jason: get ur ass in here now or else...respectfully
This was the exact fun and chaotic energy Y/N wanted to share with the world on social media and TikTok. But, Jason had a different relationship with it than his boyfriend.
On the opposite end of the spectrum, Jason was a firm believer in a simpler existence, preferring face-to-face conversations over likes and retweets. He possessed a refreshing aversion to the constant buzz of notifications and the pressure to document every meal or outing.
His only exception was Twitter, where he could voice his unhinged and questionable thoughts freely without raising suspicion or judgment because it was…well, it was Twitter.
However, that did not stop Y/N from using his poor and innocent lover in his little TikTok exploits when he wanted to.
The first one was something innocent, at least in his eyes. He and Jason were in their shared apartment near Y/N’s campus. They were lying together on the couch, with Y/N parallel to the piece of furniture while Jason sat up properly with his boyfriend’s legs over him.
He was silently reading a book while Y/N pretended to scroll through social media, fidgeting now and then when Jason would accidentally tickle his feet while unconsciously rubbing his feet. Then, the sneaky little man would pull up an audio from TikTok of a man’s voice, talking as if they were on a Facetime call.
At first, Jason didn’t think anything of it when he heard the ring from his boyfriend’s phone and he knows that he frequently calls his parents or friends. Besides, Jason knows almost everyone that Y/N knows so it definitely wasn’t out of the ordinary.
So why the fuck did he not recognize that voice that was speaking on the other end of Y/N’s phone? More than ever, why was it male?!
The second he heard the random male voice ask his boyfriend why he was smiling like that, the phone was snatched out of his hand and Jason was prepared to threaten extreme bodily harm to whoever was on the other side of that phone.
So imagine his confusion when was looking back at himself.
When he noticed the recording button at the bottom, he looked toward his boyfriend who was trying his best to hold in his laughs and was doing a terrible job. Y/N made sure to snatch his phone back though so Jason couldn’t delete the footage.
Jason allowed it though despite his annoyance, seeing Y/N happy and laughing always trumped over any negative feelings he was experiencing. However, he did give his boyfriend a nice gentle lesson about what happens when he plays with the vigilante’s jealous side.
It ‘twas not gentle though, not one bit.
And Y/N was a little fucker who never learned his lesson. Proud of it too.
The second time wasn’t even a week later after he’d seen a new trend going around the clock app that he just knew he wouldn’t be able to resist.
“Might be a little bit controversial but get ready with me while I give you my reasons on why cheating on your significant other is okay in certain scenarios.”
In under 5 seconds, the bathroom door shot open after the apartment sounded like a large predator had come running through it. Judging by the very unamused look Y/N was receiving, it may have been just that.
Y/N had to do his best not to laugh (or moan) at the image on his phone’s screen of a hulking, pissed-off Jason standing over him as he watched his skincare in silence. He knew his followers were going to get a kick out of this, probably detailing the filthiest things their horny little minds could cook up in his comment section like the little horny bastards they were.
Though, Y/N would be no better.
Jason still didn’t say anything, continuing to stare down at him like an angry parent who’d just been embarrassed in church by their child.
“Um, can I help you?” Y/N asked, desperately holding back the smile pulling at the corner of his lips.
Jason’s dark hair fell over his forehead, his white streak hanging lazily between as his eyes narrowed down at his smaller boyfriend, his large, intimidating arms crossed over his chest. Y/N had to take a large breath to calm down the fluttering in his stomach.
Why did his boyfriend have to be so hot? The world was not fair.
When Jason continued to not say anything, just staring silently at his lover, Y/N decided to finish his skincare in silence while checking to make sure his video was still recording.
When about five minutes passed and neither of the boys said anything, the taller and larger male started to become slightly confused. Why wasn’t Y/N saying anything? He wasn’t crazy, knowing exactly what he heard until a lightbulb went over his head and he realized what was going on.
Once Y/N finished patting his face with sunscreen, he looked up to his boyfriend to see him with a now slightly less peeved expression and more of a smug, amused look.
“What?”
“You think you’re funny, don’t you?”
“I think I’m quite hilarious actually.”
Jason didn’t say another word before turning on his heel, slowly walking out of the bathroom back towards the kitchen with that damn slutty walk of his. Seriously, why was the universe so unfair to Y/N? Then again, he definitely wasn’t complaining.
But, just because Jason realized what was going on didn’t mean he was going to just let the harmless prank go so easily. Y/N would be reminded once again how petty his boyfriend could be in the worst ways possible.
There really should be a hotline or emergency number for guys whose boyfriends decide to tease and edge them for over an hour. These crimes should not go unchecked!
Anyways…Y/N still didn’t learn his lesson. Third time’s a charm.
By this time, Jason had become well aware that Y/N would not stop using him in his little videos and pranks, so he figured if you can’t beat em, join em. He got his own TikTok account and only followed his boyfriend while also doing his best to keep up with whatever trends were going around, especially with couples so he could stay one step ahead.
This proved very useful, as when the ‘Water’ song by Tyla became a trend all over TikTok, Jason was more than aware of what his boyfriend was trying to do when he noticed from the corner of his eyes him recording him, pretending like he was just watching the videos.
Ah ah ah, gonna have to try harder than that, babe. Jason didn’t even budge like he was going to look, not like he would’ve either way.
But, he was NOT prepared to come home one day to find his boyfriend with his tripod set up, starting the countdown timer to record a video. The second the video started recording and Jason realized what song was playing, he didn’t waste a second before running and tackling Y/N out of the camera view before he could even hit the first beat.
He didn’t care if he fell for that one, those moves were for Jason’s eyes only. Something else the vigilante was going to have to remind his boyfriend about.
But, at least when Y/N looked at the footage, he realized he finally had something to post for that trend where people ran and tackled their significant others to that Barbie Girl remix. He’d always wanted to do that trend but hadn’t met Jason yet, so he was a bit too single to do it.
The fourth time was something also a little bit simple, less of a prank and more of Y/N just being a little shit that went looking for trouble.
When Jason was once again in the kitchen cooking, with his usual tank-top and jogger combo, Y/N thought it a perfect opportunity for him to get some revenge on his boyfriend since the gargantuan male always found it funny to slap Y/N on his butt hard as shit. Vengeance was needed.
So, when Jason wasn’t looking, Y/N walked into the kitchen positioning his phone in another spot so it could see the entire action, knowing if he tried to be sneaky, the vigilante would still catch on to him and turn around. He walked up behind him and gave his boyfriend a little hug as usual and a kiss on his back, something the towering male pretended not to be giddy at.
However, his sweet, tender moment was interrupted when he felt a medium-palm land on his ass with a precision aim, leaving a tingling sting behind.
“Payback!” Y/N decreed, already turning around and running for their shared room.
When he went back and looked at the footage later, he had to admit, the view of Jason turning around slowly as Y/N scurried away was very amusing. Especially considering he layered the video with the Wii Sports fencing music as his mammoth-sized man stalked after him like a predator cornering its prey.
His vengeance did not last long.
By this time, Jason had become somewhat of a regular presence on Y/N’s TikTok account, and all of his followers wanted more content with the two of them together.
So, after a long time coming, Y/N had managed to successfully convince Jason to do a video with him on camera. They decided to do the Alphabet challenge, something Y/N thought he’d have an easy win at.
He was not prepared for his boyfriend's extensive vocabulary.
“Are you ready to start, honey?” Y/N started sneakily, thinking his boyfriend wouldn’t catch it.
“Bet you thought you were slick, huh?” Jason replied with his usual smug look.
“Can you be any less smug?” Y/N said with a playful eye roll.
“Don’t act like you don’t like it.”
At that point, it was almost like they weren’t even doing a challenge, but rather doing their usual relationship banter back and forth that just happened to be getting recorded. The longer it went on, the more chaotic it became, both boyfriends pulling the absolute wildest sentences they could think of out of their mouths to throw the other ones off.
“Suck my ass.”
“Turn around”
He’d also underestimated Jason’s lack of shame and vulgarness.
“Explain how you get a body like that?”
“From fucking whiny little pretty boys like you.”
Oh.
Yeah, he should’ve thought this one through a little more.
They’d managed to go through the whole alphabet at least three times, going from bantering back and forth to Y/N reciting lines from movies he could both think of, to Jason reciting lines from some of his favorite books. The smaller man at some point figured he could start using lines from pop culture and trends to throw his colossal boyfriend off. However, he was absolutely not prepared for him to quote the Rachel voicemail, word for word, knowing how much that whole message always made him weak.
“This is for Rachel you big, fat, white, nasty-smelling fat BITCH.”
Why did he have to put so much emphasis on the ‘bitch’ part? He threw in the towel there and let Jason have it, swearing victory on their next face-off.
Now, Y/N didn’t think it would go any farther than that. He figured he would keep making videos pranking Jason and that now and then, the vigilante would begrudgingly join in.
Oh, he was wrooong…
Frankly, Y/N should have known Jason was playing a prank on him the second he called him by his actual name instead of one of his pet names. The vigilante always got upset at him when he used Jason’s actual name instead of babe, baby, Jaybirdie, love, or even just simple Jay.
So, when Jason was not only calling him by his name but refusing to touch and or kiss him at all. Y/N absolutely should have figured something was up.
When Jason got over his initial awkwardness of physical touch in their relationship, that meant became a touch-clingy animal. Whether a hug, hand holding, cuddling, or even simple finger grazes, he needed them all. And kissing, if Y/N ever even dared leave their bedroom, let alone their apartment without giving his giant teddy bear of a boyfriend a kiss, he basically committed the ultimate sin.
So, imagine his surprise when he wakes up and leans over to give his Jaybirdie his kiss, and the big lug rolls over to the other side of the bed before his lips can even get close. Never mind the fact that he woke up and Jason was not cuddling him, hugging, or even just touching him for the matter.
But, he figured Jason was just out of it, discombobulated after waking up or something, and needed a moment. Then, when he was getting ready for his classes and making breakfast, Jason came out and Y/N plated his food for him while grabbing some juice from the fridge.
“Thanks, Y/N.”
Immediate strike two.
Y/N immediately turned around to his lover who was slowly eating his food, rather than inhaling it like he usually does which is why Y/N always has to make extra because the man is still hungry after the first plate. He gave him a weird look and just shrugged it off like he was hearing things, continuing to fill up the glass of juice before handing it over to the vigilante.
“Thanks, Y/N.”
There it was again. Okay, so he wasn’t imagining shit.
And, now that he was thinking about it, Jason was acting really weird. He didn’t come in and hug from behind like he does when Y/N is cooking. He hasn’t made one lewd sexual joke all morning. Heck, he’s barely looked towards the smaller male since this morning.
“You’re welcome. Is everything okay?”
Finally, Jason looked up at him, but it was with a straight face instead of his usual small smile or even the smirk that he always seemed to carry.
“Yeah, why?”
“I don’t know, you just seem like you’re upset about something. Did I do something to make you mad?” Y/N asked, suddenly feeling very vulnerable and uncomfortable. He was not used to this behavior from Jason. It was almost like the beginning of their relationship when the vigilante wouldn’t be very guarded against him because he didn’t trust him yet. A feeling he was very happy to forget.
“No, nothing’s wrong. I’m fine. Are you okay?” Jason asked.
“Yeah, I’m fine. Just worried about you, I guess. You seem quiet.”
“I’m good, Y/N. You don’t need to worry about me.” Jason said, going back to scrolling on his phone while eating.
“Oh, okay,” Y/N said softly, looking down at the ground and feeling very out of place all of a sudden.
On the other end, he didn’t realize how much it was KILLING Jason on the inside to keep up this ruse. He was just about ready to fold and call it quits this morning when he turned over and avoided his boyfriend’s kiss.
Now, he felt absolutely disgusted and horrible at how hurt Y/N looked. He planned to wait it out until he got back from his classes, but he knew right at that moment he wasn’t going to be able to make it that long. He underestimated how much seeing his boyfriend upset would affect him.
“Alright, well, I’m gonna head to my class now. Text me if you want to meet up for lunch.”
“Okay,” Jason said, not saying anything else which he could see was visibly confusing Y/N even more.
He knew that Y/N didn’t like to push because of Jason’s boundaries, always rather giving him space than crowding him and trying to force him to tell him what was going on. It did nothing to help alleviate the guilt he was feeling.
When Y/N came over to try and give Jason a hug and goodbye kiss and Jason visibly moved away, the vigilante wanted to kill himself right at that moment at the wounded expression all over the boy’s face, who just moved to grab his bag, keys, and phone and damn near ran for the door. That was a clear strike three for the college student.
Absolute shit Jason felt like.
When he heard the front door open and slam, he immediately jumped up, grabbed his phone, and ran after his boyfriend who was booking it towards the stairs.
“Y/N, wait.”
When he made no moves to slow down, Jason had to pull out the vigilante moves to catch him since he was nearly out the complex door.
“Baby, stop. I was just messing with you,” He said, grabbing his boyfriend and planting kisses all over his face.
“No, that’s not funny. Get off me you jerk,” Y/N said not making any move to push Jason off which the vigilante smiled at.
“I’m sorry, but now you know how it feels,” Jason showed Y/N his phone that had been recording the entire interaction, “Payback,” He declared, clearly mocking the smaller boy.
Y/N rolled his eyes before heading back inside with his boyfriend who showered him with love and kisses for his prank but made fun of him the entire time. And it didn’t stop there.
Jason did scare pranks, couples challenges where they had to answer questions (his favorites were the ones that came with punishments like dunking each other’s head in water or getting hit with a pillow), and more.
It was the reaction memes all over again.
But, there was still one challenge he hadn’t come across yet that Y/N did and was more than ready to do on his boyfriend.
They were currently sitting in the car, spending a day out together since Y/N's load from his classes was light and there weren’t any cases Jason was working on with himself or his family either. They were parked in a parking garage outside a shopping center, having just come back from shopping and grabbing some food inside when Y/N set up the camera.
“Babe, what are you doing?” Jason asked while stuffing his face with the freshly baked pretzel bites they got.
“Saw this new couple challenge on TikTok and wanted to do it,” He said, setting up the phone mount and adjusting it so it had him and Jason in full view.
“So, I saw this new challenge where couples are asking their partners random questions about each other and seeing who knows more about the other. So me and my husband are going to do the same thing and I’m going to start.” Y/N said into the camera.
The moment it came out his mouth, Y/N could see the initial surprise on his face turn into a small smile, but he didn’t say anything or question him, so he kept going. As he did his best to think up random questions to ask Jason, he kept referring to him as his husband, increasing the smile to a shit-eating grin the longer it went.
“Why are you smiling like that?” Y/N asked.
“I’m your husband now?” Jason asked, turning to him with a raised eyebrow.
“Yeah, is that a problem?” Y/N asked with his own raised eyebrow.
“Absolutely not,” Jason said, not saying another word as Y/N ended the video. He pulled out his phone as they finished their food and Y/N showed the original challenge that everyone was doing, agreeing with him when he called the guy from the original video a complete idiot.
But, he definitely noticed Jason not being as discreet as he thought he was, immediately noticing Jason’s browser on his phone being pulled up to engagement rings.
Oh boy.

☀️ | Jason Todd/Red Hood | ☀️
☀️ | Masterlists | ☀️
#solar-wing ☀️#☀️🪽.fanfic#☀️🪽.dcposts#☀️🪽.txt#gay#social media#tiktok#dc#dcu#dcau#dc universe#dc comics#dc x reader#dc x male reader#x reader#x male reader#jason todd#jason todd fanfiction#jason todd x reader#jason todd x male reader#red hood#red hood fanfiction#red hood x reader#red hood x male reader
336 notes
·
View notes
Text
I'm starting to believe that if you want to be a true political radical and you want to be an ethical human being, your willingness to dismantle institutions must be inversely proportional to your willingness to put human lives at risk.
The more radical your politics, the more dangerous your proposals are. Which doesn't have to be inherently bad as long as you uphold the value of human life with all the zeal with which you demand radical change.
Yes, that means you must be more averse to violence than your less radical peers.
Otherwise, you're just justifying, paving the road for, or committing mass violence.
597 notes
·
View notes
Note
Omg you're taking six of crows requests?!?
Can I get a Kaz x fem!reader where the two of them are a couple (or trying to be) like Kaz is less snappy towards her, they're working on his touch aversion and everything.
But then on a heist gone wrong reader is hurt/stabbed/shot and falls into the Harbour, and Kaz is terrified because of the water but he's more terrified of losing his girl and he realizes that none of the other crows will reach her in time so he dives into the water to save her and when he drags her back onto the dock they just hug each other and the reader is apologizing for ruining the heist, Kaz is just holding her tightly and telling her it's ok, she's safe and that's how the rest of the crows find them, curled up at the end of the dock. Maybe some soft kisses?
Kaz trying to deal with his trauma in ways like this makes me happy
His Star
Requested By: anonymous!
Warnings: Drowning, reader gets stabbed in the arm, Kaz deals with some trauma flashbacks/anxiety, possibly OOC Kaz.
Genre: Hurt/Comfort
Prompt: None
She/Her pronouns used to refer to reader.
Author’s Note:
hey!! sorry this one took so long, I haven't written for Kaz for a WHILE so I hope this meets your request!
Word Count: 1321

Kaz loved you.
Or, at least, you thought he did. He had never told you explicitly, but then, the ruthless young man had never told many people of his affections for them, choosing instead to close himself off to the world instead of facing his feelings.
Despite the mask he put over his emotions every day, you could still tell he loved you through the way he treated you, how he didn’t snap at you like he snapped at the other crows, and the way he looked at you.
Oh, how he looked at you.
Kaz Brekker looked at you as though he was a tired man, bound to the ground of the earth, weak and broken, and you were a star in the dark, endless sky waiting to lead him home, your brightness and your beauty incomparable to anything else.
There were many times Kaz had wanted to touch you, to reach his gloved hand out and graze it against your cheek, or to squeeze your thigh for comfort as you sat beside him, but he couldn’t. He feared that if he did, it would bring everything back. Bring Jordie’s death back. And the possibility was too painful to try.
You understood, of course, you would never push him to do anything he didn’t want to, so you left it alone. You never asked, you barely even thought, because even the idea of making Kaz uncomfortable or upset made guilt squeeze your heart sharply. You would listen if he brought up the idea, but you’d never do it yourself. You’d never put that burden on him over something he couldn’t control.
So you made do with what you had, you loved him in other ways, helping him with planning heists, gathering information to make his job easier, making sure he ate, checking up on him every so often (despite his protests), giving him small smiles across the Crow Club when you could see he was getting frustrated. Little things that made your presence known, but that didn’t intrude too much on his life, and you were happy that way.
“Y/N!” Jesper’s voice broke your thoughts as you slid down the rain-soaked tiles of the building you were scaling, landing gracefully on your feet as you shot along the gutter at the bottom and leaped onto the next one.
“What?” You yelled, hoping he would catch it over the raging wind, but all you heard in response was silence, and you realised you could no longer hear the cracking of his boots against the tile.
Risking a look behind you, you caught your gaze on Jesper’s long figure clambering back up the roof, two others, Inej and Wylan, caught your eye as well, though, where Kaz was you had no idea, and you skidded to a halt, stopping for a moment as you watched the security of the bank you’d just attempted to rob begin gaining on you, their yells rising far above the torrential weather, you watched the other Crows running along the top of the roof, you only caught on to why they were doing this as you turned back, and felt a swift, violent pain crash through your upper arm, you let out an ear piercing scream as the shock and pain overwhelmed you, making your vision blur and your knees buckle underneath you. Almost as soon as you made a noise, you heard Jasper’s pistols shoot rounds into your attacker’s body, quickly able to take out some other guards from his high-up position, yet nobody came to save you as your body tumbled into the freezing harbour water that cascaded against the walls of the bank.
Kaz yelled your name as he watched you disappear off the side of the roof and into the waters below. He had already chosen to stay behind when he realised that you had not heard Jesper’s call to retreat upwards, and he thanked the Saints that he did when he began racing towards the edge of the roof, still screaming your name as he searched for your body in the blackness beneath him.
For the first time in a while, Kaz took a sharp, relieved inhale at the sight of your head poking above the water, and soon your arms came thrashing with it.
As you caught sight of Kaz, you began yelling, mostly unintelligible words, but he heard his name ring in his ears, and he swore he felt his heart tear itself out of his chest when he recognised the fear in your voice.
The fear in your voice that brought him back to that night. With Jordie. Jordie and the boat. And the eerie silence only broken every so often by the groans of the wood and the shifting of clothes against the bodies of the victims that the plague had so cruelly taken.
No. Kaz scolded himself. Stop. Stop, you have to help Y/N. She’ll die if you don’t help her.
He didn’t give himself time to think again before throwing himself into the freeze after you, and almost immediately he felt the same horrible effect that he felt that night with Jordie begin to take hold.
He pushed through it as he kept his mind on you. He couldn’t let you die.
If you died, he didn’t know what he would do with himself, he likes to tell himself that he could get through anything. That grief didn’t affect him anymore.
But with you? You were his star, and if you weren’t there anymore, his sky would go dark.
Kaz could hear your sobs echoing through the night air as he pulled himself through the current and closer to you. Almost as soon as he touched your skin with his gloved hands, he had to stop himself from letting the panic take over, soon becoming grounded once again by your whimpers and pleas for help.
“C-come here, Y/N.” He stammered out, the temperature of the water mixed with the adrenaline coursing through his veins making his speech slurred and awkward as he pulled you towards his chest.
You soon found yourself approaching the harbour, and Kaz made it his first priority to hoist your body up onto the wooden decking, quickly pulling himself up after.
As soon as you were safely out of the water, you backed yourself up against a wall, leaning to the side to cough up what you’d managed to inhale during your panic. Kaz soon made his way over to you, rubbing your back gently as you grasped the wall for support, before falling back against it, still shaking with the sobs that left your lips. You soon felt Kaz move his hand hesitantly to the back of your neck, before taking a deep breath and pulling you in closer to him, holding you tightly.
“I’m sorry…” You cried, taking the collar of his soaked jacket into your hands as he shushed you. “I’m so, so sorry, Kaz, I- I ruined everything. I’m so useless-” You buried your head in his jacket as he shook his head, staring down at you with as serious a stare as he could manage, despite his heart rate going at 30 miles per hour.
“No, no, Y/N, stop it. You didn’t ruin the heist. It was doomed from the start, it was a stupid idea anyway. All that matters is that you’re safe, do you understand me? You’re alright, and you’re with me, and nothing’s going to happen to you.” Kaz’s voice managed to soothe your racing heart and mind, and your gentle nods soothed his own as he dared to press a gentle kiss to your lips.
That was how the Crows found you both that night. Kaz wrapped protectively around you, every so often placing gentle kisses to your hair, and you, his star, encased safely in his arms, having never felt so much love from anybody in your life.
#kaz brekker#kaz brekker x reader#x reader#self insert#reader insert#six of crows#soc#shadow and bone#leigh bardugo
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
I thought y'all should read this
I have a free trial to News+ so I copy-pasted it for you here. I don't think Jonathan Haidt would object to more people having this info.
Tumblr wouldn't let me post it until i removed all the links to Haidt's sources. You'll have to take my word that everything is sourced.
End the Phone-Based Childhood Now
The environment in which kids grow up today is hostile to human development.
By Jonathan Haidt
Something went suddenly and horribly wrong for adolescents in the early 2010s. By now you’ve likely seen the statistics: Rates of depression and anxiety in the United States—fairly stable in the 2000s—rose by more than 50 percent in many studies from 2010 to 2019. The suicide rate rose 48 percent for adolescents ages 10 to 19. For girls ages 10 to 14, it rose 131 percent.
The problem was not limited to the U.S.: Similar patterns emerged around the same time in Canada, the U.K., Australia, New Zealand, the Nordic countries, and beyond. By a variety of measures and in a variety of countries, the members of Generation Z (born in and after 1996) are suffering from anxiety, depression, self-harm, and related disorders at levels higher than any other generation for which we have data.
The decline in mental health is just one of many signs that something went awry. Loneliness and friendlessness among American teens began to surge around 2012. Academic achievement went down, too. According to “The Nation’s Report Card,” scores in reading and math began to decline for U.S. students after 2012, reversing decades of slow but generally steady increase. PISA, the major international measure of educational trends, shows that declines in math, reading, and science happened globally, also beginning in the early 2010s.
As the oldest members of Gen Z reach their late 20s, their troubles are carrying over into adulthood. Young adults are dating less, having less sex, and showing less interest in ever having children than prior generations. They are more likelyto live with their parents. They were less likely to get jobs as teens, and managers say they are harder to work with. Many of these trends began with earlier generations, but most of them accelerated with Gen Z.
Surveys show that members of Gen Z are shyer and more risk averse than previous generations, too, and risk aversion may make them less ambitious. In an interview last May, OpenAI co-founder Sam Altman and Stripe co-founder Patrick Collison noted that, for the first time since the 1970s, none of Silicon Valley’s preeminent entrepreneurs are under 30. “Something has really gone wrong,” Altman said. In a famously young industry, he was baffled by the sudden absence of great founders in their 20s.
Generations are not monolithic, of course. Many young people are flourishing. Taken as a whole, however, Gen Z is in poor mental health and is lagging behind previous generations on many important metrics. And if a generation is doing poorly––if it is more anxious and depressed and is starting families, careers, and important companies at a substantially lower rate than previous generations––then the sociological and economic consequences will be profound for the entire society.
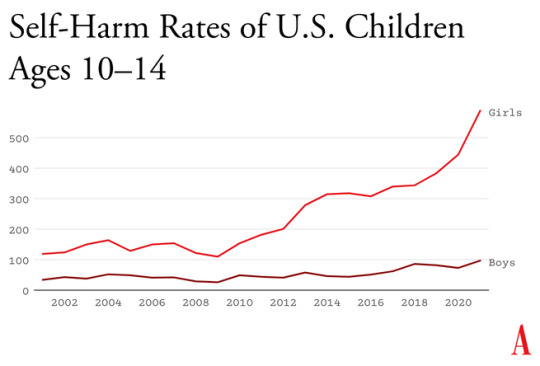
What happened in the early 2010s that altered adolescent development and worsened mental health? Theories abound, but the fact that similar trends are found in many countries worldwide means that events and trends that are specific to the United States cannot be the main story.
I think the answer can be stated simply, although the underlying psychology is complex: Those were the years when adolescents in rich countries traded in their flip phones for smartphones and moved much more of their social lives online—particularly onto social-media platforms designed for virality and addiction. Once young people began carrying the entire internet in their pockets, available to them day and night, it altered their daily experiences and developmental pathways across the board. Friendship, dating, sexuality, exercise, sleep, academics, politics, family dynamics, identity—all were affected. Life changed rapidly for younger children, too, as they began to get access to their parents’ smartphones and, later, got their own iPads, laptops, and even smartphones during elementary school.
As a social psychologist who has long studied social and moral development, I have been involved in debates about the effects of digital technology for years. Typically, the scientific questions have been framed somewhat narrowly, to make them easier to address with data. For example, do adolescents who consume more social media have higher levels of depression? Does using a smartphone just before bedtime interfere with sleep? The answer to these questions is usually found to be yes, although the size of the relationship is often statistically small, which has led some researchers to conclude that these new technologies are not responsible for the gigantic increases in mental illness that began in the early 2010s.
But before we can evaluate the evidence on any one potential avenue of harm, we need to step back and ask a broader question: What is childhood––including adolescence––and how did it change when smartphones moved to the center of it? If we take a more holistic view of what childhood is and what young children, tweens, and teens need to do to mature into competent adults, the picture becomes much clearer. Smartphone-based life, it turns out, alters or interferes with a great number of developmental processes.
The intrusion of smartphones and social media are not the only changes that have deformed childhood. There’s an important backstory, beginning as long ago as the 1980s, when we started systematically depriving children and adolescents of freedom, unsupervised play, responsibility, and opportunities for risk taking, all of which promote competence, maturity, and mental health. But the change in childhood accelerated in the early 2010s, when an already independence-deprived generation was lured into a new virtual universe that seemed safe to parents but in fact is more dangerous, in many respects, than the physical world.
My claim is that the new phone-based childhood that took shape roughly 12 years ago is making young people sick and blocking their progress to flourishing in adulthood. We need a dramatic cultural correction, and we need it now.
1. The Decline of Play and Independence
Human brains are extraordinarily large compared with those of other primates, and human childhoods are extraordinarily long, too, to give those large brains time to wire up within a particular culture. A child’s brain is already 90 percent of its adult size by about age 6. The next 10 or 15 years are about learning norms and mastering skills—physical, analytical, creative, and social. As children and adolescents seek out experiences and practice a wide variety of behaviors, the synapses and neurons that are used frequently are retained while those that are used less often disappear. Neurons that fire together wire together, as brain researchers say.
Brain development is sometimes said to be “experience-expectant,” because specific parts of the brain show increased plasticity during periods of life when an animal’s brain can “expect” to have certain kinds of experiences. You can see this with baby geese, who will imprint on whatever mother-sized object moves in their vicinity just after they hatch. You can see it with human children, who are able to learn languages quickly and take on the local accent, but only through early puberty; after that, it’s hard to learn a language and sound like a native speaker. There is also some evidence of a sensitive period for cultural learning more generally. Japanese children who spent a few years in California in the 1970s came to feel “American” in their identity and ways of interacting only if they attended American schools for a few years between ages 9 and 15. If they left before age 9, there was no lasting impact. If they didn’t arrive until they were 15, it was too late; they didn’t come to feel American.
Human childhood is an extended cultural apprenticeship with different tasks at different ages all the way through puberty. Once we see it this way, we can identify factors that promote or impede the right kinds of learning at each age. For children of all ages, one of the most powerful drivers of learning is the strong motivation to play. Play is the work of childhood, and all young mammals have the same job: to wire up their brains by playing vigorously and often, practicing the moves and skills they’ll need as adults. Kittens will play-pounce on anything that looks like a mouse tail. Human children will play games such as tag and sharks and minnows, which let them practice both their predator skills and their escaping-from-predator skills. Adolescents will play sports with greater intensity, and will incorporate playfulness into their social interactions—flirting, teasing, and developing inside jokes that bond friends together. Hundreds of studies on young rats, monkeys, and humans show that young mammals want to play, need to play, and end up socially, cognitively, and emotionally impaired when they are deprived of play.
One crucial aspect of play is physical risk taking. Children and adolescents must take risks and fail—often—in environments in which failure is not very costly. This is how they extend their abilities, overcome their fears, learn to estimate risk, and learn to cooperate in order to take on larger challenges later. The ever-present possibility of getting hurt while running around, exploring, play-fighting, or getting into a real conflict with another group adds an element of thrill, and thrilling play appears to be the most effective kind for overcoming childhood anxieties and building social, emotional, and physical competence. The desire for risk and thrill increases in the teen years, when failure might carry more serious consequences. Children of all ages need to choose the risk they are ready for at a given moment. Young people who are deprived of opportunities for risk taking and independent exploration will, on average, develop into more anxious and risk-averse adults.
Human childhood and adolescence evolved outdoors, in a physical world full of dangers and opportunities. Its central activities––play, exploration, and intense socializing––were largely unsupervised by adults, allowing children to make their own choices, resolve their own conflicts, and take care of one another. Shared adventures and shared adversity bound young people together into strong friendship clusters within which they mastered the social dynamics of small groups, which prepared them to master bigger challenges and larger groups later on.
And then we changed childhood.
The changes started slowly in the late 1970s and ’80s, before the arrival of the internet, as many parents in the U.S. grew fearful that their children would be harmed or abducted if left unsupervised. Such crimes have always been extremely rare, but they loomed larger in parents’ minds thanks in part to rising levels of street crime combined with the arrival of cable TV, which enabled round-the-clock coverage of missing-children cases. A general decline in social capital––the degree to which people knew and trusted their neighbors and institutions––exacerbated parental fears. Meanwhile, rising competition for college admissions encouraged more intensive forms of parenting. In the 1990s, American parents began pulling their children indoors or insisting that afternoons be spent in adult-run enrichment activities. Free play, independent exploration, and teen-hangout time declined.
In recent decades, seeing unchaperoned children outdoors has become so novel that when one is spotted in the wild, some adults feel it is their duty to call the police. In 2015, the Pew Research Center found that parents, on average, believed that children should be at least 10 years old to play unsupervised in front of their house, and that kids should be 14 before being allowed to go unsupervised to a public park. Most of these same parents had enjoyed joyous and unsupervised outdoor play by the age of 7 or 8.
2. The Virtual World Arrives in Two Waves
The internet, which now dominates the lives of young people, arrived in two waves of linked technologies. The first one did little harm to Millennials. The second one swallowed Gen Z whole.
The first wave came ashore in the 1990s with the arrival of dial-up internet access, which made personal computers good for something beyond word processing and basic games. By 2003, 55 percent of American households had a computer with (slow) internet access. Rates of adolescent depression, loneliness, and other measures of poor mental health did not rise in this first wave. If anything, they went down a bit. Millennial teens (born 1981 through 1995), who were the first to go through puberty with access to the internet, were psychologically healthier and happier, on average, than their older siblings or parents in Generation X (born 1965 through 1980).
The second wave began to rise in the 2000s, though its full force didn’t hit until the early 2010s. It began rather innocently with the introduction of social-media platforms that helped people connect with their friends. Posting and sharing content became much easier with sites such as Friendster (launched in 2003), Myspace (2003), and Facebook (2004).
Teens embraced social media soon after it came out, but the time they could spend on these sites was limited in those early years because the sites could only be accessed from a computer, often the family computer in the living room. Young people couldn’t access social media (and the rest of the internet) from the school bus, during class time, or while hanging out with friends outdoors. Many teens in the early-to-mid-2000s had cellphones, but these were basic phones (many of them flip phones) that had no internet access. Typing on them was difficult––they had only number keys. Basic phones were tools that helped Millennials meet up with one another in person or talk with each other one-on-one. I have seen no evidence to suggest that basic cellphones harmed the mental health of Millennials.
It was not until the introduction of the iPhone (2007), the App Store (2008), and high-speed internet (which reached 50 percent of American homes in 2007)—and the corresponding pivot to mobile made by many providers of social media, video games, and porn—that it became possible for adolescents to spend nearly every waking moment online. The extraordinary synergy among these innovations was what powered the second technological wave. In 2011, only 23 percent of teens had a smartphone. By 2015, that number had risen to 73 percent, and a quarter of teens said they were online “almost constantly.” Their younger siblings in elementary school didn’t usually have their own smartphones, but after its release in 2010, the iPad quickly became a staple of young children’s daily lives. It was in this brief period, from 2010 to 2015, that childhood in America (and many other countries) was rewired into a form that was more sedentary, solitary, virtual, and incompatible with healthy human development.
3. Techno-optimism and the Birth of the Phone-Based Childhood
The phone-based childhood created by that second wave—including not just smartphones themselves, but all manner of internet-connected devices, such as tablets, laptops, video-game consoles, and smartwatches—arrived near the end of a period of enormous optimism about digital technology. The internet came into our lives in the mid-1990s, soon after the fall of the Soviet Union. By the end of that decade, it was widely thought that the web would be an ally of democracy and a slayer of tyrants. When people are connected to each other, and to all the information in the world, how could any dictator keep them down?
In the 2000s, Silicon Valley and its world-changing inventions were a source of pride and excitement in America. Smart and ambitious young people around the world wanted to move to the West Coast to be part of the digital revolution. Tech-company founders such as Steve Jobs and Sergey Brin were lauded as gods, or at least as modern Prometheans, bringing humans godlike powers. The Arab Spring bloomed in 2011 with the help of decentralized social platforms, including Twitter and Facebook. When pundits and entrepreneurs talked about the power of social media to transform society, it didn’t sound like a dark prophecy.
You have to put yourself back in this heady time to understand why adults acquiesced so readily to the rapid transformation of childhood. Many parents had concerns, even then, about what their children were doing online, especially because of the internet’s ability to put children in contact with strangers. But there was also a lot of excitement about the upsides of this new digital world. If computers and the internet were the vanguards of progress, and if young people––widely referred to as “digital natives”––were going to live their lives entwined with these technologies, then why not give them a head start? I remember how exciting it was to see my 2-year-old son master the touch-and-swipe interface of my first iPhone in 2008. I thought I could see his neurons being woven together faster as a result of the stimulation it brought to his brain, compared to the passivity of watching television or the slowness of building a block tower. I thought I could see his future job prospects improving.
Touchscreen devices were also a godsend for harried parents. Many of us discovered that we could have peace at a restaurant, on a long car trip, or at home while making dinner or replying to emails if we just gave our children what they most wanted: our smartphones and tablets. We saw that everyone else was doing it and figured it must be okay.
It was the same for older children, desperate to join their friends on social-media platforms, where the minimum age to open an account was set by law to 13, even though no research had been done to establish the safety of these products for minors. Because the platforms did nothing (and still do nothing) to verify the stated age of new-account applicants, any 10-year-old could open multiple accounts without parental permission or knowledge, and many did. Facebook and later Instagram became places where many sixth and seventh graders were hanging out and socializing. If parents did find out about these accounts, it was too late. Nobody wanted their child to be isolated and alone, so parents rarely forced their children to shut down their accounts.
We had no idea what we were doing.
4. The High Cost of a Phone-Based Childhood
In Walden, his 1854 reflection on simple living, Henry David Thoreau wrote, “The cost of a thing is the amount of … life which is required to be exchanged for it, immediately or in the long run.” It’s an elegant formulation of what economists would later call the opportunity cost of any choice—all of the things you can no longer do with your money and time once you’ve committed them to something else. So it’s important that we grasp just how much of a young person’s day is now taken up by their devices.
The numbers are hard to believe. The most recent Gallup data show that American teens spend about five hours a day just on social-media platforms (including watching videos on TikTok and YouTube). Add in all the other phone- and screen-based activities, and the number rises to somewhere between seven and nine hours a day, on average. The numbers are even higher in single-parent and low-income families, and among Black, Hispanic, and Native American families.
In Thoreau’s terms, how much of life is exchanged for all this screen time? Arguably, most of it. Everything else in an adolescent’s day must get squeezed down or eliminated entirely to make room for the vast amount of content that is consumed, and for the hundreds of “friends,” “followers,” and other network connections that must be serviced with texts, posts, comments, likes, snaps, and direct messages. I recently surveyed my students at NYU, and most of them reported that the very first thing they do when they open their eyes in the morning is check their texts, direct messages, and social-media feeds. It’s also the last thing they do before they close their eyes at night. And it’s a lot of what they do in between.
The amount of time that adolescents spend sleeping declined in the early 2010s, and many studies tie sleep loss directly to the use of devices around bedtime, particularly when they’re used to scroll through social media. Exercise declined, too, which is unfortunate because exercise, like sleep, improves both mental and physical health. Book reading has been declining for decades, pushed aside by digital alternatives, but the decline, like so much else, sped up in the early 2010s. With passive entertainment always available, adolescent minds likely wander less than they used to; contemplation and imagination might be placed on the list of things winnowed down or crowded out.
But perhaps the most devastating cost of the new phone-based childhood was the collapse of time spent interacting with other people face-to-face. A study of how Americans spend their time found that, before 2010, young people (ages 15 to 24) reported spending far more time with their friends (about two hours a day, on average, not counting time together at school) than did older people (who spent just 30 to 60 minutes with friends). Time with friends began decreasing for young people in the 2000s, but the drop accelerated in the 2010s, while it barely changed for older people. By 2019, young people’s time with friends had dropped to just 67 minutes a day. It turns out that Gen Z had been socially distancing for many years and had mostly completed the project by the time COVID-19 struck.
You might question the importance of this decline. After all, isn’t much of this online time spent interacting with friends through texting, social media, and multiplayer video games? Isn’t that just as good?
Some of it surely is, and virtual interactions offer unique benefits too, especially for young people who are geographically or socially isolated. But in general, the virtual world lacks many of the features that make human interactions in the real world nutritious, as we might say, for physical, social, and emotional development. In particular, real-world relationships and social interactions are characterized by four features—typical for hundreds of thousands of years—that online interactions either distort or erase.
First, real-world interactions are embodied, meaning that we use our hands and facial expressions to communicate, and we learn to respond to the body language of others. Virtual interactions, in contrast, mostly rely on language alone. No matter how many emojis are offered as compensation, the elimination of communication channels for which we have eons of evolutionary programming is likely to produce adults who are less comfortable and less skilled at interacting in person.
Second, real-world interactions are synchronous; they happen at the same time. As a result, we learn subtle cues about timing and conversational turn taking. Synchronous interactions make us feel closer to the other person because that’s what getting “in sync” does. Texts, posts, and many other virtual interactions lack synchrony. There is less real laughter, more room for misinterpretation, and more stress after a comment that gets no immediate response.
Third, real-world interactions primarily involve one‐to‐one communication, or sometimes one-to-several. But many virtual communications are broadcast to a potentially huge audience. Online, each person can engage in dozens of asynchronous interactions in parallel, which interferes with the depth achieved in all of them. The sender’s motivations are different, too: With a large audience, one’s reputation is always on the line; an error or poor performance can damage social standing with large numbers of peers. These communications thus tend to be more performative and anxiety-inducing than one-to-one conversations.
Finally, real-world interactions usually take place within communities that have a high bar for entry and exit, so people are strongly motivated to invest in relationships and repair rifts when they happen. But in many virtual networks, people can easily block others or quit when they are displeased. Relationships within such networks are usually more disposable.
These unsatisfying and anxiety-producing features of life online should be recognizable to most adults. Online interactions can bring out antisocial behavior that people would never display in their offline communities. But if life online takes a toll on adults, just imagine what it does to adolescents in the early years of puberty, when their “experience expectant” brains are rewiring based on feedback from their social interactions.
Kids going through puberty online are likely to experience far more social comparison, self-consciousness, public shaming, and chronic anxiety than adolescents in previous generations, which could potentially set developing brains into a habitual state of defensiveness. The brain contains systems that are specialized for approach (when opportunities beckon) and withdrawal (when threats appear or seem likely). People can be in what we might call “discover mode” or “defend mode” at any moment, but generally not both. The two systems together form a mechanism for quickly adapting to changing conditions, like a thermostat that can activate either a heating system or a cooling system as the temperature fluctuates. Some people’s internal thermostats are generally set to discover mode, and they flip into defend mode only when clear threats arise. These people tend to see the world as full of opportunities. They are happier and less anxious. Other people’s internal thermostats are generally set to defend mode, and they flip into discover mode only when they feel unusually safe. They tend to see the world as full of threats and are more prone to anxiety and depressive disorders.
A simple way to understand the differences between Gen Z and previous generations is that people born in and after 1996 have internal thermostats that were shifted toward defend mode. This is why life on college campuses changed so suddenly when Gen Z arrived, beginning around 2014. Students began requesting “safe spaces” and trigger warnings. They were highly sensitive to “microaggressions” and sometimes claimed that words were “violence.” These trends mystified those of us in older generations at the time, but in hindsight, it all makes sense. Gen Z students found words, ideas, and ambiguous social encounters more threatening than had previous generations of students because we had fundamentally altered their psychological development.
5. So Many Harms
The debate around adolescents’ use of smartphones and social media typically revolves around mental health, and understandably so. But the harms that have resulted from transforming childhood so suddenly and heedlessly go far beyondmental health. I’ve touched on some of them—social awkwardness, reduced self-confidence, and a more sedentary childhood. Here are three additional harms.
Fragmented Attention, Disrupted Learning
Staying on task while sitting at a computer is hard enough for an adult with a fully developed prefrontal cortex. It is far more difficult for adolescents in front of their laptop trying to do homework. They are probably less intrinsically motivated to stay on task. They’re certainly less able, given their undeveloped prefrontal cortex, and hence it’s easy for any company with an app to lure them away with an offer of social validation or entertainment. Their phones are pinging constantly—one study found that the typical adolescent now gets 237 notifications a day, roughly 15 every waking hour. Sustained attention is essential for doing almost anything big, creative, or valuable, yet young people find their attention chopped up into little bits by notifications offering the possibility of high-pleasure, low-effort digital experiences.
It even happens in the classroom. Studies confirm that when students have access to their phones during class time, they use them, especially for texting and checking social media, and their grades and learning suffer. This might explain why benchmark test scores began to decline in the U.S. and around the world in the early 2010s—well before the pandemic hit.
Addiction and Social Withdrawal
The neural basis of behavioral addiction to social media or video games is not exactly the same as chemical addiction to cocaine or opioids. Nonetheless, they all involve abnormally heavy and sustained activation of dopamine neurons and reward pathways. Over time, the brain adapts to these high levels of dopamine; when the child is not engaged in digital activity, their brain doesn’t have enough dopamine, and the child experiences withdrawal symptoms. These generally include anxiety, insomnia, and intense irritability. Kids with these kinds of behavioral addictions often become surly and aggressive, and withdraw from their families into their bedrooms and devices.
Social-media and gaming platforms were designed to hook users. How successful are they? How many kids suffer from digital addictions?
The main addiction risks for boys seem to be video games and porn. “Internet gaming disorder,” which was added to the main diagnosis manual of psychiatry in 2013 as a condition for further study, describes “significant impairment or distress” in several aspects of life, along with many hallmarks of addiction, including an inability to reduce usage despite attempts to do so. Estimates for the prevalence of IGD range from 7 to 15 percent among adolescent boys and young men. As for porn, a nationally representative survey of American adults published in 2019 found that 7 percent of American men agreed or strongly agreed with the statement “I am addicted to pornography”—and the rates were higher for the youngest men.
Girls have much lower rates of addiction to video games and porn, but they use social media more intensely than boys do. A study of teens in 29 nations found that between 5 and 15 percent of adolescents engage in what is called “problematic social media use,” which includes symptoms such as preoccupation, withdrawal symptoms, neglect of other areas of life, and lying to parents and friends about time spent on social media. That study did not break down results by gender, but many others have found that rates of “problematic use” are higher for girls.
I don’t want to overstate the risks: Most teens do not become addicted to their phones and video games. But across multiple studies and across genders, rates of problematic use come out in the ballpark of 5 to 15 percent. Is there any other consumer product that parents would let their children use relatively freely if they knew that something like one in 10 kids would end up with a pattern of habitual and compulsive use that disrupted various domains of life and looked a lot like an addiction?
The Decay of Wisdom and the Loss of Meaning
During that crucial sensitive period for cultural learning, from roughly ages 9 through 15, we should be especially thoughtful about who is socializing our children for adulthood. Instead, that’s when most kids get their first smartphone and sign themselves up (with or without parental permission) to consume rivers of content from random strangers. Much of that content is produced by other adolescents, in blocks of a few minutes or a few seconds.
This rerouting of enculturating content has created a generation that is largely cut off from older generations and, to some extent, from the accumulated wisdom of humankind, including knowledge about how to live a flourishing life. Adolescents spend less time steeped in their local or national culture. They are coming of age in a confusing, placeless, ahistorical maelstrom of 30-second stories curated by algorithms designed to mesmerize them. Without solid knowledge of the past and the filtering of good ideas from bad––a process that plays out over many generations––young people will be more prone to believe whatever terrible ideas become popular around them, which might explain why videos showing young people reacting positively to Osama bin Laden’s thoughts about America were trending on TikTok last fall.
All this is made worse by the fact that so much of digital public life is an unending supply of micro dramas about somebody somewhere in our country of 340 million people who did something that can fuel an outrage cycle, only to be pushed aside by the next. It doesn’t add up to anything and leaves behind only a distorted sense of human nature and affairs.
When our public life becomes fragmented, ephemeral, and incomprehensible, it is a recipe for anomie, or normlessness. The great French sociologist Émile Durkheim showed long ago that a society that fails to bind its people together with some shared sense of sacredness and common respect for rules and norms is not a society of great individual freedom; it is, rather, a place where disoriented individuals have difficulty setting goals and exerting themselves to achieve them. Durkheim argued that anomie was a major driver of suicide rates in European countries. Modern scholars continue to draw on his work to understand suicide rates today.
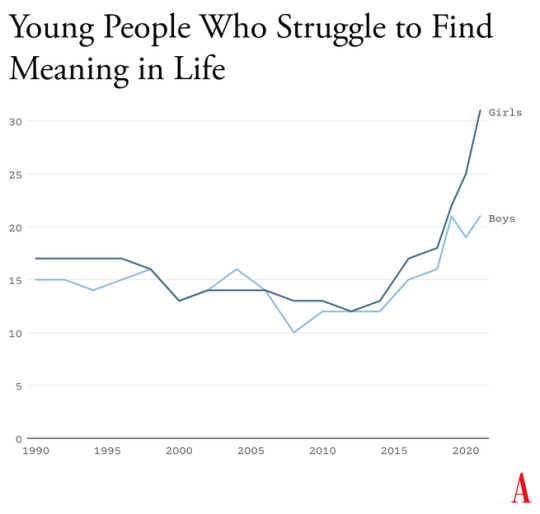
Durkheim’s observations are crucial for understanding what happened in the early 2010s. A long-running survey of American teens found that, from 1990 to 2010, high-school seniors became slightly less likely to agree with statements such as “Life often feels meaningless.” But as soon as they adopted a phone-based life and many began to live in the whirlpool of social media, where no stability can be found, every measure of despair increased. From 2010 to 2019, the number who agreed that their lives felt “meaningless” increased by about 70 percent, to more than one in five.
6. Young People Don’t Like Their Phone-Based Lives
How can I be confident that the epidemic of adolescent mental illness was kicked off by the arrival of the phone-based childhood? Skeptics point to other events as possible culprits, including the 2008 global financial crisis, global warming, the 2012 Sandy Hook school shooting and the subsequent active-shooter drills, rising academic pressures, and the opioid epidemic. But while these events might have been contributing factors in some countries, none can explain both the timing and international scope of the disaster.
An additional source of evidence comes from Gen Z itself. With all the talk of regulating social media, raising age limits, and getting phones out of schools, you might expect to find many members of Gen Z writing and speaking out in opposition. I’ve looked for such arguments and found hardly any. In contrast, many young adults tell stories of devastation.
Freya India, a 24-year-old British essayist who writes about girls, explains how social-media sites carry girls off to unhealthy places: “It seems like your child is simply watching some makeup tutorials, following some mental health influencers, or experimenting with their identity. But let me tell you: they are on a conveyor belt to someplace bad. Whatever insecurity or vulnerability they are struggling with, they will be pushed further and further into it.” She continues:
Gen Z were the guinea pigs in this uncontrolled global social experiment. We were the first to have our vulnerabilities and insecurities fed into a machine that magnified and refracted them back at us, all the time, before we had any sense of who we were. We didn’t just grow up with algorithms. They raised us. They rearranged our faces. Shaped our identities. Convinced us we were sick.
Rikki Schlott, a 23-year-old American journalist and co-author of The Canceling of the American Mind, writes,
"The day-to-day life of a typical teen or tween today would be unrecognizable to someone who came of age before the smartphone arrived. Zoomers are spending an average of 9 hours daily in this screen-time doom loop—desperate to forget the gaping holes they’re bleeding out of, even if just for … 9 hours a day. Uncomfortable silence could be time to ponder why they’re so miserable in the first place. Drowning it out with algorithmic white noise is far easier."
A 27-year-old man who spent his adolescent years addicted (his word) to video games and pornography sent me this reflection on what that did to him:
I missed out on a lot of stuff in life—a lot of socialization. I feel the effects now: meeting new people, talking to people. I feel that my interactions are not as smooth and fluid as I want. My knowledge of the world (geography, politics, etc.) is lacking. I didn’t spend time having conversations or learning about sports. I often feel like a hollow operating system.
Or consider what Facebook found in a research project involving focus groups of young people, revealed in 2021 by the whistleblower Frances Haugen: “Teens blame Instagram for increases in the rates of anxiety and depression among teens,” an internal document said. “This reaction was unprompted and consistent across all groups.”
7. Collective-Action Problems
Social-media companies such as Meta, TikTok, and Snap are often compared to tobacco companies, but that’s not really fair to the tobacco industry. It’s true that companies in both industries marketed harmful products to children and tweaked their products for maximum customer retention (that is, addiction), but there’s a big difference: Teens could and did choose, in large numbers, not to smoke. Even at the peak of teen cigarette use, in 1997, nearly two-thirds of high-school students did not smoke.
Social media, in contrast, applies a lot more pressure on nonusers, at a much younger age and in a more insidious way. Once a few students in any middle school lie about their age and open accounts at age 11 or 12, they start posting photos and comments about themselves and other students. Drama ensues. The pressure on everyone else to join becomes intense. Even a girl who knows, consciously, that Instagram can foster beauty obsession, anxiety, and eating disorders might sooner take those risks than accept the seeming certainty of being out of the loop, clueless, and excluded. And indeed, if she resists while most of her classmates do not, she might, in fact, be marginalized, which puts her at risk for anxiety and depression, though via a different pathway than the one taken by those who use social media heavily. In this way, social media accomplishes a remarkable feat: It even harms adolescents who do not use it.
A recent study led by the University of Chicago economist Leonardo Bursztyn captured the dynamics of the social-media trap precisely. The researchers recruited more than 1,000 college students and asked them how much they’d need to be paid to deactivate their accounts on either Instagram or TikTok for four weeks. That’s a standard economist’s question to try to compute the net value of a product to society. On average, students said they’d need to be paid roughly $50 ($59 for TikTok, $47 for Instagram) to deactivate whichever platform they were asked about. Then the experimenters told the students that they were going to try to get most of the others in their school to deactivate that same platform, offering to pay them to do so as well, and asked, Now how much would you have to be paid to deactivate, if most others did so? The answer, on average, was less than zero. In each case, most students were willing to pay to have that happen.
Social media is all about network effects. Most students are only on it because everyone else is too. Most of them would prefer that nobody be on these platforms. Later in the study, students were asked directly, “Would you prefer to live in a world without Instagram [or TikTok]?” A majority of students said yes––58 percent for each app.
This is the textbook definition of what social scientists call a collective-action problem. It’s what happens when a group would be better off if everyone in the group took a particular action, but each actor is deterred from acting, because unless the others do the same, the personal cost outweighs the benefit. Fishermen considering limiting their catch to avoid wiping out the local fish population are caught in this same kind of trap. If no one else does it too, they just lose profit.
Cigarettes trapped individual smokers with a biological addiction. Social media has trapped an entire generation in a collective-action problem. Early app developers deliberately and knowingly exploited the psychological weaknesses and insecurities of young people to pressure them to consume a product that, upon reflection, many wish they could use less, or not at all.
8. Four Norms to Break Four Traps
Young people and their parents are stuck in at least four collective-action traps. Each is hard to escape for an individual family, but escape becomes much easier if families, schools, and communities coordinate and act together. Here are four norms that would roll back the phone-based childhood. I believe that any community that adopts all four will see substantial improvements in youth mental health within two years.
No smartphones before high school
The trap here is that each child thinks they need a smartphone because “everyone else” has one, and many parents give in because they don’t want their child to feel excluded. But if no one else had a smartphone—or even if, say, only half of the child’s sixth-grade class had one—parents would feel more comfortable providing a basic flip phone (or no phone at all). Delaying round-the-clock internet access until ninth grade (around age 14) as a national or community norm would help to protect adolescents during the very vulnerable first few years of puberty. According to a 2022 British study, these are the years when social-media use is most correlated with poor mental health. Family policies about tablets, laptops, and video-game consoles should be aligned with smartphone restrictions to prevent overuse of other screen activities.
No social media before 16
The trap here, as with smartphones, is that each adolescent feels a strong need to open accounts on TikTok, Instagram, Snapchat, and other platforms primarily because that’s where most of their peers are posting and gossiping. But if the majority of adolescents were not on these accounts until they were 16, families and adolescents could more easily resist the pressure to sign up. The delay would not mean that kids younger than 16 could never watch videos on TikTok or YouTube—only that they could not open accounts, give away their data, post their own content, and let algorithms get to know them and their preferences.
Phone‐free schools
Most schools claim that they ban phones, but this usually just means that students aren’t supposed to take their phone out of their pocket during class. Research shows that most students do use their phones during class time. They also use them during lunchtime, free periods, and breaks between classes––times when students could and should be interacting with their classmates face-to-face. The only way to get students’ minds off their phones during the school day is to require all students to put their phones (and other devices that can send or receive texts) into a phone locker or locked pouch at the start of the day. Schools that have gone phone-free always seem to report that it has improved the culture, making students more attentive in class and more interactive with one another. Published studies back them up.
More independence, free play, and responsibility in the real world
Many parents are afraid to give their children the level of independence and responsibility they themselves enjoyed when they were young, even though rates of homicide, drunk driving, and other physical threats to children are way down in recent decades. Part of the fear comes from the fact that parents look at each other to determine what is normal and therefore safe, and they see few examples of families acting as if a 9-year-old can be trusted to walk to a store without a chaperone. But if many parents started sending their children out to play or run errands, then the norms of what is safe and accepted would change quickly. So would ideas about what constitutes “good parenting.” And if more parents trusted their children with more responsibility––for example, by asking their kids to do more to help out, or to care for others––then the pervasive sense of uselessness now found in surveys of high-school students might begin to dissipate.
It would be a mistake to overlook this fourth norm. If parents don’t replace screen time with real-world experiences involving friends and independent activity, then banning devices will feel like deprivation, not the opening up of a world of opportunities.
The main reason why the phone-based childhood is so harmful is because it pushes aside everything else. Smartphones are experience blockers. Our ultimate goal should not be to remove screens entirely, nor should it be to return childhood to exactly the way it was in 1960. Rather, it should be to create a version of childhood and adolescence that keeps young people anchored in the real world while flourishing in the digital age.
9. What Are We Waiting For?
An essential function of government is to solve collective-action problems. Congress could solve or help solve the ones I’ve highlighted—for instance, by raising the age of “internet adulthood” to 16 and requiring tech companies to keep underage children off their sites.
In recent decades, however, Congress has not been good at addressing public concerns when the solutions would displease a powerful and deep-pocketed industry. Governors and state legislators have been much more effective, and their successes might let us evaluate how well various reforms work. But the bottom line is that to change norms, we’re going to need to do most of the work ourselves, in neighborhood groups, schools, and other communities.
There are now hundreds of organizations––most of them started by mothers who saw what smartphones had done to their children––that are working to roll back the phone-based childhood or promote a more independent, real-world childhood. (I have assembled a list of many of them.) One that I co-founded, at LetGrow.org, suggests a variety of simple programs for parents or schools, such as play club (schools keep the playground open at least one day a week before or after school, and kids sign up for phone-free, mixed-age, unstructured play as a regular weekly activity) and the Let Grow Experience (a series of homework assignments in which students––with their parents’ consent––choose something to do on their own that they’ve never done before, such as walk the dog, climb a tree, walk to a store, or cook dinner).
Parents are fed up with what childhood has become. Many are tired of having daily arguments about technologies that were designed to grab hold of their children’s attention and not let go. But the phone-based childhood is not inevitable.
The four norms I have proposed cost almost nothing to implement, they cause no clear harm to anyone, and while they could be supported by new legislation, they can be instilled even without it. We can begin implementing all of them right away, this year, especially in communities with good cooperation between schools and parents. A single memo from a principal asking parents to delay smartphones and social media, in support of the school’s effort to improve mental health by going phone free, would catalyze collective action and reset the community’s norms.
We didn’t know what we were doing in the early 2010s. Now we do. It’s time to end the phone-based childhood.
This article is adapted from Jonathan Haidt’s forthcoming book, The Anxious Generation: How the Great Rewiring of Childhood Is Causing an Epidemic of Mental Illness.
183 notes
·
View notes
Note
Would you be willing to write a little blurb of Steve comforting reader who is in recovery from self harm? I know this is a very no no subject for some writers so I understand if this is a no!
fem!reader !! cw self harm (mention of the self injury, no active graphic imagery, but some details that could be evocative)
You’ve taken to curling up in whatever space he leaves. In bed, you sidle close to his side with your ear to his stomach. On the couch, you’re laying on his lap, every breath a press of ribs against his thighs. If Steve’s on a sun lounger in the backyard, you’re sitting on the ground next to him with an arm hooked over his leg and your cheek bitten by metal.
It’s sort of odd to see your arms without red cuts and welts. Curled again, you and Steve are sitting on the porch watching the sun dropping lazily to the horizon, the sky a funny shade of blue. You’re actually turned away from the sun and toward the house, Steve to the sun, like inverted commas interlinked. Your hand is on his leg, and your arm is bare and starkly uninjured.
That’s too generous, maybe. Evidence of a bad habit long to kick tracks the length of you, white and purple and red scars criss-crossed through your skin.
He’s seen them thick with dried blood and sore to the touch. Your skin aflame. Not because you’ve ever showed him of your own volition, you wouldn’t. You’ve always likened your self-injury to a contagion. “I don’t wanna put thoughts in your head,” you whispered.
It was a nice concern for you to have, but Steve isn’t at any risk of hurting himself (purposefully, at least). He has no urges. He didn’t even know people did stuff like that until he met you. Maybe that’s why it breaks his heart so much. You hurt so much. You feel terrible and you take it out on yourself and Steve just doesn’t get it, ‘cos you’re aces.
He never shied away from it, even if he didn’t like that you were doing it. He still remembers the first time he realised what you were doing, his confusion, the immediate internal recoil. How could you do that to yourself? Why would you? You’ve always been prone to that awful persisting sadness under the skin, but Steve knows a lot of sad people. He knows what it’s like to wish vehemently that you were a better version of yourself, or somebody else, or just gone.
But you’re doing better now. He resists the urge to kiss your hands whenever he sees you and you act like you aren’t doing a brave thing.
Steve’s stupid but he’s not stupid. (Or, at least he feels that way.) He knows you’re finding it hard to stop, like an addict. It’s a habit. A behaviour that takes conscious effort to break until it doesn’t. The worst bit is that you never even asked for help.
Your hand twitches on his leg.
Steve curls a hand behind your neck, kissing you softly, the silky press of your lips to his. You inhale and cut the quiet buzz of cicadas, your breath surprised but not tight.
“Sorry,” he says, “was that okay? I was just thinking about you.”
“It’s fine.” You laugh against his lips and take a kiss, evening the score. “It’s always okay. Kiss me whenever you want.”
“You looked mopey,” he says. Foot in mouth disease forever.
“I’m not mopey, just distracted.”
“I know, it’s offensive. You come over here to hang out and spend the last hour in deep thought.” He makes it clear he’s joking through his light tone and his smile, your eyes met, his hand sliding down your shoulder and your arm. He’s especially careful as his fingers run down your forearm. You watch the path of his hand as it falls, twining your fingers weakly with his. “You can tell me anything.”
“I do tell you anything.”
“Well, just telling you again.” He kisses your cheek, then, less gentle, your lips.
You have this aversion to saying the worst part out loud. There’s always a metaphor or an omission. You can’t say cut, it’s too much, but you’ve said hurt. You’ll admit to self injury but not the action. “It’s fine,” you say now.
“I think you’re doing a good job.”
You laugh softly through your nose. “Thank you.”
“I’m not kidding.” He blows a breath up his face. “Look, can I just be honest with you?”
Your smile turns uneasy at his bluntness. “Um. Are you breaking up with me?”
Steve shakes his head. “Never,” he says, pushing your sleeve up your arm slowly, and then faster when you don’t resist. “I can’t remember the last time I saw you without them.” He doesn’t say cuts either, mostly for your sake.
“Sorry.”
He shakes his head again. “For what? I’m just saying. You’ve had them this whole time and I’ve never– they’ve never stopped me from wanting to kiss your face off.” He probably shouldn’t make jokes. He backtracks. “I mean, they don’t make a difference to me, I like you even if you can’t, uh… Even if the impulse is too much. But I’m thrilled you’re, you know, not doing it.”
“I know,” you murmur.
“I love you.”
“I know.” Your voice is nearly inaudible, “That’s why it’s easier now.”
His heart swells with pride and love and an unfightable want to hug you. He slides his arms around you from under your armpits, forcing you to hug his neck, stealing a kiss to the cheek as he squeezes you forward. “I just want you to know that I get it. Like, how hard you’re working to not do it.”
“Steve,” you admonish quietly.
“Sorry, I’ll stop talking about it if you want.”
“I mean… It's kinda nice to talk about it. It’s not in my head.”
“It’s not in your head.”
“But it feels weird ‘cos it’s like, something I should be doing anyways. It’s like getting praise for washing your hands.”
Steve thinks there’s a pretty big difference between wanting to hurt yourself but resisting it and washing your hands, but he knows what you’re saying. Doesn’t agree, but doesn’t want to invalidate you either. However you need to think about it to get through it is up to you. “I can praise you for washing your hands. I want to.”
Steve encourages you to turn into the sunshine. You lay your cheek against his shoulder. “Love you,” you say, your hand on his leg.
He stares right at the sun and blinks hurriedly. “I love you too.”
#steve harrington#steve harrington x reader#steve harrington x you#steve harrington x y/n#steve harrington x fem!reader#steve harrington imagine#steve harrington fluff#steve harrington fanfic#steve harrington oneshot#steve harrington scenario#steve harrington drabble#steve harrington fic#steve harrington fanfiction#stranger things fanfiction#stranger things#stranger things fic#stranger things x reader
369 notes
·
View notes
Text
RIP Tracy Tormé, Creator of the "Holodeck Malfunction Episode" and Sliders

Tracy Tormé’s most enduring legacy in popular culture is that, while a writer on TNG’s tempestuous first and second seasons, he created the entire concept of the Holodeck Malfunction Episode.

Yes, even people who suggest you skip TNG’s first couple seasons say that “The Big Goodbye” is one you don’t want to miss. And there was a very nice tribute to Tracy Torme in an episode of Picard, which had him as the author and creator of Dixon Hill… which he is, and deserves credit for this.

I suppose I should mention I had a personal encounter with Tracy Tormé at a convention. The main thing I remember was that he looked absolutely terrified when someone asked him about what happened with “The Royale,” far and away TNG’s worst episode except the clip show, about the crew getting trapped on a hotel they can’t leave from a badly written book. To his great credit, he took responsibility for the episode not working and did not pass on the problems to the production crew.

The most extraordinary thing about Tracy Torme is that he had a Forrest Gump like ability to appear in the background of scifi culture’s greatest moments.
Not only was he inside the TNG writers’ room in 1987-88, he was around during the production of Terminator with James Cameron. Tormé was the one who, hearing about the production of the film, squealed on it to Harlan Ellison, telling Ellison that it was based on his old Outer Limits episodes, with a visual based on his script for “Demon With a Glass Hand.” In other words, he was the Gavrilo Princip who got that entire conflict started, where two of the most proud personalities in scifi butted heads, James Cameron vs. Ellison. Cameron, to this day, insists that the film company gave Ellison money and a credit because it was easier to pay him off than to go through litigation (which rings true, frankly, for risk averse production companies), and to this day Cameron insists, with his absolutely expected big dick swagger, that Ellison is a “parasite” who received money for nothing, and if it had been up to him, he wouldn’t have given him a dime.

It’s also worth mentioning that Torme also created the TV series Sliders.
Has anyone else noticed that Sliders is an incredibly right wing show? Seriously, watch it again if you haven’t seen it in years. If you haven’t watched this show since the 90s and you were a kid and all that went over your head, it’s kind of amazing how Limbaugh/Newt Gingrich era right-wing Sliders actually was. It made 24 look like Doonesbury. The targets of Sliders were 90s New Right satire: health care systems, infuriating hippies, the nanny state disallowing the public smoking of cigars, California weirdness, the drug culture, the USSR. Torme’s right wing views were less John Millius-style “blood alone moves the wheel of history” stuff, but more like that of a slobby regular joe in the 90s, Dennis Leary’s character in Demolition Man for instance, who mostly just wants to smoke cigars, ogle girls, and eat hamburgers without getting scolded by his wife. He was less “Passion of the Christ” and more “Animal House.”
I am not saying this as a negative, but merely a description. Contrary to popular belief, right wingers driven by bizarre sexual pathology and weird grudges produce amazing art, as Millius and John Swartzwelder show. A lot of Steven Universe fans love to say things like “all good art is about empathy and kindness” and I reject that notion. Good art can also be about reflecting things in the human experience like fear, trauma, cruelty, and paranoia.

For that reason, it doesn’t surprise me that Tracy Torme’s best movie script was a horror film about a traumatic experience, Fire in the Sky. An ominous movie about a vanished ranch hand who was the victim of alien abduction, in the earned finale the film’s tension builds toward, our hero remembers the true cause of his missing time: an abduction by aliens, who’s motives are emotionless and incomprehensible, and who subject him to horrific vivisection that we see in excruciating detail. Travis Walton is treated not with sadism or cruelty, but with icy detachment, by alien superintellects that view him as no different than cattle, and are to him as we are to cattle. The most terrifying detail of the film is that the classic “gray alien” look turns out to be spacesuits, revealing a far more frightening appearance underneath.


362 notes
·
View notes
Text
aventurine‘s eidolon names and possible references/symbolism they include :
( eidolon names include links to corresponding wikipedia pages. it isn’t the best source but it explains these concepts more in detail than I did ! )
e1 - prinsoner‘s dilemma - a thought experiment in which 2 parties, the titular prisoners, must both make the choice of either trusting the other and not betraying them for mutual benefit or choose not to trust the other and betray them for individual benefit
e2 - bounded rationality - a decision making process defined by trying to achieve something that is just good enough, rather than something wholly satisfactory
e3 - droprate maxing - I couldn’t find a definitive reference to anything here, it might just be a nod to aventurine‘s luck or something along those lines
e4 - unexpected hanging paradox - a paradox wherein a person is told that an event will occur in the future but isn’t told the time of said event. this could be a reference to the role aventurine plays in the penacony tbq and his views on the inevitability of his own death
e5 - ambiguity aversion - ambiguity aversion is the tendency to prefer the known over the unknown. notably, taking known risks over unknown ones. this is most likely a nod to how aventurine is known as a risk taker and could shed insight on how he chooses the risks he takes
e6 - stag hunt game - the stag hunt game is similar to the prisoner‘s dilemma idea. two hunters can either catch one hare individually or catch a stag if they work together. the hare hunt offers less risk and need for trust while the stag hunt offers more reward
#please let me know if there’s anything I forgot !#or if you have any criticism !#I mostly compiled these for fun and because I got curious#if there’s any requests I might do more characters ! :]#//#textpost //#theory //#( kind of )#fandom //#hsr //#hsr#honkai star rail#hsr aventurine#aventurine#aventurine honkai star rail#kakavasha
91 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Write a Schizoid Character
Schizoid Personality Disorder (SzPD) affects an estimated 1% of the population, similar to rates of autism, but is widely overlooked both in real life and in fiction - to the point where it is often colloquially labelled "the silent disorder". This is a somewhat comprehensive guide in how to write a character with SzPD, from someone who has it.
Quick research guide
I'm writing this guide with the underlying assumption that you've already done some cursory reading into the basics of SzPD. At this point, you need to understand two things: One is that this disorder is incredibly poorly researched, due to schizoids often not seeking treatment for the disorder itself (they sometimes seek treatment for comorbidities like depression or anxiety); and two, as a result of this, there is a lot of over-simplified misinformation out there about SzPD. This disorder often gets boiled down, even by mental health professionals, to the DSM-V or IDC-10 diagnostic criteria, which are criticised widely in the schizoid community for being incredibly superficial descriptions of overt SzPD. This is the kind of case where you need to seek out the SzPD specialists or the schizoids themselves for information about the disorder.
Akhtar's profile is a good overview. Psychologist Elinor Greenberg has a quora where she answers all sorts of questions about SzPD, and she typically hits the nail on the head. Other resources include Schizoid Angst, a youtube channel run by a man who has SzPD (this convo in particular is really good). If you're interested in a deep dive, I recommend reading The Divided Self by R.D. Laing for a deeper understanding of the inner workings of schizoids, as well as the relationship between SzPD and the rest of the schizophrenia spectrum.
Understand the "root" of SzPD
SzPD typically forms as the result abuse, neglect or abandonment in childhood. Schizoids have learned through trauma that emotional intimacy, vulnerability, and dependence on other people all have the potential to harm them badly, and as a result, they tend to avoid those things. In that sense, schizoids don't have a problem with other people, per se. Understanding this fact can help you write your schizoid character with more realism and nuance.
For example, it's a common misconception that all schizoids are averse to having sex. Many schizoids are, to be fair - but plenty of schizoids also frequently engage in hook-up culture, or form other sexual relationships. Physical intimacy can be entirely seperate from emotional intimacy, and thus pose no real risk to a person with SzPD. It's also possible for schizoids to form good relationships with other people, if those relationships are based on non-emotional grounds, such as recreational interests, work, religion, etc.
You can show this in your schizoid character by thinking about which of your other characters your schizoid might gravitate towards. In general, they will feel safest with characters who place few (or no) emotional demands on them, don't place high value on phatic gestures, don't pry into their emotional state or background, respect their need for independence and agency, and so on.
Overt or Covert?
Once you've researched the disorder a bit, you need to decide whether your schizoid character is overt or covert. The overt/covert split is about 50%/50%, so neither is more likely than the other.
Overt schizoids tend to be a lot more blunt about their indifference, visibly detached and aloof, and are typically way less likely to engage in social settings (or be in social settings at all). These are the characters who have blunt affect, ie. won't have much of an emotional reaction to their surroundings, even if it directly involves them (ex. getting praised/criticised). They may have odd speaking patterns, such as stilted or vague speech, and can sometimes come across as cold and uncaring. Overt schizoids are noticably reluctant to reveal what's going on in their internal world, so they might also come across as enigmatic, secretive, or mistrustful.
If your character is an overt schizoid, think about how their behavior and personality are percieved by other characters, what kind of reactions might arise. Think about how your schizoid character might navigate these reactions - after all, they're probably used to getting comments. How do they react if someone comments on how disinterested/moody they seem? Do they tell the person to fuck off? Do they raise an eyebrow, and that's that?
Covert schizoids, or "secret" schizoids, experience the exact same symptoms as overt SzPD, but they hide it behind what's called a false-self system. You can think of it as a form of compulsive masking. Apart from perhaps vaguely eccentric behavior, you typically won't be able to tell that a secret schizoid has SzPD unless you know what you're looking for. If your character is a secret schizoid, they will behave in a way that seems socially engaged and interested, maybe even extroverted, but they will be emotionally withdrawn and safe within an internal world.
If your character is a covert schizoid, your other characters might not notice that anything is out of the ordinary with them at all - until they learn more about your character's lifestyle. Secret schizoids are not as used to being confronted about their odd behavior as overt schizoids are, and, depending on the character overall, might respond to these confrontations with awkwardness, defensiveness or confusion. Many secret schizoids are also unaware that they have SzPD, but are instead just vaguely aware that their behavior and preferences seem strange and different to other people.
Figure out the internals
An intricate internal fantasy life makes for a well-thought-out, sharply self-aware character. Schizoids spend most of their time in their own heads, so you need to have a good understanding of your character's internal world, fantasies and reflections, and how these things affect their behavior, priorities and decisions.
For many schizoids, their fantasy life is rooted in their own lives, either their past, present, or future - what-ifs, what-if-nots and could've-beens. They'll have internal "interactions" with other people they know, play out entire conversations and scenarios, and respond and react much more vividly than they tend to in real life. For other schizoids, their fantasies exist in a world entirely seperate to our own, with its own rules and structure, which they can explore to their own liking. For others yet, they think up fictional stories, sometimes inspired by real life, sometimes not.
Themes in the internal world often reflect the schizoid's own struggle with independence and intimacy. A lot of schizoids use their fantasies as a safe and sufficient way to feel "connected" to others. Others have violent, vengeful fantasies, which often juxtapose the indifferent demeanor - these fantasies tie in to the need for independence and emotional control, sometimes referred to as schizoid omnipotence.
Beyond the intricate fantasies, consider your character's moral beliefs. Schizoids tend toward idiosyncasy - we're in the "odd and eccentric" cluster for a reason. Akhtar described this quality as "occasionally strikingly amoral, at other times altruistically self-sacrificing." Take some time to figure out how this might express itself in your character, and how it is percieved by the characters around them.
Schizoids and relationships
You know how borderlines have their favorite person, and narcissists have their chosen person? A schizoid might just stumble upon someone who will become their interest person, or IP.
An IP is someone outside their immediate close family who the schizoid feels safe enough to be vulnerable with, are genuinely interested in, and who the schizoid forms an honest-to-god emotional connection to. This relationship can be either romantic or platonic in nature. If you choose to give your schizoid character an IP, make sure to emphasize how much this relationship stands out as uniquely meaningful to the schizoid - this is the one person they are even capable of having a genuine bond with, and that bond alone can keep them grounded against feelings of cosmic isolation. Your schizoid isn't likely to take this for granted.
An interesting tidbit of information is that schizoids paradoxically tend to gravitate towards relationships with highly extroverted, emotional people, to the point where the schizoid-hysteric relationships are an entire category of psychological research. Here's a really good snippet that describes how that dynamic tends to play out.
(Also keep in mind that just because a schizoid doesn't have an IP does not necessarily mean they are miserable. A lot of schizoids are capable of finding their own peace with whatever tools they have available.)
Another notable term for schizoid relationships is the controversial stock friend. A stock friend is a person who considers themself friends with the (typically covert) schizoid, and who thinks they have an emotional connection with them, but who the schizoid feels no emotional connection to, has no real interest in, and only interacts with out of convenience or happenstance. Is this immoral? Are schizoids leading people on, or are we justified in masking to avoid a constant stream of awkward confrontations, that have the potential to hurt other people's feelings? Who knows.
Splitting
You might have heard of idealization/devaluation-splitting as it pertains to borderline PD (bad/good) or narcissistic PD (worthy/unworthy). Splitting happens in SzPD as well, along the axis of safe/unsafe.
Schizoids will occasionally cut other people out of their lives, and this usually happens when they get overwhelmed with another person's attempts at emotional intimacy, or their boundaries have been deliberately or repeatedly crossed. They will often view the person as relentlessly prying, controlling, demanding, or dangerous, and will desperately seperate themself from that person as a way to avoid being consumed, or "smothered". At this point, if the other person doesn't let the schizoid get away, the schizoid might become overtly hostile. This is a fear response.
If you want to write a schizoid splitting, be aware that a split with a schizoid usually marks the end of the relationship altogether - especially if the relationship hasn't lasted for very long, and double especially if the person isn't the schizoid's IP. Once a schizoid has lost trust in someone, that trust is very, very difficult to build back up, even if both parties agree to try. Your schizoid character is going to be incredibly wary of the other person, and the relationship is probably never going to feel like it did before.
Beware of stereotypes
Every once in a while I'll encounter a story that features a character who has very obvious schizoid traits, and almost every single time, their arc leaves me disappointed and frustrated. Here are some tropes I would personally avoid writing for a schizoid character.
"He just needed love all along." Kill this trope, no exceptions. Strong emotional intimacy can erode or overpower a schizoid's sense of self, and usually leads to feelings of smothering, being trapped/crushed by the other, and losing autonomy and independence. A schizoid is capable of love on their own specific terms, but if it's on the terms of other people, they will strongly feel like it's something being forced on them against their will. They might still outwardly "accept it" as a form submission or compliance, but it will not be out of love. This trope gives me psychic damage.
"He sacrificed his life for others, which proves that he cared all along." This trope isn't necessarily bad, it just always leaves me with this impression that neurotypicals can only interpret caring when it happens in the extremes. And while it's true that schizoids can sometimes be altruistically self-sacrificing, it's kinda depressing to see schizoid-like characters die all the time. There are other ways you could show schizoid altruism that would also leave the door open for more closure for the character themself.
"He turned evil and violent." While this trope isn't quite as common as it is with other disorders, notably those from cluster B, it does still exist. So here's your friendly reminder that mentally ill and neurodivergent people are more likely to be the victims of violence than to be perpetrators, by far. I'm not saying you should never write a schizoid bad guy, you certainly can - I'm just telling you to be very careful about how you go about it, so you don't end up sending the wrong kind of message.
Conclusion
Schizoid characters are cool, and I wish there were more well-written canonically schizoid characters out there. But I'm also clearly biased, so what do I know
#essays#writing advice#neurodivergence#szpd#im supposed to write mm and here i am. procrastinating by spending 4 hrs writing a hyperspecific post about fictional schizoids
243 notes
·
View notes