#what does this have to do with modern greece
Text
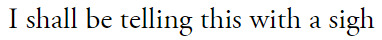

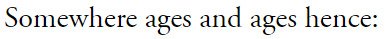

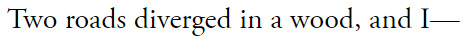


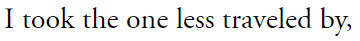



NICO: WE SHARED THE LIFT THIS MORNING! I WAS GOING TO THE POOL TRAMPOLINE WITH MY TWO DAUGHTERS AND HE WAS GOING TO THE RACETRACK.
PINKHAM: VERY DIFFERENT LIVES YOU'RE CURRENTLY LEADING.
#that line from nico is like /the/ modern brocedes thesis to me#like this is their happy ending!!! it is not the one they dreamed of all those years ago in greece but is a happy ending.#it's not multiple shared championships or racing against each other for years or anything their 13 year-old-selves would've dreamed up but#it is them achieving their dreams. lewis has 7 wdcs and is aiming for an 8th. nico has a loving wife and 2 daughters he'd die for. they are#both doing the things they love. would it have been nice if those dreams included each other? yeah. would it have been nice that when ppl#mention their names it would be to talk about what great friends they are instead of how they tore each other apart? absolutely! but they#were doomed from the start. so maybe it doesn't matter that they didn't get their traditional 'happy ending'. at least they had a happy#start and a semi-happy middle. at least they have the lift to see each other. at least nico's daughters get to keep lewis in their lives in#a way nico will never get to again. they will never share a bowl of frosties again but at least their roots are so thoroughly tangled#together that they can never look back without haunting each other. at least they still have that.#anyway for all the non-americans who reblog or like this. the poem is 'the road not taken' by robert frost. very famous in america#every middle/high schooler has to analyze/read this poem at some point. i don't know how popular he is outside of america so i thought id#leave a note ig.#anyway. i am going crazy and i need to lie down. that 2nd line was sooo hard to find a photo for. wth does 'hence' even mean???#brocedes edit#brocedes#f1 web weaving#f1#nico rosberg#lewis hamilton#f1 edit#nr6#lh44#web weaving
95 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dissecting ancient Greek wedding customs (or “How to adapt the clusterfuck they are into something somewhat doable for the 21st century”)
This post is going to be a bit different. I could stick to writing about the customs we know of from a purely historical perspective, and while it would be informative, it wouldn’t reflect what I’ve actually been up to. Some of you might already know, but I’m getting married, so I approached this topic with the intent of seeing what I could do (and get away with).
So this post is going to be more about method and the practical challenges that come with doing the groundwork of adapting very old (and often outdated) traditions in a way that makes sense for our modern times.
I do have some disclaimers to make before I get started:
Most (if not all) of the literature around ancient Greek marriage is hetero-normative. However, this does NOT mean that marriage rites shouldn’t be adapted for queer marriages or that queer marriages can’t be done within Hellenic paganism. It’s our job as reconstructionists and revivalists to rework and adapt to our needs.
Similarly, this post is bound to mention or detail cult practices that are no longer in line with our modern sensibilities. I also want to make it clear that this post is not a tutorial. I’m not saying how things should be done, I’m only exposing elements that I consider reworkable and propose suggestions so that it can help others make their own research and decisions, with the level of historicity that they deem fit.
While the wedding customs from fifth century BC Athens are decently known, the ones from other cities and regions of Greece are much more obscure outside of anecdotal and fragmentary details (with the exception of Sparta). For this reason, the Athenian example is what I’ll be using as foundation. If you reconstruct practices from other areas of the Greek World, you might find something valuable in this article: The Greek Wedding Outside of Athens and Sparta: The Evidence from Ancient Texts by Katia Margariti.
Basic/simplified structure
The typical Athenian wedding would spread over three days, and be marked by several steps, some of which are listed below. Note that the order of these steps is not precisely known and might have been flexible:
Pre-wedding:
Decorating: korythale at the door, decoration of the nuptial bedroom
The Proteleia
Filling of the loutrophoros
Wedding day
Nuptial bath
Adornment of the bride
Wedding Feast
Hymenaios
Anakalypteria
Nymphagogia
Katachysmata
Day after
Epaulia
Gamelia
Final sacrifices
Some of these steps included specific customs and traditions, not all of which are reconstructible for various reasons.
Decorations
The korythale: the korythale was a sprig, usually from an olive tree (or laurel), which was placed at the groom’s door (and perhaps the bride’s too). The word in interpreted as deriving from “koros” and “thallein”, which would translate “youth-blossom”.
The korythale is very reminiscent of the eiresione, which was a similar kind of branch of laurel used during the Thargelia and/or the Pyanepsia that had apotropaic purposes. Athenian weddings included a procession from the bride’s home to the groom’s house, so the presence of the korythale at the doors would indicate that a wedding was taking place involving the decorated homes.
While I haven’t seen any one make this interpretation, I would still be tempted to argue that decorating the thresholds of houses has a similar protective and luck-bringing purpose than the eiresione, which was also hung above the door of Athenian houses.
The thalamos (nuptial bedroom): While there is no doubt the houses were properly decorated for the occasion, we have mention of special care given to the nuptial bedroom.
It’s important to understand that the procession from the bride’s house to the groom’s went up to the bedroom door, it was generally an important location and its preparation is seen represented on ancient pottery. Euripides mentions the adornment of the bed with fine fabrics, while Theocritus mentions the smell of myrrh (sacred to Aphrodite). There is also evidence that, in the Imperial period, the practice of hanging curtains to create a canopy above the bed was adopted, very likely from Egypt.
When it comes to adapting this today, it is pretty straightforward and there is plenty of room for personalization. The korythale could be challenging depending on how easily available olive or laurel are in your area. I would also argue that the custom could be more loosely adapted so that instead of being at the houses’ doors, it could take the form of a floral arrangement at the door of whatever venue you are using.
Proteleia
In short, the proteleia refers to sacrifices and offerings that would be made to various gods before the wedding. The exact timing of these is more or less unknown, but we have reasons to believe they could be done a day or a few days before the wedding, and perhaps also on the day of the wedding. These offerings were made independently by each family.
It is in this context that the offering of a lock of hair and of childhood items is best known for brides. The recipients of the offerings are varied: In Athens the most mentioned are the Nymphs and Artemis, but various sacrifices to Aphrodite, Hera, Athena and Zeus were also performed. In other parts of Greece, pre-nuptial customs often included sacrifices to local heroines. Plutarch, in the 2nd century AD (and therefore way after the focus of this post) mentions the main five nuptial deities to be Zeus Teleios, Hera Teleia, Aphrodite, Peitho and Artemis.
Today, I believe the exact choice of who to offer to and what to offer very much comes down to personal preferences and circumstances. While we assume that both families made prenuptial sacrifices, we know very little of the groom’s side of things, since the focus was on the bride, and the rite of passage aspect was not present for the groom in Ancient times. This is a gap that leaves room for modern innovation eg. including Apollon to either replace or accompany Artemis or choosing a group of deities that is more couple-centric rather than family-centric.
Personally, I have settled on Aphrodite, Hera and Artemis and have integrated a Spartan custom that includes the mother of the bride in the sacrifice to Aphrodite. Hera Teleia will receive a lock of my current hair, while Artemis will receive a lock of hair from my first haircut as a child (that my mother has kept all these years), alongside some other trinkets. The groom will honour Zeus Teleios in a passive way. And I will honour the Nymphs through the the rite I will explain next.
Nuptial baths
Both bride and groom had a ritual bath before the wedding. Its purpose was of cleansing and purificatory nature, and is consistent with other water-based pre-sacrifice purifications. What made the bride and groom's baths distinctive was their preparation. The bath water used to be drawn at a specific spring or river. At Athens, the water for bridal baths came from the Enneakrounos, the fountain house for the spring Kallirrhoe, but each city had its dedicated source. The water was carried in a special vase named the loutrophoros (bathcarrier) and the act of fetching the water and bringing it back to the homes constituted a procession. The loutrophoros was often given as offering to the altar of the Nymphs after the wedding. It was an important symbol of marriage, to the point that, if a woman died before being married, she would often be buried with a loutrophoros.
This will be more or less difficult to adapt depending on circumstances and environment, but the logic of a purifying bath (or shower even) can be kept (though I would discourage bathing in water you are not sure of the cleanliness of). The idea of having a specific vessel can also be kept. Personally, I plan to have a special vessel for some type of purified water, and while I may not bathe in it, I plan to sprinkle it and/or wash my hands with it.

Adornment of the bride (and groom)
Traditionally, the bride would have a nympheutria (which we could equate as a bridesmaid, but seems to have often been a female relative) charged of helping the bride get ready. I won’t get into the details of the clothing we know about, mostly because there seems to be a lot of variation, and because I consider this to be a very personal choice. However, we can note that both groom and bride were adorned with a wreath or a garland of plants that were considered to have powers appropriate for the occasion (sesame, mint, plants that were generally considered fertile or aphrodisiac). Perfume is also something attested for both bride and groom, especially the scent of myrrh. The bride would wear a crown, the stephane, which could be made out of metal or be vegetal (the stephane is now the object of its own crowning ceremony in Greek Orthodox weddings). The bride’s shoes were also particular for the event, and named nymphides. The bride’s veil was placed above the crown.
Hymenaios and Feast
I am grouping these two since they are linked. The feast was more or less the peak of the wedding ceremony and lively with music and dances, as Plutarch indicates (Moralia, [Quaest. conv.] 666f-67a):
But a wedding feast is given away by the loud cries of the Hymenaios and the torch and the pipes, things that Homer says are admired and watched even by women who stand at their doors.
The hymenaios was a sung hymn in honour of the couple and the wedding, and there were other songs that were specifically sung at weddings. However the hymenaios wasn’t only for the feast, these songs would be sung also during the processions. The hymenaios also had the purpose of ritually blessing the couple, a ritual that bore the name of makarismos.
As for the feast, it was obviously abundant with food and the prenuptial sacrifices provided the meat that would be served. There is otherwise very little difference with what a modern wedding feast would be like: food, drink, music and dance around which gathered friends and relatives of the couple. Like today, the wedding cake(s) was an important part of the celebration. It was called sesame and consisted of sesame seeds, ground and mixed with honey and formed into cakes to be shared with the guests.
Anakalypteria
Note that there is a bit of a debate around this step, which is the unveiling of the bride. Some believe the bride kept her face veiled until this part of the wedding, where her face would be uncovered for the groom to see. Others interpret this step the other way around, where the bride is then veiled as a result of being now married. The timing of the unveiling is also up for the debate. It might have been during the feast (at nightfall), or after once the couple was escorted to the bridal chamber. There doesn’t seem to be a clear consensus.
The concept of unveiling the bride is otherwise something that isn’t unknown to us as a modern audience. As with everything else, how to interpret and modernize it is up to personal preference.
Nymphagogia and Katachysmata
The nymphagogia aka the act of “leading the bride to her new home” took place at night, likely after the feast. It is at this point that the groom ritually led the bride to his home by taking her by the wrist in a ritual gesture known as χεῖρ’ ἐπὶ καρπῷ (cheir’ epi karpo). The relatives and friends of the couple formed a festive procession that accompanied them to their new home accompanied by music and songs. The mother of the bride led the procession carrying lit torches, while the groom’s mother awaited for the new couple in their home, also bearing lit torches.
Once there, the rite of the katachysmata would happen. The couple would be sat near the hearth and the guests would pour dried fruits, figs and nuts over the bride and groom as a way to incorporate them into the household and bless the union with prosperity and fertility. As part of this rite, the bride ate a fruit (either an apple, quince or pomegranate). It is only after this step that the couple would be escorted to the bridal chamber.
These two rites are tricky to adapt in a modern context because of how location-specific they are (and that’s not even taking into account the implications of having family escort you to your bedroom etc). My take would be that the katachysmata is not too far off from the custom of throwing rice/flowers at the couple after the ceremony, and could probably be incorporated as such. The torches could also be replaced by any source of light placed in a meaningful location, depending on the where the wedding is being held. The nymphagogia could also do with an update, the easiest of which could simply be holding hands while leaving the wedding ceremony.
The day after (Epaulia, Gamelia & sacrifice)
The epaulia refers to wedding gifts to the couple, which would be given the day following the ceremony. At this point, it is implied that the couple has consummated their marriage and are officially newly-weds. Pausanias informs us that the term “epaulia” (also?) refers to the gifts brought by the bride’s father in particular and included the dowry.
After the epaulia, the bride's incorporation into her husband's house was complete. This might have been when the groom held a feast for his phratria (aka direct family), as a way to conclude the wedding.
As for final sacrifices, the bride herself may have marked the end of her wedding by dedicating her loutrophoros at the sanctuary of Nymphe, south of the Acropolis.
The epaulia could be adapted, in modern terms, with having a registry. Should someone choose to have a specific vessel linked to the ritual bath today, it could very well be kept, dedicated to the Nymphs and used as a small shrine. Considering how symbolic the object is, there is also room for it to become a piece of family heirloom.
Final words
This is really only a small summary of what a wedding could have looked like, sprinkled with a few ideas of how to manage the gaps, discrepancies and limitations. As I said in my introductions, there are details I haven’t mentioned. Some of the customs detailed here have clear modern counterparts, but others don’t. I’d like to conclude by addressing these.
First, the ancient Greek (Athenian) wedding is completely devoid of priestly participation. It was entirely planned, organized and led by the two families. Religious responsibilities were entirely self-managed. I find this point important to remember because it makes it much more accessible than if modern Hellenic pagans had to seek out an external authority.
Some of you might have noticed the absence of wedding vows, at least in a formal form like the one we are used to in our modern days (derived from Christian and Jewish traditions), this is not an oversight, there simply were none that we know of. As a sidenote, I would also advise against turning a wedding vow into a formal oath. I’m still debating on what to do myself, but I’m leaning towards a religiously non-binding vow that won’t curse me should things go wrong.
Adapting the structures and rites of the ancient wedding to today’s framework of ceremony will naturally lead to changing the order of things, on top of sacrificing elements for the sake of simplicity, practicality, personal preferences and, very likely, visibility. Unless you’re lucky enough to do a private elopement, chances are that relatives and friends might be there, and not all might know or even approve of your faith. I hope this post shows that there can be ways to include traditional religious elements that will go unnoticed to the untrained eye, like I hope it showed that the private nature of the ancient Greek wedding rites is a significant advantage for modernization.
#hellenic polytheism#hellenic paganism#hellenic pagan#heradeity#greek history#ancient greece#zeus deity#aphrodite deity#artemis deity#hellenic reconstructionism#wedding rites
739 notes
·
View notes
Text
One of the things I hear a lot from Gentile witches and neo-pagans who want to work with Lilith or claim to work with Lilith, is that she is actually a Mesopotamian goddess, usually either Ishtar/Inanna or Erishkigal, and that it was the Jews, with their horrible patriarchy juice, who slandered her and cast her down, and so the Jews do not deserve to say what happens to her and it isn't antisemitism to work with her, or to completely ignore what the Jews say about what she is in a Jewish context.
Lilith is not Ishtar or Erishkigal. However, there is a Mesopotamian figure that is pretty stinking analogous to Lilith, and is probably her folkloric ancestor, by which I mean the idea of Lilith probably comes from this Mesopotamian figure. In fact, Lilith almost certainly is either a Jewish version of this figure, or, they are both descended from the same Near Eastern and Mediterranean basin folkloric figure. That figure is Lamashtu.
Lamashtu is, much like Lilith, the supernatural embodiment of maternal and infant mortality, a figure of power and terror, who functions as a way to embody and cope with the profound dangers that are pregnancy, childbirth, and infancy without effective medical care. the Mesopotamians never worshiped Lamashtu, but they did seek to appease her, including making symbolic gifts to her, to keep her from visiting them, and killing them or their children.
An interesting side note is that there is also a Mesopotamian figure who specifically opposes Lamashtu and functions as the protector of pregnant women and infants, and that figure is Pazuzu, a wind spirit, who ruled over other wind spirits, including ones called the Iilu in the Akkadian language. Akkadian is a Semitic language, related to Hebrew, and this word is probably a cognate of Lilith, but the Iilu probably have no relationship to the figure of Lilith except her name. You might know Pazuzu as the demon featured in the movie, The Exorcist, and ironic fate for a mythological protector of women and children.
Anyway, if you'll remember, I implied above that the Lamashtu/Lilith figure, was present in various guises throughout the Mediterranean basin and the Near East, so there are of course figures analogous to both of them throughout the region, such as Lamia of Greece, and the Strix of Rome.
So if you really really want to work with a figure who functions as the supernatural embodiment of maternal and infant mortality, Lamashtu, Lamia, or the strix would all be excellent options that don't come from an extant closed religious practice. All the baby killing, none of the antisemitism and cultural appropriation.
While all three figures are almost certainly descended from the same folkloric root, they're all subtly different, because as stories and characters travel, they change. as such, they all have particular good points about them as figures of veneration.
Lanashtu is the OG bad bitch, who commanded fear, respect, and offerings, like a mythological mafiosa, collecting protection money.
Lamia has attached to her the story that she was one of Zeus's dubiously willing lovers, who was screwed over first by Zeus, the embodiment of patriarchical rule, then by a jealous Hera, the embodiment of patriarchal marriage, so if what attracted you to Lilith was the story from the Alphabet of Ben Sira, about a victim of the patriarchy getting her own back through violent vengeance, Lamia might be the girl for you. With her however, the emphasis is less on her murder of children, then on her seducing and eating men, though she does also get strongly associated with killing children, especially boys.
And the strix is particularly interesting, because the word comes down to us in the modern Italian word for witch, striga. Indeed, one of the theories as to where the witch figure came from in Early Medieval, and then Early Modern Christianity, was as the strix demon made human. This might explain the close association between Early Modern Witchcraft and infant mortality, including Italian stories of witches causing infants to die seemingly natural deaths, so that they could dig them up and eat them after their funerals, something that ties these human supposed witches very closely to demonic folkloric antecedents. If you are looking for a figure of unfairly maligned female power, the strix and her close association with later human witches, might be the one for you.
All three of these figures, much like Lilith herself, are reflections, both of the power women wielded even within patriarchal societies, over the process of pregnancy, birth, and childrearing, and also the powers of death and loss that everyone was subject to. There is something powerful, transgressive, and even healthy in acknowledging the fears and dangers presented by this death and loss,and for some people, that might take the form in venerating the underlying powers. If this is something that would be spiritually meaning for you, and you wish to work with such a figure, and you are not Jewish, please respect the fact that Lilith is part of a closed religious practice, and remember that Lilith has sisters, in other parts of the Mediterranean basin and the Near East, who are not from extant closed cultures, and who might serve your needs better anyway.
666 notes
·
View notes
Note
I wonder why christian misrepresentation are rarely talked about if compared to other religion misrepresentation. Like, I've seen people really vocal about Greek myths misrepresentation in LO and such (and it's valid because it's a culture and religion) but I rarely saw the same thing with christian even though there are many media who use christian religion innacurately, to the point where it comes off as using it as an aesthetic and not a proper religion.
Is it because of rampant religious trauma especially in western world? No ulterior motives on this question. I'm not a christian and yet I'm curious about this. I apologize if this sounds harsh.
I obviously don't have The Answer(tm) to this but personally speaking (and I'm about to get VERY personal here so take this with MOUNTAINS OF SALT), I think it's just the obvious - Christian mythology is one of the most well-documented and strongly protected out of virtually any other religion on the planet. Especially here in the West, it's commonplace for kids to go to Sunday school, for couples to have Christian weddings even if they're not practising Christians themselves, even the American anthem references the Christian God. It's simply not as easy to 'misrepresent' it because the representation is written into our very fabric of society. Even Greece itself is primarily made up of Orthodox Christians.
So anyone that does 'misrepresent' it are either completely mislead hardcore Christians, or people who are doing it intentionally, such as with the intent to make a parody of it or to deconstruct it through a different context or whatever have you. And of course, people will still get mad at those things, if you're implying that people aren't vocal about Christian misrepresentation then frankly IDK what to tell you there LOL If you want a contextual example in the realm of webtoons, Religiously Gay was dragged to hell and back during its launch for having a very crude and insulting depiction of St. Michael, and frankly, yeah I don't disagree because what the fuck is this-

(like at best it's just terrible character design lmao that said, there's also plenty else to criticize Religiously Gay for, including its fetishy representation of gay relationships and the fact that it's still just the "naive person who looks and acts like a child hooks up with mean person in a position of power" trope, blech, but the character design is definitely the first thing you notice)
There are even plenty of hardcore Christians who will deadass claim "misrepresentation" over things that ARE factually correct but they just haven't read the actual Bible and simply cherry pick what works for their own agenda. And of course those people are routinely called out by people like myself who know for a fact that Jesus wouldn't have promoted the war crimes that many modern day Christians are committing and justifying today. So it really depends on the definition of "misrepresentation" here.
The issue specifically with LO and Rachel that I personally call her out for (and many others) is that she's called herself a "folklorist" and claimed she's so much more knowledgeable on Greek myth than anyone else, while making a complete mockery of the original mythologies while not being honest about her intent as to whether LO is actually supposed to be a legitimate retelling OR a parody (because it sure acts like the latter more than the former, but she still seems to expect us to take it seriously and consider her knowledge of Greek myth superior?) Which leads to a lot of her teenage audience claiming shit like "Persephone went down to the underworld willingly" and "Apollo did assault Persephone in the original myths actually" and the classic "why would Lore Olympus lie or make up fake myths?"

You just can't pull off this extent of erasure with Christian mythology because we have a whole ass book of it that's been preserved, sold on shelves, and systematically integrated into society for thousands of years. Of course, there are people who will still try their damned best to twist the Bible to match their own bigotry with the whole "Jesus hates gays" bullshit (he would never), but it's met with equal amounts of 'misrepresentation' that are actually fully well-read and are intentionally subverting and changing things to either critique, parody, or restore the original intent of a lot of stories in the Bible without all the manufactured right-wing crap.
Greek myth, on the other hand, has some stories that are well preserved, and others, not so much. And in the modern day outside of the poems and hymns, you'll also rarely, if ever, see anyone use stories from Greek myth to ostracize, torture, and murder other people. "Misrepresenting Christianity" is more often done by actual Christians who are using the Bible to commit hate crimes than the people who have actually read the Bible and are just taking creative liberties with it for the sake of deconstructing / parodying / analyzing / subverting it. Veggie Tales "misrepresents" Christian stories because obviously Moses wasn't a fucking cucumber lmao but it still accomplishes its goal by retelling Christian stories in a way that's fun and educational for children.
By comparison (on the whole, I'm not comparing LO to Veggie Tales LMAO) LO just isn't clear in its intentions beyond Rachel's initial statements that she was trying to "deconstruct" the myths, while labelling herself as a folklorist. Therefore, I'm going to criticize how she does it because the way she's done it up until now has been very mishandled and has resulted in a lot of misinterpretations of the myths simply for the sake of fandom. And yes, these people exist in Christian media as well - they're called TV evangelists.
And that's my (very heavy) two cents.
#here's your reminder that missionaries are colonizers#find me the Hellenistic pagans knocking on people's doors asking them if they want to hear about the glory of Aphrodite lmao#honestly it also depends on what you're surrounding yourself with#obv if you take part in the LO fandom and avoid what's going on in the christian world then what you experience and see will seem skewed#like even i could be very wrong in my opinion based on my own experiences as someone who lives in the west-#maybe there ARE pagans knocking on doors and using greek myth to commit hate crimes#so yeah we all gotta try not to fall for survorship bias#there are plenty of stories of people getting mad about christian mythology and its misrepresentations on BOTH sides#lo critical#lore olympus critical#anti lore olympus#webtoon critical#ama#ask me anything#anon ama#anon ask me anything
169 notes
·
View notes
Text
But first, time to say good-bye
It was to be a late departure (bureaucracy will someday kill us all...) from Athens, an endlessly diverted way North through a very early summer and some fitful sleep near the border, where poppies were already in bloom and elusive to the camera:

I promised to share with you my story with Mycenae the day I would leave Greece for good. Yesterday was the day, so here goes.
I first went to Mycenae on a horrendously rainy day, in November 2018. The place struck me as a haphazard settlement of sorts in the wake of some ancient apocalypse, which was absolutely correct. We stayed in my colleague from Culture and Press' car, munched on some horribly stale koulouria as all hell broke loose outside, when she finally told me: ' you know what, I am happy we made it here: in Mycenae, you can only hear and tell the truth, you know'.
I have to say I ogled in suspicion. I was wet, hungry and completely unused to the Greek way of dressing everything up in mythology. She spoke Greek as I speak French and knew perfectly well what she was doing. She was casting a spell - an unbreakable one, for which I will forever be grateful. Oh, and as all myths would have it, the Lion Gate was closed, by the time we arrived.
It took me almost two years to go back there, during the pandemic, scared summer of 2020, when everything was empty and glorious to fully take in, like a big gulp of colors and sounds and life. My digs were to be always the same: unassuming Petite Planète, the last B&B in town, a stone throw away from Agamemnon's treasury, owned by the Dassis clan of archaeologists.
Their story begins in Constantinople, around 1875, when Konstantinos, a young orphan, begged Heinrich Schliemann to take him along to wherever he was traveling. He quickly became indispensable and helped with the first digs in Mycenae. He was the one who found Agamemnon's mask:

When the digging was over, Schliemann bought him a tiny house for two pence and a half and told him to stay there. 'Many people will come to visit and they will need food and a roof. Make sure you do your best and it will make you a rich man.'
And they came. In droves. If you ask nicely, V. will show you their reception rosters, safely tucked away in a bank vault, in Argos. I had the privilege to see Virginia Woolf's signature and I was stunned. Schliemann's two pence house is now doubled by a garish modern addition you can see from the main road as La Belle Hélène B&B ('my cousin Agamemnon is a greedy idiot', says V), but Schliemann's room is piously kept as it was when the strange German gentleman left them to their fate. As is, they did not become rich, but that does not matter. You will always find a place at their wonderful table, where Mamma Dassis cooks the same food they ate back in Constantinople and they would not have it otherwise. The new, bigger and better B&B is called Petite Planète because of V's father undying passion for Saint Exupéry's Little Prince. It permeates everything without being obtrusive, because sometimes 'the essential is invisible to the eye'.
Back in 2020, they were worried. Very worried. The Lion Gate was open again, but the 'cretins at Google' wouldn't have it and kept on listing it as closed, on their maps. People were canceling their bookings. The village stood unusually quiet and forlorn.
I made no promises. But I did phone some people at the Greek Ministry of Culture. The least person I expected to be of any help, H, a transparent, mousey freeloader, who was always the last to leave all of our events in the hope we'd take her to dinner in town, happened to be some sort of underling at the Archaeological Sites Department. She immediately understood what I wanted her to do.
Three days after I left Mycenae, on my road trip to the Mani peninsula, I received this message in my Booking inbox:
This started it all. And from that moment, all my Greek roads will lead there. It's also been a long time since I have trouble forcefully paying them for my monthly stays (booking and paying in advance helps, though), something they adamantly refused last time I went there:
'G., the girl wants to pay.'
'This is ridiculous, of course. This girl is family.'
Someday, I just know I will be back. For good.



After five years and a half, many more fabulous stories (Mycenean potter and poet, anyone? mad postman? Kyria Stamatoula and her goats? Kyrios Pandelis and his jams?) the only thing I know about Greece is that, for all its (many) misgivings, this land is about two things:
Friends and Heroes.
64 notes
·
View notes
Note
Apologies if this questions sounds stupid or ignorant, but I'm genuinely trying to educate myself. Can Jews be Jewish *and* a different race, so does a Jewish identity supersede another racial identity? Just wondering because a lot of Ashkenazi Jews I know (in real life or online) push back against the idea that they are white. I've heard European Jews say that they are not considered white, do not have white privilege, etc. so they are not white. But I've also seen a lot of Jews of color identify with both their Jewish identity and their "racial" identity (ravenreveals on Instagram explains how she identifies as Black *and* Jewish, and one of my friends identifies as an Asian Jew). So is there a reason many European (Ashkenazi?) Jews don't identify as white/identify as only Jewish? I'm sorry if this is offensive in any way, this isn't my intent :)
Sorry it took me so long to answer, I am swamped with asks haha
Yes, it's possible to be Jewish and a different race, as Judaism isn't a race, but an ethnoreligion, or even better described as a tribal nation.
Now, first I'm going to push back on you equating European with Ashkenazi. Ashkenazi is a specific term referring to Jews whose ancestors settled in the Rhine valley after the Roman expulsion from Judea. Many of these Jews eventually migrated eastward to Eastern Europe and Westward to British Isles, while others stayed in the Rhine valley region. But not all Jews whose ancestors settled in Europe are Ashkenazi.
There are Sephardi Jews, obviously, whose ancestors settled in the Iberian peninsula following the Roman expulsion, and then later migrated to North Africa, Northwestern Europe, Eastern Europe, and West Asia following the Spanish and Portugese inquistions.
There are also Italki Jews in Italy and Romaniote Jews in Greece, all of which are unique communities of Jews whose ancestors settled in Europe and who are not Ashkenazi.
Additionally, not all Ashkenazi Jews are racialized as white. Ashkenazi does not refer to your race, but rather who your ancestors are and/or what community traditions you follow. There are Ashkenazi Jews of every race.
The reason why lots of what-you-perceive-as-white Jews don't identify as white is because Judaism precedes the modern constructs of race (yes, race is a construct, not an immutable science) and because whiteness is highly subjective and fluid, just as non-whiteness is. Because race is a construct, which race a person is perceived as varies by where they are and by which people they are around.
Jewish "whiteness" is also conditional- and as Jews we don't like to leave ourselves vulnerable to shifting statuses. Jewish "white-passing-ness" can also be a tool of violence, either by denying the racial reality of antisemitism, or by being 'proof' that Jews are shape-shifting inflitrators of the white race. Hitler's Final Solution was total extermination precisely because he feared many Jews would pass as white and spread their Jewish blood among the Aryans, and so the total extermination of Jews was deemed as necessary, like one would exterminate a parasite.
This of course doesn't mean that no Jew has ever had access to the privilege afforded to whiteness. In the post-Holocaust era, many Jews have tried to successfully assimilate into whiteness to access even a little bit of privilege in order to protect themselves. I'm not going to lie and say that if I was pulled over at a traffic stop, my lighter complexion wouldn't give me more grace at the hands of the police officers than someone with darker skin would. Because yes, sometimes I am racialized as white and therefore access the privilege of whiteness.
But that doesn't mean I don't feel deeply uncomfortable when I'm filling out a form and the only options for race and even ethnicity are "white", "black", "hispanic", and "asian". Because while at the end of the day I'll check "white", it's only because I don't want to be accused of fraud (even though Middle Eastern or just Jewish would fit me better, but that's not an option). But that's just me. Some Jews are fine calling themselves "white Jews". Two Jews three opinions and all.
Someone introduced me to the phrase "racialized white/black/etc" a few years ago, and I think it makes much more sense. Because race is entirely dependent on perception and how others racialize you. I am not White, but sometimes I am racialized as white. Other times, I am racialized as "not-quite-white-but-we-don't-know-how-to-categorize-you-so-we're-just-going-to-try-and-guess-and-ask-wildly-invasive-questions".
At the end of the day, call Jews what they want to be called, and don't try and push labels on us. If a Jew doesn't want to be called white, don't call them white. Because race, ethnicity, religion, and all that is complicated, and Judaism predates all of that, so naturally Jews are going to have mixed feelings about it all.
#jumblr#race vs ethnicity vs haplogroup#judaism#jewish identity#jewish experience#if jew know jew know
272 notes
·
View notes
Text
Something I like about epic the musical is that it Gives it's changes to the original text an actual Purpose
( The first couple paragraphs are basically a rant regarding retellings. If you only want to hear about epic Skip to paragraph 4)
1. I am a bit annoyed by the lack of. Understanding as to why RETELLINGS aren't the most historicaly accurate things in the world. Sorry to break this to you, but that's both just how they work and I would guess how they reach success. Ancient Greece is a much different culture than our own, And most of us would be terrified to actually live back then. When you are Trying to create content That is based on ancient Greece And you want it to be successful/ At least reach a wide, and notably, MODERN audience. You're likely going to have to take some creative liberty And change a few things. Don't get me wrong, YOU DO NOT HAVE TO LIKE RETELLINGS KNOWING THAT FACT ( Me personally, I'm not the biggest fan of Miller's novels Even though I do like epic) BUT IT IS SOMETHING TO BE AWARE OF. And because of that I don't think I would ever expect a retelling to be perfectly accurate And I don't. I had interest in mythology LONG before epic the musical But I didn't actually read the Odyssey until getting into epic. I did not expect it To be just like the musical, I knew Odysseus was going to be much more of an asshole, along with other characters. The odyssey and epic are different pieces of media to me And I am not less of a mythology nerd for liking epic ( Though I will admit that sometimes I take tiny little fun facts of mythology And like to think of them in the context of epic, but that's just for fun.)
2. The Only time being a fan of retellings is wrong as if you genuinely believe they are perfectly accurate And refuse to listen to anything else ( Which has definitely happened, And mythology nerds have the right to be annoyed at that)
3. Some people only like to consume real mythology media, Others like both real mythology and retellings, Others only like to engage with retellings (I would hope they have the self-awareness to know It's not real mythology, From what I've seen some do and some don't, Unfortunately)
4. Ok. now on to what the title of this long ass rant says
I like that epic the musical Retells the story, Not only to both cater to modern audience But Also with its OWN purpose of man versus monster.
Obviously, this is not the point of the original text. Mythos Odysseus does not give a single fuck About the stuff that epic odysseus does. I don't know why the creator Decided to rewrite it this way, (If he's ever said why let me know) But I would assume he wanted to make something about the oddessy And this was simply a very creative way to Translate that for modern audience.
I like this because, yes, holy damn. It does have changes from the original text. But it's not JUST changing it. It's changing it with a purpose
It feels reminiscent of some kind of Dramatic play. the way that epic characterizes.
Polites' kind nature is Representative of the Concept of being merciful Represented in his lines such as " This life is amazing when you greet it with open arms" /"There is so much guilt inside your heart, So why not replace it?"
While in contrast you have eurylochus with more ruthlessness and cautious nature, this is Found in some of his lines such as "You rely on wit, and people die on it" /"we don't know what's ahead" / "I say we strike first. We don't have time to waste so lets raid the place-" /"Let's just cut our losses, You and I and let's run"
And then you have Odysseus, the man/monster. The first act of this Musical is his internal struggle With what He should be On that scale. And the other characters Represent this struggle in the song monster
" Is the cyclops struck with gilt when he kills, is he up in the middle of the night? Or does he end my men to avenge his friend and then Sleep knowing he has done him right?
When the witch turns men to pigs to protect her nymphs, is she going insane? Or did she learn to be colder when she got older and now she saves them the pain?
When a God comes down and makes a Fleet drown Is he scared that he's doing something wrong? Or does he keep us in check So we must respect him and now no one dares to piss him off"
He then Applies this to himself
" Does a soldier use a wooden horse to kill sleeping trojans cause he is vile? Or does he throw away his remorse and save more lives with guile?"
And this marks his turning point of deciding that Ruthlessness It's ultimately worth it if it means Getting home, as aeolus says "The end Always justifies the means"
It's in my opinion, a very creative way to go about retelling a myth. Is it accurate? Absolutely not. For example, circe (From what we know) is not protecting When she turns men into pigs, For all we know, she could just do it because Shits and giggles.
Her character and most others in epic is changed from the original. But it's not ONLY changing for the sake of apeling to the modern Western audience and being successful like Many other retellings. It is also and mainly changing for the sake of influencing the plot that Jorge Rivera herrans crafted For the sake of Retelling epic. It is creative and I enjoy it despite knowing it's not accurate.
#epic the musical#odysseus#the oddyssey#tagamemnon#the iliad#greek mythology#again you do not need to like epic the musical or any other retellings#you are allowed to only like greek mythology itself#as a history enjoyer i understand the frustration and think its COMPLETELY valid to be annoyed when someone uwu's a figure#hell i would be annoyed if someone did that to the EPIC THE MUSICAL version of odysseus#he's still an asshole he's still a killer and a liar in epic just a lot more guilty about it then he would be in the oddessy#if all retelling fans had self awareness that its just a retelling and didn't “soft boi” either myth or retelling#i think we'd all be much happier
84 notes
·
View notes
Text
About the Development of Myths

Okay, I will talk about more of the specific gods tomorrow again (starting first with the other gods from Stray Gods and then just looking over a variety of gods - I might start just with the greeks and then... venture into other mythologies). But first let me talk about the entire basis of what I have been talking about so far with the origins of Pan and Persephone: Their mythology is not a fixed thing.
Something that I would say education in general really fails on is properly expressing the amount of changes that cultures go through. I wrote about this before just in terms of history: There is not THE middle ages, not THE ancient Egypt, not THE ancient Greece and so on. All of those historical periods lasted for at least a thousand years. Now imagine that in like 500 years someone goes and looks at the 20th and 21st century as: "The World War and Globalisation period". Which I think there is a good chance this will at some point be known at (assuming we do not manage to eradicate our species before that, that is). Yet, you and I both know that if we were talking to someone from 1923 there would be very little we had in common.
Sure, this effect got massively accelerated thanks to the internet. But... You gotta have to assume that the Roman dude from 100 BC would also live in a very different world from the Roman dude of 200 BC. Because a hundred years is always going to involve a lot of change.
The reason we look at those old cultures as unchanging is, that they do not change anymore. And everyone who is neither working with that kinda stuff, nor is a complete geek, will just look at that culture as ONE FIRM THING rather than something fluent.
This is also true in terms of religion and related traditions, though we in the west are even more prone to it than other cultures. Because we do assume Christianity as this one thing. And the bible as this one unchanging thing. Hence the core believe is the same and, so the reasoning goes, was always the same. In fact, if you went to a religious school it is kinda how you were taught. The bible is one thing and always was the same thing. Only... It wasn't and even the basic we hve now does not matter.
Just look at the many Christian subreligions. They all in some way or form believe in Jesus, the one big God and all of that - but what they take from that widely differs. And the bible really does not have a big impact onto what ideals they hold and how they hold mass and how they pray and what not. If you think about it, you will easily see that, right? And if you just look a bit into what you might have learned about history in relation to Christianity, you will also know that this has changed. The role of Jesus has changed. How much the Holy Spirit is looked upon as an active actor. Which saints get venerated. All of that has changed a lot in just the last 50 years. And has changed a ton between the different countries.
And what I now need you to keep in mind that this was the exact same with the Ancient Gods and the religion attached to them. That holds true for the Greek Gods, the Roman Gods, the Egyptian Gods, the Norse Gods... all of them. The way they were worshipped changed over those thousand(s of) years they were worshipped.
So, let me once again talk about the Proto-Indo-European culture. Which is always a doosy and I love it.
The Proto-Indo-Europeans originates probably in the areas of modern day Ukraine and/or Romania and/or southern Russia some time around 5000 BC (scholars argue a bit about the exact temporal placement, just that it was somewhere between 7000 BC and 4000 BC). We do not really know a lot about them, because they did not write stuff down. But we do know that they had horses, were patriarchal, and that they worshipped a polytheistic pantheon that at least involved a Sky Father as one of the highest gods, who controlled the weather and was especially associated with storms and lightning.
These Proto-Indo-Europeans started breaking apart and travelling. Some into Asia, some into Europe and the Arabian/Persian areas. They brought with them their language and religion.
Now, it should be noted that they were not the "original humans" or anything. And that whereever they went... in most areas there were already other people living there, with whom they intermingled. Also whatever land they ended up settling was different, had different environments and this was included into their religious practice. Which made their religion over the years differ bit by bit. So from their pantheon sprang a lot of the pantheons we know today.
But... again, a lot of places they settled had already people living there. Who had their own worship. And that stuff often was also included and merged. Sometimes those other worships were very far reaching, sometimes very local. But some of those deities were picked up and either made part of whatever pantheon was there to come or was merged with an already existing god. And this happened again and again during the time that whatever pantheon was prayed to.
How do we know that, if it was not written down?
Well, mostly due to some archeology, but mostly due to comparative mythology and comparative linguistics. Two fields of science that basically involve people going over a lot of languages or mythologies (which, by the way, at times also includes fairytales and other oral narratives that are not necessarily held as "true", but still told) and basically finding things the reoccur. As well as going back over whatever written stuff we do have and noticing the shifts happening between a text written in 600 BC and a text written in 200 BC.
Now, for all the stuff we have two things that help a lot: a) The old Hindi writings and b) the written stuff from Egypt. Because both go really far back and were very well documented in writing. So basically we always can compare stuff to that and see shifts more clearly.
But, yeah... Technically all the pantheons are very much related. At some point Zeus, Jupiter, Diespiter, Thor, Tinia and Tian originated from the same character. You can even kinda see it in how similar the names are. Susanoo in Shinto-Mythology probably came from this, too, at least in the iteration we actually know about. (There can be some arguments made that a lot of the Shinto gods were shifted through the Buddhist contact, as the original indigenous Japanese cultures were very likely not Indo-European in origin. But given that the Ainu are the only culture whose oral tradition managed to survive this long, while the others either vanished or merged in a way influenced by Buddhism, which comes from Indo-European culture... yeah, it is there now.)
So, what I am saying: Mythology is shifting and always has been shifting. Same goes with religion. Hence the evolution of the Greek Pantheon.
Fun fact: Through comparative mythology we can also find the origins of YHW, the Abrahamitic god. Or God, as you might know him. He is a fascinating one, as he probably started out as a local god associated with harvest and weather in Southern Egypt and was then picked up by the Semitic cultures. He got a more pronounced role in the Canaanite pantheon, where at some point he merged with Baal, the war god. And through some trials and tribulations he finally ended up merging with El(hoim), the top god of the pantheon, with a part of the Canaanites splitting from the culture and developing into what would become the Jewish culture.
Super fascinating stuff. I love it.

#stray gods#hades#history#mythology#proto indo european#early history#neolithic#ancient greece#ancient rome#ancient egypt#greek mythology#christian mythology#egyptian mythology
158 notes
·
View notes
Text
I was going to do a double post but I figured I’d condense this because the posts would’ve related anyways:
For the newest chapter 267, literally wtf was Persephone’s “meltdown”?
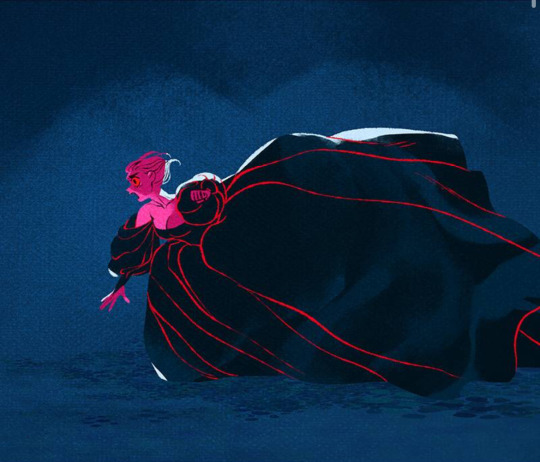
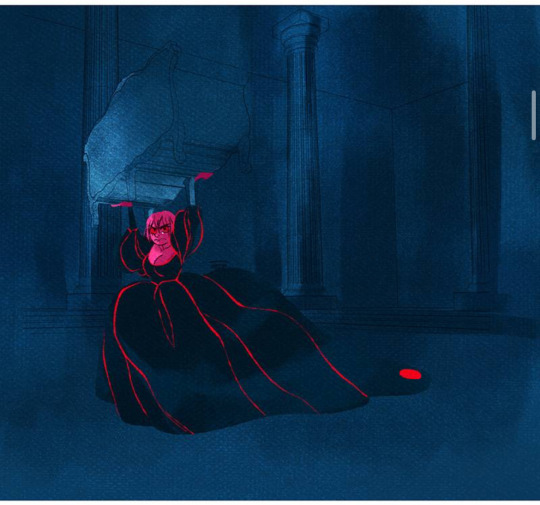



I don’t know what Rachel was thinking, but there was zero dramatic impact in Persephone picking up a single couch and throwing it, especially since for the large majority of the chapter, we see her in such a disheveled state.
I was hoping for a really cool moment like back before the trial arch when she sprouts those vines from her back. Imagine if that had happened and she reopened her old scars, that would’ve been sick. Plus, it would’ve been a cool parallel to the scars that Demeter has.

BUT while going back and looking for this panel, I reread the scene where Persephone sells the comb Hades gave her and discovered this:
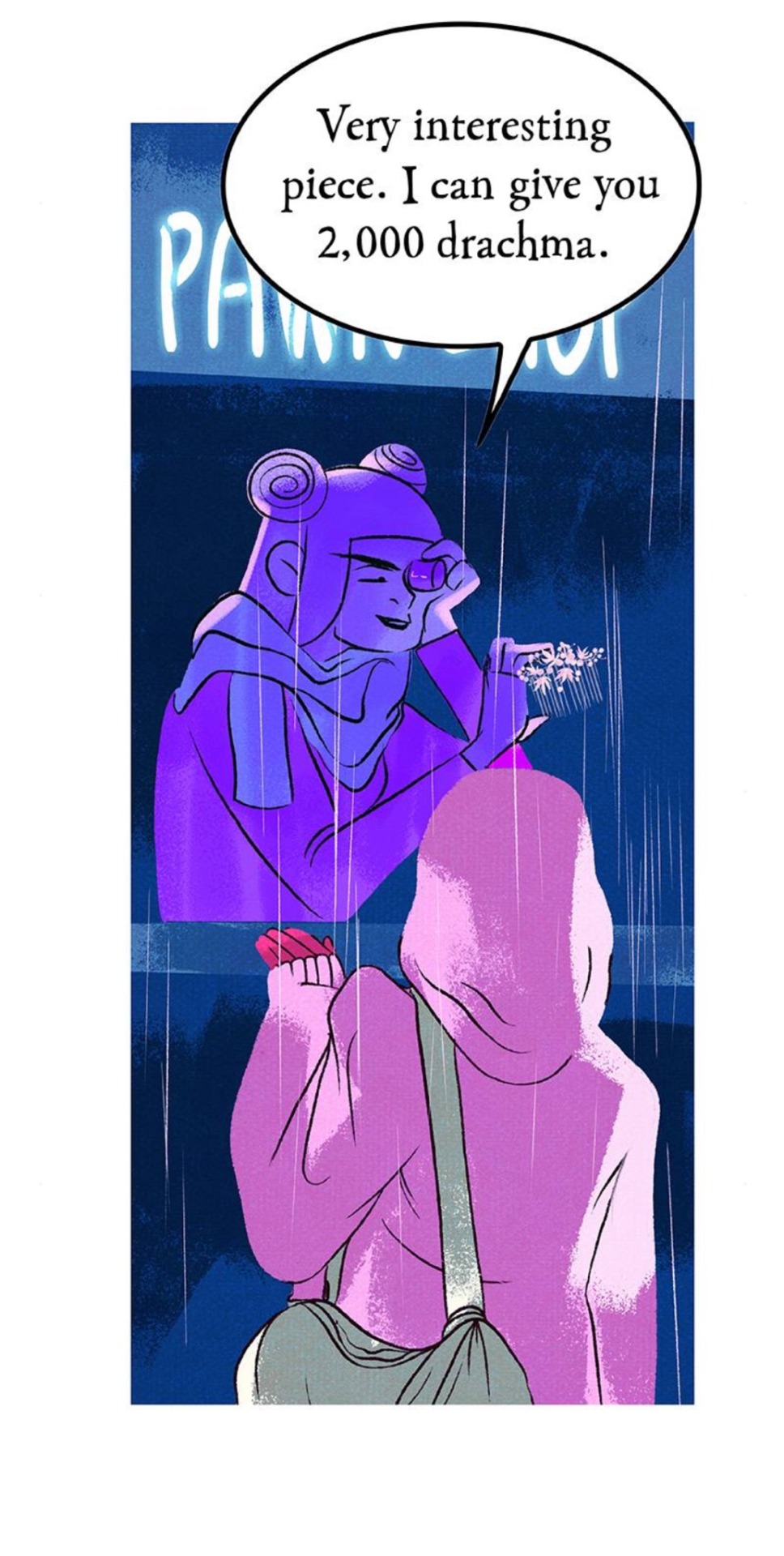


Maybe I’m being nitpicky, but why tf does Persephone have cash? Yes, yes, the realms are more modern, yada, yada, but drachma in Ancient Greece were coins like the Athenian drachma pictured below:

Greece didn’t start printing paper drachma until the 1900s, and even then, the colors of the paper were mainly earthy colors like red, light brown, and yellow. The 500 drachma was green, but not the aggressive green that is associated with American currency and not the green depicted in the above panel.
Maybe I’m reading too much into it, but this is yet again just another example of the disrespect Rachel has for Greek culture. Not only that, but how Rachel has either Americanized or Eurocentricized a story that should’ve remained Greek centric. Like, she couldn’t even depict the currency used by Greece (before it got replaced by the euro in 2002)? As people here have heard me say before: the devil is in the details. I know that the end of the day, it probably doesn’t matter to Rachel or a large majority of her audience. But it does. But all these little missed details, all these slights, have stacked on top of each other and amalgamated into what we have today.
Anyways. 
#anti lore olympus#lo critical#anti lo persephone#unpopular lo#lore olympus#unpopular lore olympus#anti lo#lore olympus critical#lo critique#lore olympus criticism#lore olympus hate#lo hate#Greeks if you want to chime in feel free#anti lo hades#also why does Persephone shrink in the 2 panels#like she shrinks when she throws the couch
83 notes
·
View notes
Photo









“Here's where things get intellectually very interesting. They are swept up by Catherine's idea of a new Russia.
So Catherine has this idea, which is very elegant. It's also a classically colonial idea: that these lands that have just been conquered, these are virgin territories.
So the place is renamed. What's now Southern Ukraine, where the Cossacks had had power, and the Crimean Peninsula, where the Crimean Khanate had had power, these places are renamed “New Russia”.
Now that word “new” is magical, right? Like with New England, or New South Wales, or New Caledonia.
More than 200 years later, 300 years later, people are gonna be still drawn by this notion of New Russia.
But when you say something is new, you're not saying it's yours, you're saying that we want it to be ours, right? That's the whole point.
So Novorossiya does not mean something which is Russian, it means something that we're gonna make Russia, we're gonna pretend that nothing else is there.
And how do you do that?
Well, you send multiple expeditions of the Russian Imperial Academy of Sciences to Crimea to name everything, find all the species, map everything.
Because science is one of the tools by which you gather imperial knowledge.
And then the naming — I mean, one has to admit this is quite brilliant on Catherine's part. They rename everything.
So all the Turkic names, the Muslim names, the Crimean Tatar names, are replaced.
And what are they replaced with? Greek names or names that sound Greek.
Like Kherson, that city that's being fought over right now. Mariupol, sounds Greek sorta, right? That's the whole idea.
They took the old names and then they replaced them with Greek names. And when they founded new places, they gave them Greek, or Greek-ish, Greek sounding, Greco whatever names.
And the point of this is to say that Russia is connected with the classical world. And in that we're European. We're in the enlightenment.
Connecting Russia with the classical world, going back all the way 2000 years, means that you obliviate everything that happens in between.
So the Crimeans don't matter, the Ukrainians don't matter, it's Russia here alone with its historical destiny, which goes all the way back to Greece.
And so it's New Russia, but it's justified by this connection to the classical world.”
Source: Timothy Snyder: Making of Modern Ukraine. Class 11.Ottoman Retreat, Russian Power,Ukrainian Populism
980 notes
·
View notes
Text
Something fascinating I recently learned about Hadestown is that its story has roots in real life with the industrialization of Eleusis, the site of Demeter and Persephone's Mysteries in Ancient Greece, and how it turned the holy site into a railway and steel capital--much like what Hades does with Hadestown.
This article talks about what happened and efforts to rebuild: https://www.cnn.com/travel/article/greece-eleusis-city-of-culture/index.html
"A blessing and a curse, industry kept thousands out of poverty but it also caused major environmental degradation, especially in the 1960s and 1970s when exponential growth was unregulated.
Smog obscured the beautiful views. The bay transformed into a ship graveyard. Eleusis became a modern version of the underworld, the “sacred way” having morphed into a road to hell."
Another article talks about responses to the city's welfare in writing, like poetry and art: https://www.lrb.co.uk/blog/2023/march/eleusinian-mysteries
The good news is that efforts to rebuild and help the city have been ongoing since the early 2000s. There's a lot of work to do but I hope it all works out!
59 notes
·
View notes
Note
Neighbour AU + Mutual pining (mickcedes or brocedes please) 💙
[Trope mash up prompts] This might have to become a series, because I got 1k into this and realized I hadn't even gotten to the mutual pining! But here you go, mickcedes monaco neighbours AU:
After breaking up with his girlfriend of four years, Mick musters the courage to ask Seb for his realtor so he can get the hell out of his sister’s place. Gina is awesome—the best sister Mick could ask for—but it’s clear that she’s become somewhat peeved after six weeks of taking care of her older brother.
Seb’s realtor is a terrifying blonde woman named Britta, and when Mick meets her for coffee—black for Britta and a cappuccino for Mick—she pulls up a map of Europe on her phone, holds it out to Mick and says, “Where do you want to go?”
Mick swallows. He has the force of his family’s bank account behind him, which really means he could go anywhere. He pictures himself in the UK, in Greece, in Norway, in a beautiful island cottage in Croatia and says, “I’ve always wanted to live in Monaco.”
“Monaco,” says Britta, tilting her head in consideration. “We can do Monaco.”
-
Three days later, Britta texts Mick a plane ticket to Nice, the receipt for a rental car, and a link to tour a residential high rise virtually. Mick opens the link and flips through images of a sun-drenched condo on the sixth floor. He’s not much of a designer, but he imagines a dining room table beside the french doors that open onto the balcony, a flatscreen on the wall of the living room, and family photos on the mantel.
He could live with it, he thinks. I like it, he texts Britta.
-
Britta holds open the door for Mick, awfully gentlemanly, and nods at the doorman like she’s already met him. The lobby is bright and modern, and a plaque made from sun-bleached driftwood reads BIENVENUE on the front desk.
The elevator ride to the sixth floor is uneventful, Britta and Mick leaning against opposite walls. The floor numbers tick upwards on the LED panel above the door. Britta tucks her hands behind her back and assesses Mick coolly.
“You know,” she says, conversationally. “If Sebastian ever treats you unfairly, you can tell me, and I’ll sort him out. He can be a selfish little man when he isn’t thinking straight.”
“Thanks,” Mick squeaks, willing the elevator doors to open. It’s difficult to categorize anything Seb does as unfair when Mick still has stars in his eyes looking at him. It’s Sebastian Vettel, his dad’s protege.
“I’m serious,” says Britta, fiercely.
As if sensing Mick’s discomfort, the elevator jolts to a halt, and a ding signals their arrival at the sixth floor. Britta makes an after you kind of gesture, and Mick slips out of the elevator.
-
When Mick and Britta are done touring the apartment, Mick accepts Britta’s offer to show him around the city. He’s been here before on family vacations, but not since… Well, that doesn’t bear thinking about.
Britta locks the door to the apartment behind them, and Mick turns around to stride towards the elevator, and runs smack into another body carrying a box of something green.
“Desole,” says Mick, mustering disused French. He shoots an arm out to help the stranger balance his box of what looks like—asparagus and artichokes and various varieties of leafy greens.
“Pas grave,” says the stranger, clutching his box of produce to his chest. Mick pulls back, and the stranger transfers the box to one arm, using his freed hand to sweep the hair out of his eyes.
The stranger is bright blonde with fine wrinkles at the corners of turquoise eyes like he’s older than his otherwise smooth features suggest. He’s dressed in linen from head to toe, a pair of designer sandals on his feet that Mick only recognizes from his mother’s beach wardrobe.
Britta snorts behind him. The stranger looks past Mick and wrinkles his nose at her.
The awkward encounter is over in a matter of seconds, and the stranger is brushing past Mick, presumably to get to his apartment, while Britta ushers Mick towards the elevator. Mick shakes his head clear while Britta pushes the button for the lobby.
“Do you know him?” Mick asks.
“Ha,” says Britta, a thin smile growing on her jaw. “Sebastian does. That’s Nico Rosberg, an angel investor in the sustainable energy sector. He lives in Monaco with his husband, a designer.”
“Rosberg as in Keke Rosberg?” says Mick.
“That’s the one,” says Britta.
-
A month later, Mick finds himself on a plane to Nice for the second time, his most important belongings crammed in a mountain of suitcases and stowed with the rest of the luggage. Seb offered to fly with him and help Mick set up, but Mick felt somewhat guilty for stealing Britta for so long and wanted to prove to no one in particular that he could make the move by himself.
He retrieves his new keys from the front desk, and after an afternoon he has most of the important things assembled, which is to say a toaster, an espresso machine and a bedframe. He opens his laptop and half-heartedly scrolls through an online furniture store, but gives up on the third page of bespoke credenzas. He doesn’t even know where he would put a credenza.
In the end, he wraps himself up in the one sheet he bothered to bring with him and passes out on top of the mattress.
-
Mick wakes to a knock on his door. He experiences a fleeting thought that he’s still staying with his sister, and it’s her boyfriend knocking on the door to take her out for breakfast before he realizes he’s in his new apartment in Monaco and Gina is thousands of kilometres away. He flings the sheet off his torso, still wearing yesterday’s t-shirt and joggers, and slogs through the apartment to answer the door.
When Mick tugs the door open, Nico Rosberg is standing on the other side, a basket of greens once again clutched in his hands. Another man, with a deeper complexion, stylish facial hair, and a face stacked with piercings, stands at his shoulder, looking somewhat bored.
“Hi?” says Mick, uncertain.
“Hello neighbour!” says Nico Rosberg, foisting the basket on Mick. “We wondered when you’d move in. I’m Nico, and this is my partner Lewis. We live two doors down.” Nico gestures vaguely at the other end of the hallway. “Lewis, say hello,” he sing-songs.
“Hey, man,” says Lewis.
“Uh,” says Mick, struggling under his new armful of kale and other vegetables. “Thanks? Can I…” he glances backwards into the apartment and notes the kitchen, which is empty of everything but the toaster and coffee machine. “Invite you in for coffee?”
Nico laughs ebulliently. “Of course not. We wouldn’t dream of taking advantage of your hospitality when you’ve just moved in. If you need anything from us, though, just knock.” He grins flatly at Mick, lips closed. Something about it reminds Mick of Britta.
“Thanks,” says Mick. “I’ll just…” he breaks off.
“Great,” says Nico, still smiling his flat smile. “Wonderful to meet you. I’m sure we’ll be seeing you around.”
Nico spins on his heel, links his arm through Lewis’s and tugs him down the hall. Mick blinks, steadying himself, and nudges the door closed with his foot, hauling the basket of produce into the kitchen. He sets it on the counter and pulls back to scrutinize it. What the fuck is he going to do with 10 kilos of kale?
32 notes
·
View notes
Note
Treehouse Ask: I hope you are doing well this holiday season? My ask regards Morpheus' proposal of marriage to Reader. How does she feel about becoming his wife? She's currently adjusting to becoming his queen, but how does she feel about the idea of tying her mortal self to him in holy matrimony?
Hi!!! Thank you sm for resending this ask and I hope you’re doing well too.
Yesterday I had a surgical procedure where they stuck some really big needles into my spinal column while I was under anesthesia to inject steroids. Still feeling pretty achy and not great, but big needles will do that to you lol.
Anyways on to the good stuff.
I’m going to start with getting into Morpheus and then Reader’s perspectives, to add context.
I’ve mentioned before about how I’m approaching Morpheus as a very old fashioned/proper being used to a specific standard and protocol when it comes to interpersonal relationships of all kinds. Not only is he a royal king, but he’s also an ancient god who follows ancient rules (for the most part). As a king and a god, he wouldn’t be beholden to any of his partners or feel a sense of accountability from them. They just weren’t equals. He could do as he pleased and demand what he wanted and they couldn’t. His past marriage with Calliope and past romances with Nada, Killala, and Alianora reflect this. (I also want to emphasize that the reason why Morpheus behaved this way in the past in treehouse is because that’s simply the way he learned how to behave in relationships. That was custom, both in the Waking world, which affects the dreaming, and the custom when it comes to royalty and people in power in general. And he was/is a selfish being so this feeds into that for him.)
He does truly love Reader and want to marry her, but the only way he knows how to love her is how he loved people in the past, which was dysfunctional/neglectful/toxic. Morpheus never learned how to be another way.
But he wants Reader more than he’s ever wanted anyone else and is like, if I can obtain her and secure her to me, everything else will fall into place! A lil delulu lol, but he’s not the god of thinking shit through.
On the other hand, Reader is a modern woman. Not just a modern woman, a modern woman who walked into this relationship with the expectation of modern treatment. Being treated equitably, being mutually responsible and accountable towards one another. Complete trust, honesty, and respect.
She’s not truly opposed to marrying him, but she’s less concerned with the “marriage” part of this equation as she is about the parts of a relationship that make a marriage successful. Can she trust him, will he remain true to her, will he protect her and not mistreat her, will he remain obsessed with her and not grow distant or bored. That’s where Morpheus’s one track mind and her clash.
She wants this relationship but on her terms, not solely his, from a position that can be negotiated from.
While Reader clearly isn’t secure in their relationship at the moment, she’s secure enough in herself that she isn’t afraid to hold Morpheus accountable even if it might jeopardize their future.
Spoiler alert - she does eventually agree to marry him and they have a fairy tale wedding before the baby is born and I’m sooo excited hehe.
But right now they’re essentially going through marriage negotiations, as royalty once arranged marriages. But they’re not negotiating over alliances or land or titles, Morpheus finally has met his match who wants something much more important than those things.
And every time she refuses Morpheus, he comes back with a better offer, so to speak. He’s already learned he can’t dazzle her with jewels and gold and things. He has to actually change for the better as a person to keep her. (More Hades and Persephone influences!)
(The way I see it, Calliope’s royal father, King Zeus, would have done all of the negotiating with Morpheus over their marriage. That’s what was done in Ancient Greece and what was/is done all over the world. Negotiating over the possession of Calliope, taking her from her father’s house and adding her to Morpheus’s house (aka family). This is a scenario that naturally lent itself to objectifying Calliope, placing her on a lower status to her husband.)
Reader is a very very special character to me. Not only does she represent me and how I view the world and how I view other people, she also represents the person I wish I could be and the strength/courage/bravery I wish for all people. By giving her her happy ending that she acquired on her own merits and strengths, not by compromising who she was but because she stuck to her guns, I hope to give us all a future where we love and are loved for who we are, not in spite of it.
#treehouse#the sandman#dream of the endless x you#dream of the endless x reader#sandman#dream of the endless#morpheus x reader#morpheus x you#lord morpheus#morpheus#lord morpheus x reader#lord morpheus x you#sandman comics#the sandman comics#the sandman tv show#sandman tv show#sandman season 2#sandman netflix#the sandman netflix
56 notes
·
View notes
Note
why pjo's portrayal of the greek gods is fucked up and how it's affected perceptions surrounding ancient Greece.
*breaks down the door to your inbox with an axe*
start talking now oh my god I want to hear your hot take so bad. I've been interested in religious studies (primarily the Hellenistic and early Roman religious atmosphere (of course acknowledging that the word religion is post-Enlightenment and conceives of supernatural belief as a subjective individual belief, which is inconsistent with how supernatural matters were dealt with in the Ancient world) and how they intersect with early Christianity and proto-Christianity) and I've been fascinated with the Greek gods and I need your hot take on why their portrayal is wrong and leads to incorrect assumptions about Ancient Greece.
oh you bet your bottom dollar i will talk about this. true to the post from which this originated, i will prep no material and all this is off the top of my head so don't quote me!
If you follow my Greek mythology sideblog, you'll know i am unequivocally a Zeus defender. Now I can make a million posts about Zeus alone but I will take a more holistic approach on the gods in general and the perception of Ancient Greece.
The West has been obsessed with Ancient Greece for centuries: the culture, philosophy, history, mythology, mathematical and scientific advancements, and much more. Now it's one thing to take interest in a country's history or a historical era; it is completely another to claim it as your own and make it an ideal state of life to achieve, because if you know literally anything about Ancient Greece, it was anything but. What I'm trying to say here is that Ancient Greek culture has been commodified, glorified, rewritten, and reclaimed by the West when it was never theirs to do so. I've often seen this sentiment expressed by Greeks about their homeland: "The history comes first, the people second." I think a prime modern example of this mindset was when same-sex marriage was legalised in Greece, which was a huge step forward for an Orthodox country with an extensive history of homophobia, but people outside of Greece began making jokes of Greece "returning to their own values" (referring to Ancient Greek practices of pederasty which is hugely problematic and not at all representative of any gay rights if you know what it entails) and people excited to "finally hold lesbian weddings in Lesbos" (signifying the West's perception of Greece as simply a tourist hotspot and not a country with an intricate history and culture). In short, Greece is already unfairly used for the West's agenda of glorification and attempts to build itself a culture that frankly isn't theirs at all.
Now, how does this involve pjo? A lot, my friends, a fucking lot. The publication and popularity of the Percy Jackson series has simply exacerbated all the aforementioned issues in this post. First off, the worldbuilding on which The Lightning Thief relied and the rest of the series ultimately holds is that "Olympus moves with the centre of Western power", which is just. Wow. There are a million things wrong with this concept that would need its own post, so I recommend this article called The Whitening Thief that essentially explains the white supremacy of it all. If you do not want to read the full article, the main premise is that the Percy Jackson series equates Westernism with civilisation and that without it there was "chaos and darkness", which as Paule describes it, is "sipping at a pretty racist cocktail".
note: I have realised how aggressively off-topic this is to the original statement I made, I'm getting there, I promise (although I did warn you it was something I could talk on for hours with little material)
Let's finally delve into the depiction of Greek gods in Percy Jackson. I'll actually start on a bit of a positive note that apart from the weird (for lack of a better term) comparisons of Hades to Adolf Hitler, the original Percy Jackson and the Olympians had some okay characterisation of the gods (I have some reservations about the goddesses on which I will elaborate later). They're prideful and neglectful parents (the myths actually contradict that latter part but I digress) but each with their own complexities and concerns. To use Zeus as an example because he's actually the god who falls short the most in terms of consistent characterisation in my opinion, he lets Percy live in TLT "for the sake of peace in [his] family", indicating a care and sense of duty for Olympus and for his fellow gods, and while he lets his pride and paranoia get the better of him at times, he is shown as a serious authority figure and someone who's trying to keep his realm together, and such characteristics wouldn't be too far off from his mythical counterpart.
But as the series progresses, either Rick got lazy or he attempted to further capitalise his work to make it more palpable, he turns the gods into caricatures by excessively inflating one characteristic they may have into their entire personalities. Returning to Zeus, his paranoia is amplified to an absurd extent that one can simply not fathom why the gods would be the better option than the Titans. As I said initially, he had bouts of paranoia that would be almost normal for someone with such a powerful position, but this is completely derailing any connection with his mythological counterpart, he may as well be an OC with the same name and title as him. To use other gods as an example because I promised a holistic approach and I have seemed to only talk about Zeus (sorry!), the writing of the goddesses Hera, Artemis, Aphrodite, and Athena is simply misogynistic. I'm sorry, there is no other way I can find myself to describe it. Typically feminine goddesses Hera and Aphrodite are extremely demonised and condemned for their flaky and vain attitude; Hera is the evil stepmother archetype and Aphrodite ultimately becomes weak and useless. The "virgin" (quotations referring to Athena) goddesses Artemis and Athena also don't seem to extend past superficial, unoriginal characteristics like being a vehement man-hater who kicked out two sapphics from the Hunt and a goddess who Rick stops at nothing to render her a horrible parent and person (using the Roman myth of Medusa, exaggerating her prideful nature, etc) respectively. And you cannot tell me they're not misogynistic portrayals because just a few minutes on pjo tiktok will show you just how many times Hera is referred to as a bitch (keep my wife's name out of your fucking mouth!!). Then there is TOA and COTG, which makes me want to cry just thinking about Zeus' portrayal there (yes we're going back there). The god who was consistently thought of as a gracious, protective saviour of the people in Ancient Greece (full list of epithets of Zeus, read at your leisure) is an abusive autocratic tyrant?
To go back onto the topic, how do Riordan's works affect the overall perception of Ancient Greece? Well, as I said before, it contributes to the white supremacist view of Ancient Greece as the epitome of civilisation and the glorification of the era, but it also turns Ancient Greece into a fandom to an extreme extent. Now, obviously, I'm not talking about people with a healthy obsession with Ancient Greek history and Mythology (myself included) who like to engage in content about it. I'm talking about people who claim Ancient Greece as an extension of Western, mostly American culture, and ultimately engage in a form of cultural appropriation that strips Greeks of their own history and narrative. This includes writing 'feminist' retellings of Greek myths, taking Riordan's (inaccurate) readings of the mythology as indisputable fact, and removing the myths from their historical and cultural context. People forget that much of these myths were stories written for entertainment and take them as a sort of Hellenic Bible (which delves into the Christianisation of Greek Mythology but that's a whole other post). In short, Westerners think they can do whatever the fuck they want with Greek mythology and Greek gods because they think it's theirs with which to play around, ultimately ignoring the country, history, and the culture from which they actually originate, and it's thanks to Rick Riordan that this attitude has blown up to an insane extent.
*sighs* Thank you for coming to my TedTalk and I seriously admire you if you made it this far.
#diya answers#i wrote all this instead of doing the pile of homework i have so yeah enjoy#sunset-telepath#rr crit
47 notes
·
View notes
Note
Do you have any reliable sources about beauty in Ancient Greece that you can recommend? Something that would help a person draw mythological characters with more credibility?
For example, something that would help someone draw a character described as beautiful or very beautiful (Helena, Achilles, Penelope, Aphrodite, etc.) and actually look like they would be seen as beautiful or very beautiful in the context of the work. Or even clothes and accessories! The popular idea of Greek clothing is kind of generic (you know, that idea of "just put on soft-looking white fabrics, put a laurel wreath on their head and they'll look Greek enough" and even women, even high-class ones, having rather simple hairstyles.)
I don't intend to post, it's more for practice. So if the source you know is very dense, it's okay because, as it is an exercise, the study part is important. In case you respond, I would like to thank you in advance for giving me some of your time.
Do I count as a reliable source? XD It's just that all the knowledge I have about this comes from snippets of information throughout my life and not so much a targeted study, the sources of which I would have kept.
I would argue however that most of the information you can find on the Internet (apart from ones manipulated by political motives, both western appropriation of the Greek culture AND wokism) is fairly reliable, because thankfully it is based on the very scripts and statues of the Ancient Greeks, so it's hard to go that wrong. Those are the legit sources.
For example, Homer uses two epithets to characterize Greeks again and again; καλλικνήμιδες and ευπλόκαμοι. The former means "with beautiful legs" and the latter means "with beautiful long hair". Both were apparently beautiful features Greeks took pride in. The leg one is particularly used for warriors, which means they had toned, long, lean and strong legs. The hair is used for both sexes, as both sexes had very long hair until the classical period, often worn in many braids. In general, up to the Archaic period, the beauty standards weren't dissimilar to the ones of Minoan and Mycenaean times. The long hair Greek men had before the classical era (and beyond it for some Greeks, such as the Spartans) is rarely seen in modern representations. I don't know if it was the beauty standard or the universal truth but Ancient Greek depicted themselves almost always with wavy or curly hair, almost never straight or curly with very tight rings.
The skintone difference between men and women was also a totally legit beauty standard - handsome men were tanned, which was a sign they were roasting under the sun doing tough, manly things, warring, sailing, farming etc Beautiful women are constantly called λευκώλενος which means "with white arms, hands". Women showed their noble demeanour or descent by staying at home being dutiful wives, avoiding the harshness of the sun, dust and dirt. Being fair was the beauty standard for women. This differentiation between men and women was ongoing from Minoan up to Classical times, and most likely beyond this as well.
Beautiful women are also described to have doe eyes or cattle eyes, meaning expressive and elongated almond eyes. Having quick-glancing, clever, shining eyes ("ελικώπις") was very valued too. Goddesses such as Athena are often called "γλαυκώπις" which means "bright, white eyed". Of course it doesn't literally mean "white", unless Athena was indeed imagined like that, but with bright, light eyes. Other than that, the eyecolour is not often mentioned. The majority obviously had brown and hazel eyes, however there were blue and green eyes, there is scant art about it. But it isn't clear what the beauty standard for eyecolour was - what interested the Greeks more was the shape, size and expression of the eye. They were charmed by spirited eyes. "The eye is the window to the soul" type of thing.
Being blonde was considered a sign of noble or even divine descent, therefore it was considered very beautiful and not very common. There are sources that Greek women in later antiquity died their hair with some dyes to make them appear a little lighter. So a beautiful Greek man or woman could be blonde, but not Scandinavian or grey blonde, more like dirty blonde, gold blonde, strawberry blonde.
Throughout all sources in existence, Greeks were very interested in the health and good physique. A handsome man had to be lean, strong and toned. I mean, there are countless six pack ancient statues at a time it was crazy hard to achieve this. Greeks weren't fond of the bear type of strong though, all male bodies in sculptures look lean, even the heracleian (herculian) ones which are sturdier are still lean compared to the modern very muscular or the bear type. Greeks also found proportions and symmetry very important.
On the other hand, according to statues of the Classical period and onwards a beautiful woman should have some fat on her, be juicy and soft, especially in the belly and the hips, signs of fertility. Nice arms were meaty and soft and nice breasts were perky and round. Legs were comparatively leaner and long, since as I said Greeks took pride in that. A beautiful woman could either be a little plump or toned, depending on the region again.
Based on the statues, ideal facial traits was a straight (not curvy), proportionate nose and medium or full curvy lips.
From the classical period onward it all became about the beard for men, in place of their earlier fascination with beautiful hair. A handsome mature man kept his hair neatly cut and had a strong, thick beard, not very long. Before a young man could grow a decent beard, the beauty standards for him were more feminine, with a boyish softer youthful charm (still ripped af though XD). Cheeks in young men and women are round, however the chin is usually well defined.
As for fashion. Fashion was indeed modest and somewhat plain after the archaic times, it is not a stereotype. What you could play with to make the outfit fancier is the accessories, jewellery, belts, pins etc. If you want something more special, draw early Archaic or Mycenean or Minoan women, whose clothing was very interesting and vibrant, with a lot of geometric cuts and bold colours.
Good make-up involved an emphasis in making the face appear whiter (chalk and lead hazard), charchoal for eye-liner and thickening of the eyebrows and red iron oxide for the lips.
Yes, please, skip on the excessive laurel wreath usage, not that it wasn't a thing but we can have enough of it.

Late Archaic kouros. Note the sixpack, the tall toned legs, the long braided hair.
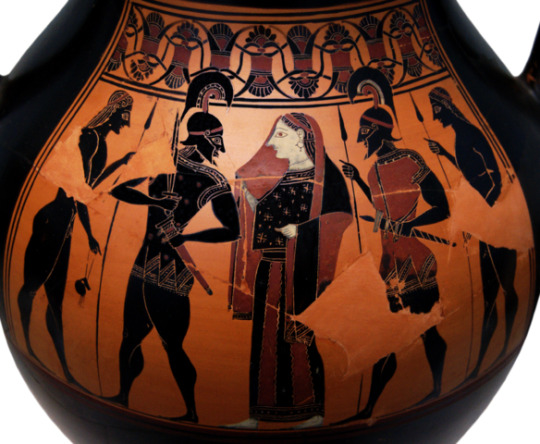

Different skintone standards between men and women. Helen wears some fancy outfit here as well.

Large expressive almond eyes in a Minoan woman. Also the make-up. Minoans are pre-Greeks, but they had similar beauty standards and fashion sense with the Mycenaeans and then they mixed with them anyway.

Idea for elaborate Late Myceanean - Early Archaic fashion. Souce here, you're gonna like it.

The Caryatids in Amphipolis are IMO some of the prettiest female statues in Ancient Greek art. This is a relatively recent discovery and the monument has not yet opened to visitors.
Medici Aphrodite (Venus de Medici), Hellenistic era. Aphrodite was juicy.

You might as well reach fifty, the sixpack and v-line are ALWAYS there. Beauty wise, men might have actually had it harder than women in Ancient Greece XD
youtube
Ancient Greek jewellery with dates for reference.

The statue of Antinous in Delphi is a statue we definitely do not talk enough about. Even though the body is toned and the muscles are defined, a beautiful young man is portayed with cheeks and softer angles in the face.
This is what I know, I think it's a pretty safe summary, however any followers with specific sources can add them in the comments. Hopefully all this will help you out with your practice!
#greece#ancient greece#beauty standards#ancient greek art#beauty in ancient greece#ancient greek statues#ancient greek#greek culture#historical fashion#anon#ask#long post#tw long post#tw long#traditional clothing
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
brazilian idioms and expressions that i think are cool
"Tem mão não é?" (lit. 'Don't you have hands?') - When someone asks you to do something they could clearly do themselves
"Águas pasadas não movem moinhos" ('Past waters don't move mills') - Being overtly attached to the past won't bring you anything.
"Pimenta nos olhos dos outros é refresco" ('Pepper on other peoples' eyes is refreshing') - When something bad happens to someone else, it's usually good because it's not your problem.
"E no cu não vai nada?" ('And up your arse goes nothing?') - When someone (usually your boss) asks you to do a long list of things you don't want to.
"Em terra de cego, quem tem um olho é rei" ('On the land of the blind the one-eyed man is king') - When you suck at a skill but you're still better than everyone you know. For example, say you take a trip to Beijing with your friends. None of them speak Mandarin, but you can understand it pretty well, though you cannot read it and your pronunciation is subpar. In this situation, you're the one-eyed king. It's also a common saying in Germany: Unter den Blinden ist der Einäugige König.
"Manja rola" (lit. 'Dick measurer') - Someone who is always subservient to a cause or a person with the intention of gaining their approval.
"Presente de grego" (lit. 'Greek gift') - A well-intentioned gift that actually makes your situation worse, in reference to the famous tale of the Trojan Horse of Ancient Greece.
"Escravoceta" (lit. 'pussyslave') - A man who does everything a woman tells him to in the hopes of someday sleeping with her.
"Cão que ladra não morde" ('Dogs who bark don't bite') - People who constantly make verbal threats rarely ever fulfill them.
"Teu cu" (lit. 'Thy arse') - Used when you disagree with someone but don't have a proper argument - or don't care enough to form one.
"A pressa é inimiga da perfeição" ('Hurry is perfection's enemy') - Being patient is key, hastily finishing something won't make it any good.
"No cu do mundo" ('On the world's asshole') - A far-off place isolated from modern society, usually in the countryside.
"Quem não tem cão, caça com gato" ('One who has no hound hunts with a cat') - If you think you don't have what it takes to do something, do your best with what you have.
"Nem aqui, nem na China" ('Not here, not in China') - A fancy way of saying "no fucking way". This won't happen, neither here, nor in any corner of the world.
"Nem fudendo" (idk how to translate that) - Same as above, but funner and less fancy.
"Ensinar padre a rezar missa" ('Teaching a priest how to pray') - Trying to teach someone (or bragging about) a skill they already excell at. Like mansplanning, but fancier.
"O seguro morreu de velho" ('Safety died of old age') - People who value their well-being and safety above other things tend to do better in life.
"Negócio da China" ('A deal made in China') - A particularly advantageous deal, usually business-related.
"Quando a esmola é demais, o mendigo desconfia" ('When the donations are too much, the homeless man grows suspicious') - When an offer or gift is too good to be true.
#there's like 500 of these#i'm just writing down the ones i remember rn#memes#explore#explorepage#funny#fyp#fypツ#hilarious#writers on tumblr#female artists#foryoupage#artists on tumblr#tumblr fyp#fypシ#fypage#viral#foryou#brasil#brazil#idioms#language#etymology#language stuff#linguistics#portuguese#loan words
61 notes
·
View notes