#greek history
Text
Despite Sparta’s reputation for superior fighting, Spartan armies were as likely to lose battles as to win them, especially against peer opponents such as other Greek city-states. Sparta defeated Athens in the Peloponnesian War—but only by accepting Persian money to do it, reopening the door to Persian influence in the Aegean, which Greek victories at Plataea and Salamis nearly a century early had closed. Famous Spartan victories at Plataea and Mantinea were matched by consequential defeats at Pylos, Arginusae, and ultimately Leuctra. That last defeat at Leuctra, delivered by Thebes a mere 33 years after Sparta’s triumph over Athens, broke the back of Spartan power permanently, reducing Sparta to the status of a second-class power from which it never recovered.
Sparta was one of the largest Greek city-states in the classical period, yet it struggled to achieve meaningful political objectives; the result of Spartan arms abroad was mostly failure. Sparta was particularly poor at logistics; while Athens could maintain armies across the Eastern Mediterranean, Sparta repeatedly struggled to keep an army in the field even within Greece. Indeed, Sparta spent the entirety of the initial phase of the Peloponnesian War, the Archidamian War (431-421 B.C.), failing to solve the basic logistical problem of operating long term in Attica, less than 150 miles overland from Sparta and just a few days on foot from the nearest friendly major port and market, Corinth.
The Spartans were at best tactically and strategically uncreative. Tactically, Sparta employed the phalanx, a close-order shield and spear formation. But while elements of the hoplite phalanx are often presented in popular culture as uniquely Spartan, the formation and its equipment were common among the Greeks from at least the early fifth century, if not earlier. And beyond the phalanx, the Spartans were not innovators, slow to experiment with new tactics, combined arms, and naval operations. Instead, Spartan leaders consistently tried to solve their military problems with pitched hoplite battles. Spartan efforts to compel friendship by hoplite battle were particularly unsuccessful, as with the failed Spartan efforts to compel Corinth to rejoin the Spartan-led Peloponnesian League by force during the Corinthian War.
Sparta’s military mediocrity seems inexplicable given the city-state’s popular reputation as a highly militarized society, but modern scholarship has shown that this, too, is mostly a mirage. The agoge, Sparta’s rearing system for citizen boys, frequently represented in popular culture as akin to an intense military bootcamp, in fact included no arms training or military drills and was primarily designed to instill obedience and conformity rather than skill at arms or tactics. In order to instill that obedience, the older boys were encouraged to police the younger boys with violence, with the result that even in adulthood Spartan citizens were liable to settle disputes with their fists, a tendency that predictably made them poor diplomats.
But while Sparta’s military performance was merely mediocre, no better or worse than its Greek neighbors, Spartan politics makes it an exceptionally bad example for citizens or soldiers in a modern free society. Modern scholars continue to debate the degree to which ancient Sparta exercised a unique tyranny of the state over the lives of individual Spartan citizens. However, the Spartan citizenry represented only a tiny minority of people in Sparta, likely never more than 15 percent, including women of citizen status (who could not vote or hold office). Instead, the vast majority of people in Sparta, between 65 and 85 percent, were enslaved helots. (The remainder of the population was confined to Sparta’s bewildering array of noncitizen underclasses.) The figure is staggering, far higher than any other ancient Mediterranean state or, for instance, the antebellum American South, rightly termed a slave society with a third of its people enslaved.
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
"Women only started working very recently so a woman's place is the house-" shut up and feast your eyes at old photos of women from around the world doing physical labor only for them to return home and solely care for 5-10 children and the elderly parents of their husband.
Greek women represent:
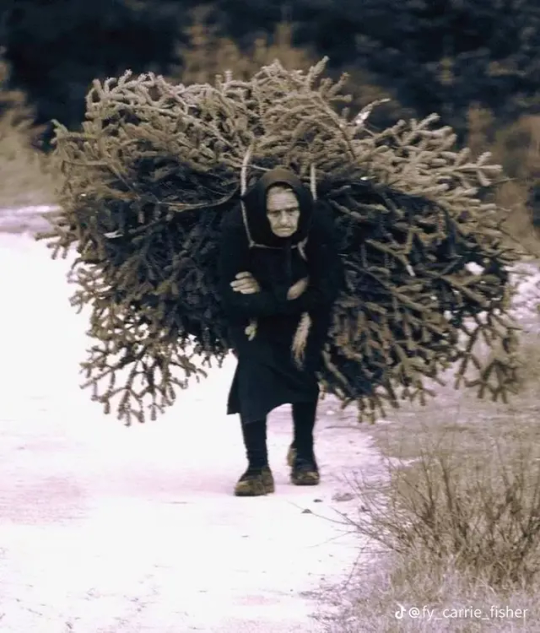
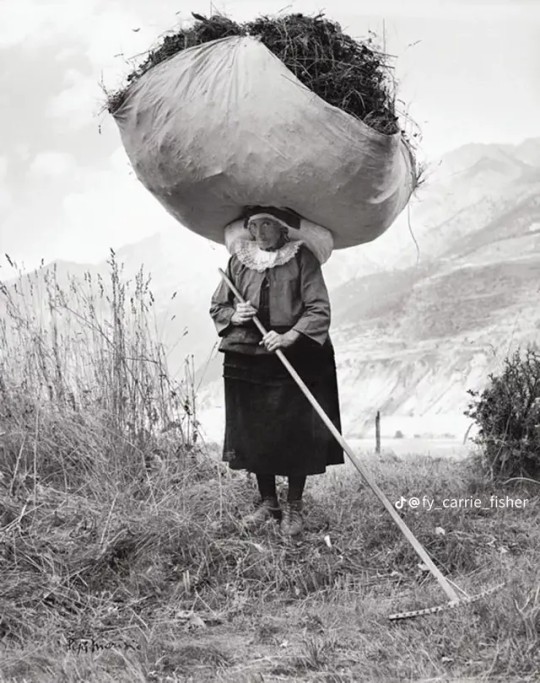
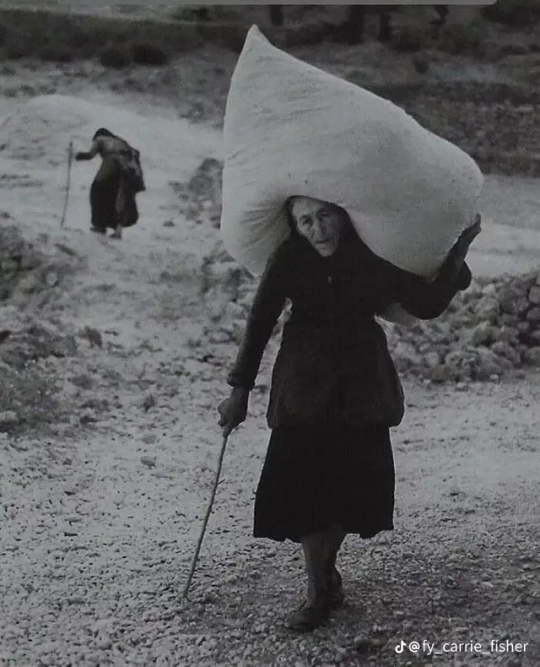
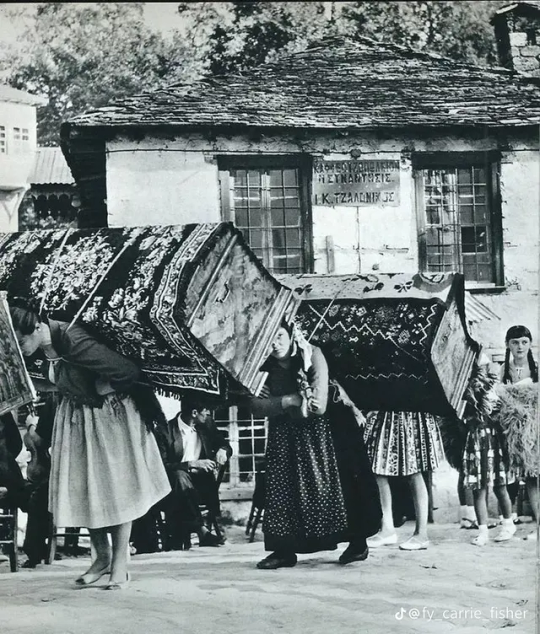





These photos show Greek women doing the type of physical labor they would perform more often than not. At the luckiest working conditions for rural women (aka most of the country) they would start working the fields as children and when they got older they would work the same fields with their own babies on their backs.
On the way home from the fields, sometimes the women would carry the wood and the mule would carry the man so he could rest.
Of course, we can talk about the manual labor that is rubbing cloth and metal for hours on end, chopping and carrying wood to light a fire for a large cauldron your size, and stirring it for hours.
But we can also talk about how it wasn't for them to break and carry rocks in baskets for the making of new roads. They would gather salt, olives, and grapes and carry them on large baskets filled to the brim. For salt they carried thirty kilos each trip, doing fifty trips each, stepping shoeless on the grains of salt.
Carrying water was also their job, often moving large barrels with all the water a house of 10 needed upon hills that horses and mules had trouble ascending.
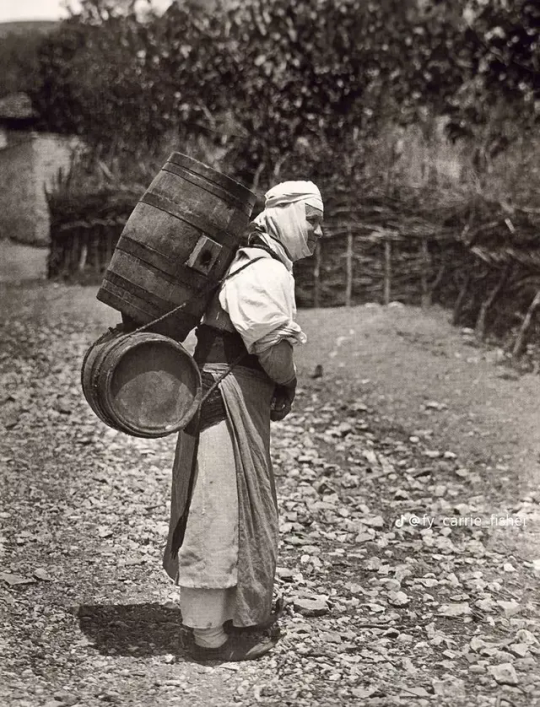
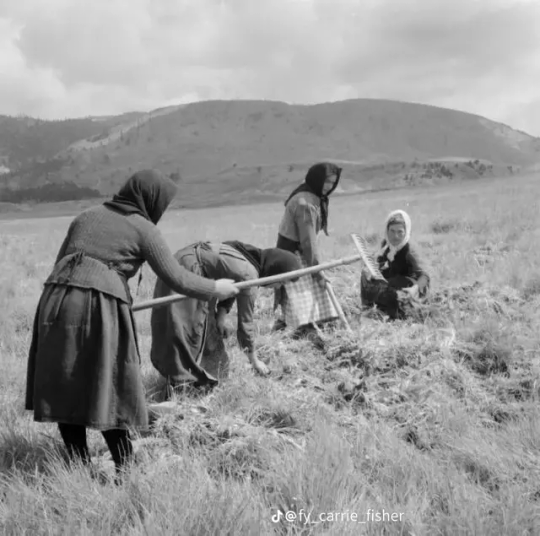
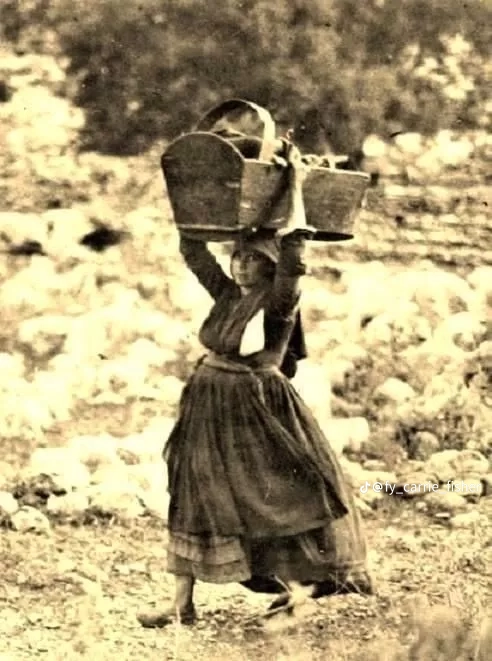
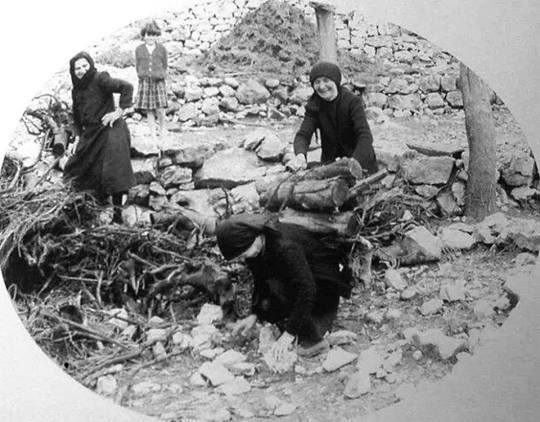
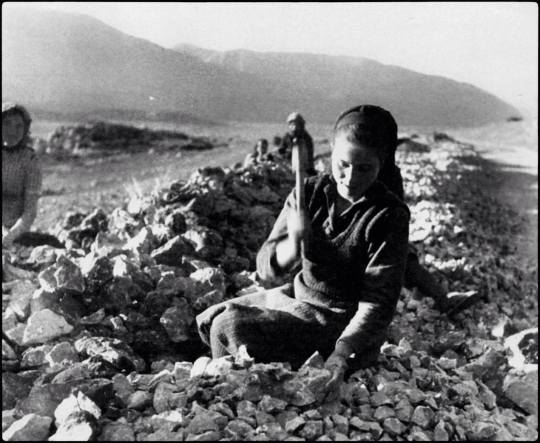
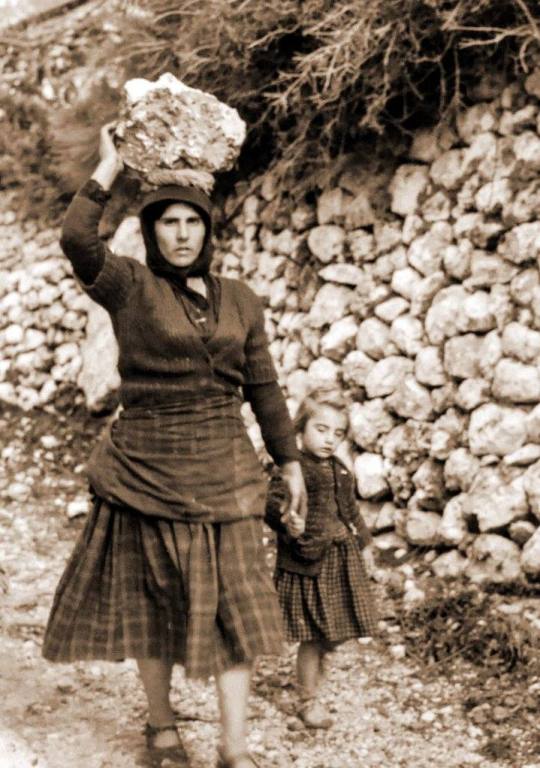
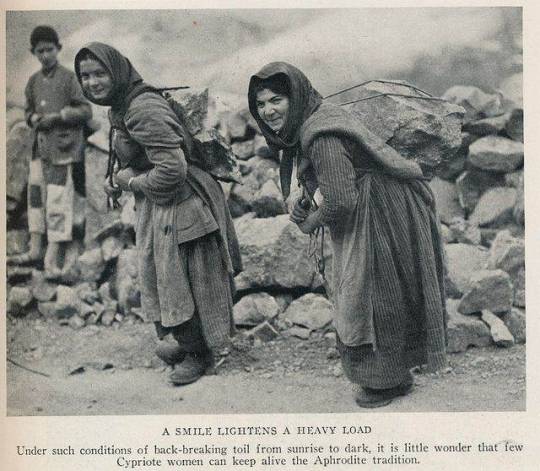
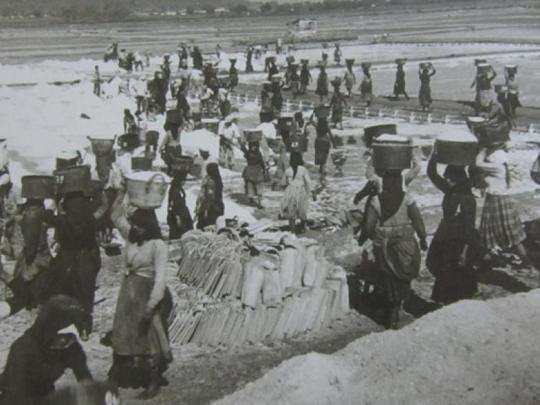












(more photos for salt mining and carrying here)
It's no hyperbole to say these women carried their incomes and households on their backs. "The good she-housekeeper is a slave and a lady" the old Greek saying goes. A "good woman" was a woman who could be strong and work at home and in the field, often described with the qualities of a mule. Men took their wives out in the fields so much that some who were a bit more educated had to make their husbands sign that they wouldn't ask them to work alongside them in the fields! (source in Greek)
Some of these photos are also from 1970. I'm missing a photo from Leukada showing women carrying baskets of the stones they broke, and I'll add it here when I find it.
Basically, women were out of the house forever. A woman who got to stay home and never perform any labor had some type of privilege (wealth, status etc). Same as the many privileged men around the world who didn't perform any labor at all.
===================================
If my posts have helped you in any way consider buying me a ko-fi 💖
#greek women#greece#greek history#vintage#vintage photo#manual labor#working class#greek people#working class history
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
You thought Black Cleopatra was bad?

New Netflix documentary claims Italy conquered Greece “after breaking through its weak resistance” in WW2.
For the record, Greece successfully blocked Italy’s invasion, then counterattacked and then repelled Italy’s counterattack. It has even become a meme, like, it is actually well known. That was happening for about half a year. Greece ceded after Germany came to Italy’s aid with the collaboration of Bulgaria, surrounded the country and invaded from all sides. It took the three of them an extra two months to fully occupy the country. Overall it was one of the longest resistances in Europe, maybe the second after Russia, and if not, certainly among the longest anyway. During the occupation, Greece also had one of the most notable partisan resistance groups.
Who makes these Netflix documentaries after all? Because literally even history nerd YouTubers make infinitely better documentaries than Netflix.
This one, I really take issue with. People died. Grandparents fought. Inaccuracy is disgrace.
651 notes
·
View notes
Text
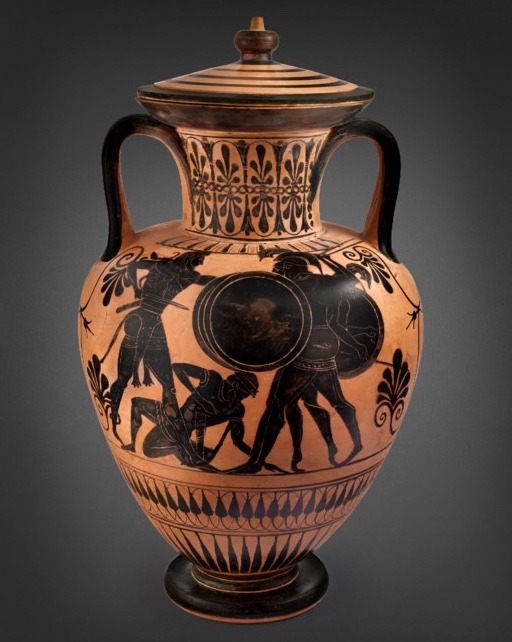
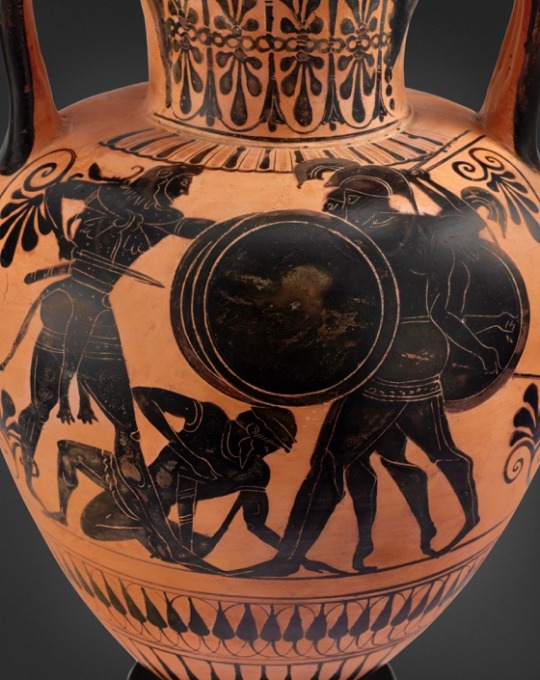


AN ATTIC BLACK-FIGURED NECK-AMPHORA AND LID
CIRCA 510 B.C.
#AN ATTIC BLACK-FIGURED NECK-AMPHORA AND LID#CIRCA 510 B.C.#pottery#ancient pottery#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#ancient greece#greek history#greek art
458 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dissecting ancient Greek wedding customs (or “How to adapt the clusterfuck they are into something somewhat doable for the 21st century”)
This post is going to be a bit different. I could stick to writing about the customs we know of from a purely historical perspective, and while it would be informative, it wouldn’t reflect what I’ve actually been up to. Some of you might already know, but I’m getting married, so I approached this topic with the intent of seeing what I could do (and get away with).
So this post is going to be more about method and the practical challenges that come with doing the groundwork of adapting very old (and often outdated) traditions in a way that makes sense for our modern times.
I do have some disclaimers to make before I get started:
Most (if not all) of the literature around ancient Greek marriage is hetero-normative. However, this does NOT mean that marriage rites shouldn’t be adapted for queer marriages or that queer marriages can’t be done within Hellenic paganism. It’s our job as reconstructionists and revivalists to rework and adapt to our needs.
Similarly, this post is bound to mention or detail cult practices that are no longer in line with our modern sensibilities. I also want to make it clear that this post is not a tutorial. I’m not saying how things should be done, I’m only exposing elements that I consider reworkable and propose suggestions so that it can help others make their own research and decisions, with the level of historicity that they deem fit.
While the wedding customs from fifth century BC Athens are decently known, the ones from other cities and regions of Greece are much more obscure outside of anecdotal and fragmentary details (with the exception of Sparta). For this reason, the Athenian example is what I’ll be using as foundation. If you reconstruct practices from other areas of the Greek World, you might find something valuable in this article: The Greek Wedding Outside of Athens and Sparta: The Evidence from Ancient Texts by Katia Margariti.
Basic/simplified structure
The typical Athenian wedding would spread over three days, and be marked by several steps, some of which are listed below. Note that the order of these steps is not precisely known and might have been flexible:
Pre-wedding:
Decorating: korythale at the door, decoration of the nuptial bedroom
The Proteleia
Filling of the loutrophoros
Wedding day
Nuptial bath
Adornment of the bride
Wedding Feast
Hymenaios
Anakalypteria
Nymphagogia
Katachysmata
Day after
Epaulia
Gamelia
Final sacrifices
Some of these steps included specific customs and traditions, not all of which are reconstructible for various reasons.
Decorations
The korythale: the korythale was a sprig, usually from an olive tree (or laurel), which was placed at the groom’s door (and perhaps the bride’s too). The word in interpreted as deriving from “koros” and “thallein”, which would translate “youth-blossom”.
The korythale is very reminiscent of the eiresione, which was a similar kind of branch of laurel used during the Thargelia and/or the Pyanepsia that had apotropaic purposes. Athenian weddings included a procession from the bride’s home to the groom’s house, so the presence of the korythale at the doors would indicate that a wedding was taking place involving the decorated homes.
While I haven’t seen any one make this interpretation, I would still be tempted to argue that decorating the thresholds of houses has a similar protective and luck-bringing purpose than the eiresione, which was also hung above the door of Athenian houses.
The thalamos (nuptial bedroom): While there is no doubt the houses were properly decorated for the occasion, we have mention of special care given to the nuptial bedroom.
It’s important to understand that the procession from the bride’s house to the groom’s went up to the bedroom door, it was generally an important location and its preparation is seen represented on ancient pottery. Euripides mentions the adornment of the bed with fine fabrics, while Theocritus mentions the smell of myrrh (sacred to Aphrodite). There is also evidence that, in the Imperial period, the practice of hanging curtains to create a canopy above the bed was adopted, very likely from Egypt.
When it comes to adapting this today, it is pretty straightforward and there is plenty of room for personalization. The korythale could be challenging depending on how easily available olive or laurel are in your area. I would also argue that the custom could be more loosely adapted so that instead of being at the houses’ doors, it could take the form of a floral arrangement at the door of whatever venue you are using.
Proteleia
In short, the proteleia refers to sacrifices and offerings that would be made to various gods before the wedding. The exact timing of these is more or less unknown, but we have reasons to believe they could be done a day or a few days before the wedding, and perhaps also on the day of the wedding. These offerings were made independently by each family.
It is in this context that the offering of a lock of hair and of childhood items is best known for brides. The recipients of the offerings are varied: In Athens the most mentioned are the Nymphs and Artemis, but various sacrifices to Aphrodite, Hera, Athena and Zeus were also performed. In other parts of Greece, pre-nuptial customs often included sacrifices to local heroines. Plutarch, in the 2nd century AD (and therefore way after the focus of this post) mentions the main five nuptial deities to be Zeus Teleios, Hera Teleia, Aphrodite, Peitho and Artemis.
Today, I believe the exact choice of who to offer to and what to offer very much comes down to personal preferences and circumstances. While we assume that both families made prenuptial sacrifices, we know very little of the groom’s side of things, since the focus was on the bride, and the rite of passage aspect was not present for the groom in Ancient times. This is a gap that leaves room for modern innovation eg. including Apollon to either replace or accompany Artemis or choosing a group of deities that is more couple-centric rather than family-centric.
Personally, I have settled on Aphrodite, Hera and Artemis and have integrated a Spartan custom that includes the mother of the bride in the sacrifice to Aphrodite. Hera Teleia will receive a lock of my current hair, while Artemis will receive a lock of hair from my first haircut as a child (that my mother has kept all these years), alongside some other trinkets. The groom will honour Zeus Teleios in a passive way. And I will honour the Nymphs through the the rite I will explain next.
Nuptial baths
Both bride and groom had a ritual bath before the wedding. Its purpose was of cleansing and purificatory nature, and is consistent with other water-based pre-sacrifice purifications. What made the bride and groom's baths distinctive was their preparation. The bath water used to be drawn at a specific spring or river. At Athens, the water for bridal baths came from the Enneakrounos, the fountain house for the spring Kallirrhoe, but each city had its dedicated source. The water was carried in a special vase named the loutrophoros (bathcarrier) and the act of fetching the water and bringing it back to the homes constituted a procession. The loutrophoros was often given as offering to the altar of the Nymphs after the wedding. It was an important symbol of marriage, to the point that, if a woman died before being married, she would often be buried with a loutrophoros.
This will be more or less difficult to adapt depending on circumstances and environment, but the logic of a purifying bath (or shower even) can be kept (though I would discourage bathing in water you are not sure of the cleanliness of). The idea of having a specific vessel can also be kept. Personally, I plan to have a special vessel for some type of purified water, and while I may not bathe in it, I plan to sprinkle it and/or wash my hands with it.

Adornment of the bride (and groom)
Traditionally, the bride would have a nympheutria (which we could equate as a bridesmaid, but seems to have often been a female relative) charged of helping the bride get ready. I won’t get into the details of the clothing we know about, mostly because there seems to be a lot of variation, and because I consider this to be a very personal choice. However, we can note that both groom and bride were adorned with a wreath or a garland of plants that were considered to have powers appropriate for the occasion (sesame, mint, plants that were generally considered fertile or aphrodisiac). Perfume is also something attested for both bride and groom, especially the scent of myrrh. The bride would wear a crown, the stephane, which could be made out of metal or be vegetal (the stephane is now the object of its own crowning ceremony in Greek Orthodox weddings). The bride’s shoes were also particular for the event, and named nymphides. The bride’s veil was placed above the crown.
Hymenaios and Feast
I am grouping these two since they are linked. The feast was more or less the peak of the wedding ceremony and lively with music and dances, as Plutarch indicates (Moralia, [Quaest. conv.] 666f-67a):
But a wedding feast is given away by the loud cries of the Hymenaios and the torch and the pipes, things that Homer says are admired and watched even by women who stand at their doors.
The hymenaios was a sung hymn in honour of the couple and the wedding, and there were other songs that were specifically sung at weddings. However the hymenaios wasn’t only for the feast, these songs would be sung also during the processions. The hymenaios also had the purpose of ritually blessing the couple, a ritual that bore the name of makarismos.
As for the feast, it was obviously abundant with food and the prenuptial sacrifices provided the meat that would be served. There is otherwise very little difference with what a modern wedding feast would be like: food, drink, music and dance around which gathered friends and relatives of the couple. Like today, the wedding cake(s) was an important part of the celebration. It was called sesame and consisted of sesame seeds, ground and mixed with honey and formed into cakes to be shared with the guests.
Anakalypteria
Note that there is a bit of a debate around this step, which is the unveiling of the bride. Some believe the bride kept her face veiled until this part of the wedding, where her face would be uncovered for the groom to see. Others interpret this step the other way around, where the bride is then veiled as a result of being now married. The timing of the unveiling is also up for the debate. It might have been during the feast (at nightfall), or after once the couple was escorted to the bridal chamber. There doesn’t seem to be a clear consensus.
The concept of unveiling the bride is otherwise something that isn’t unknown to us as a modern audience. As with everything else, how to interpret and modernize it is up to personal preference.
Nymphagogia and Katachysmata
The nymphagogia aka the act of “leading the bride to her new home” took place at night, likely after the feast. It is at this point that the groom ritually led the bride to his home by taking her by the wrist in a ritual gesture known as χεῖρ’ ἐπὶ καρπῷ (cheir’ epi karpo). The relatives and friends of the couple formed a festive procession that accompanied them to their new home accompanied by music and songs. The mother of the bride led the procession carrying lit torches, while the groom’s mother awaited for the new couple in their home, also bearing lit torches.
Once there, the rite of the katachysmata would happen. The couple would be sat near the hearth and the guests would pour dried fruits, figs and nuts over the bride and groom as a way to incorporate them into the household and bless the union with prosperity and fertility. As part of this rite, the bride ate a fruit (either an apple, quince or pomegranate). It is only after this step that the couple would be escorted to the bridal chamber.
These two rites are tricky to adapt in a modern context because of how location-specific they are (and that’s not even taking into account the implications of having family escort you to your bedroom etc). My take would be that the katachysmata is not too far off from the custom of throwing rice/flowers at the couple after the ceremony, and could probably be incorporated as such. The torches could also be replaced by any source of light placed in a meaningful location, depending on the where the wedding is being held. The nymphagogia could also do with an update, the easiest of which could simply be holding hands while leaving the wedding ceremony.
The day after (Epaulia, Gamelia & sacrifice)
The epaulia refers to wedding gifts to the couple, which would be given the day following the ceremony. At this point, it is implied that the couple has consummated their marriage and are officially newly-weds. Pausanias informs us that the term “epaulia” (also?) refers to the gifts brought by the bride’s father in particular and included the dowry.
After the epaulia, the bride's incorporation into her husband's house was complete. This might have been when the groom held a feast for his phratria (aka direct family), as a way to conclude the wedding.
As for final sacrifices, the bride herself may have marked the end of her wedding by dedicating her loutrophoros at the sanctuary of Nymphe, south of the Acropolis.
The epaulia could be adapted, in modern terms, with having a registry. Should someone choose to have a specific vessel linked to the ritual bath today, it could very well be kept, dedicated to the Nymphs and used as a small shrine. Considering how symbolic the object is, there is also room for it to become a piece of family heirloom.
Final words
This is really only a small summary of what a wedding could have looked like, sprinkled with a few ideas of how to manage the gaps, discrepancies and limitations. As I said in my introductions, there are details I haven’t mentioned. Some of the customs detailed here have clear modern counterparts, but others don’t. I’d like to conclude by addressing these.
First, the ancient Greek (Athenian) wedding is completely devoid of priestly participation. It was entirely planned, organized and led by the two families. Religious responsibilities were entirely self-managed. I find this point important to remember because it makes it much more accessible than if modern Hellenic pagans had to seek out an external authority.
Some of you might have noticed the absence of wedding vows, at least in a formal form like the one we are used to in our modern days (derived from Christian and Jewish traditions), this is not an oversight, there simply were none that we know of. As a sidenote, I would also advise against turning a wedding vow into a formal oath. I’m still debating on what to do myself, but I’m leaning towards a religiously non-binding vow that won’t curse me should things go wrong.
Adapting the structures and rites of the ancient wedding to today’s framework of ceremony will naturally lead to changing the order of things, on top of sacrificing elements for the sake of simplicity, practicality, personal preferences and, very likely, visibility. Unless you’re lucky enough to do a private elopement, chances are that relatives and friends might be there, and not all might know or even approve of your faith. I hope this post shows that there can be ways to include traditional religious elements that will go unnoticed to the untrained eye, like I hope it showed that the private nature of the ancient Greek wedding rites is a significant advantage for modernization.
#hellenic polytheism#hellenic paganism#hellenic pagan#heradeity#greek history#ancient greece#zeus deity#aphrodite deity#artemis deity#hellenic reconstructionism#wedding rites
739 notes
·
View notes
Text

The earliest example of someone chewing on the end of their pencil that I know of
Bone styluses from a 5th century BC grave at Acharnai, outside of Athens. Now in archaeological museum at Acharnai. My photo.
Go forth and gnaw on your pencils, future archaeologists will love it. #DailyArchaeology
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

Apollo and Diana, an 1848 marble statue by American artist and sculptor Thomas Crawford.
This captures their essence quite well imo!
#artemis#goddess artemis#goddess diana#marble statue#marble sculpture#apollo#apollon deity#god apollo#greek gods#greek mythology#ancient greek#greek history#roman mythology#roman gods#roman history#rome#spqr#Thomas Crawford#Diana#theoi
347 notes
·
View notes
Text
All tragedies deal with fated meetings; how else could there be a play? Fate deals its stroke; sorrow is purged, or turned to rejoicing; there is death, or triumph; there has been a meeting, and a change. No one will ever make a tragedy—and that is as well, for one could not bear it—whose grief is that the principals never met.
Mary Renault, The Mask of Apollo
#book quotes#mary renault#mask of Apollo#literature#books and libraries#greek tragedy#greek history#greek myths#ancient greece
162 notes
·
View notes
Text

Any ideas?
#historical memes#history#history memes#meme#memes#historical#ancient history#Ancient Greece#Greek history#Ancient Greek history#macedon#Macedonia#Alexander#Alexander the great#alexander of macedon#Hephaestion#Hephaestion and Alexander#there I told you#I fucking love them
227 notes
·
View notes
Text
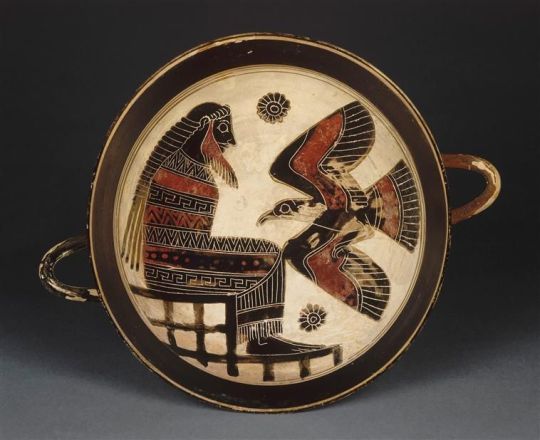

Lakonian kylix featuring Prometheos and his friend, the Eagle.
The hair - facial and head - is so quintessentially Spartan, it’s not funny. And he has his braids in a braid, right? That’s what’s going on back there? Like a super-braid.
Saw this called a Spartan king somewhere along the way. Think that might be a bit of a push, but I do like the idea that some perioikic craftsman was like - ‘Y’know, if I could depict anyone having their liver pecked out on the daily, you know who I’d choose…’
Anyway - This is 7th Century Lakonianware (from before the great cultural shift).
#ancient sparta#ancient greece#lakedaimon#7th Century BCE#spartan hairstyles#sparta#ancient history#greek history#spartan history#ancient greek history#greek mythology#prometheus
292 notes
·
View notes
Text
a post in honor of lord byron's 200th death anniversary —
the greeks were very fond of byron, who when he died in 1824 was a military commander and notable influence in their war of independence. as one of the most (if not the most) famous members of the philhellenist movement, byron used his poetic platform to try to remind people of greece's reputation as the source of western traditions in art and culture. the greeks then honored byron by decorating his coffin with a laurel wreath (below). they also erected statues for him, like this one below in athens depicting him being crowned with a laurel wreath (a symbol of greatness, especially in poetry/music [which historically overlapped]) by a female personification of greece. to this day, some statues of byron are annually wreathed in tradition, and the names byron/vyron/vyronas are still used in greece for roads, towns, and people in his honor.
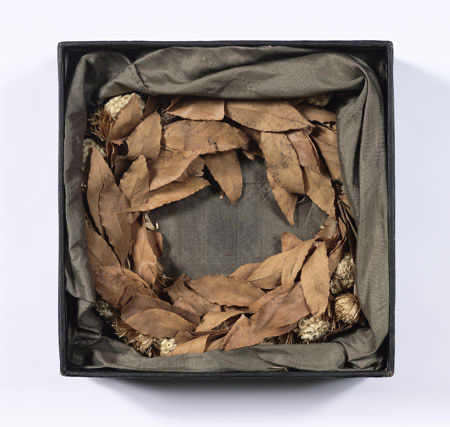


"’Tis sweet to win, no matter how, one’s laurels,
By blood or ink; ’tis sweet to put an end
To strife; ’tis sometimes sweet to have our quarrels,
Particularly with a tiresome friend:
Sweet is old wine in bottles, ale in barrels;
Dear is the helpless creature we defend
Against the world; and dear the schoolboy spot
We ne’er forget, though there we are forgot.
But sweeter still than this, than these, than all,
Is first and passionate love — it stands alone,
Like Adam’s recollection of his fall;
The tree of knowledge has been pluck’d — all ’s known —
And life yields nothing further to recall
Worthy of this ambrosial sin, so shown,
No doubt in fable, as the unforgiven
Fire which Prometheus filch’d for us from heaven."
— excerpt from Lord Byron's Don Juan, Canto the First (writ 1818, pub. 1819).
"The mountains look on Marathon –
And Marathon looks on the sea;
And musing there an hour alone,
I dreamed that Greece might still be free;
For standing on the Persians' grave,
I could not deem myself a slave."
— excerpt from Lord Byron's Don Juan, Canto the Third (writ 1819, pub 1821) — this stanza is part of a section often published on its own under the title "The Isles of Greece."
"Byron was at once a romantic dreamer, who wanted life to square up to his illusions, and a satirical realist, who saw what was before him with unusual clarity and found its contradictoriness amusing. The clash between the two Byrons is nowhere more noticeable than in his last writings, done on Cephalonia and at Missolonghi during the months before his death. There we see the Greece he dreams of, and the Greece which, in different ways, destroys him."
— excerpt from Peter Cochran's "Byron's Writings in Greece, 1823-4."
"Oh, talk not to me of a name great in story;
The days of our youth are the days of our glory;
And the myrtle and ivy of sweet two and twenty
Are worth all your laurels, though ever so plenty.
What are garlands and crowns to the brow that is wrinkled?
'Tis but as a dead-flower with May-dew besprinkled.
Then away with all such from the head that is hoary!
What care I for the wreaths that can only give glory!
Oh FAME! - if I e'er took delight in thy praises,
'Twas less for the sake of thy high-sounding phrases,
Than to see the bright eyes of the dear one discover,
She thought that I was not unworthy to love her.
There chiefly I sought thee, there only I found thee;
Her glance was the best of the rays that surround thee;
When it sparkled o'er aught that was bright in my story,
I knew it was love, and I felt it was glory."
— Lord Byron's "Stanzas Written on the Road Between Florence and Pisa" (November, 1821). What is illustrated here, and what I try to illustrate all throughout this assortment, is Byron's conflation of love and glory, and the idea that poetry and politics are both ways to deserve and achieve — not fame, but what fame seems to promise — love.
"But 'tis not thus—and 'tis not here
Such thoughts should shake my Soul, nor now,
Where Glory decks the hero's bier,
Or binds his brow.
The Sword, the Banner, and the Field,
Glory and Greece around us see!
The Spartan borne upon his shield
Was not more free.
Awake (not Greece—she is awake!)
Awake, my Spirit! Think through whom
Thy life-blood tracks its parent lake
And then strike home!"
— excerpt from Lord Byron's "On This Day I Complete My Thirty-Sxith Year" (1824).
"What are to me those honours and renown
Past or to come, a new-born people's cry
Albeit for such I could despise a crown
Of aught save Laurel, or for such could die;
I am the fool of passion, and a frown
Of thine to me is as an Adder's eye
To the poor bird whose pinion fluttering down
Wafts unto death the breast it bore so high –
Such is this maddening fascination grown –
So strong thy Magic - or so weak am I."
— although the much more popular and published "On This Day I Complete My Thirty-Sxith Year" is often believed to be Byron's last poem, the above is likely Byron's actual last poem. Like the former, it wasn't solely written for Greece, but for his page Lukas Chalandritsanos who he was in unrequited love (or lust) with. It is sometimes titled "Last Words on Greece" (named so by his friend and sometimes-editor Hobhouse).
#queud#literature#english literature#lord byron#romanticism#history#dark academia#poetry#aesthetic#greece#greek#greek history#poems#lit#on this day#byron#byronism#academia#greek war#war#web weaving
74 notes
·
View notes
Text
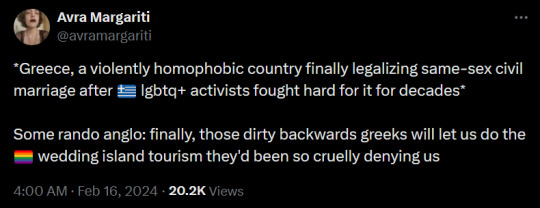
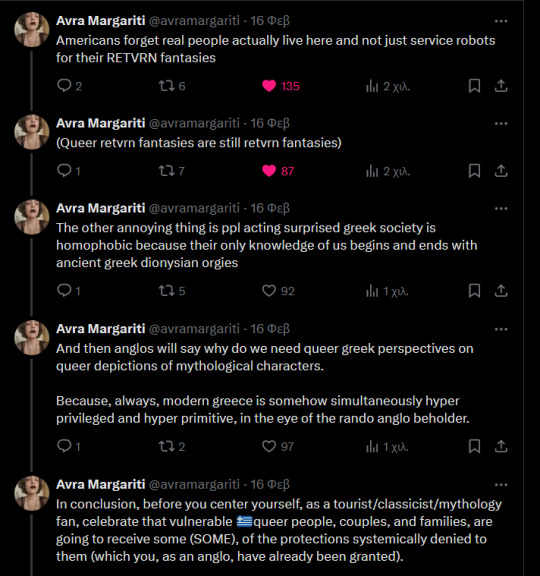
This! The tweet references this tweet where foreigners proceeded to rejoice about their vacation in Greece as a first reaction after hearing about how the brutal reality of queer Greeks has been alleviated. Are you for FUCKING REAL people?? You make me wanna puke! Were we ever people to you? Or just a fancy destination and some vague ancient texts of a "dead" language, that you never cared to associate with the actual Greek culture and people??
I saw the majority of these comments came from USians and I implore you specifically to shut your fucking face. This shouldn't be your reaction to a foreign marginalized group (that is still in danger) gaining rights. The privilege of living in the country that controls Greece has gotten to your head, and unfortunately, I see this attitude from all US marginalised groups also.
You are clearly NOT ready to discuss how your country has been profiting from exploiting our culture, and that the way you see us for centuries now reeks of the neocolonialist attitudes.
Even when we are happy when for the first time in our history our existence is legal MUST WE cater to your voyeurism and "ancient Greek" fantasies? Not to mention the continuous eyerolls I had seeing people expressing they thought Greece is a gay paradise since antiquity... B R U H .... It was never legal or non-shameful for us to be gay! N E V E R . Check ancient texts and laws. It was never legal or pleasant for us here!
More from the tweet here:
#if you care about lgbt+ people in Greece reblog or repost this please#LGBT+ GREEK PEOPLE OWE YOU NOTHING#WHEN WILL YOU SEE US AS FUCKING PEOPLE#I'M SO FUCKING TIRED#lgbt+ community#lgbt+ history#queer history#greek history
381 notes
·
View notes
Text
When the Varangians honoured the woman who killed her near-rapist
The Varangian Guard (Greek: Τάγμα τῶν Βαράγγων, Tághma tōn Varángōn) was an elite unit of the Byzantine Army from the tenth to the fourteenth century who served as personal bodyguards to the Byzantine emperors. The Varangian Guard was known for being primarily composed of recruits from northern Europe, including mainly Norsemen from Scandinavia but also Anglo-Saxons from England. The recruitment of distant foreigners from outside Byzantium to serve as the emperor's personal guard was pursued as a deliberate policy, as they lacked local political loyalties and could be counted upon to suppress revolts by disloyal Byzantine factions.
The Byzantines had mixed feelings about them, on one hand considering them barbarians and brutes with too much love for alcohol, on the other hand admitting their fierce loyalty to the emperor and their military prowress. They never fled a battle and they would fight to their death. They were also considered fair traders in their transactions between the Byzantine Empire and their northern homelands.
One incident which took place in 1034 helped soldify a positive image of the Varangians to the Byzantines' eyes, so much that the Byzantine Greek chronicler Ioannis Skylitzis, described it in his works as "αξιαφήγητον" (axiaphíyiton, worthy of mentioning / narrating).
According to Skylitzis, a group of Varangians were transferred in the Thracesian Theme (Greek: θέμα Θρᾳκησίων, thema Thrakēsiōn), a military division that at the time encompassed west Asia Minor (not Thrace). One of them once encountered a local woman in an uncrowded place. The man approached the woman suggestively but she rejected his advances. The man attempted to rape her and she seized his sword and killed him. His death was instant as she pierced him through his heart.
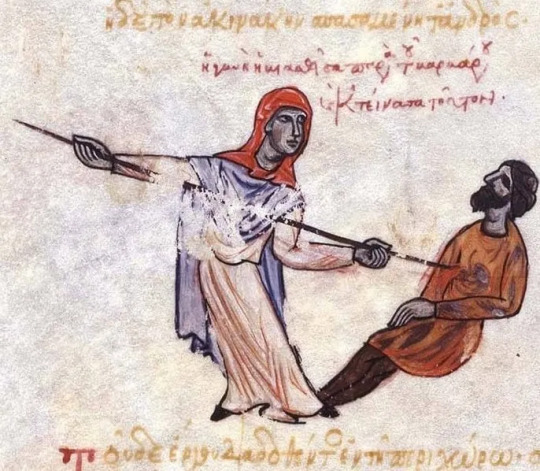

Art in Skylitzis' manuscript where the woman is erroneously depicted to kill the man with a spear instead of a sword.
Once the incident became known in the area, the Varangians made a gathering in which they agreed to honour the woman for killing their companion. They offered her all the valuable belongings of the killed Varangian, whom they left unburied. According to Varangian law, the rapists of married women were punished with execution, therefore the Varangians reasoned that the woman simply implemented the law by killing their companion.

The manuscripts of Skylitzis are kept in the National Library of Madrid.
Sources:
ΜΗΧΑΝΗ ΤΟΥ ΧΡΟΝΟΥ
www.in.gr
#history#byzantine empire#east roman empire#byzantine history#varangian guard#greek history#ioannis skylitzis
511 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Marble Head of Apollo Unearthed in Greece
The excavation, carried out by a group of students of the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki in the archaeological site of Philippi Kavala, brought to light important findings. Among other things, they discovered a rare head of Apollo dating back to the 2nd or early 3rd century AD.
The statue dates back to the 2nd or early 3rd century AD and it probably adorned an ancient fountain.
Natalia Poulos, Professor of Byzantine Archaeology, led the excavation, which included fifteen students from the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki (11 undergraduates, 2 master’s, and 2 PhD candidates), Assistant Docent Anastasios Tantsis, and Professor Emeritus of Byzantine Archaeology Aristotle Mendzo.
Archaeologists say, this year the excavation continued east of the southern main road (decumanus) at the point where it meets the northern axis of the city (the so-called “Egnatia”). The continuation of the marble-paved road was revealed, on the surface of which a coin (bronze phyllis) of the emperor Leo VI (886-912) was found, which helps to determine the duration of the road’s use. At the point where the two streets converge, a widening (square) seems to have been formed, dominated by a richly decorated building.
Archaeologists say evidence from last year’s excavations leads them to assume it was a fountain. The findings of this year’s research confirm this view and help them better understand its shape and function.
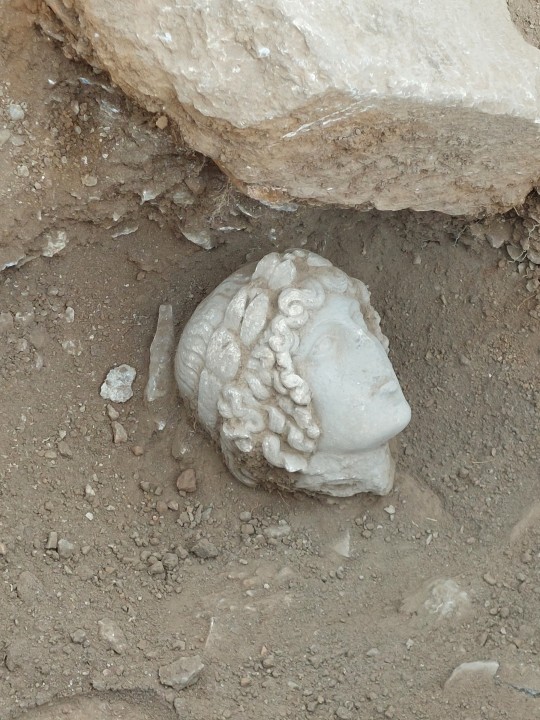

The research of 2022 brought to light part of the rich decoration of the fountain with the most impressive statue depicting Hercules as a boy with a young body.
The recent excavation (2023) revealed the head of another statue: it belongs to a figure of an ageneous man with a rich crown topped by a laurel leaf wreath. This beautiful head seems to belong to a statue of the god Apollo. Like the statue of Hercules, it dates from the 2nd or early 3rd century AD and probably adorned the fountain, which took its final form in the 8th to 9th centuries.

In classical Greek and Roman religion and mythology, Apollo is one of the Olympian gods. He is revered as a god of poetry, the Sun and light, healing and illness, music and dance, truth and prophecy, and archery, among other things.
Philip II, King of Macedon, founded the ancient city of Philippi in 356 BC on the site of the Thasian colony of Crenides near the Aegean Sea. The archaeological site was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2016 for its outstanding Roman architecture, urban layout as a smaller reflection of Rome itself, and significance in early Christianity.
By Oguz Buyukyildirim.


#The Marble Head of Apollo Unearthed in Greece#Philippi Kavala#marble#marble statue#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#ancient greece#greek history#greek art
192 notes
·
View notes
Text
Iliad Book 1

#classical civilisation#classics#greek gods#homers iliad#the iliad#trojan war#apollo#greek classics#greek god#im a healer but#agamemnon#tagamemnon#greek history#menelaus#achilles#homer the poet#classics memes#apollo god#incorrect iliad#iliad#homer's iliad#i know he's also the god of plagues but this is funne so :p
179 notes
·
View notes
Text
“But in a solitary life, there are rare moments when another soul dips near yours, as stars once a year brush the earth. Such a constellation was he to me.”
― Madeline Miller, Circe
#Madeline Miller#Circe#The Song Of Achilles#troy#achilles#achilles x patroclus#patrochilles#patroclus#greek#classical mythology#greek mythology#mythology#greek history#history#literature#lit#english literature#classic lit#academia#soft academia#dark academia aesthetic#chaotic academia#romantic academia#reading#to read list#poet#readblr#quotes#quote#booklr
2K notes
·
View notes