#Bacteriology
Photo
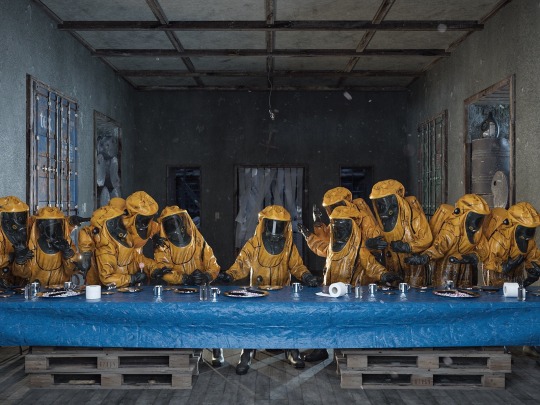
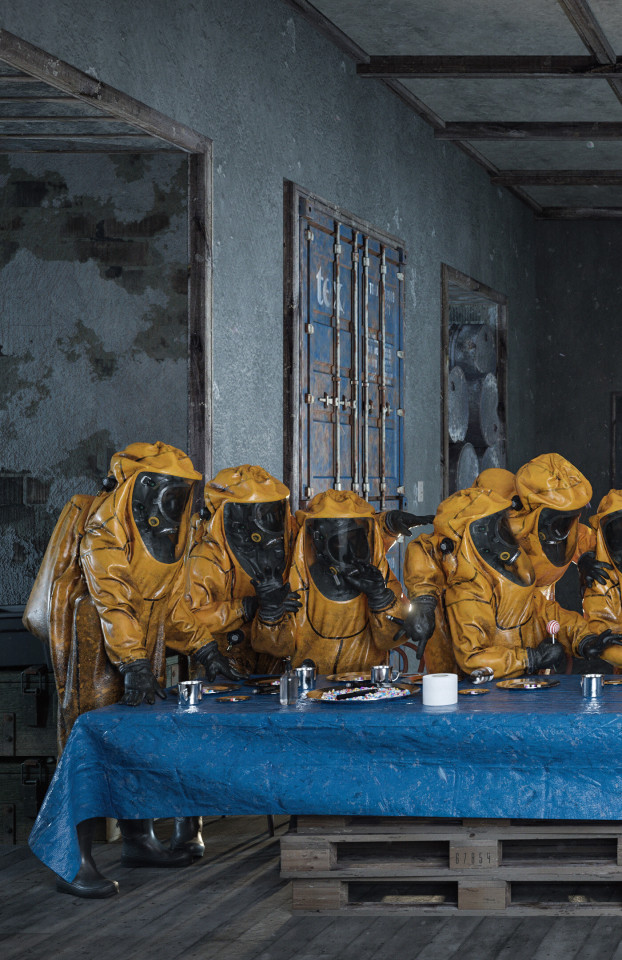
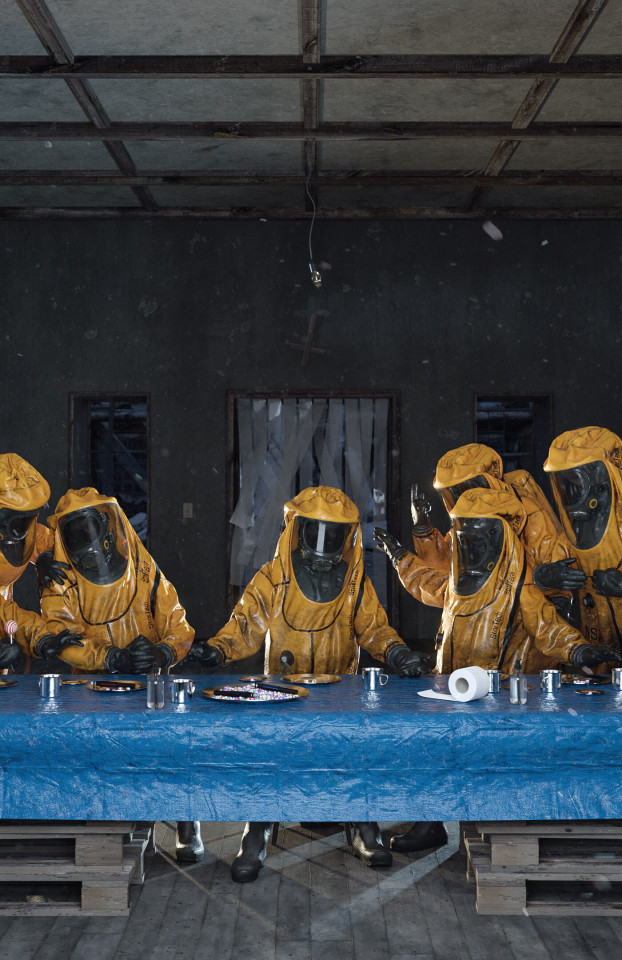
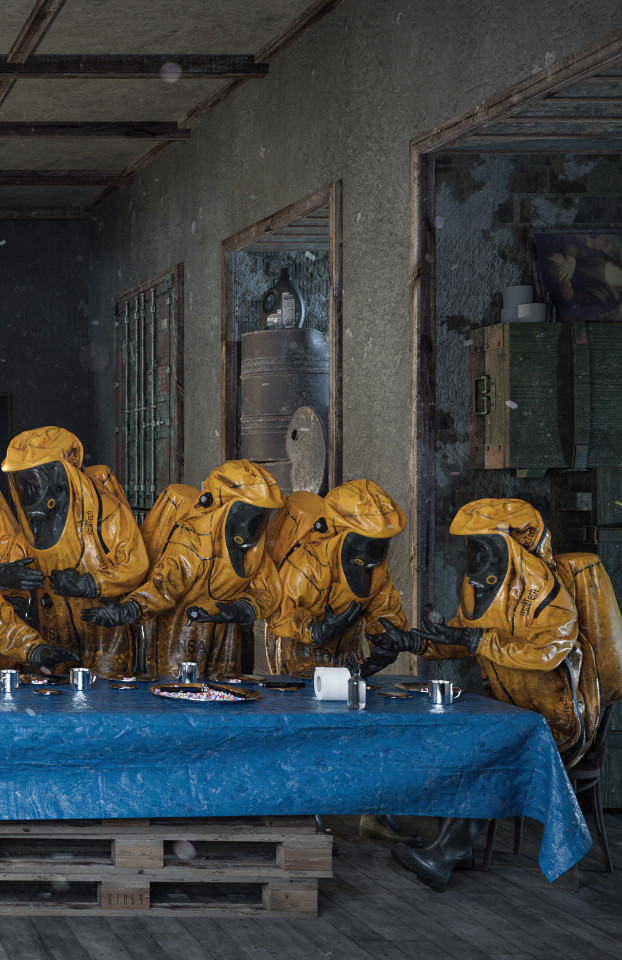




“The Last Supper" ☢️ (Details) by Adam Skovran
#Adam Skovran#The last supper#bacteriology#Chemical Warfare#Nuclear warfare#artwork#reunion#the end of the world#end of the times#art
7K notes
·
View notes
Text

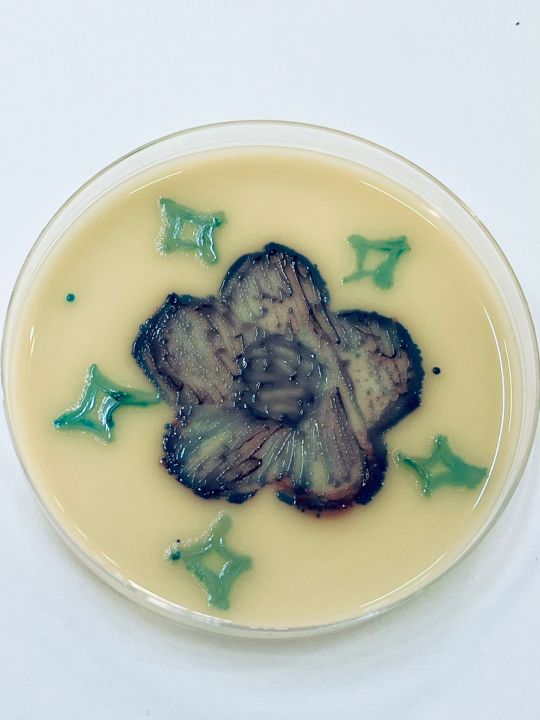
Hiiii!!
Could you guys please vote for my agar art in this contest? 🌿🌸
It would mean the world to me 🥹
#med student#med studyblr#studyblr#student#study#studies#medicine#university student#microbiology#agar art#agar#bacteria#bacteriology#art
157 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hello, Mr. Holmes! How are you?
So, long story short, I ended up with an optical microscope in my room more or less 4 months ago, with 200 previously made slides (secured in a proper box), and lots of new ones too, for me to prepare myself. I love microbiology (it's one of my hyperfixations, curse my neurodivergency) and now I love it even more (my mother has had to drag me away from the microscope - I named it Wesley - in the middle of the night multiple times now).
After much conversation, I finally convinced my mom to buy me the proper equipment to prepare the slides!
So, I'm sending this ask to you, as I know you also have a microscope and that you use it a lot: what kind of equipment do you recommend me buying (gloves, scalpel blades, tints, etc), while still remembering that all of the stuff needs to stay in my room (properly taken cared of by me, of course)?
For example, I'm unsure if different dyes are used for different smears and specimens due to it's affinity (I've noticed that on 'organic matter' slides, images are usually tinted purple or pink, while on plant-based slides, images are usually tinted green and blue, with a few red structures.) Considering that I don't have access to a mortuary, I will mostly make plant slides. There must be a difference in the dyes then, right?
Sorry for the long text! Hope this isn't too much of a bother.
- a 17-year-old :)
Congratulations on your new light microscope. I do hope you get the best out of it. I am overjoyed that someone else appreciates the art of microscopy and microbiology.
However, you need to be careful to not strain your eyes. It is recommended to take breaks every 15 minutes to close your eyes or focus on something in the distance to reaccommodate your eyes. And get up every 40 minutes, stretch and correct your posture. And it is recommended to not use a microscope more than 5 hours per day. John has to chase me away from my microscope sometimes to take a break when I sit there for hours, my posture like a Caridea.
Concerning equipment, you will obviously need a scalpel or other sharp blade to make very thin slices of your specimen, as thin as possible. And forceps to move your samples (best just get a whole dissection kit it has everything). Obviously slides and coverslips, pipettes for the stains or water, maybe some tubes. A pen to label your slides. In many staining procedures ethanol or acetone is also used. A waste jar to safely dispose of any chemicals, but be careful what you mix. A rack for staining and containers. I would recommend nitrile gloves, some people are sensitive to latex.
The dyes you use depend on the specimen. For example in histological slides of tissues hematoxylin and eosin are most commonly used (short HE-stain). That's what you most likely saw on your slides, it's blue, purple and pink.
Hematoxylin is a basic compound extracted and oxidised from the logwood tree (Haematoxylum campechianum), and it stains acidic compounds in the cells (or basophilic because they have an affinity for basic substances). For example nucleic acids like DNA or RNA get stained by hematoxylin because they are basophillic. And where are lots of nucleic acids? In the nucleus and ribosomes, that is why they appear blue to purple in the staining because they bind hematoxylin.
Eosin is an acidic compound, and stains basic or acidophilic compounds red or pinkish, like proteins, collagen, cytoplasm, extracellular matrix.

(Ductus epididymidis with HE-stain)
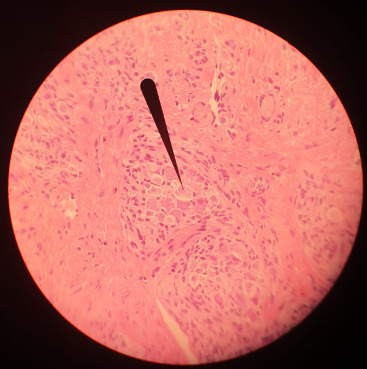
(Tongue HE-stain, pointer marking a ganglion; that is my picture)
Of course there are more specific stains for specific tissues like Golgi's silver staining for neurons.
For plants toluidine blue is often used, high affinity for acidic tissues, and can stain blue to green to purple.
It is often combined with safranin, a basic azine, which is probably the red stain you saw. It stains polysaccharides and lignin, woody parts of the plant. Safranin and astrablue is also often combined, astrablue stains non-lignified parts of the plant.
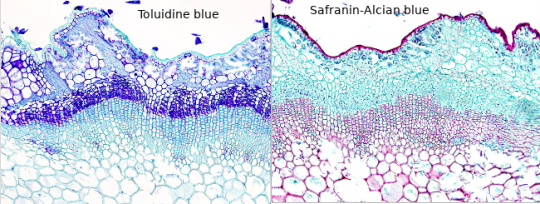
(Ulex europaeus stem; not my pictures I don't have any samples currently, source Atlas of plant and animal histology)
Safranin is also used in bacteriology, in the famous Gram staining. In Gram staining you use crystal violet (blue/purple), Lugol's iodine solution, then wash it with ethanol and add safranin (red) as a counter stain. Bacteria is gram-positive if the crystal violet stays in their thick murein cell wall, can't be washed out with the ethanol and the bacteria stays blue. Gram-negative appear red because of the counterstain.
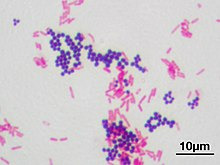
(Staphyloccocus aureus (violet, gram positive) & Escherichia coli (red, gram negative); not my picture, source Wikipedia)
However, I am not sure whether you have access to any of those substances, if they are too expensive for you or if they are too hazardous if used in your own room for a prolongued time. Of course those substances need to be stored properly, and your own room is probably not a good place, especially for ethanol or acetone. The fumes. I would recommend to ask your biology or chemistry teacher whether they can recommend anything further and where to buy said solutions in your area, and if they can't they are idiots. There are also many useful resources and tutorials on Youtube.
Another fascinating experiment for your microscope, that you can perform without buying any chemicals, is a hay infusion. You put hay into a container filled with water, and let it sit undisturbed for a week in a sunny area but not in direct harsh sunlight. During that time the microorganisms in the hay are reproducing in the solution, feeding on the polysaccharides of the hay. Protozoans also flourish in the hay infusion and eat the bacteria. It might get cloudy and a bit foul smelling (best not do it in your own room if you don't want to sleep next to a rotting smell).
When you put a drop of the solution onto a slide and look at it in the microscope, you should see a variety of microorganisms like bacteria (like Bacillus subtilis), amoeba, ciliates, heliozoa, algae et cetera. At different depths of the liquid you should find different kinds of organisms, because of differing oxygen content.
However, pathogens can also occur in the hay infusion so handle it carefully and work sterile, wash your hands properly.
And even if you don't work at a morgue you can still get tissue samples to experiment on, after all meat is sold in supermarkets, basically the same as a human body. And at the butchers they even sell organs like chicken hearts, pig kidney, liver, blood et cetera. Or observe your own hair under the microscope.
Which kind of samples and slides were included in your starter kit? Be careful to not leave them lying around in the sunlight, or the stain might fade. Always store them in the proper box.
#roleplay#rp#sherlock roleplay#sherlock rp#johnlock roleplay#johnlock rp#sherlock#bbc sherlock#sherlock holmes#sherlock holmes rp#sherlock holmes roleplay#science#scientist#research scientist#histology#microscope#microscopy#bacteria#bacteriology#pathology#anatomy#biology#chemistry#scientists#pictures#he stain#specimen#samples#slides#sherlock replies
46 notes
·
View notes
Text



Biology Keychains - Diatoms and Soil Bacteria!
Designed by me, available now on my Etsy!
#artists on tumblr#digital art#biology#etsy#graphic design#marine biology#microbial#microbiology#diatoms#bacteriology#bacteria#algae bloom#algae#small business#keychain#charm#cute#merch#mu's wares
147 notes
·
View notes
Text
Leptospirosis in California Sea Lions

With the arrival of August comes the return of the California sea lions to our area of the coast, and with the sea lions comes leptospirosis. 7/31/23 is when I first heard the sounds of their barking in the bay from my apartment, which was the first sign of their return from migration.
Leptospirosis is a bacterial disease that's caused by the Leptospira bacteria. Lepto outbreaks have occurred in Cali sea lions in our area throughout the years, and it tends to occur in two-year time periods every 4-5 years or so. i.e., if a lepto outbreak occurs one year, it's common for it to occur for one more year afterwards.
Usually, pinnipeds don't need to drink fresh water since they get their water from their food. Lepto, however, damages their kidneys which ends up dehydrating the sea lions. This means that occasionally Cali sea lions will seek out water. My mentor told me about one sea lion that wandered far out of the water into a neighborhood one summer, dazed and disoriented and looking for fresh water!
Leptospirosis can be passed from animals to humans through direct contact, primarily through urine, so keep your pets leashed and keep your distance from wild animals!
#marine biology#biology#zoology#bacteriology#microbiology#wildlife#bacteria#animals#pinnipeds#sea lions#science
98 notes
·
View notes
Text
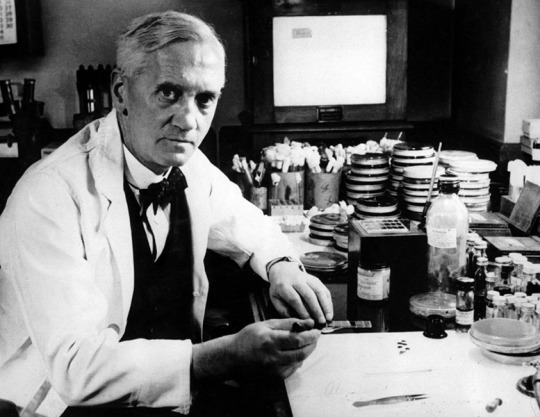




Alexander Fleming – Scientist of the Day
Alexander Fleming, a Scottish bacteriologist, died Mar. 11, 1955, at age 73.
read more...
#Alexander Fleming#bacteriology#penicillin#antibiotics#histsci#histSTM#20th century#history of science#Ashworth#Scientist of the Day
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
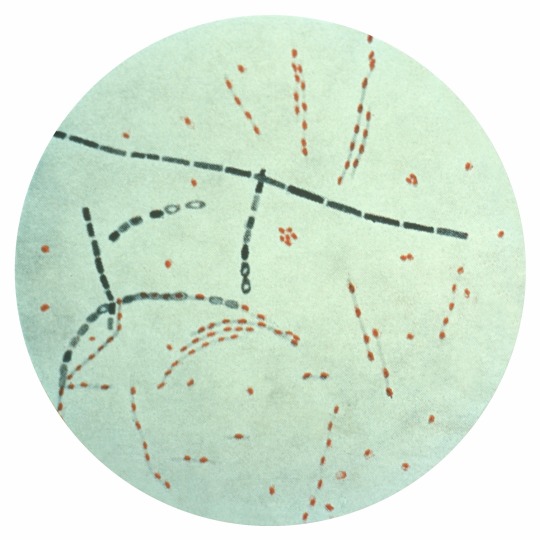
Bacillus anthracis
“Photomicrograph of Bacillus anthracis from an agar culture demonstrating spores; Fuchsin-methylene blue spore stain.” - via Wikimedia Commons
#bacillus anthracis#anthrax#microbiology#micrograph#wikipedia#wikipedia pictures#wikimedia commons#nature#microbes#spore stain#infectious diseases#bacteria#bacteriology#spore former
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Weird Microorganism Iceberg
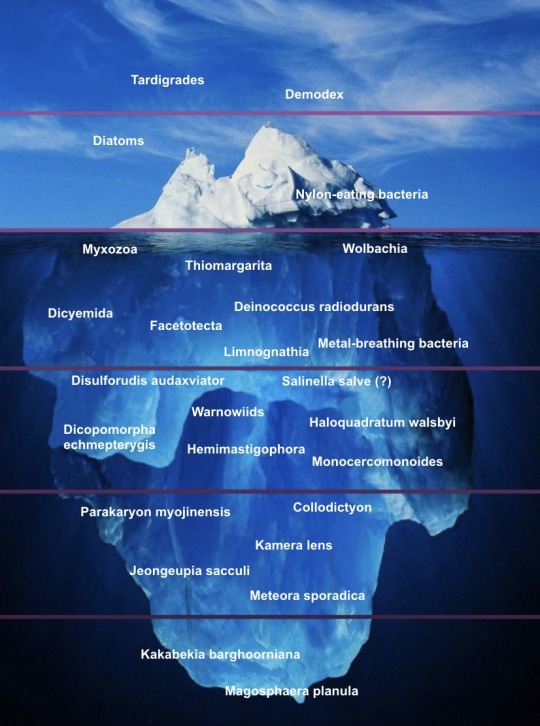
I basically made this on an impulse, please don’t take it too seriously. Feel free to suggest more organisms!
Explanations under the cut.
Tardigrades: You probably all know this one. Commonly said to be polyextremophiles, but this isn’t actually true; while they can survive extreme conditions, they don’t thrive in them. Something you might not know about them is that all of their body segment genes are equivalent to arthropod head genes — meaning they are basically walking heads.
Demodex: Eyelash mites.
Diatoms: Geometric silicon shell creatures.
Nylon-eating bacteria (Paenarthrobacter ureafaciens KI72): Exactly what it says on the tin.
Myxozoa: Single-celled parasitic cnidarians. Lack digestive systems, circulatory systems, gonads, and even muscles in some species. Also may or may not be autonomous cancer cells.
Thiomargarita: The only macroscopic bacteria. Honorary microorganisms for the purposes of this image.
Wolbachia: Parasitic / mutualistic bacteria genus that has created numerous insect species through their effects on reproduction. (Infected females can become capable of parthenogenesis, while infected males are either killed, turned into females, or limited to reproducing only with females infected by the same strain.)
Deinococcus radiodurans: A bacterium which unofficially holds the title of “most extreme extremophile”. Can survive incredibly high doses of radiation, as well as high acidity and very low temperatures.
Dicyemida: Symbiotic (once mistakenly thought to be parasitic) animals that live in cephalopod kidneys. Have alternation of generations and used to be known as “Rhombozoa” (“rhombus animals”).
Facetotectans: Parasitic crustaceans with an unknown adult form. Attempts to artificially induce metamorphosis only produce another juvenile stage, as far as anyone can tell.
Metal-breathing bacteria: Bacteria which use nanowires to accept electrons from metals.
Limnognathia: One of the smallest animals, and has 15-part extensible jaws.
Disulforudis audaxviator: The only known organism to comprise a single-species ecosystem. Lives over a mile underground and feeds off the byproducts of radioactive decay.
Salinella salve: Possibly nonexistent simple animal, allegedly cultured by Johannes Frenzel in 1892 but never found by anyone else.
Warnowiids (Warnowiaceae): A family of dinoflagellates which have modified some of their organelles into an eye… which somehow works well enough for them to aim their stingers at prey, despite them having no brain (or even other cells) to process the images.
Haloquadratum walsbyi: A square that lives in salt.
Dicopomorpha echmepterygis: The smallest known insect, a parasitoid wasp smaller than a Paramecium.
Hemimastigophora: A group of organisms recently discovered to be an early-splitting branch of the eukaryotes.
Monocercomonoides: A genus of “excavate” “protists” (both terms are polyphyletic, lol) that lack mitochondria… or even the genes for them.
Parakaryon myojinensis: The only complete incertae sedis, for which not even the domain is known. Has an odd mix of eukaryote and prokaryote-like features, leading to speculation that they represent a second incidence of endosymbiosis (aka Eukaryota 2.0). Also my blog’s namesake.
Collodictyon: Considered unclassifiable for a long time. Not really that weird in and of itself, tbh.
Kamera lens: Continuing the theme, this is an alga that has proven weirdly difficult to classify despite having been known for centuries (though it’s been narrowed down to the Ochrophyta). Its funny name makes it a pain to look up.
Jeongeupia sacculi: Recently-discovered multicellular(!) bacterium. Unlike everything else on here, it doesn’t have a Wikipedia page (yet).
Meteora sporadica: “Protist” which moves by rowing with a pair of arm-like appendages. Another difficult-to-classify organism, although a study from earlier this year suggests they are related to the Hemimastigophora.
Kakabekia barghoorniana: Apparent Paleoproterozoic living fossil that looks like an umbrella.
Magosphaera planula: A sphere which splits apart into amoeba-like cells, observed by Ernst Haeckel in 1869. Also possibly nonexistent / misidentified.
75 notes
·
View notes
Text
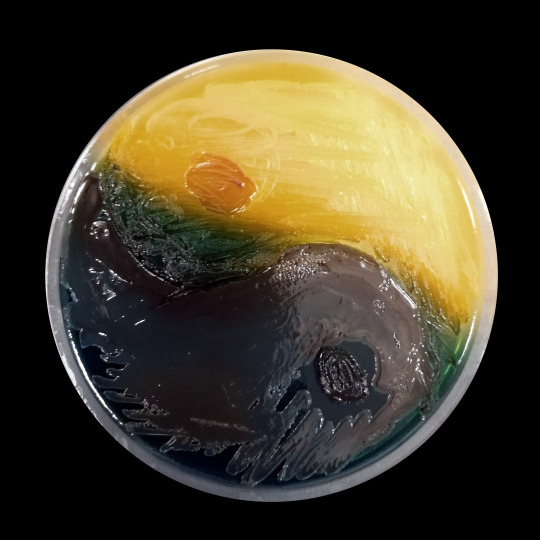
It's not the best "microbiology" art, but it has a very interesting background. Two bacteria from two different clinical cases were inoculated on the TSCB medium. This metallic blue spilling bacterium is of course Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The yellow one (positive reaction on TSCB medium) is Vibrio metschnikovii isolated from chronic UTI in a dog. It was an unusual microbiological diagnosis. But what can you do when even your dog has a better holiday than you?
Problems with urination (in this dog) began just after returning from the Mediterranean, the owners and the dog intensively used the charms of warm and salty water.
#veterinary#veterinarymedicine#veterinaryjobs#laboratory#microbiology#microbiologist#jobapplication#bacteriology#examination#numbers#lookingforjob#microscope#urinarytractinfection#art#rarediseases#i.o.a.g.
172 notes
·
View notes
Text
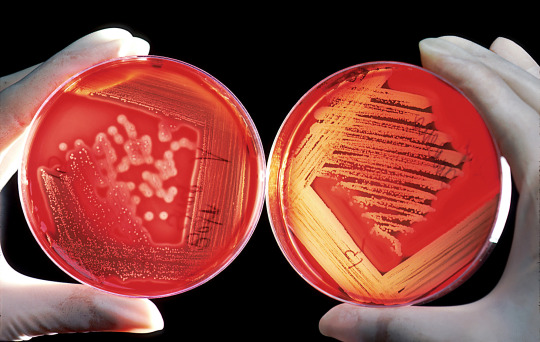
Sheep blood is added to growth media to enhance the nutrients available for bacterial growth. Laboratory scientists grow various bacteria on this medium as well as numerous other media, in order to help assess infections in humans and animals. The image on the right shows growth of a beta-hemolytic streptococcus. The bacterium has produced a hemolytic compound that has lysed the red blood cells surrounding each colony. The plate was properly streaked to attain isolated colonies. The plate on the left is growing a Staphylococcus species. The plate was streaked too heavily, so isolated colonies were not attained.
23 notes
·
View notes
Text





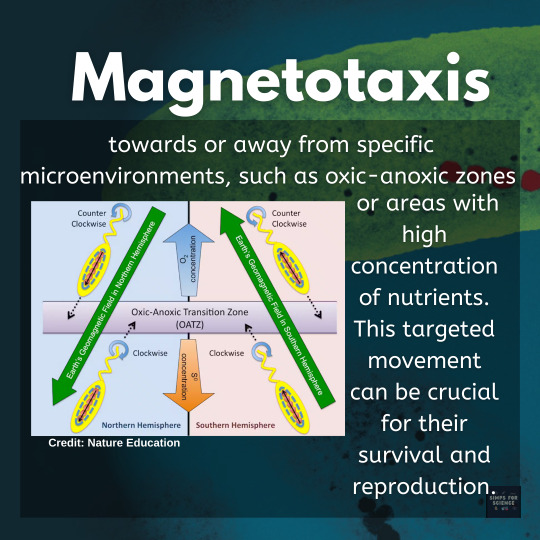

🤔💭 Have you ever imagined anything like a 'Living Compass' ?🧭🦠These tiny titans cum bacteria have superpowers: they navigate using Earth's magnetic field! Swipe ➡️ through this post to know how these beings are able to sense north ⬆️ 🧲 wherever they go!
#science#science facts#education#discover#scicomm#study blog#explore#research scientist#physics#earth#bacteria#bacteriology#microbiology#microbes#microbiota#microbiome#magnetism#magnetic#magneto#magnetite#magnetic field#magnets#magnetosphere#scientist#scientific illustration#cool science#scifi#sci fi and fantasy#scifiedit#simps for science
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

Day 3/100 of productivity.
Today I had a bacteriology class which I found interesting and fascinating. These are some pictures I took 2 months ago during a summer school, but I figured they would be suitable for this topic.
15 notes
·
View notes
Text

31 notes
·
View notes
Text

14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lysogeny

Patreon
#studyblr#notes#my notes#microbiology#microbio#microbiology notes#microbio notes#molecular biology#microorganisms#pathogens#biology#bio#biology notes#bio notes#science#life science#biological science#health science#laboratory science#microscopy#microbial organisms#bacteria#bacteriology#note cards#flashcards#flash cards
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
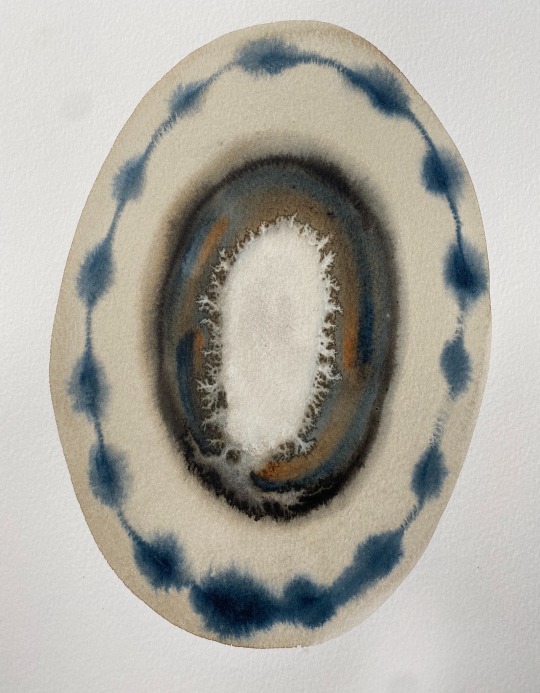

sacrēd circle paintings by Artist Rose Eads
No.33 + No.100 𖦹 shop art .:. source
#artists on tumblr#art#fine art#abstract art#my art#abstract painting#ancient art#ancient history#zoology#marine art#esoteric art#ethereal art#fungicore#visionary art#biomorphic#biochemistry#bacteria#bacteriology#pastels#dreamy art#dreamcore#kunst#angelcore#pastelcore#scientific illustration#illustration#illustrator#strangecore#mycologist#mycology
5 notes
·
View notes