#Non-Ductile
Text
Protect Your Infrastructure from Natural Disasters
Our ordnance construction service ensures the longevity and functionality of installations from initial planning and design to construction and maintenance. Contact us now!
#Engineering Contractor#Seismic#Construction#Structural#Soft-Story#Retrofit#Earthquake#Non-Ductile#Ordinance#Multifamily Construction
0 notes
Text
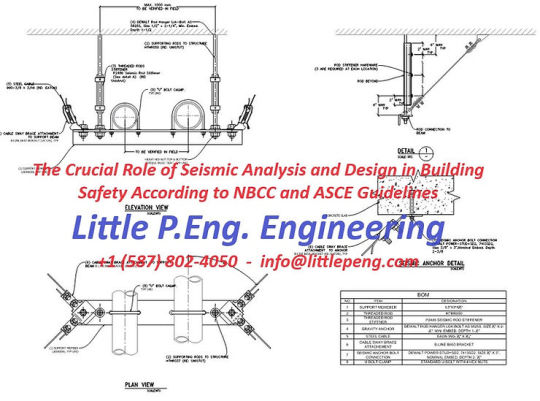
The Crucial Role of Seismic Analysis and Design in Building Safety According to NBCC and ASCE Guidelines
Seismic analysis and design are fundamental aspects of structural engineering that ensure buildings and their non-structural components can withstand the forces generated by earthquakes. These practices are not just essential for the safety and integrity of structures but are also mandated by comprehensive guidelines and codes such as the National Building Code of Canada (NBCC) and the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE). This article delves into the importance of seismic analysis and design for buildings and non-structural components, guided by the principles set forth in the NBCC and ASCE.
Understanding the Risks
Earthquakes pose a significant risk to life and property. The unpredictable nature of seismic events, combined with the potential for catastrophic damage, underscores the need for rigorous building standards. Seismic analysis and design aim to mitigate these risks by ensuring buildings can endure seismic forces without collapsing, thus safeguarding occupants and minimizing economic losses.
NBCC and ASCE Guidelines: A Benchmark for Safety
The NBCC and ASCE have established benchmarks for seismic safety in the construction industry. The NBCC, applicable in Canada, and the ASCE's standards, widely adopted in the United States and internationally, provide a framework for assessing seismic risks and implementing necessary design and construction practices.
Seismic Analysis
Seismic analysis involves evaluating how a structure responds to earthquake-induced forces. This process helps engineers understand potential stress points and the overall behavior of a building during seismic events. Both the NBCC and ASCE recommend detailed analysis methods, including linear dynamic analysis, nonlinear dynamic analysis, and modal response spectrum analysis, among others. These methodologies help in designing structures that are not only compliant with safety standards but also economically viable.
Design Considerations
The design phase is critical in integrating seismic resilience into buildings. The NBCC and ASCE guidelines emphasize the importance of ductility, redundancy, and energy dissipation in structural elements. Ductility allows parts of the structure to deform under seismic loads without failing, while redundancy ensures that if one part of the structure fails, others can take over the load-carrying responsibilities. Energy dissipation mechanisms are incorporated to reduce the energy transferred to the structure during an earthquake, thereby limiting damage.
Non-Structural Components
Seismic safety extends beyond the structural elements of a building. Non-structural components, including mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems, as well as architectural elements like ceilings, partitions, and facades, play a crucial role in building functionality and occupant safety. The NBCC and ASCE guidelines require these components to be anchored and braced appropriately to prevent detachment or collapse, which could cause injury or block egress paths during an earthquake.
The Path Forward
In conclusion,
the seismic analysis and design of buildings and their non-structural components, as per the standards of the NBCC and ASCE, are indispensable in the pursuit of creating earthquake-resilient communities. These practices embody a proactive approach to disaster mitigation, emphasizing the critical importance of preparedness and the implementation of engineering solutions that protect both people and their environments.
Tags:
NBCC
ASCE
structural integrity
structural engineering
earthquake resilience
energy dissipation
building codes
seismic design
non-structural components
mechanical systems
disaster preparedness
plumbing systems
ductility
architectural elements
seismic safety standards
seismic risks
anchoring
bracing
electrical systems
redundancy
building safety
linear dynamic analysis
structural components
seismic analysis
modal response spectrum analysis
nonlinear dynamic analysis
earthquake mitigation
seismic guidelines
occupant safety
earthquake-induced forces
Seismic Bracing Experts
Located in Calgary, Alberta; Vancouver, BC; Toronto, Ontario; Edmonton, Alberta; Houston Texas; Torrance, California; El Segundo, CA; Manhattan Beach, CA; Concord, CA; We offer our engineering consultancy services across Canada and United States. Meena Rezkallah.
#NBCC#ASCE#structural integrity#structural engineering#earthquake resilience#energy dissipation#building codes#seismic design#non-structural components#mechanical systems#disaster preparedness#plumbing systems#ductility#architectural elements#seismic safety standards#seismic risks#anchoring#bracing#electrical systems#redundancy#building safety#linear dynamic analysis#structural components#seismic analysis#modal response spectrum analysis#nonlinear dynamic analysis#earthquake mitigation#seismic guidelines#occupant safety#earthquake-induced forces
0 notes
Text
Notes for Metallic Bonding
METALLIC BONDING AND STRUCTURE
Delocalised electrons - electrons that are not associated with one specific atom and are free to move within the molecule structure
Metallic bond - the electrostatic attraction between a lattice of cataions and a sea of delocalised electrons.
In metals, state which electrons are the delocalised electrons present between positive ions in the lattice = valence electrons
Mg(s) has metallic bonding in the interaction between positive metal ions and delocalised valence electrons in a three-dimesional lattice structure. The metal itself is neutral and is made up of many, many atoms.
Identify the ways in which solid metals are similar to solid ionic and covalent network substances:
I. Lattice structures II. Non-directional bonding III. Electrostatic attractions between positive and negative species
Solid metals, ionic compounds and network covalent solids form three-dimensional lattices. In all three types of bonding there is an electrostatic attraction between positively and negatively charged species. Metallic – between cations and delocalised electrons, ionic – between cations and anions, covalent – between positive nuclei and shared electron pair.
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND APPLICATION OF METALS
Lustre (shiny appearance)
Delocalised electrons in a metal lattice interact with visible light. When visible light hits the surface of a metal, the electrons absorb some of that energy and vibrate. This vibration generates a second wave of light, which radiates from the surface.
Sonority (sound when struck)
When a metal surface is struck, the free electrons in the metallic lattice can move easily, propagating the incoming sound energy easily throughout the material.
Malleability (can be reshaped on compression) & Ductility (can be drawn out into a wire)
When stress is applied (for example, by bending, hitting with a hard object or pulling), layers within the lattice shift in response to that stress. As these layers shift, the cations in the lattice remain surrounded by delocalised valence electrons, meaning the metallic bonding also remains unaffected.
Electrical conductivity
The delocalised valence electrons can move throughout the metallic lattice. When a potential energy difference is applied to the metal, the delocalised electrons are repelled by the negative terminal and attracted to the positive terminal. This is why metals can conduct electricity in their solid state and why metals are used for electrical wires and cables.
Thermal conductivity
Thermal conductivity in metals is a result of the free electrons in the lattice.
STRENGTH OF THE METALLIC BOND
Strength of the metallic bond
The smaller the radius of the metal ion, the stronger the metallic bond. This is because of the shorter distance between the positive nucleus of the cation and the surrounding delocalised electrons. Dictionary
Charge of the metal ion
The higher the ionic charge, the stronger the metallic bond. This is because:
greater charge on the metal ion
greater number of delocalised valence electrons
The greater the ionic charge and the smaller the ionic radius, the stronger the metallic bond. The stronger the metallic bond, the higher the melting point.
TRANSITION METALS
As there are a large number of valence electrons from both the s and d orbitals, this results in a greater electron density within the metallic lattice. This increased electron density in turn increases the strength of the metallic bond.
Hardness
valence electrons (delocalised) increase attraction and increase metallic bond which results in greater hardness
Electrical Conductivity
Transition elements are electrically conductive. These metals form their metallic bonds through the delocalisation of electrons in unfilled d orbitals. The electrostatic attraction between metal ions in the lattice and delocalised electrons increases with an increasing number of electrons in d orbitals.
In comparison to s block metals, the melting point and electrical conductivity of transition metals are HIGHER and HIGHER
#academia#study#study tips#ib#student#study motivation#high school#studyblr#chaotic academia#studyspo#chemistry#notes#study notes#chem#stem#stemblr#school#college#metallic bond#organic chemistry#stem academia#stem student#stem studyblr
11 notes
·
View notes
Photo
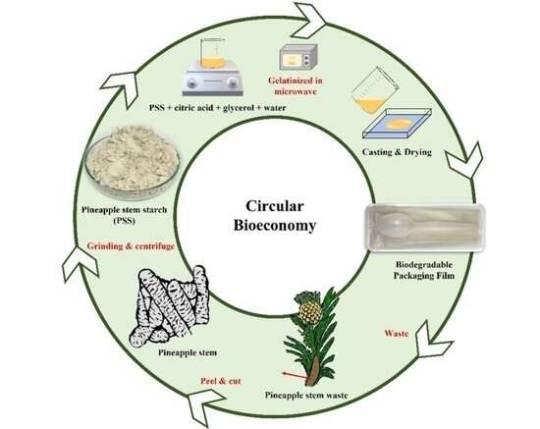
Harnessing the potential of pineapple stem starch film as a biodegradable packaging material
A group of researchers from universities in Thailand and Malaysia have collaborated to develop a unique film that is good for the environment and can decompose naturally. They made this film using leftover pineapple stems, which helps reduce the use of harmful plastic films. This new film has the potential to be used as packaging material, contributing to a more sustainable way of doing business and promoting a circular economy.
In the study published in Membranes, Associate Professor Taweechai Amornsakchai from Mahidol University, Thailand led his team of researchers to successfully developed a biodegradable starch film derived from pineapple stem waste, offering a sustainable alternative to non-biodegradable petroleum-based films commonly used for single-use applications that do not require high strength. The key ingredient utilized in this film is high amylose starch extracted from pineapple stems, which serves as the matrix for the material. To enhance its ductility and flexibility, glycerol and citric acid were incorporated as additives.
Maintaining a fixed glycerol content of 25%, the researchers experimented with varying levels of citric acid, ranging from 0% to 15% by weight of starch. This approach allowed for the preparation of films with a wide spectrum of mechanical properties, catering to diverse application requirements. As the concentration of citric acid increased, the resulting film exhibited a softer and weaker nature while demonstrating enhanced elongation at the point of fracture. The mechanical properties of the films spanned a broad range, from a strength of approximately 21.5 MPa with 2.9% elongation, to a strength of about 6.8 MPa with 35.7% elongation.
Read more.
#Materials Science#Science#Biomaterials#Packaging#Plants#Pineapples#Starch#Biodegradable#Materials Characterization
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
an immovable rock: the story of executive dysfunction
Sometimes it’s maddening, the frustration of not being able to get where you need to. Your mind races but it doesn’t get anywhere because your mind is a desperate beggar stuck in a maze and it’s been promised a lifetime’s worth of money if it figures out a way to a non-existent end; money is what makes one live in today’s world after all. Nothing gets done, not because it was the fault of anyone who bothered me. Nothing gets done, not because the weather did not know which mood to pick today. Nothing gets done, not because my table is wobbly and my laptop’s battery fluctuates. Nothing gets done, and I don’t know why. My hands are willing and able, although the joints play hard to get by stiffening my wrists alongside their immalleability. My tactile touches are ductile but the mind and spirit are unwilling. Money needs to come in, but I am unable to come out. Rather, my brain is unable to perform and put out. Therefore, I sit here, at this wooden desk, the make of my parents’ dying hopes and dreams, and type as I, Sisyphus, try to come to terms with the simple truth of an immovable rock.
~ mom-thoughts-speaketh
#my writing#poetry#poets on tumblr#poems on tumblr#original poem#poem#writers and poets#executive dysfunction#neurodivergent#brainrot#adhd brain#adhd things#the struggle is real#the pain never ends
18 notes
·
View notes
Text

Do you have any confusion about choosing the Steels and Materials?
Bridging the Gap Between Steel and Carbon Steel! … Remember, when it comes to steel, Virat Special Steels is your trusted guide!🔥
Steel:
Steel is an alloy primarily composed of iron, along with other elements such as carbon, silicon, and manganese. It contains carbon, silicon, and manganese in varying proportions.
Properties:
Steel has moderate strength. It is less hard compared to carbon steel. Steel is more ductile (can be shaped and bent). It is non-corrosive. Some types of steel (like nickel steel) are not magnetic. Steel can be alloyed with elements like chromium, nickel, and molybdenum to enhance specific properties.
Applications:
Used in construction, automobiles, airplane parts, and various industrial applications.
Global Production: The steel industry produces approximately 1.3 billion tons of steel annually.
Carbon Steel:
Carbon steel is a type of steel where carbon is the primary alloying element. It contains less than 2% carbon (without other noticeable alloying elements). As the carbon content increases, carbon steel becomes harder and stronger but less ductile and malleable.
Types:
- Mild Steel: Contains 0.05% to 0.29% carbon.
- Medium Carbon Steel: Contains 0.30% to 0.59% carbon.
- High Carbon Steel: Contains 0.60% to 0.99% carbon.
- Ultra Carbon Steel: Contains 1.00% to 2.00% carbon.
- Finish: Carbon steel usually has a lusterless finish.
In summary, steel is a broad category that includes carbon steel. Carbon steel, in turn, varies based on its carbon content and properties. It’s essential to choose the right type of steel for specific applications.
Virat Special Steels is one of the most reputable Tool Steel & Die Steel and Mold Steel Suppliers in India. Special steel is provided in all sizes and shapes (flat, round, and bars) depending on customer requirements. Based in #Gurgaon (Haryana) & #Ludhiana (Punjab) India.
Product List:
DIE STEELS ( HH 370 - 410 BHN ) DIN-1.2714 / AISI L6 )
HOT DIE STEELS (DIN 2343, 2344 / AISI H11, H13)
PLASTIC MOULD STEELS (DIN 2738, 2311 , AISI P 20 )
HIGH SPEED STEELS (DIN 3243 , 3343 / AISI M2 , M35)
HCHCr. (DIN 2379 , 2080 / AISI D2 , D3)
ALLOY STEELS, EN-SERIES ETC.
For more information visit
https://www.viratsteels.com/
Watch now: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c4h5KqyzVd0
Any further queries feel free to contact us :
Email: [email protected] or Call: +91 98140 21775
#ludhiana#india#viratsteels#gurgaon#viratspecialsteels#toolsteelsupplier#gurugram#pune#steel#iso9001#SteelTrades#MetalIndustry#DieSteels#ToolSteel#HighSpeedSteels#PlasticMouldSteels#hot work steel#cold work steel#HCHCr#DB6Steel#H13Steel#H11Steel#P20Steel
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
I dont want to work i especially dont want to work at this company why am i even interviewing i was reading someones review on glassdoor and they said in their interview they were asked "whats the reinforcement difference between ductile and non ductile frames" like girl i could not asnwer that i dont fucking KNOWWWWi dont remember!!!!! Do u think they will take who cares as an answer
#why should i have to study for an interview for a job i dont really even wanttttt#honestly best case scenario is i have an average interview and i dont get the job bc i dont want to embarrass myself but i also dont want#an offer bc then i would have to consider working there#sidney talks shit
3 notes
·
View notes
Note
What even is pipebomb actually? Bomb shaped pipe? Pipe shaped bomb? Bomb in a pipe? Sending bomb through a pipe?
Pipe bombFrom Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
For the professional wrestling term, see
Shoot (professional wrestling)
. For the website, see
Thepipebomb.com
.
A tripwire-triggered pipe bomb mock-up used to train US military service personnel
A pipe bomb is an improvised explosive device which uses a tightly sealed section of pipe filled with an explosive material. The containment provided by the pipe means that simple low explosives can be used to produce a relatively huge explosion due to the containment causing increased pressure, and the fragmentation of the pipe itself creates potentially lethal shrapnel.
Premature detonation is a hazard of attempting to construct any homemade bomb, and the materials and methods used with pipe bombs make unintentional detonation incidents common, usually resulting in serious injury or death to the assembler.
In many countries, the manufacture or possession of a pipe bomb is a serious crime, regardless of its intended use.
Contents
1Design
2Operation
3Modes of failure
4Minimum evacuation distances
5Uses
6See also
7References
5.1Notable incidents
Design[edit]
Different pipe bombs' appearances, from a bomb awareness report issued by the US Department of State
The bomb is usually a short section of steel water pipe containing the explosive mixture and closed at both ends with steel or brass caps. A fuse is inserted into the pipe with a lead running out through a hole in the side or capped end of the pipe. The fuse can be electric, with wires leading to a timer and battery, or can be a common fuse. All of the components are easily obtainable.
Generally, high explosives such as TNT are not used, because these and the detonators that they require are difficult for non-state users to obtain. Such explosives also do not require the containment design of a pipe bomb.
Instead, explosive mixtures that the builder can more readily obtain themselves are used, such as gunpowder, match heads, or chlorate mixtures. These can be easily ignited by friction, static electricity, and sparks generated when packing the material inside the tube or attaching the end caps, causing many injuries or deaths amongst builders.[1]
Sharp objects such as nails or broken glass are sometimes added to the outer shell or inside of the bomb to increase potential injury, damage, and death.
Operation[edit]
Pipe bombs concentrate pressure and release it suddenly, through the failure of the outer casing. Plastic materials can be used, but metals typically have a much higher bursting strength and so will produce more concussive force. For example, common schedule 40 1-inch (25 mm) wrought steel pipe has a typical working pressure of 1,010 psi (7.0 MPa), and bursting pressure of 8,090 psi (55.8 MPa),[2] though the pipe sealing method can significantly reduce the burst pressure.
The pipe can rupture in different ways, depending on the rate of pressure rise and the ductility of the casing material.
If the pressure rise is slow, the metal can deform until the walls become thin and a hole is formed, causing a loud report from the gas release, but no shrapnel.
A rapid rate of pressure rise will cause the metal to shatter into fragments, which are pushed outward in all directions by the expanding gases.
Modes of failure[edit]
Pipe bombs can fail to explode if the gas pressure buildup is too slow, resulting in bleed-out through the detonator ignition hole. Insufficiently tight threading can also bleed gas pressure through the threads faster than the chemical reaction pressure can rise.
They can also fail if the pipe is fully sealed and the chemical reaction triggered, but the total pressure buildup from the chemicals is insufficient to exceed the casing strength; such a bomb is a dud, but still potentially dangerous if handled, since an external shock could trigger rupture of the statically pressurized casing.
Minimum evacuation distances[edit]
If any type of bomb is suspected, typical recommendations are to keep all people at a minimum evacuation distance until authorized bomb disposal personnel arrive. For a pipe bomb, the US Department of Homeland Security recommends a minimum of 21 m (69 ft), and an outdoors distance of 366 m (1,201 ft).[3]
Uses[edit]
Pipe bombs are by nature improvised weapons and typically used by those without access to military devices such as grenades. They were successfully used in the Spanish Civil War (1936–1939). During World War II, members of the British Home Guard were trained to make and use them.[4]
In Northern Ireland, there have been hundreds of pipe bomb attacks since the mid-1990s (towards the end of the "Troubles"). Most of the attacks have been launched by loyalist paramilitaries, especially the Red Hand Defenders, Orange Volunteers and Ulster Defence Association.[5][6] However, they have also been used by Irish republican paramilitaries and by anti-drugs vigilante group Republican Action Against Drugs. They are also used extensively in the south of Ireland by feuding criminals, including drug dealers, mainly in the capital city of Dublin.
As well as users such as criminals, paramilitaries, and militias, they also have a long tradition of recreational use for amusement or mischief with no intention to cause injury to anyone, but due to the dangers of premature ignition and of shrapnel, pipe bombs are much more dangerous than alternatives such as dry ice bombs or potato cannons.
Notable incidents[
edit
]
This 1886 engraving was the most widely reproduced image of the
Haymarket riots
. It inaccurately shows Fielden speaking, the pipe bomb exploding, and the rioting beginning simultaneously.
[7]
On 4 May 1886, a pipe bomb was thrown during a rally at Haymarket Square in Chicago, Illinois, United States.[8] It reached a police line and exploded, killing policeman Mathias J. Degan.[8] The bomb was made from gas-pipe filled with dynamite and capped at both ends with wooden blocks.[8]
From August 1977 to November 1977 Allan Steen Kristensen planted several bombs across Copenhagen, Denmark injuring 5 but killing no one.
In 1985, Palestinian American anti-discrimination activist Alex Odeh was killed in California by a pipe-bomb. Activists from the Jewish Defense League are suspected of being the bombers.[9][10]
On December 16, 1989, Federal Judge Robert Vance was assassinated in his home in Mountain Brook, Alabama when he opened a package that contained a pipe bomb mailed by Walter Leroy Moody in Mountain Brook, Alabama.
On 27 July 1996, Eric Rudolph used a pipe bomb in the Centennial Olympic Park bombing during the 1996 Summer Olympics in Atlanta, Georgia, United States. It killed two people and injured 111.[11]
During the preparation of the Columbine High School Massacre, Eric Harris and Dylan Klebold had experimented with pipe bombs. During their testing and experimentation, Eric Harris had posted their results on his website. During the massacre, Harris and Klebold had used their pipe bombs as makeshift hand grenades, alongside various other bombs they had crudely manufactured.
On 11 December 2010 a suicide bomber detonated one out of six pipe bombs close to a major shopping district in Stockholm, Sweden, killing himself with no other casualties in what is known as the 2010 Stockholm bombings.[12]
In October 2018, pipe bombs without triggering devices[13] were sent to various liberal and political figures in the United States. Recipients included political activist and investor George Soros, former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton, former President Barack Obama, former CIA Director John Brennan, and former Attorney General Eric Holder.[14][15]
On 6 January 2021, a pipe bomb was found at the headquarters of the Republican National Committee, during the certification of President-elect Joe Biden. An unidentified object was also found at the headquarters of the Democratic National Committee, resulting in an evacuation.[16]
See also[edit]
Improvised explosive device
TM 31-210 Improvised Munitions Handbook
References[edit]
^ Dias, Gary A.; Dingeman, Robbie (2004). Honolulu CSI: An Introduction to Forensic Science and Criminal Investigation. Bess Press. p. 87. ISBN 978-1-57306-228-2.
^ Wrought Steel Pipe - Bursting Pressures. "The bursting pressures are based on Barlow's formula. The working pressures are based on factor 8. Dimensions according ASME/ANSI B36.10/19". www.engineeringtoolbox.com.
^ "Bomb Threat Stand-Off Distances" (PDF). The National Counterterrorism Center.
^ Introduction by Campbell McCutcheon (30 September 2012). Home Guard Manual 1941. Amberley Publishing Limited. p. 77. ISBN 978-1-4456-1103-7.
^ Wood, Ian.S (2006). Crimes of Loyalty: A History of the UDA. p. 248. ISBN 978-0-7486-2427-0.
^ Gassman, Michele. "Violence - Chronology of 'Pipe-Bomb' Attacks". Conflict Archive on the Internet. Retrieved 5 January 2021.
^ "Act II: Let Your Tragedy Be Enacted Here, Moment of Truth". The Dramas of Haymarket. Chicago Historical Society. 2000. Archived from the original on 15 March 2008. Retrieved 19 January 2008. The details are factually incorrect, because by all accounts Fielden ended his speech before the bomb was thrown, and because the riot did not begin until after the explosion. In [this] depiction, the speech, the explosion, and the riot all take place at once.
^ Jump up to:a b c Lawson, John Davison; Robert Lorenzo Howard (1919). American State Trials: A Collection of the Important and Interesting Criminal Trials which Have Taken Place in the United States from the Beginning of Our Government to the Present Day. Thomas Law Books. p. 64. a fuse with a cap is put into that hole.
^ Greg Krikorian, Evidence emerges in ‘85 Santa Ana slaying, Los Angeles Times, October 11, 2007, B-1.
^ Friedman, Robert I., The California Murder Case That Israel Is Sweeping Under the Rug : Justice: In 1985, Alex Odeh was killed by a pipe bomb in Orange County. The FBI has three suspects, but they are in Israel; extradition is unlikely, Los Angeles Times, May 13, 1990
^ "Rudolph reveals motives". CNN.com. 19 April 2005.
^ Sweden: Stockholm suicide bombings could have been 'catastrophic', London: The Telegraph, 12 December 2010
^ Bojorquez, Manuel (October 29, 2018). "Package bomb suspect Cesar Sayoc had list of 100 names in van, official says". CBS News. Archived from the original on February 7, 2019. Retrieved February 5, 2019.
^ "Investigation of Suspicious Packages". Federal Bureau of Investigation. Retrieved 26 October 2018.
^ "FBI Director Christopher Wray's Remarks Regarding Arrest of Cesar Sayoc in Suspicious Package Investigation". Federal Bureau of Investigation. Retrieved 26 October 2018.
^ Benner, Katie; Haberman, Maggie; Schmidt, Michael S. (6 January 2021). "An explosive device is found at the R.N.C., and the D.N.C. is evacuated". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 7 January 2021.
US5,386,758–Apparatus and method for disarming pipe bombs
Categories
:
Improvised explosive devices
Insurgency weapons
Navigation menu
Not logged in
Talk
Contributions
Create account
Log in
Article
Talk
Read
Edit
View history
Main page
Contents
Current events
Random article
About Wikipedia
Contact us
Donate
Contribute
Help
Learn to edit
Community portal
Recent changes
Upload file
Tools
What links here
Related changes
Special pages
Permanent link
Page information
Cite this page
Wikidata item
Print/export
Download as PDF
Printable version
In other projects
Wikimedia Commons
Languages
Deutsch
Español
Français
Bahasa Indonesia
Italiano
Português
Русский
Tiếng Việt
中文
15 more
Edit links
This page was last edited on 16 November 2022, at 10:47 (UTC).
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License 3.0; additional terms may apply. By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Wikipedia® is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a non-profit organization.
- 💛 Themis
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Classification of Pipes based on their Materials and Uses
Pipes are products of circular tubing used for transporting fluids. Pipes are built to withstand a certain pressure, which is determined by the temperature at which they will be used. Pipes can vary in many ways depending on factors like their size, schedule, material, pressure and temperature resistance, and so on. The industrial sector makes use of several pipe types for a variety of applications. Pipes are used extensively in a wide variety of industries, including the oil and gas industry, petrochemical as well as chemical industries, process industries, the power sector, the food and beverage industry, HVAC manufacturers, steel manufacturers, pipeline manufacturers, plumbing manufacturers, refineries, and many others. In today's contemporary industrial plants, piping is absolutely essential. Different criteria are used to determine the type of pipe to be used. A variety of pipes used extensively in manufacturing industries will be discussed further in this article.
Types of Pipes based on Material:
Most commonly, pipes are categorised according to the raw material from which they are made. Both plastic and metal pipes are often used, yet there are distinct differences between the two.
Metallic Pipes
Non-metallic Pipes
Metallic Pipes:
Metallic pipes refer to those that are fabricated from metal rather than other materials. They are classified as under:
● Pipes made up of ferrous materials
● Pipes made up of non-ferrous materials
- Pipes made up of ferrous materials:
These pipes are heavier and more durable than others. The primary element of these pipes is iron. Ferrous material pipes are typically constructed of
● Carbon steel pipes
● Stainless steel pipes
● Alloy steel pipes
● DSS pipes
● Cast Iron pipes
● Ductile Iron pipes, etc
This group of pipes can withstand higher pressures and temperatures. Jindal pipes for Oil, Gas and Water supply supplied by Tube Trading Co., used in industrial settings including refining, chemical and petrochemical processing, power generation, etc. are typically formed of ferrous elements.
- Pipes made up of Non-ferrous materials:
Pipes from this assortment are not primarily made of iron. The likes of brass, aluminium, copper, etc., are what they're often crafted from. Some typical examples of non-ferrous pipes are
● Aluminium and its alloy pipes.
● Copper and its alloy pipes.
● Nickel and its alloy pipes.
● Titanium and its alloy pipes.
● Zirconium and its alloy pipes.
Non-metallic Pipes:
Commonly employed in services where the temperature is not a factor, non-metallic pipes are becoming more and more common. Most of the non-metallic pipes are utilised in the water industry as well as drainage systems. If you are looking for the most distinguished supplier of Jindal spiral welded coated pipes in India, Tube Trading Co. is the most trustworthy supplier in Gujarat, India.
The most regularly used types of non-metal pipes are:
● PE/HDPE Pipes
● CPVC/PVC/UPVC/ Pipes
● PP pipes
● Reinforced thermoplastic pipes
● ABS Pipes
● Composite pipes
● Asbestos and Cement Pipes
● Vitrified clay pipes
Composite pipes', as well as reinforced plastic primary benefits, are their extreme resistance to corrosion and long lifespan. where metal pipes are often made to last up to 25 years. Reinforced plastic and composite pipes can survive for up to half a century with no problems. But the temperature is their biggest restriction. Metallic pipes can withstand the high temperatures that are required in some industrial processes. Stormwater, gravity service, the irrigation industry, and culverts are common applications for cement pipes made from reinforced concrete.
Pipes, classified on the basis of the industry:
- For Power Piping as well as Chemical Industries:
These pipes can withstand extreme heat and pressure without breaking down. The chemical, electricity, petrochemical, steel, oil, and gas industries all rely heavily on pipes constructed of ferrous materials. They are often developed in accordance with international standards such as ASME B31.3 and ASME B31.1. They are typically chosen for their high pressure, temperature, and corrosion resistance tolerance. Being an excellent supplier of industrial pipes and tubes, Tube Trading Co. can fulfil all of your Jindal spiral welded coated pipes requirements.
- For the Plumbing industry:
Plumbing pipes can be made from a variety of materials, including plastic (PVC), metal (Copper and PEX), plastic (ABS), cast iron (galvanised steel), or steel (cast iron). Their primary function is to transport water from one location to another.
- Pipes for the Pipeline industry:
Line pipes are what you'll typically hear people refer to when they talk about pipes utilised in the pipeline industry. These pipes are typically designed according to API 5L specifications. Pipes according to API 5L standards are available in a wide range of grades for transporting liquids such as oil, natural gas, and water. In addition to DSS, FRP, SS, GRE, SDSS, etc., there are a variety of other materials used for pipelines.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Beginner's Guide to Copper Nickel Alloy Pipes: Everything You Need to Know
Copper nickel alloy pipes are a vital component in various industries, known for their exceptional corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, and durability. Whether you are a beginner exploring plumbing solutions or a seasoned professional looking to delve deeper into materials, understanding copper nickel alloy pipe is essential. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through everything you need to know about these versatile pipes, from their composition to their applications and benefits.
Understanding Copper Nickel Alloy Pipes:
Copper nickel alloy pipes, also known as cupronickel pipes, are composed of copper and nickel, along with other trace elements such as iron and manganese. These alloys are categorized based on their nickel content, typically ranging. The varying compositions offer different properties suitable for specific applications.
Composition and Properties:
The composition of copper nickel alloy pipes plays a crucial role in determining their properties. Higher nickel content increases resistance to corrosion and erosion, while copper enhances thermal conductivity and malleability. These pipes exhibit excellent resistance to seawater, making them ideal for marine applications. Additionally, they offer good ductility, allowing for easy fabrication and installation.
Applications of Copper Nickel Alloy Pipes:
Copper nickel alloy pipes find extensive use across various industries due to their unique combination of properties. Some common applications include:
Marine: Used in shipbuilding, offshore platforms, and desalination plants due to their resistance to seawater corrosion.
HVAC: Utilized in heat exchangers and condensers for efficient heat transfer.
Petrochemical: Suitable for transporting corrosive fluids in refineries and chemical processing plants.
Plumbing: Widely used in plumbing systems for residential, commercial, and industrial purposes.
Power Generation: Employed in power plants for cooling systems and steam condensers.
Automotive: Used in automotive heat exchangers and brake lines for their thermal conductivity and durability.
Advantages of Copper Nickel Alloy Pipes:
Copper nickel alloy pipes offer several advantages over other materials, making them a preferred choice in many applications:
Corrosion Resistance: Resistant to corrosion in seawater, brackish water, and various chemical environments, prolonging the lifespan of piping systems.
Thermal Conductivity: Excellent heat transfer properties ensure efficient cooling and heating in HVAC systems and power generation applications.
Durability: Withstand high pressures and temperatures, reducing the risk of leaks and failures in critical installations.
Low Maintenance: Require minimal upkeep, resulting in cost savings over their lifespan.
Environmentally Friendly: Recyclable and non-toxic, contributing to sustainable practices in construction and manufacturing.
Copper Pipe Fittings - Enhancing Performance and Versatility:
In addition to copper nickel alloy pipes, the use of appropriate fittings is essential to ensure optimal performance and durability. Copper pipe fittings, such as elbows, tees, couplings, and flanges, facilitate seamless connections and transitions in plumbing and piping systems. These fittings are available in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different requirements, providing flexibility in design and installation.
Copper Nickel Tubes - A Closer Look at Versatile Tubing Solutions:
Copper nickel tubes, like pipes, offer excellent corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity. They are commonly used in heat exchangers, condensers, and hydraulic systems where efficient heat transfer and durability are paramount. Available in seamless and welded constructions, copper nickel tubes are suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications across diverse industries.
Conclusion: Copper nickel alloy pipes are indispensable components in numerous industries, offering a perfect balance of durability, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. Understanding their composition, properties, and applications is essential for maximizing their potential in various engineering and construction projects. By harnessing the versatility and reliability of copper nickel alloy pipes, we can create sustainable and resilient infrastructure to meet the challenges of tomorrow.

0 notes
Text
Versatile Engineering Construction Firm
Our comprehensive general engineering contractor services cover everything from site development to project management, ensuring seamless execution and superior outcomes. Contact us now!
0 notes
Text
Rubber Compounds Typical Properties Of Elastomers
The versatile material adapts properly to sealing surfaces, compensates irregularities and seals at very low stresses. Instant adhesives treatment very quickly when confined between surfaces, triggered by the humidity on the surfaces. Cyanoacrylates are chosen for bonding small elements to realize extraordinarily quick fixturing. They are clear and easy to apply and be part of all kinds of dissimilar materials. From among the varied kinds of merchandise, the most typical merchandise are listed under.
ptfe gaskets
It offers many desirable features, which makes the fabric a popular selection for use in gasket purposes. PTFE gaskets present superb purity and resistance in a variety of industries from meals preparation, aerospace, automotive and construction. It is probably considered one of the most valuable engineering materials out there due to its versatility. As a semi-crystalline plastic that doesn’t take up UV light, it also reveals wonderful resistance to daylight.
PTFE presents good weathering resistance and the fabric can be unable to absorb any UV gentle. It is resistant to wreck from a variety of common acids, bases in addition to solvents. PTFE also includes a broad functioning temperature vary from -200°C to +260°C. These unique options mix to allow our PTFE gaskets to provide constant sealing properties across virtually any setting. Uniflon 58 – Specifically designed for use in low bolt loaded irregular flanges.
Although the fibres have a multi-directional orientation, tensile energy is significantly greater along the longitudinal axis. TEADIT® 24 BB is suitable to chop or punch gaskets from and has a full width adhesive tape on one facet, accredited for use with foodstuffs (also out there without adhesive tape). Advantages - all physical properties of 100 percent pure PTFE - gaskets can be economically reduce from the tape - intricate shapes can be cut or... A gasket sheet manufactured by increasing 100% virgin PTFE using a proprietary course of that produces a uniform and highly fibrillated microstructure with equal tensile power in all directions.
(2) Reduced inner diameter optimized for glass lined metal functions.(3) Reduced inner diameter for ductile iron pipe and different specialty applications. Compared to other gasketing materials, GORE Universal Pipe Gasket (Style 800) is more gas-tight, providing larger leak resistance at greater temperatures. Backed by specialists with decades of expertise, Sealmax continues to grow as a dependable braided and graphite packings manufacturer along with its wide selection of gaskets by catering to reputed clients all through Asia. Machined Square Section Type – This design of manufacture provides continuity with pipeline bore for smooth move and is beneficial the place flange sealing width is restricted or where the insert thickness is greater than 3mm. Synthetic Filled PTFE – A artificial polymer could be added to PTFE that can be lower in friction to all of the above fillers. It is non-abrasive so is beneficial on applications the place there are soft material mating faces and also fits dry working applications particularly nicely.
Lathed envelopes can be produced with an inside diameter 2 to 4 mm thicker to provide greater diffusion sealing. Products from the KLINGER® top-chem range are tailor-made to supply the characteristics required by their target industries. Amongst others, this consists of tightness even at low surface pressures, high resistance towards robust acids or strong alkaline solutions as well as good properties at medium and low temperatures. The Rubber Company supply a broad range of gasket and sealing products to suit any utility and setting. Our friendly, informative staff are readily available to ensure that you all the time get the best product to go well with your distinctive requirements. Moreover, you've the likelihood to obtain the corresponding product knowledge sheet.
1 note
·
View note
Text
API Globe Valve Manufacturer
SVR Global is the leading API globe valve manufacturer in USA and supplies top notch quality valves in various oil and gas industries, chemical industries in Chicago, New York and Houston. API stands for American Petroleum Institute. API Globe valves are operated to control the flow of fluids in the system. They are usually used for throttling the flow apart from controlling as well. These valves have a stem which moves up and down to control the flow of fluids & a disc and seat that is attached to the body of the valve. Globe valves are the best among other valves for controlling and regulating the flow of fluids. These valves are bi-directional which means they can move in either direction inside the valve. The fluid flow in globe valves is highest when its disc is raised. They are operated manually and automatically.
Parts:
•Body: The body of an API globe valve is a shell that houses all the internal parts of the valve.
•Bonnet: The bonnet is a cover that sits on top of the valve body and provides access to the internal parts of the valve. It is usually bolted to the valve body and can be removed for maintenance or repair.
•Disc: The disc, also known as the plug or the disk, is a movable component that regulates the flow of fluid through the valve. It can be moved up or down by the valve stem to open or close the valve.
•Stem: The stem is a threaded rod that connects the valve disc to the valve handwheel or actuator. It is used to control the position of the valve disc and regulate the flow of fluid.
•Seat: The seat is a sealing surface that is in contact with the valve disc to provide a tight shut-off. It is usually made of a resilient material such as rubber, , or metal.
•Packing: The packing is a set of seals that prevent leakage of fluid through the valve stem. It is typically made of graphite or other flexible materials.
•Gland: The gland is a component that compresses the packing material around the valve stem to provide a tight seal. It is usually made of metal.
Industry:
•Electric power industries
•Oil and gas industries
•Petroleum industries
•water and wastewater industries
•Marine Industries
•Construction Industries
•Mining industries
Applications:
•Oil and gas industry - for controlling the flow of fluids, gases, and steam.
•Chemical industry - for resisting corrosive chemicals and high-pressure environments.
•Power plants - for controlling the flow of steam and water in high-pressure and high-temperature.
•Water treatment plants - for regulating water flow and pressure.
•Petrochemical industry - for regulating the flow of petrochemicals and gases.
•Marine industry - for regulating the flow of seawater and fluids.
•Mining industry - for regulating the flow of water and slurries in mining operations.
•Fire protection systems - for controlling the flow of water or other fire suppression agents in case of a fire.
•Aerospace industry - for regulating the flow of fluids, gases, and propellants in aerospace applications.
•Biotechnology industry - for regulating the flow of gases and liquids in bioreactors and fermentation systems.
•Pulp and paper industry - for regulating the flow of chemicals and fluids in pulp and paper production processes.
•Wastewater treatment plants - for regulating the flow and pressure of wastewater and sludge in treatment processes.
Advantages
•Excellent throttling capabilities
•Simple to use and clean the valve
•Can also work as a stop-check valve
•Quick and a safe shutdown
•Durable throughout its life span
•It has a Non-rotating stem
•The seats of these valves are very easy to resurface.
•Safe to use and dependable as well
SVR Global, the API globe valve manufacturer in USA provides top-notch quality valves which are not only durable and strong but also comes at pocket-friendly prices.
Description:
Body material: Cast Iron, Cast steel [A216 WCB, WCC, LCB, LCC, WC6, WC9), Ductile Iron, Stainless Steel [SS316, SS304, SS316L, SS904L, CF8, CF8M, F304, F316, F31L, F51, F3, F55, F91]
Class: 150 – 2500; PN10 – PN 450
Size: DN 10 – DN 1200
Ends: Butt weld, Flanged, threaded, socket weld
Operations: Hand-wheel operated, Pneumatic actuated, Electric actuated, Gear operated
Visit our website for more information- https://svrglobal.net/products/api-globe-valve/
0 notes
Text

Periodic Table Championship:
Round 1, Day 1, Nickel vs. Actinium
The fourth match of our periodic table championship is element 28, nickel, versus element 89, actinium. Let’s meet our challengers:
Nickel is a hard, ductile, transition metal that crystalizes in the face-centered cubic crystal structure. The element is one of four ferromagnetic elements at room temperature and is primarily used in the production of stainless steels, followed by nickel- and copper-based alloys. The name of this element comes from the name of a sprite from German mythology, as copper-nickel ores were difficult to refine into copper.
Actinium is a soft, radioactive actinide element that crystalizes in the face-centered cubic crystal structure. The element is one of the first four non-primoridal radioactive elements isolated, however, it is very difficult to separate from lanthanum and thus has no practical commercial applications. The name of this element comes from the Greek word meaning ray or beam, as actinium's radioactivity gives it a pale blue glow.
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
What are the Uses of Aluminium Coil? Let’s Explore Their Endless Applications
Aluminium is an exceptional metal known for its low density and lightweight properties. Aluminium coils exhibit various metal attributes, including excellent ductility, rust resistance, and corrosion resistance compared to other metals. These versatile coils find numerous applications both in industrial settings and daily life. While many may be aware of the versatility of aluminium coils, let’s delve into their specific use cases.
Versatile Aluminium Coil Characteristics
Non-Corrosive -Aluminium boasts exceptional corrosion resistance, even in harsh industrial environments. Its natural oxide layer protects against many corrosive substances, ensuring durability
Machinability and Casting: -Aluminium’s lower melting point than steel makes it more malleable and easier to cast into various shapes and moulds, streamlining production processes and reducing costs
Lightweight yet Durable: — Aluminium is lightweight yet robust with its low density. It’s a preferred choice in aerospace construction. Additionally, its recyclability contributes to sustainability
Non-Magnetic and Non-Sparking- Aluminium is non-magnetic due to its crystalline structure and quickly forms an oxide layer upon scratching, preventing sparking.
Excellent Thermal and Electrical Conductivity — Free electrons in aluminium’s structure make it an effective electrical and thermal conductor, ensuring efficient heat dissipation
Soft and Ductile: — Aluminium’s malleability and ductility allow for easy shaping, enabling engineers to create innovative designs, like micro channel coils, for improved heat transfer
Non-Toxic- Aluminium poses no harm to human health upon exposure
Malleable and Ductile: — Aluminium’s high elasticity allows for wire production

Aluminium Coil Specifications
Dimensions:-Aluminium coils come in various sizes, with inner diameters typically at 508 mm, 406 mm, or 610 mm. The recoiler machine’s capacity determines the outer diameter, and the thickness varies from 0.2 to 8mm, with most coils falling between 0.2mm and 2mm
Weight Calculation: The weight of an aluminium coil can be estimated using the <b>formula: Weight = (Coil Diameter/2 * π — Inner Diameter/2 * π)* Coil Width*Density of Aluminium.
Considerations When Choosing Aluminium Coils
Supplier History Select suppliers with a proven track record and an established online presence for reliability and credibility
Machining Compatibility : Ensure that the chosen aluminium coil is compatible with machining processes and welding if required.
Price vs. Value : Balance cost and value by considering the intended use and grade of aluminium
Formability : Evaluate the formability of the aluminium coil, considering the desired metal-forming processes
Supplier Reliability :Choose suppliers with ample stock to avoid interruptions in supply.
End-Use Applications : Align the coil grade with the specific requirements of the intended applications.
Price : Seek competitive pricing that reflects the material’s quality and value without compromising essential characteristics.
Aluminium coils offer many applications across industries due to their remarkable properties and adaptability, making them a valuable material choice
Applications of Aluminium Coil
Building and Construction
Aluminium coil is a versatile material widely used in many building and construction applications. Its lightweight yet robust properties make it an ideal choice for various purposes, including roofing materials, window frames, facade panels and more. Its outstanding durability ensures suitability for indoor and outdoor projects, with resistance to adverse weather conditions such as sunlight, rain, snow and high temperatures, guaranteeing longevity and preventing rust or wear concerns
Electrical and Electronics
They are used in the electrical and electronics sector. It’s malleable nature, lightweight design and resistance to corrosion make it an excellent choice for various purposes, including household appliances, electronic components, switchgear housing, motor insulation and transformers. Its exceptional heat conductivity contributes to efficient cooling systems, while its adoption in consumer electronics, like mobile devices and televisions, allows for more compact and streamlined designs. The aluminium coil protects against external electromagnetic interference, enhancing its usability in this field
Consumer Goods
Aluminium coils are pivotal in producing everyday consumer items, including packaging materials, kitchen tools, and playthings. The inherent corrosion resistance properties of aluminium render it the preferred option for packaging perishable foods. Manufacturers harness aluminium coils to fabricate containers, bottles and foil packaging, capitalising on its inherent shaping flexibility for crafting household items and kitchen utensils.
Industrial Utilisation
Aluminium coils find vast applications in industry, functioning as sheet metal for diverse industrial apparatus such as air conditioning and ventilation systems, containers and storage tanks. Their malleability makes them particularly suitable for shaping intricate components, obviating the need for welding or joining processes.
Transportation
These coils have gained a reputation in transportation because of their lightweight characteristics and corrosion resistance. These attributes render them highly suitable for the fabrication of vehicles, augmenting structural integrity with minimal weight increment. They also effectively mitigate noise levels and provide protection against environmental factors, encompassing rain, snow, wind and debris. These coils are frequently used in constructing trailer body liners due to their durability and adaptability, rendering them the material of choice for transportation-related purposes
Different Uses and Applications of Aluminium Foil by Marudhar Industries
Marudhar Industries offers a diverse array of applications for aluminium foil. Their versatile products are applied in various industries, such as food packaging, pharmaceuticals, insulation, etc. Aluminium foil from Marudhar Industries is a dependable solution for preserving food freshness, ensuring pharmaceutical product integrity and providing efficient insulation.
Our range of foil products caters to a broad spectrum of needs, demonstrating the adaptability and utility of aluminium foil in different sectors. Now You Much About What are the Uses of Aluminium Coil? Let’s Explore Their Endless Applications
0 notes
Text

Polymeric Selections
Polymeric Self adhesive Vinyl selections are requested by higher requirement customer scope who are looking for long term use both indoor and outdoor so needs the materials to be with superior whether resistance capability, or better tension of materials so as to apply on non flat surfaces such as vehicles, rough walls, containers…
Another advantage of Polymeric Self adhesive vinyl is the excellent low shrinkage feature, so even after times, the graphics will stay as originally presented. To generally conclude the characteristic of polymeric self adhesive vinyl:
*3-5years durability
*Adopting polymer PVC film with good ductility
*Dimensional stability
*Adopting removable adhesive technology to remove images without residual adhesive
*Good visual performance
*Obvious matte surface features
*Suitable for a wide range of surface applications
0 notes