#novel structure
Text
Alternative Story Structures/Patterns (a.k.a how to avoid that damn triangle)
Disclaimer: these are all taken from Jane Alison's Meander, Spiral, Explode under the idea that we should draw more from patterns in nature when structuring works of fiction. Alison is a white woman, and a lot of non-western storytelling (especially utilizing different structures other than the triangle/wave) was pioneered by Authors of Color. I highly recommend you also research types of non-western nonlinear storytelling that Authors of Color have been utilizing and pioneering way before western storytellers even began to think about them. Here's a great article, and here's another one to begin your research there!
I'm gonna start each section with a quote from Meander, Spiral, Explode that I think explains them best, and then extrapolate where I can from there!
Waves
I've already discussed this one! If you wanna know my thoughts and feelings about the wave (a.k.a Evil Triangle That Might Have Some Uses, Maybe) you can check out this post here!
Wavelets
"Once I translated the dramatic arc to a wave, I began to think that energy in narrative might also flow in smaller waves, wavelets. Dispersed patterning, a sense of ripple or oscillation, little ups and downs, might be more true to human experience than a single crashing wave: I'm more likely to feel some tension, a small discovery, a tiny change, a relapse. The same epiphanies every week..."
I love the idea of this, and her comparison to the human experience. I feel like we sort of tried to accomplish this by adding various peaks to the original triangle, but sometimes a narrative can have multiple waves. She talks a lot about how this can show up as patterning in stories as well, moving back and forth between two different energies that could be important to a character, back and forth between motivations. I don't know if that makes any sense, wavelets aren't really my style, but I know they'll resonate with someone, because what are we doing if not trying to connect to the human experience?
Meanders
"A meander begins at one point and moves towards a final one, but with digressive loops. Italo Calvino says that "digression is a strategy for putting off the ending, a multiplying of time within the work, a perpetual evasion or flight. Flight from what? From death of course!" The Meander river in Turkey gave us the word, and speaking of how an actual river flows, Peter Stevens (in Patterns in Nature) says it "winds and turns in a quiet but seemingly desperate manner to avoid the straight schuss to the bottom"... In either case, there's deliberate slowness, a delight in curving this way or that, luxuriating in diversions, carving slow labyrinths of time."
OHHHHH THE MEANDERING NARRATIVE. I do enjoy this one, it isn't my favorite, but it is very very good. I specifically love the part she mentions about the narrative being afraid to reach its end. Sometimes characters meander, they want to experience the slowness, to stop and enjoy the things that are going on around them before moving forward with the plot. If you learn how to use the meander to your advantage, people who have a tendency to under-write could seriously be helped out by trying to do this. Also, sometimes people's minds just wander. Why should a narrative not wander too? A river will always end up spilling out somewhere, after all.
Spirals
"A spiraling narrative could be a helix winding downward– into a character's soul, or deep into the past– or it might wind upward, around and around to a future. Near repetitions, but moving onward. What gives a spiraling narrative a good sense of ending? Good question, for spirals could go on forever."
and also
"I wonder if first-person retrospective narratives– especially obsessive ones– might naturally follow a vortex."
Can you tell which quote gave me my epiphany about Verity and To Make a Fool of Death? Maybe it's mixed in with the radial narrative (right below this!!) but a spiraling narrative is truly a beautiful thing. This one and the radial one are both truly very deeply character focused, which makes me happy. The idea of telling a story based around a character, or just always coming back to the central of the character, is deeply fascinating. At another point in this chapter, she compares the spiral narrative to like the spiraling of a panic attack: you start thinking, and then you think more, and the problem becomes bigger, and you just keep going and then you cannot stop. Whether your spiraling narrative is fast, slow, or somewhere in between (not even gonna go off on a tangent about combining some of the patterns like a meandering spiral), it wanders around but remains true to the central core of what STARTED the panic attack, and will always have come from that true center.
Radials or Explosions
"Unlike in a spiral, the story itself– the incidents we see dramatized– barely moves forward in time. Instead, a reader might have a sense of being drawn again and again to a hot core– or, conversely, of trying to get away from that core. You might already know the end at the start and get many fractured views of things avoiding that moment. You might feel a sense of violent scatteration from a central point. Radials can be centrifugal or centripetal, but linear they are not."
This one might just be my favorite. Her example for it is truly perfect, too. She uses Gabriel García Márquez's Chronicle of a Death Foretold to talk about the point of this one. The entire story revolves around the death of this one man, we know he's going to die from the beginning of the story, and everyone else knows it too. We get the reactions of people to the idea of his death, the effect his death has on others, the WHY of his murder, and so on and so forth. The entire story centers around the hot core of the death of the main character, and that is BEAUTIFUL. I don't know what else to say about this kind of narrative outside of that example, because it does exactly what the radial/explosive narrative requires of it. Vignettes that all center around a big, dramatic point. That kind of thing. I love it, I can't get enough.
Networks or Cells
"So, again, any complex narrative will be a little spatial: certainly the spiraling or radial ones we looked at are. I think the idea of spatiality becomes most clear in cellular texts made discrete parts that gain power through patterns of images or ideas rather than sequential incidents." [section removed where she's talking about three examples provided to prove her point] "In all three, no linear chronology makes the parts cohere; instead, you draw the lines."
and also
"Translating to natural patters, I think of Peter Stevens's words about honeycombs or foam: 'chunks of space, miniature rooms, each one different from its neighbors and yet perfectly interlocked with those neighbors'."
I feel like these really speak for themselves. Think like... a short story collection, right, where all of the stories are seemingly unrelated, but you're able to connect the dots in your own mind and realize how these narratives are actually entwined in some truly beautiful ways? This method places a lot of trust on the reader, and I think that's important. As long as you have readers who have an ounce of critical thinking skills, of course. Stories like this are particularly interesting, especially when you as a writer have to decide how to subtly connect them all, or how MUCH you even want them to be connected.
Fractals
"The most fractal works– meaning fractals of fractals– were stream-of-consciousness narratives, although it's not clear whether that style reveals depths of consciousness or the writer's imagination. But fractals forming the shape of a whole narrative are what interest me: Texts that start with a "seed" or blueprint that spawns several more."
and also, in reference to Caryl Phillips' Crossing the River, an example of a Fractal Narrative:
"Instead the book is polyphonic, taking the points of view of four characters and delivering them in different styles: letters, diary entries, mixtures of third person and first. Yet the stories all grow from a single seed..."
I cut off the last one, but to give some context: Phillips' Crossing the River is the point of view of four characters across time periods that are stories that are inherently related to each other, in that they all stem from the same fractured point, but the linear plot lines do not connect. That's why it's so interesting. It kind of reminds me of the butterfly effect, right, but in a narrative sense. One action that someone takes will fracture, splitting across the story and creating so many smaller, new stories that are just as integral and wouldn't have happened without that first fracture. Will it all come together and will the fracture heal and reconnect at the end? Idk, maybe, it can. It's more of an exercise in seeing what happens based off of one simple event.
Additionally...
She has an entire chapter at the end called "Tsunami?" where she talks about David Mitchell's Cloud Atlas, which is like... a wave, right, a symmetrical wave, but SO MUCH MORE THAN THAT. Remember in "networks or cells" where I was talking about stories that don't seem to be connected but then there's a beautiful through line that somehow magically connects them all? And then in the wave post, when I talk about symmetry and traveling up the wave and down the wave so that the end reflects the beginning again? Cloud Atlas does all of that and more. I couldn't recommend this book enough. It's impossible to explain. It's perfectly written. I honestly don't even really consider it one of my favorite books, but I know that it has FEW rivals for how actually good it is. And, again, PLEASE DO NOT WATCH THE MOVIE.
If anyone wants extrapolation on any of these specifically, I'd be happy to talk about them in their own individual posts, if you've got something specific you want to know more about!! I mean fuck, I might write more about them later on just because I want to and I have feelings. All I really did here was just kinda explain them. And, once again, I encourage you to seek the perspectives of Authors of Color for this one as well. Countries that aren't North American/European have been doing this way longer than us, and those formats deserve some fucking respect.
I also of course have a few people that have asked to be tagged in my posts like this, and if you'd like to add yourself to this list, please let me know! I'll be posting a bunch of these as I go through grad school, so there's a lot to learn! @approximately20eggs @faeriegutz @moonscribbler @marigoldispeculiar
#writeblr#creative writing#writers#writing life#writing#writing reference#story structure#writing advice#fiction writing#writers of tumblr#novel writing#writing community#writing concept#grad school#studying#novel structure#about the author#my writing#my wips#long post
574 notes
·
View notes
Text

#writing#writers#writers on tumblr#writing community#writerscommunity#writer things#writing tips#novel writing#writerslife#writers and readers#novel structure#novel outline#story outline
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
Creating a book map
https://plottr.com/features/
As a determined pantser writer, I resist the outline and prefer to thrash out a mini version of my opus in the format of the 3DayNovelContest. Then, once I get it all down, I go back and create a structure around the blathering I’ve just completed. It takes a long time, but eventually I get everything laid out.
With my latest book, Spit and Polish, I found I was…
View On WordPress
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Character Development and Novel Structures are Creepy Besties. Here's why.
Character Development and Novel Structures are Creepy Besties. Here’s why.
I am a big fan of boiling things down to simple components and not spending a ton of time on things blathering on, so let’s get to it, okay?
Novel structure and character development are related.
Not just that, they are creepy best friends. You know the kind. They do EVERYTHING together, drink the same soy-caramel latte, have the same crushes on Bowen Yang, borrow each other’s clothes.
In your…

View On WordPress
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
New video dat!
We're beginning a writing tips series on How to Structure your novel.
#writer#bookworm#books#author#bookstagram#reading#bookdragon#amreading#writing#amwriting#writingtips#writingaid#writingadvice#story structure#novel structure#Youtube
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Top Five Tips for Structuring a Novel
The Top Five Tips for Structuring a Novel
Structuring a novel can be a daunting task, but it’s an essential part of the writing process. A well-structured novel not only keeps your readers engaged, but it also helps you to effectively communicate your story and ideas. Here are the top five tips for structuring a novel:
Begin with an outline.
An outline is a great way to organize your thoughts and plot points before you start writing.…

View On WordPress
#Amwriting#antagonist#Author#beginning#chapter breaks#end#Fiction#Horror Fiction#Indie Publishing#middle#novel structure#outline#protagonist#subplots#Writing
0 notes
Text
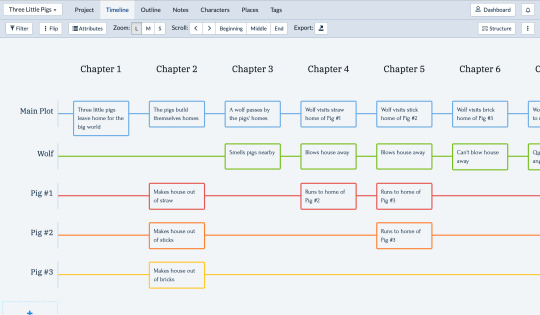
Scarlet Hollow decision tree
People occasionally ask to see a decision tree for Scarlet Hollow, so a while back I put one together for episodes 1-4! It’s not comprehensive, as most scenes at this point have at least some variation due to any number of tracked variables, but it accounts for most of the really major deviations.
For those who don’t want spoilers but would like to hear about how we kinda structure the game: I like to talk about it as more of a braid than a tree, which is not a new concept or anything, but I feel like it helps other narrative designers understand how to limit the absolute vastness that you can get with branching structures. The narrative branches off at decision nodes, but instead of continuing down significantly different routes, it comes back together at key moments. So there’s a single narrative throughline to the game-- events unfold in the town and you witness them in some capacity, but your perspective on them, who you’re with, the options available to you, all these are impacted by other choices you’ve made along the way, including the character traits you chose at the start of the game.
It’s not necessarily easier than doing routes, since it means Tony and I have to keep track of a ridiculous number of little variations including one-off dialogue choices players have made AND steering players to the important narrative moments can be tricky, but I think it makes for an interesting player experience! People get so excited when, say, a line at the end of Episode 4 calls back to something they said when they first met Tabitha at the beginning of Episode 1.
ANYWAY, HUGE SPOILERS UNDER THE CUT, do not proceed if you don’t want to know about basically everything that’s currently in the game!

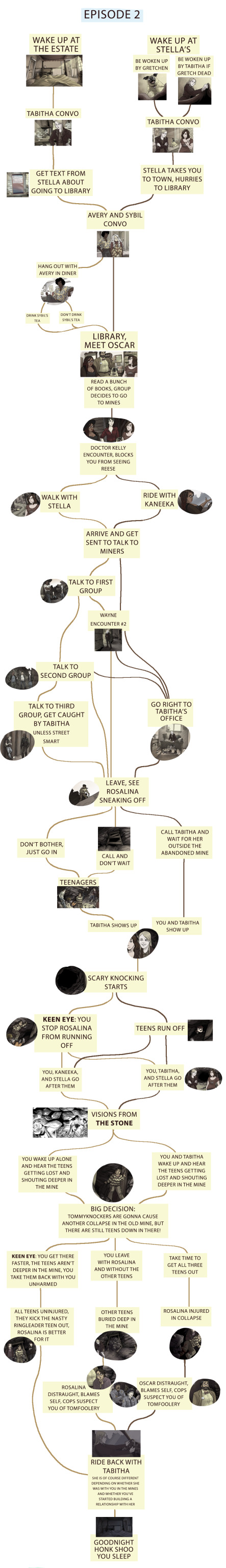
Things start to get a little hard to read from here on out....
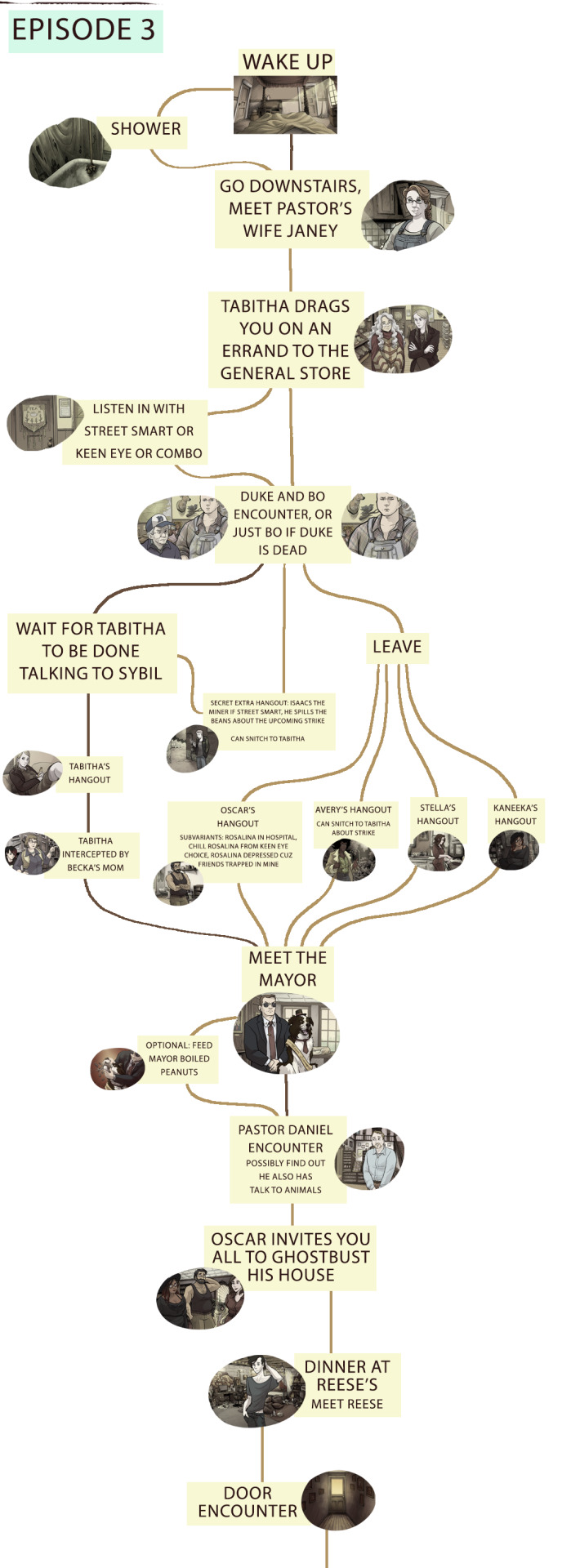
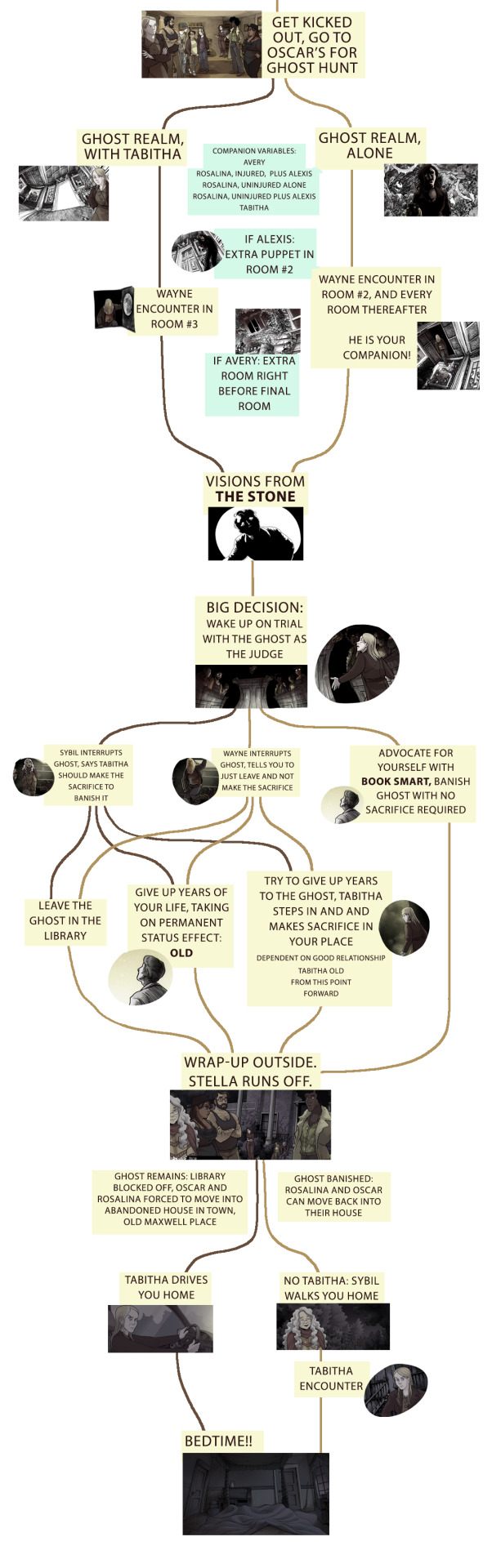
Episode four had to be broken into four images and looks like spaghetti
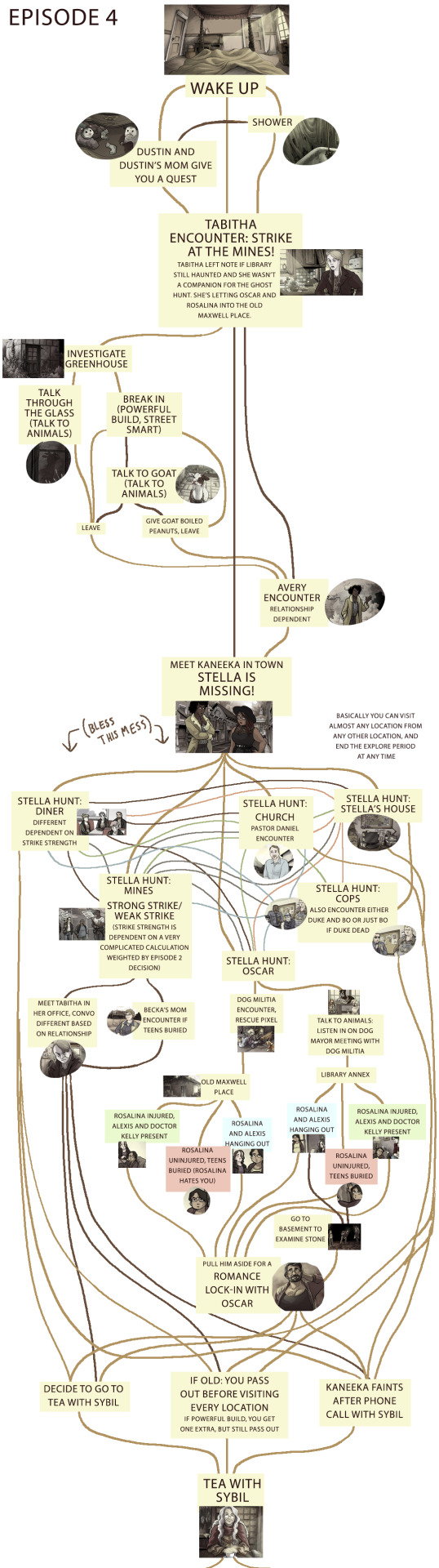
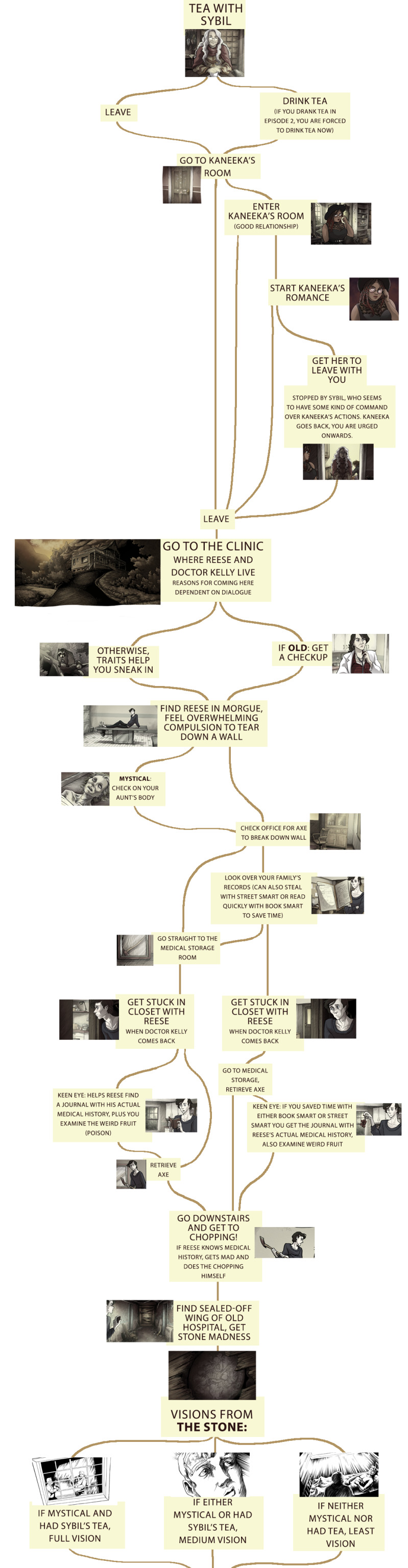
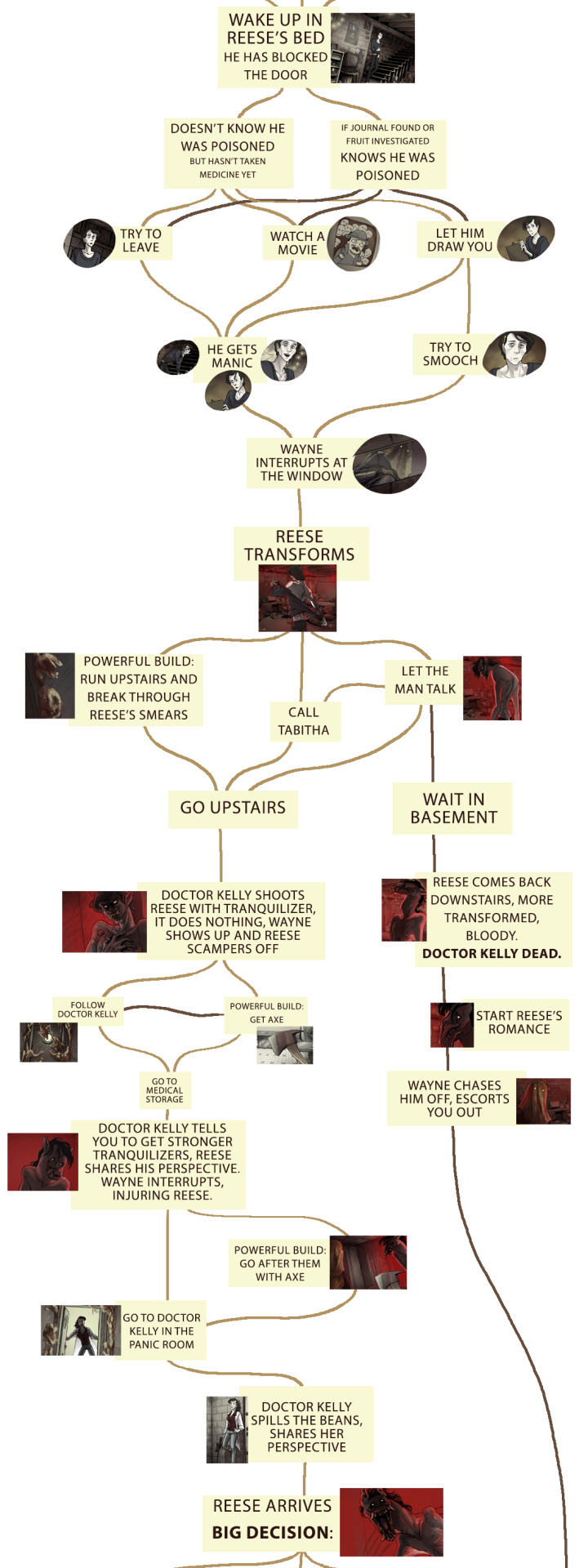
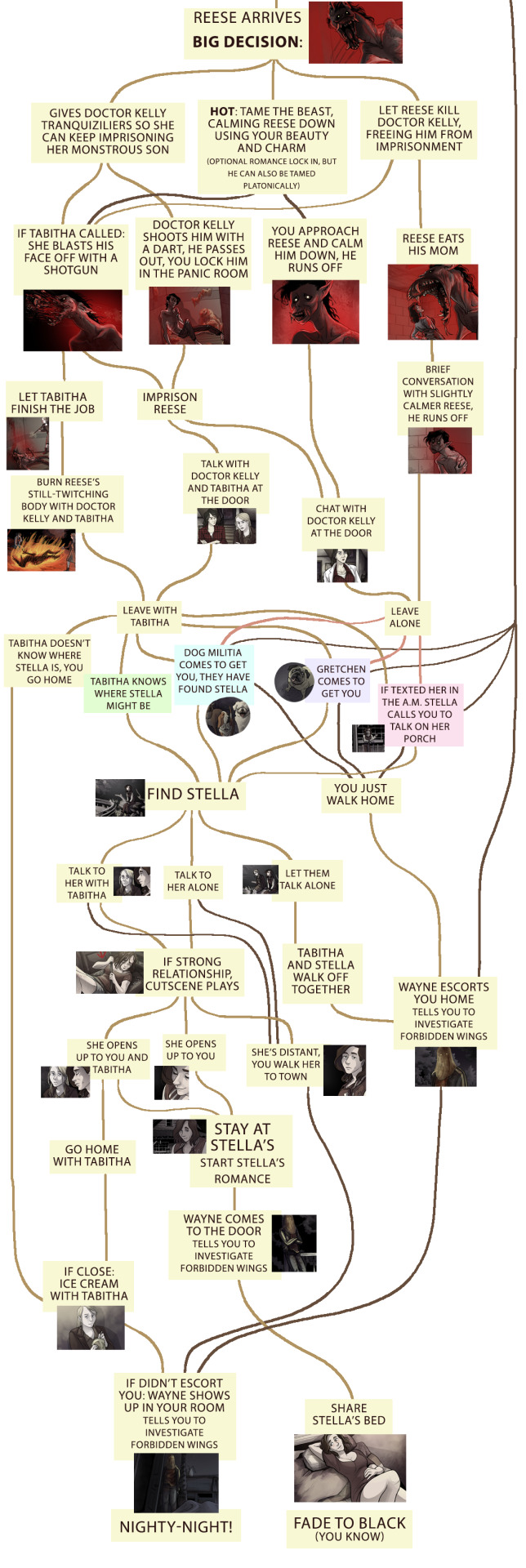
I’ll make another one of these for Episode 5 after it comes out sometime next year! (I know that’s a bit of a wait but it’ll be worth it >:D)
#scarlet hollow#spoilers#visual novel decision tree#narrative structure#video game narrative#we don't use trees like this while we're in development#we tend to just remember all this stuff#or reference the game files if we need calrification!#i made this as a resource for people who don't necessarily read the discord religiously#and wanna know how to get certain outcomes#and to see if a map could be drawn without being too impossible to read#getting there with the episode four stuff.......
594 notes
·
View notes
Text
529 notes
·
View notes
Text
you know now that i’ve finished gomens s2 i could probably write an essay on my mixed feelings. what about when a work is - especially so in some parts - very fucking good. thematically interesting and consistent, characterisation that is so painfully human and told in a fascinating manner. but due to a lack of conclusion - inherent because of the format (tv series) - it feels an inherently different sort of narrative to the original. i do not think good omens season two is bad - not at all, but what i do think is it is now a very fundamentally different type of story than that of the book. not because the events of the show don’t happen in the book but because the style of storytelling is altogether different. it’s inherently going to be the case when one of the original creators has sadly passed on, and it doesn’t necessarily make it bad - however it does make it not what personally made me love the book of good omens in the first place. maybe it’s because i came in with certain expectations given that i have read a lot of sir terry pratchett’s other work and basically none of neil gaiman’s, but it’s just a different format of story. like the difference between an epic poem and a serialised story.
#good omens#gomens 2#gomens spoilers#this isn’t saying it is bad#i enjoyed it and i think the ending makes sense#but that’s not why i love the novel#this isn’t a bad thing adaptations are allowed to differ from source material#but it means my personal feelings are weird and conflicted and mixed#great performance from david and michael#a bit weird pacing and structure at times#the ending is the most solid part and where it finds it’s feet#but it is just a different type of story that does actually span over seasons#as opposed to the original#i think in future i’m gonna view them as two separate divergent works#good omens and good omens legends
343 notes
·
View notes
Text
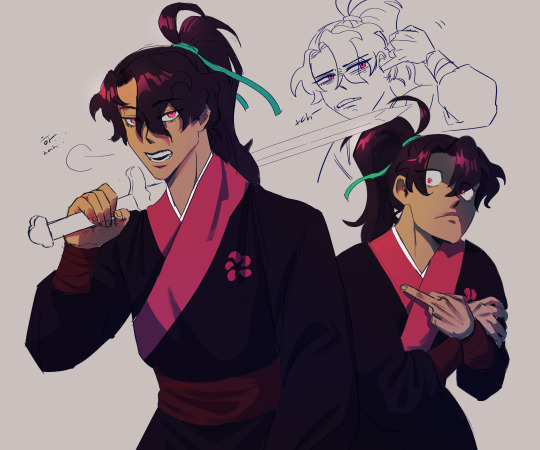

yknow i was trying to figure out how to draw him pretty and then immediately got sidetracked into drawing him as a bastard as the author intended.
#return of the mount hua sect#return of the blossoming blade#화산귀환#fanart#art#digital art#alp art#alp fanart#i wanted to draw him pretty because it's such a funny funfact to me#but also. mainly i just wanted to draw pretty eyes#every time i draw him it dissolves into silly expressions moments#he is annoyingly hard to draw#even when standing still he has bastard energy#and his bangs drive me insane.#basically i kinda wanted to figure out the structure of his face before pushing it into extreme expressions but#-gestures wildly- it never works out#he looks different every time i draw him#anyways. heres my boy. read the novel its good#also read the manhwa that's good too#its a very funny story#will it also make you cry? yes. that's the fun is it not.
264 notes
·
View notes
Text
The 5-Act Story Structure
The 5-Act Story Structure, often associated with classical drama and Shakespearean plays, offers a more nuanced approach to storytelling than the 3-Act structure. It is designed to provide a deeper exploration of themes, characters, and conflicts. This structure is divided into five parts: Introduction, Rising Action, Climax, Falling Action, and Denouement.
Act 1: Introduction sets up the story by introducing characters, settings, and the initial situation or conflict.
Act 2: Rising Action builds upon the foundation laid in the first act, developing the story's main conflict and complicating the characters' lives.
Act 3: Climax is the turning point of the story, where tensions reach their peak, and the main conflict is confronted head-on.
Act 4: Falling Action deals with the aftermath of the climax, leading towards a resolution but still containing elements of conflict and tension.
Act 5: Denouement resolves the remaining conflicts, wraps up loose ends, and concludes the story, often leaving the audience with something to ponder.
The 5-Act Structure is particularly suited for stories that require intricate plotting, detailed character arcs, and a gradual buildup to a climactic confrontation. It allows for a more layered exploration of themes and a complex interweaving of subplots, making it ideal for epic narratives, complex dramas, and stories with a wide scope of characters and settings.
Compared to the 3-Act and 7-Act structures, the 5-Act structure offers a balance between complexity and manageability. It’s best used when the story demands depth and complexity but still needs to maintain a coherent and focused narrative arc. It is perfect for stories where the journey, including its ups and downs, is as important as the destination.
Happy Writing!
See Slaying Fiction for more fun posts!
#writing#novel writing#tumblr writers#writer#fiction#creative writing#writeblr#writing community#writing tips#writing advice#5-act#story structure#story writing#slaying fiction
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
Outline I like (especially for shorter works)
Note: I learned this in film class (which is why it says "defines the movie" at the top, but I've also had success using it for non-film writing. It's basically a three-act structure, but I find for non-novels it's easier to work with than Save The Cat, for example.
Another note: Unraveling The Map is rarely a whole scene in and of itself in my personal experience - I usually use it to create an opening image that leads into the Launch Point, which I make the first scene
Unraveling The Map - Do you have an opening scene that defines the movie?
The Launch Point - Where are we, and who are we with?
The First Leg - What’s a normal day look like in this world?
Change Course - What sets our characters off on their journey from normalcy?
The Foot of the Mountain - Okay, we’re going on this journey together. (choosing the direction for solving the problem)
Climbing The Side - It starts hard, but you get used to the problems as you go.
Through The Cave - Do you have a B story? Set that story off on its own now too.
Reassess the Problem - You’re at the middle. Is there another way to get it done?
Try and Fail - Things begin to fall apart, can they handle it?
The Fall - The worst thing happens, something so bad you don’t think you can get up.
The Hidden Clue - What do your characters discover about themselves/the problem that they never saw before?
Race To the Finish - They’re up and running no matter what
The Treasure Chest - Did they get what they came for?
Where We Go From Here - Show us the world in a new light, hint what’s next.
#writing#writing advice#writers on tumblr#writeblr#outlines#outlining#mountain expedition outline#three act structure#novels#movies#short film#short stories#launch point#through the cave#foot of the mountain#treasure chest#writing tips#writing process#olive's writing vibes
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Worldbuilding and Writing Fiction are two separate skills.
Someone reblogged one of my shitposts yesterday (the one about intimidating myself out of worldbuilding) expressing confusion in the tags about how anyone could be intimidated out of writing through worldbuilding too much.
This was kind of baffling to me, because I think I've seen it 50-60 times now, especially with new, ambitious writers who are starting off with deep fantasy or science fiction projects. When you talk to them, they've often sunk months or even years of worldbuilding into the project, but when you ask how far they've come on the fiction side of things, they usually have writer's block, haven't started writing the story, or say they're not ready yet. 'I'm starting soon' is a common refrain. 'I just have a little bit more left to do.'
The main reason for this - I feel - is that worldbuilding and writing are two different skills. Someone who spends 5 years worldbuilding has learned how to get really good at worldbuilding, but that doesn't mean anything about how good their writing will be. Many folks think worldbuilding will automatically make a story better, but sometimes worldbuilding can become unwieldy and stressful, especially in the case of a) entirely new worlds / secondary world fantasy, or b) complex worldbuilding. Definitely not talking about contemporary romance here, lol. (Though no shade to that, I've had a lot of fun worldbuilding for those stories too).
Going from worldbuilding to writing is launching into an entirely new space. If you find writing new stories easy, that won't be a problem for you, in fact you may not even have realised they're too different skills before now.
If you find writing new stories intimidating, sometimes having hundreds or thousands of things about your world to try and constantly remember can feel overwhelming and mess with the executive function needed to start a chapter.
In some cases, worldbuilding can make it much easier to start a story. But it really depends on what you're needing to do. If you're just writing a contemporary story where you need to research two characters and two jobs, you're generally going to be just fine.
If on the other hand, you have the equivalent of a 500 page Wiki behind-the-scenes, it can feel overwhelming very quickly.
New writers fall into this trap the most, I feel. They become accustomed to what worldbuilding feels like, and they hedge on writing the actual fiction, because they just have more experience worldbuilding and keep waiting for their confidence in worldbuilding to become 'confidence in starting the story.' It doesn't work that way. They're different skills.
They might even be better at worldbuilding than writing! But that just means - if they really want to be a writer - that writing is the skill they really need to work on the most. That can be a comfort zone issue too. It can also be a 'only about 5-10% of all this work will ever appear in the story' issue, where folks want to share the worldbuilding more than the characters or plot, and therefore are just not inspired to work on their story. It can be a 'I want this story to be as good as my worldbuilding' issue. It can be a 'I find the worldbuilding part easy' issue. There are lots of reasons people stall out in worldbuilding and then feel intimidated to write the actual story.
This can also happen with established writers who become aware that the more they know about their world, the more they don't know about their world. It can start to feel like - if you write 10 articles for yourself, you end up with 100 more to write. If you write those 100 articles, you have another 300 to write. Worldbuilding never ends. Worldbuilding can be endless, and if you're an immersive writer, you can get lost very easily in the details, or in not knowing what details are critical and what details aren't. (A hint here is that you'll figure that out really fast when you start writing).
Stalling in worldbuilding can be a lot of things, it can tell you that there's something broken in the world, something broken in the story, it can tell you more about your insecurities, it can tell you how good you are at one skill and where you might need practice in another. It's super informative!
But, generally speaking, the advice I tend to give to many new writers is to try not to let your worldbuilding period last too long. Ideally, put a timer on it and see how it feels to start writing your story once the timer has gone off (3 months, 6 months, 3 weeks, put it in your phone or in your calendar, and start the first chapter, or some random scene, once that time is up).
If, after that period of time lapses, you still aren't ready to start your story, something bigger might be going on. It's an opportunity to dig deeper into the situation. And sometimes just ask yourself if you're using the idea of a novel as an excuse to do what you love most: Worldbuilding. If that's the case, there are other jobs you can parlay a solid worldbuilding ability into. It doesn't have to lead to novels. :)
But yeah it's super super common for many writers to stall out between worldbuilding and writing, and to feel overwhelmed by their own worldbuilding.
New writers get affected by it the most based on observation and hanging around writing forums, and the advice that gets asked quite often specifically on 'when do I go from worldbuilding to writing the story,' but established writers experience it too, because as Gene Wolfe once said to Neil Gaiman: "You never learn how to write a novel, Neil. You just learn how to write the novel you are on."
#on writing#on worldbuilding#dodgy advice#worldbuilding and writing are two different skills#and writing one novel in one world#doesn't necessarily teach you how to write another novel in another world#likewise worldbuilding doesn't teach you how to write the novel that will follow#it just gives you a lot of meat for the structure itself#some folks don't notice a difference and never realise they're different skills#some people just notice that worldbuilding makes things easier#and for the rest of us it can definitely be a mixed bag
260 notes
·
View notes
Text
It is Super Natural: Four Basic Elements To Your Story
It is Super Natural: Four Basic Elements To Your Story
When I talk about novel structure, I talk a lot about Dwight Swain who wrote Techniques of the Selling Writer.
Swain has some really cool elemental aspects that he talks about and no, they don’t have to do with inciting incidents or the climax—at least not initially, and I thought it would be fun if we had a little series where we explored this both here on the podcast and on my Write Better…

View On WordPress
#carriejones#motivation reaction units#mru#novel structure#podcast#write better now#writing#writingtips
0 notes
Text
sure we could ask ourselves what azula would've been like if she wasn't a princess. but we don't have to because that's rangi. that is rangi
#its another way the kyoshi novels made the most out of their structure as a prequel#go go stuck up army brat girl give us a character representating how the fire nation will change in the next few hundred years#r.post#rangi#azula#kyoshi novels
263 notes
·
View notes
Text
reading collision course and I love the way they write spock's family arguments. sarek and spock go back and forth calmly declaring the other's point of view to be illogical until amanda has to intervene and cry, "stop it, you're tearing this family apart!" and demand they apologise, which obviously neither of them do. sarek doesn't want to give spock sensitive information because he wants to keep him safe, but spock interprets it as a lack of trust and a challenge to his vulcan nature. sarek calls his viewpoint flawed and hangs up on them. amanda turns to spock and assures him sarek didn't mean to be so nasty. in true teenage fashion, spock basically says yeah, right, then decides if he's not vulcan enough for his parents maybe he can be human enough for starfleet. spock ends things by basically half-disowning himself. it's just dysfunctional enough to be both funny and heartwrenching and I love it
#calm structured debate destroys local family#collision course#novels tag#william shatner#star trek novels#star trek tos#spock#sarek#amanda grayson#journey to babel
53 notes
·
View notes