#norwegian wolves archive
Photo
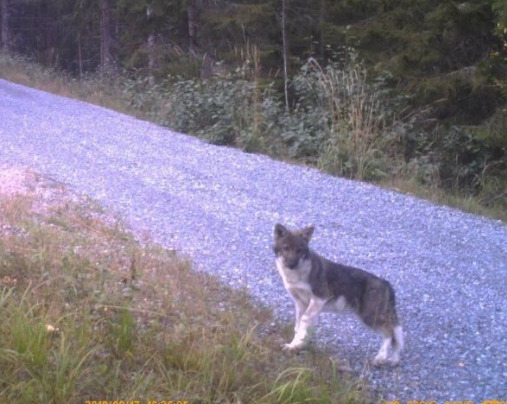


Both of these animals belong to the Norwegian Mangen pack (pictures taken in 2019). Looking at these pictures makes it kind of hard to believe the scientists’ claim that these are indeed pure wolves. Pure wolves do not have white markings like this. However, I wonder if it is possible that this is a mutation?
#wolfdog#wolfdogs#norwegian wolves archive#mangen pack#mangenreviret#mangenflokken#mangen#wild wolfdog#wild wolfdogs#color#coloration#fur#markings#norway#norwegian#archive
834 notes
·
View notes
Photo




Wodan
Wodan is the chief God of the Germanic pantheon, he has countless of names in many languages. He is the God of wisdom, knowledge, battle, magic, death, healing and the runes. Most things we know about his life are from the eddas because of course the Germanic people did not write their stories down until Christianity spread.
His name comes from the proto-Germanic word Wodanaz which means rage, it still means rage in different Germanic languages. This God personally holds a special place in my heart. Through my work with seidr I have come into contact with him several times, if I want to write down everything I know about him, this post would be way too long so I will keep it short.
The earliest mention of him comes from the Romans. Tacitus stated that the Suebi viewed Wodan as their most important deity. His latinized name is Mercury although this Roman/Greek God has no similarities with Wodan beside the fact that they both escort the dead. Both are also depicted with a staff but that's where their likeness ends. An interesting thing to notice is that Jupiter (chief God of the Romans) is used to describe Thor/Donar instead. A hint to the fact that Wodan became chief during the migration period.
The nine herbs charm from England mentiones Wodan as well. It was written somewhere in the 10th century AD, This is centuries after Christianity was introduced but people seem to still fall back on Wodan in times of healing. Here is the charm:
"A serpent came crawling but it destroyed no one
when Woden took nine twigs of glory,
And then struck the adder so that it flew into nine
There archived apple and poison
that it never would re-enter the house."
There is also an Old English rune poem that basically explains the futhark. This is the stanza for the ansuz rune:
"god is the origin of all language
wisdom's foundation and wise man's comfort
and to every hero blessing and hope"
The word Os is used for God. Christians did not use this word to speak of their God but this rune is however directly related to Wodan.
He is also mentioned in the Old English poem Maxims I:
"Woden worhte weos" Woden made idols. The last written record that I want to mention is the Merseburg charm which I have written about before:
"Phol and Woden travelled to the forest.
Then was for Baldur's foal its foot wrenched.
Then encharmed it Sindgund (and) Sunna her sister,
then encharmed it Frija (and) Volla her sister,
then encharmed it Woden, as he the best could,"
A fibula from 7th century Frisia depicts Wodan flanked by two wolves. There are also coins found in Frisia that depict Wodan. There are a few more written sources and archeological finds but if I add them all here, this article would be incredibly long.
Wodan is later known as Odin in the Scandinavian world but there are quite some differences between the two created because of cultural differences and time periods. Both Wodan and Odin came from the same incarnation Wodanaz.
Wodan: Skilled sorcerer, God of Death, trickster, God of knowledge, bringer of the runes, still has two eyes, shaman, represents rage, leader of the wild hunt, God of war, God of healing, carries a staff and spear, ravens, deceiver, possession, was a feared God because of his tricks,
Odin: Skilled in battle and magic, God of Knowledge, bringer of the runes, one-eyed, shaman, shapeshifter, dead fighters go to walhalla to fight for him, God of war, owner of Sleipnir, carries a staff and spear, two ravens and two wolves guide him, more closely related to the Sami culture.
There are still some traditions in the Netherlands that are linked to Wodan: Sinterklaas, Midwinterhoorn blazen, Hanging the placenta of a horse in an oak tree, Sint Maarten, possibly the game paalzitten.
I am sure that other countries have traditions left as well. If you know of any, mention them in the comments. Have a nice Wodan's day (wednesday)
Wodan/Odin's names in different (Germanic languages):
Proto-Germanic: Wodanaz
Old English: Wōden
Old Saxon: Wōdan
Old High German: Wuotan
Old Frisian: Weda
Old Norse: Óðinn
Dutch: Wodan/Woen
English: Odin
Norwegian: Odin
Maybe some of you guys can add to this list because I am not sure if he was called by a different name in Denmark and Sweden.
Pictures: depiction of Wodan, the coins, Frisian fibula, Wodan as the wanderer, Wodan as a shaman and a depiction that relates more to the Scandinavian Odin.
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
vargamor
read it on the AO3 at https://ift.tt/2HvtLFC
by mountainsbeyondmountains
"Vargamor (Norwegian)- a witch, a psychic. A woman who consorts with wolves."
Words: 1410, Chapters: 1/1, Language: English
Fandoms: A Song of Ice and Fire - George R. R. Martin, Game of Thrones (TV)
Rating: Not Rated
Warnings: No Archive Warnings Apply
Categories: F/M
Characters: Sansa Stark, Jon Snow, Joffrey Baratheon, Arya Stark, Petyr Baelish, Shae (ASoIaF), Tyrion Lannister
Relationships: Jon Snow/Sansa Stark
Additional Tags: Alternate Universe, Mythology - Freeform, Warging, Mostly Book Verse, listen sometimes the muse just takes you and.... this is what results
read it on the AO3 at https://ift.tt/2HvtLFC
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Gulag Historian Returns to Prison
Acquitted of child pornography, Yury Dmitriyev now faces charges of sexual assault.
— By Evan Gershkovich | July 14, 2020 | The Moscow Times

Sofia Miroyedova
Respected Gulag historian Yury Dmitriyev has spent decades calling attention to one of the darkest chapters in Russia's history. He now faces up to 15 years in prison on sexual assault charges in a case his allies say has been trumped up to silence him.
The Moscow Times Profiled Dmitriyev in 2018:
Yury Dmitriyev normally hates Moscow. The concrete, the commotion, the pollution. As much as he can, he stays in Karelia, where he was born, raised and has spent his 62 years. In the northwestern region bordering Finland and the Baltic and White Seas, he can usually be found in the woods or in his study, writing.
Yet on a pleasant evening in mid-May, Dmitriyev, a prominent researcher of Soviet crimes, was happy to be in the metropolis. Accompanied by his elder daughter, Yekaterina Klodt, and his lawyer, Viktor Anufriyev, old friends greeted him with grins and tight hugs in a courtyard outside Teatr.doc, a progressive theater, ahead of a human rights awards ceremony.
One month earlier, Dmitriyev had been cleared of child pornography charges. Authorities had detained him in December 2016 after investigators found nude photos of his 11-year old adopted daughter; Dmitriyev said he took the photos to monitor her physical changes as she was prone to illness. From the outset, human rights defenders claimed that the case was fabricated to silence an outspoken activist.
If the arrest came as a shock to those who knew him, so too did his acquittal: Fewer than one percent of criminal defendants in Russia are cleared.
But authorities, human rights defenders now say, weren’t done with the historian just yet. Only a month after the awards night, a judge annulled the April decision, starting the trial anew.
Then, two weeks later, prosecutors brought additional charges to the table: This time they claimed that Dmitriyev had sexually assaulted his daughter. As of late June, the historian was back in jail facing another uphill legal battle, his freedom having been fleeting.
“The new charges are a chance for the prosecution to get it right,” Anufriyev said. “They failed the first time, so officials are giving them another chance to get the job done.”
Digging and Documenting
Two decades ago, Dmitriyev discovered a set of mass graves in a Karelian forest containing the bodies of more than 9,500 victims of Josef Stalin’s Great Terror. Poring over KGB documents, the head — and sole employee — of Memorial’s Karelia branch spent the next 20 years documenting each victim’s story.
“What makes Yury unique is that he combines both the digging and the documenting,” said Sergei Krivenko, a colleague of Dmitriyev’s at Memorial and a member of the Presidential Human Rights Council. “Some people work on compiling books of names, some people search for the exact locations of the killings. No one has dedicated themselves to both the way Yury has.”
“No one has dedicated themselves to both digging and documenting the way Yuri has.”
Those who know Dmitriyev say he toiled everyday. “He’s been doing this work for the past 30 years, and I’m 33,” said Klodt, his elder daughter. “I’m so used to it that, for me, his work is no different than a dentist’s.”
Since the fall of the Soviet Union in 1991, historians say, the state has supported them in locating and memorializing the burial sites of the estimated 15 to 30 million victims of Stalin’s rule. At the location Dmitriyev discovered — Sandarmokh — local authorities helped build roads and erect monuments and aided with an annual gathering at the site.
But in recent years, human rights defenders say, the climate has become less hospitable. Those who spoke with The Moscow Times pointed to a resurgence in Stalin’s popularity as a significant reason: In June last year, Russians voted him the “most outstanding” person in history. In second place was President Vladimir Putin, who has accused the West of “excessive demonization” of the Soviet leader.
Others pointed to a surge in nationalism since 2014, when Russia annexed Crimea and got involved in Ukraine. “There were many foreigners killed at Sandarmokh — Norwegians, Poles, Finns and Ukrainians, including around 200 intellectuals,” Krivenko said. “This is a very important place for Ukrainians especially, and a delegation would visit the site annually.”
Dmitriyev organized the memorial visit every year on Aug. 5. He invited foreign delegations and led discussions, Krivenko said. After the events in Crimea and Ukraine, the discussions often turned to politics.
“I think this is why they went after him,” Krivenko said. He also pointed to an October 2016 decision to add Memorial to a register of “foreign agent” organizations that receive foreign funding. “I think this gave the local siloviki” — officials with ties to law enforcement — “a signal that they could go after us.”
Two months later, in December, Dmitriyev was first arrested.
Prison as a Work Trip
The day after the awards night, Dmitriyev was invited to speak with human rights students at the Sakharov Center, named after the Nobel Prize-winning human rights activist.
Klodt had come with him and complained that she wasn’t feeling well. “Maybe they should put you in prison for a year too so they can toughen you up,” her father joked.
Quick to laugh, thin and slightly disheveled, Dmitriyev presented an unimposing figure. But when the subject of his work came up, he turned deadly serious.
“I don’t fight the system. That’s a dead end, and I’m already old now,” he told The Moscow Times before the event. “I fight for memory. I fight so anyone who wants to can learn about their relatives, regardless of whether the government wants it or not. These people existed at some point. They worked and loved and had children. I’m for protecting the freedom of private life and of those memories.”
Without those memories, Dmitriyev continued, today’s generation cannot judge whether their government is laudable or acting improperly.
“The people I dig up were in the same prison, walked the same halls and were behind the same bars.”
“When a person knows the history of their family for multiple generations, they can understand what our state is doing right and what it’s doing wrong,” he said. “Called upon by the state to do this or that, they’ll say, ‘No, my great-grandfather was summoned in the same way and it ended badly for him. So maybe it’ll end badly for me as well.’”
Dmitriyev shrugged at the subject of his time in prison. “I don’t make a great tragedy out of that year,” he said. “I just think of it as a work trip. I’ve gained a better understanding of what my heroes — the people I dig up and write about — were thinking. They were in the same prison, walked the same halls and were behind the same bars.”
More difficult, he said, was being separated from his younger daughter. Dmitriyev himself was adopted, and at some point he decided he wanted to care for an orphaned child too. He hoped he’d be able to talk to her again by the end of the year. “It’s a humane policy by the prosecutor’s office,” he joked. Then he turned serious again: “I can handle it, I’m a tough person. But what about the child? She thinks everyone has abandoned her.”
Into the Forest
After Dmitriyev was first arrested, the girl was taken in by her biological grandmother. Klodt said the family and the grandmother maintained regular communication. But when Dmitriyev was acquitted, Klodt said, the grandmother cut off all communication with the family. Then she sent a letter to the prosecution demanding the acquittal be overturned.
Anufriyev, Dmitriyev’s lawyer, believes that local authorities pressured her into writing the letter. He also says that the new charges of sexual assault are founded solely on a June 6 meeting between investigators and the girl during which, Anufriyev says, they coerced her into saying what they wanted. “They say they’re helping the child, but really they’re making her suffer,” he said.
Reached by phone, Tatyana Kordyukova, a spokesperson for the prosecutor’s office, said she couldn’t comment on the case and referred The Moscow Times to the Investigative Committee. The Investigative Committee, in turn, did not respond to requests for comment.
On July 25, the retrial of the first case will begin. The Investigative Committee is currently researching the new charges, a process which could take months. The original charges carry up to 15 years in prison; the new charges up to 20.
This time, though, Anufriyev says Dmitriyev is better prepared. “After his last stint in prison, he now knows that we can fight and win this thing,” he said.
Klodt, too, is ready for the fight. “I’m not constantly hysterical like last time,” she said. “I understand that something needs to be done. I’m not giving up.”
His colleagues say they won’t give up either. When Dmitriyev was first arrested, human rights defenders, artists and writers across the country spoke out for him and wrote letters to Putin. Still, they are sober about the possible outcome.
“This is the atmosphere for us right now,” Krivenko said. He pointed to the case of Oleg Sentsov, a Ukrainian filmmaker accused of terrorism after he had refused to accept the annexation of Crimea, and Memorial colleague Oyub Titiyev, who is also in prison on charges widely believed to be fabricated.
“The only good thing from all this is that the president is showing us how it all happened in the 1930s — how people were blamed, how siloviki read signals from the top,” Krivenko said. “We used to study this in archives, now we see it in real life.”
During his short stint out of prison, Dmitriyev returned to work. Anatoly Razumov, a historian and one of Dmitriyev’s closest friends, stayed at his house from the night before the acquittal was overturned until June 19. The entire time, he says, Dmitriyev worked on a book he had to put off when he was first arrested.
In May, asked if he would return to his work or if he feared doing so would anger certain parties, Dmitriyev was unmoved. “If you’re afraid of wolves, you shouldn’t go into the forest,” he replied.
1 note
·
View note
Text
tagged by: princesiddies (indirectly)
rules: answer the questions and tag 20 people
Name: Michael Cornelius Mell
Nickname: Mikey, ‘Slushie’
Alias (if you have any): Nathan (by my MPD headspace members), Z3roR3tr0
Zodiac sign: Sagittarius
Height: 5’2
Orientation: Bi
Nationality: Norwegian, Irish, English
Favourite fruits: Cantaloupe
Fav season: Summer
Fav scent: Pumpkin Spice Wax Melts (scentsationals)
Fav colour: the colour of galaxies (blues, reds, purples, blacks, greys, etc.)
Fav animals: Birds, Wolves, Snakes
Coffee, tea, hot 🍫: Coffee
Average hrs of 💤: 2-6
Fav fictional character: Defalt (WD), Ushiwaka ♡(Okami)
No. of blankets you 💤 with: 2
Dream trip: to finally see my sister @ladyluxlord and her S/O: Void
Blog created: sometime on 2011 i think, but wasnt active until 2014? look at my archive idk
illl tag as many people as i can off the top of my head cause idk 20 but yeah, everyone who i tag and not tag is free to do this if theyd like :P
@ladyluxlord @biohazard-barrels @spadescribbles @hidekuni-art @whyamiheere :) @lemonsandcream @randomartchick
1 note
·
View note
Text
Tagged by @mama-germany. Thank you!
Rules: answer 20 questions and tag some folks you’d like to get to know better.
Name: Alexander
Nickname: Alex, or Eh Dubb, or Weebee (mispronunciation of my last name), or Weebster (cooler version of my last name), or Baboy-po (translates to Mr. Pig... it’s Filipino, long story)
Zodiac sign: Taurus
Height: 5′9″ give or take an inch
Orientation: Straight
Ethnicity: Canadian-American, with a bit of German, Russian, and Norwegian mixed in
Favorite fruit: Gotta be pomegranates. My parents have a lovely pom tree in the backyard and every October it gives a couple dozen pomegranates about the size of two fists. So sweet and juicy...
Favorite season: tbh whenever I can go about my day comfortably in a sweater and jeans, I’m happy. Spring is pretty good for that.
Favorite flower: Heck... this again. The flowers on the pomegranate tree are actually quite pretty. Cherry blossoms are lovely, too. Don’t think they count but I’m not really a flower guy. :/
Favorite scent: Petrichor, Mexican BBQ, freshly peeled citrus...
Favorite color: Dark reds and monochromes
Favorite animal: I said dolphins last time but I don’t think that’s totally true... Wolves. I really like wolves.
Coffee, tea, hot cocoa: All of em, though my balance between them is far off from what I’d like
Average sleep hours: 7 hours on Monday, every other Tuesday, Wednesday, and Friday mornings. 9-10 hours every other time.
Dog or cat person: Dogs, no question.
Favorite fictional character: Ugh... Guts from Berserk, Ira Gamagoori from Kill la Kill, Lalatina/Darkness from Konosuba, Joker from Mass Effects 1-3, my nine (incredibly fluid) OCs, Mr. Darling (forgot his real name) from Monster Musume... I could go on for hours.
Number of blankets: 2 nowadays, but I’m looking forward to when I can go back to 1
Blog created: I thought for sure I created in late 2012, but my archive only goes back to October 2013, so...
Number of followers: 134 (though I’m pretty sure less than half are actually human)
(I realized about halfway through I’ve done this one already... ah well)
I’mma tag... erm... y’know what y’all just go ahead and pretend I tagged you. Pretty sure I tagged everyone I wanted to tag last time :/
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ch. 2: “The Empress of Mars” Analysis Doctor Who S10.9: Friday, Odin & the Doctor; Missy’s 2 Faces; Etc.
Apologies for getting these 3 chapters for “The Empress of Mars” out after the airing of “The Eaters of Light.” I post first on Archive Of Our Own, which I did before the 10th episode. With photos, it takes more time to post here.
If you missed the 1st chapter, check it out Ch. 1: Fastballs, Mars-Not-Mars, Rassilon References, Etc.
NOTE:
TPEW = “The Pyramid at the End of the World”
TRODM = “The Return of Doctor Mysterio”
THORS = “The Husbands of River Song”
CAL = Charlotte Abigail Lux, the little girl from the Library
TOS = The Original Series of Star Trek
TNG = Star Trek: The Next Generation
Norse Mythology & Vikings Have a Big Role
Roman and Egyptian mythology aren’t the only mythological references in “The Empress of Mars.” Norse Mythology, for example, has a huge role in the episode, as well as other Viking references.
Egil & Eagle
At NASA, we see a sign “EGIL” in front of the Doctor in the image below, which refers to Egill Skallagrímsson (Anglicized as Egil Skallagrimsson). The Doctor, The Ghost, is associated here with Egil. At first we see the sign without the Doctor.

According to Wikipedia, Egil “was a Viking-Age poet, warrior and farmer. He is also the protagonist of the eponymous Egil's Saga. Egil's Saga historically narrates a period from approximately 850 to 1000 CE and is believed to have been written between 1220 and 1240 CE.”
Egill was born in Iceland, the son of Skalla-Grímr Kveldúlfsson and Bera Yngvarsdóttir, and the grandson of Kveld-Úlfr ("Night Wolf"). His ancestor, Hallbjorn, was Norwegian-Sami.
Here’s another wolf reference, where the Doctor-mirror is the grandson of a metaphorical wolf.
When Grímr arrived in Iceland, he settled at Borg, the place where his father's coffin landed. Grímr was a respected chieftain and mortal enemy of King Harald Fairhair of Norway.
OK, the term “Borg” automatically conjures thoughts of several Star Trek: TNG episodes where alien cyborgs known as the Borg show up to assimilate people, turning them into Borg and absorbing them into the collective. They first show up in the episode “Q Who?” Um… I never thought about this before, but wow, just change Q to Doctor! Captain Picard gets converted to a Borg in “The Best of Both Worlds.” Part 1 was the finale to Season 3, while Part 2 was the premiere of Season 4.
Egill composed his first poem at the age of three years. He exhibited berserk behaviour, and this, together with the description of his large and unattractive head, has led to the theory that he might have suffered from Paget's disease. As professor Byock explains in his Scientific American article, Paget's disease causes a thickening of the bones and may lead eventually to blindness. The poetry of Egill contains clues to Paget's disease, and this is the first application of science, with the exclusion of archaeology, to the Icelandic sagas.
Here’s a reference to blindness.
Egil had a very bloody history. At times, he was marked for death, but his epic poetry, fit for kings, saved him. So words saved him, just like they have saved the Doctor time and time again.
“Egil” is another overloaded word, as its homophone is “eagle.” The Doctor is either a bird, being a proxy of Zeus, or Zeus, himself. Zeus’s Roman equivalent is Jupiter. In Norse mythology, Odin is the chief god. He’s not a one-to-one correspondence, though, to Zeus and Jupiter, like the typical Greek and Roman gods are to each other. Odin, among other things, is also a god of war like Mars. He’s a tyrannical leader who is not concerned with justice, and this sounds like Morbius, who may be the possessed Doctor.
Odin, too, was a shape-shifter and turned himself into an eagle. It’s one of his many disguises.
Valkyrie Has Multiple Meanings
The Martian probe Valkyrie, while probing the Martian ice caps, is named for multiple references.
Operation Valkyrie & “Let’s Kill Hitler”
Operation Valkyrie was a German plan during WWII to assassinate Hitler, take control of German cities, disarm the SS, and arrest the Nazi leadership. Although the participants made lengthy preparations, the plot failed. Of course, this also refers to the 11th Doctor episode “Let’s Kill Hitler,” where River was engineered to kill the Doctor. Of course, that lengthy plot failed, too, at least for the time being.
In “The Lie of the Land,” we saw the Doctor involved in a totalitarian government with the Truth logo, which looked like it could be a type of Nazi logo with an SS (mirrored Ss). Interestingly, Daleks were created as symbols of the Nazis.
Valkyries of Norse Mythology
In Norse mythology, valkyries are female figures who decide the fate of those who die in battle.
According to Wikipedia:
Selecting among half of those who die in battle (the other half go to the goddess Freyja's afterlife field Fólkvangr), the valkyries bring their chosen to the afterlife hall of the slain, Valhalla, ruled over by the god Odin. There, the deceased warriors become einherjar (Old Norse "single (or once) fighters"). When the einherjar are not preparing for the events of Ragnarök, the valkyries bear them mead. Valkyries also appear as lovers of heroes and other mortals, where they are sometimes described as the daughters of royalty, sometimes accompanied by ravens and sometimes connected to swans or horses.
Ravens and horses are certainly significant. In fact, ravens are indirectly referenced at least 4 times in the current story. We’ll examine more about the raven in a few minutes. And we’ll look at them in more depth in regards to Clara and the Doctor in the next chapter.
Valkyries today tend to be romanticized in a way, but in heathen times, they were more sinister and sound like they have a connection to the 12 Monks. According to Norse-Mythology.org:
The meaning of their name, “choosers of the slain,” refers not only to their choosing who gains admittance to Valhalla, but also to their choosing who dies in battle and using malicious magic to ensure that their preferences in this regard are brought to fruition. Examples of valkyries deciding who lives and who dies abound in the Eddas and sagas. The valkyries’ gruesome side is illustrated most vividly in the Darraðarljóð, a poem contained within Njal’s Saga. Here, twelve valkyries are seen prior to the Battle of Clontarf, sitting at a loom and weaving the tragic destiny of the warriors (an activity highly reminiscent of the Norns). They use intestines for their thread, severed heads for weights, and swords and arrows for beaters, all the while chanting their intentions with ominous delight. The Saga of the Volsungs compares beholding a valkyrie to “staring into a flame.”
The Norns sound very similar to the 3 Fates, which we examined in my analysis in TPEW, where I likened the Monks to weaving a tapestry and compared them to the 3 Fates who weave destinies. It seems likely then that the 12 Monks may symbolize the 12 Valkyries, who are weaving the tragic destiny to come.
Valhalla & the Cloister Wraiths
Valhalla is a the hall where the dead are deemed worthy of dwelling with Odin, and it’s located on Asgard, which brings in the references to the Doctor and River picnicking on Asgard. This picnic entry in River’s diary came up in “Silence in the Library,” as well as “The Husbands of River Song.”
Wolves guard Valhalla’s gates, and eagles fly above it.
According to Norse-Mythology.org:
Odin presides over Valhalla, the most prestigious of the dwelling-places of the dead. After every battle, he and his helping-spirits, the valkyries (“choosers of the fallen”), comb the field and take their pick of half of the slain warriors to carry back to Valhalla. (Freya then claims the remaining half.)
According to Norse-Mythology.org:
The dead who reside in Valhalla, the einherjar, live a life that would have been the envy of any Viking warrior. All day long, they fight one another, doing countless valorous deeds along the way. But every evening, all their wounds are healed, and they are restored to full health. They surely work up quite an appetite from all those battles, and their dinners don’t disappoint. Their meat comes from the boar Saehrimnir (Old Norse Sæhrímnir, whose meaning is unknown), who comes back to life every time he is slaughtered and butchered. For their drink they have mead that comes from the udder of the goat Heidrun (Old Norse Heiðrun, whose meaning is unknown). They thereby enjoy an endless supply of their exceptionally fine food and drink. They are waited on by the beautiful Valkyries.
But the einherjar won’t live this charmed life forever. Valhalla’s battle-honed residents are there by the will of Odin, who collects them for the perfectly selfish purpose of having them come to his aid in his fated struggle against the wolf Fenrir during Ragnarök – a battle in which Odin and the einherjar are doomed to die.
From what we’ve seen in “Hell Bent,” the Cloister Wraiths are, at least in one way, like the dead who reside in Valhalla. As the Doctor said, they are the dead manning the battlements. We may be experiencing the unreality of the symbolic Valhalla right now. The relative calm before the Ragnarök storm.
The Ice Queen Mirroring a Valkyrie or Odin
The Ice Queen, Iraxxa, decided who died and who lived, especially when it came to Colonel Godsacre. (God’s acre actually means “a churchyard or a cemetery, especially one adjacent to a church.”) Therefore, Iraxxa is mirroring a Valkyrie or even Odin, given her position of leader of the hive.
Odin, Ravens & the Valkyries
According to Wikipedia,
In Germanic mythology, Odin is a widely revered god. In Norse mythology, from which stems most of the information about the god, Odin is associated with healing, death, royalty, the gallows, knowledge, battle, sorcery, poetry, frenzy, and the runic alphabet, and is the husband of the goddess Frigg. In wider Germanic mythology and paganism, Odin was known in Old English as Wōden, in Old Saxon as Wōdan, and in Old High German as Wuotan or Wōtan, all stemming from the reconstructed Proto-Germanic theonym wōđanaz.
BTW, WOTAN is a reference to a 1st Doctor story called “The War Machines.” According to the TARDIS Wikia, “WOTAN was one of the first artificial intelligences created on Earth by Professor Brett. Its name stood for Will Operating Thought ANalogue.” It goes on to say, “Deciding to conquer the world, WOTAN ordered the construction of mobile, armed computers which were designated War Machines. These were constructed in locations across London.”
Anyway, according to WizardRealm.com:
Odin (or, depending upon the dialect Woden or Wotan) was the Father of all the Gods and men. Odhinn is pictured either wearing a winged helm or a floppy hat, and a blue-grey cloak. He can travel to any realm within the 9 Nordic worlds. His two ravens, Huginn and Munin (Thought and Memory) fly over the world daily and return to tell him everything that has happened in Midgard. He is a God of magick, wisdom, wit, and learning. He too is a psychopomp; a chooser of those slain in battle. In later times, he was associated with war and bloodshed from the Viking perspective, although in earlier times, no such association was present.
Interestingly, Odin has ravens. And this is another example of how “The Empress of Mars” has quite a few indirect references to ravens. Because Clara is associated with a raven, it brings up a reference to her, too. However, there are very pointed Clara references, which we’ll examine in the next chapter.
Being the god of magic, wisdom, wit, and learning, Odin has a lot in common with Merlin. Odin actually disguises himself as an old man and travels Midgard (Earth) looking for heroes for the coming of Ragnarök.
According to WizardRealm.com:
If anything, the wars fought by Odhinn exist strictly upon the Mental plane of awareness; appropriate for that of such a mentally polarized God. He is both the shaper of Wyrd and the bender of Orlog; again, a task only possible through the power of Mental thought and impress. It is he who sacrifices an eye at the well of Mimir to gain inner wisdom, and later hangs himself upon the World Tree Yggdrasil to gain the knowledge and power of the Runes. All of his actions are related to knowledge, wisdom, and the dissemination of ideas and concepts to help Mankind. Because there is duality in all logic and wisdom, he is seen as being duplicitous; this is illusory and it is through his actions that the best outcomes are conceived and derived. Just as a point of curiosity: in no other pantheon is the head Deity also the God of Thought and Logic. It's interesting to note that the Norse/Teutonic peoples also set such a great importance upon brainwork and logic. The day Wednesday (Wodensdaeg) is named for him.
It’s really interesting that Odin’s wars are fought on the “Mental plane of awareness.” This corresponds to the Doctor being a creature of pure thought through the Great Work. This also corresponds to him being a mirror of CAL, who is also a being of pure thought in a mental plane of awareness.
Odin & the Doctor
In “The Girl Who Died,” the Doctor pretended to be Odin when the Vikings took him and Clara captive. We then saw another extraterrestrial claiming to be Odin, shown below. His helmet is obviously symbolic in some ways of a bird. Are the wings those of an eagle or a raven? There are symbolic feathers on the top of the helmet, too, but that’s where the similarities to a bird end.

The crest looks more like something a Roman soldier would wear on his helmet. And then there’s the weird part covering his forehead that looks like 2 eyes and a nose. Is the representation supposed to be 2 faces in One? The symbolic eyes are empty, perhaps, representing The Ghost. Odin is a dark mirror of the Doctor, and it seems to me from the symbolism that Odin represents the possessed Doctor, who has an augmented eye. That could be a reference to the Eye of Harmony.
The Doctor actually does more than just pretend to be Odin in this episode. Like Odin in mythology, the Doctor decides life and death here. He assumes Odin’s role. Ashildr dies, and the Doctor literally brings her back to life, another signal of the coming of Ragnarök. Clara represents a valkyrie, the Doctor’s helping spirit.
But this isn’t all. Extraterrestrial (ET) Odin in “The Girl Who Died” has a connection to the “Robot of Sherwood.” The sheriff’s boar emblem looks very much like ET Odin’s helmet when placed behind someone’s head. Check out this image below of the arrow bearer in this perfectly centered camera shot where the emblem of the boar’s ears (yellow arrow) now looks like the wings on Odin’s helmet.

In fact, the sheriff looks a lot like Odin without the helmet.
Interestingly, we have seen a character in TRODM, Lucy Fletcher, whose name means arrow maker or to furnish (an arrow) with a feather. Through all the mirrors we’ve examined, she connects to Amy, who connects to River. Susan connects to River, too. And River may connect to Missy. We know Missy has been controlling the Doctor through Clara, and she’s running a con game now.
Who’s Behind Controlling the TARDIS?
Check out the image below in the darkened TARDIS when Nardole goes to get some gear to help Bill after she falls into the pit. The bookcase is lit, which is very abnormal. And it’s only one bookcase in particular. This indicates it’s River.
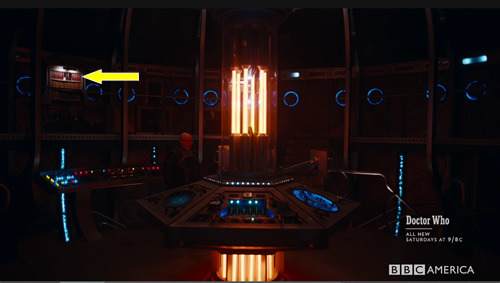
In fact, interestingly, Missy has 2 faces when we first see her at the end of “The Empress of Mars.” The blue arrow points to her face that looks like it’s inside the TARDIS, while the yellow arrow points to her other face. The TARDIS symbolizes the Doctor’s wife and the Doctor’s mind.

The Doctor is being controlled by his wife is what part of the subtext is pointing to. We saw in “The Lie of the Land” analysis that with the 2nd Doctor story “The Mind Robber,” where the Master was the author who controlled things in the same way River controlled things in “The Angels Take Manhattan” with her novel. We know River is one of the architects of the rescue plan.
Friday Has a Norse Connection
Of course, the name Friday comes from Robinson Crusoe. However, given the plot along with Friday’s name, appearance, and references, there are other allusions intended, too, making Friday a brilliant name with overloaded meanings.
Friday & Odin
“Friday,” as the actual day of the week, is named after Odin’s wife. In Old English, her name is Frīge, so it’s "Frīge's day." Other spellings, according to Wikipedia, are Frigg (Old Norse), Frija (Old High German), and Frea (Langobardic).
So the character Friday automatically has a connection to Odin and can represent Odin’s wife. However, there’s more.
Like Friday, Odin has one eye.
In fact, according to Norse-Mythology.org:
Odin’s quest for wisdom is never-ending, and he is willing to pay any price, it seems, for the understanding of life’s mysteries that he craves more than anything else. On one occasion, he hanged himself, wounded himself with his spear, and fasted from food and drink for nine days and nights in order to discover the runes.
On another occasion, he ventured to Mimir’s Well – which is surely none other than the Well of Urd – amongst the roots of the world-tree Yggdrasil. There dwelt Mimir, a shadowy being whose knowledge of all things was practically unparalleled among the inhabitants of the cosmos. He achieved this status largely by taking his water from the well, whose waters impart this cosmic knowledge.
When Odin arrived, he asked Mimir for a drink from the water. The well’s guardian, knowing the value of such a draught, refused unless the seeker offered an eye in return. Odin – whether straightaway or after anguished deliberation, we can only wonder – gouged out one of his eyes and dropped it into the well. Having made the necessary sacrifice, Mimir dipped his horn into the well and offered the now-one-eyed god a drink.
Odin’s story of trading an eye for a different type of perception and knowledge meshes with the concepts of the Eye of Harmony and the Matrix. We’ve examined how the Matrix gives the gift of prophecy.
ENGIN: Yes. Trillions of electrochemical cells in a continuous matrix. The cells are the repository of departed Time Lords. At the moment of death, an electrical scan is made of the brain pattern and these millions of impulses are immediately transferred to the
DOCTOR: Shush. I understand the theory. What's the function?
ENGIN: Well, to monitor life in the Capitol. We use all this combined knowledge and experience to predict future developments.
And the Eye of Harmony from TRODM clearly has to do with the Matrix. The Eye, as the 8th Doctor said in the movie, is his.
DOCTOR: Lee, this is my Tardis. This is my Eye and I'm in my own body. The Master has run out of all his lives. Now he plans to steal mine. That's the truth!
Anyway, in Friday’s case, because he defers to Iraxxa, he symbolically could represent Odin in disguise as an old man. After all, he did tell the Doctor:
DOCTOR: Why have you really come back?
FRIDAY: (sigh) I am old and tired and spent.
The reversed roles of the queen and Friday could also possibly be explained through the gender change.
Friday & The Vikings
After the Doctor and Bill discuss the Ice Warrior, Bill mentions a movie and an eye gouging when Friday is present, tying the movie to Friday.
DOCTOR: Yes. The indigenous species. An ancient reptilian race. They built themselves a sort of bio-mechanical armour for protection. The creature within is at one with its carapace. The Ice Warriors. They could build a city under the sand, yet drench the snows of Mars with innocent blood. They could slaughter whole civilisations, yet weep at the crushing of a flower.
BILL: Like The Vikings.
DOCTOR: Yes. Yes, very much.
BILL: Yeah, Kirk Douglas and Tony Curtis. Oh, the theme tune is amazing! There's this brilliant bit where his eye gets gouged out
(Friday stops and Bill notices the missing eye.)
Friday’s missing eye resembles that of Kirk Douglas’ character in the 1958 movie The Vikings.
Wikipedia says
The King of Northumbria is killed during a Viking raid led by the fearsome Ragnar (Ernest Borgnine). Because the king had died childless, his cousin Aella (Frank Thring) takes the throne. The king's widow, however, is pregnant with what she knows is Ragnar's child because he had raped her during that fateful raid, and to protect the infant from her cousin-in-law's ambitions, she sends him off to Italy. By a twist of fate, the ship is intercepted by the Vikings, who are unaware of the child's kinship, and enslave him.
BTW, the queen sends the child with the monks.
Many years later, we see that the boy has grown into a young man named Erik (Tony Curtis), who is still a slave. After some events take place, Erik in retaliation orders his falcon to attack Einar (Kirk Douglas), Ragnar's legitimate son and heir. The falcon gouges out Einar’s left eye.
The enmity between the half brothers is exacerbated when they both fall in love with the same woman, Princess Morgana, who is to marry King Aella but gets captured in a raid. In a way, this is like the 11th and 12th Doctors with River. BTW, I forgot to mention this, but the Doctor in Missy’s execution scene in “Extremis” and in the scenes in “The Lie of the Land” wears an old raggedy coat, which would represent the 11th Doctor. In fact, the 11th Doctor’s theme music does play in the latter episode.
Anyway, at one point Aella captures Ragnar and, according to Wikipedia, “orders the Viking leader bound and thrown into a pit filled with starved wolves. To give Ragnar a Viking's death (so that he can enter Valhalla), Erik, who is granted the honour of forcing him into the pit, cuts the prisoner's bonds and gives him his sword. Laughing, Ragnar jumps to his death. In response to Erik's "treason", Aella cuts off his left hand, puts him back on his ship and casts him adrift.”
(Amy cuts off Rorybot’s hands in “The Girl Who Waited.” Rorybot is sentient. So is this movie scene significant to the story?)
In the end, Erik and Einar fight for Morgana, and Erik mortally wounds Einar. Wikipedia says, “Echoing the scene with Ragnar, Erik gives Einar a sword, so that he too can enter Valhalla. In the final scene, Einar is given a Viking funeral: his body is placed on a longship, which is set on fire by flaming arrows.”
Friday not only represents Einar with his eye gouged out, but also Erik, as a servant.
Erik is a hybrid, half-Northumbrian and half-Viking, mirroring the hybrid nature of the Doctor.
Also, it’s interesting that Erik and Einar are half brothers because I’ve wondered for quite some time if the Master and Doctor were brothers (as was originally planned in Classic Who) or half brothers. The idea that the Doctor has a half brother has come up in the subtext before. In fact, it most likely relates to Castor and Pollux, which we’ll look at below.
The idea of Valhalla and a Viking funeral for the Doctor is important for several reasons. The first is that Rory gave the Doctor a Viking funeral in “The Impossible Astronaut” after River killed him. (Interestingly, though, there is a hidden face of the Doctor’s in the reflection in River’s helmet. Things didn’t quite happen the way they appeared.)
The ideas of Valhalla and a Viking funeral lead to redemption for the Doctor and his fate. We’ll look at this more in the next chapter when we examine the Victorians.
The First Time We See Friday
The first time we see Friday, something curious takes place. The Ice Warrior comes toward the Doctor in a threatening manner. However, the Doctor diffuses the situation with an Ice Warrior greeting.
DOCTOR: I know your people of old. I was once an Honorary Guardian of the Tythonian Hive.
(A rifle bolt is moved.)
However, we then hear Godsacre’s voice, and he says and does something curious.
GODSACRE: Don't move. I'll sort this beggar out.
(A red-coat with white pith helmet is pointing what ought to be a Martini-Henry breech loading rifle at them.)
DOCTOR: No, no, no, no! You don't understand. This creature is no threat. He may look like a monster to you
(A rifle shot at the Doctor's feet makes him jump back.)
GODSACRE: I wasn't talking to you. Are you all right, Friday?
The Doctor is portrayed as the monster here, not Friday. To make that clear, the Doctor even says, “He may look like a monster to you…”
This really is interesting behavior, especially since the Doctor looks human here in this altered reality. What does he really look like?
Friday, the Doctor & Shakespeare’s Henry V
Since the Doctor is metaphorically Shakespeare, it seems as though there may be another connection with both the Doctor, Friday, and Henry V. Since they can be a symbol of Odin, walking through Midgard in disguise, they could also symbolically be King Henry V, who disguises himself as a commoner and walks around camp, where nobody recognizes him as the king.
Actually, we already saw this type of thing with Queen Liz 10 in “The Beast Below,” where she walked around with her mask on, not wanting to be recognized. Therefore, we should expect that something like this is happening now.
If the Doctor has been possessed, mind controlled, or some other type of usurpation, then there is a disguise of sorts going on.
Castor & Pollux: The Master/Missy & the Doctor?
Are the Master/Missy and the Doctor mirrors of Castor and Pollux from Greek and Roman mythology? The references have come up in the subtext before, and it seems appropriate to consider this since the plan in Classic Who was to have the Master and the Doctor be brothers. However, once Roger Delgado, the 1st Master, died in a car crash, the plans never came to fruition. In fact, the 3rd Doctor, Jon Pertwee, who was good friends with Delgado, left DW because of Delgado’s death.
Anyway, there are multiple versions of the Castor and Pollux myth, where they could be brothers or half brothers, depending on the version. Since The Vikings refers to half brothers, I’ll concentrate on that version.
Castor and Pollux were twin brothers, together known as the Dioscuri or Dioskouroi. According to Wikipedia:
Their mother was Leda, but they had different fathers; Castor was the mortal son of Tyndareus, the king of Sparta, while Pollux was the divine son of Zeus, who seduced Leda in the guise of a swan. Though accounts of their birth are varied, they are sometimes said to have been born from an egg, along with their twin sisters or half-sisters Helen of Troy and Clytemnestra.
In Latin the twins are also known as the Gemini or Castores. When Castor was killed, Pollux asked Zeus to let him share his own immortality with his twin to keep them together, and they were transformed into the constellation Gemini. The pair were regarded as the patrons of sailors, to whom they appeared as St. Elmo's fire, and were also associated with horsemanship.
There was a common belief that one child would live among the gods, while the other was among the dead. That’s interesting since the Doctor is associated in multiple ways with ghosts.
Anyway, here’s yet another reference to Zeus. We know the Doctor has been cast as either a proxy to Zeus or Zeus, himself. However, there are multiple versions of the Doctor. Is one the father and one the son while a third is a ghost? Like in the Trinity?
We also see other important references. We know horses are important. Sailors could also possibly refer to space and time travelers. And the topic of eggs comes up a lot. For example, we saw the moon as an egg in “Kill the Moon.” Missy, too, mentioned that Nardole looks like and egg in “The Lie of the Land”:
MISSY: You haven't been to see me in six months. No-one has! Not even that bald bloke who looks like an egg.
However, eggs also come up in other episodes, like the 9th Doctor episode, “The End of the World,” which we looked at in the analysis of “The Lie of the Land.” And there’s an indirect reference to eggs in “The Empress of Mars” where the Doctor mentions “Tythonian Hive” when he meets Friday.
DOCTOR: By the moons, I honour thee. I'm the Doctor. What is your name?
(The Ice Warrior growls. He has one eye missing and a scrape across the helmet nose guard.)
DOCTOR: I know your people of old. I was once an Honorary Guardian of the Tythonian Hive.
(A rifle bolt is moved.)
The Tythonian Hive reference, BTW, makes no sense when relating it to Ice Warriors. The term refers to the 4th Doctor episode “The Creature from the Pit.” However, there are other important pieces of information in that episode. For example, it also refers to a pit, which Bill happens to fall into in “The Empress of Mars.”
“The Creature from the Pit,” the Egg & the Y symbol
I had never seen “The Creature from the Pit” before, so I was surprised when I watched it that there were no hives or references to Ice Warriors. I haven’t seen this happen before with a reference that didn’t make sense, but obviously, we are supposed to get other things out of that reference.
When it comes to this episode, many things don’t make sense. There is a giant structure that looks like a flat wall, but the Doctor calls it an egg and eggshell and says it’s alive:
ADRASTA: Yes. My huntsman heard you say that the shell was alive.
DOCTOR: Alive and screaming in pain.
ADRASTA: The shell? Then why can no one hear it?
DOCTOR: Because it can only be detected on very low frequency wavelengths.
ADRASTA: What's the shell screaming about?
DOCTOR: Ah. More to the point, for whom is it screaming? Its mummy? By the pyramids, imagine the size of its mummy.
Not only is it an egg, but here’s something once again that is looking possibly for it’s mummy, like “The Empty Child.” Also, it’s screaming but can’t be heard like the Star Whale in “The Beast Below.” Both the Empty Child and the Star Whale are metaphors for the Doctor.
Nardole is associated with an egg, just like the Doctor is with the moon as an egg concept. And Nardole is an unactualized mirror for the Doctor. The egg also symbolizes going back to the beginning. This meshes with other things we’ve examined like how the universe was only 23 million years old in “The Pilot.” Also, the Doctor’s timeline is going backwards, and we see that in the opening credits.
In “The Creature from the Pit,” there’s also a pit, of course, with a creature in it. The Doctor actually jumps into the pit, like the 10th Doctor jumped into the pit in “The Satan Pit.” Both find gigantic creatures. Bill falls into the pit in “The Empress of Mars” and finds a gigantic hive and the sinister Captain Catchlove.
However, the 4th Doctor calls the creature a giant brain. Um… this doesn’t make sense, either.
Here’s what the TARDIS Wikia says
The Tythonians were massive, blob-like organisms, sometimes hundreds of feet long. They were glowing green and had an outer membrane that was deeply creased. They had no true limbs, but had two large pseudopods. One pseudopod was shaped like the letter Y, while the other was simply a large tube. They had no vocal cords and communicated with the aid of Tythonian communicators. Tythonians could live for forty thousand years.
The Y shape refers to a plague of deaths. The humanoids throw people down into the pit for the creature to eat.
While this all is important, I also see the whole pit and creature reference important, which refer back to “The Satan Pit” and the war for freedom from slavery. The 4th Doctor does help free the creature in the pit, who actually doesn’t eat people.
Therefore, this episode is hugely symbolic of what is happening in Season 10; however, not by the Tythonian Hive reference.
Living Underground As a Theme
Not only do the Ice Warriors live underground, but the Silurians do too, as we saw in the 11th Doctor episodes “The Hungry Earth” and “Cold Blood.” In the 1st Dalek story, “The Daleks,” the Daleks also live underground. The creature in “The Creature from the Pit” and the Beast in “The Satan Pit” also live underground.
In all these cases, it’s not really by choice. They are forced to live underground because conditions on the surface are problematic, or the creatures are imprisoned underground.
It’s interesting that on Gallifrey everything looks dead, as far as the landscape is concerned. The Doctor and Master talked about how it used to be beautiful with grass, trees, etc. While people live in the doomed city, where do they get their food from? Of course, we are only seeing a small portion of the planet, but it still makes me wonder.
Skaro looks much the same.
Tunnels & The Thing
Interestingly, Bill mentions the movie The Thing, tunnels, and how the Doctor would like the movie because everyone dies. The latter seems really odd for the Doctor we know, unless we consider the Doctor as the mirror to alternate-Donna in “Turn Left.” Both have to die, along with the parallel world. The Master, Morbius, the Valeyard, and some others would also like to see everyone die.
BILL: (walking away) Oh, it's like the underground tunnels in The Thing.
DOCTOR: The what?
BILL: It's a movie. You'd like that one too. Everybody dies.
There are several movie versions of The Thing. In the 1982 version, the setting is in Antarctica, which fits the Ice Warriors. Where is the ice for the Ice Warriors anyway? The setting is reminiscent of “The Planet of the Ood” and the large brain found on the ice. Also, it also is the setting of “The Seeds of Doom,” another 4th Doctor usurpation story that we looked at.
The creature from a crashed spaceship can perfectly duplicate other beings, like “The Zygon Invasion” and “The Zygon Inversion.” This creates a very similar situation that we saw in “Midnight,” where at first Skye got possessed and people freaked out. The being then possessed the Doctor, and they freaked out even more. It was mob mentality and a witchhunt, just like the movie. And they turned on each other.
This also brings in the idea of “Love & Monsters,” the 10th Doctor episode where Victor Kennedy/The Abzorbaloff, absorbs people into his body.
Here are more themes that are being repeated.
The Next Chapter
In the next chapter, we’ll examine the Victorians and how Clara fits in in multiple ways, along with the ravens. I’ll show you what I call collective symbolism vs. individual symbolism.
Go to next chapter => Ch. 3: Clara, Ravens, Victoria(ns), Oh My!
#doctor who#twelfth doctor#bill potts#nardole#clara oswald#river song#eleventh doctor#amy pond#rory williams#tenth doctor#meta#analysis#the empress of mars
0 notes
Text
Hyperallergic: An Itinerant Museum Picks Apart the Language of Dehumanization
Museum of Nonhumanity, installation view (all images courtesy Momentum 9)
MOSS, Norway — A museum located inside of a kunsthall folded into a larger biennial, Laura Gustafsson and Terike Haapoja’s project for Momentum 9 is a multilayered institutional critique. Their Museum of Nonhumanity, on view at the Nordic Biennial of Contemporary Art in Moss, Norway, attempts to undermine the Western, colonial, patriarchal thinking that leads to systems of oppression, as well as the cultural centers complicit in othering, or drawing distinctions between different groups. A tall order indeed.
The museum comprises scaffolding and screens instead of walls, underscoring its temporary, unfinished quality (“being dismantled, under construction,” as Haapoja describes it to me). Their exhibition medium is primarily language itself. Throughout a 70-minute performance, archival texts, images, and dictionary entries in Norwegian and English flash on the screens mounted around the deep, dark room on the second floor of the Momentum kunsthall. Meticulously arranged, the material all relates to 14 different themes, beginning with “person” and ending with “display.” Melancholy music, heavy on violin, emanates from the ceiling. During three of the themes (“resource,” “boundary,” and “anima”), visitors can also listen to audio material with headphones placed on benches around the staggered screens. Around the back, more typical history museum fare awaits, including stuffed animals and the Norwegian constitution. These all come from nearby institutions, grounding the peripatetic work in a specific local culture.
Museum of Nonhumanity, installation view
Gustafsson and Haapoja present their language without comment. Watching stark, bold text regarding the Dred Scott case (the law labeling American slaves as three-fifths of a person), rules about animal experimentation, and the definition of the word “tender” flit across the monochromatic screens, the audience begins to analyze juxtapositions, gaps, and relevance among the assorted ideas. Depending on time of entry and duration of stay, viewers will experience the language and trajectory differently. The underlying idea — that language shapes dehumanization and othering — becomes quickly apparent. The subtle pleasure of viewing comes from gradually grasping the nuances of this process in a reflective atmosphere.
Though the pair originally considered building a massive installation of physical items to present their themes, they decided to focus instead on language, which, though immaterial, has shaped many of the world’s structures. Gustafsson and Haapoja first launched the roving museum in Finland, where they also held seminars about gender equality, empathy, and animal rights and set up a vegan café. The duo envisions the museum as a kind of utopia, “an imaginary institution in a world where there’s no more dehumanization,” says Gustafsson. In Moss, they will similarly organize site-specific programming. In June, they opened an edition in Santarcangelo, Italy, as part of a larger city festival. They’re currently in conversation with stateside organizations about bringing the project to the US. Their itinerant museum has the capacity to reach international audiences while addressing local concerns — a rare, democratic feat. They’ll also preserve the project through a book they’re publishing, featuring their source material, images of the installation, and essays.
Museum of Nonhumanity, installation view
Under Gustafsson and Haapoja’s direction, the concept of nonhumanity grows to encompass wolves, human embryos, and the Tutsi people in Rwanda. The idea of comparing how we treat these groups is a dicey proposition, which the pair acknowledges. “It’s quite delicate,” says Gustafsson; “people get offended.” Haapoja adds, “What we’re really trying to do is to show … [that] the structures of oppression are the same. The linguistic, the reasoning, and the rhetorics of how you do it — the strategy, somehow, that’s the same.”
As I viewed the work, I began considering just how “nonhuman” each element was, as though there was some kind of hierarchy. Wolves seem more nonhuman to me than embryos, which are certainly less human than Rwandan men and women. While this kind of categorization and labeling contributes to the kind of detrimental othering that leads to civil war, colonialism, and enslavement, it also bolsters the pro-choice cause and decisions to test potentially life-saving drugs on mice. Watching the displayed text leads to uncomfortable revelations about viewers’ own values, prejudices, and hypocrisies and asks us to reconsider the merit of certain categorizations over others.
The final section, “display,” includes Encyclopedia Britannica’s definition of “natural history and natural science museums.” The “natural world” it describes notably omits humans, while its undemocratic underpinnings are clear in the final line: “These museums have their origins in the cabinets of curiosities built up by prominent individuals in Europe during the Renaissance and Enlightenment.” For hundreds of years, the wealthy elite have been dictating what we can and can’t see, designating what will be preserved for posterity. As the Oxford Dictionary definition of “spectator” crosses the screen (“a person who watches at a show, game, or other event”), the work addresses its viewer, asking us to consider our own position to the themes explored. Are we merely receiving language and recycling it, or are we actively questioning it and the structures it produces? Ditto for the way we consume museum offerings — both objects and text.
Museum of Nonhumanity, installation view
If the Museum of Nonhumanity promotes a healthy rejection of elite institutional culture, it also advocates for greater acceptance of the sentient world around us. Critiquing power structures is nothing new, but Haapoja and Gustafsson are offering a powerful, physical, and very real alternative. Walk out of their exhibition and you may feel more skeptical of the biennial format and the framework that financially supports it. More than that, you might feel a greater connection to the life around you, outside the museum. Haapoja describes the xenophobia currently plaguing Scandinavia: a “specific kind of racism that comes from not being exposed to any difference.” Worldwide, populism increasingly trumps acceptance. As far as museum takeaways go, a unifying and consideration-inducing sentiment can sound a little ethereal and mawkish, but the Museum of Nonhumanity’s graceful, understated choreography makes it seem like just what we need.
Museum of Nonhumanity continues at Momentum 9 (Momentum Kunsthall, Henrik Gernersgate 8, N-1530, Moss) through October 11.
The post An Itinerant Museum Picks Apart the Language of Dehumanization appeared first on Hyperallergic.
from Hyperallergic http://ift.tt/2uAzhxk
via IFTTT
0 notes
Text
8 Viking Myths Busted
By: Emma Mason
Bearded, violent beyond reason and singularly successful at suppressing everyone around them. This, says Janina Ramirez, is the popular – yet questionable – image of Vikings. But how violent were they really, and did they actually wear horned helmets? These are myths that need to be unpicked…
An image of Viking sailors making the voyage across the Atlantic between Europe and America. One sailor is seen wearing a horned helmet. In reality, says Janina Ramirez, Viking helmets would have been simple skullcaps. Painting by NC Wyeth, c1350. (Image by Hulton Archive/Getty Images)
The Viking Age stretched from the ninth to the 11th century. During this time Viking culture had a huge impact on great swathes of Europe, Asia, Africa and even America – many centuries before Columbus sailed the oceans. They could navigate the known world and commanded respect wherever they went. Yet the Vikings are surrounded by myths. Here are eight of them busted…
Myth 1: They wore horned helmets
Let’s get this out of the way straight off. There is no evidence that the Vikings wore horned helmets, and nothing like this has ever been discovered in any archaeological dig. They certainly wore helmets but they would have been simple skullcaps, designed to protect the head from impact. Having a pair of horns on your head in battle would not have been helpful if warriors were striking at you with clubs, swords or axes.
The helmet plaques from Sutton Hoo and Vendel suggest that god-like warriors donned helmets with protruding ‘horns’ (although these are actually hook-beaked birds), but the Viking raiders and traders did not.
The modern idea of Vikings in horned helmets originated in the 19th century, but it was Richard Wagner’s The Ring Cycle [a cycle of four operas by the German composer based loosely on characters from the Norse sagas] that seared it into the modern imagination. Costume designer Carl Emil Doepler (1824–1905) created horned helmets in the 1870s for the Viking characters, and so the myth was born. Numerous cartoonists, filmmakers and artists have continued this fantasy right up to the present day.
Detail of a Viking helmet from grave one at Vendel, Uppland, Sweden, 7th century. In the Swedish History Museum’s collection in Stockholm. (Photo by CM Dixon/Print Collector/Getty Images)
Myth 2: They were a defined group
‘The Vikings’The term ‘Viking’ comes from Old Icelandic ‘Viking-r, a creek-dweller’. The Viken was the primary mercantile region of Norway, so it is possible that this apparently homogenous group of people got their name from the extensive trading they undertook out of their busy ports. The word ‘Viking’ later becomes synonymous with ‘naval raids/naval expeditions’ and begins to function more as a verb. Individuals or groups would go ‘a-Viking’, which would mean they would leave their native lands during the warmer summer months, travelling in longboats to regions where they could trade and raid.
Contemporary writers don’t use the term ‘Viking’ to speak of a group of people. Instead they referred to Norse Men, people from the North, or simply pagans (remember, those recording events were usually Christian scribes). What’s more misleading still is that ‘Viking’ has been used to denote the entire Scandinavian region, including Denmark, Norway and Sweden. Each of these regions was governed by different leaders and they would have seen themselves as distinct from one another.
These were also very varied landscapes. The more northern regions, particularly the mountainous areas of Norway, were difficult to farm because of hostile weather, while southern parts, in the plains of Denmark, were more fertile. There were occasions when Scandinavian rulers combined their forces for greater military might, but the term ‘Viking’ is like describing all ‘Northern Europeans’ as the same.
Myth 3: They were extremely violent
The Vikings earned a place in history due to their protracted raids on often vulnerable monastic sites. Populated by literate scribes, these were the worst places to attack if you wanted a good record in Christian historical documents. Alcuin of York wrote to Bishop Higbald, declaring: “Never before has such terror appeared in Britain as we have now suffered from a pagan race. . . .The heathens poured out the blood of saints around the altar, and trampled on the bodies of saints in the temple of God, like dung in the streets.”
There is certainly evidence of the violent means Vikings used to suppress people, particularly in Britain. Many skeletons have been found with the instruments of their death still wedged in their bones. A skeleton in the North Hertfordshire Museum has a Viking spear head stuck in its neck. However, while some Vikings clearly deserved their reputation as ‘wolves of war’, others lived peaceful existences – farming, trading and integrating across the four continents that they settled.
What’s more, these were violent times, and the Vikings’ aggression was matched or exceeded by other groups during this period. One of the most famous names of the early medieval period, Emperor Charlemagne, carried out a form of genocide on people in Saxony. In the ‘Massacre of Verden’ in AD 782 his army murdered more than 4,500 Saxons who had been given to him by an ally. This was violence at its most stark. And yet, because Charlemagne had a Christian biographer writing a favorable account of his life, was killing pagans and was seen as ‘father of the church’, his place in history was secure.
11th-century stained glass representing Emperor Charlemagne c800 in Saint-Saulge, France. (Photo by Keystone-France/Gamma-Keystine via Getty Images)
Myth 4: They took what they wanted and sailed away
Finds from Scandinavia do indicate that many Vikings pillaged the places they reached, bringing back coins from across the known world to be buried in hoards back in their homelands. However, many chose to remain in the lands they encountered, establishing lasting and important settlements.
One of the earliest and most extensive Viking settlements was Dublin, established by AD 841. Dublin grew into an industrially strong city with a thriving port and a mint where the first Irish coins were made. It wasn’t just Dublin that changed and developed under the Vikings. In York, the Anglo-Saxon city was relocated further towards the mouth of the river and settled by Vikings as a new and vibrant town – Jorvik. Iceland owes its settlement almost entirely to Vikings, under Ingólfr Arnanson in AD 874.
Normandy is another example of how Viking settlement could grow from violence into peaceful settlement. The Normans got their name from being ‘north-men’, yet they were given land in the north of France by king Charles III (aka Charles the Simple, 879–929) in an attempt to keep further Viking attacks at bay. Charles even gave his daughter to the Norwegian chieftain Rollo [who gained Normandy from Charles the Simple] in marriage, and the Viking settlers soon embraced French language and culture to develop into a new breed of conquerors.
Decorative Viking hoard cup made from gold and decorated with animals and foliate patterns. Found buried in England. (Photo by Universal History Archive/UIG via Getty Images)
Myth 5: They were godless pagans
They say history is written by the victors, but in the case of the Vikings, history is written by Christians. This meant that while few accounts of Viking religion survive, there are many documents written by Christian scribes that describe them as pagan and godless. This is not supported by the information we can glean from archaeology and later Scandinavian texts.
Viking religion was structured, hierarchical and based on a number of established narratives. It was not a religion of the book, and the mythology was transmitted orally.
The Vikings didn’t practise their religion in temples but rather, like the ancient Celts, held places like groves and rivers sacred. It seems that priests were involved in religious ceremonies, and these were drawn from the heads of families. Priestly office was one of the honours bestowed on kings. The priest would perform sacrifices, either of objects, animals or people.
Viking cosmology differentiated between life on Earth – Midgard – and other spiritual realms. The gods were thought to inhabit Asgard, while the sacred tree Ysgadrill stretched its roots to the lands of the gods, giants and the dead. There were at least six realms, with a special place reserved for warriors – Valhalla.
Myth 6: They were ignorant and illiterate barbarians
The Vikings were not the ignorant and illiterate barbarians that Christian writers of the time believed them to be. While they didn’t write long texts like the Sagas until later in the Viking Age, they had developed a complex script – runes – that was loaded with symbolism. Each letter in the runic alphabet was also connected with a word; the ‘f’ rune was called ‘feoh’, which meant ‘wealth’ or ‘cattle’ – this makes sense within a barter society, as cattle hides were a way of measuring wealth.
Runes could carry spiritual meaning too, and texts record how certain runes were connected with specific gods or goddesses. Rune stones included lengthy dedications and personal names. Smaller inscriptions survive on personal items like combs and weapons.
Far from illiterate barbarians, the Vikings were some of the greatest naval engineers and travellers the world had seen. Prehistoric carvings and stone ships testify to the importance of boats within prehistoric Scandinavian society and religion. By the ninth century they had developed advanced ships that could traverse the hostile Northern Atlantic Ocean. They travelled further than any single race before the modern age, and took huge risks whenever they set out on a voyage.
Viking runestone. (Photo By DEA/G DAGLI ORTI/De Agostini/Getty Images)
Myth 7: They treated their women badly
Viking society was mainly governed by ‘jarls’, the most important of whom could become kings. It was a largely military society, in which strength at arms was prized, yet wise and learned men and women could also wield power.
Women played an important role in Viking society. They were guardians of the keys to both property and wealth, particularly when their menfolk were abroad. There is evidence that some were trained to be military leaders too, with shield-maidens described throughout the mythology. Women were held in high esteem, with two buried within the famous Oseberg ship.
One of the most venerated characters in the Germanic pantheon was Freyja, goddess of sex, beauty, gold and death. She rides a chariot pulled by two cats and is accompanied by the boar Hildisvini.
Women did seem to have spiritual roles within Viking society, with wands discovered in many female graves. Furthermore, they had significantly better legal rights than their Christian counterparts and could divorce their husbands if they were violent or disrespectful towards them.
Myth 8: They were beardy and unkempt
Far from unkempt barbarians, Viking men and women were quite vain. Many finds like tweezers, combs and razors have been discovered, and it seems they went to great pains over their appearance.
They didn’t live in dark, dirty huts, but often in large and luxurious halls, like the magnificent ‘Heorot’ recorded in the epic poem Beowulf, which was the setting for lavish feasts, gifts of gold and display of skills at arms.
Viking period bone and deer antler comb and case from the Viking settlement at York, which is in the Yorkshire Museum, York. (Photo by CM Dixon/Print Collector/Getty Images)
The Vikings also had a good diet, which included a lot of fish – unsurprising given that most settlements were near to the coast. Evidence of Viking latrines shows they feasted on elk, bear, puffin, salmon and trout.
Dr Janina Ramirez is a British art and cultural historian and television presenter. She presented a BBC documentary on Icelandic literature, The Viking Sagas, and is author of The Private Lives of the Saints: Power, Passion and Politics in Anglo-Saxon England.
The post 8 Viking Myths Busted appeared first on Familiar Territory.
from 8 Viking Myths Busted
1 note
·
View note
Text
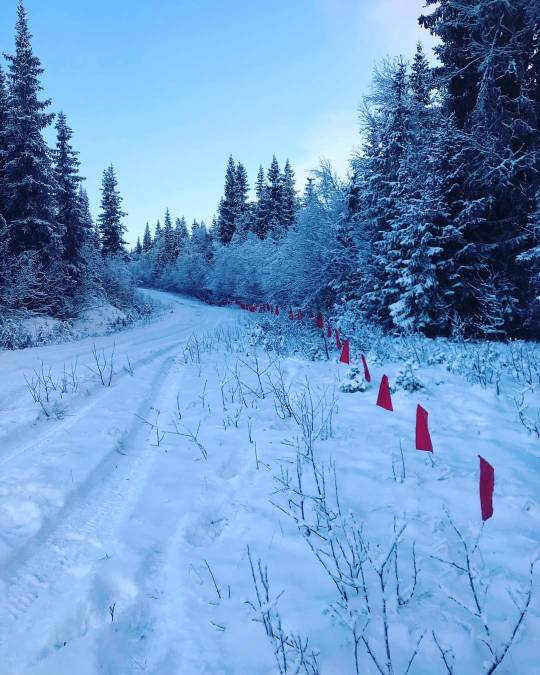

Winter and tracking snow means annual wolf hunt in Norway.
A male was shot today within this flag ring. His mate jumped over it and escaped.
47 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
THE WOLF DIVIDING NORWAY - The hunter vs. the environmentalist
“With unique access to remote communities in the snow-capped landscape of Norway, this film follows characters on either side of a fierce debate on whether to cull the wolf population. For decades the topic has split political parties, families and communities across the country, with environmentalists world-wide criticising Norway for how it handles its tiny population of critically endangered wolves. Here, a group of hunters await news from the government on whether their yearly hunt will be permitted, while the environmentalists anticipate the worst. With angry threats on both sides, the film takes a deep dive into what’s at stake for both groups, as well as the wider world.”
Trigger warning: Contains clips of blood and dead wolves.
#wolf human conflict#conflict#wolves and humans#video#videos#norwegian wolves archive#canis lupus lupus#hunting wolves#wolf hunting#culling#wolf debate#debate#documentary#documentaries#norway#norwegian#political#politics#norwegian wolf conflict#@silver-bullet-bitten#letjenna#the letjenna pack#letjenna pack#dead#animal death#dead animal#blood#death
41 notes
·
View notes
Photo
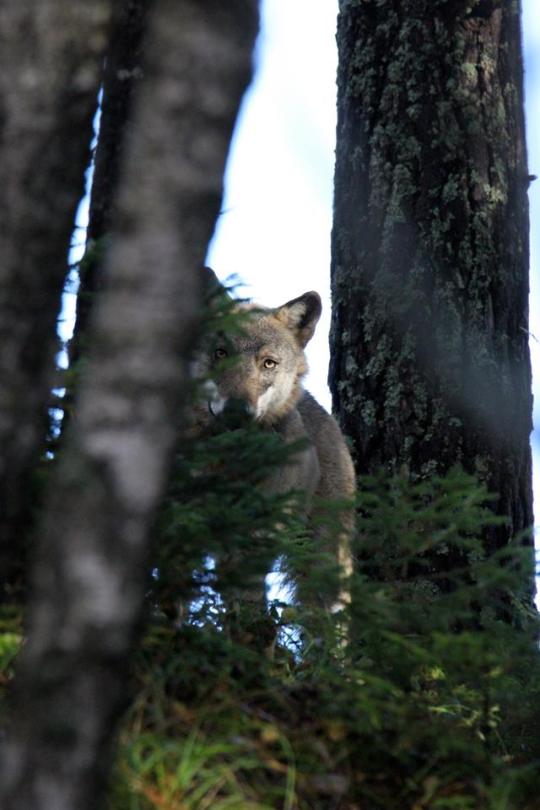

Södertörn female by Haoujin Gezeni
#wolf#wolves#canis lupus#animals#nature#wildlife#norwegian wolves archive#canis lupus lupus#södertörn female
627 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Picture by Helena Walle
The breeding male of the Østmarka pack (picture) is missing, and have been for a while. Everything points to the fact that he’s dead. Whether it was a natural death or not is of course unknown, but research by Skandulv says that every second wolf that dies is a victim to illegal hunting. A former breeding female of the pack - Frøya - also dissapeared a couple years back.
The Østmarka territory lies right outside Oslo, the capital of Norway, and is a very controversed pack. Both loved and hated. The remaining part of the pack consists of a breeding female and two pups from this year’s litter.
#østmarka pack#breeding male#male#canis lupus lupus#norwegian wolves archive#illegal hunting#skandulv#norway
190 notes
·
View notes
Photo





Pictures by Robert Huldt
Oh my! Pictures taken of this year litter of the Norwegian Letjenna pack 😍
Here’s also a recording of the pups howling together with the adults.
#he actually got a question if he was scared of them while shooting these#??#wolf#wolves#wildlife#norway#norwegian#pups#pup#puppies#puppy#litter#letjenna pack#norwegian wolves archive#wild wolves#wild wolf#wild#2017 litter#canis lupus lupus#eurasian wolf#eurasian#eurasian wolves
1K notes
·
View notes
Photo

Picture by Jan Christian Niemistö
Don’t you even think about it, young girl!
The Södertörn female is still going strong. I’m suprised how well the situation with her is working out. She is not very shy at all, and there are almost daily videos and pictures of her following riders and dog owners on their walks. She is keeping her 20-25 metres distance though. She seems like a very calm and friendly wolf. In comparison, the Vallentuna male living on the other side of Stockholm, which is the same age, and came from the same area in Norway, was a real hooligan, killing anything he came across (cats, lots of dogs, hens etc). He was also more reckless in the way he approached humans.
I hope the Södertörn female finds a mate soon, she has been alone for some while now and she’s probably lonely. She reminds me a little bit of Romeo.
#wolf#wolves#cattle#animals#nature#wolves and other animals#wolves and humans#södertörn female#norwegian wolves archive
84 notes
·
View notes
Photo

The Østmarka female and two healthy pups (Video)
#østmarka pack#østmarka female#pups#litter#puppies#pup#puppy#summer#2017 litter#norwegian wolves archive#canis lupus lupus#wild#wild wolves#wild wolf#wildlife camera
105 notes
·
View notes