#japanese grammar
Text
接続詞(せつぞくし)
conjunctions - words that are used to link phrases together
情報を加える // Adding information:
しかも besides
そのうえ moreover, on top of that
さらに moreover, on top of that
そればかりか not only that, but also...
そればかりでなく not only that, but also...
情報を対比する // Putting into contrast:
それに対して in contrast
一方 whereas
他の可能性・選択肢を言う // Giving alternatives:
あるいは or perhaps (presenting another possibility)
それとも or (presenting another option within a question)
結論を出す// Drawing a conclusion:
そのため for that reason
したがって therefore
そこで for that reason (I went ahead and did...)
すると thereupon (having done that triggered sth. to happen)
このように with this (adjusting a conclusion to the arguments given beforehand)
こうして in this way
理由を言う // Giving a reason:
なぜなら...からだ the reason is
というのは...からだ the reason is
逆説を表現する // Expressing a contradiction:
だが however, yet, nevertheless (contradicting what one would have expected)
ところが even so (spilling a surprising truth)
それなのに despite this, still
それでも but still (despite a certain fact, nothing changes)
説明を補う // Amending one's explanation:
つまり that is, in other words (saying the same thing using different words)
いわば so to speak (making a comparison)
要するに to sum up, in short
説明を修正する // Revising one's explanation:
ただし however (adding an exception to the information stated beforehand)
ただ only, however
もっとも however (obviating any expectations that might arise through the previous statement)
なお in addition, note that (adding supplementary information)
話題を変える // Changing the subject:
さて well, now, then (common in business letters after the introductory sentence; is often ignored in tranlations)
ところで by the way
#文法#grammar#conjunctions#japanese grammar#jlpt n2#japanese langblr#japanese language#language#japan#japanese#japanese vocabulary#langblr#linguistics#studyblr#study blog#studyspo#study motivation#study aesthetic#study notes#learning japanese#nihongo#日本語#日本語の勉強#light academia#light acadamia aesthetic
666 notes
·
View notes
Text
Credit to @japanese_with_josh
I found this really helpful to hear a real life situation- not just from a textbook!
#japanese#language learning#studyblr#日本語#japan#langblr#japanese grammar#study japanese#nihongo#study#learn japanese#langblog#study kanji#travel#jlptn5#kanji#languages#language study#study abroad
667 notes
·
View notes
Text
JLPT Grammar みたいだ・らしい・っぽい
What is the difference in usage among みたいだ、らしい、and っぽい? These grammar points can be difficult to differentiate, so I have gathered some notes and examples here. These grammar points are JLPT N4 or N3 grammar points.
★みたいだ★

Used for first-hand information or information you are observing for yourself.
Often used for something that has characteristics of something else (metaphorical similarities).
Most common in spoken language.
ここの砂は星みたいな形をしている。
ここ の すな は ほし みたいな かたち を して いる。
The grains of sand here are in the shape of a star.
このアパートは誰も住んでいないみたいだ。
この アパート は だれ も すんで いない みたい だ。
It looks like no one lives in this apartment building.
明日は雨みたいね。
あした は あめ みたい ね。
It looks like rain tomorrow.
リンさんみたいに日本語がうまくなりたい。
I want to be able to speak Japanese as well as Lin.
★らしい★

Used for things you infer, or information you have from another source.
Often used to something that has especially strong characteristics of its group (stereotypical similarities).
Most common in spoken language.
今日は春らしい暖かい日でした。
きょう は はる らしい あたたかい ひ でした。
Today was a warm spring-like day.
*Note: It is spring, and this is a stereotypically spring day.
私は女性らしい洋服はあまり着ない。
わたし は じょせい らしい ようふく は あまり きない。
I don't often wear feminine type clothes.
寝すぎるのは体に悪いらしいです。
ねすぎる の は からだ に わるい らしい です。
Sleeping too much is apparently bad for your body.
*Note: Second-hand source of information.
今日は君らしくないな。
きょう は きみ らしくない な。
You don't seem like yourself today.
★っぽい★

Can be used to say what something is like.
Can be used to say that something appears to be the opposite of what you would expect.
Can be used to describe something that someone is likely to do or often does.
Note:
When following a noun or い-adjective, the meaning is similar to -ish, -like, -ly. The number of adjectives that can be used with this grammar are limited. Usually negative when used after a noun or adjective, but not always.
When following a verb, the meaning is easy to do, often do. This grammar cannot be used with all verbs.
あの小学生は大人っぽい。
あの しょうがくせい は おとなっぽい。
That elementary school student acts like an adult.
油っぽい食事は好きじゃない。
あぶらっぽい しょくじ は すき じゃ ない。
I don't like oily foods.
飽きっぽいから何事も成功しないのだ。
あきっぽい から なにごと も せいこう しない の だ。
You don't succeed in anything because you are quick to lose interest.
年を取ると、忘れっぽくなる。
とし を とる と、わすれっぽく なる。
As one gets older, one tends to become more forgetful.
#日本語#japanese#japanese language#japanese langblr#japanese studyblr#langblr#studyblr#文法#japanese grammar#jlpt n3#jlpt n4#tokidokitokyo#tdtstudy
144 notes
·
View notes
Text
The difference between あのー and えーっと
As I touched on in my japanese goncharov post, it’s amazing how much novel research, entertainment, and art are locked behind a language barrier. Even though as english speakers, we are privileged to have many things translated into our language, it’s a simple fact that most things will not be translated into most languages.
I am a huge fan of ゆる言語学ラジオ, a japanese podcast about linguistics. The hosts recently released a book, 言語沼, which goes into detail about some of the subconscious rules native japanese speakers follow but aren’t consciously aware of (an english equivalent might be that adjective-ordering rule we follow e.g. big brown cow, not brown big cow). I’m finding it fascinating, and I wanted to discuss some of it here in english, because I think people learning japanese would find some of these things really useful. It’d be a shame if this knowledge stayed stuck behind the japanese language barrier when the people who would find it the most useful can’t speak japanese fluently enough to read it!
The book talks about how most Japanese people will think of 「あのー」 and 「えーっと」 as having the exact same meaning - they’re both “meaningless” filler words. Despite their belief that they’re the same, those same native speakers will subconsciously only use あのー in one particular type of situation and 「えーっと」 in another, and even feel confused or annoyed if they hear another speaker use one in the wrong context.
So what’s the actual difference? 「えーっと」 is used when the speaker is taking time to remember or solve something. For example, the following exchange is very natural:
Person A: 7 x 5は?
Person B: えーっと、35だ
This makes it a pretty versatile filler word! You can use it pretty much anywhere. Another example would be when you’re talking to yourself, trying to remember where you left your keys.
えーっと、鍵どこ置いたっけ?
On the other hand, あのー is much more specific. It can only be used when you’re taking time to figure out the best way to phrase something. For example, when you’re trying to get a stranger’s attention.
あのー、ちょっといいですか?
In contrast, if Person A was addressed with 「えーっと、ちょっといいですか?」by Person B, they’d feel it was rude because instead of considering how to say something, B is considering what to say, which gives the impression that they hadn’t even figured out what they needed to ask before addressing Person A.
This gives 「あのー」 a more ”polite” feeling than 「えーっと」, even though neither is actually more polite than the other. They’re just used in different circumstances.
Let’s quickly look at the example with the lost keys again. If you replace the filler word:
あのー、鍵どこ置いたっけ?
It is very unnatural. The authors of the book jokingly say that it sounds like you’re talking to a ghost, because 「あのー」 is only used when you’re figuring out how to phrase something, and you wouldn’t worry about that if you’re talking to yourself.
Also, did you know even japanese children properly use each filler word in the correct situation? Despite almost all japanese people (even as adults) being unaware of this rule, they’re subconsciously abiding by it even as children - just from listening to their parents follow the same rules!
It really is amazing how good your subconscious mind is at acquiring language, and how terrible your conscious mind is at it. If you’re not already, I highly recommend integrating a lot of simple language content (e.g. youtube, kids shows, etc) into your study routine - listening to people talk is simply the fastest way to become fluent in your target language.
#langblr#japanese#language learning#language acquisition#japanese language#language#linguistics#learning japanese#japanese grammar#jimmy blogthong
120 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pitch, Please Pt. 1 [new series alert]







This was launched on the Seitokai IG (seitokaisnihongo). Keep reading this post to get information that is written on the graphics (and the IG caption).
This is a new series that I've been working on for a bit! It'll be discussing pitch accent, dialects, listening comprehension, and anything else that may fall within that category.
If there's a particular dialect that you'd like for us to cover in this series, feel free to stick it in the reblogs, my inbox, my asks, on the Seitokai instagram, or the Seitokai discord server!
Without further ado, here is what the posts say above!
Pitch, Please! Let's talk about pitch accent.
What is it?
Pitch accent, known as 高低アクセント(kōtei akusento) in Japanese, refers to when a language uses pitch to distinguish between homonyms rather than stress/volume. For example: あめ, meaning rain (high pitch to low) vs あめ, meaning candy (low pitch to high pitch).
Pitch accent can vary by region and dialect. The previous example was based on standard/Tokyo dialect. However, the pitch accent is swapped with the Kansai dialect. あめ, meaning rain goes from low pitch to high and あめ, meaning candy goes from high pitch to low.
There are four (4) pitch accent patterns: 平板 (へいばん), 頭高 (あたまだか), 中高 (なかだか), and 尾高 (おだか). These will be discussed in further detail in a later post within this series.
How to work on it?
Listen to native speakers (podcasts, news channels, videos, etc.)
Converse with native speakers (if possible)
Mimic the correct pronunciation
Be willing to ask for help and accept correction
Resources
Online Japanese Accent Dictionary & Prosody Tutor Suzuki-kun
NHK Japanese Language Pronunciation and Accent Dictionary
Renshuu.org, Kanshudo.com, Forvo.com
Dogen's Japanese Phonetics Video Series
MIA add-on for Anki
MacOS dictionary
HelloTalk
If you're looking for fellow learners, there are over 500 of us in the Seitokai discord server (shameless plug) and we'd love to have you!
#japanese#learn japanese#study japanese#pitch accent#japanese dialects#japanese grammar#kanji#vocab#jlpt#reading practice#listening comprehension#reading comprehension#shay's back with another post#pitch please#linguistics#seitokai#grammar
234 notes
·
View notes
Text
understand, see, hear · particle が · particle と
(。•̀ᴗ-)✧ N5 grammar [ことのは lesson 18]

わかる, みえる, きこえる
The particle を is generally used to indicate the direct object with transitive verbs, but with the verbs: 分かる (わかる -> to understand), 見える (みえる -> to see), 聞こえる (きこえる -> to hear) you have to use the particle が
example: スパイン語(ご)が分(わ)かりますか
translation: do you understand Spanish?
particle が
we have seen the particle が being used to indicate the direct object of some verbs, but it can also express a relationship between two contrasting or opposing clauses.
example: 冬(ふゆ)ですが、 今日(きょう)は 暑(あつ)いです
translation: it is winter, but it's hot today
particle と
✩ with (accompained by): this particle is used to indicate specify the person or animal with whom an action is being performed. person/animal と -> with person/animal
example: ケンくんとこの映画(えいが)を見(み)ました
translation: I saw this movie with Ken
✩ exhaustive list nouns: this particle is used at the end of a list of two or more objects (inanimate or animate). Noun A + と + Noun B -> Noun A and Noun B
example: サラさんに 本(ほん)と辞書(じしょ)をあげました
translation: I have my book and dictionary to Sarah.
またね~@inkichan
꒰ა ˚₊ ✧・┈・╴﹕꒰ ᐢ。- ༝ -。ᐢ ꒱﹕╴・┈・𐑺 ‧₊˚໒꒱
#japanese#nihongo#studyblr#learn Japanese#learning Japanese#japanese langblr#langblog#japanese studyblr#日本語#n5#JLPT N5#grammar#basic grammar#japanese grammar#ことのは
123 notes
·
View notes
Text
N5 Grammar list
[x] だ / です (da / desu): to be (copula)
[x] だけ (dake): only, just
[x] だろう (darou): probably
[x] で (de) – 1: at, in
[x] で (de) – 2: with, by
[x] でしょう (deshou): I think, probably
[x] が (ga) – 1: subject marker
[x] が (ga) – 2: but, however
[x] くらい (kurai): about, approximately
[x] まだ (mada): still, not yet
[x] まで (made): until, till, to, even
[x] まえに (mae ni): before
[x] ませんか (masen ka): let’s, won’t you
[x] ましょう (mashou): let’s, shall we
[x] も (mo): also, too, as well
[x] もう (mo): already, anymore
[x] な (na): don’t do
[x] ないでください (naidekudasai): please don’t
[x] がある (gaaru): there is (used for non-living things)
[x] がいる (gairu): there is (used for living things)
[x] ほうがいい (hou ga ii) 1: it’d be better to
[x] ほうがいい (hou ga ii) 2: it’d be better to not
[x] いちばん (ichiban): the most
[x] か (ka) 1: or (A or B, choice between 2 objects)
[x] か (ka) 2: question particle
[x] から (kara) 1: because, since
[x] から (kara) – 2: from
[x] けれども (keredomo): but, although
[x] のがじょうず (no ga jouzu): to be good at
[x] のがすき (no ga suki): like / love doing
[x] のがへた (no ga heta): to be bad at
[x] たい (tai): want to
[x] たことがある (takotogaaru): have done before
[x] なる (naru): to become
[x] に (ni): in, at, to, for
[x] に/へ (ni/e): to
[x] にいく (ni iku): to go in order to
[x] にする (nisuru): to decide on
[x] の (no) – 1: of (indicates possessive)
[x] の (no) – 2: Verb nominalizer
[x] ので (node): because of, the reason is that
[x] ている (teiru): is/are/am doing
[x] てください (tekudasai): please do…
[x] てもいい (temo ii): is okay, is alright to, can
[x] てから (tekara): after doing
[x] てはいけない (tewaikenai): must not, may not
[x] と (to): and, with
[x] つもりだ: plan to, intend to
[x] や (ya): and
[x] より ~ のほうが ~ (yori ~ nohouga ~): is more ~ than
217 notes
·
View notes
Text
quantifier floating and differential object marking in japanese!! (??)

ok ok ok before you say sasha, not everyone has multiple degrees in linguistics, let ME just say, i bet you already know something about what i’m going to talk about here! so don’t be scared!! 全然怖くないから行こう!!
what is quantifier floating?
well, before we get to quantifier floating, let’s take a short detour to quantifiers themselves. you probably already know what these are even if you don’t know this particular name for them: it’s words like 二人 (ふたり), 1匹 (いっぴき), and 5冊 (ごさつ). you may have also heard these words referred to by the name classifiers (especially if you’ve studied a language like mandarin before). anyway, quantifiers are just words that specify an amount of something—in english, they’re words like “some” or “every.” easy!
ok, so what is japanese quantifier floating? compare these two sentences:
先生を二人探しています。
二人の先生を探しています。
if you had to guess, in which one of these sentences is 二人 “floating”? the first one, right? it’s just sort of sitting between を and the verb without any particle indicating what it’s doing there. so this is the phenomenon known as quantifier floating, and there is actually a slight difference between a floating quantifier and a quantifier attached pre-nominally with の, like in the second sentence.
what is differential object marking?
do you speak any spanish? how about hebrew? in these languages and others, there is a grammatical strategy available to speakers that allows them to distinguish between any old noun and nouns that are personally known or familiar to them. compare these two spanish sentences:
busco un profesor de japonés. = i’m looking for a japanese professor.
busco a un profesor de japonés. = i’m looking for this japanese professor...
in sentence 2, the preposition a has been inserted before the object un profesor, ‘a teacher.’ the function of this preposition is to indicate that the speaker already knows this particular professor, almost like saying “i’m looking for my japanese professor.” sentence 1, on the other hand, has no such implication, and the sense is that you are looking for just any professor who would be able to teach you japanese. so, there’s the difference: familiar nouns get “differentially marked” in object position in these kinds of languages.
what do these things have to do with each other in japanese?
now, you probably already know that japanese does not have the kind of differential object marking used in spanish, mostly because there are no articles, definite or indefinite, in japanese. so why am i bringing it up? as it turns out, even though there is no grammatical differential object marking in japanese, there are still strategies available to get a similar semantic idea across. let’s return to the first two example sentences and now translate them:
先生を二人探しています。 = i’m looking for two teachers.
二人の先生を探しています。 = i’m looking for these two teachers...
notice the difference? in japanese, when a quantifier is not floated (i.e., when it’s attached pre-nominally with の), it gives the implication that the speaker is already familiar with the noun being quantified. in other words, quantifier floating reduces quantifiers to their most basic function: as a marker of amount. in sentence 1, it doesn’t really matter who the two teachers are—the speaker is probably just looking to hire any two teachers, so long as they can teach the necessary subject. but in sentence 2, the implication is that the speaker is looking for two particular teachers, maybe who co-teach a class together or who always get coffee after school together. so, while this is not differential object marking in the strict, grammatical sense, japanese uses this quantifier-placement strategy to produce a similar semantic result.
and there you have it!! that wasn’t actually that scary, right? linguistics is not as crazy as everyone says it is, we just have a “terminology problem” that makes stuff sound 10x more complicated than it really is. (seriously, this is an actual issue in the field. people can’t understand each other bc they were trained on different sets of terminology lol. #academia)
anyways, i hope this was clear and helpful, and feel free to send me any asks about grammar or semantics or whatever!! 週末を楽しんでね!!✌️

#langblr#japanese langblr#日本語#linguistics#japanese grammar#sorry i have no actual sources for this but if anyone wants one i will go find some!!#just lmk#sasha.txt#grammar
279 notes
·
View notes
Text
N5 Grammar Review: Vない
The ない form of the verb is used to mean "not" or "don't". I'm going to make some posts about grammar that uses this form soon, but first I thought it'd be good to go over how exactly we get the ない form.
To make the ない form:
Group 1: change the last 'u' in the dictionary form to 'a', then add ない:
書く(かく)→ 書かない [to write -> not write]
話す(はなす)→ 話さない [to speak -> not speak]
立つ(たつ)→ 立たない [to stand -> not stand]
遊ぶ(あそぶ)→ 遊ばない [to play -> not play]
読む(よむ)→ 読まない [to read -> not read]
知る(しる)→ 知らない [to know -> not know]
Be careful! If the verb ends in う, it becomes わ:
歌う(うたう)→ 歌わない [to sing -> not sing]
買う(かう)→ 買わない [to buy -> not buy]
Group 2: add ない to the stem:
食べる(たべる)→ 食べない [to eat -> not eat]
寝る(ねる)→ 寝ない [to sleep -> not sleep]
見る(みる)→ 見ない [to see -> not see]
教える(おしえる)→ 教えない [to teach -> not teach]
Group 3 of course is a bit different:
する → しない [to do -> not do]
来る(くる)→ こない [to come -> not come]
The ない form is used in casual speech to mean "don't/doesn't do":
Particles in brackets because you can drop them in casual speech.
魚(は)食べない
さかな(は)たべない = I don't eat fish
父(は)雑誌(を)読まない
ちち(は)ざっし(を)よまない = My dad doesn't read magazines
コーヒー(を)全然飲まない
コーヒー(を)ぜんぜん のまない = I don't drink coffee at all
Other than that, the ない form is used a lot as a base for more complex grammar. It's important to get to grips with it early on.
I'm still a beginner myself (I'm only N4 level!) so please let me know if I've made any mistakes!
#japanese langblr#learning japanese#japanese grammar#japanese for beginners#beginner japanese#n5#n5 grammar
99 notes
·
View notes
Text
How To Read and Understand Japanese Sentences.
As you know, Japanese language is a SOV (Subject-Object-Verb) pattern while English is SVO pattern.
Some learners may know a good amount of vocabulary words but they still cannot understand the meaning of a sentence even if they know how to read every single word in that sentence. Why is that so?
This may be due to learners reading the wrong way. In order to understand Japanese sentences, follow the following steps:
1. Identify the subject with the noun followed by either a は or が. (Usually in the beginning of a sentence but there are some writers who purposely put the subject in the middle.)
2. Read the end of the sentence to locate the verb. Yes, you read this right. Just go straight to the end of the sentence to identify the verb.
Example:
私はその人を常に先生と呼んでいた。
In this sentence, the subject is 「私は」。Next, go straight to the end and identify the verb
Here, the verb is 「呼んでいた」 which means "called".
So now, you know what the subject is doing with 私は and 呼んでいた which means "I called."
Next, read the rest of the middle part 「その人を常に先生と…」 meaning "that person always teacher"
The whole sentence means "I always called that person as teacher."
Note: This sentence is the first opening line from the Japanese classic literature novel 「こころ」 by 夏目漱石。
#japanese#japanese grammar#jlpt#jlpt n1#jlpt n2#jlpt n3#jlpt n4#jlpt n5#language#learn japanese#nihongo
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
JLPT N2 grammar notes ~たとたん(に)
~たとたん(に)as soon as ~; right after ~
Attached to a verb that expresses a momentary movement or change. In the sentence that follows, something a bit unexpected happens.
Not used for speaker’s wishes/intentions (~よう), lobbying/urging (~ませんか・~なさい).
疲れていたので、ベッドに入ったとたん、眠ってしまった。(Because I was tired, I fell asleep as soon as I got to bed.)
夏は窓を開けたとたん、蚊が入ってくる。(In the summer, as soon as you open a window, mosquitoes come in.)
掃除機のスイッチを入れたとたん、家の電気がすべて消えてしまった。(As soon as I turned on the vacuum cleaner, all the electricity in the house went out.)
An example from figure skating:
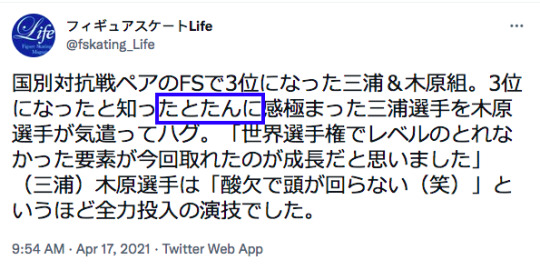
3位になったと知ったとたんに感極まった三浦選手を木原選手が気遣ってハグ。(As soon as he realized they had gotten third place, an emotional Miura-senshuu hugged Kihira-senshuu caringly.)
60 notes
·
View notes
Text
改まった形|Polite Forms
In formal settings like in a business meeting or at a public gathering some words are switched with politer forms. You often hear them when somebody is giving a speech, holding a presentation or on TV. But they appear in written form as well, especially in business context. Basically, everywhere where keigo is used, it is also expected to apply politer forms.
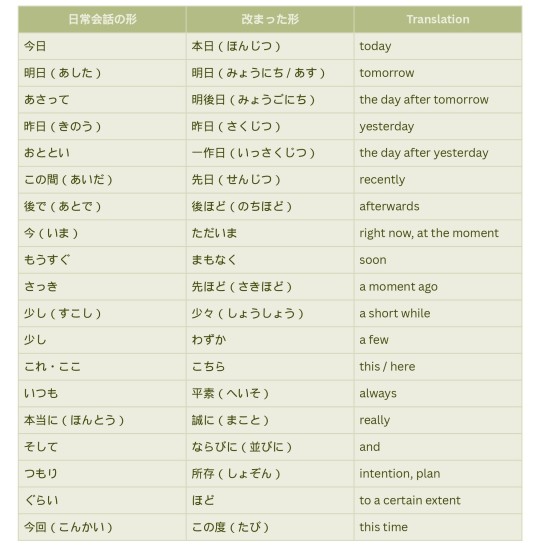
#文法#敬語#japanese langblr#langblr#studyblr#study movitation#learning japanese#japanese vocabulary#japan#japanese#study blog#study notes#language blog#keigo#japanese studyblr#japanese grammar#japanese language#日本語#日本語の勉強#nihongo
156 notes
·
View notes
Text


カフェで日本語を勉強している૮꒰ྀི >⸝⸝⸝< ꒱ྀིა これはげんき2の練習だ。皆、日本語が頑張ってね!
#japanese#language learning#studyblr#日本語#japan#langblr#japanese grammar#nihongo#learn japanese#study kanji
125 notes
·
View notes
Text
JLPT Grammar げ・がち・っぽい・気味
What is the difference in usage among げ、がち、っぽい、and 気味? These grammar points can be difficult to differentiate, so I have gathered some notes and examples here. These grammar points are JLPT N3/N2 grammar points.
★~げ★

This is used it to describe something or someone (not yourself) who looks~ / seems~ / appears to~.
It is similar to そ��に・そうな (sou ni / sou na), but げ (ge) is much more restricted with what words it can be paired with.
It is usually used to describe things like one’s emotions or state of being, whereas そう (sou) can be used with more general things like weather, etc.
Although this grammar is mostly used with adjectives, it can also be used with some verbs and nouns.
何か、言いたげだね。
They look like they want to say something.
ずいぶん、自信ありげだね。
You seem very confident.
そりゃあちょっとあやしげに見えますからね、そう思いませんか?
Well, that looks a little suspicious, don't you think?
同級生にテストの結果を聞くと、嬉しげな顔で100点だったと答えてくれた。
When I asked my classmate how they did on the test, they answered with a happy face that they got a perfect score.
★~がち★

This is usually used for something negative.
ありがち = tend to have
になりがち = tend to become ~
遅れがち = tend to be late
留守がち = tend to be absent
彼は、学校をサボりがちです。
He is always skipping school.
ずっと曇りがちの天気が続いている。
The constant cloudy weather keeps continuing.
一人暮らしなので、コンビニ弁当ばかり食べがちだ。
I live alone, so I tend to only eat convenience store meals.
私は空腹の時は機嫌が悪くなりがちだ。
When I am hungry I easily get into a bad mood.
★~っぽい★

① When following a noun or い-adjective, this means -ish, -like, -ly. Note: The number of adjectives that can be used with this are limited.
子供っぽい = childish, childlike
男っぽい = manly, like a man
女っぽい = womanly, like a woman
油っぽい = oily, lots of oil
② When following a verb, this means easy to do, or often do~. Note: This cannot be used with all verbs.
忘れっぽい = easy to forget, often forget
怒りっぽい = easy to anger, often angry
このコート、デザインはいいけれど、生地が安っぽいね。
This coat has a nice design, but the material looks cheap.
油っぽい食事は好きじゃない。
I don't like oily foods.
年を取ると、忘れっぽくなる。
As you get older, you become more forgetful.
君は飽きっぽいから何事も成功しないのだ。
You do not succeed in anything because you are quick to lose interest.
★~気味 (ぎみ)★

This is used to express that something looks or seems to be a certain way.
疲れ気味 【つかれぎみ】= looks / seems tired.
太り気味 【ふとりぎみ】 = looks / seems large
遅れ気味 【おくれぎみ】= tends to be late
寝不足気味 【ねぶそくぎみ】= looks / seems to be sleep deprived
残業続きで疲れ気味だ。
I've been feeling rather tired because of continuous overtime work.
新入社員は緊張気味の顔をしていた。
The new employee looked nervous.
彼は人の名前を忘れ気味である。
He tends to forget people's names.
彼女は遠慮気味にそう言った。
She said that hesitantly.
#日本語#japanese#japanese language#japanese langblr#japanese studyblr#langblr#studyblr#文法#japanese grammar#jlpt n2#jlpt n3#tokidokitokyo#tdtstudy
107 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why are anime translations so bad?
Disclaimer: I have never done any professional translation, and I don’t watch dubbed/subbed anime very often. But recently I watched a few episodes of subbed Demon Slayer at a friend’s place, and I noticed how bad some of the translations were. It reminded me of my childhood, watching subbed Ghibli movies and thinking “that english sounds weird”. As a kid I thought it was an unavoidable part of translation, but now that I can speak Japanese, I realise that we can do so much better with translations!
This post is my attempt to identify what a “bad” translation is, and hazard some guesses at what mistakes translators make that lead to these bad translations.
Examples are from Ranking of Kings, episodes 10 and 11. Screenshots taken from Crunchyroll.
What do I mean by bad?
Reason 1: They don’t sound like natural English.
If a character in an english cartoon said some of the stuff that characters in anime say in translations, it would sound very unnatural. Anime-translation english is unnatural and awkward sounding.

ダイダ様、久しぶりに街に出てみますか?
Price Daida, it’s been a while, so why don’t we go down into town?
This example sounds awkward. What’s with the random “so” in the middle of the sentence? No one in English media talks like that. If you just remove the “so” and replace it with a full stop, we get a much more natural sounding sentence.
Price Daida, it’s been a while. Why don’t we go down into town?
Or even something like this:
Price Daida, why don’t we go into town? It’s been a while since you’ve been down there.
Reason 2: They don’t fit the character.

This screenshot shows the character Kage speaking (the black blob). He has a character trait of being kind of immature and almost never using polite Japanese, even to royalty, which is very disrespectful. The original translation makes him sound so formal! Kage is supposed to sound like a 15 year old who tries way too hard to be rough and intimidating. Can you imagine someone like that saying “You may say those things”?
いやいやいや、なんかいい感じなこと言ってるけど、違うからね!
No, no, no! You may say those feel-good things, but reality is different!
It doesn’t preserve his characterisation at all. Way too formal and not juvenile enough! A better translation would be:
No, no, no! Nice motivational speech, but they’re just words!
The devil’s advocate & descriptivism
Now, I’ll preface this by saying I am a hardcore descriptivist. I’m not saying that these translations are wrong, or that the resulting English is incorrect English. What I’m saying is that they do not achieve the goals of a good translation, those goals being preserving what is being said and how it’s being said.
It could be argued that by now, anime translations have become a new dialect of English. Anime fans have come to expect the awkward-sounding phrasing, and instead might see natural English as unexpected. This is a fine rebuttal of my first point (it sounds awkward) but not of my second point (speech-pattern-based characterisation is often lost). Even then, anime translations are not exclusively for established anime fans. First time viewers may be put off by the unnatural language choices and strange turns of phrase. “Anime is cringe” they might say, and they wouldn’t be wrong. A good translation should be understandable to the entire target audience, and first time or casual viewers certainly make up a large portion of that target audience.
Why do the translations end up so bad?
They err on the side of direct translation over meaning-based translation
Often, it seems like the main nouns and verbs in the sentence get translated verbatim, and the rest of the translation is forced to bend around those. In addition, they do not consider how a similar sentiment might be phrased in english. Even if it’s a japanese way of saying something, they preserve the individual words instead of changing the whole sentence. Let’s look at the Kage example from before:
いやいやいや、なんかいい感じなこと言ってるけど、違うからね!
No, no, no! You may say those feel-good things, but reality is different!
I’ve coloured the text so you can see which pieces got translated separately. In this example, basically every word is being translated separately. Now let’s look at my example:
いやいやいや、なんかいい感じなこと言ってるけど、違うからね!
No, no, no! Nice motivational speech, but they’re just words!
I’m translating the entire middle verb phrase as one atomic piece of meaning. It’s not individually important that, for example, the specific word 言ってる was used, so it’s not important that I translate it directly to the word “say”. What is important is that Kage is saying that Despa is saying some nice stuff, but it doesn’t change the facts. I have a feeling that the more you can group words together and translate them as a whole phrase, the more natural the translation ends up sounding (and the more characterisation you can preserve).
They use weird words, due to dictionary translation
Let’s look at another example:

兄上は弱者だと、どこか甘えていないか?
Aren’t they sort of spoiling Brother, just because he’s a weakling?
In this example, the word 弱者 is translated as “weakling”. “Weakling” is a pretty rare word to hear outside of anime. That’s probably the best direct translation if we’re looking at the word 弱者 out of context. However, words always appear in context. Both times the word 弱者 is used to refer to a person in this episode, it’s used to refer to disabled people (Bojji, who is deaf, and a citizen, who is both blind and deaf). The citizen is actually not physically weak, in fact he looks pretty chunky and strong, so 弱者 is not being used to refer to his physical strength, only his disability. The English word “weakling” strongly suggests physical weakness, so I don’t feel like it’s appropriate here. Instead, I feel like a more appropriate translation would be:
Do you think Brother gets special treatment, just because he’s so pathetic?
Daida is immature and heartless at this point in his character. He has contempt for both Bojji and the citizen, and sees them as weak, but he also feels pity for them. I think the word “pathetic” sums up his emotions for them much better than the word “weakling”, as well as not coming loaded with the incorrect “physical weakness” connotation.
As a side note, you may have noticed I translated the first part of the sentence differently too. That’s another example of how (in my opinion) grouping words together to translate a phrase as a whole results in a much more natural phrasing.
They try to preserve the original grammar
An important skill to have when translating is knowing which aspects of the phrase are important to preserve in translation, and which parts are not important. Word order and grammar are almost never important enough to preserve.

ダイダ様こそ、選ばれた人間。
Prince Daida, you are one who is chosen.
In this example, the past tense verb 「選ばれた/chosen」modifying the noun 「人間/person」 seems to have been determined to be important to preserve by the translator, which leads to the awkward phrasing “one who is chosen”. In reality, the minutia of the original grammar is not important to preserve - we can translate 選ばれた人間 as a set phrase rather than translating the words individually:
Prince Daida, you are one of the chosen few.
Again, we can see that the translation is improved by grouping words together and translating the phrase as a piece of atomic meaning!
Anime translation is a naturally restrictive medium
For dubs, the characters’ mouth movements need to match up. This really narrows down the possibilities of translation options. It means that sub-optimal word choices may be used, and the rhythm of speech may be forced into an odd speed in places.
For subs, although the syllables and mouth movements don’t need to match up as perfectly as they do in dubs, the subtitles still end up needing to be applied over the same moments of speech. However, often, if the given situation in the anime was to be completely reframed in English, maybe no one would have said anything at that moment. There are times when someone would say something in Japanese that you would expect someone to not say anything in english.


デスパー:弟子の悪口は許しますけど、私の悪口は許しませんよ!!
カゲ:逆でしょ!!!!
Despa: You can insult my apprentice, but I won’t let you insult me!
Kage: You’ve got it backwards!
In Japanese comedy, the role of ツッコミ (best translation is “the straight man”) is ubiquitous and plays the part of a laugh track - telling audiences when to laugh. In this case, Kage is playing the part of ツッコミ by pointing out that what Despa has said is the opposite of what you’d expect him to say. In this example, I feel like if this was an English cartoon, Kage wouldn’t have said anything. English speaking comedies generally expect/trust audiences to get the jokes without them being explicitly pointed out. I feel like this shows how attempting to fit subtitles to every spoken phrase can lead to slightly unnatural turns of phrase, since the translator is attempting to fit some speech into a place where there wouldn’t have been any in the first place. In my opinion, the best “translation” for the above would have been to cut the 1 second clip where Kage butts in with his line altogether.
———
Again, I should reiterate that I’m not a translator. I’m very keen to hear counter-arguments if you disagree with what I’ve said! Translations have got me really interested recently and I’m hungry for more opinions.
#langblr#japanese language#japanese#japanese grammar#learning japanese#linguistics#translation#language acquisition#language learning#language#anime#ranking of kings
331 notes
·
View notes
Text
Recommendation: Apps for Japanese Learning




Over the years, I've downloaded and tested many apps. Though my favorite app was discontinued (I miss you, mindsnacks Japanese), there are still others that I don't think I'll be removing from my phone any time soon. In light of duolingo's horrible update causing a large migration and search for other apps, I thought I'd share some of my favorites. Also, some of these apps have websites or discords for you to interact with other users or to ask support questions.
For those who cannot use/don't like the graphics, the written out version is below the break.
Lingo Legend
RPG-based language learning game that I was a beta tester for. It also offers Spanish, French, Japanese, Korean, Mandarin Chinese, German, Italian, and Portuguese. Uses spaced repetition.
Offers beginners, intermediate, and advanced levels.
User can jump between lessons and difficulty levels.
Available on ios and android
Manabi Reader
Caters to all JLPT levels and offers reading options on an array of topics (including news, games, reddit). Can hilight words and look up in-app. User can also paste a link within the app to read.
Companion app available (Manabi Flashcards).
Available on ios
TODAI: EASY Japanese News
Aggregates news from various sources.
Offers practice JLPT exams in-app.
Offers grammar resources and in-app dictionary that can generate flashcards from words saved in notes.
Offers audio listening, as well as videos with transcriptions.
Available on ios and android. Also has a website.
Shirabe Jisho
Offline dictionary app.
User can favorite words, make lists, take notes, make flashcards, etc.
User can search for words in kana, romaji, drawing, or through radical (or radical building).
Available on ios
Renshuu
Think quizlet, but solely for Japanese. You can create your own lists, use others, play shiritori, earn prizes and interact on forums.
You can study grammar, kanji, vocab, flashcards, learn and submit mnemonics. You can also friend people.
Available on ios and android. Also has a website (of which I am an avid user).
Connect with me: Ko-fi Shop & Tips | Discord | Studygram | Ask Box
↳ psst! my ko-fi shop has learning resources on it. try to check back for new things bc im always working on something to add in there
#onigiristudies#heydilli#jpnstudynet#look toki#looktoki#look asta#japanese#langblr#study japanese#learn japanese#language apps#jlpt#jlpt kanji#jlpt studies#kanji#japanese grammar#日���語#勉強#learning through immersion#bookblr#studyblr#hey guys#kingyo hut#my shop#thanks for reading my research posts and my suggestion posts
1K notes
·
View notes