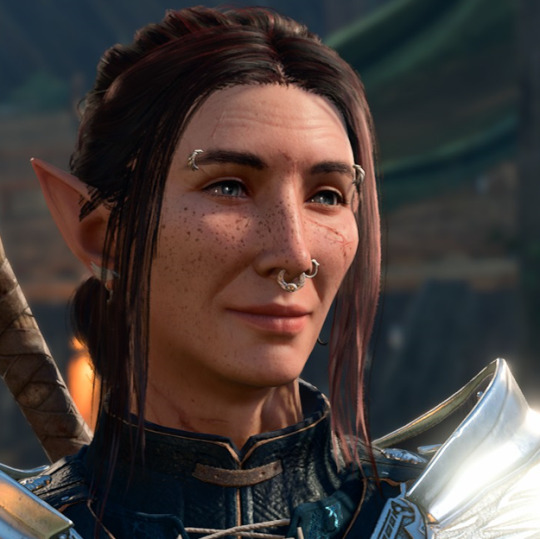
#despot bear
Text
oh tbh is your autism creature? well this is MY autism creature so get on my level
#radiohead#autism#neurodivergent#shitpost#despot bear#modified bear#yes im a filthy radiohead cretin point and laugh
346 notes
·
View notes
Text
I don't listen to radiohead but these bears man

33 notes
·
View notes
Text
i literally spend at least 2 hours a week just looking at various pictures of the terracotta army. utterly entranced. look at the details in the hair. you'd never see ANY of this when they're lined up in formation, but they're there.
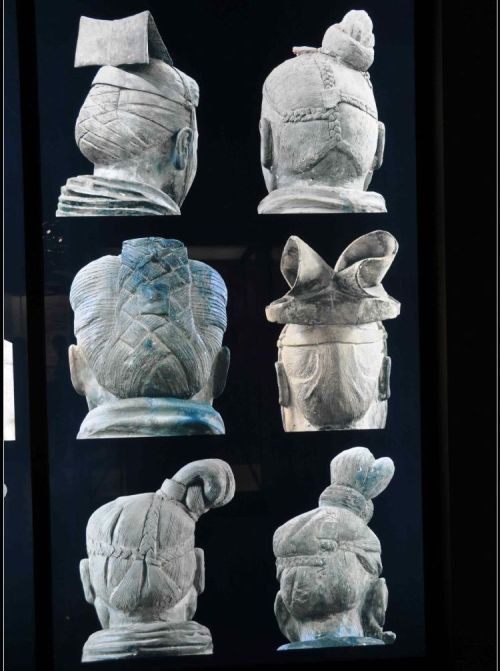

theres about 8000 of these guys down there, no two faces are alike. they're works of art. they're the manifestation of a cruel despot's delusions of grandeur. a talisman against the terrible inevitability of death, both pathetic and strangely pitiful. like watching a child clinging to his blanket, begging you not to turn off the light. they were a bunch of insignificant clay statues from a side chamber that was so small and unremarkable, no one bothered to write down the location. they were modelled after real people. their only purpose was to serve qin shi huang in the afterlife, so he could reign in heaven as he did on earth. now the emperor is just a ghost and his pawns are immortal. my dad and i visited them in the dead of winter, on a weekday, just so we wouldn't have to deal with tourists like us. the place had easily 500 people--not including the ones below ground. we traveled to xian via the old "green skin" diesel train. there are faster means, like highspeed rail but dad insisted i try the authentic way, the same way he would have traveled when he was my age it was also like, a quarter of the price but im sure that had nothing to do with it! back in the 80s carriages would get so packed people had to have their luggage passed in via the windows. as we chugged along, i read my book and my dad made us cup noodles. car is just a shortened version of "carriage", the word is the same but the mechanism is different. it's the same in chinese. i think if i told someone from the warring states period i could travel from the Kingdom of Qi to Qin in just four hours with my metal carriage, i'd be laughed out of town--or accused of being a spy and sentenced to 'death by carriage.' we hopped off the train at 4am and took a different "carriage." the taxi driver joked; "basically every dynasty put their capital in xian, stick a shovel anywhere and you'll turn up some national treasure or another." i wonder what it would have felt like to be a farmer digging a well and then out pops a remarkably realistic human head. statistical analysis show the soldier's faces bear a strong similarity to people living in the region today. the taxi stopped in front of a jewellery-hawking tourist trap and refused budge an inch until we went inside. did you know the terracotta soldiers were originally multi-coloured and painfully gaudy, just like the greek marbles? they were made assembly-line style. the arms and legs were made from the same workshops that made clay plumbing pipes and roof tiles. for quality control, the artisans were required to stamp their names. the workers who built these tombs were executed shortly afterwards, because only dead men can be trusted with secrets. qin shi huang's mausoleum is unlikely to be excavated in my father's lifetime, or mine, not unless i'm willing to take a BIG ONE for the team... instead of the tomb, they built some kind of qin shi huang-themed theme park next to it. not only was it tacky as hell the entrance fee was like $50. we went to the museum and i looked at bronze tools and pottery shards for three hours. look why can't we just crack the thing open i can't be the only one here whos dying from curiosity what if we all just took turns digging
#qin shi huangs terracotta army#warring states#qin dynasty#thinking about Her...<3 bronze tools and pottery shards <3#my writing
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
“On the one hand, my quest for revenge on the despot who destroyed my idyllic hometown bottomed out when I finally got him at my mercy and realized that his own horrific life circumstances had left him a bitter, unsatisfied shell of a person and that killing him could bring no plausible catharsis, only pointlessly adding another body to a growing stack. On the other hand, my initial impulse to seek revenge directly resulted in my piecemeal accruement of a found family with whom I found a positive feedback loop of character growth and moral maturation, which was in large part what made it possible for me to envision a life outside the narrow dictates of my shortsighted revenge quest. Also, we toppled a tyrannical government and ran every errand on this half of the continent. Honestly there are a lot of second-and-third-order positive effects of how badly I used to want to kill that guy. And obviously I’m a consequentialist now, since I didn’t kill that guy, so obviously I’d like to preserve those effects if at all possible. So I guess if I was to generalize from this whole experience, I’d say that we need to institutionally cultivate the impulse to seek violent revenge on wrongdoers, I mean it really gets you off your ass, but we also have to cultivating and elide the secret, load-bearing expectation that you should call it off at the very last second. We might need to train a whole secret corps of sleeper found family members, to inject themselves into organically forming epic revenge quest parties, prime the soil, so to speak, subtly draw the revenge party’s attention to, like, the material causes at the root of human of evil, or stuff like that, put the brakes on the pain train juuuuust enough to get us back in that sweet sp- fuck. Someone already had this idea, didn’t they. That’s what this whole thing was. This thing we just did. Fuck. I was going to make a fucking fortune franchising this. Fuck”
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Thinking once again about the anniversary dinner, and about how the unusual isolation of Canaan House gives us the wrong impression about the lives of the scions, who would normally be surrounded by those retainers, attendants, and domestics forbidden in the Emperor's letter.
The Fifth clearly not only can and do cook, but enjoy doing so. If they're casually throwing together a dinner party for 20 people, you have to assume they've done something in that ballpark before.
But for all that we get Magnus' self-effacing comments about being better at making dessert than duelling and non-threatening, apron-wearing Abigail, this is something that will be very much a hobby for them. Abigail is the feudal despot of perhaps the most powerful House in the Dominicus System, and Magnus is a chief civil servant at the heart of the imperial bureaucracy. They may have the facilities to and enjoy cooking for each other and their friends. But they are almost certainly not doing that regularly.
Nor are they hosting a dinner party in quite the way us plebs would think about it.
Most of us probably don't casually invite 20 friends, acquaintances, and rivals round on whim, but then again, most of us don't have the domestic assistance they're clearly used to and still have access to in Canaan House:
"The appearance of two skeletons bearing an enormous tureen of food...under Abigail's direction, they filled everyone's bowl..."
"...the various Houses stood around with warm cups in their hands to watch the skeletons clear up...listening to...the clatter of skeletons with used up knives and forks."
They may have cooked a fantastic spread, but it seems like the tables have been set (with those "yellowing tablecloth[s]" brought out of "deep storage") by the skeleton servitors. The food has been served and cleared away by them. Perhaps they have also been involved in some of the preparation - after all, it is much more pleasant to cook when you don't have to chop onions for 20.
#the locked tomb#tlt meta#abigail pent#magnus quinn#I once briefly found myself on 'private chefs to the wealthy' Tik Tok#Where bringing in staff to help prep and to serve the intimate dinner party for your closest 20 friends seems to be the done thing
109 notes
·
View notes
Text
𝖘𝖎𝖈 𝖘𝖊𝖒𝖕𝖊𝖗 𝖙𝖞𝖗𝖆𝖓𝖓𝖎𝖘
A well regulated Militia, being necessary to the security of a free State, the right of the people to keep and bear Arms, shall not be infringed. — U.S. Constitution Second Amendment
The militia of the United States consists of all able-bodied males at least 17 years of age... — 10 U.S. Code § 246
Patrick Henry
* “Guard with jealous attention the public liberty. Suspect everyone who approaches that jewel. Unfortunately, nothing will preserve it but downright force. Whenever you give up that force, you are inevitably ruined.”
George Mason
* “To disarm the people…[i]s the most effectual way to enslave them.”
James Madison
* “The right of the people to keep and bear arms shall not be infringed. A well regulated militia, composed of the body of the people, trained to arms, is the best and most natural defense of a free country.”
* “The ultimate authority, wherever the derivative may be found, resides in the people alone.”
Noah Webster
* “Before a standing army can rule, the people must be disarmed; as they are in almost every kingdom of Europe. The supreme power in America cannot enforce unjust laws by the sword; because the whole body of the people are armed, and constitute a force superior to any bands of regular troops that can be, on any pretense, raised in the United States.”
Samuel Adams
* “The Constitution shall never be construed to prevent the people of the United States who are peaceable citizens from keeping their own arms.”
Richard Henry Lee
* “A militia when properly formed are in fact the people themselves…and include, according to the past and general usuage of the states, all men capable of bearing arms… “To preserve liberty, it is essential that the whole body of the people always possess arms, and be taught alike, especially when young, how to use them.”
Thomas Jefferson
* “I prefer dangerous freedom over peaceful slavery.”
* “What country can preserve its liberties if their rulers are not warned from time to time that their people preserve the spirit of resistance. Let them take arms.”
* “The laws that forbid the carrying of arms are laws of such a nature. They disarm only those who are neither inclined nor determined to commit crimes…. Such laws make things worse for the assaulted and better for the assailants; they serve rather to encourage than to prevent homicides, for an unarmed man may be attacked with greater confidence than an armed man.”
* “The Constitution of most of our states (and of the United States) assert that all power is inherent in the people; that they may exercise it by themselves; that it is their right and duty to be at all times armed.”
**********************************
No emergency justifies the violation of any of the provisions of the United States Constitution.
----------------------------------------------
Ex parte Milligan, 71 U.S. 2 (1866) which yet stands to this day: "The Constitution of the United States is a law for rulers and people, equally in war and in peace, and covers with the shield of its protection all classes of men, at all times, and under all circumstances. No doctrine, involving more pernicious consequences, was ever invented by the wit of man than that any of its provisions can be suspended during any of the great exigencies of government. Such a doctrine leads directly to anarchy or despotism..."
----------------------------------------------
Volume 16, American Jurisprudence 2d, § 52: “It is sometimes argued that the existence of an emergency allows the existence and operation of powers, national or state, which violate the inhibitions of the Federal Constitution. The rule is quite otherwise.
No emergency justifies the violation of any of the provisions of the United States Constitution. An emergency, however, while it cannot create power, increase granted power, or remove or diminish the restrictions imposed upon power granted or reserved, may furnish the occasion for the exercise of power already in existence, but not exercised except during an emergency... The Constitution of the United States is the law for rulers and people, equally in war and in peace, and covers with the shield of its protection all classes of men, at all times, and under all circumstances”
----------------------------------------------
Volume 16, American Jurisprudence 2d, § 177: "The general misconception is that any statute passed by legislators bearing the appearance of law constitutes the law of the land. The U.S. Constitution is the supreme law of the land, and any statue, to be valid, must be in agreement.
It is impossible for both the Constitution and a law violating it to be valid; one must prevail. This is succinctly stated as follows: The general rule is that an unconstitutional statute, though having the form and name of law, is in reality no law, but is wholly void, and ineffective for any purpose; since unconstitutionality dates from the time of its enactment, and not merely from the date of the decision so branding it.
An unconstitutional law, in legal contemplation, is as inoperative as if it had never been passed. Such a statute leaves the question that it purports to settle just as it would be had the statute not been enacted.
Since an unconstitutional law is void, the general principals follow that it imposes no duties, confers no rights, creates no office, bestows no power or authority on anyone, affords no protection, and justifies no acts performed under it... A void act cannot be legally consistent with a valid one. An unconstitutional law cannot operate to supersede any existing valid law. Indeed, insofar as a statute runs counter to the fundamental law of the land, it superseded thereby. No one is bound to obey an unconstitutional law and no courts are bound to enforce it."
----------------------------------------------
“All laws, rules and practices which are repugnant to the Constitution are null and void ...if any statement within any law which is passed is unconstitutional, the whole law is unconstitutional.” Marbury v. Madison, 5th U.S. 2 Cranch 137, 180.
----------------------------------------------
"Even a state of war and the declaration of secession by the people cannot suspend the Constitution or remove its protection." Houston County v Martin, 232 Ala 511, 169 So. 13.
145 notes
·
View notes
Text
LAZAREVIC SISTERS V
Olivera Lazarevic

Early Life
Olivera Lazarević, also often referred to in Byzantine and Greek sources as Maria, was the fifth child and youngest daughter of Knez Lazar and his wife Milica.
She was likely born around 1372/1373 and raised in her father’s capital, Kruševac, receiving the same education as her elder sisters, under the guidance of their mother and maternal aunt, Nun Jefimija.
Like most in her family, she was a fanatic of the arts and literature. Though she was never an artist in her own right, she acted as a patron of it.
There is a folk legend that in her youth, Olivera caught the attention of the Serbian knight, Miloš Obilić, who happened to be a frequent visitor at her father’s court and was considered one of the family.
This attraction led to a marriage proposal by Obilić, yet he was refused by her father, using her young age as an excuse.
Marriage to Sultan Bayezid I
Following the Battle of Kosovo in the summer of 1389, and the death of Sultan Murad I and execution of Knez Lazar, the Serbs abided themselves in a vassalage to the Ottomans due to the Hungarian attacks, who wanted to take charge of Serbia and the advancement of the Ottomans.
To officialize this "ending" vendetta, a proposal was made to the then regent, Milica, of a union of peace with the newly crowned Sultan Bayezid, son of Sultan Murad. Although the mother tried to fight and prolong her final decision, by the end of that same year, her youngest daughter was betrothed to the new Sultan.
The Serbian lords, who were quite unhappy about this betrothal, involved themselves in some sort of intrigues to make Bayezid suspicious in order to prevent this union. However, it obviously did not prevail.
It is unclear if the wedding reception took place in late 1389 or in the spring of 1390. As stated by Konstantin Kostenecki in his biography of Stefan Lazarević written in 1431, he reports that after the Ottoman ambassadors and Milica agreed on the marriage, Stefan appeared before Bayezid with his sister Olivera and the marriage took place. As far as we know, the proposal was accepted in late 1389.
Nonetheless, one thing is for sure, and that is the fact that the reception took place no later than the spring of 1390. This is because the joint action of the Serbs and Turks against the Hungarians in northern Serbia, southern Hungary, and eastern Bosnia took place already in the spring or at the latest in the summer of that year, meaning by the spring of 1390, Olivera was married to the same man who gave orders for her father’s execution.
The wedding seems to have been kept quiet as it appears to have taken place in a mosque, following a Muslim ceremony. Many Serbian lords and people were unhappy about their Orthodox Christian Princess marrying a Muslim, even if it brought some temporary peace to Serbia.
According to Ducas, a 15th-century historian, on top of many talents of silver from Serbia's mines, Bayezid received "a tender virgin."
With this marriage came a new title and epithet. Ottomans referred to her as "Devlet Hatun," meaning "State Woman" or "Queen," while she also earned a Greek nickname/epithet, "Despina," meaning female despot, queen, or mistress.
It appears that for the rest of her life, she was referred to by this epithet instead of her actual name.
A Woman of Great Influence
Despite the unfavorable circumstances in which this political marriage began, it is noted by historical and contemporary historians that Bayezid loved and valued the counsel of his wife, Despina. It is accepted that the couple welcomed three daughters together; the eldest bears an unknown name, the second in line is Pasa Melek, and the youngest is Oruz.
Her legendary beauty, noble background, and education played a key role in Bayezid’s favoritism of her over all his other consorts and in his trust in her counsel.
From the moment she arrived until his last breath, she remained his main and favorite wife, and had influence on her husband's politics, which played in favor of her people.
Despina was, of course, blamed for having introduced European customs, wine, and mass partying into the once "pious" Ottoman court, and for "whispering in her brother’s favor." However, these criticisms were mostly due to the fact that she was a Christian wife and remained one even though she had influence over her husband. This of course, played a role in the Muslim Ottomans distain of her.
Though it is unknown if Despina reciprocated the same sentiment towards her husband, it is noted that wherever Bayezid went, he could not sperate from the Serbian Princess, and thus he took her everywhere with him, suggesting that throughout their marriage she remained a loyal companion.
Throughout his reign, and despite coming and going concubines, Bayezid remained devoted to one woman: Despina.
According to Serbian sources, her biggest accomplishments were to partake in Bayezid’s decision to transfer a vast portion of Vuk Branković’s lands (her brother-in-law through Mara) in 1397, following the man’s death and place them under the governance of her younger brother, Stefan.
The other was to save her brother from Bayezid’s wrath in 1398 when he was accused of conspiring with the King of Hungary. Stefan came to the Sultan after the failed attempt of his mother to defend him. It is believed that Olivera was the one who stepped up, and her brother was forgiven upon admitting his fault.
Captivity
Following the aftermath of the Battle of Ankara in 1402, a battle which Bayezid and his sons, Mustafa and Musa, lost and were taken as captives, Timur sent his generals to plunder Bursa, taking many treasures from the palace with them, including Bayezid's concubines. Eventually, they made their way to Yenisehir, where Despina was hiding with two of her daughters.
Despina and her household were brought to Timur and later to Bayezid, who was being kept captive in a tent. Although they were treated with respect at first, events occurred that led to Bayezid being humiliated and kept in an iron cage, while his wife was forced to perform menial tasks at festivities.
Unable to bear the insult made towards his wife, Bayezid committed suicide in his iron cage and was temporarily buried in Akşehir, where he had passed.
Timur is believed to have felt great guilt because of this and released Bayezid’s entourage. He married Despina’s daughters to the son of one of his generals and the other to his grandson, Ebu Bakr Mirza. Both daughters moved to Samarkand where they lived with their families.
In 1404, Despina was released along with her step-son, Musa, during the transfer of Bayezid’s body to his personal mosque in Bursa. It is assumed she attended his second funeral.
As the Advisor of the Despots
Following her release, nothing is known or recorded about Despina's whereabouts until the 1420s. It is believed by some that she might have stayed in Bursa or somewhere nearby with her youngest daughter until she grew tired of the battle for the throne going on between Bayezid’s sons and later moved to Serbia.
Or, she might have stayed until the time her youngest daughter was married off.
After her return to Serbia, she took her place at her already widowed brother's side as his comforter and trusted advisor. However, she never lived at court but instead had her own residence in the courtyard of Belgrade.
She was extremely popular, respected, and valued in her homeland. Even during her lifetime, the Serbs referred to her as “Esther” due to her sacrificial marriage to a persecutor of the Christians.
During her stay in Dubrovnik, it is plausible she met with her sister and brother-in-law, Sandalj Hranic, though some historians believe she was there for diplomatic reasons, possibly to acquire information on her brother-in-law to inform her younger brother; the now Despot Stefan Lazarevic.
In 1427, her younger brother passed away, but this did not end her influence. Soon after, she acted as an advisor to her nephew, Durad Brankovic, and from 1430 onwards, moved with his family to Smederevo, the new capital.
Murad II, the Ottoman Sultan at the time, must have believed that since Stefan Lazarevic had died without any children to proclaim as heir, then the state should pass from Stefan to his step-grandmother, Olivera, and thus to himself.
As a result of this situation and threat to their state, historians believe it was Despina who planned Mara Brankovic's marriage to Murad in order to prevent the Ottomans from advancing. And thus, the marriage was concluded in 1435 in the Ottoman capital.
Though this marriage, unlike Olivera's own marriage, did not prevent Ottoman expansion in Serbia.
In 1441, while her nephew Durad was in exile, she traveled from Dubrovnik to Bar, where it is believed she was able to convey secret diplomatic letters to her nephew.
Later Life
Nothing is known about the later life of Despina from 1443 onwards; they lost track of her.
The last time she is mentioned alive is in a 1443 document, in which her sister, Jelena, names her as her executor in her will. She left money to Despina in order to build a burial place for her and to distribute some of the money to the poor.
After this, nothing more is recorded; it is unknown when, where, and how she died.
Issue
Unkown Hatun
Pasa Melek Hatun
Oruz/Uruz Hatun
( Sources: Osmanlı Sarayı’nda Bir Sırp Prenses/ Mileva Olivera Lazarevic by Mustafa Çağhan Keskin, КЋЕРИ КНЕЗА ЛАЗАРА ИСТОРИЈСКА СТУДИЈА ПОГОВОР by Jelka Redep, Dve srpske sultanije : Olivera Lazarevic (1373-1444) : Mara Brankovic (1418-1487) by Nikola Giljen, “КЋЕРИ КНЕЗА ЛАЗАРА ИСТОРИЈСКА СТУДИЈА ПОГОВОР” by Jelka Redep, Dve srpske sultanije : Olivera Lazarevic (1373-1444) : Mara Brankovic (1418-1487) by Nikola Giljen, The European Sultanas of the Ottoman Empire by Anna Ivanova Buxton )
#Olivera Lazarevic#olivera despina#despinahatun#lazarevicdynasty#history#art#illustration#lazarevicsisters#ottoman empire#middle ages#hatun#despina hatun#geology#biography
48 notes
·
View notes
Text
oh oh sure I can fuck emperor calamari and the horned up bear and the petplay devil woman and the bdsm incubus but I CANT fuck the tyrannical despot who's one of the main villains of the game????
yeah ok. fine game. you think you're so great, don't you, well, some of us have taste.
87 notes
·
View notes
Text
When they say I have my mother's smile, I smile too.
I don't. I don't have my mother's grace. I don't have my mother's strength to bear through pain with poise. I don't have my mother's elegance to hold broken pieces of my own heart with benevolent despotism in my own hands.
I was carved from my father's flesh. I feel rage, untamed and unleashed. I feel grief, writhing and twisting my insides till I am all but consumed in its clutches. I feel hurt and pain; not like a knife that has been stabbed-quick and twisted;but like walking on nails-a continuous sting, eternal pain, far more malicious and damning. My tears aren't shed with elegance either-no, they aren't drops that escape the corners of my eyes. I sob. I sob with my mouth stuffed and ears blocked.
Grief looks ugly on me. As does fury. I am not my mother's daughter, I am my father's.
127 notes
·
View notes
Text
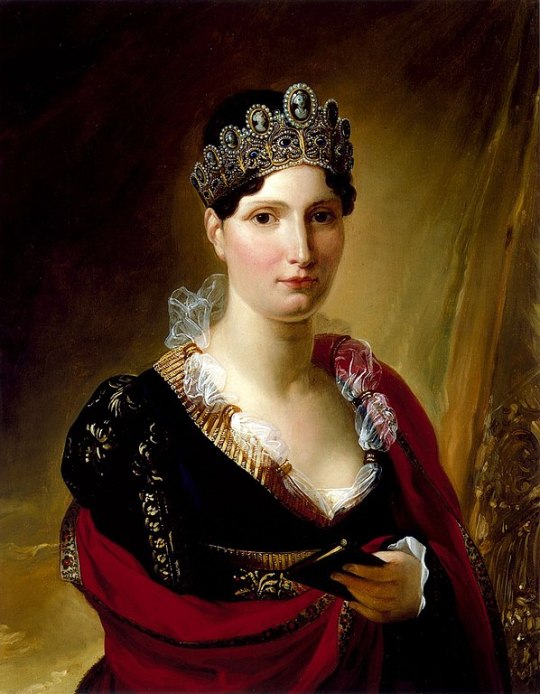

Elisa Bonaparte Baciocchi by Joseph Franque, 1812
Elisa Bonaparte was born on January 3, 1777. She was not as well-known as her sisters, beautiful Pauline and treasonous Caroline, but she was more capable than either of them. In fact, she was the Bonaparte sibling most like Napoleon, although she had the least influence over him. Napoleon himself said, “Elisa has the courage of an Amazon; and like me, she cannot bear to be ruled.” In 1805, he made her the Princess of Piombino and Lucca, where she formed an elaborate court, in imitation of the one in Paris. She took her duties seriously, ruling as a benevolent despot.
Elisa did such a good job that, in 1809, Napoleon made her Grand Duchess of Tuscany, a place she had long had her eye on. She moved her court to the Pitti Palace in Florence, which she refurbished in competition with Caroline’s court in Naples. Elisa's husband, Félix Baciocchi, commanded the local military division under his wife’s supervision. The two lived apart and took lovers.
When Napoleon’s empire began to crumble in 1814, Elisa broke away from her brother, hoping to save her own position. It was no use, as the Tuscans showed no sign of attachment to her and Elisa and Baciocchi had to flee. They tried, unsuccessfully, to make off with the silver and furniture from several of the palaces.
When Napoleon escaped from Elba and returned to France in March of 1815, the Austrians arrested Elisa and imprisoned her. She was released once Napoleon was safely on his way to exile on St. Helena. Elisa was given permission to live in Trieste, where she assumed the title of Countess of Compignano. She died of infection on August 7, 1820, at the age of 43.
When news of Elisa’s death reached Napoleon, he shut himself up alone for several hours. When he emerged, he said, “There is the first member of my family who has set out on the great journey; in a few months I shall go to join her.” He died nine months later, on May 5, 1821.
For more about Elisa, see "Elisa Bonaparte Baciocchi, Napoleon's Capable Sister."
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
Them

#boognish#despot bear#tbh creature#autism creature#yippee#yipee#yippie#yipppeeee#aaaaaaaaaa#modified bear#the scrunklies#scringly dingly
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
Saw furiosa and I’m putting some thoughts under the spoiler-
- the child actress was great, loved her
-overall just loved our short peek at the green place, very cool and solar punk. Not quite what I expected but totally love it
-wish I was able to identify the vulvalini war leader to who she was in mmfr
-really liked the kind of vignette structure that was used
-but yeah the first vignette or two was really really good, I loved Mary Jo bassa, I loved the tension of her and furi protecting the secret location
-I didnt like dementus in the trailers, but he was a lot smarter/more canny than expected. He approached furi in the right way and I think the audience really did love/hate him
-dementus at the citadel was great, loved how we established Joe’s power, but also dementus’s charisma and ability to lead a group as a ‘caring’ despot
-plus motorcycle chariot, iconic no notes
-gastown trojan horse was fine, def overshadowed by other stuff
- the parley scene, his nipples came off
- overall the handoff of furi and organic mechanic felt a little weird but I mean plot holes gonna plot hole
-teddy bear is iconic tho
-also lol at organic mechanic never aging
-aging in general was all over the place
- okay so furi is with the wives for not that long at all, and just nobody notices when she escapes???
-tho i guess rictus probably would have killed her anyway
-BLACKTHUMB BLACKTHUMB BLACKTHUMB
-idk just seeing furi build the war rig made me happy, and managing to get through the environment on her own
-basically all the of the stowaway was the high point of the move
- the war rig getting built
-the war with octoboss
-like that was cool as shit, all those kites
-love the miller just consistently raises the bar and makes this world crazier
- I think there was more CGI in this one, but overall combat still looked very very good
- coming down to the final two felt very tense, overall just great fight
-I think this is also when we saw the best acting out of Anya Taylor joy, the silent stare works when there’s crazy combat everywhere
-hey pissboy
-praetor Jack felt fine here, keeping her around was justified
-the time skip here was the worst tho
-like she just went from stowaway to driving the rig???
-idk i feel like that was the part of the story i was most interested in and they skipped it all
-also I hate her hair, like why???
-it also like never came up the she is literally the only woman with like any kind of power in the citadel???
-apparently the answer to how was some big strong awesome man protected her just because???
-like I just didn’t understand their chemistry
-also like nobody realized this was a wife that escaped a few years ago???
- so like I think the bulletown scene suffered just because like I didn’t care so much about this guy and don’t see why she did
-the dark dementus scene was alright I guess
-hi max! Is it implied he got her back to citadel?
- solo vengeance quest next, liked zooming out of there without rictus and scrotus
-but honestly Taylor joy just got way out acted by Hemsworth in that last vignette
-he was really really good
-and like she just stared
-like maybe it would have worked better if she had more dialogue
- but also I’m just not sure I found her as compelling out of a fight scene in general
-the peach tree was cool tho
-I was hoping to see my boy ace, but if he was there I missed it :(
In conclusion I have a lot of opinions please talk to me about them
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Cyrus Extended Universe
I love one (1) elf very much. How much? So much that I can't stop putting him in scenarios, spawning an intricate web of AUs, LIs, and slight variations that, while perfectly sensible to me, is a lot for anyone else to keep track of.
This chart & the liner notes under the cut sketch Cyrus Hawke's development across DA2, as well as how I've reinterpreted the character in BG3 with links to fics & character & ship tags uwu
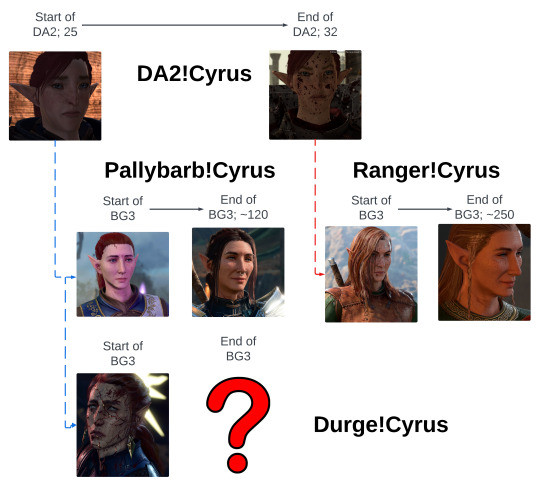
And, of course, there are some things that all versions of Cyrus have in common:
A lover AND a fighter
Sword & shield tank
Loyal as a pup and twice as pretty
Duty comes first, and his first duty is to protect & care for his loved ones
Struggles with his sense of self beyond that duty
Feels like he's always falling short of being good enough & constantly trying to make up for it
Difficulty connecting with his body as more than a line of defense
Sensitive about having his body modified with magic, including benign healing
Fears being made a symbol-- reduced to his armour, his weapon, his title, and made to be the instrument of someone else's will
Has had his kindness and eagerness to serve others taken advantage of
Can't sit still to save his life
Loves nature, gardening, and lavender especially
Stubborn, determined, bad at letting go
Despises injustice and abuse of power
DA2!Cyrus


Playable Elfs Mod
Start of DA2 (25)
Blue!Hawke. Defined by his cheerful, trusting, and giving nature, Cyrus' unwavering commitment to his friends, family, and community make him the brightest light in Kirkwall's Alienage.
But there's a dark side to his selflessness, which his new friends are quick to notice: his overprotectiveness, his willingness to sacrifice himself recklessly and needlessly, his singular regard for the well-being of others at the expense of his own, even the pride he seems to take in his ability to endure pain...
End of DA2 (32)
Red!Hawke. Bearing the weight of Kirkwall on his back has left Cyrus bitter, disillusioned, and tired. As the title of Champion has eaten away at him, he has had to fiercely guard his heart and sense of self, only ever softening for those he loves, to whom he is still ruthlessly devoted.
When Anders asks to pay the price for the Chantry explosion, Cyrus feels he has no choice but to oblige him.
Romancing Varric; QPPs with Merrill and Fenris; besties with Isabela; complicated mutually requited mutual martyrdom exes with Anders
Fics: Little Prince; if i was any closer i could only lose me
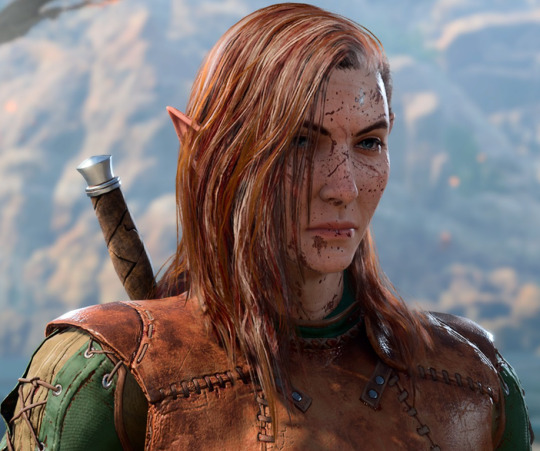
Pallybarb!Cyrus (~120)


Oath of Devotion/Oathbreaker Paladin & Wildheart (Bear Heart) Barbarian
Romancing Karlach & Halsin; ending in Avernus with Karlach and Wyll
Cyrus' oath was born out of pure, unadulterated, selfless commitment to those around him-- first the other orphans in the Lower City of Baldur's Gate, and then to anyone he came across as a young adventurer.
Initial unfazed by getting tadpole-d, Cyrus is devastated when he breaks his oath in the Shadowlands, viewing it as a profound personal failure and a sign of worthlessness. With Karlach's help, he comes to understand that neither he nor his value are defined by his oath, and he decides to remain an oathbreaker, despite the heavy absence in his soul.
Fic: h-llowed
Ranger!Cyrus (~250)
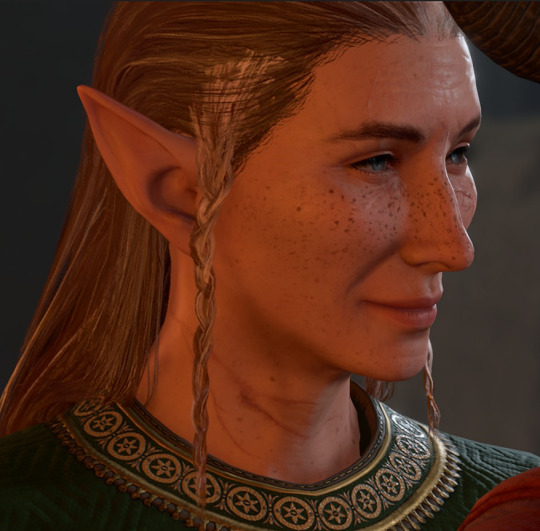


Gloomstalker Ranger & Champion Fighter
Romancing Wyll; ending as Grand Duke Wyll's husband
A century and a half ago, Cyrus was a selfless and naive paladin. He swore his Oath of Devotion to the exiled heiress of Iriaebor. Seeing the potential of his blind loyalty, she named him her Champion, and while he helped her reclaim her city, the two became lovers. As a ruler and a partner, however, she was despotic. Kept caged by her for decades, Cyrus eventually broke his oath to kill her.
He fled the city and made a new life for himself as a hunter in the Wood of Sharp Teeth, but he lived there in self-imposed isolation, determined never to let his guard down or let anyone into his heart again.
...Until he meets Wyll :)
Fic: The Cicatrix: The Functional Stage of Wound Healing
Durge!Cyrus (???)

Harbinger Aasimar (mod + head); Ghostslayer Blood Hunter (mod) & Ancestral Guardians Barbarian (mod)
What if you took a guy who has trouble defining himself outside of his ability to bleed and to make others bleed in order to protect his friends... and you obliterated every other reference point by which he might construct a sense of self. Would that be fucked up or what.
He is the sacrificial lamb he is the wolf in sheep's clothing he is the dog guarding the flock
Romancing Astarion & Wyll
#there are also. technically some other variations of da2!cyrus but explaining all of it would require its own chart adopfijdasf#cyrus hawke#cyrus bg3#durge!cyrus
23 notes
·
View notes
Photo
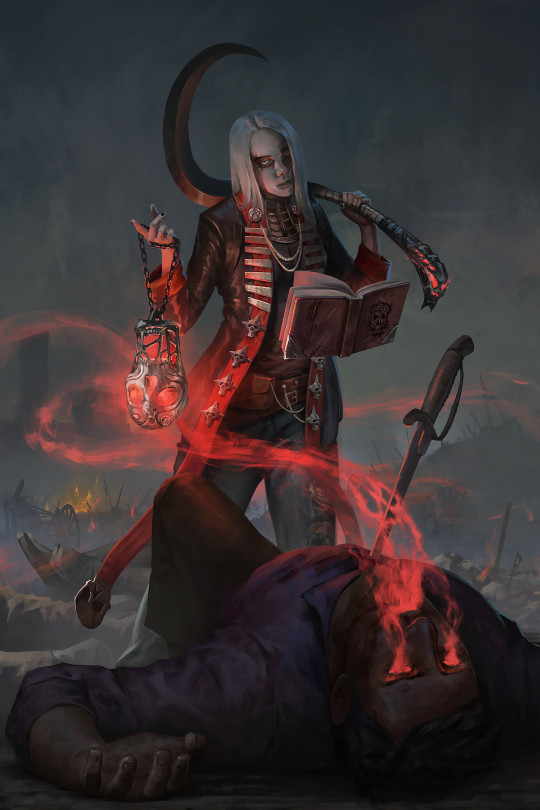

Villain: Dematoth, the Devil of No-Man’s Land
“‘Listen Crowbait, you’ve got two choices. Me, or bearing those wounds of yours for a lingering eternity, until that pain and the aftertaste of sepsis are all that’s left of you. Plenty of other sundered souls on this battlefield who’d jump at my offer, so... what’s it going to be?
War profiteers come in all shapes and sizes, and even after the fighting’s done there’s still opportunity to be found. While the victors look for survivors to slay or ransom and the corpsepickers hunt for rings and baubles, Dematoth moves among the spirits of the fallen looking for those pained, desperate, and willing to make a deal. Is a century of service worth sparing yourself the pain of a wound that will not fade? or what about a personal escort to a cushy part of the underworld in exchange for a secret that could ruin the lives you’ve left behind? The devil knows how to drive a hard bargain but she seldom needs to, the bodies are always piling up somewhere and a new sucker dies every minute.
Sour and Sullen, the devil of no-man’s land cares little for the morality games of her kin, considering most mortals to be a means to an end at best and a waste of her time at worst. While the party might stumble across Dematoth out reaping fresh souls after a battle, she’s more likely to act as an unseen arms dealer among the forces of evil, offloading battalions of revanants and cursed objects to would be diabolists and greater fiends in exchange for various favours. In this way, the party can end up fighting a gang of early-game bandits only to be met with an unexpected postmortem rematch.
Hooks:
For the last few years Dematoth has been following a bloody band of mercenaries, adding fallen sadists and victims to her horde of stolen souls as the sellswords grow rich off of their contracts. This easy arrangement is due to be interrupted when the mercenaries get contracted out by another minor villain to act as muscle for a looming confrontation with the party, motivating the usually indolent devil to start getting proactive. While the heroes may have thought they were only fighting mundane threat, they’ll soon find themselves dealing with curses and other malevolent phenomenon alongside the ruthless mercs and petty despot they thought they were originally facing.
Following a number of otherworldy signs and nightmarish attacks, the party eventually realize they’re on the trail of a rampaging demon that arose from the soul of a famously wicked warrior. Tracking the entity back to the defiled tomb of its greatest foe, the party encounter Dematoth stalking the hallways on a hunt of her own. As the Devil of Noman’s land explains it, this isn’t a ghost that can be put to rest with silver and emotional catharsis, their quarry can only be bound, an art that far outstrips the party’s current skill. If they’re smart they’ll make an alliance with her, distracting and weakening the demon while she does her thing and stuffs it in her ominous skull lantern. Can the party believe her? or is there a better means of dealing with this infernal threat?
In peacetime, Dematoth likes to engineer little accidents where brave individuals get themselves killed due to their own foolhardy actions, appearing in various guises to point the avricious and the adventurous towards a sudden end. After her mark is dead, she appears, claiming to be a psychopomp who guides the courageous to their appointed afterlife after they’ve unburnded themselves of earthly regrets. This racket is an excuse to get the departed to agree to one of her deals or cough up some valuable information before the real spirit guides arrive, and can provide a delightful post-death hook for those heroes who fall in combat.
#fiend#demon#low level#mid level#wasteland#plains#field#fighter#Cleric#mercenaries#undead#dnd#dungeons and dragons#d&d#5e#villain#warfare#monster hunt#Psychopomp
285 notes
·
View notes
Note
Sorry for just sliding into your asks like this, but ever since I saw you incorporating existing songs into your D&D:HAT fics, I have been haunted by the concept of Edgin composing "Poet, Soldier, King" for Xenk. Because I'm old enough to remember that fandom phenomena and Xenk definitely fits the Messianic Archetype.
Just. Bear with me. The first verse is open-and-shut, though I suppose you could replace "city" with something else if you want, like "despot" or "regime" or even a generic "evil". This is of course a reference to Szass Tam but could also be Ed's cynical take the possible consequences of Xenk's do-goodery.
The second verse was definitely meant to be sarcastic and mock Xenk's antiquated speech but you know how tsunderes in-denial work. Because Xenk's no-bullshit sincerity did cut Ed to the quick and the core both — and your writings show you also believe Xenk's words live rent free in Ed's mind.
The last verse doesn't really work in the context of Faerûn, and I also don't think Ed would play up Xenk as a conqueror too much, so here's my proposed alternative:
There will come a champion
Whose heart is blessed by Torm
He will succor one and all
(I would've put the Triad in there but it didn't fit the meter, boo!)
Because c'mon. What is more classic than an I-hate-him rant that just ends up more and more flattering until it's an unintentional love confession? Although by the time Ed finishes this verse he's probably reached the Actively Pining stage.
Anyways, now that I've put this idea into the world and foisted it upon you, I hope I may finally know peace. 🙏
I really love this idea, so I hope you don't mind me posting this ask publicly, because I think it would be done more justice in fanart or a gifset (the Xedgin fandom has some insanely good artists what the heck) than in a fanfic! I hope that my sharing this gives someone in the fandom some inspiration!
#xedgin#dungeons and dragons: honor among thieves#dnd honor among thieves#dndhat#xenk yendar#edgin darvis#dnd movie#honor among thieves#seriously how many tags does this movie have!?#mads answers things#msbeeinmybonnet
13 notes
·
View notes
Text

Chapter 4: Mutual Aid Among the Barbarians
The great migrations. — New organization rendered necessary. — The village community. — Communal work. — Judicial procedure — Inter-tribal law. — Illustrations from the life of our contemporaries — Buryates. — Kabyles. — Caucasian mountaineers. — African stems.
It is not possible to study primitive mankind without being deeply impressed by the sociability it has displayed since its very first steps in life. Traces of human societies are found in the relics of both the oldest and the later stone age; and, when we come to observe the savages whose manners of life are still those of neolithic man, we find them closely bound together by an extremely ancient clan organization which enables them to combine their individually weak forces, to enjoy life in common, and to progress. Man is no exception in nature. He also is subject to the great principle of Mutual Aid which grants the best chances of survival to those who best support each other in the struggle for life. These were the conclusions arrived at in the previous chapters.
However, as soon as we come to a higher stage of civilization, and refer to history which already has something to say about that stage, we are bewildered by the struggles and conflicts which it reveals. The old bonds seem entirely to be broken. Stems are seen to fight against stems, tribes against tribes, individuals against individuals; and out of this chaotic contest of hostile forces, mankind issues divided into castes, enslaved to despots, separated into States always ready to wage war against each other. And, with this history of mankind in his hands, the pessimist philosopher triumphantly concludes that warfare and oppression are the very essence of human nature; that the warlike and predatory instincts of man can only be restrained within certain limits by a strong authority which enforces peace and thus gives an opportunity to the few and nobler ones to prepare a better life for humanity in times to come.
And yet, as soon as the every-day life of man during the historical period is submitted to a closer analysis and so it has been, of late, by many patient students of very early institutions — it appears at once under quite a different aspect. Leaving aside the preconceived ideas of most historians and their pronounced predilection for the dramatic aspects of history, we see that the very documents they habitually peruse are such as to exaggerate the part of human life given to struggles and to underrate its peaceful moods. The bright and sunny days are lost sight of in the gales and storms. Even in our own time, the cumbersome records which we prepare for the future historian, in our Press, our law courts, our Government offices, and even in our fiction and poetry, suffer from the same one-sidedness. They hand down to posterity the most minute descriptions of every war, every battle and skirmish, every contest and act of violence, every kind of individual suffering; but they hardly bear any trace of the countless acts of mutual support and devotion which every one of us knows from his own experience; they hardly take notice of what makes the very essence of our daily life — our social instincts and manners. No wonder, then, if the records of the past were so imperfect. The annalists of old never failed to chronicle the petty wars and calamities which harassed their contemporaries; but they paid no attention whatever to the life of the masses, although the masses chiefly used to toil peacefully while the few indulged in fighting. The epic poems, the inscriptions on monuments, the treaties of peace — nearly all historical documents bear the same character; they deal with breaches of peace, not with peace itself. So that the best-intentioned historian unconsciously draws a distorted picture of the times he endeavours to depict; and, to restore the real proportion between conflict and union, we are now bound to enter into a minute analysis of thousands of small facts and faint indications accidentally preserved in the relics of the past; to interpret them with the aid of comparative ethnology; and, after having heard so much about what used to divide men, to reconstruct stone by stone the institutions which used to unite them.
Ere long history will have to be re-written on new lines, so as to take into account these two currents of human life and to appreciate the part played by each of them in evolution. But in the meantime we may avail ourselves of the immense preparatory work recently done towards restoring the leading features of the second current, so much neglected. From the better-known periods of history we may take some illustrations of the life of the masses, in order to indicate the part played by mutual support during those periods; and, in so doing, we may dispense (for the sake of brevity) from going as far back as the Egyptian, or even the Greek and Roman antiquity. For, in fact, the evolution of mankind has not had the character of one unbroken series. Several times civilization came to an end in one given region, with one given race, and began anew elsewhere, among other races. But at each fresh start it began again with the same clan institutions which we have seen among the savages. So that if we take the last start of our own civilization, when it began afresh in the first centuries of our era, among those whom the Romans called the “barbarians,” we shall have the whole scale of evolution, beginning with the gentes and ending in the institutions of our own time. To these illustrations the following pages will be devoted.
Men of science have not yet settled upon the causes which some two thousand years ago drove whole nations from Asia into Europe and resulted in the great migrations of barbarians which put an end to the West Roman Empire. One cause, however, is naturally suggested to the geographer as he contemplates the ruins of populous cities in the deserts of Central Asia, or follows the old beds of rivers now disappeared and the wide outlines of lakes now reduced to the size of mere ponds. It is desiccation: a quite recent desiccation, continued still at a speed which we formerly were not prepared to admit.[114] Against it man was powerless. When the inhabitants of North-West Mongolia and East Turkestan saw that water was abandoning them, they had no course open to them but to move down the broad valleys leading to the lowlands, and to thrust westwards the inhabitants of the plains.[115] Stems after stems were thus thrown into Europe, compelling other stems to move and to remove for centuries in succession, westwards and eastwards, in search of new and more or less permanent abodes. Races were mixing with races during those migrations, aborigines with immigrants, Aryans with Ural-Altayans; and it would have been no wonder if the social institutions which had kept them together in their mother countries had been totally wrecked during the stratification of races which took place in Europe and Asia. But they were not wrecked; they simply underwent the modification which was required by the new conditions of life.
The Teutons, the Celts, the Scandinavians, the Slavonians, and others, when they first came in contact with the Romans, were in a transitional state of social organization. The clan unions, based upon a real or supposed common origin, had kept them together for many thousands of years in succession. But these unions could answer their purpose so long only as there were no separate families within the gens or clan itself. However, for causes already mentioned, the separate patriarchal family had slowly but steadily developed within the clans, and in the long run it evidently meant the individual accumulation of wealth and power, and the hereditary transmission of both. The frequent migrations of the barbarians and the ensuing wars only hastened the division of the gentes into separate families, while the dispersing of stems and their mingling with strangers offered singular facilities for the ultimate disintegration of those unions which were based upon kinship. The barbarians thus stood in a position of either seeing their clans dissolved into loose aggregations of families, of which the wealthiest, especially if combining sacerdotal functions or military repute with wealth, would have succeeded in imposing their authority upon the others; or of finding out some new form of organization based upon some new principle.
Many stems had no force to resist disintegration: they broke up and were lost for history. But the more vigorous ones did not disintegrate. They came out of the ordeal with a new organization — the village community — which kept them together for the next fifteen centuries or more. The conception of a common territory, appropriated or protected by common efforts, was elaborated, and it took the place of the vanishing conceptions of common descent. The common gods gradually lost their character of ancestors and were endowed with a local territorial character. They became the gods or saints of a given locality; “the land” was identified with its inhabitants. Territorial unions grew up instead of the consanguine unions of old, and this new organization evidently offered many advantages under the given circumstances. It recognized the independence of the family and even emphasized it, the village community disclaiming all rights of interference in what was going on within the family enclosure; it gave much more freedom to personal initiative; it was not hostile in principle to union between men of different descent, and it maintained at the same time the necessary cohesion of action and thought, while it was strong enough to oppose the dominative tendencies of the minorities of wizards, priests, and professional or distinguished warriors. Consequently it became the primary cell of future organization, and with many nations the village community has retained this character until now.
It is now known, and scarcely contested, that the village community was not a specific feature of the Slavonians, nor even of the ancient Teutons. It prevailed in England during both the Saxon and Norman times, and partially survived till the last century;[116] it was at the bottom of the social organization of old Scotland, old Ireland, and old Wales. In France, the communal possession and the communal allotment of arable land by the village folkmote persisted from the first centuries of our era till the times of Turgot, who found the folkmotes “too noisy” and therefore abolished them. It survived Roman rule in Italy, and revived after the fall of the Roman Empire. It was the rule with the Scandinavians, the Slavonians, the Finns (in the pittäyä, as also, probably, the kihla-kunta), the Coures, and the Lives. The village community in India — past and present, Aryan and non-Aryan — is well known through the epoch-making works of Sir Henry Maine; and Elphinstone has described it among the Afghans. We also find it in the Mongolian oulous, the Kabyle thaddart, the Javanese dessa, the Malayan kota or tofa, and under a variety of names in Abyssinia, the Soudan, in the interior of Africa, with natives of both Americas, with all the small and large tribes of the Pacific archipelagoes. In short, we do not know one single human race or one single nation which has not had its period of village communities. This fact alone disposes of the theory according to which the village community in Europe would have been a servile growth. It is anterior to serfdom, and even servile submission was powerless to break it. It was a universal phase of evolution, a natural outcome of the clan organization, with all those stems, at least, which have played, or play still, some part in history.[117]
It was a natural growth, and an absolute uniformity in its structure was therefore not possible. As a rule, it was a union between families considered as of common descent and owning a certain territory in common. But with some stems, and under certain circumstances, the families used to grow very numerous before they threw off new buds in the shape of new families; five, six, or seven generations continued to live under the same roof, or within the same enclosure, owning their joint household and cattle in common, and taking their meals at the common hearth. They kept in such case to what ethnology knows as the “joint family,” or the “undivided household,” which we still see all over China, in India, in the South Slavonian zadruga, and occasionally find in Africa, in America, in Denmark, in North Russia, and West France.[118] With other stems, or in other circumstances, not yet well specified, the families did not attain the same proportions; the grandsons, and occasionally the sons, left the household as soon as they were married, and each of them started a new cell of his own. But, joint or not, clustered together or scattered in the woods, the families remained united into village communities; several villages were grouped into tribes; and the tribes joined into confederations. Such was the social organization which developed among the so-called “barbarians,” when they began to settle more or less permanently in Europe.
A very long evolution was required before the gentes, or clans, recognized the separate existence of a patriarchal family in a separate hut; but even after that had been recognized, the clan, as a rule, knew no personal inheritance of property. The few things which might have belonged personally to the individual were either destroyed on his grave or buried with him. The village community, on the contrary, fully recognized the private accumulation of wealth within the family and its hereditary transmission. But wealth was conceived exclusively in the shape of movable property, including cattle, implements, arms, and the dwelling house which — “like all things that can be destroyed by fire” — belonged to the same category.[119] As to private property in land, the village community did not, and could not, recognize anything of the kind, and, as a rule, it does not recognize it now. The land was the common property of the tribe, or of the whole stem, and the village community itself owned its part of the tribal territory so long only as the tribe did not claim a re-distribution of the village allotments. The clearing of the woods and the breaking of the prairies being mostly done by the communities or, at least, by the joint work of several families — always with the consent of the community — the cleared plots were held by each family for a term of four, twelve, or twenty years, after which term they were treated as parts of the arable land owned in common. Private property, or possession “for ever”, was as incompatible with the very principles and the religious conceptions of the village community as it was with the principles of the gens; so that a long influence of the Roman law and the Christian Church, which soon accepted the Roman principles, were required to accustom the barbarians to the idea of private property in land being possible.[120] And yet, even when such property, or possession for an unlimited time, was recognized, the owner of a separate estate remained a co-proprietor in the waste lands, forests, and grazing-grounds. Moreover, we continually see, especially in the history of Russia, that when a few families, acting separately, had taken possession of some land belonging to tribes which were treated as strangers, they very soon united together, and constituted a village community which in the third or fourth generation began to profess a community of origin.
A whole series of institutions, partly inherited from the clan period, have developed from that basis of common ownership of land during the long succession of centuries which was required to bring the barbarians under the dominion of States organized upon the Roman or Byzantine pattern. The village community was not only a union for guaranteeing to each one his fair share in the common land, but also a union for common culture, for mutual support in all possible forms, for protection from violence, and for a further development of knowledge, national bonds, and moral conceptions; and every change in the judicial, military, educational, or economical manners had to be decided at the folkmotes of the village, the tribe, or the confederation. The community being a continuation of the gens, it inherited all its functions. It was the universitas, the mir — a world in itself.
Common hunting, common fishing, and common culture of the orchards or the plantations of fruit trees was the rule with the old gentes. Common agriculture became the rule in the barbarian village communities. True, that direct testimony to this effect is scarce, and in the literature of antiquity we only have the passages of Diodorus and Julius Caesar relating to the inhabitants of the Lipari Islands, one of the Celt-Iberian tribes, and the Sueves. But there is no lack of evidence to prove that common agriculture was practised among some Teuton tribes, the Franks, and the old Scotch, Irish, and Welsh.[121] As to the later survivals of the same practice, they simply are countless. Even in perfectly Romanized France, common culture was habitual some five and twenty years ago in the Morbihan (Brittany).[122] The old Welsh cyvar, or joint team, as well as the common culture of the land allotted to the use of the village sanctuary are quite common among the tribes of Caucasus the least touched by civilization,[123] and like facts are of daily occurrence among the Russian peasants. Moreover, it is well known that many tribes of Brazil, Central America, and Mexico used to cultivate their fields in common, and that the same habit is widely spread among some Malayans, in New Caledonia, with several Negro stems, and so on.[124] In short, communal culture is so habitual with many Aryan, Ural-Altayan, Mongolian, Negro, Red Indian, Malayan, and Melanesian stems that we must consider it as a universal — though not as the only possible — form of primitive agriculture.[125]
Communal cultivation does not, however, imply by necessity communal consumption. Already under the clan organization we often see that when the boats laden with fruits or fish return to the village, the food they bring in is divided among the huts and the “long houses” inhabited by either several families or the youth, and is cooked separately at each separate hearth. The habit of taking meals in a narrower circle of relatives or associates thus prevails at an early period of clan life. It became the rule in the village community. Even the food grown in common was usually divided between the households after part of it had been laid in store for communal use. However, the tradition of communal meals was piously kept alive; every available opportunity, such as the commemoration of the ancestors, the religious festivals, the beginning and the end of field work, the births, the marriages, and the funerals, being seized upon to bring the community to a common meal. Even now this habit, well known in this country as the “harvest supper,” is the last to disappear. On the other hand, even when the fields had long since ceased to be tilled and sown in common, a variety of agricultural work continued, and continues still, to be performed by the community. Some part of the communal land is still cultivated in many cases in common, either for the use of the destitute, or for refilling the communal stores, or for using the produce at the religious festivals. The irrigation canals are digged and repaired in common. The communal meadows are mown by the community; and the sight of a Russian commune mowing a meadow — the men rivalling each other in their advance with the scythe, while the women turn the grass over and throw it up into heaps — is one of the most inspiring sights; it shows what human work might be and ought to be. The hay, in such case, is divided among the separate households, and it is evident that no one has the right of taking hay from a neighbour’s stack without his permission; but the limitation of this last rule among the Caucasian Ossetes is most noteworthy. When the cuckoo cries and announces that spring is coming, and that the meadows will soon be clothed again with grass, every one in need has the right of taking from a neighbour’s stack the hay he wants for his cattle.[126] The old communal rights are thus re-asserted, as if to prove how contrary unbridled individualism is to human nature.
When the European traveller lands in some small island of the Pacific, and, seeing at a distance a grove of palm trees, walks in that direction, he is astonished to discover that the little villages are connected by roads paved with big stones, quite comfortable for the unshod natives, and very similar to the “old roads” of the Swiss mountains. Such roads were traced by the “barbarians” all over Europe, and one must have travelled in wild, thinly-peopled countries, far away from the chief lines of communication, to realize in full the immense work that must have been performed by the barbarian communities in order to conquer the woody and marshy wilderness which Europe was some two thousand years ago. Isolated families, having no tools, and weak as they were, could not have conquered it; the wilderness would have overpowered them. Village communities alone, working in common, could master the wild forests, the sinking marshes, and the endless steppes. The rough roads, the ferries, the wooden bridges taken away in the winter and rebuilt after the spring flood was over, the fences and the palisaded walls of the villages, the earthen forts and the small towers with which the territory was dotted — all these were the work of the barbarian communities. And when a community grew numerous it used to throw off a new bud. A new community arose at a distance, thus step by step bringing the woods and the steppes under the dominion of man. The whole making of European nations was such a budding of the village communities. Even now-a-days the Russian peasants, if they are not quite broken down by misery, migrate in communities, and they till the soil and build the houses in common when they settle on the banks of the Amur, or in Manitoba. And even the English, when they first began to colonize America, used to return to the old system; they grouped into village communities.[127]
The village community was the chief arm of the barbarians in their hard struggle against a hostile nature. It also was the bond they opposed to oppression by the cunningest and the strongest which so easily might have developed during those disturbed times. The imaginary barbarian — the man who fights and kills at his mere caprice — existed no more than the “bloodthirsty” savage. The real barbarian was living, on the contrary, under a wide series of institutions, imbued with considerations as to what may be useful or noxious to his tribe or confederation, and these institutions were piously handed down from generation to generation in verses and songs, in proverbs or triads, in sentences and instructions. The more we study them the more we recognize the narrow bonds which united men in their villages. Every quarrel arising between two individuals was treated as a communal affair — even the offensive words that might have been uttered during a quarrel being considered as an offence to the community and its ancestors. They had to be repaired by amends made both to the individual and the community;[128] and if a quarrel ended in a fight and wounds, the man who stood by and did not interpose was treated as if he himself had inflicted the wounds.[129] The judicial procedure was imbued with the same spirit. Every dispute was brought first before mediators or arbiters, and it mostly ended with them, the arbiters playing a very important part in barbarian society. But if the case was too grave to be settled in this way, it came before the folkmote, which was bound “to find the sentence,” and pronounced it in a conditional form; that is, “such compensation was due, if the wrong be proved,” and the wrong had to be proved or disclaimed by six or twelve persons confirming or denying the fact by oath; ordeal being resorted to in case of contradiction between the two sets of jurors. Such procedure, which remained in force for more than two thousand years in succession, speaks volumes for itself; it shows how close were the bonds between all members of the community. Moreover, there was no other authority to enforce the decisions of the folkmote besides its own moral authority. The only possible menace was that the community might declare the rebel an outlaw, but even this menace was reciprocal. A man discontented with the folkmote could declare that he would abandon the tribe and go over to another tribe — a most dreadful menace, as it was sure to bring all kinds of misfortunes upon a tribe that might have been unfair to one of its members.[130] A rebellion against a right decision of the customary law was simply “inconceivable,” as Henry Maine has so well said, because “law, morality, and fact” could not be separated from each other in those times.[131] The moral authority of the commune was so great that even at a much later epoch, when the village communities fell into submission to the feudal lord, they maintained their judicial powers; they only permitted the lord, or his deputy, to “find” the above conditional sentence in accordance with the customary law he had sworn to follow, and to levy for himself the fine (the fred) due to the commune. But for a long time, the lord himself, if he remained a co-proprietor in the waste land of the commune, submitted in communal affairs to its decisions. Noble or ecclesiastic, he had to submit to the folkmote — Wer daselbst Wasser und Weid genusst, muss gehorsam sein — “Who enjoys here the right of water and pasture must obey” — was the old saying. Even when the peasants became serfs under the lord, he was bound to appear before the folkmote when they summoned him.[132]
In their conceptions of justice the barbarians evidently did not much differ from the savages. They also maintained the idea that a murder must be followed by putting the murderer to death; that wounds had to be punished by equal wounds, and that the wronged family was bound to fulfil the sentence of the customary law. This was a holy duty, a duty towards the ancestors, which had to be accomplished in broad daylight, never in secrecy, and rendered widely known. Therefore the most inspired passages of the sagas and epic poetry altogether are those which glorify what was supposed to be justice. The gods themselves joined in aiding it. However, the predominant feature of barbarian justice is, on the one hand, to limit the numbers of persons who may be involved in a feud, and, on the other hand, to extirpate the brutal idea of blood for blood and wounds for wounds, by substituting for it the system of compensation. The barbarian codes which were collections of common law rules written down for the use of judges — “first permitted, then encouraged, and at last enforced,” compensation instead of revenge.[133] The compensation has, however, been totally misunderstood by those who represented it as a fine, and as a sort of carte blanche given to the rich man to do whatever he liked. The compensation money (wergeld), which was quite different from the fine or fred,[134] was habitually so high for all kinds of active offences that it certainly was no encouragement for such offences. In case of a murder it usually exceeded all the possible fortune of the murderer “Eighteen times eighteen cows” is the compensation with the Ossetes who do not know how to reckon above eighteen, while with the African tribes it attains 800 cows or 100 camels with their young, or 416 sheep in the poorer tribes.[135] In the great majority of cases, the compensation money could not be paid at all, so that the murderer had no issue but to induce the wronged family, by repentance, to adopt him. Even now, in the Caucasus, when feuds come to an end, the offender touches with his lips the breast of the oldest woman of the tribe, and becomes a “milk-brother” to all men of the wronged family.[136] With several African tribes he must give his daughter, or sister, in marriage to some one of the family; with other tribes he is bound to marry the woman whom he has made a widow; and in all cases he becomes a member of the family, whose opinion is taken in all important family matters.[137]
Far from acting with disregard to human life, the barbarians, moreover, knew nothing of the horrid punishments introduced at a later epoch by the laic and canonic laws under Roman and Byzantine influence. For, if the Saxon code admitted the death penalty rather freely even in cases of incendiarism and armed robbery, the other barbarian codes pronounced it exclusively in cases of betrayal of one’s kin, and sacrilege against the community’s gods, as the only means to appease the gods.
All this, as seen is very far from the supposed “moral dissoluteness” of the barbarians. On the contrary, we cannot but admire the deeply moral principles elaborated within the early village communities which found their expression in Welsh triads, in legends about King Arthur, in Brehon commentaries,[138] in old German legends and so on, or find still their expression in the sayings of the modern barbarians. In his introduction to The Story of Burnt Njal, George Dasent very justly sums up as follows the qualities of a Northman, as they appear in the sagas: —
To do what lay before him openly and like a man, without fear of either foes, fiends, or fate;... to be free and daring in all his deeds; to be gentle and generous to his friends and kinsmen; to be stern and grim to his foes [those who are under the lex talionis], but even towards them to fulfil all bounden duties.... To be no truce-breaker, nor tale-bearer, nor backbiter. To utter nothing against any man that he would not dare to tell him to his face. To turn no man from his door who sought food or shelter, even though he were a foe.[139]
The same or still better principles permeate the Welsh epic poetry and triads. To act “according to the nature of mildness and the principles of equity,” without regard to the foes or to the friends, and “to repair the wrong,” are the highest duties of man; “evil is death, good is life,” exclaims the poet legislator.[140] “The World would be fool, if agreements made on lips were not honourable” — the Brehon law says. And the humble Shamanist Mordovian, after having praised the same qualities, will add, moreover, in his principles of customary law, that “among neighbours the cow and the milking-jar are in common.” that, “the cow must be milked for yourself and him who may ask milk;” that “the body of a child reddens from the stroke, but the face of him who strikes reddens from shame;“[141] and so on. Many pages might be filled with like principles expressed and followed by the “barbarians.”
One feature more of the old village communities deserves a special mention. It is the gradual extension of the circle of men embraced by the feelings of solidarity. Not only the tribes federated into stems, but the stems as well, even though of different origin, joined together in confederations. Some unions were so close that, for instance, the Vandals, after part of their confederation had left for the Rhine, and thence went over to Spain and Africa, respected for forty consecutive years the landmarks and the abandoned villages of their confederates, and did not take possession of them until they had ascertained through envoys that their confederates did not intend to return.
With other barbarians, the soil was cultivated by one part of the stem, while the other part fought on or beyond the frontiers of the common territory. As to the leagues between several stems, they were quite habitual. The Sicambers united with the Cherusques and the Sueves, the Quades with the Sarmates; the Sarmates with the Alans, the Carpes, and the Huns. Later on, we also see the conception of nations gradually developing in Europe, long before anything like a State had grown in any part of the continent occupied by the barbarians. These nations — for it is impossible to refuse the name of a nation to the Merovingian France, or to the Russia of the eleventh and twelfth century — were nevertheless kept together by nothing else but a community of language, and a tacit agreement of the small republics to take their dukes from none but one special family.
Wars were certainly unavoidable; migration means war; but Sir Henry Maine has already fully proved in his remarkable study of the tribal origin of International Law, that “Man has never been so ferocious or so stupid as to submit to such an evil as war without some kind of effort to prevent it,” and he has shown how exceedingly great is “the number of ancient institutions which bear the marks of a design to stand in the way of war, or to provide an alternative to it.”[142] In reality, man is so far from the warlike being he is supposed to be, that when the barbarians had once settled they so rapidly lost the very habits of warfare that very soon they were compelled to keep special dukes followed by special scholæ or bands of warriors, in order to protect them from possible intruders. They preferred peaceful toil to war, the very peacefulness of man being the cause of the specialization of the warrior’s trade, which specialization resulted later on in serfdom and in all the wars of the “States period” of human history.
History finds great difficulties in restoring to life the institutions of the barbarians. At every step the historian meets with some faint indication which he is unable to explain with the aid of his own documents only. But a broad light is thrown on the past as soon as we refer to the institutions of the very numerous tribes which are still living under a social organization almost identical with that of our barbarian ancestors. Here we simply have the difficulty of choice, because the islands of the Pacific, the steppes of Asia, and the tablelands of Africa are real historical museums containing specimens of all possible intermediate stages which mankind has lived through, when passing from the savage gentes up to the States’ organization. Let us, then, examine a few of those specimens.
If we take the village communities of the Mongol Buryates, especially those of the Kudinsk Steppe on the upper Lena which have better escaped Russian influence, we have fair representatives of barbarians in a transitional state, between cattle-breeding and agriculture.[143] These Buryates are still living in “joint families”; that is, although each son, when he is married, goes to live in a separate hut, the huts of at least three generations remain within the same enclosure, and the joint family work in common in their fields, and own in common their joint households and their cattle, as well as their “calves’ grounds” (small fenced patches of soil kept under soft grass for the rearing of calves). As a rule, the meals are taken separately in each hut; but when meat is roasted, all the twenty to sixty members of the joint household feast together. Several joint households which live in a cluster, as well as several smaller families settled in the same village — mostly débris of joint households accidentally broken up — make the oulous, or the village community; several oulouses make a tribe; and the, forty-six tribes, or clans, of the Kudinsk Steppe are united into one confederation. Smaller and closer confederations are entered into, as necessity arises for special wants, by several tribes. They know no private property in land — the land being held in common by the oulous, or rather by the confederation, and if it becomes necessary, the territory is re-allotted between the different oulouses at a folkmote of the tribe, and between the forty-six tribes at a folkmote of the confederation. It is worthy of note that the same organization prevails among all the 250,000 Buryates of East Siberia, although they have been for three centuries under Russian rule, and are well acquainted with Russian institutions.
With all that, inequalities of fortune rapidly develop among the Buryates, especially since the Russian Government is giving an exaggerated importance to their elected taishas (princes), whom it considers as responsible tax-collectors and representatives of the confederations in their administrative and even commercial relations with the Russians. The channels for the enrichment of the few are thus many, while the impoverishment of the great number goes hand in hand, through the appropriation of the Buryate lands by the Russians. But it is a habit with the Buryates, especially those of Kudinsk — and habit is more than law — that if a family has lost its cattle, the richer families give it some cows and horses that it may recover. As to the destitute man who has no family, he takes his meals in the huts of his congeners; he enters a hut, takes — by right, not for charity — his seat by the fire, and shares the meal which always is scrupulously divided into equal parts; he sleeps where he has taken his evening meal. Altogether, the Russian conquerors of Siberia were so much struck by the communistic practices of the Buryates, that they gave them the name of Bratskiye — “the Brotherly Ones” — and reported to Moscow. “With them everything is in common; whatever they have is shared in common.” Even now, when the Lena Buryates sell their wheat, or send some of their cattle to be sold to a Russian butcher, the families of the oulous, or the tribe, put their wheat and cattle together, and sell it as a whole. Each oulous has, moreover, its grain store for loans in case of need, its communal baking oven (the four banal of the old French communities), and its blacksmith, who, like the blacksmith of the Indian communities,[144] being a member of the community, is never paid for his work within the community. He must make it for nothing, and if he utilizes his spare time for fabricating the small plates of chiselled and silvered iron which are used in Buryate land for the decoration of dress, he may occasionally sell them to a woman from another clan, but to the women of his own clan the attire is presented as a gift. Selling and buying cannot take place within the community, and the rule is so severe that when a richer family hires a labourer the labourer must be taken from another clan or from among the Russians. This habit is evidently not specific to the Buryates; it is so widely spread among the modern barbarians, Aryan and Ural-Altayan, that it must have been universal among our ancestors.
The feeling of union within the confederation is kept alive by the common interests of the tribes, their folkmotes, and the festivities which are usually kept in connection with the folkmotes. The same feeling is, however, maintained by another institution, the aba, or common hunt, which is a reminiscence of a very remote past. Every autumn, the forty-six clans of Kudinsk come together for such a hunt, the produce of which is divided among all the families. Moreover, national abas, to assert the unity of the whole Buryate nation, are convoked from time to time. In such cases, all Buryate clans which are scattered for hundreds of miles west and east of Lake Baikal, are bound to send their delegate hunters. Thousands of men come together, each one bringing provisions for a whole month. Every one’s share must be equal to all the others, and therefore, before being put together, they are weighed by an elected elder (always “with the hand”: scales would be a profanation of the old custom). After that the hunters divide into bands of twenty, and the parties go hunting according to a well-settled plan. In such abas the entire Buryate nation revives its epic traditions of a time when it was united in a powerful league. Let me add that such communal hunts are quite usual with the Red Indians and the Chinese on the banks of the Usuri (the kada).[145]
With the Kabyles, whose manners of life have been so well described by two French explorers,[146] we have barbarians still more advanced in agriculture. Their fields, irrigated and manured, are well attended to, and in the hilly tracts every available plot of land is cultivated by the spade. The Kabyles have known many vicissitudes in their history; they have followed for sometime the Mussulman law of inheritance, but, being adverse to it, they have returned, 150 years ago, to the tribal customary law of old. Accordingly, their land-tenure is of a mixed character, and private property in land exists side by side with communal possession. Still, the basis of their present organization is the village community, the thaddart, which usually consists of several joint families (kharoubas), claiming a community of origin, as well as of smaller families of strangers. Several villages are grouped into clans or tribes (ârch); several tribes make the confederation (thak’ebilt); and several confederations may occasionally enter into a league, chiefly for purposes of armed defence.
The Kabyles know no authority whatever besides that of the djemmâa, or folkmote of the village community. All men of age take part in it, in the open air, or in a special building provided with stone seats, and the decisions of the djemmâa are evidently taken at unanimity: that is, the discussions continue until all present agree to accept, or to submit to, some decision. There being no authority in a village community to impose a decision, this system has been practised by mankind wherever there have been village communities, and it is practised still wherever they continue to exist, i.e. by several hundred million men all over the world. The djemmâa nominates its executive — the elder, the scribe, and the treasurer; it assesses its own taxes; and it manages the repartition of the common lands, as well as all kinds of works of public utility. A great deal of work is done in common: the roads, the mosques, the fountains, the irrigation canals, the towers erected for protection from robbers, the fences, and so on, are built by the village community; while the high-roads, the larger mosques, and the great market-places are the work of the tribe. Many traces of common culture continue to exist, and the houses continue to be built by, or with the aid of, all men and women of the village. Altogether, the “aids” are of daily occurrence, and are continually called in for the cultivation of the fields, for harvesting, and so on. As to the skilled work, each community has its blacksmith, who enjoys his part of the communal land, and works for the community; when the tilling season approaches he visits every house, and repairs the tools and the ploughs, without expecting any pay, while the making of new ploughs is considered as a pious work which can by no means be recompensed in money, or by any other form of salary.
As the Kabyles already have private property, they evidently have both rich and poor among them. But like all people who closely live together, and know how poverty begins, they consider it as an accident which may visit every one. “Don’t say that you will never wear the beggar’s bag, nor go to prison,” is a proverb of the Russian peasants; the Kabyles practise it, and no difference can be detected in the external behaviour between rich and poor; when the poor convokes an “aid,” the rich man works in his field, just as the poor man does it reciprocally in his turn.[147] Moreover, the djemmâas set aside certain gardens and fields, sometimes cultivated in common, for the use of the poorest members. Many like customs continue to exist. As the poorer families would not be able to buy meat, meat is regularly bought with the money of the fines, or the gifts to the djemmâa, or the payments for the use of the communal olive-oil basins, and it is distributed in equal parts among those who cannot afford buying meat themselves. And when a sheep or a bullock is killed by a family for its own use on a day which is not a market day, the fact is announced in the streets by the village crier, in order that sick people and pregnant women may take of it what they want. Mutual support permeates the life of the Kabyles, and if one of them, during a journey abroad, meets with another Kabyle in need, he is bound to come to his aid, even at the risk of his own fortune and life; if this has not been done, the djemmâa of the man who has suffered from such neglect may lodge a complaint, and the djemmâa of the selfish man will at once make good the loss. We thus come across a custom which is familiar to the students of the mediaeval merchant guilds. Every stranger who enters a Kabyle village has right to housing in the winter, and his horses can always graze on the communal lands for twenty-four hours. But in case of need he can reckon upon an almost unlimited support. Thus, during the famine of 1867–68, the Kabyles received and fed every one who sought refuge in their villages, without distinction of origin. In the district of Dellys, no less than 12,000 people who came from all parts of Algeria, and even from Morocco, were fed in this way. While people died from starvation all over Algeria, there was not one single case of death due to this cause on Kabylian soil. The djemmâas, depriving themselves of necessaries, organized relief, without ever asking any aid from the Government, or uttering the slightest complaint; they considered it as a natural duty. And while among the European settlers all kind of police measures were taken to prevent thefts and disorder resulting from such an influx of strangers, nothing of the kind was required on the Kabyles’ territory: the djemmâas needed neither aid nor protection from without.[148]
I can only cursorily mention two other most interesting features of Kabyle life; namely, the anaya, or protection granted to wells, canals, mosques, marketplaces, some roads, and so on, in case of war, and the çofs. In the anaya we have a series of institutions both for diminishing the evils of war and for preventing conflicts. Thus the market-place is anaya, especially if it stands on a frontier and brings Kabyles and strangers together; no one dares disturb peace in the market, and if a disturbance arises, it is quelled at once by the strangers who have gathered in the market town. The road upon which the women go from the village to the fountain also is anaya in case of war; and so on. As to the çof it is a widely spread form of association, having some characters of the mediaeval Bürgschaften or Gegilden, as well as of societies both for mutual protection and for various purposes — intellectual, political, and emotional — which cannot be satisfied by the territorial organization of the village, the clan, and the confederation. The çof knows no territorial limits; it recruits its members in various villages, even among strangers; and it protects them in all possible eventualities of life. Altogether, it is an attempt at supplementing the territorial grouping by an extra-territorial grouping intended to give an expression to mutual affinities of all kinds across the frontiers. The free international association of individual tastes and ideas, which we consider as one of the best features of our own life, has thus its origin in barbarian antiquity.
The mountaineers of Caucasia offer another extremely instructive field for illustrations of the same kind. In studying the present customs of the Ossetes — their joint families and communes and their judiciary conceptions — Professor Kovalevsky, in a remarkable work on Modern Custom and Ancient Law was enabled step by step to trace the similar dispositions of the old barbarian codes and even to study the origins of feudalism. With other Caucasian stems we occasionally catch a glimpse into the origin of the village community in those cases where it was not tribal but originated from a voluntary union between families of distinct origin. Such was recently the case with some Khevsoure villages, the inhabitants of which took the oath of “community and fraternity.”[149] In another part of Caucasus, Daghestan, we see the growth of feudal relations between two tribes, both maintaining at the same time their village communities (and even traces of the gentile “classes”), and thus giving a living illustration of the forms taken by the conquest of Italy and Gaul by the barbarians. The victorious race, the Lezghines, who have conquered several Georgian and Tartar villages in the Zakataly district, did not bring them under the dominion of separate families; they constituted a feudal clan which now includes 12,000 households in three villages, and owns in common no less than twenty Georgian and Tartar villages. The conquerors divided their own land among their clans, and the clans divided it in equal parts among the families; but they did not interfere with the djemmâas of their tributaries which still practise the habit mentioned by Julius Caesar; namely, the djemmâa decides each year which part of the communal territory must be cultivated, and this land is divided into as many parts as there are families, and the parts are distributed by lot. It is worthy of note that although proletarians are of common occurrence among the Lezghines (who live under a system of private property in land, and common ownership of serfs[150]) they are rare among their Georgian serfs, who continue to hold their land in common. As to the customary law of the Caucasian mountaineers, it is much the same as that of the Longobards or Salic Franks, and several of its dispositions explain a good deal the judicial procedure of the barbarians of old. Being of a very impressionable character, they do their best to prevent quarrels from taking a fatal issue; so, with the Khevsoures, the swords are very soon drawn when a quarrel breaks out; but if a woman rushes out and throws among them the piece of linen which she wears on her head, the swords are at once returned to their sheaths, and the quarrel is appeased. The head-dress of the women is anaya. If a quarrel has not been stopped in time and has ended in murder, the compensation money is so considerable that the aggressor is entirely ruined for his life, unless he is adopted by the wronged family; and if he has resorted to his sword in a trifling quarrel and has inflicted wounds, he loses for ever the consideration of his kin. In all disputes, mediators take the matter in hand; they select from among the members of the clan the judges — six in smaller affairs, and from ten to fifteen in more serious matters — and Russian observers testify to the absolute incorruptibility of the judges. An oath has such a significance that men enjoying general esteem are dispensed from taking it: a simple affirmation is quite sufficient, the more so as in grave affairs the Khevsoure never hesitates to recognize his guilt (I mean, of course, the Khevsoure untouched yet by civilization). The oath is chiefly reserved for such cases, like disputes about property, which require some sort of appreciation in addition to a simple statement of facts; and in such cases the men whose affirmation will decide in the dispute, act with the greatest circumspection. Altogether it is certainly not a want of honesty or of respect to the rights of the congeners which characterizes the barbarian societies of Caucasus.
The stems of Africa offer such an immense variety of extremely interesting societies standing at all intermediate stages from the early village community to the despotic barbarian monarchies that I must abandon the idea of giving here even the chief results of a comparative study of their institutions.[151] Suffice it to say, that, even under the most horrid despotism of kings, the folkmotes of the village communities and their customary law remain sovereign in a wide circle of affairs. The law of the State allows the king to take any one’s life for a simple caprice, or even for simply satisfying his gluttony; but the customary law of the people continues to maintain the same network of institutions for mutual support which exist among other barbarians or have existed among our ancestors. And with some better-favoured stems (in Bornu, Uganda, Abyssinia), and especially the Bogos, some of the dispositions of the customary law are inspired with really graceful and delicate feelings.
The village communities of the natives of both Americas have the same character. The Tupi of Brazil were found living in “long houses” occupied by whole clans which used to cultivate their corn and manioc fields in common. The Arani, much more advanced in civilization, used to cultivate their fields in common; so also the Oucagas, who had learned under their system of primitive communism and “long houses” to build good roads and to carry on a variety of domestic industries,[152] not inferior to those of the early medieval times in Europe. All of them were also living under the same customary law of which we have given specimens on the preceding pages. At another extremity of the world we find the Malayan feudalism, but this feudalism has been powerless to unroot the negaria, or village community, with its common ownership of at least part of the land, and the redistribution of land among the several negarias of the tribe.[153] With the Alfurus of Minahasa we find the communal rotation of the crops; with the Indian stem of the Wyandots we have the periodical redistribution of land within the tribe, and the clan-culture of the soil; and in all those parts of Sumatra where Moslem institutions have not yet totally destroyed the old organization we find the joint family (suka) and the village community (kota) which maintains its right upon the land, even if part of it has been cleared without its authorization.[154] But to say this, is to say that all customs for mutual protection and prevention of feuds and wars, which have been briefly indicated in the preceding pages as characteristic of the village community, exist as well. More than that: the more fully the communal possession of land has been maintained, the better and the gentler are the habits. De Stuers positively affirms that wherever the institution of the village community has been less encroached upon by the conquerors, the inequalities of fortunes are smaller, and the very prescriptions of the lex talionis are less cruel; while, on the contrary, wherever the village community has been totally broken up, “the inhabitants suffer the most unbearable oppression from their despotic rulers.”[155] This is quite natural. And when Waitz made the remark that those stems which have maintained their tribal confederations stand on a higher level of development and have a richer literature than those stems which have forfeited the old bonds of union, he only pointed out what might have been foretold in advance.
More illustrations would simply involve me in tedious repetitions — so strikingly similar are the barbarian societies under all climates and amidst all races. The same process of evolution has been going on in mankind with a wonderful similarity. When the clan organization, assailed as it was from within by the separate family, and from without by the dismemberment of the migrating clans and the necessity of taking in strangers of different descent — the village community, based upon a territorial conception, came into existence. This new institution, which had naturally grown out of the preceding one — the clan — permitted the barbarians to pass through a most disturbed period of history without being broken into isolated families which would have succumbed in the struggle for life. New forms of culture developed under the new organization; agriculture attained the stage which it hardly has surpassed until now with the great number; the domestic industries reached a high degree of perfection. The wilderness was conquered, it was intersected by roads, dotted with swarms thrown off by the mother-communities. Markets and fortified centres, as well as places of public worship, were erected. The conceptions of a wider union, extended to whole stems and to several stems of various origin, were slowly elaborated. The old conceptions of justice which were conceptions of mere revenge, slowly underwent a deep modification — the idea of amends for the wrong done taking the place of revenge. The customary law which still makes the law of the daily life for two-thirds or more of mankind, was elaborated under that organization, as well as a system of habits intended to prevent the oppression of the masses by the minorities whose powers grew in proportion to the growing facilities for private accumulation of wealth. This was the new form taken by the tendencies of the masses for mutual support. And the progress — economical, intellectual, and moral — which mankind accomplished under this new popular form of organization, was so great that the States, when they were called later on into existence, simply took possession, in the interest of the minorities, of all the judicial, economical, and administrative functions which the village community already had exercised in the interest of all.
#organization#revolution#mutual aid#anarchism#daily posts#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#anarchy#anarchists#libraries#leftism#social issues#economy#economics#climate change#anarchy works#environmentalism#environment#solarpunk#anti colonialism#a factor of evolution#petr kropotkin
14 notes
·
View notes