#1 Regional (Rome)
Text
0 notes
Note
You wanna know what I just realized....You know how in chapters 1-4 MC/Yu kept asking Crowley to go home. But Once Chapter 5-7 they stopped asking to go home and gave up. Why? Did they just change their minds once they got friends or did they just give up on trying completely until Orthro put it back in their brain? Or Did they just gave up on asking adults period?

Oooh, interesting topic 🤔
I went back in each book to see when instances of Yuu asking about going home were brought up and (shockingly) this actually happens very little, maybe a few times max in the main story (not counting the prologue):
***Main story spoilers (INCLUDING book 7) below the cut!!***
In 1-19, Yuu does NOT ask Crowley; Crowley is the one who brings the topic up. He claims he is in the library to research a way to send Yuu home, and definitely is not reading the latest edition to a new novel before anyone else (which, come on, we all know Crowley is just giving a convenient excuse for himself). Crowley's presence here is then used to inform us of a way to dethrone Riddle via duel.
In 2-4, Yuu DOES ask Crowley when summoned to his office. Crowly then says he is busy preparing for an inter-dorm Magift/Spelldrive tournament, so he hasn't made any progress for Yuu. In 2-14, Yuu also wonders about when they will be able to go home while talking around the campus at night, but does not discuss it further with others.
In 3-6, Yuu does NOT ask Crowley; again, Crowley is the one to bring up the topic when trying to get Yuu to convince Azul to stop his shady dealings. He uses their rising food bills and all that "effort" he's putting into researching as a means to guilt trip Yuu into agreeing.
In 4-2, Yuu DOES ask Crowley if he's actually researching. This occurs because Crowley is all decked out for vacationing in a tropical destination, so Yuu of course questions whether he's doing any real work. Crowley defends himself by saying "When in Rome, do as the Romans do!" and that he's broadening his knowledge base by researching in a southern region.
After book 4, there are no new explicit or even implied scenes of Yuu asking Crowley anything about home. However, 5-33 does feature a flashback to the prologue in which Crowley is struggling to find Yuu's home on a map.
There isn't really a strong mention of Yuu going home in book 6, unless you want to count Yuu talking to Mickey through the mirror and wondering what's on the other side.
7-10 and 7-11 has Ortho to concluding that the mirror with Mickey could be a "connection" to Yuu's original world, and can thus serve as a route home.
Most discussion of Yuu going home is concentrated in the prologue (as it is an important piece of the set-up and explanation for Yuu's presence in Twisted Wonderland), as well as book 7, when the issue becomes very relevant again. There is the occasional instance of Crowley using "oh, there might be information here about a potential way home" as an excuse to rope Yuu into an event's story (ie Glorious Masquerade), but nothing meaningful ever comes from it. These are just contrivances to bring Yuu and Grim along for a more immersive self-insert experience.
If you want a boring answer as to why Yuu asks/seems to care so little about going home and stops completely by the start of book 5, I would wager it's the metacontext. Even in books 1 through 4, Yuu going home is mentioned like maybe once and then is dismissed for the rest of the book. You’ll also notice that in these instances where Yuu going home is mentioned, they are almost immediately then used as a springboard to propel the problem of the week onto them to resolve. Yuu going home isn’t a plot point for most of the main story, it’s a plot device to force Yuu into an OB boy’s path.
There is very little urgency granted to finding a way home because you, the player, WANTS to be in this magical world even if Yuu, the actual in-game character, may be uneasy being away from their friends, family, and home world. Yuu's unease is most likely not depicted or not frequently brought up because it would interfere with the player's enjoyment of the escapism to another world. These desires very obviously clash with one another. However, because the game itself is trying to tell you its story, it has to provide a reason (no matter how nonsensical it is) for there to be no progress made in the search (thus keeping Yuu in Twisted Wonderland), and that reason often happens to be Crowley's incompetence. This is not true of all iterations of Yuu (as the light novel has a strong focus on Yuuya’s anxieties about being in a new world), but it must be this way specifically for in-game Yuu since they are the most easy one for players to project into.
If you're looking for a meatier answer, consider this: book 5 is the turning point in the main story. Before book 5, Yuu seems to defer to Crowley for finding a way home. They don't really wonder or investigate into this area on their own. By the start of VDC/SDC training, it's mid to late winter, or about halfway through the year. Given that Yuu is incentivized by the promise of renovations to let the NRC Tribe boys use Ramshackle as their base of operations, I get the impression that maybe Yuu thinks they'll be stuck in Twisted Wonderland for longer than initially anticipated. Rather than an "I give up", it feels like a "boy, this is taking a while so might as well upgrade the accommodations and make myself as comfy as possible while I wait it out" This thought is helped by the fact that book 5 is also the first time when both Yuu and Crowley don't mention them going home, but also nothing disparaging or hopeless is referenced. As I've said before, we still get a flashback from Yuu which is centered on them going home, so it's clearly still a topic on their mind. It's just not consistently shown to us so as to not interfere with players self-inserting or to avoid making the gaming experience not fun by focusing on Yuu's distress or worries.
Many other significant things happen in book 5 which makes it the "turning point": Malleus reveals his true identity to Yuu, Grim finally going a little feral from the blot stones, and Yuu seeing and speaking with Mickey clearly. From there, Yuu starts thinking about the mirror and how it could lead into another world. They begin to take more agency in their own return, later confiding in their friends about Mickey and what he means for them.
Book 6 mostly glosses over Yuu going home because... well, let's be honest, there's a lot more immediately at stake with six students being kidnapped and experimented on. Yuu's focus and concern is on getting them (and especially Grim) back safely. They weren't thinking about themselves or their own situation back then, they were thinking of others.
Going home returns in book 7 because it has story significance once again. Yuu going back to their own world adds to the growing dread and sense of loneliness that our OB boy for the evening, Malleus, feels over Lilia's departure. It helps to push him closer to the brink of snapping. What's more, this contributes to the overall themes and questions that book 7 poses: those of farewells, change, and leaving friends behind. These are sentiments that Ace, Deuce, and Grim discuss in 7-17, and they parallel Malleus's own anxious thoughts. In all previous books, Yuu's own quest to get home is not closely tied to the themes of a particular book, or it simply was not relevant to mention (it would disrupt the ongoing conflict or pacing).
Finally, to more address each of the specific things asked by the asker (since I know the information in this post is sort of all over the place and might be hard to match up to each question):
[Yuu] stopped asking to go home and gave up. Why?
Yuu did not frequently ask about going home to begin with. (Again, likely because on a metatextual level, the story needs an excuse for Yuu, ie the player, being present in Twisted Wonderland and experiencing its happenings.)
At that point, it comes down to individual interpretation as to why, but personally I believe Yuu realized that the solution was more complicated than just poofing up a portal home, so they decided to make themselves comfortable while they waited for updates rather than keep asking only to be constantly disappointed. Later on, events going on around Yuu become too hectic for them to focus on their own wants.
Did [Yuu] just change their mind once they got friends?
Wouldn’t this imply that Yuu didn’t consider Adeuce and Grim “real” friends until the start of book 5??? I just don’t think that’s true; they were friends way before this point, not hanging out with each other for convenience’s sake. Why would they sit together at lunch every day? Why would Yuu try to help Ace make amends with Riddle? And why would Ace defend Yuu when Riddle insults their upbringing? Why would Yuu try to free the idiots of their anemones at the risk of going homeless themselves? Why would Adeuce use public transportation to go all the way from the Queendom of Roses to Sage’s Island because of a SOS text from Yuu? The same logic goes for the Ramshackle Ghosts, who are very friendly with Yuu and Grim. They play games with them, tell them about the school, and even do Yuu’s chores for them while they’re held hostage in Scarabia.
I also think gaining friends isn’t necessarily a strong enough reason for Yuu to renounce their old life and suddenly be committed to staying. Yes, it can be said that this could change depending on individual interpretation of Yuu—but assuming a very basic backstory, a regular person would not be so quick to forgo their old friends, family, etc. I don’t think new friendships are a significant motivator for Yuu no longer asking about home.
Or did they just give up on trying completely until Orthro put it back in their brain?
Yuu didn’t stop thinking about going home just because they stopped asking about it. Post book 4, they are shown to have flashbacks to earlier discussions of going home. Yuu hardly ever expresses thoughts about their original world or wanting to go back (most likely to not break the self-insert immersion of their character), so it’s easy to perceive this as “Yuu gave up completely/Yuu forgot about it until book 7”.
Or did they just gave up on asking adults period?
I believe Crowley is the only adult Yuu really asks about finding a way back. I doubt Yuu actually thinks all adults are as useless in this endeavor as Crowley is, but we aren’t ever shown Yuu communicating in this manner to other adults. Crowley is the only “required” adult to interact with on account of being the headmaster typically forcing you into the plot anyway.
In conclusion (I know I keep bringing this point up, but it’s because I truly believe in it), this is all probably done for convenience and/or to allow the player to fantasize and imagine themselves or their own Yuusonas navigating these circumstances. They don't want to constantly keep the story gloomy by having Yuu angst about how they miss home or how badly they want to go back. They want you, the player, to enjoy the world and the people of Twisted Wonderland and never want to leave, even if it may be contradictory to what Yuu themselves fails to express in the narrative.
This is 100% intentional, and it's made clear because it ties in very deeply with the themes in book 7, which is when the idea of Yuu going home becomes extremely relevant again. Book 7 creates an analogy between a digital pet that Malleus owns and how sad he is that its lifespan has to end, that the digital pet is just "fiction designed to amuse". This is also true of what Twisted Wonderland (the game) is. The player is in the same circumstances as Malleus, who is too attached to his fiction and doesn't want to let it go.
As much as the game's structure encourages self-inserting, it cannot be denied that, ultimately, the perspective of the player ≠ the perspective of Yuu. The player does not actually have to worry about never returning home or being stuck in a foreign world, at the mercy of strangers (which, if not for entertainment purposes, would be something truly terrifying to deal with). The player is glimpsing into this other world for fun and can step away whenever they want. Yuu can't.
askhdvasoydvuealalf I know this was a lot, but I hope it made sense and properly communicated my thoughts ^^
#twst#twisted wonderland#Malleus Draconia#Dire Crowley#Ace Trappola#Deuce Spade#Riddle Rosehearts#Yuu#Grim#Mickey Mouse#Ortho Shroud#Azul Ashengrotto#Lilia Vanrouge#disney twisted wonderland#disney twst#question#spoilers#notes from the writing raven#Ramshackle Ghosts#twst theory#twisted wonderland theory#twisted wonderland theories#twst theories#twst light novel#twisted wonderland light novel#Kuroki Yuuya#Yuuya Kuroki
187 notes
·
View notes
Text
If you don’t have records but can reasonably extrapolate your family remained in the same area use the year/era of the first regional government/title/tribe you know your family lived under (if you know your family lived under Ottoman rule but don’t know anything else/earlier you can say your knowledge goes back to the 1600s, etc.)
188 notes
·
View notes
Text
More notes on the development of Roman imperialism and colonialism:
Rome began as a city warring with other cities and city-states in Italy. Its growth was haphazard and, in some ways, accidental. They don't seem to have thought of it as an "empire" in the sense of "our land and sea," until the 1st century BCE.
Before then, the Roman empire was characterized by active military control, not by thinking of lands as "Roman territory." This was not the USA trying to grab all the land it could in manifest destiny; this was a city-state that primarily aimed to enrich and defend itself, and often used military occupation to do so.
The Romans did not like to think of themselves as an expansionist power, but as fighting defensive wars for themselves and their allies. However, the Roman system of alliance building - and sometimes provoking other countries - frequently "pulled" Rome into wars anyway. And Roman generals who really wanted a war could often invent justifications for it. Caesar's conquest of Gaul is one of many wars that started as "protecting an ally from invasion" but which soon became opportunistic power-grabs.
Even so, this self-concept as "defenders" partly explains why the Romans mostly left defeated Italian communities intact, only demanding troop levies and sometimes confiscating part of the land. Draining conquered peoples dry or wiping them out was not the goal, and the Romans actually prided themselves on being relatively "merciful" to their neighbors (by classical standards). However, as Rome's sphere of influence grew, and the distance from Rome to defeated (and potentially rebellious) communities increased, they began stationing permanent military outposts in certain regions.
Roman colonies originated as military outposts. They served a quadruple purpose: 1) to punish communities that had rebelled or fought wars against Rome; 2) to reward Roman veterans; 3) to relieve economic tensions in Rome itself; and 4) to suppress further rebellion by maintaining Roman outposts in the region.
This is in contrast to Greek and Phoenician colonies, which were usually established by traders, and the USA's westward expansion, which aimed to replace indigenous peoples en masse.
Similarly, the word "province" originally referred to a task or assignment, not a geographic area. A proconsul might be assigned the "province" of Spain of Sicily in the sense of "keep this region from revolting."
Economic exploitation came later. The Punic Wars marked a turning point in which Rome stationed generals overseas for extended periods of time to prevent insurgency among subject peoples, not Italian allies who were acknowledged as mostly self-governing. These generals had immense latitude to do as they saw fit, and with the promise of armed protection, Roman businessmen soon saw opportunities for mining, slave plantations, and more. This is also why Spain, Sicily, and certain other regions were abused much more harshly than Italy itself.
In the 1st century BCE we see a slow shift toward conquest of lands being sought for its own sake, rather than as a by-product of war. By the reign of Augustus, writers imagined Rome conquering the whole world.
Julius Caesar's conquest of Gaul occurred midway through this ideological shift. Hence he felt the need to justify his conquest by presenting his side of the story in his Commentaries, but the public response to his needless invasion of Britain was overwhelmingly positive. Conquest, if successful, was beginning to justify itself.
However, the Romans also gradually came to see themselves as responsible for the government of long-term provinces, and take measures to curb abuse of provincials. Caesar himself installed one of the biggest reforms limiting corruption. (Yes, he was a bit of a hypocrite...)
The gradual expansion of citizenship across the empire and military recruitment from provincials gradually put pressure on the Romans to value more than just Italian interests. We first see this with Julius Caesar's attempt to extend Latin Rights to Sicily and citizenship to Cisalpine Gauls; it reached its final form when the Edit of Caracalla made all free inhabitants of the empire citizens in 212 CE. The "Romanization" of Europe did not happen by displacing the original inhabitants of provinces, but by incorporating them.
Sources: SPQR by Mary Beard; A Companion to the Roman Republic, ed. Rosenstein and Morstein-Marx, chapters 6-7. See also my previous post on this topic.
#jlrrt reads#a companion to the roman republic#nathan rosenstein#robert morstein-marx#colonialism#imperialism#there were some cases of mass displacement and genocide btw. but at the risk of hair-splitting: these occurred as part of wars#rather than as the goal of roman colonialism per se#jlrrt essays
69 notes
·
View notes
Text

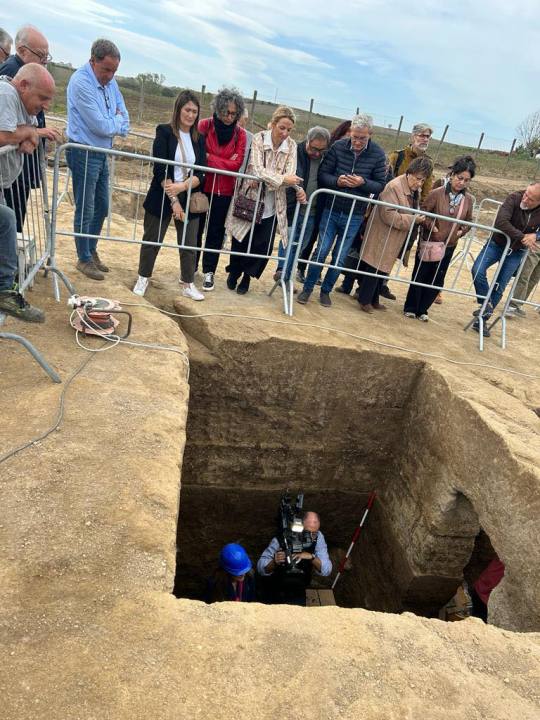
A 2,600-Year-Old Unopened Etruscan Tomb Discovered in Italy
Community leaders and archeologists in central Italy recently gathered in the municipality of Montalto di Castro for the opening of a tomb that dates back more than 2 1/2 millennia, the municipality announced in a social media post last week.
"Today … we witnessed the opening of an ancient Etruscan tomb buried at the Osteria Necropolis in Vulci," the municipality of Montalto di Castro, which sits along the Mediterranean Sea about 100 miles northwest of Rome, wrote Oct. 27 on Facebook, calling the grand unveiling "a day of culture and history" in a translated statement.


Historians say the Etruscans built their civilization on a portion of the land that is now modern-day Italy, beginning as early as 900 B.C., and operated as a network of city-states not completely unlike the Roman Republic that came after it. The Etruscans dominated Italy until falling, as a result of the Roman-Etruscan wars, to the then-expanding Roman empire around the 4th century B.C.
Vulci, an archaeological site in the northern Lazio region not far from Montalto di Castro, was once a rich Etruscan city. Its ruins have become a popular spot for tourist visits and as well as a place of interest for archaeological excavations.
The tomb discovered there earlier this year was found remarkably intact when it was officially opened at the end of October, for the first time in about 2,600 years, according to the Italian online magazine Finestre sull'Arte, which focuses on ancient and contemporary art. It was opened and explored following the opening of a similar tomb in the area this past April, the magazine reported. Montalto di Castro Mayor Emanuela Socciarelli attended the opening along with Simona Baldassarre, the councilor of culture for the Lazio region, Simona Carosi, the manager of the Superintendency of Archaeology for the province of Viterbo and southern Etruria, and Carlos Casi, the director of the Vulci Foundation, which helped lead the excavation alongside archeologists.
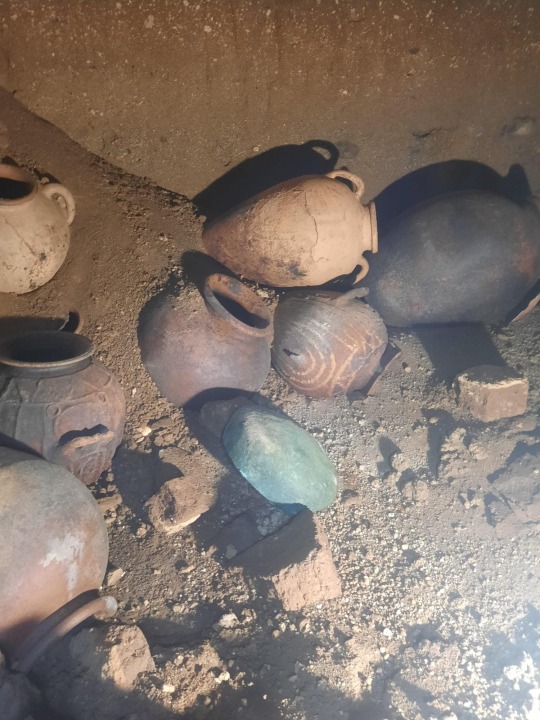


Archaeologists found a collection of long-lost treasures inside the ancient tomb, including a collection of pottery and amphorae, which are tall jars with two handles and a narrow neck typically associated with ancient Greek or Roman cultures. The jars contained wine from Greece, likely from the island of Chios, Finestre sull'Arte reported. It could be a relic of the wine trade happening at that time in history.
Utensils, cups, iron objects, and a variety of ceramics and decorative accessories were also found inside the tomb in perfect condition, as was a tablecloth that may have been used for a funerary ritual offering called "the last meal" or "meal of the dead." A bronze cauldron was also found.
The stockpile of personal belongings found inside the tomb suggests the family for whom it was constructed was probably quite wealthy in their day.
The complex structure and layout of the burial site is also important to archeologists and historians, Casi told the Italian news outlet Il Messaggero, noting that the tomb "appears to be characterized by a partition saved in the rock which creates a passage arch between the dromos, i.e. the short corridor with steps, and the vestibule, from which the two rooms were accessed, the front one and the one on the left: the usual one on the right is missing, evidently because the space had already been occupied by other tombs."
By EMILY MAE CZACHOR.


#A 2600-Year-Old Unopened Etruscan Tomb Discovered in Italy#Montalto di Castro#Osteria Necropolis in Vulci#ancient tomb#ancient grave#ancient necropolis#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#roman history#roman empire#etruscan history
129 notes
·
View notes
Text

This is a message to my black brothers and sisters
Learn about your history
Ethiopia is one of the oldest countries in Africa; the emergence of Ethiopian civilization dates back thousands of years. Abyssinia or rather "Ze Etiyopia" was ruled by the Semitic Abyssinians (Habesha) composed mainly of the Amhara and Tigray, the Cushitic Agaw. In the Eastern escarpment of the Ethiopian highlands and more so the lowlands was the home of the Arab-descended Harari that founded Sultanates such as Ifat and Adal and the Afars. In the central and south were found the ancient Sidama and Semitic Gurage, among otheres. One of the first kingdoms to rise to power in the territory was the kingdom of D'mt in the 10th century BC, which established its capital at Yeha. In the first century AD the Aksumite Kingdom rose to power in the modern Tigray Region with its capital at Aksum and grew into a major power on the Red Sea, subjugating South Arabia and Meroe and its surrounding areas. In the early fourth century, during the reign of Ezana, Christianity was declared the state religion. Ezana's reign is also when the Aksumites first identified themselves as "Ethiopians", and not long after, Philostorgius became the first foreign author to call the Aksumites Ethiopians.[The Aksumite empire fell into decline with the rise of Islam in the Arabian peninsula, which slowly shifted trade away from the Christian Aksum.[citation needed] It eventually became isolated, its economy slumped and Aksum's commercial domination of the region ended.The Aksumites gave way to the Zagwe dynasty, who established a new capital at Lalibela before giving way to the Solomonic dynasty in the 13th century. During the early Solomonic period, Ethiopia went through military reforms and imperial expansion that allowed it to dominate the Horn of Africa.
How did Ethiopia Resist Imperialism?
Ethiopia, formerly Abyssinia, is one of the world’s oldest countries. Dating to around 400 BCE, the region is documented in the in the King James Version of the Bible as the Kingdom of Axum. Along with Rome, Persia, and China, Axum was considered one of the four great powers of the era. Throughout the millennia of its history, the willingness of the country’s people—from farmers to kings—to come together as one, coupled with its geographic isolation and economic prosperity, helped Ethiopia score decisive victories against a series of global colonialist forces.
Ethiopia is considered “never colonized” by some scholars, despite Italy's occupation from 1936–1941 because it did not result in a lasting colonial administration.
Seeking to expand its already considerable colonial empire in Africa, Italy invaded Ethiopia in 1895. In the ensuing First Italo-Ethiopian War (1895-1896), Ethiopian troops won a crushing victory over Italian forces at the Battle of Adwa on March 1, 1896. On October 23, 1896, Italy agreed to the Treaty of Addis Ababa, ending the war and recognizing Ethiopia as an independent state.
On Oct. 3, 1935, Italian dictator Benito Mussolini, hoping to rebuild his nation’s prestige lost in the Battle of Adwa, ordered a second invasion of Ethiopia. On May 9, 1936, Italy succeeded in annexing Ethiopia. On June 1 of that year, the country was merged with Eritrea and Italian Somalia to form Africa Orientale Italiana (AOI or Italian East Africa).
Ethiopian Emperor Haile Selassie made an impassioned appeal for assistance in removing the Italians and re-establishing independence to the League of Nations on June 30, 1936, gaining support from the U.S. and Russia. But many League of Nations members, including Britain and France, recognized Italian colonization.
It was not until May 5, 1941, when Selassie was restored to the Ethiopian throne, that independence was regained.
Ethiopia's ability to resist being swept up in the "Scramble for Africa" can be credited to the stability of its longstanding imperial government, beginning with the Abyssinian Empire in the 13th century, and lasting into the late 20th century, with the exception of a brief Italian occupation during the 1930s. King Menelik II, the Emperor during the period of rampant European exploration and colonization in Africa, was careful to cultivate an alliance with the smaller surrounding kingdoms of North Africa, and with European powers including Italy and Russia. When Italy began to turn the sights of their imperial ambitions toward Ethiopia, the Ethiopian military became the only African kingdom able to successfully resist the military might of European colonial power, using Russian-supplied weapons to defeat the Italian invading force at the Battle of Adwa in 1896. In the aftermath of the battle, in exchange for permanent recognition as an independent empire, Menelik II granted Italy the right to claim the neighboring territory of Eritrea under their imperial umbrella.
Ethiopians have a history of taming lions.
Many Emperors kept pet lions including Halie Selassie. Occasionally visitors like Kwame Nkrumah could pet one of the lions!
This practice of keeping lions is said to date back thousands of years to the Axumite period.The descendants of the Royal Lions currently live in the Addis Ababa zoo.

Meet his imperial majesty, the King of the Jungle.
And if, with his thick, shaggy mane Challa seems to have something of a frisky regal air about him - it's because he knows that he is a genuine blue blood.Challa is a direct descendant of Mochuria and Mollua - royal lions, which the late Emperor Haile Selassie kept as pets. The Emperor's practice of keeping pet lions is said to date thousands of years back to the Axumite period.Years ago in Ethiopia, Lions were pets to the people, some were used like donkeys, some like dogs kept at home. Emperor Haile Selassie of Ethiopia had lions he kept as pets, while some Ethiopians could even ride on them. These were not wild lions, they grew up with humans and became domesticated.They didn't go after human blood or other animals, lions roamed around the streets of Ethiopia and live was beautiful with them. Ethiopia is in East Africa, it's a rugged, landlocked country split by the Great Rift Valley, Ethiopia is a place of ancient culture, they believe and still hold on to ancient affairs.
Any lion that goes wild was immediately hunted killed, they were only killed if they kill a human and not animals like goats and chickens. They forbid killing and eating of any lion because lions were pets used in different palaces.
Ethiopia as a country had its origin in about 980 B.C., which makes it one of the oldest nations in the world.
Due to this very long history and an unmatched diversity of people and cultures, the country has often been described as a “museum of peoples”. With such a highly diverse population, Ethiopia houses an intricate tapestry of language and ethnic groups.
Also nicknamed the “Land of 13 Sunshine’s”, Ethiopia is often described as one of the most enthralling and enchanting places in the world – and definitely in Africa.
Ethiopia may not be the first place any traveller think of when planning or booking a next holiday, but it may just as well soon be the case. As African country Ethiopia can boast about having been at peace for at least the previous 15 years or more years and its economy is consequently one of the fastest growing in the world.
With the added bonus of an astounding diversity of landscapes, mixture of cultures and history that tracks back to when homo sapiens first started to raise itself up onto two legs, a traveller suddenly may look forward to a surprising and breath-taking travel destination.
But talking about planning and holiday dated, you probably didn’t know that this unique nation even has its own calendar?
This is but one of a myriad fascinating facts about the country, of which a number are discussed in this article. Looking at the country’s ancient and statutory history, its religion, culture, people and natural phenomena, here are at least 44 random but fascinating facts that you can ponder in anticipation of a visit to this eastern African country in the near future:
Fact number 1 – The oldest people in the world probably lived here.
Fact number 2 – Ethiopia is the oldest independent country in Africa and the only African country that could evade colonial rule.
Fact number 3 – Ethiopia was one of the first African forces to achieve a significant victory over a European colonial power.
Fact number 4 – Ethiopia has a rich history of rulers, including emperors and queens.
Fact number 5 – Ethiopia is perceived to be the diplomatic capital of the African continent
Fact number 6 – Ethiopia is the country with the second highest population in Africa, and with almost 1,5 % of the world population.
Fact number 8 – Ethiopia has the most orphans in the world.
Fact number 10 – Addis Ababa is the highest capital city in Africa.
Fact number 11 – More than 200 dialects are spoken by the peoples of the country.
Please like and share so others can see, drop your comments below and let me know what you think.
98 notes
·
View notes
Text
Folklore Fact - Gryphons/Griffins
Gryphons, griffins, griffons, however you prefer to spell it (I personally use gryphon) - let's talk their folklore and mythology!

(Attic pottery depicting a satyr and a griffin and an Arimaspus from around 375-350 BC, Eretria.)
You probably already know the common popular culture concept of a gryphon: a big, vicious beast that attacks people and probably eats them and/or carries people away to its nest to feed them to its babies. Not much about it has changed in legend, though in a lot of popular culture today, it has seemed to lose its divinity. Gryphons - griffins, whatever you prefer - have quite the robust history, like so many creatures of myth and folklore. Unlike some, however, they have changed very little over time.
Note that this article a general overview of concepts, not a detailed history.
Let's start with etymology, because I just love that stuff. The word "griffin" comes from the Greek word "gryps," which referred to a dragon or griffin and literally meant "curved [or] hook-nosed." Late Latin spelled it "gryphus," a misspelling of grypus, a Latinized version of the Greek (source: https://www.etymonline.com/, one of my favorite websites).
Griffins are said to have the head and wings of an eagle and body of a lion. They may or may not also have pointed ears, depending on the depiction (they more often did, overall, though the griffin of Crete is a notable exception). They were said to guard the gold in the mountains of the north, specifically the mountains of Scythia. The one-eyed Arimaspian people rode on horseback and attempted to steal the griffins' gold, causing griffins to nurture a deep hatred of and hostility toward horses.
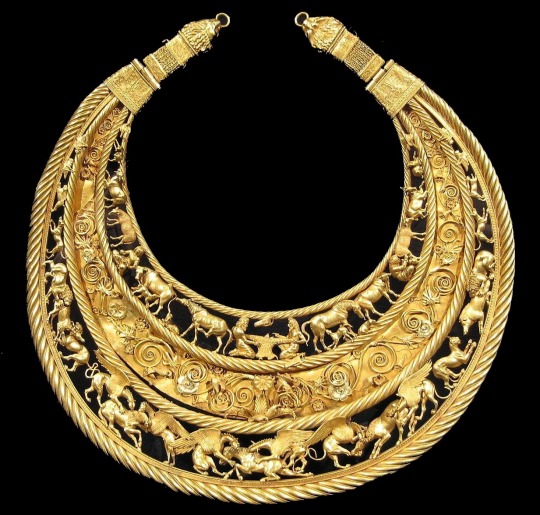

A Scythian pectoral, thought to have been made in Greece, depicting - among other things - griffins slaughtering horses. Griffins really, really hate horses.

The famous griffin in the palace of Knossos at Crete, from the Bronze Age (restored).
Griffins appear in truly ancient civilizations, not only Greece but also ancient Egypt and civilizations to the east, including ancient Sumeria. Griffins were later said to also dwell in India and guard gold in that region, and they continued to appear in art throughout ancient Persia, Rome, Byzantium, and into the Middle Ages throughout other regions such as France; they were depicted in ancient Greece with relative frequency and occasionally of considerable importance.
Griffins appeared in many ancient Greek writings, including Aristeas in the 7th century BC. Herodotus and Aeschylus preserved and continued these writings in the 5th century BC, including lines such as,
"But in the north of Europe there is by far the most gold. In this matter again I cannot say with assurance how the gold is produced, but it is said that one-eyed men called Arimaspoi (Arimaspians) steal it from Grypes (Griffins). The most outlying lands, though, as they enclose and wholly surround all the rest of the world, are likely to have those things which we think the finest and the rarest." Herodotus, Histories 3. 116. 1 (trans. Godley) (Greek historian C5th B.C.), source: https://www.theoi.com/Thaumasios/Grypes.html (a wonderful site)
Physical descriptions of the griffin were not commonplace until some later works, and even then, their appearance wasn't always agreed upon. Even the notion of griffins having wings was sometimes disputed. Some scholars even got pretty wild, claiming griffons had no wings at all but instead skin-flaps that they used to glide. They apparently hated awesome things, so it turns out there were always boring people who thought they knew everything, wanted to explain everything "logically," and generally assume they were the smartest ever while also ruining mystique. They would make great scientists today.
Griffins were, however, often said to be holy in nature. They were referred to as the "unbarking hounds of Zeus" by Aeschylus, who warned others never to approach them. Gryphons were also considered sacred to several gods, including prominently Apollo, who was said to depart Delphi each winter, flying on a griffon (griffin, gryphon, etc, I keep swapping this around, I know; my brain spells it differently because I've read way too many sources), and he also is occasionally depicted as hitching griffins to his chariot in addition to riding one. This was particularly prominent in the cults of Hyperborean Apollo, one of the many endless and fascinating cults of ancient Greece.

Medieval bestiary depiction of a griffin slaughtering a horse.
Even by the Middle Ages, gryphons still hated and slaughtered horses and guarded gold, elements that certainly persisted throughout their legends. They also killed men and carried them away to their nests, similar to the manner in which Aeschylus warned people to stay away from gryphons even back when. We can obviously assume griffons were never cuddly, so that isn't much of a change.
Griffins also did not entirely lose their divine relations even into the Middle Ages. Christianity often used positive portrayals of griffins to represent and uphold certain positive tenets of Christian faith; likewise, they became important symbols of medieval heraldry, used to represent a Christian symbol of divine power, as well as general courage, strength, and leadership, especially in a military sense. The depiction of the griffin as a powerful and majestic creature - killing horses and men or not - throughout its history is no doubt because they are a combination of two beasts often considered noble symbols of bravery, power, and divinity: the lion and the eagle, kings of land animals and birds, respectively.
That's a general overview! As you can see, griffins aren't always so bad, at least not compared to some of the other creatures out there from folklore and myth.
( If you like my blog, be sure to follow me here and sign up for my free newsletter for more folklore and fiction, including books!
Free Newsletter - maverickwerewolf.com (info + book shop) — Patreon — Wulfgard — Werewolf Fact Masterlist — Twitter — Vampire Fact Masterlist — Amazon Author page )
#folklore#mythology#gryphon#griffin#fantasy creature#gryphons#griffins#griffon#folklore fact#folklore thursday#greek myth#myth#persian myth#medival#medieval folklore#history
15 notes
·
View notes
Note
What do you think is the correct word for "greater Mandalorian space"? I've seen 'Mandalase', don't remember where though, and have been using Tra'Manda in my own fics. Is there anything established in canon/fanon?
Good question! I’ve pondered it myself and the answer I’ve arrived at is that there should probably be several words.
See, what is meant by “the greater Mandalorian space” probably varies depending on the time and the speaker and the context, because the Mandalorian civilisation is a bit like the Roman civilisation: do you mean Rome the city, Rome the administrative region, the Roman Empire, or the Roman world as a cultural area?
For Mandalore we have at least these different senses:
Mandalore the planet (“Mandalore actual” or Manda’yaim)
Mandalore system (which includes at least three other inhabited planets and moons)
Mandalore sector
The entire area of space administered by the Mandalorian government (which is never really defined in canon)
Mandalorian Empire (historical)
The wider Mandalorian cultural area/area influenced or historically a part of the Mandalorian Empire
The indented words are from the unedited parts of my dictionary, so they are somewhat tentative and I’m not necessarily married to them. However this is what I currently have.
#1
The first is easy, the planet Mandalore is called Manda’yaim in Mando’a.
Manda’yaim: 1 the planet Mandalore, the fifth planet in the Mandalore system, capital world of the Mandalorians; 2 during periods of diaspora, can also refer to other Mandalorian areas or enclaves
haat’manda’yaim: Manda'yaim proper; planet Mandalore in contrast to its satellite Concordia, other planets in the Mandalore system, other Mandalorian worlds, or Mandalorian enclaves of the Mandalorian diaspora
#2
The Mandalorian system we can probably form directly from the word for a star system, perhaps Mando’tolase, lit. Mandalorian system, assuming tolase is also the word used for star systems and not just for other kinds of systems (not sure which way I lean on it tbh). Or Manda’tolase, if you subscribe to the fandom take that the star Mandalore is named Manda (or a variation thereof).
Or people might colloquially refer to the Mandalorian system also as Manda’lase.
I imagine there’s probably some kind of interplanetary law which defines what area of space is considered to belong to a planetary system and what is “international waters”/deep space.
#3-4
The third is what I suppose you were asking about. I’ve seen Manda’lase all over the place, but I don’t actually know where it came from—if anyone does know, please let me know! Linguistically the derivation goes something like this: manda ‘the shared Mandalorian oversoul’ > manda’la ‘having the Mandalorian soul, i.e. Mandalorian’ > Manda’lase ‘all of Mandalorians collectively’. In any case, I rather like it and have been using it myself since it seems about as established as anything in Fando’a.
Edit: Manda’lase appears to have been coined by Batsutousai; thanks for @johamur for pointing it out!
Mando’tra, Mandalorian space could also work. Manda’tra, substituting the word mando ‘mandalorian’ for manda ‘soul’, sounds to me a bit like the emphasis is on the shared culture less than the shared administration. Not that Mandalorians themselves necessarily see a big difference there.
It’s unclear whether Mandalore sector refers to a geographical area or an administrative region. I guess in everyday speech, people might conflate the two and use Manda’lase for both. So you might end up with a definition something like the following:
Manda’lase: 1 Mandalorian space; 2 Mandalorian system; 3 Mandalorian sector (colloquially)
In any case, I haven’t come up with a word for sector I like yet, although it’s on my list of needed words.
#5-6
For the historical Mandalorian Empire, I have:
Mando’alorai (or Mand’alorai): 1 Mandalorian Empire (historical); 2 still sometimes used of the regions that used to be governed by the Empire as a cultural area
alorai (n): 1 empire; 2 realm, domain, holding, governed area
Where alorai is either a portmanteau of alor + veeray, or alor + the same nominal suffix -ai we have in e.g. parjai.
Another option is:
Ori’Manda’lase: Mandalorian Empire (lit. Great Mandalore); Greater Mandalore, the historical region of space once controlled by the Mandalorian Empire
ori’manda’la (a): imperial (of Mandalorian Empire specifically, not other empires); of or belonging to Greater Mandalore, the historical region once controlled by Mandalorian Empire
ori’manda’lase tugoten (n): Mandalorian Empire Revivalism (Revanchism), an ideology on Mandalore that supports the revival of the Mandalorian Empire and a return to Mandalore's conquering days.
ori’manda’lase tugotenii (n): Mandalorian Empire revivalist, a supporter of Mandalorian Empire Revivalism. Tugotenii for short.
I’m using revivalism and revivalist over revanchism and revanchist, because in the Star Wars universe revanchists could be confused with supporters of Revan.
In any case, I think context should determine whether you mean the historical empire as a nation state, or the historical empire as a current area of cultural influence. Most reasonable beings would use Mandalorian Empire in either of these two senses, but then you have the likes of Tor Vizsla, who’d probably use a term with a similar sense to “Greater Russia”, i.e. areas that “should” belong to or be returned to Mandalorian governance.
I have some other scattered words and thoughts about Mandalorian government and citizenship, but this is already pretty long. In any case, that’s what a quick search through my dictionary file brought up, hope you found something to your liking!
#mando’a#mandoa#star wars#meta: mandalorians#mando’a language#mandalorians#mando'a#mando’a extended dictionary#ranah talks mando’a#ranah answers#answered asks#asks
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Hubs of Humanity 1
Prologue:
Back in the early 23rd century, as humanity began spreading its wings into the cosmos, the European Space Convention envisioned a groundbreaking project. They named it HUSB – Harmony of Urbanity and Space Bridges or as the public called it “The Hubs of Humanity”. At the projects core stood the idea to create a network of space stations and infrastructure pieces, each intricately designed to reflect Europe’s intricate designs and reflecting the architectural wonders of a wide range of European cities. It was like taking a slice of Paris, a bit of Barcelona, small snippets of Amsterdam and tiny amounts of Vienna and sprinkling their iconic look´s into the seemingly infinite abyss of interstellar space. The cities in the sky fostered significant cultural exchange, scientific collaboration, and good old human connection. Picture space stations modeled after the elegance of avant-garde designs of Berlin, the timeless charm of Rome or the sophistication of the medieval center of Prague.
Construction kicked of on a massive scale and for a while the project was the talk of the galaxy. The stations became marvels of their own right, embodying the spirit of humanity and its creativity. But as fate would have it, the early days of the 24th century brought a devastating cosmic cataclysm. An insidious computer virus, born from the depths of the digital unknown, infiltrated the project´s communication networks and databases. It spread like a raging wildfire, leaving chaos in its wake, and toppling the human economy and causing the once-thriving interconnected system into disarray. The fallout left a haunting legacy for the project, as the collapse progressed and databases where wiped clean many station dwellers decided to abandon their ships, leaving them adrift and causing them to vanish into the vast expanse of space without any trace left. They became cosmic ghosts, silently orbiting in the darkness, their stories and beauty lost to the void. Quickly forgotten by the rebuilding civilization that emerged from the ashes. Their memory fading into obscurity becoming fragments of an era long gone by. The civilization moved continually forward, leaving behind the mysterious past.
Many generations passed, and with the shift of cosmic currents, some of the long-forgotten stations reemerged from the cosmic background, having become new, beautiful obscure or even haunting shells of their former selves. Slowly many of them revealed new and diverse tapestries of fates. Some not just remnants but thriving hubs of life, sustained by reformed ecosystems and their resourceful inhabitants which had found a way to adapt to the sudden challenges of having to find ways to sustain their ways of living in space. Others had undergone large alterations, their original purposes re-imagined by advanced AI and machinery which was once designed to keep the stations operational. These technological custodians ensured the continued existence and advancement of these magnificent stations, evolving them into marvels of automated efficiency and sustainability.
The Hubs of Humanity: Aetherian Arboretum
Now after many of them had been long forgotten and become legends of a marvelous past the first of these celestial relics appeared at the edge of Humanities capital solar system. As it floated trough the vast reaches of the cosmos by pure chance it passed the outermost surveillance satellites of the Human system SOL1. There it was a space station which echoes the grandeur of an age long gone. A picturesque and mesmerizing blend of elegance and the neon glow of a bygone era. Tall ornate structures with their sinuous curves and intricate floral motifs rise from the main ring like structure and into the star lit fabric of space. Facades adorned with dim luminescent neon colors cast a surreal picture upon any eyes there to observe it. As it silently orbited throughout the cosmic ballet of space rocks of a region referred to as the Oort cloud it was greeted by a group of space vessels. Drawn towards it they cautiously approach the abandoned celestial haven.
As a group of explorers set foot onto it for the first time again, they marvel at the fusion of design and cosmic functionality. As they wander the deserted streets, the air is filled with an eerie silence, only broken by the occasional rustle of leaves and the distant hum of nature overtaking the space. Vines gracefully cascade town the sides of once bustling structures as they intertwine wit the fading light of neon signs that once proclaimed the names of businesses now long forgotten. The corridors and walkways once trodden by station dwellers, now play host to a delicate tapestry of nature. Moss covering lower grounds and growing through cracks in the flooring and resilient ferns and flowers also pushing their way through the seams. Tables, doors, and windows adorned with wrought-iron designs being claimed by encroaching vines. The almost ghostly neon glow flickering and casting a dreamlike scene into the explorers´ eyes. The grand arches and domes of the once famous trading hub now softened by the embrace of ivy and climbing roses.
Amid this fantastic scene of haunting beauty, unexpected inhabitants had found their niche – flocks of chickens, descendants of once domesticated birds, had adapted to the continuous darkness of the abandoned space station. Their plumage had taken on otherworldly beauty as it reflected the surrounding hues of dim neon lights. Their feathers colored in ethereal blends of deep purples, electric blues, and luminous greens they created a mesmerizing spectacle of shimmers and shadows as they moved through the silent station. These avian inhabitants adapted to the perpetual darkness of the station developing nocturnal rhythms and clucking that harmonized with the faint hum of the station´s former vibrancy. They had become the unexpected guardians of this rediscovered neon-lit legacy.
As the explorers reluctantly tore themselves away from these mesmerizing scenes, they delved deeper into the bowels of the ship, where they uncovered relics and objects of the once flourishing and passionate inhabitants. It also became evident that the station had undergone its profound metamorphosis, triggered by the exhaustion of its fusion systems and batteries several generations ago. The once state-of-the-art machinery had gracefully transitioned into a state of energy conservation. Basic life support systems hummed softly, maintaining the atmospheres delicately balanced atmosphere as the surroundings were bathed in the perpetual dim glow of neon lights, nurturing the lush flora overtaking the stations interiors. The artificial gravity modifier, a relic of advanced technology, continued to function on a minimal level. Its low persistent hum serving as an unseen orchestrator, allowing the abundance of plants and neon-feathered chickens to thrive in their cosmic sanctuary.
As the explorers continued their way through the corridors, they marveled at the ingenious processes that had sustained the stations delicate balance over the years. In this cosmic tapestry, the explorers sensed a quiet resilience. An enduring legacy left by a bygone era that unwittingly had given rise to this flourishing microcosm. The space station, now reemerged as a living testament to adaption, whispering its story of metamorphosis through the hushing echoes of its few still operational automated systems, the soft neon-glow of plant lights, and the vibrant clucks of chickens against the backdrop of the celestial stage.
With high anticipation, the explorers access the ship´s extensive database, eager to unveil the secrets hidden within the almost dreamlike structure they had been navigating. As the displays flickered to life, they revealed intricate schematics and blueprints of the station. The designation “Aetherian Arboretum” adorned the digital representations of the mighty station´s architecture. The name resonated with an ethereal quality, capturing the essence of this celestial haven. Armed with the new knowledge of the station´s identity, the explorers felt a deeper connection to it. As it stood as a testament to human ingenuity and the enduring spirit of exploration as it transcended its initial purpose as a hub of exploration and trade, evolving into a beacon of life amid the cosmic abyss. The name now etched into humanity’s records once again it was soon to become a thriving celestial haven again.
The news of the Arboretum´s rediscovery and its unique transformation captured the imagination of Earthlings in a wildfire. Recognizing its unique historical and ecological significance, authorities and swiftly declared it a protected zone and placed it under historic and natural preservation. The once-abandoned station a testament to the harmonious coexistence of nature and technology, underwent careful restoration with the goal of preserving its unique atmosphere while allowing eager tourists to experience the surreal beauty of the station in a small selected section. During the beginning of its restoration, the celestial sanctuary was moved in a stable orbit around Saturn, creating a celestial backdrop that added to the mystique of the cosmic destination. As visitors disembarked onto the transformed space station, they marveled at the now again neon-lit arches, domes and towers, the vibrant flora and the more than enthusiastic clucking of the specially adapted chickens. Educational Programs were established quite quickly to inform about the Arboretum´s rich history, its transformation and the unique ecosystem within it. Conservationists closely monitoring the neon-feathered chickens, ensuring their well-being and natural behavior are not disturbed in any significant way. As the space station orbited Saturn, the "Aetherian Arboretum" stood not only as a destination for eager earthlings but as a symbol of the boundless potential for exploration, preservation, and the celebration of the cosmic wonders that unfolded beyond the confines of Earth.
#humans are weird#humans are odd#scifi#sci fi#science fiction#scifiseries#futurism#scifi worldbuilding
12 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hey,
I just finished 'I loved Rome more'.
I was absolutely blown away by it, if i must confess, it's something I've read again and again over the last 3 years. It's a truly beautifully heart-wrenching pain that amazes in it sweetness.
I wanted to ask how your version of Revan's story ends. How Alek's story ends (obviously he is dead, but what happened between him and Revan after this point? did they talk? reconcile?).
What happens to Revan?
Would you ever see yourself touching this work again?
Thank you for such a kind message! "Rome" is one of my most favorite fics I've written so I'm glad you enjoyed it!!
To answer your questions (going to add the message Qs too!):
1. How does their story end?
I left it open intentionally, since that way readers can interpret their end journey in a way they best feels fit: want a tragedy? Revan keeps trying to achieve something impossible because her pride and her inability to stop moving won't let her rest and attempt to work through the closure of Malak's death and his ghost becomes an albatross around her neck. want something more hopeful? revan finds a way to bring Malak back in the unknown regions and gives the universe a cosmic middle finger.
My personal headcanon, which you definitely don't need to subscribe to because death of the author, is somewhere in the middle: revan finds happiness in having a purpose again, Malak finds peace in no longer having to fight anything and accompanies her, as always, for the ride. There's a kind of simple happy ending in that, I think!
2. Would I see myself coming back to this work?
This particular fic is 100% complete in my mind and I'm happy where it went! I do, one day, want to get back in and finish the story's sister fic about exile and bao-dur, "give place to better," which will follow kotor 2 (and will likely include this version of revan and Malak in flashbacks)
3. What's the title mean?
The title is from the Shakespeare play Julius Caesar, where Anthony says (paraphrase) "it's not that I loved Caesar any less, but that I loved rome more" regarding his decision to assassinate caesar, his close friend. I feel like the statement really sums up their dynamic in the fic--Malak might be the person Revan loves most in the world, but she loved her purpose more than him until it was too late
Thank you again for the message!!
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Friday the 13th and Freya (or Frigga)s Day
Why not being wrong doesn't exactly mean it's right.
So, the idea that Friday the 13th was associated with Freya (or Frigga) and therefore sacred for women is circulating again.
What if we take this apart for a kernel of truth. I'm going to leave the Patriarchy, the Catholic Church and the unlucky part out for a moment and just look at the Freya/Frigga part. (Even amoung the Norse crown, there doesn't seem to be full agreement about which goddess this refers to with some speculating it may have varied regionally. I'll leave it up to the Norse crowd to sort that out. For right now - we just need a goddess starting with F)
First, we're going to start with the Norse calendar. Because to have a Friday the 13th, you need a calendar with a Friday and a 13th. And we may be in luck!
See the Norse followed a lunar calendar with each month starting with the new moon and sacred to the sun. So, if we count that as 1 and follow the current days of the week - every month will have a Friday the 13th. (I haven't been able to completely verify that this was exactly how the Norse counted their days. In fact, they may have worried about counting less than we do because - hey, just look up at the moon.)
But this means - every Friday would have been sacred to Freya/Frigga. Even Friday the 13th. And Friday the 6th. Friday the 20th. Friday the 27th.
You aren't going to deprive a goddess of her due acknowledgement on her day.
So, yes, Friday the 13th would have been sacred to Freya/Frigga
And then the Patriarchy (Darth Vader Music)
Look, the Julian and Gregorian calendars were solar calendars that don't match the Norse lunar calendar so it looks more like we've just got two myths intersecting with a specific, reoccuring day in the Norse calendar.
Except - in Latin it's Veneris (Viernes for Spanish speakers) and in Rome was associated with the planet Venus. (Yes the goddess but the Romans had an odd thing going on with planets).
We've still got our usual set of Fridays. So, why not make all Fridays unlucky?
The usual thought is that 13 was associated Judas and the Last Supper. Which is why we have superstitions around the number 13. And, well, Jesus was crucified on a Friday. So possibly over time, those two came together to make Friday the 13th very unlucky.
But it is unlikely that either Freya or Frigga were involved in the matter. But you may still celebrate your favorite goddess on a Friday.
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
Certainly! Here's a list of some of the world's best places to visit:
1. **Paris, France**: Known as the City of Love, Paris is famous for iconic landmarks like the Eiffel Tower, Louvre Museum, and Notre-Dame Cathedral.
2. **Rome, Italy**: Home to ancient ruins like the Colosseum and the Roman Forum, as well as Vatican City and St. Peter's Basilica.
3. **Kyoto, Japan**: Rich in history and culture, Kyoto is filled with beautiful temples, traditional tea houses, and stunning gardens.
4. **New York City, USA**: The Big Apple offers a mix of culture, art, food, and entertainment, with attractions like Times Square, Central Park, and the Statue of Liberty.
5. **Machu Picchu, Peru**: This ancient Incan city nestled in the Andes Mountains offers breathtaking views and a glimpse into the region's rich history.
6. **Santorini, Greece**: Famous for its white-washed buildings with blue domes, stunning sunsets, and crystal-clear waters, Santorini is a picturesque island paradise.
7. **Great Barrier Reef, Australia**: One of the world's most spectacular natural wonders, the Great Barrier Reef is a haven for snorkelers and divers.
8. **Serengeti National Park, Tanzania**: Known for its vast plains and diverse wildlife, including the Big Five, the Serengeti offers unforgettable safari experiences.
9. **Marrakech, Morocco**: With its bustling medinas, vibrant souks, and stunning architecture, Marrakech is a feast for the senses.
10. **Iguazu Falls, Argentina/Brazil**: This awe-inspiring natural wonder consists of 275 individual waterfalls and spans the border between Argentina and Brazil.
11. **Dubai, UAE**: A modern marvel with skyscrapers, luxury shopping, and desert adventures, Dubai is a city of contrasts.
12. **Banff National Park, Canada**: Majestic mountain landscapes, turquoise lakes, and abundant wildlife make Banff a must-visit destination for nature lovers.
13. **Bora Bora, French Polynesia**: Famous for its overwater bungalows and pristine beaches, Bora Bora is the ultimate tropical getaway.
14. **Angkor Wat, Cambodia**: The largest religious monument in the world, Angkor Wat is a stunning example of Khmer architecture and a UNESCO World Heritage site.
15. **Rio de Janeiro, Brazil**: Known for its lively carnival, iconic beaches like Copacabana and Ipanema, and the towering Christ the Redeemer statue overlooking the city.
These are just a few of the countless amazing places to visit around the world, each offering its own unique charm and experiences.
#best places to visit#best places to travel#good place#top places#the mandalorian#super mario#across the spiderverse#the owl house#ted lasso#donald trump#yellowjackets#wally darling#rwby#taylor swift
7 notes
·
View notes
Note
How was voting done in ancient rome?
Anon...you sent me down a whole rabbit-hole...and I'm still not quite sure I understand it all. But here's how I think it worked, and I welcome any corrections from folks who know more.
Rome's voting system changed a lot over the years. We have the most information about the late republic, so let's focus on that:

(I've left out the Curiate Assembly, which was mostly irrelevant at this point, and some other fiddly bits.)
Tribes and Centuries
If you were a Roman voter, you would be part of both a tribe and a century. Your tribe roughly meant which "region" your vote was associated with, though by the late republic people had moved around so much that didn't really mean anything. Your century was assigned by censors based on your wealth status. Only male citizens could vote, not women, slaves or non-Roman residents.
When you voted, the majority of your tribe or century's votes would all be counted as one vote in the election. If 60% of your tribe voted for Lucius Tiddlypuss, but you were one of the 40% who voted for Gnaeus Nautilus, tough shit. Tiddlypuss gets one vote counted and Nautilus gets nada.
To make things worse, not all tribes or centuries were equally powerful. The wealthiest centuries (equestrians and "first class enlisted") were much smaller than the poor and working-class centuries, so rich people's individual votes counted for more. And they got to vote first, and the election was over as soon as a candidate reached a majority of total votes, so poor centuries often didn't get to vote at all.
The tribal voting system was a little more fair. Its voting order was randomized. But since all elections took place in Rome, the rural voters who could make it were usually small in number - and rich enough to travel. So rural tribes were disproportionately powerful. Plus, the tribes were of different sizes again, so (for instance) freedmen's votes could be "diluted" by concentrating them in a few big urban tribes. Still, the tribal system was seen as more representative of the lower classes in practice.
On the upside, by this era, elections and plebiscites had written ballots that you could cast secretly. This reduced the power of patrons over their clients, and masters over freedmen.
Voting for People
To elect higher magistrates, like consuls, censors and praetors, you have to gather with your century in the Centuriate Assembly outside the city walls. Why? Because the Centuriate Assembly is technically based on soldier ranks, classed by how much gear each soldier could afford, and you can't be within Rome's city limit while in military formation. The tops "enlisted"-level centuries vote first, each century's vote counts for 1, then the equestrians vote in their groups, and so on until a candidate reaches over 50% of the total possible votes.
(Note: Cicero refers to 193 centuries, so most scholars believe that was the number in his lifetime. But not everyone agrees, and the Centuriate Assembly seems to have been reorganized a few times.)
Now let's vote for lower offices, like curule aediles, quaestors and military tribunes. The pontifices are also elected here. You can go back inside Rome's walls now, because the Tribal Assembly sorts voters into tribes, not military ranks. The order in which the tribes vote is randomized (in theory). If you're voting for a pontifex, only 17 random tribes out of 35 get to vote. Or, if you're living between 81 and 63 BCE, you don't get to vote for pontifices at all. Blame Sulla for that.
Finally, we'll vote in the tribunes of the plebs and plebeian aediles. If you're one of the 90%+ of Romans who are plebeian, you'll vote in the Plebeian Council, which works just like the Tribal Assembly except that there's a big "No patricians allowed!!" sign. Only plebs can vote, and only plebs can run for these offices!
Or at least, that's how most historians think it worked. It's not actually clear if the Plebeian Council was another name for the Tribal Assembly, a separate entity, or merged into it at some point. So whenever I say "Plebeian Council," put a mental asterisk after it.
Once someone is elected as a quaestor, tribune of the plebs, or a higher rank, he stays in the Senate for life unless the censors kick him out or a trial strips him of office. This year's consuls and praetors will become next year's proconsuls and propraetors, who govern provinces and sometimes take on other special assignments. Pontifices also hold their priesthoods for life, and can take on other jobs, too.
Voting for Laws
We've elected our dudes! Can you go home? Nope! Rome also has a lot of plebiscites, or referendums.
Most laws came from the Senate. The Senate voted on a bill, usually proposed by a consul, and if a majority of Senators approved the bill would go to the Plebeian Council. Most of the time, the Plebeian Assembly approved the bill, and it became law. But sometimes it refused, and the bill would either die, or have to be revised in the Senate before the Council would vote on it again.
Occasionally a tribune of the plebs would propose a bill directly to the Plebeian Council, without getting Senate approval first. Or, more rarely, a higher magistrate might. This was a great way to piss off the Senate! However, if the bill passed, the Senate had to abide by it anyway.
Changes to the System
Even just in the 54-year period I chose, the rules shifted sometimes. The biggest change was Sulla's constitutional reform, in which:
Tribunes of the plebs could no longer propose legislation or hold higher offices.
Thus, nearly all legislation came from the Senate instead of the Plebeian Council.
Pontifices were chosen by other pontifices, no longer elected.
The number of magistracies and overall size of the Senate was expanded.
Holding a magistracy of quaestor-level or higher automatically enrolled its holder in the Senate; before, that had to be ratified by the censors.
And more details, not related to elections and plebiscites, that I won't go into here.
Some of these changes were rolled back after Sulla's death. Tribunes were restored to their full powers by 70 BCE, and pontifices became publicly elected again from 63 onward.
Rome's last fully "free" elections took place in 50 BCE. After that, Caesar's civil war and dictatorship, his habit of appointing his supporters to government offices, and even more civil wars all fouled everything up. Augustus restored regular elections, but didn't step down, so they became little more than a popularity contest with no real power.
If you rewind back in time, you'll see other changes, too. Before 104 BCE, pontifices were chosen by other pontifices, just like Sulla preferred. Before 219, the Plebeian Council needed the Senate to ratify its laws, and before 287, its laws only applied to plebs. If you go way back to the 5th century, the Curiate Assembly I left out starts being relevant. There was a gradual shift toward the Plebeian Council gaining more power over time, and patrician-only offices gradually being opened to plebeians.
Once again, I'm not a historian, so please let me know if I got something wrong. Thank y'all for reading this long-ass post!
#i mainly wrote this up because i couldn't find any diagrams of the system that made sense to me#hopefully this will help other folks feel less confused than i was#roman voting#jlrrt essays#roman elections#also i voted in my party primary yesterday! if you're a US american be sure to look up when voting starts for you! <3
36 notes
·
View notes
Text


2,000-Year-Old Goth Cemetery Unearthed in Poland
Archeologists in Poland have uncovered a vast Goth cemetery brimming with silver jewelry dating back to the fourth century.
Olaf Popkiewicz, an archaeology video content creator on YouTube, spotted the jewelry — two silver necklaces; two silver fibulae, or brooches; and beads that once belonged to a third necklace — while walking along the Wda River. He notified a team of park archeologists who excavated the site, which sits within the protected Wda landscape park in central-northern Poland.


"In three weeks, we managed to explore over 250 square meters [2,700 square feet] of the cemetery and discover 50 Gothic graves," park representatives wrote in a translated Facebook post. Buried alongside the dead, archeologists found a rich collection of grave goods, including pottery, brooches, amber beads and more jewelry decorated with snake motifs.
The excavated area likely represents a fraction of the ancient burial site, which researchers believe may span more than 2.5 acres (1 hectare). "This is probably only the beginning of our adventure," the post said.


The Goths were a Germanic tribal people who, according to some accounts, migrated from Scandinavia and settled across Europe in the first century A.D. These "barbarians" famously sacked Rome in A.D. 410 and later split into two kingdoms: the Visigoths, who flourished in Iberia and southwest Gaul (modern-day France); and the Ostrogoths, who dominated in Italy. These kingdoms were relatively short-lived, however, and the last Goths fell to the Moors in A.D. 711.
Gothic tribes inhabited northern Poland between the first and fifth centuries, during their southward migration from Scandinavia to the Roman Empire. More than 2,000 Goth burials have previously been unearthed in the region near the village of Wielbark, which revealed an early Goth culture that stretched from the southern coast of the Baltic Sea to what is now western Ukraine.


The newly excavated site revealed both buried remains in pit graves and cremations in urn burials. When researchers analyzed urns discovered near Wielbark in 2019, they found that some of them had been crafted specifically for cremation as they could not retain liquid, making them useless for everyday purposes such as cooking.
Goths living in what is now Poland during Roman times were talented gold- and silversmiths, according to Magdalena Natuniewicz-Sekuła, a researcher at the Institute of Archeology and Ethnology of the Polish Academy of Sciences in Warsaw who was not involved with the new find.




In 2020, archeologists discovered a Goth burial ground in the village of Weklice, also in northern Poland, holding hundreds of silver ornaments that "were made of a very high-quality metal, the fineness of which even exceeded the composition of currently produced jewelry," Natuniewicz-Sekuła told the news website Science in Poland. The quality of the jewelry — including bracelets, clasps and outfit decorations — was as high as ornaments from the Roman Empire, she added.
Archeologists hope to excavate the rest of the Goth cemetery discovered at Wda landscape park before it degrades. "Unfortunately, the conditions of a large part of the cemetery means that urgent excavations are needed to help save and preserve the site," park representatives wrote on Facebook.
By Sascha Pare.



#2000-Year-Old Goth Cemetery Unearthed in Poland#Wda Landscape Park#ancient tombs#ancient graves#ancient necropolis#silver#ancient jewelry#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#gothic history#gothic warriors
42 notes
·
View notes
Text
Saints&Reading: Wednesday, 13, March, 2024
march 1_march 29
VENERABLE JOHN CASSIAN THE ROMAN, ABBOT (435)

Saint John Cassian the Roman was born around 360, probably in Lesser Scythia (in Dacia Pontica). His pious Christian parents gave him an excellent classical education, and also instructed him in the Holy Scriptures and in the spiritual life.
Saint John entered a monastery in the diocese of Tomis, where his friend and relative Saint Germanus labored as an ascetic. In 380, desiring to venerate the Holy Places, Saint John went to Jerusalem with his sister and his friend Saint Germanus. The two monks stayed at a Bethlehem monastery, not far from where the Savior was born.
After five years at the monastery, Saints John and Germanus traveled through the Thebaid and the desert monasteries of Sketis for seven years, drawing upon the spiritual experience of countless ascetics. The Egyptian monks taught them many useful things about spiritual struggles, prayer, and humility. Like honeybees they journeyed from place to place, gathering the sweet nectar of spiritual wisdom. The notes Saint John made formed the basis of his book called CONFERENCES WITH THE FATHERS in twenty-four chapters.
Returning to Bethlehem for a brief time, the spiritual brothers lived for three years in complete solitude. Then they went back to Egypt and lived there until 399. Because of the disturbances caused by Archbishop Theophilus of Alexandria to the monasteries along the Nile, they decided to go to Constantinople, after hearing of the virtue and holiness of Saint John Chrysostom. The great hierarch ordained Saint John Cassian as a deacon and accepted him as a disciple. John and Germanus remained with Saint John Chrysostom for five years, learning many profitable things from him.
When Chrysostom was exiled from Constantinople in 404, Saints John Cassian and Germanus went to Rome to plead his case before Innocent I. Cassian was ordained to the holy priesthood in Rome, or perhaps later in Gaul. After Chrysostom’s death in 407, Saint John Cassian went to Massilia [Marseilles] in Gaul (now France). There he established two cenobitic monasteries in 415, one for men and another for women, based on the model of Eastern monasticism.
At the request of Bishop Castor of Aptia Julia (in southern Gaul), Cassian wrote THE INSTITUTES OF CENOBITIC LIFE (De Institutis Coenobiorum) in twelve books, describing the life of the Palestinian and Egyptian monks. Written between 417-419, the volume included four books describing the clothing of the monks of Palestine and Egypt, their schedule of prayer and services, and how new monks were received into the monasteries.The last eight books were devoted to the eight deadly sins and how to overcome them. Through his writings, Saint John Cassian provided Christians of the West with examples of cenobitic monasteries, and acquainted them with the asceticism of the Orthodox East.
Cassian speaks as a spiritual guide about the purpose of life, about attaining discernment, about renunciation of the world, about the passions of the flesh and spirit, about the hardships faced by the righteous, and about prayer.
Saint John Cassian also wrote CONFERENCES WITH THE FATHERS (Collationes Patrum) in twenty-four books in the form of conversations about the perfection of love, about purity, about God’s help, about understanding Scripture, about the gifts of God, about friendship, about the use of language, about the four levels of monasticism, about the solitary life and cenobitic life, about repentance, about fasting, about nightly meditations, and about spiritual mortification. This last has the explanatory title “I do what I do not want to do.”
Books 1-10 of the CONFERENCES describe Saint John’s conversations with the Fathers of Sketis between 393-399. Books 11-17 relate conversations with the Fathers of Panephysis, and the last seven books are devoted to conversations with monks from the region of Diolkos.
In 431 Saint John Cassian wrote his final work, ON THE INCARNATION OF THE LORD, AGAINST NESTORIUS (De Incarnationem Domini Contra Nestorium). In seven books he opposed the heresy, citing many Eastern and Western teachers to support his arguments.
In his works, Saint John Cassian was grounded in the spiritual experience of the ascetics, and criticized the abstract reasoning of Saint Augustine (June 15). Saint John said that “grace is defended less adequately by pompous words and loquacious contention, dialectic syllogisms and the eloquence of Cicero (i.e. Augustine), than by the example of the Egyptian ascetics.” In the words of Saint John of the Ladder (March 30), “great Cassian reasons loftily and excellently.” His writings are also praised in the Rule of Saint Benedict.
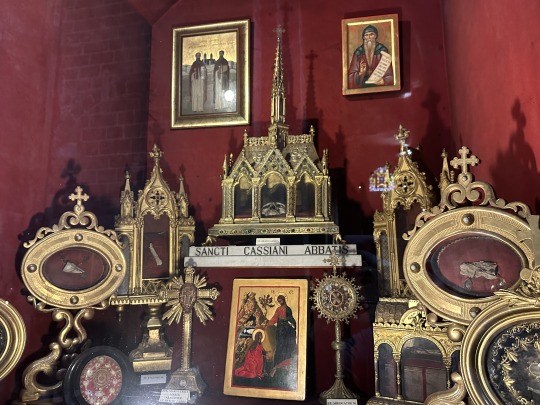

St John Cassian relics in the main Church of St Victor Abbaye in Marseille France.
Saint John Cassian lived in the West for many years, but his spiritual homeland was the Orthodox East. He fell asleep in the Lord in the year 435. His holy relics rest in an underground chapel in the Monastery of Saint Victor in Marseilles. His head and right hand are in the main church.
THE MONK LEO, CAPPADOCIAN MONASTIC

Saint Leo of Cappadocia fulfilled the commandment to love his neighbor by suggesting to the Saracens, who had captured three sickly monks, that he take the place of these infirm captives with himself, since he was healthy and able to work.
While journeying in the desert, Saint Leo weakened and was not able to go any farther. He was beheaded with the sword, thereby laying down his life for his neighbor.


JOEL 2:12-26
12 Now, therefore, says the Lord, Turn to Me with all your heart, With fasting, with weeping, and with mourning. 13 So rend your heart, and not your garments; Return to the Lord your God, For He is gracious and merciful, Slow to anger, and of great kindness; And He relents from doing harm. 14 Who knows if He will turn and relent, And leave a blessing behind Him-- A grain offering and a drink offering For the Lord your God? 15 Blow the trumpet in Zion, Consecrate a fast, Call a sacred assembly; 16 Gather the people, Sanctify the congregation, Assemble the elders, Gather the children and nursing babes; Let the bridegroom go out from his chamber, And the bride from her dressing room. 17 Let the priests, who minister to the Lord, Weep between the porch and the altar; Let them say, "Spare Your people, O Lord, And do not give Your heritage to reproach, That the nations should rule over them. Why should they say among the peoples, 'Where is their God?' " 18 Then the Lord will be zealous for His land, And pity His people. 19 The Lord will answer and say to His people, "Behold, I will send you grain and new wine and oil, And you will be satisfied by them; I will no longer make you a reproach among the nations. 20 But I will remove far from you the northern army, And will drive him away into a barren and desolate land, With his face toward the eastern sea And his back toward the western sea; His stench will come up, And his foul odor will rise, Because he has done monstrous things. 21 Fear not, O land; Be glad and rejoice, For the Lord has done marvelous things! 22 Do not be afraid, you beasts of the field; For the open pastures are springing up, And the tree bears its fruit; The fig tree and the vine yield their strength. 23 Be glad then, you children of Zion, And rejoice in the Lord your God; For He has given you the former rain faithfully, And He will cause the rain to come down for you-- The former rain, And the latter rain in the first month. 24 The threshing floors shall be full of wheat, And the vats shall overflow with new wine and oil. 25 So I will restore to you the years that the swarming locust has eaten, The crawling locust, The consuming locust, And the chewing locust, My great army which I sent among you. You shall eat in plenty and be satisfied, And praise the name of the Lord your God, Who has dealt wondrously with you; And My people shall never be put to shame. Then you shall know that I am in the midst of Israel: I am the Lord your God And there is no other. My people shall never be put to shame. And it shall come to pass afterward That I will pour out My Spirit on all flesh; Your sons and your daughters shall prophesy, Your old men shall dream dreams, Your young men shall see visions. 26 You shall eat in plenty and be satisfied, And praise the name of the Lord your God, Who has dealt wondrously with you; And My people shall never be put to shame.
#orthodoxy#orthodoxchristianity#easternorthodoxchurch#originofchristianity#spirituality#holyscriptures#bible#saints
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
10 minutes of Mike Patton insulting people in italian
June 2nd 2015, Milan. Mike is on fire. Metallica were the headliners at Sonisphere.
youtube
Min 0:10: Pirla! (It's a typical Milanese insult, and it roughly means "stupid". Plural or singular, it is always "pirla").
Min 0:20: Com'è che state? Tutto bene? // How are you guys? Is everything alright? ("Com'è che state": this sentence structure is absolutely native).
Min 0:29: ma vai a cagare! (Ok, I can translate it with "Fuck off" or "go to hell" but it literallymeans "Go and take a shit". We use it a lot).
Min 0:55: Cazzarola! (It's a term we use to say "cazzo" [=dick, but in the meaning of "fuck!"] but in a less vulgar way. It's not really a swear word; in central Italy, "cazzarola" means "pot").
Min 1:02: Mike is trying to get Roddy to say "cazzarola".
Min 1:18 Ma vaffanculo! // Fuck Off!
Min 1:25: Roddy tries again with his 'cazzarola,' but with poor results.
Min 1:34: ssshhhssshhh, giriamoci (?), un po' di basso // Turn around (I'm not sure about it, sorry), some bass.
Min 1:44: coglioni! (Here we go: 'coglioni' literally means 'balls,' and we often use it to tell someone they're a complete idiot. It's a strong insult but everything depends on the context)
Min 2:08: eh, minchia! (This word is Sicilian and it means 'cazzo,' but in Milan, it's used quite a lot).
Min 2:32: Mike was explaining that in Italy, June 2nd is Republic Day, in a way similar to the Fourth of July in the US; when Roddy said, "We don't speak Italia"n, Mike replied "Devi imparare, cazzo!" = you have to learn it, damn it!
Min 3:05: scusa(temi), devo tintarmi un po'! Milano style. Che dici? // Sorry, I need to tan, Milan style. What do you think? (Mike is using the second person singular form for most of the concert, but he should have said 'scusatemi' and "cosa ne dite?". 'Devo tintarmi' doesn't exist in Italian, but it's understandable. I'm almost sure that he took 'tintarmi' from 'Tintarella di Luna' by Mina, LOL. 'Tintarella' means 'tan' in an informal way, but we say 'devo prendere la tintarella' or 'devo abbronzarmi.' I guess 'devo abbronzarmi' was too hard to remember)
Min 3:57: He was amazed by those mirrors xD but at least this time he didn't throw it at people. And Mike... Don't you know that in Italy if you break a mirror, you'll have 7 years of bad luck???
Min 5:56: daje, daje milanesi! Zen. Ti chiediamo per favore di... zen. Meditazione. Pirli! Meditazione. Coglioni! Non iniziamo se non cantate. // Come on, Milanesi! Zen. We're kindly asking you... be zen. Meditation. Pirli! Meditation. We won't start until you sing. ("Daje" is absolutely Roman style. It has many uses, but most commonly, it's a way to say 'come on').
Min 6:53: siamo felici o no? Va bene! Se non siete felici dopo questa canzone... // Are we happy or not? If we are not happy after this song...
Min 7:23: bravi merdallari! (It's a way to poke fun at metalheads; it's a blend of 'merda' (shit) and 'metallari' (metalheads). It's a very colloquial term, and Mike has used it many times over the years. If you consider that most of the crowd was there for Metallica, you'll understand why he said that).
Min 7:28: sti cazzo di milanesi, ma va a cagare! // these fucking milanese people! (see min 0:29 for "vai a cagare!")
Min 7:44: Mike tries to get Roddy to say 'ma va a cagare,' but Roddy is still stuck on 'cazzarola.'
Min 7:53: lui sta dicendo che vuole un cazzone. È vero eh, un cazzone! // He is saying he wants a big dick. It is true huh, a big dick!
Min 8:21: A guy in the crowd says, 'che Dio ti fulmini.' He's probably from Tuscany because he used 'sfulmini,' which is typical of that region. By the way, he's saying 'may God strike you' to Mike.
Min 8:36: ah coglioni! (we already knew this LOL)
Min 8:40: ma chi cazzo sta a grida'? Who the fuck is screaming? (Okay, I'm from a small town in the south of Rome, and he has a strange Roman accent for most of the concert. I could honestly cry because of this, my accent on his lips. In proper italian it should be "chi cazzo sta gridando?")
Min 8:41: The same guy from the crowd: ah stronzo! // You jerk!
Min 8:43: Volete i Metallica? Anche noi, anche noi. Abbia(te) pazienza. Puttana di hippy di merda! Ti vedo, eh! // You want Metallica? So do we, so do we. Have some patience. Shitty hippie bitch! I see you, huh. (I don't know what happened here, he was talking to some people over there I guess. And Roddy speaking spanish with no reason makes me pee myself laughing).
Min 9:22: ah pirla! (ok he loves this one LOL)
Min 9:29: questa è l'ultima. Oh, finalmente! Sì, sto per venire pure io (looking at someone in the crowd). No, eh? Però il bocchino che fanno i mianesi (laughs) quasi quasi... Roddy, guarda. // This is the last one. Oh, finally! Yes, I'm about to come as well (looking at someone in the crowd). No, huh? But the blowjob the Milanese people give (laughs) I'm half tempted... Roddy, look. (another chaotic interaction, LOL)
Min 10: 08: Oh! Milano! Ci sono due frociacci in prima fila a petto nudo che mi... (ansima). Però lui eh (indica Roddy) No? Devi (far) crescere la barba un pochino, ragazzo mio. Insomma, grazie! // Oh! Milan! There are two shirtless fa*gots in the front row making me... (he pants). But him (pointing to Roddy), right? You need to grow a beard a little, my boy. Anyway, thanks! (That word is native and offensive, sorry Mike I don't like this one).
Min 10:40: Volete Vasco Rossi. // You want Vasco Rossi. (Vasco Rossi is a famous Italian rock star, but he is controversial because he hasn't done anything significant since (for me) at least 1998. Mike knows that metalheads hate Vasco)
NB: Min1:02, In the audience, you can hear 'porco D+o,' which is a blasphemy. In this video is missing but Mike said it while singing. You can hear him saying it at min 1:17 in this video: https://youtu.be/XXA4-MBDSqA?si=pCSMHqkBd5fCW4-4
In Italy, it's pretty normal to hear folks dropping swear words that target God, the Mother of Jesus, and the saints. This quirk in our culture might have something to do with the strong presence of the Pope and the whole Catholic thing, LOL. Anyway, despite these words being considered quite rude and definitely not for everyone, they've somehow become part of our everyday language. We use them for emphasis, to wrap up a chat, as greetings, or just as linguistic spice. Now, let me be clear, they're super vulgar, and plenty of folks find them offensive. If you use them, you might not make the best impression, but, unless you're talking to your grandma, most people won't raise an eyebrow. In that context, it doesn't sound all that strange. Coming from Mike, I admit it's quite funny. Oh, and when foreigners are learning Italian, the first lesson is often on swear words and dirty talk – it's like an unspoken rule or something.
In general, not happy about a couple of insults here and the way he involved Roddy in some jokes about his homosexuality that he couldn't understand. If he had called me a "puttana" I would have punched him in the face LOL. In this concert, Mike's Italian has declined significantly compared to the past.
13 notes
·
View notes