#royal scottish museum
Text

Some years ago a lady brought to the Royal Scottish Museum in Edinburgh a trout covered with a fine coat of white fur. It was pleasingly mounted on a wooden shield and was labelled as follows:
FUR BEARING TROUT
Very Rare
Caught while trolling in Lake Superior off Gros Cap, Near Sault Ste. Marie, district of Algoma. It is believed that the great depth and the extreme penetrating coldness of the water in which these fish live has caused them to grow their dense coat of (usually) white fur. Mounted by ROSS C. JOBE, Taxidermist of Sault Ste. Marie, Ont.
Visiting the museum to find out more about her unique fish, the lady was told that it was undoubtedly a trout (either brown or brook) and that its fine white coat was undoubtedly from a rabbit, whereupon she immediately presented the fish to the museum. She had bought this fake in good faith which indicates that the idea of a fur-bearing trout did not seem outlandish to her.
―Stanley Peter Dance, Animal Fakes & Frauds, 1976
#fur bearing trout#fur-bearing trout#fearsome critters#animal fakes & frauds#s peter dance#taxidermy#hoax#royal scottish museum#national museum of scotland#ross c jobe#photographer unknown#popular post
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
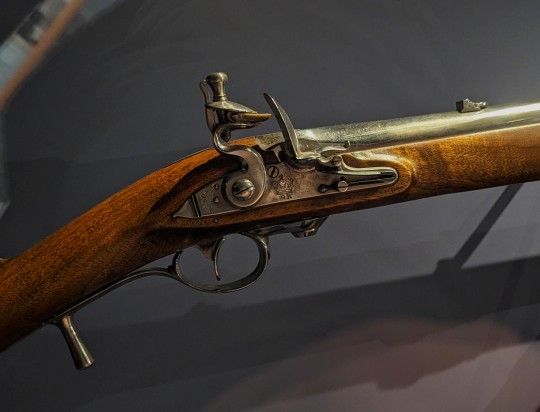

"Ferguson" Breech-Loading Rifle from Aberdeen, Scotland dated to 1776 on display at the Royal Scots Dragoon Guards Museum in Edinburgh Castle, Scotland
These rifles were invented by Lieut-Colonel Patrick Ferguson of Pitfour, Aberdeenshire. Ferguson's improved quick thread breech-loading rifle was an improvement on an earlier invention. He served as a subaltern in the Royal North British Dargoons (Scots Greys) from 1759 to 1762. Ferguson was killed in South Carolina at the Battle of King's Mountain in 1780 during the American Revolutionary War.
Photographs taken by myself 2023
#military history#18th century#hanover#gerogian#british empire#scotland#scottish#royal scots dragoon guards museum#edinburgh#barbucomedie
104 notes
·
View notes
Text
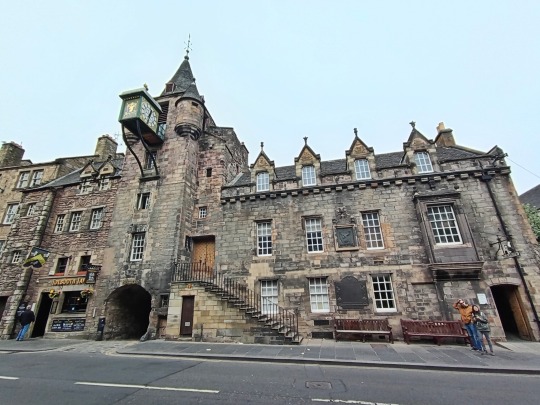




Canongate today.
#scotland#scottish#history#edinburgh#canongate#my pix#phone photography#Huntly House#Museum of Edinburgh#Old Tolbooth#Royal Mile
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

Edinburgh's elegant tribute to Scottish authors along the Royal Mile
#The Writers' Museum#Lawnmarket#Royal Mile#Edinburgh#Sir Walter Scott#Robert Louis Stevenson#Robbie Burns#UK#Scottish authors#Lady Stair's House#English literature#1622
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
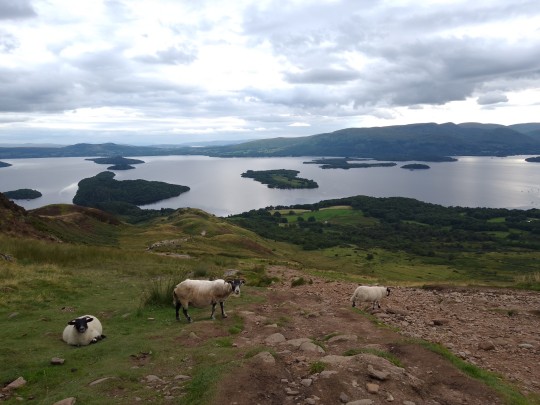
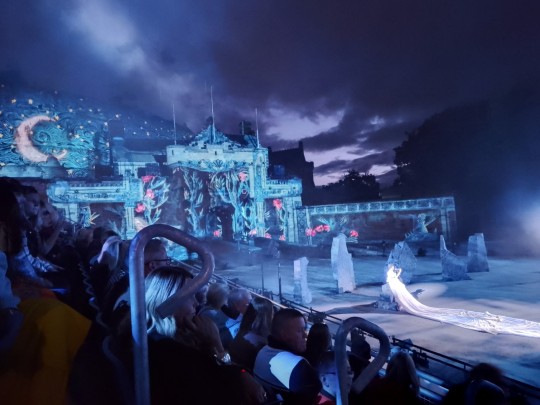




#back home#Scotland#Glasgow#university of Glasgow#Poudlard#loch Lomond#conic hill#Scottish sheep#Edinburgh#royal Edinburgh military festival#tattoo festival#castle#hunterian museum
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Edinburgh, Scotland - A Tale of History and Natural Beauty
A Tale of History and Natural Beauty – Edinburgh, Scotland
Explore the enchanting city of Edinburgh, where history unfolds against a backdrop of natural beauty. Scotland is calling in 2023, and we invite you to discover the cultural richness and scenic wonders that make Edinburgh a captivating destination.
Scotland is Calling 2023
Exploring Edinburgh – Top Recommendations
1. Discover…

View On WordPress
#Arthur&039;s Seat#Dean Village#Dynamic Earth#Edinburgh#Edinburgh Castle#Edinburgh Festival Fringe#halal dining in Edinburgh#Holyrood Palace#National Museum of Scotland#Princes Street Gardens#Royal Mile#Royal Yacht Britannia#Scotch whisky#Scotland#Scottish cuisine#Scottish National Gallery
0 notes
Text
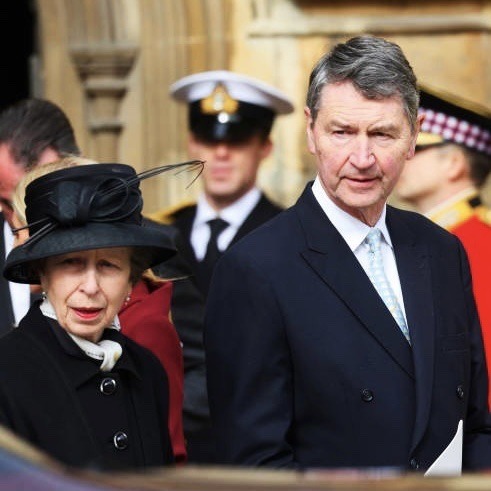









The Princess Royal’s Official Engagements in February 2024
01/02 Visited ReBoot (Moray Computer Recycling) in Forres. 🖥️
As Warden, opened the Queen Elizabeth II classrooms at Gordonstoun School. 🏫
Visited Lossie Community Hub at the Warehouse Theatre, in Lossiemouth. 🎭
Unofficial Sir Tim, as Chair of the Board of Trustees, attended the opening ceremony of the Zimingzhong 凝时聚珍: Clockwork Treasures from China's Forbidden City exhibition at the London Science Museum. 🐉🧧🕰️
03/02 With Sir Tim As Patron of the Scottish Rugby Union, attended the Six Nations Rugby Match between Wales and Scotland at Principality Stadium in Cardiff. 🏴🏴🏉
05/02 Visited Dressability Clothing Alterations Charity in Swindon, to mark its 25th Anniversary. 👗🪡🧵
As Commandant-in-Chief (Youth) of St John Ambulance, attended the dedication of a new Community Response Unit in Devizes, Wiltshire. 🚑
06/02 Held an Investiture at Windsor Castle. 🎖️
As Patron of the Royal College of Occupational Therapists, attended the launch of Nottingham West Primary Care Network’s Interactive Group Therapy at Plumptre Hall. 🩺
As President of the UK Fashion and Textile Association Limited, visited GH Hurt and Son in Nottingham. 🪡
With Sir Tim As Royal Fellow of the Royal Academy of Engineering, attended the announcement of the winner of The Queen Elizabeth Prize for Engineering at the Science Museum in London. ⚙️🥂
07/02 As Colonel-in-Chief of The Royal Logistic Corps, visited the Defence Explosive Ordnance Disposal, Munitions and Search Training Regiment at St George’s Barracks in Bicester. 💥
As President of the Commonwealth War Graves Commission, visited the Commission’s Headquarters in Maidenhead. 🪦
As Patron of Catch22, visited the Commissioned Rehabilitative Services at Community Links in London. 🔗
08/02 As Vice Patron of the British Horse Society, visited Wormwood Scrubs Pony Centre in West London. 🐎
As President of the Royal Yachting Association, attended the Annual Luncheon at Trinity House in London. 🛥️🥪
09/02 In Wales, Princess Anne; 🏴
As Royal Patron of the National Coastwatch Institution, visited Worms Head Station in Rhossili, followed by a Reception at South Gower Sports Club in Scurlage. 🔎🍾
Visited Newport Medieval Ship. 🚢
Visited Newport Transporter Bridge which is undergoing maintenance. 🌉
10/02 With Sir Tim As Patron of the Scottish Rugby Union, attended the Six Nations Rugby Match between France and Scotland at Murrayfield Stadium in Edinburgh. 🇫🇷🏴🏉
12/02 As Patron of Swinfen Telemedicine, attended a Meeting at the Royal Society of Medicine. 💊
As Chancellor of the University of Edinburgh, held a Dinner at Buckingham Palace. 🎓
13/02 Held an Investiture at Windsor Castle. 🎖️
As Master of the Corporation of Trinity House, chaired the Quarterly Meeting of the Court at Trinity House. 📆
14/02 As Royal Patron of the National Coastwatch Institution, visited Hengistbury Head Station near Bournemouth. 🌊
As Colonel-in-Chief of the Intelligence Corps, visited I Company at Hamworthy Barracks in Poole. 🕵️♀️
15/02 Visited the Ordnance Survey National Mapping Agency in Southampton. 🗺️
With Sir Tim Attended Evensong and the James Caird Society’s Dedication Service followed by a Reception in Westminster Abbey, to mark the 150th Anniversary of the birth of Sir Ernest Shackleton. 🔭🧭🇦🇶
16/02 Visited knife crime community group ‘Off the Streets’ North Northamptonshire in Wellingborough. 🚫🔪
20/02 As President of the UK Fashion and Textile Association, visited Laxtons Limited in Baildon near Bradford. 🧶
As President of the UK Fashion and Textile Association, visited Marton Mills in Otley, West Yorkshire. 🪡
21/02 In Doncaster, South Yorkshire, Princess Anne;
Visited Agemaspark Precision Engineering Company. ⚙️
Visited Haith Group Vegetable Processing Machinery Company. 🥕🥦
As Patron of the Butler Trust, visited HM Prison and Young Offender Institution Doncaster. 🚓👮♀️
As Past Master of the Worshipful Company of Carmen, attended a Joint Services Awards Dinner at Painters’ Hall in London. 🍽️
22/01 Visited London South Bank Technical College and Lee Marley Academy. ✏️👷
As Patron of Save the Children UK, visited Mary’s Living and Giving Shop in Wandsworth. 👚
23/02 unofficial Departed Heathrow Airport for Namibia 🇬🇧✈️🇳🇦
24/02 unofficial Arrived at Windhoek Hosea Kutako International Airport in Namibia. ✈️🇳🇦
Representing The King, Princess Anne called upon Mrs Monica Geingos (widow of Dr Hage Geingob). 🖤
Unofficial Sir Tim represented Princess Anne, Patron of the Scottish Rugby Union, at the Six Nations Rugby Match between Scotland and England at Murrayfield Stadium in Edinburgh. 🏴🏴🏉
25/02 Representing The King, Princess Anne attended the Burial Service for Dr Hage Geingob at Heroes’ Acre. 🕊️
Later attended a State Luncheon given by The President of Namibia at State House. 🍽️
26/02 unofficial Arrived at Heathrow Airport from Namibia. 🇳🇦✈️🇬🇧
With Sir Tim Attended the British Horseracing Authority’s Thoroughbred Industry Employee Awards at Ascot Racecourse. 🐎🏆
27/02 With Sir Tim Attended a Service of Thanksgiving for the late King Constantine II at St George’s Chapel in Windsor Castle with members of 🇬🇧, 🇬🇷, 🇩🇰 and 🇪🇸 royal families.
28/02 As Patron of the Royal College of Emergency Medicine, attended the Emergency Medicine Trainees' Association Annual Conference at Hilton Newcastle Gateshead. 💉💊
As Royal Patron of the Motor Neurone Disease Association, attended a Rugby League Reception at Leeds Rhinos Rugby Club, in Headingley, Leeds. 🦽🏉
29/02 unofficial Departed from Heathrow Airport for the United Arab Emirates 🇬🇧✈️🇦🇪
Unofficial Sir Tim, as President of Never Such Innocence, attended a 10th anniversary celebration for the charity at Edinburgh Castle. 🏰
Total official engagements for Anne in February: 44
2024 total so far: 85
Total official engagements accompanied by Tim in February: 6
2024 total so far: 23
FYI - due to certain royal family members being off ill/in recovery I won’t be posting everyone’s engagement counts out of respect, I am continuing to count them and release the totals at the end of the year.
#busy princess 👑#please see red comment#aimees unofficial engagement count 2024#princess anne#princess royal#tim laurence#timothy laurence#court circular#february 2024#not all engagements are on here ❤️
34 notes
·
View notes
Text

HOAX of the Day: Bare-fronted Hoodwink
Description: In 1950, the scientific journal Bird Notes published an article about a newly discovered bird called the Bare-fronted Hoodwink. However, this was the invention of amateur ornithologist MFM Meiklejohn. On April 1st, 1975, the bird was put on display at the Royal Scottish Museum in Edinburgh.
95 notes
·
View notes
Text
OFMD Stede Bonnet as a Macaroni: Wealth, Gender and Sexuality in the 18th Century Fashion World
Historical Inaccuracy in Our Flag Means Death? Never!
Historical inaccuracy! I hear you cry. A Macaroni in 1717!?! It is true macaroni fashion was really a late-18th century fashion trend, seemingly reaching its peak in the 1770s. However Our Flag Means Death is nothing if not historically inaccurate. Stede’s costumes seem to take inspiration from across the 18th century rather than worrying about what would have actually been worn in 1717.
Early 18th century suits tended to have round necklines, loose-fitting sleeves with wide cuffs, long waistcoats that stoped just above the knee, and coats with full skirts just a little longer that the waistcoat.

[Left: Matthew Prior, oil on canvas, c. 1713-1714, by Alexis-Simon Belle, photo credit: St John's College, University of Cambridge, via Art UK.
Middle: Matthew Hutton of Newnham, Hertfordshire, oil on canvas, c. 1715, by Johannes Verelst, photo credit: National Trust Images, via Art UK.
Right: William Leathes, Ambassador Brussels, oil on canvas, c. 1710-1711, by Herman van der Myn, photo credit: Colchester and Ipswich Museums Service: Ipswich Borough Council Collection, via Art UK.]
As the century continued we get standing collars and turned down collars but round necklines were still around as well, sleeves got tighter with smaller cuffs, the waistcoats got shorter and the coats lost their skirts.

[Left: Thomas ‘Sense’ Browne, oil on canvas, c. 1775, by Nathaniel Dance-Holland, photo credit: Yale Center for British Art, via Art UK.
Middle: Sir Brooke Boothby, oil on canvas, c. 1781, by Joseph Wright of Derby, photo credit: Tate, via Art UK.
Right: David Allan, oil on canvas, c. 1770, by David Allan, photo credit: Royal Scottish Academy/National Galleries of Scotland (Antonia Reeve), via Art UK.]
Stede’s collars are inconstant some are rounded but others are turned down and Ed’s purple suit has a standing collar. Many of Stede’s coats have wide cuffs, but most have little skirt to them. His teal suit from the pilot has a bit of a skirt but its paired with a short waistcoat.

Most of Stede’s waistcoats are short with the exception of his suits from both the wedding portrait with Mary and the the family portrait. Both suits are very straight giving him a boxy appearance and are pretty different from most of the suits we see him in.

All in all I don’t think they were aiming for historically realistic clothes but with the collars, short waistcoats, and lack of skirts I get more of a late-18th century vibe.

So what was a Macaroni?
A Classical Dictionary of the Vulgar Tongue (1785), defined macaroni as follows:
An Italian paste made of flour and eggs; also a fop, which name arose from a club, called the maccaroni club, instituted by some of the most; dressy travelled gentlemen about town, who led the fashions, whence a man foppishly dressed, was supposed a member of that club, and by contraction stiled a maccaroni.
The macaroni club was said to have comprised of young men who had gained a taste for French and Italian textiles on their Grand Tour (a traditional trip taken tough Europe by upper class men when they came of age). The earliest reference to the club is from a letter from Horace Walpole to Lord Hertford on the 6th Feb 1764:
at the Maccaroni Club (which is composed of all the travelled young men who wear long curls and spying-glasses),
In his book Pretty Gentleman: Macaroni Men and the Eighteenth-Century Fashion World Peter McNeil suggest the club was actually Almack’s. Almack’s was a private club at 50 Pall Mall that was attended by prominent Whigs including Sheridan, Fox and the Price of Wales. (p52) While the name may have originated from the men at Almack’s it was soon used to describe any man who followed the associated fashion trends.
So what were these trends?
Hair
“Still lower let us fall for once, and pop
Our heads into a modern Barber’s shop;
What the result? or what we behold there?
A set of Macaronies weaving hair.”
~ The Macaroni by Robert Hitchcock
Probably the most iconic aspect of macaroni fashion was the hair. “It was the macaroni attention to wigs that caused most consternation” explains Peter McNeil. The macaroni hair “matched the towering heights of the female coiffure, with a tall toupee cresting at the centre front. The wig generally had a long tail at the neck (’queue’), which when folded double was called the ‘cadogan’, all of which required regular dressing with pomade and powder, sometimes in the colours of pink, green or red.” (p45)
The height of the macaroni hair was a point of particular fascination in macaroni caricature exaggerating it beyond what the macaroni were probably actually wearing. Compare below Tom’s hair in the satirical print What is this my son Tom to the self portrait of Richard Cosway, who was satirised by Mary Darly as “The Miniature Macaroni” (a reference both to his height and his career as a miniature painter).

[Left: What is this my son Tom, print, c. 1774, published by Sayer & Bennett, via The British Museum.
Right: Self-Portrait, Ivory, c. 1770–75, by Richard Cosway, via The Met.]
The way Stede usually wears is hair is not particularly macaroni nor particularly 18th century for that matter. The exception to this is his wig from The Best Revenge Is Dressing Well though even this doesn’t have the iconic macaroni hight.

Interestingly both Stede and Ed are wearing flowers in their hair. While there are certainly depictions of women with flowers in there hair I’m not aware of this being a trend in mens fashion at all. However macaroni were known for wearing large nosegays.
While the tall hair was certainly iconic not all macaroni wore their hair tall. Joseph Banks, who was satirised as “The Fly Catching Macaroni” by Matthew Darly, is depicted in his portrait with a fairly typical 18th century hairstyle. Its not the hair alone that makes a macaroni, it was just one aspect of the fashion.
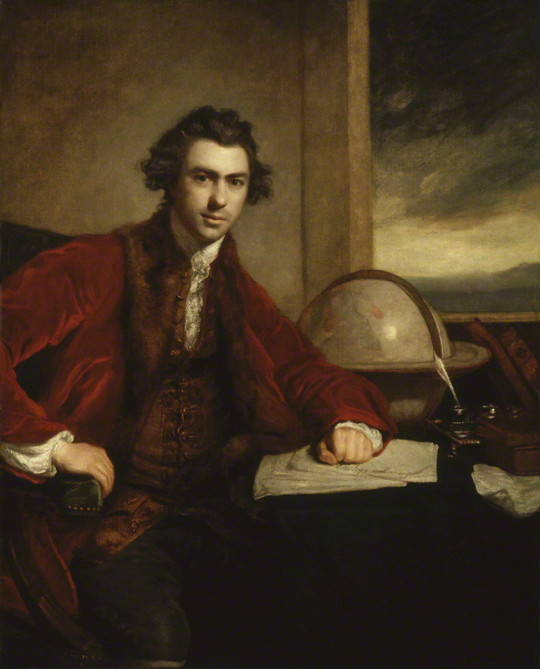

[Sir Joseph Banks, oil on canvas, c. 1771-1773, by Sir Joshua Reynolds, via Wikimedia.]
Suit
“If I went to Almack’s and decked out my wrinkles in pink and green like Lord Harrington, I might still be in vogue.” ~ Horace Walpole to Lord Hertford, 25 Nov 1764
Menswear of the period consisted of the same basic elements; shirt, stockings, breeches, waistcoat and coat. What differentiated the macaroni from others was the fabric, cut, colour and trimmings of the suit. “At a time when English dress generally consisted of more sober cuts and the use of monochrome broadcloth,” explains Peter McNeil “macaronism emphasised the effects associated with French, Spanish and Italian textiles and trimmings”. Popular amongst macaroni were brocaded and embroidered silks and velvets, sometimes further embellished with metallic sequins, simulated gemstones and raised metallic threads. Popular colours included pastels, pea-green, pink, red and deep orange. (McNeil, p30-32)
Far from wearing “monochrome broadcloth” Stede likes a “fine fabric” and dresses in a range of colours, we see him in teal, pink, purple, green, white, red, peach &c.
Tightly cut French style suits known as habit à la française were popular with macaroni. (McNeil, p14) Stede’s suits vary somewhat in cut but some are very French. The peach suit Stede wears in We Gull Way Back particularly has a very macaroni feel to me. Compare it to the English suit (left) and the French suit (right).

From the back you can see the English suit has more of a skirt to it.

Both Stede’s suit and the French suit are somewhat plain but have been paired with a floral embroidered waistcoat, while the English suit has a matching plain black waistcoat.

[Left: English suit, wool, silk, c. 1755–65, via The Met, number: 2009.300.916a, b.
Right: French suit, Silk plain weave (faille), c. 1785, via LACMA, number: M.2007.211.47a-b.]
Fabric covered button’s were common in the 18th century, you can see them on both the French and English coats above. In contrast Stede wears a lot of metal buttons. Steel buttons were popular amongst macaroni, a trend that was satirised in Steel Buttons/Coup de Bouton.

[Steel Buttons/Coup de Bouton, print, c. 1777, by William Humphrey, via The British Museum.]
Pumps and Parasols
“Maccaronies who trip in pumps and with Parasols over their heads” ~ Mrs Montagu
High heels had been popular amongst men during the 17th century. The Royal Collection Trust explains:
In the first half of the 17th century, high heeled shoes for men took the form of heeled riding or Cavalier boots as worn by Charles I. As the wearing of heels filtered into the lower ranks of society, the aristocracy responded by dramatically increasing the height of their shoes. High heels were impractical for undertaking manual labour or walking long distances, and therefore announced the privileged status of the wearer.
(Royal Collection Trust, High Heels Fit for a King)
In 17th century France Louis XIV popularised red-heels by turning them into a symbol of political privilege, which in turn spread the fashion to England. But with the sobering of menswear in England around the turn of the century the high heel and the red-heels went out of fashion. (see Bata Shoe Museum Toronto, Standing TALL: The Curious History of Men in Heels)
The high heel had a bit of a resurgence in the 1770s with macaroni fashion. The Natural History of a Macaroni snipes that the macaroni’s “natural hight is somewhat inferior to he ordinary size of men, through by the artificial hight of their heels, they in general reach that standard”. (Walker’s Hibernian Magazine, July 1777, p458)
Red-heels were reintroduced to England by young men returning from their Grand Tours. A young Charles James Fox (satirised by Mathew Darly as “the Original Macaroni”) wore such French style red-heeled shoes. The Monthly Magazine recalls a young Fox as a “celebrated “beau garçon” with “his chapeau bras, his red-heeled shoes, and his blue hair-powder.” (Oct 1806) and The Life of the Right Honorable, Charles James Fox recalls him in his “suit of Paris-cut velvet, most fancifully embroidered, and bedecked with a large bouquet; a head-dress cemented into every variety of shape; a little silk hat, curiously ornamented; and a pair of French shoes, with red-heels;” (p18) And in Recollections of the Life of the Late Right Honorable Charles James Fox B.C. Walpole recalls him as “one of the greatest beaus in England,” who “indulged in all the fashionable elegance of attire, and vied, in point of red heels and Paris-cut velvet with the most dashing young men of the age. Indeed there are many still living who recollect Beau Fox strutting up and down St. Jame’s-street, in a suit of French embroidery, a little silk hat, red-heeled shoes, and a bouquet nearly large enough for a may-pole.” (p24)
Compare the French style red-heeled shoes of Louis XIV to Stede’s red-heeled shoes.

[Left: detail of Louis XIV, oil on canvas, c. 1701, by Hyacinthe Rigaud, via Wikimedia.]
However most macaroni were depicted wearing the more standard late 18th century low-heeled bucked shoes. Where they distinguished themselves was the size and decoration of the buckles. “Such buckles could be set with pate (lead glass) or ‘Bristol stones’ (chips of quartz), or diamonds if you were very rich.” Explains peter McNeil, “The new macaroni fashion was for huge silver or plated Artois shoe buckles which the Mourning Post claimed weighed three to eleven ounces.” (p90)
While certainly not as iconic has his heels Stede also wears these sorts of shoes. Compare below the shoes from a macaroni caricature to Ed wearing Stede’s shoes (I couldn’t get a good shot of Stede wearing them).
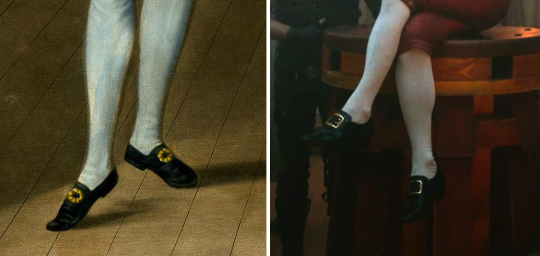
[Left: detail of How d'ye like me, print, c. 1772, published by: Carington Bowles, via The British Museum.]
“A great many jewelled accessories accompanied the macaroni look”, writes Peter McNeil, “They included hanger swords, very long canes, clubs, spying glasses and snuff-boxes.” (p68) Tragically we don’t see Stede with a fashionable dress sword or a cane but we do see him with another accessory popular amongst macaroni; a parasol.
Popular in France parasols/umbrellas were adopted by the macaroni. They were popular amongst both men and woman in France but in England they had a feminine connotation. (McNeil, p129) In the 1780s as umbrellas became more popular amongst men there was a cultural pushback to the perceived gender transgression. On the 16th of August 1780 the Morning Post complains of of the “canopy of umbrellas” bemoaning that “the effeminacy of the men, inclines them to adopt this necessary appendage of female convenience”. On the the 4th Oct, 1784, the Morning Chronicle published a letter complaining of “that vile foppish practice of sheltering under a umbrella”. The author of this tirade writes that while “the ladies should be allowed to secure their beauty and persons from the heat of the sun, or the inclemency of the weather,” because “it is natural, and has a striking effect”, that “to see a great lubberly cit, bounce from his shop, with a coat, hat, and wig that are not together worth one groat,” sheltering “from the influence of the solar beam” was “intolerable.” However:
The macaroni being of the doubtful gender, may in part claim a feminine right; his dress is too delicate to bear an heavy shower, perhaps his person is so too; but a coach, if a clean one is to be found would serve his purpose much better, as there would be less likelihood of his being washed away into the kennel, which he deserves to be kicked into for his d-----d affectation.

Wealth
Born from rich young men returning from their tours with a taste for French and Italian textiles macaroni fashion was expensive. Certainly a working class man would not be able to afford Stede’s wardrobe. Both the sheer amount of clothes he has as well has the fabrics those clothes are made of are indications of wealth. However to say that Stede’s wardrobe is only an indication of wealth would be missing part of picture.
Most rich upper class English men (including colonial) wore plain monochrome suits. Even amongst the gentry macaroni fashion was not the norm. Compare bellow George Washington (left) who was a wealthy planation owner, but notably not a macaroni, to Richard Cosway (right) who was a famous macaroni.

[Left: George Washington, oil on canvas, c. 1796, by Gilbert Stuart, via Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts.
Right: Detail of The Academicians of the Royal Academy, oil on canvas, c. 1771-72, by Johan Zoffany, via The Royal Collection Trust.]
In spite of the expense macaroni fashion was not exclusive to the upper classes. “Macaroni dress was not restricted to members of the aristocracy and gentry,” writes McNeil, “but included men of the artisan, artist, and upper servant classes, who wore versions of this visually lavish clothing with a distinctive cut and shorter jackets. Wealthier shopkeepers and entrepreneurs also sometimes wore such lavish clothing, particularly those associated with the luxury trades, such as mercers and upholsterers -” (p14)
It was possible to copy certain aspects of macaroni fashion on a cheeper budget. The hairstyle in particular was achievable without braking the bank. And there were ways to replicate the effects of certain expensive fashion trends for cheeper prices. For example patterns could be printed rather than embroidered.

[Left: printed waistcoat, cotton, c. 1770–90, via The Met, number: 35.142.
Right: embroidered waistcoat, silk, c. 1780–89, via The Met, number: 2009.300.2908.]
The Town and Country Magazine complains “we now have Macaronies of every denomination, from the colonel of the Train’s-Bands down to the errand-boy.” (McNeil, p169) The Morining Post mocks macaronies that couldn't financially keep up with the trends:
The macaronies of a certain class are under peculiar circumstances of distress, occasioned by the fashion, now so prevalent, of wearing enormous shoe-buckles; and we are well assured that the manufactory of plated ware was never known to be in so flourishing a situation.
(14 Jan, 1777)
In 18th century England, class was about more than just how much money you had. It was about pedigree. “English society was particularly alert to those whom it felt were using clothes to achieve a social status they did not merit” explains McNeil. Richard Cosway was a famous macaroni from modest background. Born to a Devonshire headmaster he was sent to London to study painting at 12. He became a very successful miniature painter and grew rich from the patronage of the Prince of Wales (later George IV) and Whig circles. In Nollekens and his Times J.T. Smith writes of Cosway:
He rose from one of the dirtiest boys, to one of the smartest of men. Indeed so ridiculously foppish did he become that Mat Darly, the famous caricature print-seller, introduced an etching of him in his window in the Strand, as ‘The Macaroni Miniature Painter’
(McNeil, p105-14)
But it was not only the Darlys that satirised Cosway Hannah Humphrey mocks Cosway as a social climber in A Smuggling Machine or a Convenient Cos(au)way for a Man in Miniature which depicts him standing under the petticoats of his much taller wife Maria. In the background there is a picture of Cosway climbing a ladder that rests upon a woman (she is believed to either be Angelica Kauffman or the Duchess of Devonshire). Below this reads:
Lowliness is Young Ambitions Ladder,
Whereto the climber upward turns his Face
But when he once attains the upmost round
He then unto the Ladder turns his back,
Looks unto the clouds - scornin [sic] the base degrees
By which he did assend.
Shak. Jul. Caesar.

[A Smuggling Machine or a Convenient Cos(au)way for a Man in Miniature, print, c. 1782, by Hannah Humphrey, via The British Museum.]
Another famous macaroni not born into the aristocracy was Julius Soubise. Brought to England from the West Indies as a slave he was taken in by Catherine Hyde, the Duchess of Queensbury. She gave him a leisured childhood, in which he was taught to play and compose for the violin, was taught to fence by Domenico Angelo, and learned oration from David Garrick. “Macaroni caricatures of Soubise parodied a foppish upstart whose outfits and entertainments, financed by the Duchess, affronted both racial and social expectations of an African male.” Writes Petter McNeil, Soubise was satirised as “a Mungo Macaroni” an “offensive term meaning a rude or forward black man.” (p118)

[Left: A Mungo Macaroni, print, c. 1772, by Matthew Darly, via The British Museum.
Right: The D------ of [...]-- playing at foils with her favorite lap dog Mungo after expending near £10000 to make him a----------*, print, c. 1773, by William Austin, via Yale Center for British Art.]
The expense of Stede’s wardrobe is a key part of the narrative. Stede has nice fancy luxurious things. Ed wants nice fancy luxurious things. Ed was born a poor brown boy and while he may be rich now he can never truly change his class. He could be as rich as Richard Cosway or Julius Soubise but to the gentry he will always be that poor brown boy.

Gender
As we have already seen in the tirade against men using umbrellas the macaroni was perceived as being of “the doubtful gender”. (The Morning Chronicle, 4 Oct, 1784)
The Natural History of a Macaroni writes that there “has within these few years past arrived from France and Italy a very strange animal, of the doubtful gender, in shape somewhat between a man and monkey,” that dresses “neither in the habit of a man or woman, but peculiar to itself”. The author states that “they are in no respect useful in this country”:
that the minister of the war department would give orders to have them enlisted for the service of America: we do not mean to put them on actual duty there. Alas! they are as harmless in the field, as they are in the chamber, but they may stand as faggots to cover the loss of real men.
(Walker’s Hibernian Magazine, July 1777, p458-9)
A “faggot” being “A man who is temporarily hired as a dummy soldier to make up the required number at a muster of troops, or on the roll of a company or regiment.” (see OED)

[The Masculine Gender & The Feminine Gender, etching with touches of watercolour, c. 1787, Attributed to Henry Kingsbury, via The Met.]
The macaroni wasn’t just considered effeminate because of the way they dressed but also because of their interests and the way walked and talked. Famous for playing fops and macaroni, the actor David Garrick did a lot to establish the character of the macaroni in the public mind. In his poem The Fribbleriad Garrick mocks the men who were offended by his performances asserting, perhaps accurately, that they were offended because it was them he mocked. He portrays a group of angry effeminate men meeting in order to seek revenge on him for his portrayal of them:
May we no more such misery know!
Since Garrick made OUR SEX a shew;
And gave us up to such rude laughter,
That few, ’twas said, could hold their water:
For He, that player, so mock’d our motions,
Our dress, amusements, fancies, notions,
So lisp’d our words, and minc’d our steps,
The macaroni had become more than simply an effeminate man, he had become a new sex. Something not quite man or woman. Something in-between. A new description of a macaroni asks the question:
Is it a man? ‘Tis hard to say - A woman then
- A moment pray -
So doubtful is the thing, that no man
Can say if ‘tis a man or woman:
Unknown as yet by sex or feature,
It moves - a mere amphibious creature.
(McNeil p169)
Sexuality
Much like today in the 18th century effeminacy was associated with homosexuality. Men who had sex with other men were known as mollies. A Classical Dictionary of the Vulgar Tongue (1785), defined a molly as “A Miss Molly; an effeminate fellow, a sodomite”. In the History of the London Clubs (1709), Ned Ward characterises mollies as follows:
There are a particular Gang of Wretches in Town, who call themselves Mollies, & are so far degenerated from all Masculine Deportment or Manly exercises that they rather fancy themselves Women, imitating all the little Vanities that Custom has reconcil’d to the Female sex, affecting to speak, walk, tattle, curtsy, cry, scold, & mimick all manner of Effeminacy.
“By the 1760′s,” explains Peter McNeil, “too much attention to fashion on the part of a man was read as evidence if a lack of interest in women”. (p152)
Macaroni were often portrayed as incapable or simply uninterested in sexual relations with women. This attitude is expressed by Mr. Bate in the following dialogue from The Vauxhall Affray; Or, the Macaronies Defeated:
Mr. Fitz-Gerall: I always though a fine woman was only made to be looked at.
Mr. Bate: Just sentiments of a macaroni. You judge of the fair sex as you do your own doubtful gender, which aims only to be looked at and admired.
Mr. Fitz-Gerall: I have as great a love for a fine woman as any man.
Mr. Bate: Psha! Lepus tute es et pulpamentum quæris?
Mr. Fitz-Gerall: What do you say, Parson?
Mr. Bate: I cry you mercy, Sir, I am talking Heathen Greek to you; in plain English I say, A macaroni you, and love a woman?
Mr. Fitz-Gerall: I love the ladies, for the ladies love me.
Mr Bate: Yes, as their panteen, their play-thing, their harmless bauble, to treat as you do them, merely to look at
While lack on interest in woman does not necessarily mean attraction to men, Matthew Darly takes the implication there in his 1771 set of macaroni caricatures which induces a print entitled Ganymede, a reference to Zeus’ male lover of the same name. Ganymede is believed to be a parody of Samuel Drybutter who had been arrested for attempted sodomy in January 1770. Darly also includes the character Ganymede in Ganymede & Jack-Catch. Jack-Catch is a reference to the infamous English executioner John Ketch. In the print Jack-Catch says, “Dammee Sammy you’r a sweat pretty creature & I long to have you at the end of my String.” Ganymede replies, “You don’t love me Jacky”. Jack-Catch is holding a noose with one hand and stroking Ganymede’s chin with the other. Jack-Catch is soberly dressed in typical 18th century menswear, while Ganymede’s dress is distinguished by his lace ruffles and styled wig. The print is not only suggesting that macaroni are sodomites but making a joke of the execution of them. The punishment for a sodomy at this time in England being death by hanging.

[Left: Ganymede, print, c. 1771, Matthew Darly, via The Met.
Right: Ganymede & Jack Catch, print, c. 1771, Matthew Darly, via The British Museum]
An anonymous letter to the Public Ledger (5 Aug, 1772) says blatantly what others had already implied. “The country is over-run with Catamites, with monsters of Captain Jones’s taste, or, to speak in a language witch all may understand, with MACCARONIES”. The writer warns macaroni who have “escaped detection” as sodomites and “therefore cannot fairly be charged” that they have not avoided suspicion:
Suspicion is got abroad-the carriage-the deportment-the dress-the effeminate squeak of the voice-the familiar loll upon each others shoulders-the gripe of the hand-the grinning in each others faces, to shew the whiteness of the teeth-in short, the manner altogether, and the figure so different from that of Manhood, these things conspire to create suspicion; Suspicion gives birth to watchful observation; and, from a strict observance of the Maccaroni Tribe, we very naturally conclude that to them we are indebted for the frequency of a crime which Modesty forbids me to name. Take warning, therefore, ye smirking group of Tiddy-dols: However secret you may be in your amours, yet in the end you cannot escape detection;
Bows on His Shoes
18th century shoes were typically buckled, laces and ribbons were simply unfashionable. As mentioned previously macaroni were distinguished by the size and decoration of the buckles. So are Stede’s bows simply ahistorical? Well there are references to 18th century men wearing laces and ribbons.
Towards the end of the 18th century laces started to come into fashion. Appeal from the Buckle Trade of London and Westminster, to the Royal Conductors of Fashion (1792) complained that despite how “tender and effeminate the appearance of Shoe Strings” the “custom of wearing them has prevailed.”
Perhaps the most intriguing reference is that of Commissioner Pierre Louis Foucault’s papers where he details the surveillance, investigation and entrapment of "pederasts” in Paris. It is important to note that the word “pederasty” was used synonymously with “sodomy” in the 18th century and did not denote age simply sex. An Universal Etymological English Dictionary (1726) defines “A pederast” as “a Buggerer” and “Pederasty” as “Buggery”.
Foucault and the men working with him identified particular clothing worn by men seeking sex with other men that he called the “pederastical uniform”. In Foucault’s papers men are described as being “attired in such a way as to be recognized by everyone as a pederast”, “clothed with all the distinctive marks of pederasty”, or simply “dressed like a pederast”. This “uniform” generally included “some combination of frock coat, large tie, round hat, small chignon, and bows on the shoes.” Jeffrey Merrick in his article on Foucault speculates that these men dressed this way to signal to each other. However when questioned by police they would understandably deny such a purpose, one man when questioned about his outfit responded that everyone “dresses as he sees fit”. (Jeffrey Merrick, Commissioner Foucault, Inspector Noël, and the “Pederasts” of Paris,1780-3)

Conclusion
I’m not saying Stede is intended to be a macaroni. If that were the case they would have given him the iconic macaroni hairstyle. However the costuming team has clearly pulled from fashion trends that were associated with effeminacy and homosexuality. While OFMD is evidently wholly unconcerned with creating period accurate costumes the costumes are still clearly inspired by historical fashions. Perhaps the curtains really are just blue but maybe Stede wears bows on his shoes because he’s gay.
#I had way too much fun doing this#our flag means death#ofmd meta#stede bonnet#queer history#macaroni#historical fiction#fashion history
196 notes
·
View notes
Text
more news on Royal Week in Scotland:
Monday 3rd July: the traditional Ceremony of the Keys will take place on the forecourt of the Palace of Holyroodhouse to mark the start of Royal Week. In the evening, HM will attend a reception on board the Royal Yacht Britannia to mark 25 years since her arrival in Edinburgh.
Tuesday 4th July: the King will view the Jubilee Gates at the entrance to Abbey Yard, Palace of Holyroodhouse, marking Queen Elizabeth II’s Platinum Jubilee. Their Majesties joined by the Princess Royal will later host guests at a garden party to celebrate the coronation year.
Wednesday 5th July: His Majesty will hold an Investiture at the Palace of Holyroodhouse and Her Majesty will meet weavers at Dovecot Studios in Edinburgh. Later, the King, accompanied by the Queen and the Duke and Duchess of Rothesay, will be presented with the Honours of Scotland at a National Service of Thanksgiving and Dedication at St Giles, following processions on the Royal Mile.
Thursday 6th July, the King and Queen will visit the Great Tapestry of Scotland visitor centre in Galashiels. TM will tour the Lochcarron of Scotland weaving mill before finishing Royal Week in Selkirk, where they will visit the marketplace and watch a performance of “Casting of the Colours”. The Duke of Edinburgh will host The Duke of Edinburgh Gold Awards Celebration at the Palace of Holyroodhouse on Thursday 6th July. HRH will also visit the Royal Lyceum Theatre in Edinburgh.
The Princess Royal will carry out engagements during Royal Week. HRH’s programme will include a visit to Scottish Fisheries Museum Trust Limited, Strathcarron Hospice and the University of Edinburgh.
ps: according to Hello Magazine: "William & Kate have a jam-packed schedule with official engagements. [They] will be in attendance for various events."
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
Nikolaj Coster-Waldau has eight seasons of faux Medieval cred thanks to his character Jaime Lannister on Game of Thrones. In an upcoming production by the BBC and CBS Studios he gets to recreate some actual 11th century history in the series King and Conqueror.
Nikolaj's character never got to rule the Seven Kingdoms. But in King and Conqueror he portrays William the Conqueror who became King of England and ultimately the founder of the royal line which still reigns in London.
George R.R. Martin was heavily influenced by English, French, and Scottish history in ASoIaF. GRRM may have had William the Conqueror in mind when writing about Aegon I Targaryen.
In 1066, the English King Edward the Confessor died without an heir. As if dying without a direct descendant to claim the throne wasn't one of the most chaotic things a king could do, Edward took it a step further: He allegedly promised the throne to both his brother-in-law, Harold Godwinson, and to a distant relative, William of Normandy.
Harold and William weren't the only ones with a claim, either. While the pope endorsed William's claim, the resulting war of succession would force Harold to fight Harald Hardrada, the king of Norway, who also claimed the thrones of Denmark and England and invaded the latter alongside Harold's brother, Tostig. Anglo-Saxon King Harold would have to defeat Harald before meeting William and his Norman invasion at the Battle of Hastings, all in the same year.
If that sounds to you like a lot of drama that could easily be its own television series, you aren't alone. CBS Studios and the BBC are teaming to produce "King and Conqueror," a show about this most pivotal event in English history. James Norton ("Happy Valley") and Nikolaj Coster-Waldau ("Game of Thrones") are attached to be the titular King Harold and William the Conqueror, respectively.
[ ... ]
Historians might disagree on whose side of the story is more accurate, but screenwriters and producers agree that no matter what happened, the 1,000-year-old story will make for great television. Michael Robert Johnson ("Sherlock Holmes") will pen the series while Baltasar Kormákur ("2 Guns") will direct.
"King and Conqueror" begins production in 2024.
There's actually a physical artistic link between the account of William's conquest in the 1060s and Game of Thrones.
After William's victory, his half-brother Bishop Odo was apparently the commissioner of a tapestry embroidered with scenes which tell the epic story of William's conquest. The cloth, now known as the Bayeaux Tapestry is an amazing 70 meters long. It can be viewed here.
So volunteers at the Ulster Museum in Northern Ireland where GoT was produced created a tapestry in the style of the Bayeaux Tapestry which tells the story of all eight seasons of GoT. See our 2019 post about it.
#game of thrones#house of the dragon#nikolaj coster-waldau#jaime lannister#william the conqueror#king and conqueror#bayeaux tapestry#guillaume le conquérant#gra o tron#trône de fer#kampen om jerntronen#pemainan takhta#a guerra dos tronos#juego de tronos#trono di spade#taht oyunları#trò chơi của ngai#valtaistuinpeli#hra o trůny#isang kanta ng yelo at apoy#гра престолів#왕좌의 게임#权力的游戏#ゲームの玉座#صراع العروش#تخت کے کھیل#गेम ऑफ़ थ्रोन्स#গেম অব থ্রোনস#ಗೇಮ್ ಆಫ್ ಥ್ರೋನ್ಸ್#игра престолов
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
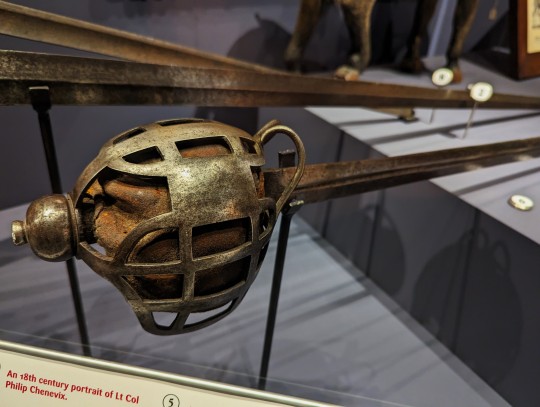

Basket-Hilted Cavalry Sword from the British Empire dated to the Mid-18th Century on display at the Royal Scots Dragoon Guards Museum in Edinburgh Castle, Scotland
Swords of this type were purchased by the colonels of the British cavalry regiments for the use of their men. The styles of hilt varied from regiment to regiment. Basket-hilted swords became popular, not just with Scottish regiments but many cavalry regiments around Europe.
The 2nd Royal North British Dragoons were part of the War of Austrian Succession (1740 - 1748) as part of the coalition forces. They fought at the battle of Dettingen in 1743 where King George II became the last British monarch to fight in a battle. In 1745 the last Jacobite Rising took place and unlike in the last risings the regiment were left in Flanders.
Photographs taken by myself 2023
#sword#british empire#cavalry#scotland#scottish#military history#18th century#georgian#hanoverian#royal scots dragoon guards museum#edinburgh castle#barbucomedie
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
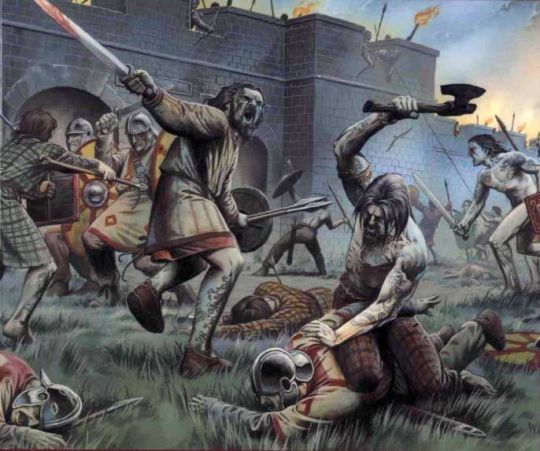









January 24th, 76AD, is said to be the likely date of birth forPublius Aelius Hadrianus, who built Hadrian’s Wall.
When the Romans invaded the British Isles they held, large parts of what is now Scotland, even after the construction of Hadrian’s Wall in AD 122, there were large forts around the country at varioustimes, the largest of which was Trimontium located at Newstead, near Melrose, in the Scottish Borders. It was occupied intermittently from about 79 to 184 AD and was the largest of the "outpost" forts after the construction of Hadrian's Wall
Hadrian’s Wall was largely abandoned for about twenty years from .AD 138, when the Romans established a new frontier in Scotland between what are now the Firths of Forth and Clyde, where they built the Antonine Wall.
The Antonine Wall was more of a very large ditch, and my old flat would have been part of the structure, part of the "wall" is on land only yards from me. I got into trouble for calling it a ditch from a Roman historian before, so will add that it was much more, the thing is it more or less looks like one just now, much of the fortifications are long gone.
Hadrian is noted for his interest in architecture and the number of provinces he visited whilst Emperor. He is likely to have visited Britain in AD 122, after some kind of conflict in the preceding years, and we know that it was in this period that construction of the Wall started. It has also been known as Picts' Wall, or Vallum Hadriani in Latin.
The origin of the Picts is clouded by the many fables and legends about them. There are numerous theories as to who the Picts were and where they came from. Experts even disagree over what they ate and drank and what language they spoke although some point to the existence of a distinct Pictish language, which today is believed to have been an Insular Celtic language, closely related to the Brittonic spoken by the Britons who lived to the south.
Often described as savages the Picts were an ancient and artistic people who defied the might of Rome which conquered the rest of Britain. They were a sophisticated , hardworking, clever people, skilled in farming and fishing.
You would have thought a savage tribe would have been an easy conquest for the Romans, but the Picts were anything but that. Picts are first recorded in history in the third century AD. Eumenius, a Roman writer, describes the "pictus" as fierce and skilled in battle. It is not clear whether "pictus" (the Latin for painted) was intended, or if this is a Latin form of some indigenous name. I prefer to think of them as the "Painted People"
Although the Romans reached Scotland and often defeated them in battle, they never conquered the Picts or Pictland. The Roman Empire's expeditions north resulted in few permanent gains.
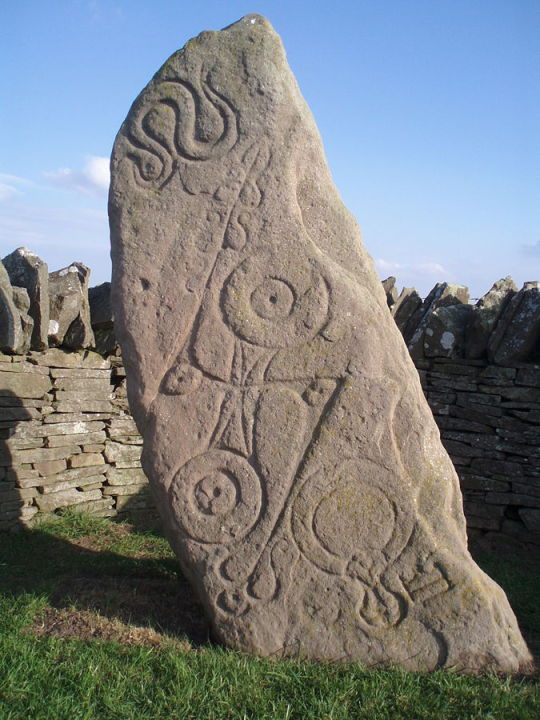
Scotland's sculptured stones, created by the Picts of ancient Alba tell the stories of a race of people who defied Rome and survived the invading Vikings, thus preserving a separate culture and race in Scotland. It is in these sometimes mighty, sometimes delicate stones that the history of ancient Scotland is now recorded.
There are many of these slabs on display in The National Museum of Scotland in Edinburgh, as well as a fine display in The Hunterian in Glasgow.
When the Romans left the Picts were often attacked by the Britons and eventually all the Pictish tribes agreed to support one High King who would rule all of Pictland.
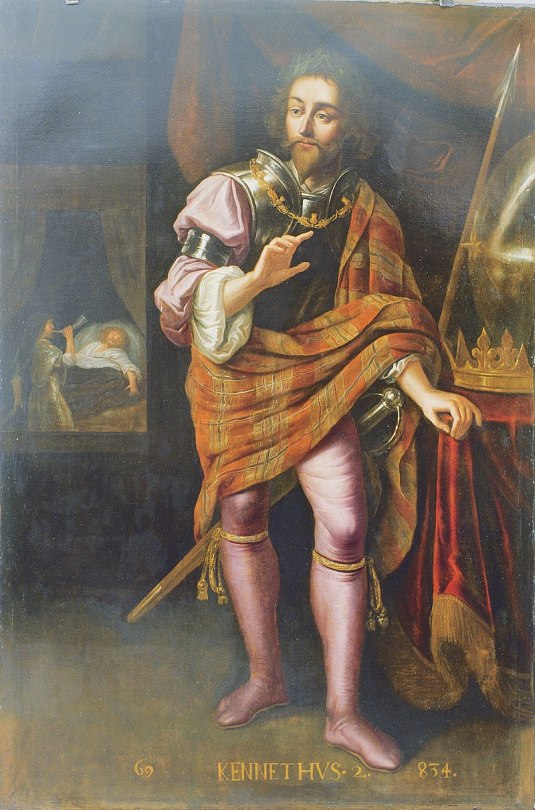
It's said the Picts, unusually, were a matrilineal society, i.e. bloodlines passed through the mother. Pictish kings were not succeeded by their sons, but by brothers, nephews or cousins as traced by the female line in a complicated series of intermarriages between 7 royal houses. It is this rare form of succession which in 845 AD gave the crown of Alba and the title Rex Pictorum - King of the Picts - to the son of a Pictish princess by the name of Kenneth, Son of Alpin, he is generally accepted by most historians as the first of the kings of Scotland, follwing on from his reign as King of Dál Riata. As usual though, not al agree on this.
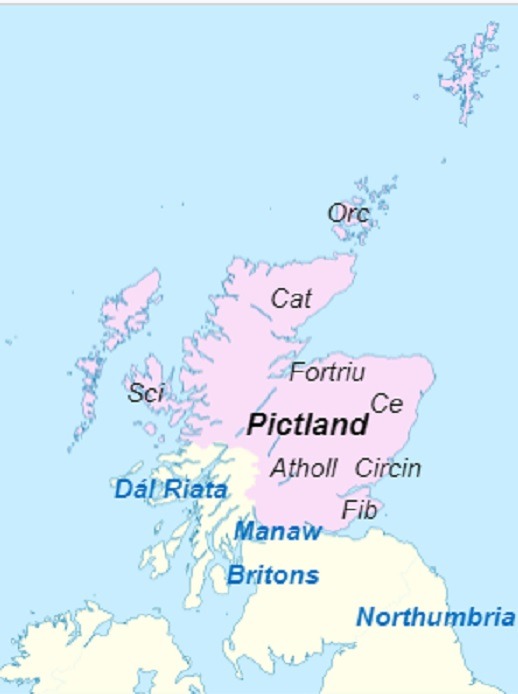
The Picts survived as a distinct people until early in the 10th century. However, there is no record of them dying out or moving elsewhere. It is most likely that the Picts simply integrated into the large population within the developing multi-ethnic nation of Scotti, Picts, Celts, Britons and Angles which we now call Scotland. The map, from wiki says this was how their lands looked as late as the 7th century. The last pics are of two Pictish people and a 15th century depiction of King Kenneth.
173 notes
·
View notes
Photo
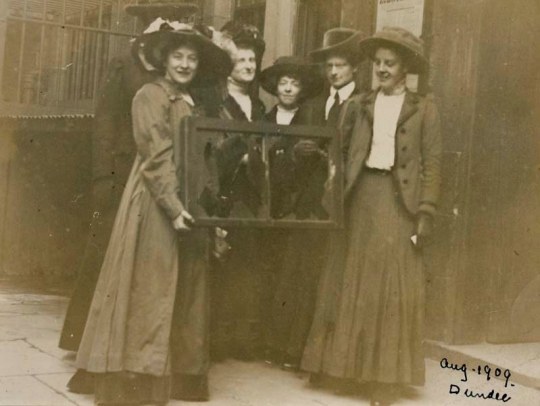

On this day, 10 February 1913, suffragettes fighting for votes for women in the UK smashed windows at the Reform, Carlton, Junior Carlton, Oxford, and Cambridge Clubs, and also at the residence of Prince Christian. Cases containing exhibits at the Royal Scottish Museum were also broken. Our new stories web app has timelines where you can learn more, for example see this story and many more in our timeline about the suffragettes: https://stories.workingclasshistory.com/tag/9355/suffragettes https://www.facebook.com/workingclasshistory/photos/a.296224173896073/2206628406188964/?type=3
127 notes
·
View notes
Text

These sketches were done by an eye witness of the Loch Ness Monster in 1936. However, Ian Lyster, who worked for Royal Scottish Museum Department for Natural History, received the drawings in 1975. The anonymous witness stated in a letter that the sighting took place by Drumnadrochit, a village near Loch Ness. The creature seen had been described as "fleshy and flabby" and having a "mangy appearance". He also stated that the creature was eating weeds or algae off of stones. Lyster explained that many things in the drawings, such as the fleshy lobes hanging from the monster, have been described in other witness accounts.
This account, among countless others, now resides at the National Museum of Scotland in their "Monster Files".
11 notes
·
View notes
Note
Assuming that you have unlimited money—which can only be used to purchase swords and sidearms and the like—what does your dream armoury look like?
This is a great question, and I've had a great time thinking about it, thank you!
I admit to coveting a Lloyd's Patriotic Fund sword -- they're so pretty, and I'm attached to the history behind them. And of course I'd add an 18th-century basket-hilted Scottish broadsword -- actually, I hear tell there were all sorts of variations of Scottish hilts being set to French blades commissioned by the Jacobite exile community in France, replacing lost, broken, or pawned weapons, and it would be cool to have examples of that.
That said, I have a pronounced preference for weapons I know how to use. A weapon should feel like an extension of your arm, and when it doesn't, it's so sad. I'm currently taking saber/cutlass lessons, so an antique Royal Navy cutlass would be lovely -- along with a decent blunted replica that I could beat up without reserve! (Can some of these funds be diverted into the time for weapons training, so I could properly enjoy these blades? I hope so!)
But my real passion is knives. There are so many cool knife designs from so many cultures! Optimized for so many functions! (Including ceremonial functions!) I of course want all the kinds of knives wielded by my blorbos, plus all the various clever blades I've coveted over the decades. I'm not, however, much into fantasy blades, even though there's a popular market for those -- I vastly prefer knife designs that were actually used by a specific people for a specific purpose.
As far as antiques vs. replicas go, I'm ambivalent. I have complicated feelings about some of the conflicts various historic weapons were used in and the fetishization of artifacts thereof; I also have complicated feelings about who gets to own rare historical artifacts, especially from a people's own cultural history. Accordingly, if I truly did have unlimited funds to spend on this, I would enjoy being able to buy museum-quality pieces that museums are unable to afford, and then put them out on permanent loan to those institutions. (Or, if the terms of my fantasy funds permit it, donating said items to the relevant institutions outright -- whichever makes better sense for the history being available to researchers and the public.) Also, you can't play with antiques like you can with replicas! So likely I'd have a decent mix of both in the collection.
And then, just for kicks, a solar-actuated signal cannon that fires at noon every day. Just because I can. :D
#clove-pinks#thank you so much for the question#and my apologies in taking so long to answer it#if I sound like a jackdaw that likes random shiny things#that would be because I'm a jackdaw that likes random shiny things#and of course I want a paid armorer to make sure everything is properly maintained#especially the historical items#because I am crap at keeping up at chores like that myself#and I wouldn't want the historical items to suffer#about me#knives
9 notes
·
View notes