#refined wheat diabetes
Note
Do you know how our understanding and treatment of diabetes has changed through history?
Oooh good question, anon!
As you may guess, diabetes mellitus is not new.

We've known about it since at least the Ebers Papyrus (1550 BCE) when the disease and a treatment was first described. This treatment was: "a liquid extract of bones, grain, grit, wheat, green lead and earth." I did not look these up, but I would guess they did not do a whole lot for the treatment of diabetes.
Later during the 6th century BCE it was first given a name when it was described by Hindu physician Sushruta as madhumeh or "honey urine."
Honey urine is a very apt descriptor for diabetes. In any type, one of the most measurable symptoms is that the person urinates a lot, and the urine tastes sweet (or, if one didn't feel like tasting, that it ferments, or that it attracts ants). This was also the first test for diabetes.
The reason for the sweetness of the urine (as well as a lot of other general info about diabetes) is spelled out more clearly in my "Don't Be That Guy Who Wrote Hansel and Gretel: Witch Hunters" post.
A Greek physician Apolonius of Memphis named it Diabetes, meaning "to siphon" (referring to the large amount of urine lost).
Roman physician Aretaeus later made the first precise description of diabetes. This included the classic symptoms of incessant thirst, copious urination, and constant hunger leading to emaciation and death. He also notes that if deprived of water, the patient will continue to urinate until they become so dehydrated that they die.
The term "Mellitus" was not added until the 1600s by an English physician Thomas Willis. This was again due to the sweetness of the expressed urine. Willis prescribed a diet of "slimy vegetables, rice, and white starch. He also suggested a milk drink which was distilled with cypress tops and egg whites, two powders (a mixture of gum arabic and gum dragant), rhubarb and cinnamon". Supposedly his patients improved if they kept to this diet, though few managed it long term. I honestly don't know how it would have worked, even temporarily.
A major breakthrough came in 1889 when it was discovered that if you removed the pancreas from a dog, the dog would become diabetic (particularly, that it would urinate large quantities of sweet urine). Up until this point it was thought that diabetes stemmed from the kidneys and bladder, or perhaps the lungs. This was the first time it had been shown experimentally that the pancreas was the problem.
Speaking of this, this was also part of a series of experiments where an English physician named Merkowski implanted a small amount of pancreas in the pancreas-less dog's fat, which reversed the diabetes temporarily. This proved that the pancreas was making something that helped regulate blood (and thus urine) sugar.
What this was wasn't figured out until 1921, when Canadian scientists Banting and Best (with help from McLeod and Collip) isolated something they called insletin (after the islets of langerhans, where the substance was being produced). It's important to note that all of these scientists hated each other so much they almost refused a Nobel Prize over it. Later, Collip would refine the substance and McLeod would rename it insulin.
Prior to insulin existing there was basically 1 vaguely useful treatment for diabetes. Unfortunately, that was starvation. So you could either die a slow and painful death by diabetes or you could die a slightly less slow but still painful death due to eating about 500 calories per day. Either way, diabetes was fatal, usually within a couple of years of diagnosis.
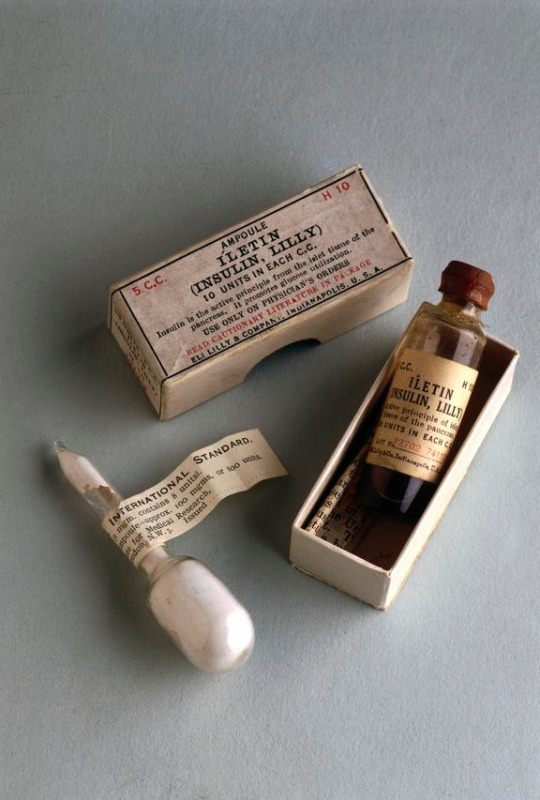
By 1923, the first commercial insulin product, Iletin, had been developed. Iletin was a U10 insulin (10 units per 1 milliliter- less potent than today's U100 and U500 insulins) and was made from pork pancreases. It took nearly a ton of pork pancreas to make 1oz of insulin. Fortunately, as a byproduct of the meat industry, pancreases were readily available.
Now, you might be thinking- no one has mentioned type 1 or type 2 yet in this entire post!
Well, you would be right, because diabetes wouldn't be split into 2 forms (insulin-dependent and non-insulin dependent) until 1979, and wouldn't be classified as types 1 and 2 until 1995. That's right- some of you were alive when there was only one kind of diabetes out there.
Now, there's more about the types in the Hansel and Gretel post, but essentially type 1 diabetes occurs when the pancreas itself stops producing insulin, usually in childhood. When this happens, the body stops being able to use sugar (insulin, a hormone, acts as a "key" to let sugar into cells for use). Without replacing that insulin, the person dies because their cells starve.
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the pancreas still produces insulin, but the cells stop responding to it correctly. This causes high sugar levels in the blood, which causes longer-term complications (infections, ulcers, blindness, neuropathy, heart and kidney disease, hyperosmolar syndrome, etc..) which eventually lead to death.
We started discovering oral drugs that worked on what would later become type 2 in the 1950s. Particularly those that worked by increasing the insulin output of the pancreas, but only when the pancreas was still producing some insulin.
Predicting which diabetics would benefit from oral therapies was challenging, but it was recognized that when the onset of diabetes was slow and came on in adulthood, the oral agents would work, while if it came on suddenly in childhood, the oral agents wouldn't. Terms like "adult onset" and "maturity onset" were common:

(Side note: if you have ever read Alas, Babylon (1955) there is a diabetic character who by today's standards clearly has type 1 diabetes, but wants to switch to the "new oral pill" (called "orinase" in the book, though they are likely referring to diabinese pictured above).)
From 1923 into the 1980s, insulin was given once or twice per day, and not particularly titrated to blood sugar. This was probably just because we didn't have a great way to measure blood sugar in real time. Pre-1970s, there was no way to test blood sugar outside of a lab setting.
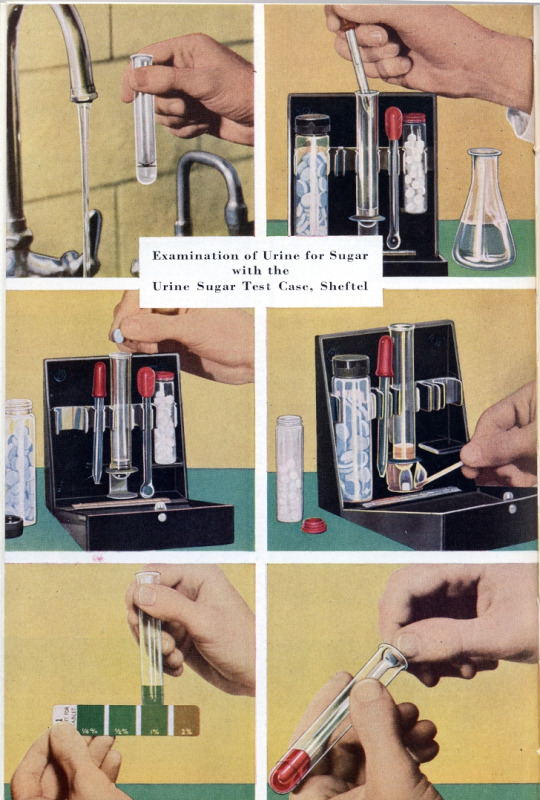
Urine testing was common starting in the 1940s, but was cumbersome as it required a flame for heating the urine. By the 1950s, a test had been developed that didn't require a flame, but was still not practical for home use. In the 1960s, paper strips were developed that changed color for different amounts of sugar in the urine. The problem with this was that the strips couldn't change color until there was sugar in the urine- a blood sugar level of over 200 by today's measurements. Low blood sugar readings were impossible at this time, and had to be treated based on symptoms.
In the 1970s, blood sugar could finally be measured by putting a drop of blood on a test strip, wiping it off, and matching the color of the test strip to a chart. While less cumbersome than urine tests, this was still something that would generally only be done at a doctor's office.

In 1983, the first home blood glucometer is developed. Finally, it was practical to take one's sugar multiple times per day, and it becomes possible to experiment with "sliding scale" insulin injections that keep tighter control of blood sugar. By the late 90s, continuous glucose monitors became available- though unlike today's CGMs that allow readings in real time on a smartphone or monitor, these had to be downloaded to a computer at regular intervals.
The 1980s were the first decade where insulin pumps become widely available. The very first pump was large and had to be carried in a backpack, but it represented a huge step forward in glucose control, as it more closely mimicked the function of a working pancreas than once-daily injections.
For the next 30 or so years you really had to work to qualify for an insulin pump, but recently it's been found that pumps greatly improve compliance with blood glucose control whether or not the person had good compliance before getting the pumps, and insurance has gotten better about covering them (though CGMs are still a pain to get insurance to cover).
The 1980s was also the decade that recombinant human insulin (insulin made by genetically modified bacteria) was first used. Up until that point the only insulins were pork and beef insulins, which some people had allergic reactions to. Recombinant insulin was closer to regular human insulin than beef or pork, and represented a big change in how insulin was made.
Today for people who take insulin to manage their diabetes, insulin is usually given as a single injection of a long-acting basal insulin, coupled with smaller doses of ultra-short-acting insulins with meals or snacks. This is the closest we've gotten to mimicking the way a pancreas would work in the wild, and keeps very tight control of blood sugar. This can be done by fingerstick blood sugar tests and individual injections of insulin, or it can be done with a CGM and pump- it just depends on the resources available to the person and their personal preference.
103 notes
·
View notes
Text

Nutrition Basics for a Healthy Lifestyle: What You Need to Know
Introduction:
Nutrition is the cornerstone of a healthy lifestyle. The food you eat not only fuels your body but also impacts your overall well-being. Understanding the basics of nutrition can help you make informed choices about what to eat, leading to improved health and vitality.
Balanced Diet: A balanced diet includes a variety of foods from all food groups: fruits, vegetables, grains, protein foods, and dairy (or dairy alternatives). Each group provides essential nutrients your body needs to function properly.
Fruits and Vegetables: Aim to fill half your plate with fruits and vegetables at each meal. These foods are rich in vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants, which support immune function and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Grains: Choose whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole wheat bread over refined grains. Whole grains are higher in fiber and nutrients, promoting better digestion and long-term health.
Protein Foods: Include a variety of protein sources in your diet, such as lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, beans, lentils, tofu, and nuts. Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues, as well as for producing hormones and enzymes.
Dairy (or Alternatives): Dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese provide calcium, vitamin D, and protein. If you're lactose intolerant or follow a vegan diet, opt for fortified plant-based alternatives like almond milk, soy yogurt, or tofu.
Portion Control: Paying attention to portion sizes is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight and preventing overeating. Use visual cues like your hand or everyday objects to estimate portion sizes:
A serving of meat or fish should be about the size of your palm.
A serving of grains or starchy foods should be about the size of your fist.
A serving of fruits or vegetables should be about the size of a tennis ball.
A serving of fats or oils should be about the size of your thumb.
Hydration: Staying hydrated is essential for overall health and well-being. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day, and limit sugary drinks like soda and fruit juices. Herbal teas and infused water can add variety to your hydration routine.
Limit Added Sugars and Processed Foods: Excess sugar consumption is linked to various health issues, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. Limit foods and beverages high in added sugars, such as candy, soda, pastries, and sugary cereals. Instead, satisfy your sweet tooth with naturally sweet foods like fruits.Additionally, minimize your intake of processed and ultra-processed foods, which often contain unhealthy fats, excessive sodium, and additives. Opt for whole, minimally processed foods whenever possible.
Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to hunger and fullness cues, and eat mindfully. Slow down and savor each bite, and stop eating when you feel satisfied, not stuffed. Eating when you're hungry and stopping when you're full can help maintain a healthy weight and prevent overeating.
Conclusion:
By following these nutrition basics, you can support your overall health and well-being, boost energy levels, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Remember, small changes can lead to big improvements in your health over time. Start with simple adjustments to your diet and build on them gradually for long-term success.
#nutrition#health#wellness#healthy living#health tips#nutrition basics#healthcare#fitness#diet#health and wellness#healthy lifestyle
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Watch the American Climate Leadership Awards 2024 now: https://youtu.be/bWiW4Rp8vF0?feature=shared
The American Climate Leadership Awards 2024 broadcast recording is now available on ecoAmerica's YouTube channel for viewers to be inspired by active climate leaders. Watch to find out which finalist received the $50,000 grand prize! Hosted by Vanessa Hauc and featuring Bill McKibben and Katharine Hayhoe!
#ACLA24#ACLA24Leaders#youtube#youtube video#climate leaders#climate solutions#climate action#climate and environment#climate#climate change#climate and health#climate blog#climate justice#climate news#weather and climate#environmental news#environment#environmental awareness#environment and health#environmental#environmental issues#environmental justice#environment protection#environmental health#Youtube
6K notes
·
View notes
Text

The Power of Fiber: Fueling Your Health and Fitness Journey
While often overlooked, fiber plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy diet and achieving your fitness goals. Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that cannot be digested by the body. Instead, it passes through the digestive system relatively intact, offering a range of health benefits. Incorporating fiber into your diet can:
1. Promote Healthy Digestion: Fiber adds bulk to your stool, aiding regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. It also supports a healthy gut microbiome, promoting optimal digestion and nutrient absorption.
2. Keep You Feeling Full: High-fiber foods take longer to digest, keeping you satiated for longer periods. This can help control appetite, reduce overeating, and support weight management goals.
3. Regulate Blood Sugar Levels: Soluble fiber, found in certain foods, can slow down the absorption of glucose, preventing blood sugar spikes. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those aiming to maintain stable energy levels throughout the day.
4. Support Heart Health: Studies show that a high-fiber diet can lower cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease and promoting overall cardiovascular health.
Fiber-Rich Foods:
1. Whole Grains: Opt for whole wheat bread, brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole wheat pasta. These provide more fiber and nutrients compared to their refined counterparts.
2. Legumes: Incorporate beans, lentils, chickpeas, and split peas into your recipes. They are not only rich in fiber but also offer plant-based protein.
3. Fruits: Enjoy the natural sweetness and fiber content of apples, pears, berries, oranges, and bananas. Remember to consume them with the skin whenever possible to maximize fiber intake.
4. Vegetables: Load up on fiber by including broccoli, Brussels sprouts, carrots, spinach, kale, and sweet potatoes in your meals. These veggies offer an array of vitamins and minerals too!
5. Nuts and Seeds: Snack on almonds, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and pumpkin seeds. They provide healthy fats, protein, and a good dose of fiber.
From promoting healthy digestion to managing weight and reducing the risk of chronic diseases, fiber plays a vital role in overall wellness. So, make sure to include fiber-rich foods in your meals and enjoy the numerous nutritional benefits they offer. Stay fit, stay healthy!
#fitblr#informational#food#health#fitness#healthy#healthy food#nutrition#healthyfood#healthy eating#healthy living#nutrients#fitblrs#running#fiber#solublefiber#insoluble fiber#my post#personal#personal fitblr#fitfam#fitspo#fitspiration#goal setting#lifestyle#life tips#nutritional#healthy diet#healthy habits
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Healthy tasty summer fare for diabetics
During the summer, it's crucial to concentrate on providing a person with diabetes with wholesome, fresh foods that support stable blood sugar levels. Here are some suggestions that the best diabetologist in Ahmedabad has given for tasty summertime fare that diabetics can enjoy:
Choose skinless chicken breasts, turkey burgers, or fish like salmon or trout when grilling lean foods. Without adding too much fat, grilling preserves the flavor.
Include a range of vibrant, non-starchy fresh veggies in your diet, such as broccoli, zucchini, bell peppers, cucumbers, tomatoes, and leafy greens. These have a lot of fiber and few carbs.
Salads: Use lush greens as a base for light salads, then top with lean proteins such as grilled chicken, prawns, or tofu. Add some vibrant vegetables, and serve with a simple vinaigrette.
Enjoy a luscious slice of watermelon, which has high water content and few calories. It might be hydrating and refreshing.
Berries contain a wealth of antioxidants and fiber, including strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries. When compared to other fruits, they have a comparatively low sugar content.
Greek yogurt: Choose unsweetened Greek yogurt, and for more flavor and texture, add fresh berries or a few almonds. Greek yogurt is a filling food option and is high in protein.
Prepare a variety of grilled veggies, such as eggplant, mushrooms, onions, and asparagus. These can be added to wraps or salads, served as a side dish, or both.
Herbal iced drinks like hibiscus, chamomile, or mint might help you stay hydrated. Avoid carbonated or sweetened drinks that are high in sugar.
Make your popsicles at home by using sugar-free or naturally sweetened ingredients like fruit purées or plain yogurt.
Choose healthy grains like quinoa, brown rice, or whole wheat bread in moderation if you're ingesting carbohydrates. Compared to refined grains, these have more fiber and minerals.
Keep in mind to watch portion sizes, take your total carbohydrate consumption into account, and engage with a trained dietitian or another healthcare professional to create a customized meal plan that meets your needs and blood sugar objectives.
For the best results, diet and concerns meet the doctors of Galaxy multispeciality hospital in Ahmedabad as they help in improving health, diet and make you live a long and healthy life.
#multispeciality hospital in ahmedabad#general physician ahmedabad#best diabetologist in ahmedabad#general physician in ahmedabad#ahemdabad hospital
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Important points to keep in mind for living a healthy life.
Remove Refined Food products from your diet.
- Refined food products like refined wheat flour, refined oil, chips, noodles, candies, and other junk food are very harmful for our health. They are linked to many chronic illnesses like inflammatory diseases, fatty liver, diabetes etc. So stop consuming them on a regular basis. Once in while is fine but not daily
Minimise the use of sugar in your diet.
- Sugar tastes very good and once we eat it our tongue wants more, but it is harmful for our bone health and causes diseases like diabetes, obesity, inflammation in our body. So stop consuming sugar and sugary products like candies, cakes, pastries etc. Use healthy sweeteners like jaggery and date powder instead. Stay tuned for Recipes of healthy cakes, sweets etc.
Include a variety of fruits in your diet.
- We should eat atleast 2-3 different types of seasonal fruits daily. You can choose any fruit. Fruits are a combination of taste and health. Fruits alkalis the body and all fruits have different benefits and we will sharing them soon.
Eat more veggies
- Veggies are more nutritious than fruits and should be consumed daily. You can choose any vegetable to include in your diet but consume different veggies the next day.
Meals on time
- Today many people are having late night dinners which is not good for our health, as food can't be digested properly and our sleep also get disturbed. We should eat all our meals on correct time. Dinner should be done around between 7-8 pm or atleast two hours before bed time.
Sleeping on time
- Today there our many people who sleep around 1 or 2 am or late than that but sleeping at a correct time is very important. Our body recover when we sleep and if we sleep to late then our body doesn't get time to recover. Sleeping late can also cause insomnia. So start sleeping before 10 pm.
Excercise
- Today, most of the people are busy in their work and don't excercise daily. Physical activity is very important for our body to be active. Less physical activity or less movement of body is linked to many chronic health conditions. We should have atleast 1-2 hours of excercise or any physical activity like playing any outdoor game such as badminton, cricket etc.
#health#health & fitness#healthy#healthy lifestyle#healthy living#healthy food#healthy habits#health is wealth
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Decoding the Indian cuisine
Indian cuisine is among the healthiest in the world thanks to the range of native foods, spices, and recipes that are found there. But recently, Indian cuisine has started to be regarded as unhealthy due to links to foods heavy in sugar and carbohydrates, which can raise cholesterol. However, traditional Indian cuisine is not only delicious but also packed with health advantages. Indian cuisine helps a number of bodily processes, including brain health, inflammation management, and immunity. The variety of Indian cuisine is its biggest draw.
Indian diet explained
Indian diet consists of a lot of grains
In India, numerous rice varieties are grown, as well as bajra, nachni, and jowar. It is regrettable that rice eating is discouraged for weight loss in the era of low-carb diets. Indian cuisine uses a variety of pulses as well. Since ancient times, dal rice and rajma rice have been common combinations in India. These mixtures make delicious protein meals that contain all the necessary amino acids.
Indian thalis
Each bowl in the traditional Indian thali is tiny in size. It consists of a few different kinds of dal, sabzi, some rice, roti, or both. A modest quantity of sweet food is also included in the thali. This thali provides a full meal by providing all necessary nutrients in the proper amounts. However, the portions of modern thalis offered in restaurants are substantially larger. The western mentality of supersizing is probably to blame for this increase in portion size in traditional Indian thalis.
Indian oils
In India, there are numerous cooking oils to choose from. Many healthy cooking oil variations are available in India, ranging from coconut oil and groundnut oil to mustard oil and peanut oil. However, the processing methods used in former periods were far healthier than those used now.
Indian salt
India was the original home of rock salt, pink salt, and black salt. But over time, we switched to a salt that was more refined, which is presumably why Indian food also started to become less healthy. Therefore, the ingredients are probably what changed Indian cuisine.
Indian curry
If prepared with the suitable ingredients and levels of oil, Indian curries are beneficial for immunity. The core cause of illnesses including diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disorders is inflammation, which the curries can reduce. The Indian curry, which is made with curry leaves, tomato, onion, black pepper, garlic, turmeric, and numerous other spices, offers many health advantages.
Wheat
Over the years, wheat in its various forms has come under a lot of scrutiny. There have been reports that wheat can cause unnecessary bloating or digestive problems among other inconveniences. However, we cannot all avoid bread and whole wheat as in our daily diet and must be consumed by many due to dietary restrictions.
Pickles and chutneys
Pickles, when made with fresh rock salt and fresh oil and ground with leafy greens and seeds make for one of the most nutritious foods you could hope to eat. In fact, the whole premise here is to declare that Indian food has always been about keeping your body and soul healthy with nourishing tasty recipes. Whether you were born in India or abroad, there is nothing more delicious than traditional Indian cuisine!
In conclusion, Indian food is high in fiber, which has a wealth of health advantages, including boosting weight loss, regulating blood sugar levels, preventing constipation, and lowering the risk of stroke or constipation.
Indian cuisine is sometimes misunderstood to be overly hot and fatty. However, when utilized properly, the colorful spices, fresh herbs, and endless combinations of flavors are a gateway to a healthy life.
Hridya foods offers healthy home style food at affordable prices. We offer varieties ranging from delicious biryanis to yummy yummy samosas, Try our healthy south indian breakfasts, mouth watering sandwiches, signature curries, snacks and appetizers, refreshing drinks and more.
Order online anytime and get the scrumptious food delivered to your office, home, parties, and events.
We accept bulk orders too!
Download the app now on google play store or App store or log on to www.hridyafoods.com
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Diet Chart for Diabetes
Introduction
Diabetes is a condition in which the sugar levels in the blood rises above the normal level. Sugar levels get increased in the blood due to decreased insulin production and unhealthy lifestyle habits. Increased level of sugar can damage the heart, eyes, liver, and other organs of the body. Ayurveda deemed Diabetes as Madhumeha which states “Sweet (honey like) urine”. Increased blood sugar levels cause excess secretion of sugar in the urine as well.
The signs and symptoms of diabetes include excess thirst, increased frequency to pass urine, digestion problems, inflammatory lesions, wasting of muscles, diarrhea, fever and necrosis.
Causes of Diabetes
Diabetes is a Kapha disorder developed due to imbalance of Kapha dosha. The imbalance can occur due to an unhealthy diet and lifestyle habits such as excess or lack of sleep, lack of physical activity, consumption of sweetened food items, unrestricted intake of yogurt, etc. Imbalanced Kapha Dosha decreases the digestive fire (Agni) which further slows down the body metabolism. This phenomenon increases the blood glucose levels in the body.
Diet Chart for Diabetes
Consumption of a balanced nutritious diet is essential to tackle diabetes by normalizing the blood sugar levels. In this segment, we have shared a generalized diet plan which if followed by diabetic patients might avoid a rise in the blood glucose levels.
Early morning- A glass or two of water + 1 teaspoon Fenugreek seeds/ Amla powder
OR
1 glass Copper pot water + 5 Mint leaves + 1 or 2 Tulsi leaves
Breakfast– Veg Oats/ Veg Idli/ Veg Vermicelli/ Veg Upma/ Veg Khichdi/ Besan pancake/ Missi Roti/ Chapatti with Vegetable or Dal/ Egg whites
Mid-morning– Sprouts/ Coconut water/ Salad/
Lunch– Chapatti with Vegetable + Dal + Salad/ Fish/ Chicken (Occasionally) (Add 1 tsp Fenugreek seed powder 30 minutes before lunch)
Evening– Roasted Chana/ Herbal tea/ Homemade soup
Dinner– Chapatti with Vegetable + Dal + Salad/ Nutri Nuggets
*Completely stop the usage of Sugar in your diet
Foods To Consume in Diabetes
Cereals: Oats, Whole grains, Whole Wheat Flour ratio: Wheat flour (1 kg) + Chana flour (250gm)
Fruits: Apricot, Peach, Loquat, Pear, Plum, Blackberry (Jamun), Melon, Papaya, Guava, Apple, Pomegranate, Orange and Amla
Vegetables: Curry leaf, Mint, Turnip, Coriander, Green pepper, Green chili, Ginger, Beetroot, Cucumber, Broccoli, Fenugreek leaves, Green beans, Peas, Pumpkin, Radish, Round gourd, Ridge gourd, Bottle gourd, Capsicum, Mushroom, Spinach, Beans, Cabbage, Cauliflower and Okra (Bhindi)
Pulses: All split lentils and legumes Frozen pulses only
Dairy products: Tofu Whole milk and Cream, Butter, Full fat Yogurt, Cheese and condensed milk
Spices: Cinnamon, Fennel, Pepper, Ginger, Turmeric, Coriander and Cumin
Drinks: Amla juice, Herbal tea, Bottle gourd juice, Bitter gourd juice, Coconut water, Neem juice and Giloy juice
Flesh foods: Chicken soup, Roasted or Grilled fish and Egg whites
Dry fruits and seeds: Sesame seeds, Flax seeds, Chia seeds, Pumpkin seeds, soaked walnuts and almonds
Oils: Olive oil, Canola oil, Soybean oil, Cow ghee (Only in small amounts) Note: 500 ml of cooking oil to be used per month
Other foods: Homemade products only All bakery items, artificial sweeteners, sweets, jams, fruit jellies, sauces, coconut bar, chocolate, cream soups, ice-cream, mayonnaise, pickles and fried foods
Foods To Avoid in Diabetes
Rice, Refined sugar, Whole refined flour and its products
Sapodilla, Dates, Grapes, Litchi, mango, banana
Potato, Taro root, Sweet potato, Eggplant,Yam, Jackfruit, Frozen and Canned vegetables,
Frozen pulses only
Whole milk and Cream, Butter, Full fat Yogurt, Cheese and condensed milk
Red chilies
Carbonated beverages, Cream based liqueurs, Alcohol, Whole milk drinks, Sugarcane juice, Canned and Packaged soup
Egg yolk, Rabbit, Turkey, Ham, Lamb, Pork, Lean beef, Crab, Lobster, Prawns, Red meat, Goose, Duck, Mutton and organ parts like Chest, Liver and Kidney
Peanuts, Raisins, Cashew and Pistachio
Hydrogenated oil, Cream, Butter and Trans-fat
All bakery items, artificial sweeteners, sweets, jams, fruit jellies, sauces, coconut bar, chocolate, cream soups, ice-cream, mayonnaise, pickles and fried foods
Doctor Tips
Go for a walk for at least 30-45 minutes.
Eat more salad to complete the intake of fiber.
Don’t skip meals, especially breakfast.
Consume seasonal fruits and vegetables.
Keep yourself hydrated by drinking 8-10 glasses of water daily.
Use herbal tea prepared with Cumin, Coriander and Fennel.
Eat 5 soaked almonds and 1 soaked walnut daily.
Reduce stress levels by doing meditation daily.
Find a Diet Consultation Online: Get Personalized diet chart for diabetes
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring the Benefits of Multigrain Atta Ingredients for Holistic Health
In today’s health-conscious world, the choice of flour in our diets is more important than ever. With a rising awareness of the benefits of whole grains, multigrain atta ingredients have become a key focus for those seeking to improve their nutritional intake. Multigrain atta, made from a blend of various grains, seeds, and sometimes legumes, offers a nutritious alternative to traditional wheat flour. This blog delves into the diverse ingredients typically used in multigrain atta, their health benefits, and how incorporating them into your diet can lead to a healthier lifestyle.

Understanding Multigrain Atta
What is Multigrain Atta?
Multigrain atta is a flour blend composed of more than one grain type, often enriched with seeds and legumes to enhance its nutritional profile. Unlike refined flours, multigrain atta retains the bran and germ of the grains, ensuring that the fiber, vitamins, and minerals remain intact. This variety of ingredients not only boosts the health properties of the flour but also adds complexity and flavor to the bread, rotis, and other dishes prepared with it.
Common Ingredients in Multigrain Atta
A typical multigrain atta may include some or all of the following grains and seeds:
- Whole Wheat: Forms the base of most multigrain atta blends, providing structure and elasticity.
- Oats: Rich in beta-glucan, a fiber that helps reduce cholesterol and blood sugar levels.
- Barley: Offers a wealth of fiber, particularly beta-glucan, and is good for digestive health.
- Ragi (Finger Millet): High in calcium and potassium, beneficial for bone health.
- Bajra (Pearl Millet): Provides essential amino acids and is high in iron.
- Jowar (Sorghum): Known for its protein quality and antioxidant properties.
- Flaxseeds: Add omega-3 fatty acids and fiber, enhancing heart health.
- Sunflower Seeds: Packed with vitamin E, magnesium, and protein.
Health Benefits of Multigrain Atta Ingredients
Enhanced Nutritional Content
Each ingredient in multigrain atta brings its own set of nutrients to the table, creating a well-rounded profile that benefits overall health. The inclusion of multiple grains ensures a higher intake of fiber, which aids in digestion and sustained energy release. This fiber-rich composition also helps in managing weight by keeping you fuller for longer.
Lower Risk of Chronic Diseases
The diverse ingredients in multigrain atta contribute to a lower risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers. This is due to their collective ability to improve cholesterol levels, reduce blood pressure, and prevent high blood sugar spikes.
Gluten-Free Options for Sensitivity and Celiac Disease
For those with gluten sensitivities or celiac disease, multigrain atta can be tailored to exclude gluten-containing grains like wheat and barley. Ingredients like buckwheat, quinoa, and amaranth can be used instead to provide a gluten-free flour blend that is still rich in nutrients and fiber.
Incorporating Multigrain Atta in Your Diet
Cooking and Baking with Multigrain Atta
Multigrain atta can be used in various recipes, from traditional Indian flatbreads like chapatis and parathas to modern baking recipes for bread, muffins, and pancakes. It adds a nutty flavor and dense texture to baked goods, making them not only tastier but also more filling.
Recipes to Try
- Multigrain Rotis: Combine multigrain atta with water and a pinch of salt to make dough. Roll out into thin circles and cook on a hot griddle for a nutritious alternative to regular rotis.
- Healthy Multigrain Pizza Base: Use multigrain atta as the base for a homemade pizza dough, adding herbs and olive oil for flavor.
- Multigrain Pancakes: Mix multigrain atta with eggs, milk, and a touch of honey for a hearty breakfast option.
Conclusion: Embracing Multigrain Atta for a Healthier Future
Multigrain atta ingredient offers a fantastic opportunity to enhance your dietary fiber intake, diversify your nutrient sources, and enjoy a richer palette of flavors and textures in your meals. As we become more aware of the impact of diet on health, switching to multigrain atta is a simple yet effective step toward a healthier lifestyle.
FAQs About Multigrain Atta Ingredients
Q: Is multigrain atta good for weight loss?**
A: Yes, the high fiber content in multigrain atta can help promote weight loss by making you feel fuller for longer, thus reducing overall calorie intake.
Q: Can multigrain atta be used in the same proportions as regular wheat flour?
A: Yes, multigrain atta can generally be used in the same proportions as wheat flour in most recipes, although you might need to adjust the moisture content slightly due to the higher absorption rate of some grains.
Q: Are there any side effects of switching to multigrain atta?
A: Some people might experience increased bloating or gas when they first increase their fiber intake. It’s recommended to increase fiber gradually to allow your digestive system to adjust.
Q: How should multigrain atta be stored?
A: Store multigrain atta in an airtight container in a cool, dry place to maintain its freshness. You can also store it in the refrigerator to extend its shelf life.
By integrating multigrain atta into your diet, you not only contribute to your health but also enjoy a variety of meals enriched with the goodness of multiple grains and seeds. Multigrain atta is not just food; it's a lifestyle choice that fosters wellness and satisfaction.
0 notes
Text
Nutrition Tips for a Healthier Life
Nutrition Tips for a Healthier Life
https://ift.tt/8SkaChu
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes is healthy and balanced. It also includes lower amounts of refined grains, processed meats, sugary drinks, and red and processed food.
A plant-based diet that is full of minimally processed or whole food products is considered to be healthy. It can include various dietary patterns rich in fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, and nuts. These diets can help lower greenhouse gas emissions and improve the health of our planet.
Here are a few nutrition tips to get you on the path to wellness.
Fruits & Veggies
According to NHS, eating at least five portions of fruit and vegetables daily is essential. These can be either fresh, frozen, or canned. For instance, you can chop a banana and add it to your morning cereal instead of eating it alone at breakfast.
One serving of fruit or vegetable is 80g, while a portion of dried fruit is 30g. Although a 150ml glass of fruit juice or vegetable juice can be counted as one portion, limit the amount of this drink to no more than one glass a day due to how these can damage your teeth.
Going for Whole Grains
Whole grains, which include whole wheat crackers, whole grain bread, and brown or wild rice, are great for keeping you full and healthy. They are also filled with protein, fiber, and vitamins B and C. If you’re looking for a more refined or processed option, choose whole grains instead of pasta and white bread.
Whole Foods
To improve your diet, choose food that is natural and unprocessed. You should add more vegetables and fruits to your diet and replace processed food with better options.
Don’t Forget Your Protein
Having a protein-rich diet can help maintain a healthy blood sugar level. Some studies suggest that high-protein diets can help lower the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Nuts and Seeds
Although some people avoid nuts due to their high fat content, they are still nutritious and can help lower your risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes. They are also filled with fiber, protein, and other nutrients.
Reduce Sugar
High-calorie drinks and food high in sugar can increase your risk of obesity and tooth decay. These can also contribute to weight gain and cause dental decay if eaten between meals.
Unsweetened fruit juices, syrups, and honey are naturally added to food and drinks, and these are referred to as free sugars, which are the kind that you should be reducing. Many packaged beverages and food products have high amounts of these.
The post Nutrition Tips for a Healthier Life first appeared on Adam Gant | Athletics.
via Adam Gant | Athletics https://adamgant.net
April 19, 2024 at 12:14PM
0 notes
Text
This recipe is healthy for several reasons:
1. Mixed Berries: Berries like strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which are beneficial for overall health. They also provide fibre, which aids digestion and helps you feel fuller for longer periods.
2. Rolled Oats: Rolled oats are an excellent source of complex carbohydrates and fibre, providing sustained energy and promoting digestive health. They also contain various vitamins and minerals like manganese, phosphorus, and magnesium.
3. Whole Wheat Flour: Using whole wheat flour instead of refined white flour adds extra fibre, vitamins, and minerals to the recipe. Whole grains like whole wheat help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
4. Honey or Maple Syrup: While these sweeteners should still be used in moderation, they are natural alternatives to refined sugars and provide some beneficial nutrients and antioxidants. However, it’s important to be mindful of portion sizes to avoid excessive sugar intake.
5. Melted Coconut Oil or Butter: While both coconut oil and butter contain saturated fats, using them in moderation can still be part of a healthy diet. Coconut oil contains medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), which are believed to have some health benefits, though more research is needed. Butter, especially if it’s from grass-fed cows, can provide essential fatty acids and fat-soluble vitamins.
6. Vanilla Extract and Salt: These ingredients are used in small amounts to enhance flavour. Vanilla extract adds sweetness without additional sugar, and a pinch of salt helps balance the flavours in the recipe.
Overall, this recipe provides a balance of carbohydrates, healthy fats, and antioxidants, making it a nutritious option for a meal or snack.
0 notes
Text

In the quest for balanced nutrition and better health, understanding how different foods impact blood sugar levels is crucial, especially for individuals with diabetes or those trying to prevent its onset. The glycemic index (GI) is a valuable tool in this endeavor, measuring how much specific foods increase blood sugar levels. Foods with a low GI are digested and absorbed more slowly, leading to a gradual rise in blood sugar and insulin levels. This article explores various food groups that have a minimal impact on blood sugar, offering a pathway to a healthier lifestyle.
1. Non-Starchy Vegetables
Non-starchy vegetables are the cornerstone of a diet that minimally impacts blood sugar levels. These vegetables are low in carbohydrates and calories but high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Examples include:
Leafy greens (spinach, kale, and lettuce)
Cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts)
Other vegetables like bell peppers, zucchini, and asparagus
Incorporating a variety of these vegetables into your diet can help keep your blood sugar levels stable.
2. Whole Grains
Whole grains are an excellent source of fiber, which slows the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream. Unlike their refined counterparts, whole grains retain all parts of the grain, including the bran, germ, and endosperm, providing more nutrients and fiber. Examples of whole grains include:
Quinoa
Barley
Oats
Brown rice
Whole wheat
3. Legumes
Legumes, which include beans, lentils, and chickpeas, are another group of foods that have a minimal impact on blood sugar. They are high in fiber and protein, both of which help to slow down the digestion process and prevent spikes in blood sugar levels. Furthermore, legumes are a great plant-based protein source, making them an excellent choice for vegetarians and vegans.
4. Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds are low in carbohydrates and high in healthy fats, fiber, and protein, making them an ideal snack for blood sugar control. They can help you feel full and satisfied without causing a significant rise in blood sugar. Examples include:
Almonds
Walnuts
Flaxseeds
Chia seeds
However, since nuts and seeds are also high in calories, it's important to consume them in moderation.
5. Fruits with Lower Glycemic Index
While fruits are a healthy part of any diet, some can cause more significant increases in blood sugar levels than others. Choosing fruits with a lower glycemic index can help manage blood sugar levels. These include:
Berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries)
Cherries
Apples
Pears
Pairing fruits with a protein or healthy fat source can also help minimize blood sugar spikes.
6. Dairy or Dairy Alternatives
Low-fat or fat-free dairy products, and unsweetened dairy alternatives, can also have a minimal impact on blood sugar. These options provide calcium and protein without significantly raising blood sugar levels. Options include:
Greek yogurt
Cottage cheese
Almond milk
Soy milk
Conclusion
Adopting a diet that focuses on foods with a minimal impact on blood sugar levels can lead to better overall health, particularly for those managing diabetes or at risk of developing it. By incorporating a variety of non-starchy vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, lower GI fruits, and healthy dairy alternatives, individuals can enjoy a rich, diverse diet that supports stable blood sugar levels. As with any dietary changes, it's beneficial to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to tailor dietary choices to your specific health needs and goals.
#usascriphelpersofficial#diabetes care#diabetes management#diabetes mellitus#diabetes treatment#diabetes symptoms#weight loss diet#diabetic#morning blood sugar#blood sugar monitoring#blood sugar control#blood sugar regulation#blood sugar#type 2 diabetes#health and wellness
0 notes
Text
Power Up with Fiber: How It Can Help Prevent Type 2 Diabetes
🌟 Power Up with Fiber: How It Can Help Prevent Type 2 Diabetes 🌟
Did you know that a simple dietary change can significantly impact your risk of developing type 2 diabetes? 🤔 Increasing your fiber intake is a powerful strategy to ward off this condition. Let's delve into the science behind fiber and explore how it can keep your blood sugar in check. 🍎🥦
🔍 Understanding Fiber's Benefits
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that our bodies can't fully digest. There are two main types:
Soluble fiber: Dissolves in water, forming a gel-like substance in your gut. This slows down digestion, leading to steadier blood sugar levels.
Insoluble fiber: Doesn't dissolve in water and adds bulk to your stool, promoting regularity.
💪 How Fiber Fights Type 2 Diabetes
Fiber's magic lies in its ability to influence blood sugar control in several ways:
Slows Sugar Absorption: Soluble fiber forms a gel that traps carbohydrates, delaying their entry into the bloodstream. This prevents blood sugar spikes often seen after refined carb-rich meals.
Improves Insulin Sensitivity: Fiber may enhance your body's ability to use insulin, a hormone crucial for regulating blood sugar.
Supports a Healthy Weight: Feeling fuller for longer is a bonus of fiber. It can help with weight management, a crucial factor in preventing type 2 diabetes.
🥗 Fiber-Rich Foods for a Healthy Plate
Here's how to add a fiber fiesta to your diet:
Fruits and Vegetables: Pack your plate with colorful options like berries, apples, leafy greens, and broccoli.
Whole Grains: Opt for brown rice, quinoa, whole-wheat bread, and oats over refined grains.
Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are powerhouses of fiber and protein.
Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, flaxseeds, and chia seeds are tasty ways to boost your fiber intake.
🚀 Making Fiber a Part of Your Lifestyle
Start small and gradually increase your fiber intake to avoid digestive discomfort. Here are some tips:
Snack on fruits and nuts instead of sugary treats.
Swap refined grains for whole grains in your meals.
Add beans or lentils to soups, salads, and stews.
Bulk up smoothies with fruits, vegetables, and chia seeds.
🍽️ The Final Bite
Incorporating a high-fiber diet is a delicious and effective way to reduce your risk of type 2 diabetes. By making smart food choices and including a variety of fiber-rich options, you can take control of your health and enjoy a balanced, diabetes-preventive lifestyle. 🥗
Remember: Consult a doctor or registered dietitian for personalized dietary advice to manage your blood sugar and overall health. 💬 What's your favorite fiber-rich food? Share in the comments below! 👇
#diabetic#type 2 diabetes#healthy recipes#healthyhabits#diabetesblog#healthguide#diabetes#health insurance#health is wealth#healthybaking
0 notes
Text
Decoding Diabetes: Understanding the Sweet Truth
In today's fast-paced world, diabetes has become a common household term, affecting millions of individuals globally. From diet plans to medical terminologies, discussions around this health condition have become increasingly prevalent. But what exactly is Sugar Defender FAQ , and why is it crucial to understand its impact on our bodies? Let's delve into the intricacies of this prevalent health concern to demystify its nature and shed light on the factors that contribute to its development.
At its core, diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood sugar levels due to the body's inability to produce or effectively utilize insulin. This crucial hormone, produced by the pancreas, helps regulate blood sugar levels and facilitates the absorption of glucose into cells for energy production. When the delicate balance of insulin production and utilization is disrupted, it can lead to various health complications. Understanding the mechanisms behind diabetes is essential for navigating its challenges and making informed lifestyle choices that can positively impact our overall well-being.
Sugar Levels Explained
When we talk about sugar levels in the context of diabetes, we are referring to the amount of glucose present in the blood. Glucose is a type of sugar that serves as the body's main source of energy. In individuals without diabetes, the body effectively regulates blood sugar levels, ensuring they remain within a healthy range.
In people with diabetes, this regulation system is impaired, leading to fluctuations in blood sugar levels. For those with Type 1 diabetes, the body does not produce insulin, a hormone crucial for glucose absorption into cells. In Type 2 diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin or becomes resistant to its effects, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels. Monitoring and managing these sugar levels are essential aspects of diabetes care.
Nutrition Tips
When managing diabetes, it's crucial to focus on a balanced diet. Aim to include a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables in your meals, as they are rich in essential vitamins and minerals that can help regulate blood sugar levels.
In addition to fruits and vegetables, incorporating lean proteins such as poultry, fish, and tofu can contribute to better blood sugar control. These sources of protein can also help you feel full longer, reducing the temptation to snack on unhealthy foods.
Lastly, remember to watch your carbohydrate intake. Opt for whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat bread over refined grains like white rice and white bread. Whole grains provide more fiber, which can slow down the digestion of carbohydrates and prevent spikes in blood sugar levels.
Managing Blood Glucose
When it comes to managing blood glucose levels, it's crucial to keep a close eye on what you eat. Opting for a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help regulate your blood sugar levels more effectively.
Regular physical activity is also key in controlling blood glucose levels. Aim to engage in a combination of aerobic exercises like walking or cycling, as well as strength training exercises, to improve insulin sensitivity and promote better blood sugar management.

In addition to diet and exercise, monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly is essential. Testing your blood sugar as recommended by your healthcare provider will give you valuable insights into how your body responds to different foods and activities, allowing you to make informed decisions to better manage your diabetes.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Enhancing Your Grocery Shopping Experience: Tips for Smart, Efficient, and Budget-Friendly Trips
Introduction:
Grocery shopping is a routine task for most people, but it's also an opportunity to make smart choices that benefit your health, budget, and the environment. Whether you're a seasoned shopper or just starting to take control of your food purchases, mastering the art of grocery shopping can lead to significant savings and satisfaction. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore strategies and tips to help you navigate the aisles of your local grocery shop with confidence and efficiency.
Understanding Your Needs:
Before heading to the grocery store, it's essential to assess your needs and create a shopping list. Take inventory of your pantry, fridge, and freezer to identify what items you already have and what you need to replenish. Consider planning meals for the week ahead to ensure you purchase the necessary ingredients.
Creating a detailed shopping list not only saves time but also helps prevent impulse purchases and reduces the risk of forgetting essential items. Organize your list by categories such as produce, dairy, proteins, grains, and snacks to streamline your shopping experience.
Navigating the Aisles: Once inside the grocery shop, it's easy to become overwhelmed by the array of choices available. However, with a well-planned list in hand, you can navigate the aisles efficiently and stay focused on your priorities.
Start with the perimeter of the store, where you'll typically find fresh produce, meats, dairy products, and bread. These whole foods are often the cornerstone of a healthy diet and should form the basis of your shopping cart. Opt for a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables to ensure you're getting a diverse range of nutrients.
When selecting packaged goods from the inner aisles, be mindful of reading labels and choosing products with minimal additives and preservatives. Compare prices and consider opting for store brands or generic equivalents to save money without sacrificing quality.
Making Healthy Choices:
Incorporating nutritious foods into your grocery haul is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. Look for whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread to provide sustained energy and dietary fiber. Choose lean proteins like chicken, fish, tofu, and legumes to support muscle growth and repair.
Limiting processed foods high in sugar, sodium, and unhealthy fats is crucial for preventing chronic diseases such as obesity, heart disease, and diabetes. Opt for natural sweeteners like honey or maple syrup instead of refined sugars and select unsalted nuts and seeds for a nutritious snack option.
Additionally, don't forget to hydrate by stocking up on water and choosing beverages like herbal tea or sparkling water over sugary sodas and fruit juices.
Stretching Your Dollar: Grocery shopping on a budget doesn't have to mean sacrificing quality or nutrition. With a few savvy strategies, you can stretch your dollar and make the most of your shopping trip.
First, take advantage of sales, discounts, and coupons to save money on staple items and household essentials. Many grocery stores offer loyalty programs or digital coupons that can lead to significant savings over time.
Consider buying in bulk for items you use frequently, such as grains, beans, and frozen vegetables. Purchasing larger quantities often results in a lower cost per unit and reduces the need for frequent trips to the store.
Another way to save money is by planning meals around seasonal produce, which tends to be more abundant and affordable. Visit local farmers' markets or participate in community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs to access fresh, locally grown fruits and vegetables at competitive prices.
Reducing Food Waste: One often overlooked aspect of grocery shopping is minimizing food waste. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, approximately one-third of all food produced globally is lost or wasted each year.
To combat food waste, shop with a mindset of buying only what you need and will use before it spoils. Choose perishable items with a longer shelf life, such as root vegetables, cabbage, and citrus fruits, and plan meals that incorporate leftovers to prevent them from going to waste.
Properly storing perishable items in the fridge or freezer can also extend their freshness and reduce spoilage. Invest in reusable storage containers and utilize meal-prep techniques to portion out servings and streamline mealtime during busy weekdays.
Embracing Sustainable Practices:
In addition to reducing food waste, adopting sustainable shopping habits can have a positive impact on the environment. Bring reusable bags to the grocery store to reduce plastic waste and opt for products with minimal packaging whenever possible.
Choose items with eco-friendly certifications such as USDA Organic, Fair Trade, or Rainforest Alliance to support ethical and environmentally responsible farming practices. Look for locally sourced products to reduce the carbon footprint associated with transportation and support your community's economy.
Consider purchasing items in bulk or investing in refillable containers for pantry staples like grains, spices, and cooking oils to minimize packaging waste. And don't forget to recycle or compost any packaging or food scraps to further reduce your environmental impact.
Conclusion:
Grocery shopping is more than just a chore—it's an opportunity to make informed choices that benefit your health, budget, and the planet. By understanding your needs, navigating the aisles strategically, making healthy choices, stretching your dollar, reducing food waste, and embracing sustainable practices, you can transform your grocery shopping experience into a fulfilling and rewarding endeavor. With these tips in mind, you'll be well-equipped to tackle your next trip to the grocery shop with confidence and efficiency.
If you are looking for a grocery shop near you please visit our site https://justsearchme.com/
0 notes
Text
Is organic atta good for health?
When we talk about organic atta the first thing that comes to your mind is our health. Organic atta, or whole wheat flour, offers several health benefits compared to refined flour. Here are five ways organic atta can be helpful for the body:
Let's discuss how the best organic atta in India is beneficial for your health:
1. Nutrient Rich: Organic atta retains more nutrients compared to refined flour because it is minimally processed. It contains essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, including B-vitamins, iron, magnesium, and zinc, which are vital for overall health.
2. Good amount of Fiber: Whole wheat flour is high in dietary fiber, which aids in digestion and helps prevent constipation. Fiber also promotes satiety, keeping you feeling fuller for longer periods, which can aid in weight management by reducing overeating.
3. Reduces Risk of Chronic Diseases: Consumption of organic atta has been linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. The fiber, antioxidants, and other nutrients found in whole wheat flour contribute to its protective effects against these diseases.
4. Stabilizes Blood Sugar Levels: Organic atta has a lower glycemic index compared to refined flour, meaning it causes a slower and steadier increase in blood sugar levels after consumption. This can help prevent spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels, making it an ideal choice for individuals with diabetes or those aiming to manage their blood sugar levels.
5. **Supports Weight Management**: Due to its high fiber content and lower glycemic index, organic atta can be beneficial for weight management. It helps regulate appetite and promotes a feeling of fullness, which can prevent overeating and support healthy weight loss or maintenance when consumed as part of a balanced diet.
Incorporating organic atta into your diet in place of refined flour can contribute to overall better health and well-being. However, it's essential to remember that moderation and balance are key, and organic atta should be consumed as part of a varied and nutritious diet. Visit Azaya Organics website today to order online.
0 notes
Text
Find Your Nutrient-Rich Millets Online for Optimal Health at The Desi Food

Are you searching for nutrient-rich millets to boost your health and well-being? Look no further! At The Desi Food, we offer a diverse range of millets that are not only delicious but also packed with essential nutrients. Shop online and discover the perfect millets for your dietary needs.
Explore a Variety of Millets Options
Variety of Millets options available online at The Desi Food. In this category, you can find a wide range of Millets options. From Siridhanyalu Millets Hamper to Barnyard Millet Rice, and from Little Millet to Proso Millet, we have everything you need to incorporate these nutritious grains into your diet. Whether you're looking for gluten-free alternatives or seeking to enhance your overall health, our millets selection has something for everyone.
Elevate Your Health with Siridhanyalu Millets Hamper
Indulge in the goodness of our Siridhanyalu Millets Hamper, featuring a unique combination of Barnyard, Browntop, Kodo, Little, and Foxtail millets. Rich in fiber content, these millets are perfect for maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet. Say goodbye to refined grains and hello to wholesome goodness with our Siridhanyalu Millets Hamper. Shop now and take the first step towards a healthier lifestyle.
Choose Safe Harvest Barnyard Millet Rice for Quality Assurance
Opt for Safe Harvest Barnyard Millet Rice for a pesticide-free and nutritious alternative to traditional rice. Grown without synthetic pesticides and GMO seeds, our millet rice undergoes rigorous testing for 149 pesticide residues to ensure maximum safety and quality. Parboiled and unpolished, it retains essential nutrients, making it highly digestible and gluten-free. With lower glucose levels than rice, it's an ideal choice for managing diabetes while providing ample proteins, calcium, and essential minerals. Elevate your culinary creations with Safe Harvest Barnyard Millet Rice and experience the goodness of nature.
Embrace the Goodness of Manna Little Millet
Discover the nutritional benefits of Manna Little Millet, packed with phytochemicals and potent antioxidants. Surpassing white rice and wheat in minerals, dietary fiber, and iron, this millet offers a wholesome alternative for your daily meals. With lower carbohydrates and higher B1 vitamins, it's the perfect choice for individuals looking to adopt a healthier lifestyle. Make the switch to Manna Little Millet and enjoy its protective effects against childhood asthma while nourishing your body with essential nutrients.
Experience PRISTINE Nutrillet Proso Millet for Versatility
Try PRISTINE Nutrillet Proso Millet for a gluten-free and versatile addition to your pantry. With a hint of nutty flavor, this millet is rich in minerals, dietary fiber, polyphenols, vitamins, and proteins, making it an ideal choice for individuals seeking a nutritious alternative to rice. Whether used as a rice substitute in dal or curries or ground into flour for flatbreads, PRISTINE Nutrillet Proso Millet offers endless culinary possibilities. Elevate your meals with this calcium-packed, gluten-free choice and experience the goodness of nature.
Enjoy the Benefits of Earthon Organic Finger Millet
Indulge in the health benefits of Earthon Organic Finger Millet, commonly known as Ragi. Abundant in iron, calcium, and thiamine, Ragi is a staple in South Indian kitchens, revered for its numerous health benefits. From controlling diabetes to aiding weight loss and cooling the body, this gluten-free whole grain is a versatile addition to any diet. Elevate your meals with the wholesome goodness of Earthon Organic Finger Millet and nourish your body with essential nutrients.
Discover the wide variety of millets options available online at The Desi Food and take the first step towards a healthier lifestyle. Place your order today and experience the nutritional power of millets delivered right to your doorstep.
1 note
·
View note