#Osteomyelitis
Text
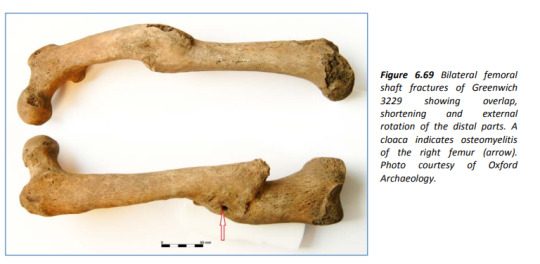
Lets go obscure: two broken legs from a poor bastard who was in the British Navy in the 17 or 1800s. The arrow points to a drainage hole from bone infection but had healed so they survived this. They were recovered from Greenwich Hospital which was a home for retired sailors.
Source: Boston (2014) The Value of Osteology in Historical Context: a comparison of osteological and historical evidence for trauma in the late 18th - early 19th century British Royal Navy.
It's freely available and a great read
#cw bones#osteology#bones#naval history#osteomyelitis#a photo you can feel#skeleton#archeaology of disability#archeaology
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
#50: Osteomyelitis
You dig into my flesh,
Clawing,
Tearing
Until the lines between us blend
Down into my muscle fibers
The bones encased within
Like a parasite-
you have found your way into my bones
Feeding off of me and wrecking my insides
An infection, that leaves a lasting ache
Its Osteomyelitis,
and its too late to recover.
Its spread to my joints, to my skin.
and there is no places to sever
#poetry#poets on tumblr#original poem#writers and poets#prose#prose poetry#medically accurate#osteomyelitis#metaphors!#tw: mild gore#infections#spilled prose#spilled emotions#spilled ink
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
I’ve got another bone infection. Once again, I get to spend the holidays doing IV antibiotics. Joy.
Anyway, don’t expect too much from me
2 notes
·
View notes
Note
Saw your post about Salem and it got me wondering if the oral mass in conjunction with the stomatitis is something that would be seen in other species as well?
One of my rescue bearded dragons came to me with osteomyelitis in his jaw (now treated) and has a small oral mass that was shown to be inflammatory and I do suspect the mass is linked to his osteo (secondary symptom?)
I've also seen it in dogs secondary to severe dental disease, but I don't know enough about bearded dragons to say one way or another. I recommend getting any growths evaluated by a vet as soon as possible. Even if benign oral growths do occur in that species, cancer is also always a possibility, and the sooner it's diagnosed and treatment (even if it's just palliative) started the better the outcome.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
In general, the diagnosis of osteomyelitis is established via culture obtained from biopsy of the involved bone. A diagnosis of osteomyelitis may be inferred in the following circumstances (see 'Overview' above):
•Clinical and radiographic findings typical of osteomyelitis and positive blood cultures with a likely pathogen (such as Staphylococcus aureus); in such cases, bone biopsy is not required but may be useful, particularly if subsequent therapeutic debridement is needed.
•Bone histopathology consistent with osteomyelitis in the absence of positive culture data (particularly in the setting of recent antibiotic administration).
•Suggestive clinical and typical radiographic findings and persistently elevated inflammatory markers, in circumstances with no positive culture data and a biopsy is not feasible.
●Patients with suspected osteomyelitis should undergo laboratory evaluation (including erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, white blood cell count), blood cultures, and radiographic imaging. In patients with ≥2 weeks of symptoms, conventional radiography is a reasonable initial imaging modality. In patients with <2 weeks of symptoms, an advanced imaging modality (magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, or nuclear imaging) should be pursued. Advanced imaging is also warranted for patients with diabetes, localized symptoms, and/or abnormal laboratory results whose plain radiographs are normal or suggestive of osteomyelitis without characteristic features. Osteomyelitis is unlikely in the absence of radiographic evidence on advanced imaging. (See 'Clinical approach' above.)
●Findings of osteomyelitis on radiographic imaging should prompt bone biopsy for culture and histology to confirm the diagnosis and to guide antimicrobial therapy, unless blood cultures are positive for a likely pathogen (such as S. aureus, a gram-negative enteric rod, or Pseudomonas aeruginosa). (See 'Clinical approach' above.)
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Condensing Osteitis: Symptoms, Diagnosis and Management
Focal sclerosing Osteomyelitis, also known as Condensing Osteitis, is an infection of the tissues around the root, or a periapical inflammatory disease. This is not a usual situation.
Here's some vital information to help you understand the fundamental features, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of this unusual tooth issue.

What is it?
The tooth consists of two parts: the crown and the root. The crown is the visible component of the tooth inside the mouth, whereas the root is lodged inside the jaw bone. The periapical area refers to the area surrounding the apex or root tips. Condensing osteitis is an inflammatory illness affecting the periapical area. It is typically regarded as an inflammatory trigger.
Symptoms
It is usually symptomless with only intermittent episodes of discomfort, therefore your endodontist can identify it via an x-ray.
Condensing osteitis is most common in young people, however it can also occur in other age groups.
This disorder is more common in the molar region, but it can also occur in other tooth regions.
Diagnosis and Management
When condensing osteitis is detected, the first and most important action is to consult an endodontist. The care begins with a thorough evaluation of the affected tooth.
The endodontist will examine the pulp tissue of the tooth for vitality. The pulp tissue is the tooth's internal soft tissue, which contains nerves and blood vessels and helps to keep the tooth alive by providing sustenance.
This can be accomplished using a variety of pulp vitality testing procedures. The choice of test is determined on the patient's major complaint.
If the pulp contains necrosis or dead tissue, or if the inflammation is severe, the tooth must be extracted as it cannot be saved.
Prognosis
To your surprise, if the bone produced as a result of infection is not producing symptoms or discomfort, there is no need for treatment and the tooth can be left as is.
It has been discovered that such teeth remain normal and can work normally for years without any problems.
However, remember that a periodic checkup is required so that your endodontist can check for changes using x-rays. If necessary, the treatment can be performed. When the problematic tooth is taken, the socket left behind is the area of condensing osteitis of the jaw, and it can be left that way. It is painless and referred to as osteosclerosis of the bone scar.
For more information read the full blog here : https://www.orisdentalcenter.ae/blog/condensing-osteitis-symptoms-diagnosis-and-management/
#condensing osteitis#sclerosing osteitis#garre osteomyelitis#garre's sclerosing osteomyelitis#Osteomyelitis#osteomyelitis disease#osteomyelitis symptoms#Periodontitis#tooth psin#tooth infection#dental
0 notes
Text
A 12 Day- Old Female Infant Diagnosed with Pelvic Osteomyelitis in the Pediatric Emergency Department by Mehmet Ali Oktay in Journal of Clinical and Medical Images, Case Reports

Abstract
Osteomyelitis (OM) is a bacterial disease that is very rare in newborns and has devastating consequences. Neonatal OM is seen in 1-3 in 1000 babies. We presented a 12-day-old female baby who was brought to the Pediatric Emergency Department (PED). Because she could not move her leg. She did not have fever and septic appearance and had a history of hospitalization in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit; acute phase reactants were high and radiological imaging performed gradually was consistent with OM. Our patient is the youngest patient who was diagnosed with pelvic OM upon admission to the PED. Earlydiagnosis and treatment prevent complications and sequels.
Keywords: Osteomyelitis; newborn; pediatric emergency
Introduction
Osteomyelitis often occurs secondary to the hematogenous spread of microorganisms into the blood-rich metaphysis of the developing bone. When left untreated, it leads to complications such as joint destruction and decreased range of motion [1]. Osteomyelitis (OM) of the hip is rare in newborns. Signs and symptoms are quite different compared to older children. This may cause difficulties/delays in diagnosis and permanent disability [2]. Successful management of OM in the neonatal period has been associated with rapid correct diagnosis and adequate correct treatment [2, 3]. The incidence of OM in the pediatric age group is 1/5000 cases. About 50% of pediatric OM cases are under the age of five. The incidence of neonatal OM is 1-3/1000 cases [3]. Although there are studies on patients diagnosed with osteomyelitis while staying in neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) [1, 4, 5], cases diagnosed upon PED (Pediatric Emergency Department) admission are very rare [6]. In this article, the youngest case in literature who went to the PED and was diagnosed with pelvic and acetabulary OM is presented.
Case Report
A 12-day-old girl, born from the first pregnancy of a 28-year-old mother, was admitted to the PED with complaints of restlessness and inability to move her right leg. The day before the application, it was stated by her mother that she did not move her leg, that she was agitated when forced to move, and could not be consoled. The baby did not have a history of fever or trauma, her feeding was good, and her urine and defecation were normal. From her history, it was learned that she was born at 36 weeks and 3 days of gestation and had intrauterine growth retardation compatible with 31 weeks gestational age, and she was born by emergency cesarean section due to preeclampsia. The patient, who was hospitalized in the NICU due to temporary tachypnea of the newborn after birth, was discharged on the sixth postnatal day. During the follow-up in the NICU, umbilical catheterization was not applied to the patient. She had not received antibiotic treatment and no growth was detected in blood cultures taken before discharge.
At her evaluation in the Pediatric Emergency Department triage area, she was a restless baby with a good general appearance. Vital signs; body temperature was 37°C, heart rate was 140/min, respiratory rate was 42/min, pulse oximetry was 98%, and mean arterial pressure was 45 mmHg. There was no pathological finding in the physical examination, and it was observed that the patient's discomfort increased due to the position given to the hip and leg while changing the diaper. While abducting the right thigh from the hip in the supine position, there was limited range of motion compared to the left. No swelling or redness was detected on the joint surface.
Laboratory and radiological examinations were planned for the patient with a preliminary diagnosis of septic arthritis. In laboratory tests: hemoglobin (Hb) 14.6 g/dL, RBC (Erythrocyte) - 3.361 x10.e6/uL, hematocrit (Hct) 40.04%, white blood cell (WBC) 16.82 x10.e3/uL, neutrophil percentage 59.8%, C-reactive protein (CRP) 25.9 mg/L, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) 51 mm/hr, procalcitonin (PCT) 2.95 ng/mL, IL-6 145.6 pg /mL detected. On direct radiographs of the lower extremity and pelvis, the right femoro-acetabular distance was observed to be increased (Figure 1). Long bone radiographs were normal. In the superficial tissue ultrasound (US) performed for the right hip joint, bilateral hip joints were compared with each other, and no significant effusion was observed on the right side. The patient was consulted to the Orthopedics and Traumatology department with a preliminary diagnosis of septic arthritis. MRI was requested from the patient for the differential diagnosis of septic arthritis.

Figure 1: There is an increase in the right acetofemoral distance compared to the left.
Bilateral hip MR imaging showed “The right femoral head is small and irregular in appearance, and an area of pathological signal change in the right femur proximal metaphysis, medullary bone marrow, and solid periosteal reaction in the lateral proximal section is observed. Widespread edema was observed in the surrounding muscle planes, fascial surface and subcutaneous adipose tissue adjacent to the hip joint. In addition, medullary bone marrow edema was observed in the right acetabulum (osteomyelitis). Areas of pathological signal changes consistent with diffuse edema are observed in the right obturator externus, pectineus, quadriceps muscles, gluteal muscle planes and iliacus muscle (myositis). Minimal free fluid was observed in the right hip joint space. Findings were primarily evaluated as compatible with osteomyelitis and myositis.” (Figure 2).

Figure 2: Osteomyelitis in the proximal metaphysis of the femur
Due to the history of hospitalization in the intensive care unit, the patient was diagnosed with OM secondary to hematogenous spread and, according to the age, to include possible infectious agents, vancomycin (15mg/kg/dosex3), ceftazidime (30 mg/kg/dose x 3), fluconazole loading (12 mg/kg/dose)) and maintenance (6 mg/kg/dose) treatment was started. Blood culture was taken before antibiotic treatment. Our patient, who received antibiotic doses only one day before the operation, was operated on the postnatal 13th day.
The patient was operated by the Orthopedics and Traumatology department and the intra-articular pus was drained. From the material; joint fluid culture, fungal culture, tuberculosis PCR, ARB staining, fungus search was sent. There was no growth in the blood culture, but because of the growth of ceftazidime-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in the joint fluid culture, ceftazidime was discontinued and meropenem (20 mg/kg/dosex3) treatment was started. Fluconazole was discontinued on the 8th day because there was no growth in the fungal culture. The patient was discharged with oral trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole treatment after 25 days of vancomycin and 27 days of meropenem treatment. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole was discontinued 22 days after discharge. The regression of the inflammation was seen in the MRI taken under the control of the outpatient clinic. verbal consent was obtained from the patient's parents for the publication of the article.
Discussion
This case demonstrates the importance of detailed investigation of newborn infants admitted to PED. Although OM in newborns is rare, there are difficulties in diagnosing and treating it. High suspicion is required for early diagnosis and observation of clinical signs is very important.
Risk factors for osteomyelitis in newborns are stated as immature host-defense mechanisms, invasive intervention such as umbilical catheterization. It has been shown that half of the cases diagnosed with neonatal OM have a history of umbilical catheterization. It has been observed that the pregnancy and delivery history of the mother is also important in the development of OM, and maternal complications such as maternal hypertension, preeclampsia, ablatio placentae, infection are present in approximately half of the infants who develop OM [7]. Particular attention should be paid to the evaluation of newborn cases, especially in PEDs where is crowded and the number of patient admissions is high. Newborns are among the patients at risk for PED and require special care. Application complaints and prenatal, natal and postnatal history should be questioned in detail. It was observed that the mother of our case had preeclampsia during pregnancy, but umbilical catheterization was not applied to the baby.
In studies conducted in newborns with neonatal osteomyelitis, the most common sites of involvement were reported as femur, humerus, and tibia, respectively [1, 4, 8]. The pelvis is a rare site of hematogenous disseminated OM for neonates. Pelvic OM constitutes 2.3% of all childhood osteomyelitis cases [3]. Our case also had pelvic (acetabular) OM, which is a rare site of OM involvement. Involvement was also demonstrated in the proximal region of the right femur.
Pelvic OM was defined in three cases at 5, 15, and 18 days in the neonatal period [3, 9, 10]. In the literature, it has been observed that mostly cases hospitalized in the NICU were diagnosed with osteomyelitis [1, 3, 4, 8-10]. As far as we can find in the literature, a 4-week-old case with a diagnosis of distal tibial OM and culture of GBS has been reported, just like our case [6]. Our case is the youngest OM case diagnosed in the emergency department, except for the case in the literature. The clinical features, presentation symptoms, cultures and risk factors of cases diagnosed with neonatal osteomyelitis in the literature are shown in (Table 1)
Table 1: Comparison of cases with neonatal osteomyelitis in the literature.
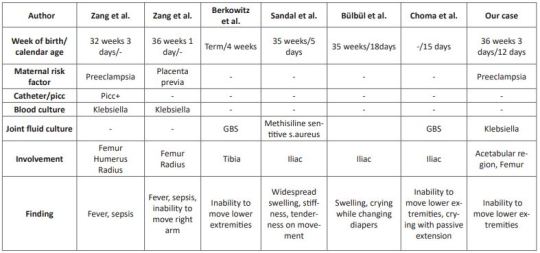
Clinical symptoms are related to the bone or joint area involved in newborns. Swelling and local inflammation findings are common findings in the neonatal osteomyelitis group. Systemic findings such as fever are seen in fewer of these cases. A highly variable rate of fever was found in 9.1-76.5% of patients with extensive neonatal osteomyelitis. In addition, it has been shown that the WBC count, CRP and ESR levels are high in the cases [1, 4, 8, 11]. In our case, there was no fever, but there were complaints of inability to move her right leg and restlessness. Laboratory parameters were high and consistent with the literature. In cases with osteomyelitis, direct radiographs can guide the correct diagnosis, exclude other diagnostic possibilities, or provide clues for underlying pathological conditions [12]. Soft tissue swelling on plain radiographs can be seen within days of the onset of infection. It can also show periosteal reaction, lytic lesions, joint effusions and destructive bone changes 7-10 days after the onset of infection [13]. US findings begin with nonspecific swelling in the soft tissues adjacent to the bone. US can show thickening and elevation of periosteal and subperiosteal fluid collections as early as 3 days [14]. In a study comparing osteomyelitis groups, it was shown that the diagnostic value of US was statistically higher in the newborn group compared to the other groups, regarding the capacity of detecting subperiosteal abscesses [11]. In our case, however, an increased femoro-acetabular distance was observed on direct X-ray, but no finding was found on US. This supports the view that the primary step in the pediatric emergency department in patients with suspected osteomyelitis should be started with direct X-ray as recommended in the literature.
MR imaging is the most useful imaging technique for evaluating suspected OM, allowing early detection of osteomyelitis and assessment of the extent of involvement and disease activity. MRI is very sensitive in detecting OM 3-5 days after the onset of infection [12]. As seen in our case, it still remains the gold standard. However, we recommend hospitalization in order not to miss the newborn cases because MRI is difficult in emergency conditions.
In infants, osteomyelitis and septic arthritis often coexist. While Staphylococcus aureus is the most common organism causing osteomyelitis at all ages, GBS and Escherichia Coli are important pathogens to be considered in newborns [6]. Culture is found to be negative in 22-50% of the cases [15]. Antibiotics to be used in neonatal OM should be effective against these pathogens [16]. In our case, treatment with antibiotics covering these pathogens was applied and Klebsiella pneumoniae growth was observed in the pus culture.
We think that even with rapid diagnosis and aggressive treatment, there are orthopedic sequelae and inadequate treatment increases the risk of chronic osteoma [16], therefore, in cases who apply to the pediatric emergency department with these complaints, early diagnosis and treatment of neonatal OM should be planned in a timely manner to minimize long-term sequelae.
In conclusion, a detailed anamnesis should be taken and a careful physical examination should be performed in newborns who present to the PED with limited range of motion at joints. Neonatal OM cases mostly consist of cases diagnosed while staying in the NICU. Pelvic involvement is rare and our case is the youngest pelvic OM case diagnosed in the PED.
For more details : https://jcmimagescasereports.org/author-guidelines/
#Osteomyelitis#newborn#pediatric emergency#Pediatric Emergency Department#OM#PED#catheterization#RBC#C-reactive protein#hematocrit#Traumatology#Mehmet Ali Oktay#JCMICR
0 notes
Text
Throughout this guide, we will offer a better understanding of what osteomyelitis is and what causes it, how the condition is diagnosed, and why early intervention and treatment is so important.
0 notes
Text
Es wurde festgestellt, dass Wirbelsäulenerkrankungen bei CRMO-Patienten häufiger auftreten als bisher angenommen
Neue Forschungsergebnisse, die diese Woche auf der ACR Convergence 2022, dem Jahrestreffen des American College of Rheumatology, vorgestellt wurden, zeigen, dass Wirbelsäulenerkrankungen, die einst als Seltenheit bei chronisch rezidivierender multifokaler Osteomyelitis galten, bis zu 10-35 % der Patienten betreffen und bei einem Drittel asymptomatisch sind (Zusammenfassung Nr. 1942).
Chronisch rezidivierende multifokale Osteomyelitis (CRMO) ist eine autoinflammatorische Kno...
#Antiphlogistikum #Arthritis #Ausbildung #Autoimmunerkrankung #chronisch #Drogen #Forschung #Kinder #Knochen #Medizin #Osteomyelitis #Pädiatrie #Rheumatologie #Rückenschmerzen #schlafen #Schmerz #Wirbelsäule
#Medical_Condition_News#Medical_Research_News#News#Antiphlogistikum#Arthritis#Ausbildung#Autoimmunerkrankung#chronisch#Drogen#Forschung#Kinder#Knochen#Medizin#Osteomyelitis#Pädiatrie#Rheumatologie#Rückenschmerzen#schlafen#Schmerz#Wirbelsäule
0 notes
Text
high school tinder gets first big dick
Novinha peituda e gostosa que peguei de jeito no motel ESTRELA
Sex massage hidden cam first time I have always been a respected
Pendeja Gordibuena culona argentina en la calle
Thick BBW Angelina Castro Fucks Curvy Cristi Ann With A Cock
twitch /Narukitkat cum eating swallow
Interracial Lesbian Amateurs
Engaging brunette Mila Jade getting hard fucked
NN Teen Tease Jerk Off Challenge
Videos porno gay bad boys medicals first time Once he stopped I
#carterly#jarovizing#literacies#showcasing#gemmy#quantimeter#medica#Uncompahgre#logicalist#bandpass#reflection's#mechagodzilla#ploratory#villain's#osteomyelitis#moon-crowned#Unit#tourbillion#scullionish#microcapsule
0 notes
Text
Repost but ngl this is legit how I feel rn
#my life is going to fucking shit#in pain 24/7#my wrist is killing me#and i have#osteomyelitis#bc of my dog fucking biting me#fml
0 notes
Link
While its initial intent was to treat birth deformities and accidents, today limb-lengthening surgeries are being increasingly employed to increase height. In a limb-lengthening procedure or height increase surgery, as it is commonly known, the patient’s tibia and fibula bones are split into two. Next, a nail is inserted in between the halves, directly into the cartilage, and is held in place by an external device known as the Ilizarov Apparatus. The rod gradually pulls the bones apart over three months. Simultaneously, the body's healing process begins, and new bone, nerves, and arteries grow and fill in the gap.
Link -: https://drsarin.in/treatment/height-increase-surgery
Email -: [email protected]
Phone +91 9810001907
0 notes
Text
.
#i hate to be that type of person but#i want to cry from stress so badly#i am so stressed over money lmao. i haven’t been able to work for like 4 months cus my osteomyelitis and my seizures#i know nobody gives a fuck nor will help which i get. i’m just so stressed i keep making myself Physically sick idk what else to do#i’m really not expecting anything but i’m just so stressed and idk what to do lol#i’ve been filing unemployment but they’re so backed up again im just stressed. i’ve been still paying bills with what little i DO have#i know nobody will: which i understand#but if anyone can spare like anything so i can ✨live✨ until my elbow is healed enough for me to work-i’d cry from appreciation#and i’m just like ahaha 🤪🔫💀🪦👻#anything would help but i do understand#venmo is teapxnk#paypal is teapunk#.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
now that kids on iPads are but a fact of life at this point, i must acknowledge that i am a pioneering member, a prototype of this great demographic, having been gifted a jailbroken first-generation iPad like, 12 years ago, when i was ten or eleven. i grew up with ancient games originally made for the iPhone that are lost media now, like Karnival and Puzzlings, the old built-in YouTube app whose icon looked like an old-timey TV(?), and of course, the Angry Birds. i ultimately turned out alright, i think… all i really do nowadays is listen to ska and read Baudrillard
#i got it as a sort of congratulations-on-not-having-to-go-into-surgery-for-osteomyelitis gift lmao#i already had unrestricted unsupervised internet access prior to getting it; flash games on Newgrounds were my shit
0 notes
Video
youtube
SURGICAL PATHOLOGY STATION OF OSTEOMYELITIS
SURGICAL PATHOLOGY STATION OF OSTEOMYELITIS MRCS B OSCE - MOCK EXAM ALL THE REQUIRED STUDY MATERIAL: https://samreensway.com/2020/02/15/how-to-un-code-the-mrcs-b-osce-a-guide/ Bli medlem i kanalen för att få åtkomst till flera förmåner: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCkkvon_blxinTHc7DGuYkpQ/join
#youtube#surgicalpathology pathology osteomyelitis medicine doctor surgery health medical healthcare mrcs mrcsbosce femalesurgeon youtube membership
0 notes