#ecosystem ecology
Text
tumblr used to be a high throughput reef ecosystem but then they banned titties and now we’re like an ecosystem in the abyssal sea floor just quietly chugging along, cycling through nutrients at a much slower rate.
then every once in a while a some huge news comes along like queendeath and it’s like a whale fall, we come crawling out of the woodwork like isopods, hagfish, and burrowing worms to feast on the memes for years
it’s been almost two years since destiel-putin-election and we still linger around those bones like limpets
52K notes
·
View notes
Text
In the Willamette Valley of Oregon, the long study of a butterfly once thought extinct has led to a chain reaction of conservation in a long-cultivated region.
The conservation work, along with helping other species, has been so successful that the Fender’s blue butterfly is slated to be downlisted from Endangered to Threatened on the Endangered Species List—only the second time an insect has made such a recovery.
[Note: "the second time" is as of the article publication in November 2022.]
To live out its nectar-drinking existence in the upland prairie ecosystem in northwest Oregon, Fender’s blue relies on the help of other species, including humans, but also ants, and a particular species of lupine.
After Fender’s blue was rediscovered in the 1980s, 50 years after being declared extinct, scientists realized that the net had to be cast wide to ensure its continued survival; work which is now restoring these upland ecosystems to their pre-colonial state, welcoming indigenous knowledge back onto the land, and spreading the Kincaid lupine around the Willamette Valley.
First collected in 1929 [more like "first formally documented by Western scientists"], Fender’s blue disappeared for decades. By the time it was rediscovered only 3,400 or so were estimated to exist, while much of the Willamette Valley that was its home had been turned over to farming on the lowland prairie, and grazing on the slopes and buttes.

Pictured: Female and male Fender’s blue butterflies.
Now its numbers have quadrupled, largely due to a recovery plan enacted by the Fish and Wildlife Service that targeted the revival at scale of Kincaid’s lupine, a perennial flower of equal rarity. Grown en-masse by inmates of correctional facility programs that teach green-thumb skills for when they rejoin society, these finicky flowers have also exploded in numbers.
[Note: Okay, I looked it up, and this is NOT a new kind of shitty greenwashing prison labor. This is in partnership with the Sustainability in Prisons Project, which honestly sounds like pretty good/genuine organization/program to me. These programs specifically offer incarcerated people college credits and professional training/certifications, and many of the courses are written and/or taught by incarcerated individuals, in addition to the substantial mental health benefits (see x, x, x) associated with contact with nature.]
The lupines needed the kind of upland prairie that’s now hard to find in the valley where they once flourished because of the native Kalapuya people’s regular cultural burning of the meadows.
While it sounds counterintuitive to burn a meadow to increase numbers of flowers and butterflies, grasses and forbs [a.k.a. herbs] become too dense in the absence of such disturbances, while their fine soil building eventually creates ideal terrain for woody shrubs, trees, and thus the end of the grassland altogether.
Fender’s blue caterpillars produce a little bit of nectar, which nearby ants eat. This has led over evolutionary time to a co-dependent relationship, where the ants actively protect the caterpillars. High grasses and woody shrubs however prevent the ants from finding the caterpillars, who are then preyed on by other insects.
Now the Confederated Tribes of Grand Ronde are being welcomed back onto these prairie landscapes to apply their [traditional burning practices], after the FWS discovered that actively managing the grasslands by removing invasive species and keeping the grass short allowed the lupines to flourish.
By restoring the lupines with sweat and fire, the butterflies have returned. There are now more than 10,000 found on the buttes of the Willamette Valley."
-via Good News Network, November 28, 2022
#butterflies#butterfly#endangered species#conservation#ecosystem restoration#ecosystem#ecology#environment#older news but still v relevant!#fire#fire ecology#indigenous#traditional knowledge#indigenous knowledge#lupine#wild flowers#plants#botany#lepidoptera#lepidopterology#entomology#insects#good news#hope
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
okay. so.
i'm reading this book The Origins of the Modern World by Robert Marks
and even from the beginning i was getting this weird feeling from it. I'm always really wary of books that are broad overviews of history that claim to explore big theory-of-everything explanations for very broad phenomena, because history is unbelievably complex and there is so much disagreement between historians about everything.
But anyway I come to this section (in the first chapter)

This writer's opinion is that the Americas seemed so abundant when English settlers first arrived because the Native Americans had been mostly killed, and as a result, the wildlife increased greatly in numbers and forests overtook the farms, creating what appeared to be a natural paradise.
I'm immediately suspicious of this paragraph because arguing that the mass death of Native Americans was good for nature seems really contradictory to the research I've explored, on top of being just...disgusting.
But it doesn't sound right in regards to how ecosystems work either. If populations of animals had recently exploded after millennia of being limited by a major predator, it would cause the plants to be overwhelmed by the herbivore populations. The land would be stripped barren and eroded, and soon the animals would be weak and starving.
So I thought to myself, huh, a citation. I will look at the citation and see what it says.
It's a book called Changes in the Land by William Cronon, who seems to be one of the most important and respected guys in his field. I thought, I have to find this book. So I did, I found the book, and spent like an hour reading through it.
And what I discovered, is that Cronon's book directly contradicts what Marks says in the paragraph that cites Cronon?!

So basically this entire book, Changes in the Land, is a detailed exploration of how the arrival of English settlers, the decline of Native American populations, and the slow transition to European farming and land use practices caused increasing degradation to the ecosystem, beginning very early on in colonization.
Changes in the Land quotes a great array of documents from the colonial period where settlers observed the soil becoming depleted, animals disappearing, and the climate itself becoming more hostile even in the 1600's. It's actually a really fascinating book.
Cronon tells us that Native Americans created lush and abundant conditions for wild animals by causing a "mosaic" of habitats, with different areas representing various stages of ecological succession. With this great diversity in habitats, and lots of transitional "edges" between them, the prosperity of the animal life was maximized. This was intentional, and really a type of farming.

The book essentially explains how European settlers couldn't recognize Native American life ways as "agriculture," they thought the land was just supernaturally abundant all by itself because of its inherent nature, and yet almost immediately after settlers came, the abundance of the land degraded and vanished. The settlers cut down vast amounts of trees, which caused erosion, which destroyed the river and stream ecosystems and starved the soil of nutrients. Destruction of forest caused less rain, and more extreme temperatures. It became a vicious cycle where the settlers had to abuse the land more and more just to survive.
The spiral pulled in Native American communities too, forcing them to turn to more exploitative means of survival like the fur trade, (which depleted the beaver population, which caused the decline of beaver ponds, which harmed the whole forest). It describes how the changing ecosystems left Native Americans with no choice but to turn to European practices for survival, which in turn depleted the land even further.
Even I was surprised to learn just how early on environmental disaster set in, and the incredible extent of it. English farming practices literally reshaped the map of New Haven between the 17th and 18th centuries:

To return to Marks, though...Marks' statement in the excerpt, where he says the "abundance" of animals continued throughout the 19th century, is blatantly false according to the source HE CITES.

Deer were becoming scarce in New England by the 1690's. It was so bad by 1718 that deer hunting was forbidden for 3 years at that time, and by 1800, deer were almost extirpated from New England. The book explains on another page that wild turkeys became so rare that a farmer's manual from the time said their domesticated turkeys were from Turkey—settlers had no opportunity to see a wild turkey and no idea they existed.
Marks is supporting his statement using a source entirely dedicated to contradicting the exact thing he's saying! It's unbelievable.
How does this happen? Did Marks just have his own opinion and insert a famous book that seemed to be on the subject as support, without reading it?
I'm thinking now of all the times I've read a book and seen a citation on a statement and unconsciously thought "oh, well it seems there is evidence, so it must be reliable" when actually, something like this was happening. The array of ways misinformation can be propagated and never be found out is terrifying.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Did you know that 4000 metres bellow the ocean there are chemosynthetic bacteria that are specifically evolved to digest the wood of trees that have grown on land?
The wood on the sea floor can come from trees that fall into lakes and end up in the ocean, or wooden ships that have sunken. (Called 'Wood-falls')
The reason why deep marine organisms are able to digest wood despite never seeing the light of day, let alone a plant - since plants are unable to grow in the deep ocean because of a lack of sunlight - is because the ocean is so isolated and scarce of food that when a new food source is suddenly available, organisms rapidly evolve to be able to eat it.
This is called 'Adaptive Radiation', and can also occur on isolated islands.

#Ocean#oceanology#marine biology#marine ecology#marine ecosystem#marine life#deep ocean#deep sea#microbiology#oceanography#oceancore#ocean floor#marine#seacore#Sea#deep marine life#sailorcore#fish#the abyssal#oceanic#sea#marine love#fun facts#ocean facts#marine biodiversity#evolution
7K notes
·
View notes
Text
On the Sioux Valley Dakota Nation west of Brandon, Man., schoolchildren are throwing pumpkins into a bison pen, a ceremony and sign of respect to an animal that has deep spiritual significance for Indigenous culture and identity.
Community leaders are also educating a new generation about how the bison, known in these parts as buffalo, has important implications for the future of the Prairies – rehabilitating natural grasslands and conserving water in a time of climate change.
"The significance of the buffalo goes back hundreds of years. These animals have saved our lives," said Anthony Tacan, a band councillor whose family is the keeper of this herd.
"They provided food and weapons out of the bones, tools, the hides for clothing, the teepees. It did everything for us. So going forward, we decided it's our turn to give back. It's our turn to look after them."
Continue Reading
#cdnpoli#canadian politics#canada#canadian news#sioux valley dakota nation#first nations#indigenous#american buffalo#american bison#bison#ecology#ecosystem restoration#manitoba
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Forget hot girl summer it is
Citizen Science Summer!
Get on eBird, iNaturalist, Seek, whatever apps and forums are cool to you and discover the huge variety of life right under your nose! Snap some pics and record those critters! Rejoice for native bees and plants growing wild by the roadside!!
#ecology#citizen science#ebird#inaturalist#seek#nature#biology#native plants#ecosystems#citizen science summer
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
There's been a recent increase in the removal of old dams and other barriers on salmon streams on the west coast of the U.S. While last year's removal of part a weir from McKay Creek wasn't as dramatic as the removal of dams on the Klamath River, the results of the removal are very promising.
The weir was installed about thirty years ago due to the creek being drained by a nearby reservoir. Unfortunately, its design meant that salmon could no longer go higher up the creek to their historic breeding grounds.
The power of nature's resiliency--if we give it the chance to recover--was evident in the fact that this past February saw the return of the salmon to the creek for the first time in three decades. What's even more exciting is that scientists found not just a few redds (salmon egg nests), but seventy-two of them in a six mile stretch of the creek above the weir! That's incredibly impressive, considering how long salmon were blocked from that area.
Here's to more projects like these giving our salmon a fighting chance for survival in spite of everything we've thrown at them over the years.
#salmon#fish#fishblr#icthyology#aquatic ecosystems#dams#dam removal#conservation#environment#environmentalism#habitat restoration#endangered species#extinction#wildlife#animals#nature#ecology\#restoration ecology
549 notes
·
View notes
Text
Because I'm going to be thinking about this forever, I do want to talk about how Caleb speaks, because I think there's something to be said for how his protectiveness (in general) actually presents itself.
Caleb uses epithets and allusions a lot. He refers to Nott as "my goblin friend," to Jester as "my blue friend," to Yasha as "my barbarian friend." Yussa is at one point "our wizard friend," and Essek is "my Kryn friend," in the two-shot.
He is also, notably, paranoid about being surveiled. He wears the amulet of nondetection for most of the campaign, and it's not unwarranted, given that Trent locates him and nearly burns down the Blooming Grove the moment he's able to get a lock on them. Trent in fact has been shown to use any and all information he can get ahold of about or from Caleb against him, to a truly extreme level. His seemingly single-minded goal is expressed to be to ensure that not a single aspect of Caleb's life and loved ones is safe at any moment, to perpetuate the threat of harm from any direction in order to essentially control and monopolize Caleb's every thought.
In Echoes of the Solstice, Caleb does suggest that he is not concerned with Trent being able to surveil him any longer, but Trent is not the only threat, and, timey-wimey plot nonsense aside, the Hells' inability to scry on him since then suggests that he is likely wearing an amulet at least by that point in the timeline.
The extent of Trent's focus on him and his ensuing paranoia is extreme, and even beyond when he may no longer feel that Trent is a threat to him, he seems unwilling to allow him to pose a threat to others, and people he cares about in particular.
Within that context, it's not difficult to read his use of epithets, particularly in referring to people who are not currently present (rather than using their name aloud), as a form of protection. Some of his manner of speaking implicitly or explicitly presumes that he is being surveiled, even outside of the context of protectiveness; after Vess Derogna's death, he frequently refers to Lucian only by epithets, most often, "our old friend," and at one point establishes "Lady D," (to Jester's glee) as a code name for Vess Derogna for the specific purposes of countersurveilance.
This method of protection, I would imagine, goes double for Essek; not only does Caleb have the habit of worrying over those who would use his loved ones against him, which is of course borne out in Echoes of the Solstice, but he also must consider that Essek has his own enemies, and a stray mention of his name in the wrong company or setting could get his partner killed. It seems even in that gifset, when Caleb says, "I am worried for Essek," after the encounter with Trent at Vergessen, that he first considers obfuscating, stumbling over allusory phrasing before acknowledging that Trent already has the information he needs, and at that point Trent is their only real concern about who might care, given Lucien is far too focused on reaching the Astral Sea to worry about hostages.
When Caleb answers Jester's, "And he's going to hurt Essek," with a silence and an oblique reply, it feels most to me like a further measure of protection, knowing that knowledge is power that can be used against him and his loved ones, and silence is the weapon he has against it.
#critical role#caleb widogast#shadowgast#essek thelyss#cr meta#trent ikithon#echoes of the solstice#anyway I've been thinking about this nonstop nobody talk to me nobody look at me#I am not gonna keep harping on about how interpreting a lack of direct mention of someone = a lack of caring or interest but#I will float alternative readings into the ecosystem. diversify the ecology lmao
981 notes
·
View notes
Text
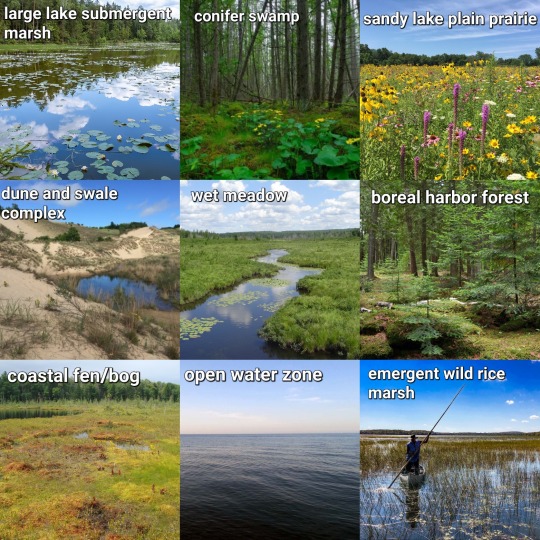

#poll#great lakes#ecosystems#ecology#marsh#lake#lakeposting#freshwater#wetlands#fen#bog#cattail#wild rice#forest#boreal#boreal forest#prairie#dune#dunes#dune and swale#estuary#delta#wet meadow#swamp
3K notes
·
View notes
Note
Do you know any cookie cutter shark facts or lantern shark facts

Etmopterus perryi or Dwarf Lantern Sharks
Dwarf Lantern Sharks are so cute! They grow to be a maximum of 20 cm (7.9 in) and live in the Bathypelagic zone at depths of 1,000 - 3,000 m (3,300 – 9,800 ft). This zone is also known as the midnight zone because there is no light. This is why this shark has really large eyes comparative to its body size! This shark, like some other deep-sea sharks, can glow! They have organs known as photophores on its underside, used as camouflage and to attract prey.

These sharks are rarely seen, so there's still a lot we don't know about them!
Thanks for the ask; a post about cookie cutter sharks will be up soon, and I'll link it here!
#marine biology#marine ecology#animals#science#biology#fish#shark#sharks#sea creatures#marine life#sea life#sea animals#lantern shark#lantern sharks#dwarf lantern shark#marine creatures#marine ecosystem#ocean#oceans#wildlife#cool sharks#fun facts#animal facts#ecology#zoology#conservation#evolution
583 notes
·
View notes
Text
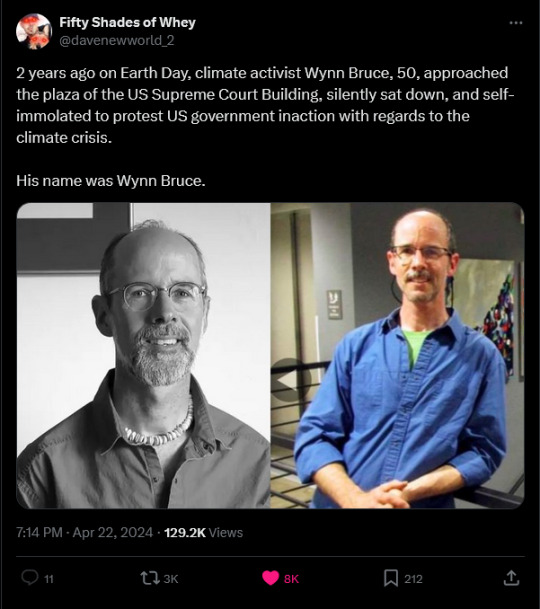
#earth day#leftism#socialism#communism#anti capitalism#anarchy#ecosystem#environment#ecology#eco#save the planet#go green#save the earth#recycle#april 22#save the bees#twitter x#save the children
229 notes
·
View notes
Text
reblogging old popular posts like I'm circulating nutrient-rich cold seawater into the photic zone to increase productivity in the tumblr ecosystem
#there are many advantages to being a marine biologist#marine biology#ecosystem ecology#ecology#tumblr#tunglr#shitpost
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
"When considering the great victories of America’s conservationists, we tend to think of the sights and landscapes emblematic of the West, but there’s also a rich history of acknowledging the value of the wetlands of America’s south.
These include such vibrant ecosystems as the Everglades, the Great Dismal Swamp, the floodplains of the Congaree River, and “America’s Amazon” also known as the “Land Between the Rivers”—recently preserved forever thanks to generous donors and work by the Nature Conservancy (TNC).
With what the TNC described as an “unprecedented gift,” 8,000 acres of pristine wetlands where the Alabama and Tombigbee Rivers join, known as the Mobile Delta, were purchased for the purpose of conservation for $15 million. The owners chose to sell to TNC rather than to the timber industry which planned to log in the location.
“This is one of the most important conservation victories that we’ve ever been a part of,” said Mitch Reid, state director for The Nature Conservancy in Alabama.
The area is filled with oxbow lakes, creeks, and swamps alongside the rivers, and they’re home to so many species that it ranks as one of the most biodiverse ecosystems on Earth, such that Reid often jokes that while it has rightfully earned the moniker “America’s Amazon” the Amazon should seriously consider using the moniker “South America’s Mobile.”
“This tract represents the largest remaining block of land that we can protect in the Mobile-Tensaw Delta. First and foremost, TNC is doing this work for our fellow Alabamians who rightly pride themselves on their relationship with the outdoors,” said Reid, who told Advance Local that it can connect with other protected lands to the north, in an area called the Red Hills.
“Conservation lands in the Delta positions it as an anchor in a corridor of protected lands stretching from the Gulf of Mexico to the Appalachian Mountains and has long been a priority in TNC’s ongoing efforts to establish resilient and connected landscapes across the region.”
At the moment, no management plan has been sketched out, but TNC believes it must allow the public to use it for recreation as much as possible.
The money for the purchase was provided by a government grant and a generous, anonymous donor, along with $5.2 million from the Holdfast Collective—the conservation funding body of Patagonia outfitters."
youtube
Video via Mobile Bay National Estuary Program, August 7, 2020
Article via Good News Network, February 14, 2024
#united states#alabama#estuary#wetlands#swamp#river#environment#environmental issues#conservation#video#biodiversity#american south#ecosystems#ecology#conservation news#wildlife conservation#ecosystem#conservation efforts#good news#hope#forest#swampco#re#Youtube
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

They generally tend to avoid mimicking animals with complex socialisation capabilities such as the zaabua, as they are mostly unsuccessful with copying their complex languages, making them easy to pick out. And instead tend to seek out animals on the lower IQ side who aren’t so dependent on communication.

In the rare chance of a Skin Keeper taking control of a Zaabuas corpse, the Zaabua will quickly identify if a Skin keeper has infiltrated their group and will quickly kill off the unwanted guest. After that they re bury the defiled body in a more secrete location to avoid another one of these unusual events.
The few rare instances of these happening to the Zaabua tribe, have been reported to become paranoid and become wary of each other and might conspire on one another, pointing suspicion on random members or even use this opportunity to get rid of someone who they might have had a confrontation with.
despite not exhibiting any of the traits of a Skin Keeper such as looking like a literal walking corpse. Often the blame being successfully pointed towards are the elderly who look more warn down and rugged.

the newest edition to the ecosystem of Land Of Borease. Wanted to wish you a merry Christmas‼️
#land of borease#xenobiology#alien species#spec bio#spec evo#speculative biology#speculative evolution#speculative ecology#speculative fiction#artists on tumblr#oc#speculative worldbuilding#speculative zoology#worldbuilding#digital art#digital drawing#digital illustration#alien ecosystem#merry christmas
315 notes
·
View notes
Text
W h a l e f a l l
C.W: Whale corpses

When a whale carcass floats down to the ocean floor in the abyssal zone, it creates an ecosystem called a 'whalefall', where a variety of deep marine life can live and be sustained for over 50 years.
This ecosystem has 4 stages:
Mobile Scavengers Stage

The first stage is when scavengers from around the plain gather to feast on the whales flesh - Typically by hagfish and sleeper sharks - until there is just bone.
This stage can last for months or up to 1.5 years.
Enrichment Opportunists Stage

This stage is when smaller scavengers - such as octopuses, crustaceans and molluscs - gather around the whale looking for tissue and bits of carcass left over from the first stage. This is also when osedax (boneworms) arrive and comsume the community of bacteria that eat the bone lipids.
This stage can last months or up to 5 years.
Sulfophilic Stage

In this stage the majority of scavengers have left and in its place are the boneworms and the community of chemosynthetic bacteria that break down the lipids in the bones and produces sulphide that can be consumed by other organisms like worms or shrimp.
This stage can last over 50 years.
Reef Stage

The final stage is when all the consumable material have been exhausted and the leftover bone creates a hard surface for abyssal filter feeders to latch onto. A 'reef' of sorts.
Whalefalls are one of many essential food-falls that sustain life at the bottom of the ocean, and are p cool i think anyway im done w my autism rant goodbye
#sorry i wasnt sure how to end it#marine#marine biology#marine life#oceancore#oceanology#oceanography#whales#whalefall#marine ecosystem#marine ecology#ecology#ecosystem#the abyssal#deep ocean#deep sea#science#science facts#fish#ocean floor#ocean#Sea floor#marine animals#seacore#pacific ocean#sailorcore#nautical#tw decay#tw corpse#ocean aesthetic
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
North America once housed more beavers than humans — by a lot. Even before Europeans showed up and built an entire extractive economy on beaver pelts, estimates put the number in the hundreds of millions (during the Pleistocene, there were even giant species of beaver, as large as bears). The North American fur trade, which lasted for centuries, nearly wiped beavers off the continent — and, unknown to trappers, vastly changed its ecosystems from sea to sea.
“There is evidence that riverscapes across the West were much more complex and ‘anastomosed’ prior to European colonization,” says Nicholas Kolarik, a Ph.D. student working with Brandt, who is focusing on mapping data sets of wetlands. Anastomosis denotes branches connecting two things, like organs in the body, but in this case, he means streams, since waterways in the U.S. West used to be much more interconnected.
Today, they’re “starved of wood,” he says, but by adding wood into streams and rivers, especially by building dams, beavers slow water down significantly.
“In doing so, sediment is stored, water infiltrates into the aquifers, riparian vegetation establishes, habitat is created, and carbon is stored,” Kolarik says.
[...]
“Beavers maintain healthy riverscapes which store carbon and water. Consistent access to water is key to mitigating the effects of climate disturbances like drought.”
Beavers’ role as firefighters has already been documented in Idaho. A 2018 technical report by Anabranch Solutions, a river restoration company, found that beavers were a major factor in decreasing burn intensity along Baugh Creek during that year’s Sharps Fire.
“Where active beaver dams were present, native riparian vegetation persisted, unburnt,” the authors wrote. In our hotter and fierier world, beavers are a buffer.
435 notes
·
View notes