#qing han
Text
[Hanfu · 漢服]The relationship between women in history is not just love rivals,
“but also thousands of years later, everyone knows that it is me and you.”
Let's get to know about them/她们 in China history.
1.【Han Dynasty】:Princess Jieyou (解忧公主) & Feng Liao (馮嫽)
Princess Jieyou (Chinese: 解忧公主; 121 BC – 49 BC), born Liu Jieyou (Chinese: 刘解忧), was a Chinese princess sent to marry the leader of the Wusun kingdom as part of the Western Han Chinese policy of heqin(和亲).
As the granddaughter of the disgraced Prince Liu Wu (劉戊) who had taken part in the disastrous Rebellion of the Seven States,her status was low enough that she was sent to replace Princess Liu Xijun (劉細君) after her untimely death and marry the Wusun king Cunzhou (岑陬).
Jieyou lived among the Wusun for fifty years and did much work to foster relations between the surrounding kingdoms and the Han. She was particularly reliant upon her attendant, Feng Liao, whom she dispatched as an emissary to Wusun kingdoms and even to the Han Court. She faced opposition from pro-Xiongnu members of the Wusun royalty, particularly Wengguimi’s Xiongnu wife. When word came that the Xiongnu planned to attack Wusun, she convinced her husband to send for aid from the Han Emperor. Emperor Wu of Han sent 150,000 cavalrymen to support the Wusun forces and drive back the Xiongnu.
In 51 BCE at the age of 70, Jieyou asked to be allowed to retire and return to the Han. Emperor Xuan of Han agreed and had her escorted back to Chang'an where she was welcomed with honor. She was given a grand palace with servants usually reserved for princesses of the imperial family. In 49 BCE, Jieyou died peacefully.
Feng Liao (馮嫽)
Feng Liao (馮嫽) was China's first official female diplomat,[citation needed] who represented the Han dynasty to Wusun (烏孫), which was in the Western Regions. It was a practice for the Imperial Court to foster alliances with the northern tribes via marriage, and two Han princesses had married Wusun kings.
Feng Liao was the maidservant of Princess Jieyou (解憂公主), who was married off to a Wusun king. Feng herself later married an influential Wusun general, whose good standing with Prince Wujiutu (烏就屠) of the kingdom later proved beneficial to the Han dynasty.
When Prince Wujiutu seized the throne of Wusun in 64 BC, after his father died, there was fear in the Imperial Court of Han that Wujiutu, whose mother was Xiongnu, would allow Wusun to become Xiongnu's vassal.
Zheng Ji, Governor of the Western Regions, recalled that Feng Liao had married into Wusun and with her familiarity of the Wusun customs, she was a prime candidate to persuade Wujiutu to ally his kingdom with Han. Wujiutu acceded and Emperor Xuan of Han (漢宣帝) sent for Feng. He praised her for her judgement and diplomacy, and appointed her as the official envoy to Wusun.
Wujiutu was conferred the title "Little King of Wusun" while his brother, the son by a Han princess, was named "Great King of Wusun". Wusun was divided between the two kings and tensions in that region were eased.
※Xiongnu: Xiongnu: A nomadic tribe that has occupied northern China for a long time. Later it gradually became a state. It harassed the borders of the Han Dynasty for a long time and robbed supplies.
------
With their efforts, the Wusun Kingdom gradually tended to support the Han Dynasty, and the Xiongnu's defeat in China also began.
------
2.【Tang Dynasty】:Shangguan Wan'er(上官婉儿)&Princess Taiping (太平公主)
Shangguan Wan'er/上官婉儿 (664 – 21 July 710) was a Chinese politician, poet, and imperial consort of the Wu Zhou and Tang dynasties. Described as a "female prime minister,"Shangguan rose from modest origins as a palace servant to become secretary and leading advisor to Empress Wu Zetian of Zhou. Under Empress Wu, Shangguan exercised responsibility for drafting imperial edicts and earned approbation for her writing style. She retained her influence as consort to Wu's son and successor, Emperor Zhongzong of Tang, holding the imperial consort rank of Zhaorong (昭容). Shangguan was also highly esteemed for her talent as a poet.Shangguan was also highly esteemed for her talent as a poet. In 710, after Emperor Zhongzong's death, Shangguan was killed during a palace coup that ended the regency of Empress Dowager Wei.
Princess Taiping (太平公主)lit. "Princess of Great Peace", personal name unknown, possibly Li Lingyue (李令月) (after 662 – 2 August 713) was a royal princess and prominent political figure of the Tang dynasty and her mother Wu Zetian's Zhou dynasty. She was the youngest daughter of Wu Zetian and Emperor Gaozong and was influential during the reigns of her mother and her elder brothers Emperor Zhongzong and Emperor Ruizong (both of whom reigned twice), particularly during Emperor Ruizong's second reign, when for three years until her death, she was the real power behind the throne.
She is the most famous and influential princess of the Tang dynasty and possibly in the whole history of China thanks to her power, ability and ambition. She was involved in political difficulties and developments during the reigns of her mother and brothers. Indeed, after the coup against Empress Dowager Wei, she became the real ruler of Tang. During the reign of Emperor Ruizong, she was not restricted by anything, the emperor issued rulings based on her views and the courtiers and the military flattered her and majority from every civil and military class joined her faction, so her power exceeded that of the emperor.
Eventually, however, a rivalry developed between her and her nephew, Emperor Ruizong's son, Crown Prince Li Longji. Both of them were hostile in power-sharing and they fought for the monopoly over power. After Emperor Ruizong yielded the throne to Li Longji (as Emperor Xuanzong) in 712, the conflict came to the political forefront, and openly, the court became a manifestation of conspiracy rather than the administration of the empire; in 713, Emperor Xuanzong, according to historical records, believing that she was planning to overthrow him, acted first, executing a large number of her powerful allies and forcing her to commit suicide.
------
The relationship between Shangguan Wan'er and Princess Taiping has always been written as "enemies" in official history, but with the phrase "千年万岁,椒花颂声", their friendship that has been buried for thousands of years was revealed.
The"千年万岁,椒花颂声" sentence comes from the epitaph written by Princess Taiping for Shangguan Wan'er. The original text is: "潇湘水断,宛委山倾,珠沉圆折,玉碎连城。甫瞻松槚,静听坟茔,千年万岁,椒花颂声”
Translation: Now that you are far away, the sky and the earth will lose their color. I'm afraid that all I can do in the future is to sit and look at the tea tree in front of your tomb. Maybe I can hear your voice again when I stand within an inch of the tomb. But this is a delusion after all, a quiet tomb, no beautiful face, a empty place of death. I hope that in a thousand or ten thousand years, there will still be people like me who remember you.
------
3.【Late Qing Dynasty】:Lü Bicheng(呂碧城) & Qiu Jin (秋瑾)
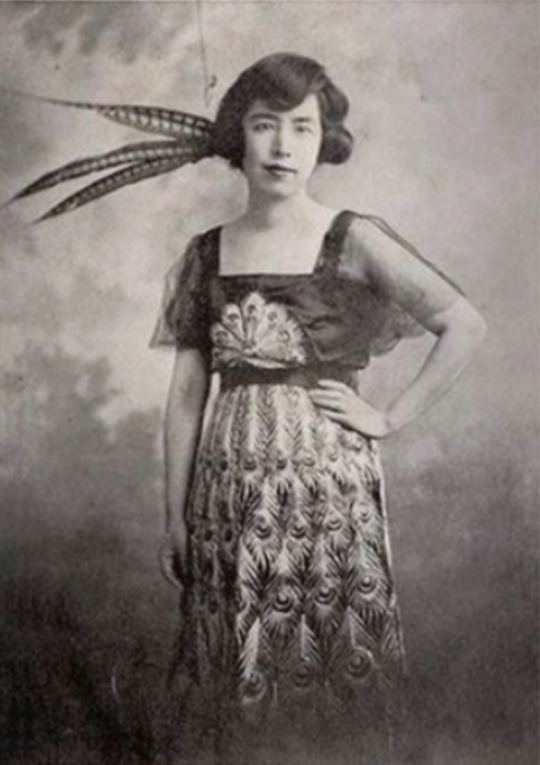

Lü Bicheng(呂碧城)also known as Alice Pichen Lee(1883–1943) was a Chinese writer, activist, newspaper editor, poet and school founder. She has been mentioned as one of the top four women in literature from the early Republic of China.
When she was four, her father retired to Lu'an, Anhui. She lived a life of comfort until the age of 12, when her father died in 1895. Because Lü Fengqi had no male heir, relatives of the Lü lineage contested for his inheritance, and Yan Shiyu and her four daughters were forced to move to Lai'an County to live with her natal family. When she was nine, Lü Bicheng was betrothed to a Wang family, but as her own family fortune declined, the Wang family broke off the marriage contract, giving the young Bicheng the stigma of a "rejected woman". The resulting emotional scar is often considered a major factor in her later decision to never marry.[8] Her widowed mother and the Lü girls were not well treated at the Yan family in rural Anhui. When Lü was 15 or 16, Yan Shiyu sent her to live with her maternal uncle Yan Langxuan (嚴朗軒), who was the salt administrator in Tanggu, the port city outside the northern metropolis of Tianjin. Her sister Huiru also joined her later.
During her stay in Tanggu, Qing China went through the tumultuous period of the failed Hundred Days' Reform of 1898, which brought about increasing awareness of women's education, and the Boxer Rebellion of 1900. In 1904, Mrs. Fang, the wife of her uncle's secretary, invited Lü Bicheng to visit a girls' school in Tianjin, but her uncle prevented her from going and severely reprimanded her. The next day, she ran away from her uncle's home, and took the train to Tianjin with no money or luggage. She wrote a letter to Mrs. Fang, who was staying at the dormitory of the Ta Kung Pao newspaper. Ying Lianzhi, the Catholic Manchu nobleman who founded the newspaper, read the letter and was so impressed by it that he made her an assistant editor. Lü Bicheng wrote a "progressive" ci that she had previously written, set to "A River Full of Red" ("Manjianghong") usually used to express heroic emotions. Ying transcribed the whole song in her diary and published it in L'impartial two days later. At the time, it was sensational for a woman to write for an influential national newspaper such as Ta Kung Pao. She was 21 years old. She used Ta Kung Pao to promote feminism and became a well-known figure.
Lü's ci poetry was published in the newspaper and it was very well received. She was the chief editor of the newspaper from 1904 to 1908. In 1904 she decided to improve education for girls. She had published her thoughts on women's rights and the general editor of the newspaper introduced her to Yan Fu who was an advocate for Western ideas. The Beiyang Women's Normal School was established that same year. At 23 Lü took on the job of principal of the school she had founded two years before. At first this school found it difficult to find girls who qualified for secondary education and students were brought in from Shanghai to make up the numbers.
Lü knew the revolutionary Qiu Jin and they had similar objectives but Lü did not join her in Japan when she was invited as she was unsure whether women should meddle in politics. She was then chosen to be secretary to Yuan Shikai, one of the most powerful people in China. When he set out to declare himself emperor of China she left, like many of his followers, and abandoned him.
--

Qiu Jin (秋瑾)8 November 1875 – 15 July 1907,was a Chinese revolutionary, feminist, and writer.Her sobriquet name is Jianhu Nüxia (Chinese: 鑑湖女俠 lit. 'Woman Knight of Mirror Lake').
Qiu was born into a wealthy family. Her grandfather worked in the Xiamen city government and was responsible for the city's defense. Zhejiang province was famous for female education, and Qiu Jin had support from her family when she was young to pursue her educational interests. Her father, Qiu Shounan, was a government official and her mother came from a distinguished literati-official family. Qiu Jin's wealthy and educated background, along with her early exposure to political ideologies were key factors in her transformation to becoming a female pioneer for the woman's liberation movement and the republican revolution in China.
In the early 1900s, Japan had started to experience western influences earlier than China. As to not fall behind, the Qing government sent many elites to learn from the Japanese. Qiu Jin was one of these elites that got the chance to study overseas. After studying in a women's school in Japan, Qiu returned to China to participate in a variety of revolutionary activities; and through her involvement with these activities, it became clear how Qiu wanted others to perceive her. Qiu called herself 'Female Knight-Errant of Jian Lake' — the role of the knight-errant, established in the Han dynasty, was a prototypically male figure known for swordsmanship, bravery, faithfulness, and self-sacrifice — and 'Vying for Heroism'
Qiu Jin had her feet bound and began writing poetry at an early age. With the support from her family, Qiu Jin also learned how to ride a horse, use a sword, and drink wine—activities that usually only men were permitted to learn at the time.In 1896 Qiu Jin got married. At the time she was only 21, which was considered late for a woman of that time. Qiu Jin's father arranged her marriage to Wang Tingchun, the youngest son of a wealthy merchant in Hunan province. Qiu Jin did not get along well with her husband, as her husband only cared about enjoying himself.While in an unhappy marriage, Qiu came into contact with new ideas. The failure of her marriage affected her decisions later on, including choosing to study in Japan.
While still in Tokyo, Qiu single-handedly edited a journal, Vernacular Journal (Baihua Bao). A number of issues were published using vernacular Chinese as a medium of revolutionary propaganda. In one issue, Qiu wrote A Respectful Proclamation to China's 200 Million Women Comrades, a manifesto within which she lamented the problems caused by bound feet and oppressive marriages. Having suffered from both ordeals herself, Qiu explained her experience in the manifesto and received an overwhelmingly sympathetic response from her readers. Also outlined in the manifesto was Qiu's belief that a better future for women lay under a Western-type government instead of the Qing government that was in power at the time. She joined forces with her cousin Xu Xilin and together they worked to unite many secret revolutionary societies to work together for the overthrow of the Qing dynasty.
Between 1905 and 1907, Qiu Jin was also writing a novel called Stones of the Jingwei Bird in traditional ballad form, a type of literature often composed by women for women audiences. The novel describes the relationship between five wealthy women who decide to flee their families and the arranged marriages awaiting them in order to study and join revolutionary activities in Tokyo. Titles for the later uncompleted chapters suggest that the women will go on to talk about “education, manufacturing, military activities, speechmaking, and direct political action, eventually overthrowing the Qing dynasty and establishing a republic” — all of which were subject matters that Qiu either participated in or advocated for.
Life after returning to China
Qiu Jin was known as an eloquent orator who spoke out for women's rights, such as the freedom to marry, freedom of education, and abolishment of the practice of foot binding. In 1906 she founded China Women's News (Zhongguo nü bao), a radical women's journal with another female poet, Xu Zihua in Shanghai. They published only two issues before it was closed by the authorities. In 1907, she became head of the Datong school in Shaoxing, ostensibly a school for sport teachers, but really intended for the military training of revolutionaries[citation needed]. While teaching in Datong school, she kept secret connection with local underground organization—The Restoration Society. This organization aimed to overthrow the Manchu government and restore Chinese rule.
Death
In 1907, Xu Xilin, Qiu’s friend and the Datong school’s co-founder was executed for attempting to assassinate his Manchu superior. In the same year, the authorities arrested Qiu at the school for girls where she was the principal. She was tortured but refused to admit her involvement in the plot. Instead the authorities used her own writings as incrimination against her and, a few days later, she was publicly beheaded in her home village, Shanyin, at the age of 31. Her last written words, her death poem, uses the literal meaning of her name, Autumn Gem, to lament of the failed revolution that she would never see take place:
秋風秋雨愁煞人
(Autumn wind, autumn rain — they make one die of sorrow)
After Qiu Jin was killed, no one dared to collect her body. Lu Bicheng endured her grief and took great risks to bury her friend. The guarding Qing army learned that the woman who came to collect the corpse was Lu Bicheng, who was famous in China, and they had no choice but to do anything.
Qiu Jin's death caused Lu Bicheng to lose a rare confidant in life. She wrote many poems in memory of Qiu Jin, recalling this like-minded friend.
Later, Lü Bicheng wrote "The Biography of the Revolutionary Heroine Qiu Jin" in English, which was published in newspapers in New York, Chicago and other places in the United States. It caused a great response and not only made many people in the world know about Qiu Jin's legendary story, but also published it in newspapers in New York and Chicago. It also makes people understand the darkness and corrupt social status quo of the Qing Dynasty. Lu Bicheng used a pen of her own to record her friendship with Qiu Jin, and also fulfilled her promise to Qiu Jin to respond with the "battle of words"
————————
📸Video & 🧚🏻 Model:@荷里寒 & @阿时Ashi_
🔗Weibo:https://weibo.com/3618951560/NEZZnpQRq
————————
#chinese hanfu#china history#woman power#woman in history#hanfu#hanfu accessories#hanfu_challenge#chinese traditional clothing#china#chinese#han dynasty#tang dynasty#late qing dynasty#feminism#revolution#漢服#汉服#中華風#girl power#hanfu girl
358 notes
·
View notes
Text
"are you lost, baby girl?" I ask and a dozen middle aged men and murderers turn towards me and blush heavily.
#2ha#chu wanning#mdzs#lan wangji#tgcf#hua cheng#mu qing#yin yu#word of honor#zhou zishu#han ying#wen kexing#mo xiang tong xiu#mxtx#svsss#lou binghe#liu qingge#shen qingqiu#thousand autumns#shen qiao#guardian#shen wei#donghua#manghua#danmei#anime#bsd#bungou stray dogs#nakahara chuuya#kunikida doppo
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
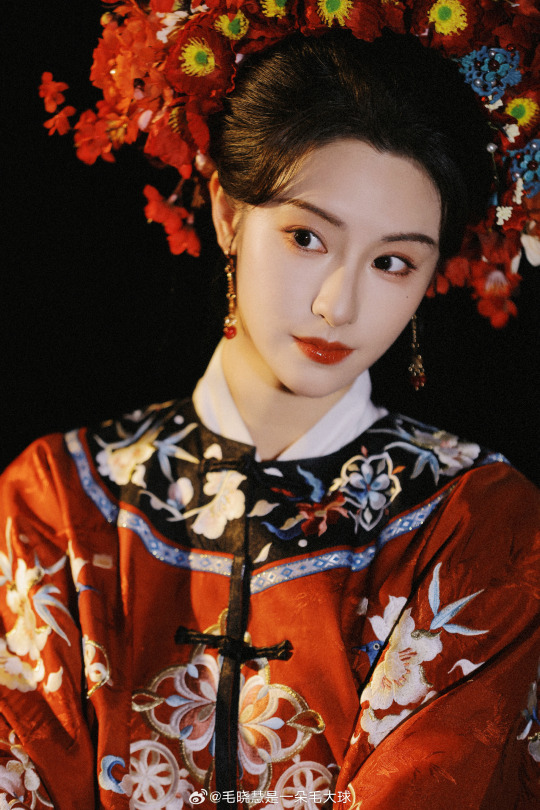
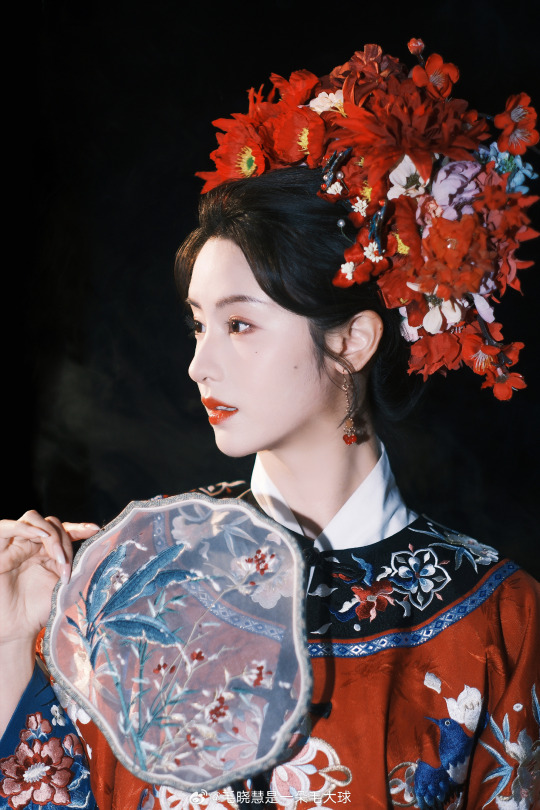









MAO XIAOHUI 毛晓慧 | qing han nv zhuang photoshoot
Mao Xiaohui: more photos here
qing han nv zhuang photoshoot: more photos here
100 notes
·
View notes
Photo
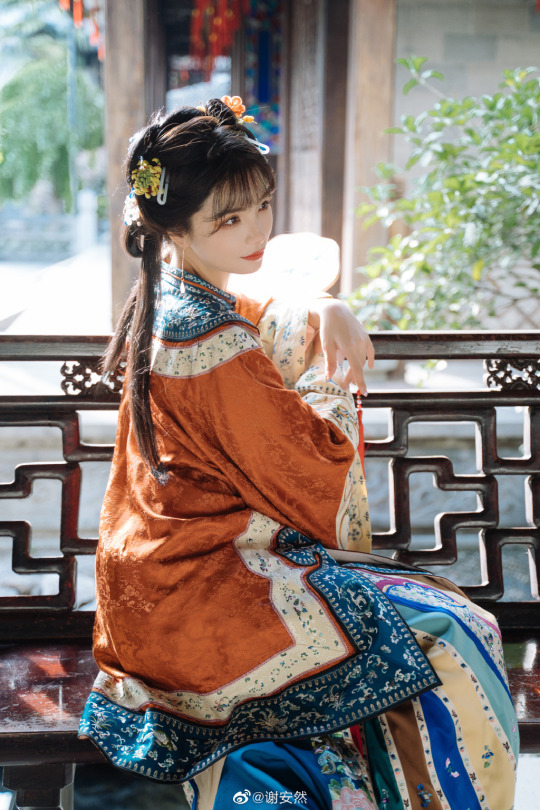
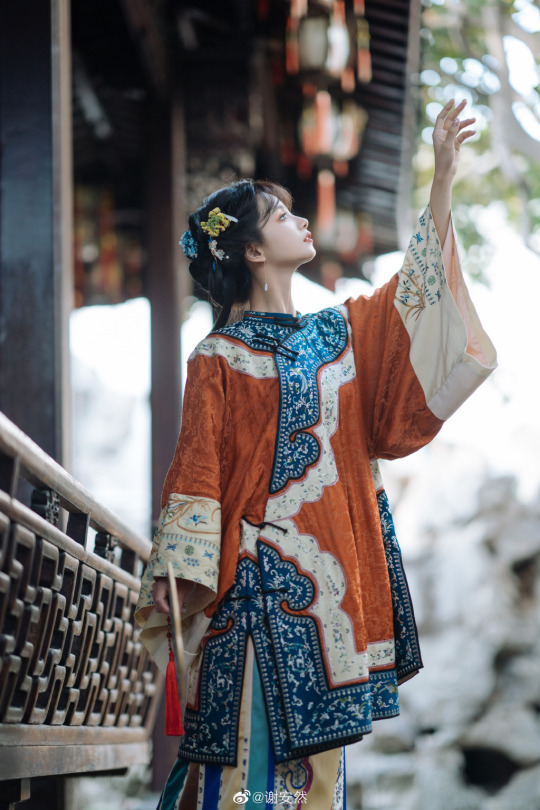
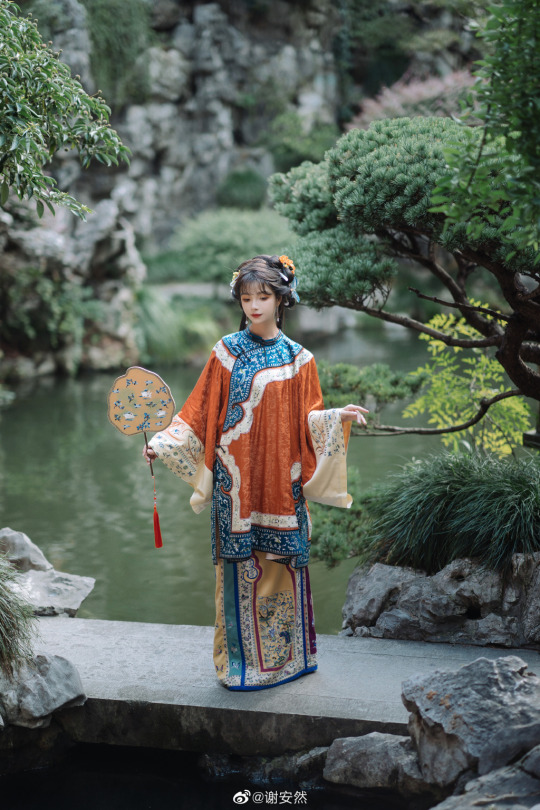
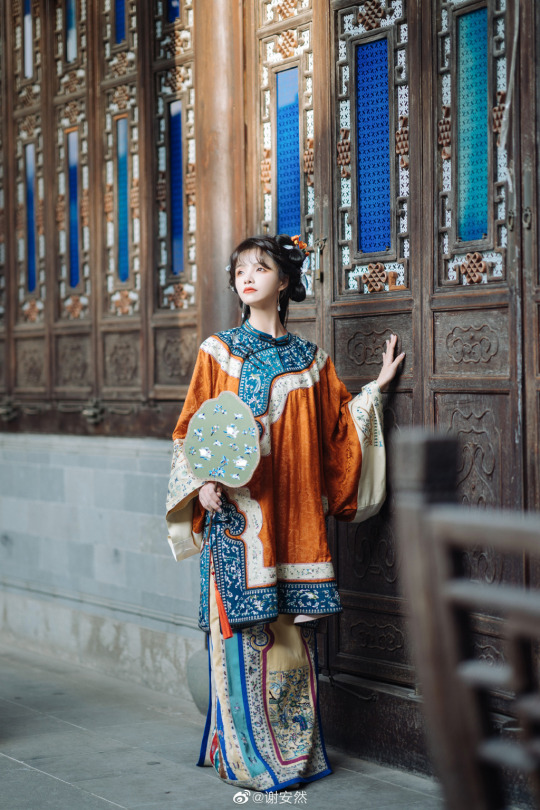
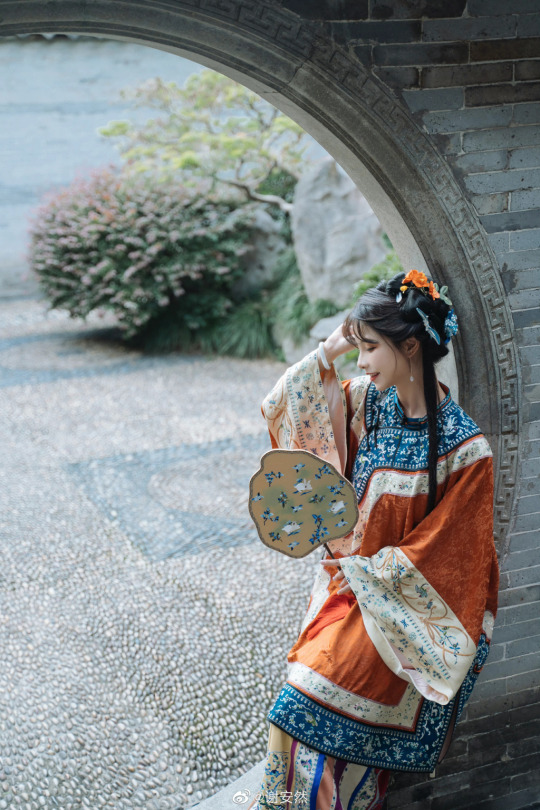








han women’s fashion in qing dynasty by 谢安然 | qing han nv zhuang 清汉女装
515 notes
·
View notes
Text












Chinese Dynasties.
Shang | Zhou | Qin | Han | Jin | Sui | Tang | Liao | Song | Yuan | Ming | Qing
#qing dynasty#han dynasty#qin dynasty#shang dynasty#ming dynasty#zhou dynasty#tang dynasty#yuan dynasty#song dynasty#jin dynasty#sui dynasty#liao dynasty#story of yanxi palace#ruyi's royal love in the palace#empress ki#house of the flying daggers#legend of xiao chuo#red cliff#zhao wei#the king's woman#legend of haolan
147 notes
·
View notes
Text









Cdrama: Different Princess (2024)
Gifs of Intro of cdrama "Different Princess"
[Different Princess] EP01 | Writer Travels into Her Book | Song Yiren/Sun Zujun/Ding Zeren | YOUKU
Watch this video on Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HFcV251ppto
#Different Princess#花青歌#Flower Green Song#Hua Qing Ge#Fa Cheng Go#2024#youtube#cdrama#chinese drama#episode 1#1st episode#Youku#Web Series#Ireine Song#Ding Ze Ren#Zhu Rong Jun#Sun Zu Jun#Zhang Yue Nan#Chen Ze#Chu Han#Chen Ming
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
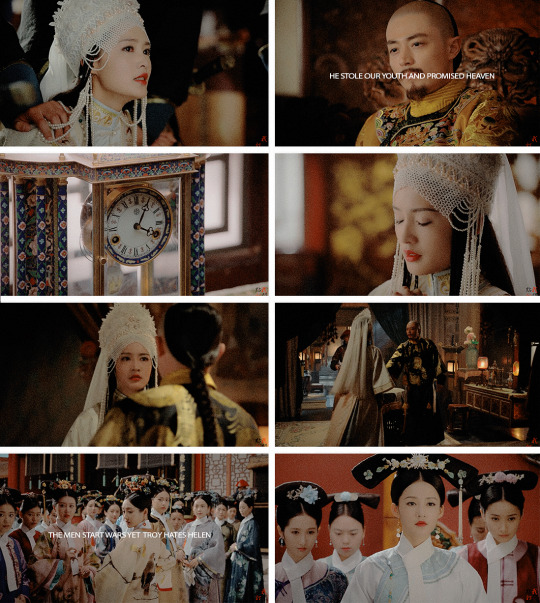

#ruyi's royal love in the palace#легенда про жуї#дорами українською#chinese drama#cdramaedit#ruyi zhuan#dramaedit#如懿传#perioddramaedit#onlyperioddramas#qing dynasty#han xiangjian#consort rong#my poor baby#maisie peters lyrics#history of man
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
Abridged History of Qing Dynasty Han Women’s Fashion (part 5: Late Qianlong & Jiaqing eras)

(artwork from 1782)
Previous posts:
Late Ming & Shunzhi era
Kangxi era
Late Kangxi & Yongzheng eras
Qianlong era
The last two decades of the Qianlong era, the 1780s and 90s, formed one aesthetic continuity with the reign of Qianlong’s successor Jiaqing (1796-1820). This period was characterized by a turn to extreme formal simplicity and what I believe to be a revival of the tastes of the Ming-Qing transition.
We see sleeves of women’s robes, tight fitting and short to create a practical look in the previous era, become wider and longer. The folded cuff design was retained, though now more difficult to manage as the sleeves became wider. In the last post I discussed how the construction of dajin similar to Manchu men’s fashion became en vogue among Han women and replaced the earlier center front closing robes----this remained the same. We see some of the first instances of binding strips being used around the collar and the dajin, which would become a highly popular and elaborate craft later in the 19th century. Around this time, the binding strips used were usually thin and minimal, commonly of a black color. Plain cloth or bead tip buttons were popularized earlier in the Qianlong era, and metal clasp buttons (zimukou) became increasingly rare. The shape of the standing collar remained the same as that of previous centuries, soft, unstiffened and tall.

Artwork from 1796 showing a group of courtesans. You can see the black binding on some of their robes. A note about the dating of this artwork: while it’s quite a common reference image for Jiaqing era fashion, I wasn’t able to find an exact date until I read about it in the book Pictures for Pleasure and Use by James Cahill (spectacular book discussing the importance of vernacular and commercial art, highly recommend) and he said the date of creation was signed in the cyclical calendar and corresponds to either 1736 or 1796. He was inclined to 1736 because of “similar face shapes” or something to Yongzheng era artworks, but since he wasn’t a fashion historian he probably wasn’t aware that the fashions depicted here would not have been possible before the 1780s, so I think 1796 is instead the correct date.
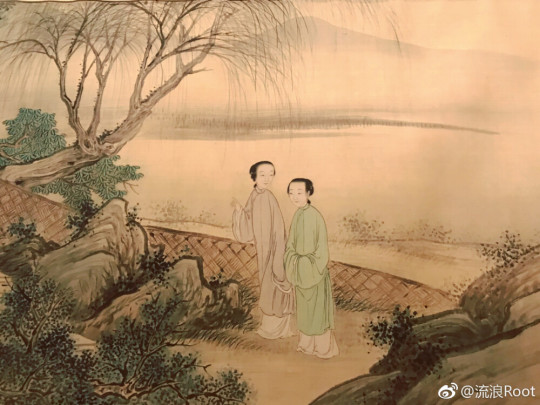

Late Qianlong/early Jiaqing era artwork, showing two austerely (and fashionably) dressed women.
The more radical departure from the previous era, however, was the complete eradication of ornament. Robes and skirts of this era were often entirely plain, with no brocaded patterns or embroidery of any kind. Gone were the roundel patterns, quatrefoil motifs on collar facings and decorative strips around skirts----only solid color blocks remained. Pastel colors like light pink, blue and green were among the most popular for robes besides bright blue and red, whereas skirts were white or black.


Late Qianlong/early Jiaqing era paintings of the Anglo-Chinese school showing the new style of plain garments.

Artwork from the era showing a woman in a light mustard robe with dusty pink cuffs, white skirt and red sash (sashes were still commonly worn).
The other significant changes happened in hairstyling. The 1780s did away with the iconic tall knots of the earlier Qianlong era, instead moving the mass and volume of hair toward the back. We see the re-emergence of the swallow tail. The front of the hair could be middle parted or completely pulled back. Flowers and other ornaments could be worn on the sides of the hairdo, behind the ears. The general shape of hairstyles stressed horizontality rather than verticality, as was the case before.

A 1943 copy of a turn of the 19th century original, showing the front and back of hairstyles.

Bust portrait showing the new hairstyle.
A unique hair accessory of the 1780s and 90s was a new iteration of the mo’e, which now had a sharply pointed triangular front and was worn high on the head instead of at the forehead. I think it became less common as the 19th century approached.
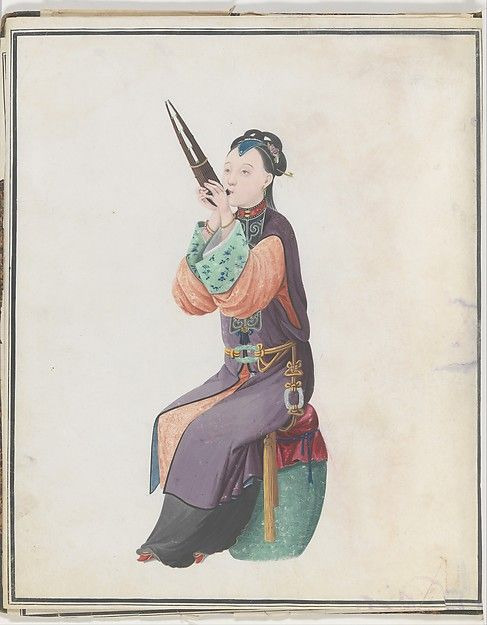

Export artwork showing a woman musician, likely 1770s or 80s as she is still wearing the ornamented, center front closing robes popular in previous decades.
Minimalism was not to last long, however, and soon decorative patterns began to reappear on robes, sleeve cuffs and skirts. Hairstyles began to gain volume and became more puffed, forming a sort of face framing crown. New styles of decorating skirts appeared, with binding going around the qunmen and the edge of each pleat, and embroidery on each individual pleat. The rectangular or circular patterned patch popular prior to the 1780s returned.

Early 19th century export painting at the Brighton Pavilion, maybe 1810s. We can see roundel patterns on the blue robe, embroidery on the cuffs and skirt, and the lady in red wears a pointed mo’e.

Presumably later Jiaqing era artwork, ca. 1810s, showing a group of women. Floral embroidery is present on the sleeve cuffs, the skirts are decorated.
#abridged history of qing dynasty han women's fashion#18th century#19th century#qianlong era#jiaqing era#qing dynasty#chinese fashion#fashion history#regency era
177 notes
·
View notes
Text

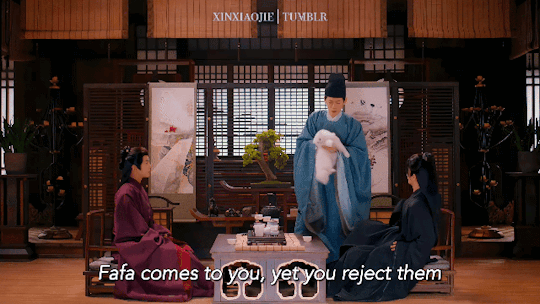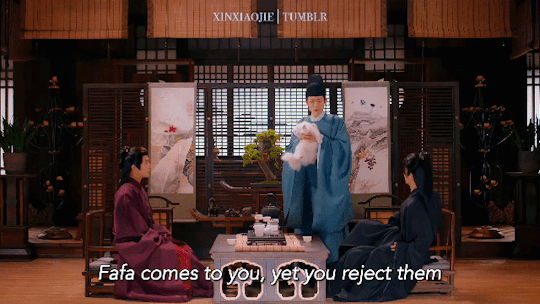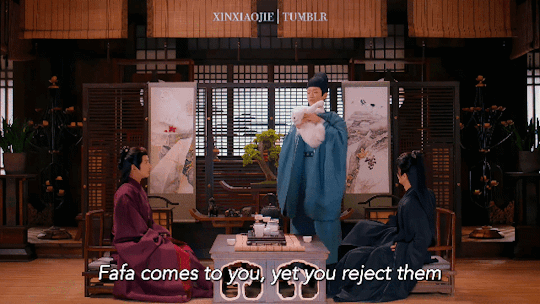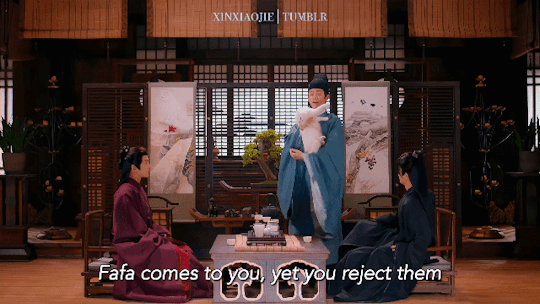








Huaihuai, Fafa & Hanhan 🐱
#花琉璃轶闻#Royal Rumours#Hua Liu Li Yi Wen#cdramasource#chineseartistsinc#asiandramasource#dramasource#dailyasiandramas#cdramaedit#chinesemedia#cdramanet#cdramagifs#chinese drama#cdrama#caps#pei jihuai#li qing#li fei#yun han#xu zheng xi#jeremy xu#xu zhengxi#ep8#ot3??? dont mind if i do i'll eat this up anyday#fafa best character in the whole show nobody @me also i feel like hanhan isnt a fan of cats bc hes a cat himself
82 notes
·
View notes
Photo
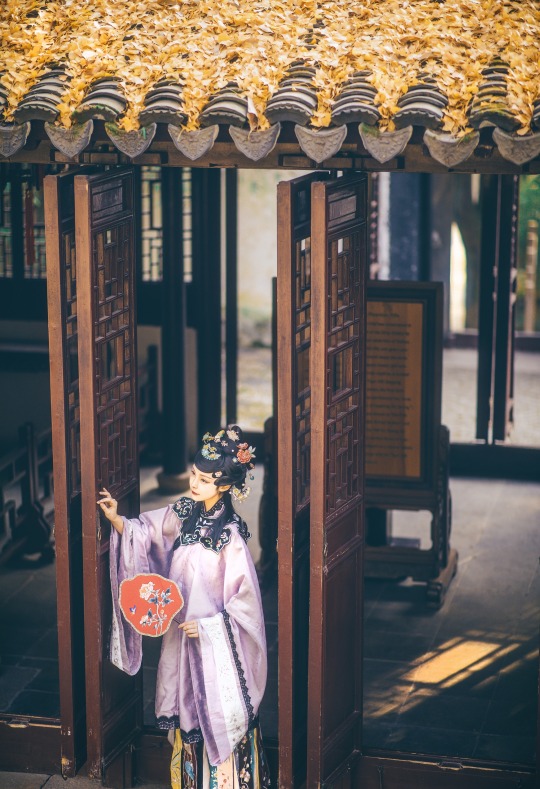
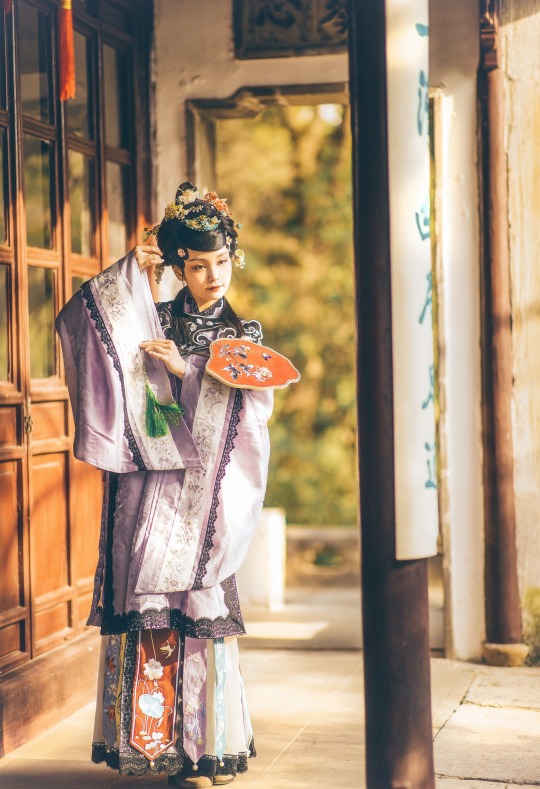
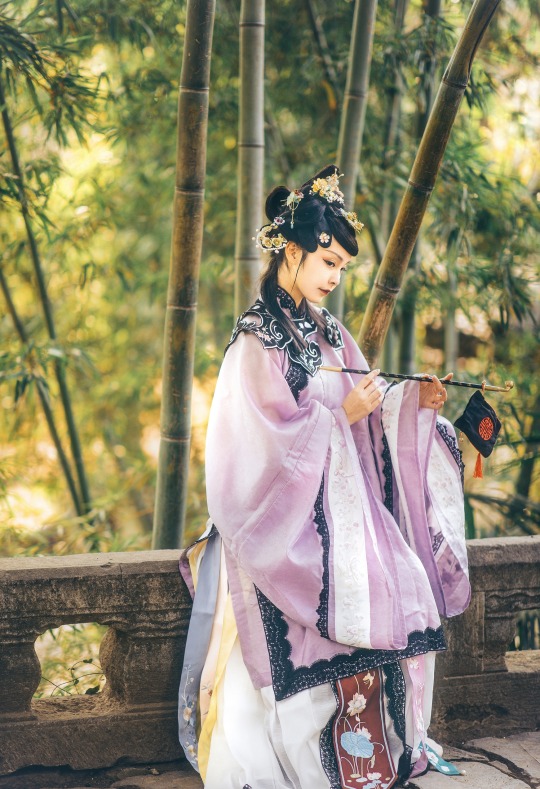
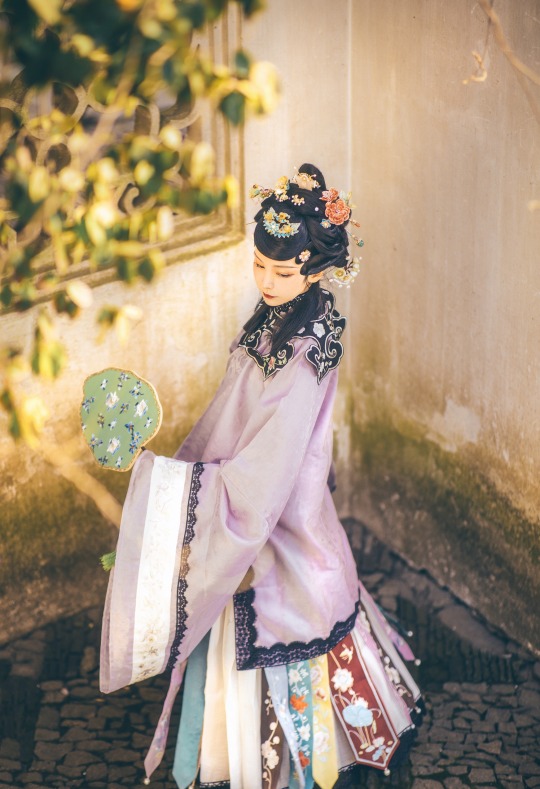
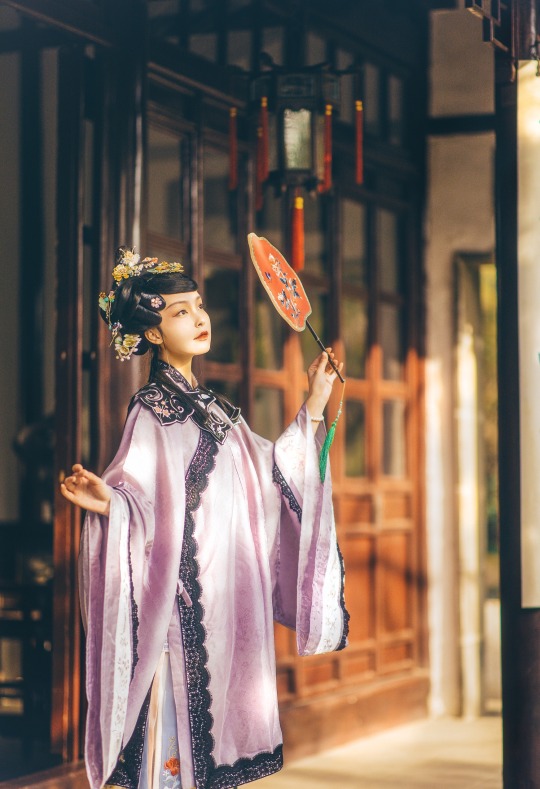
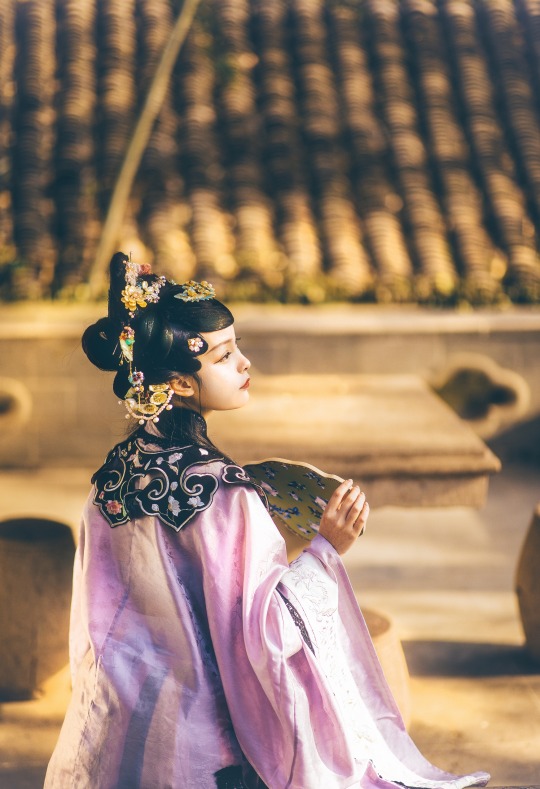
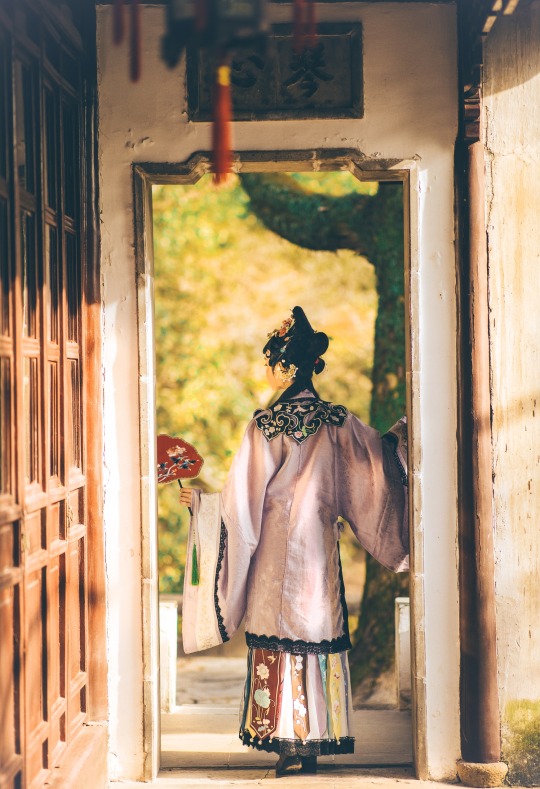
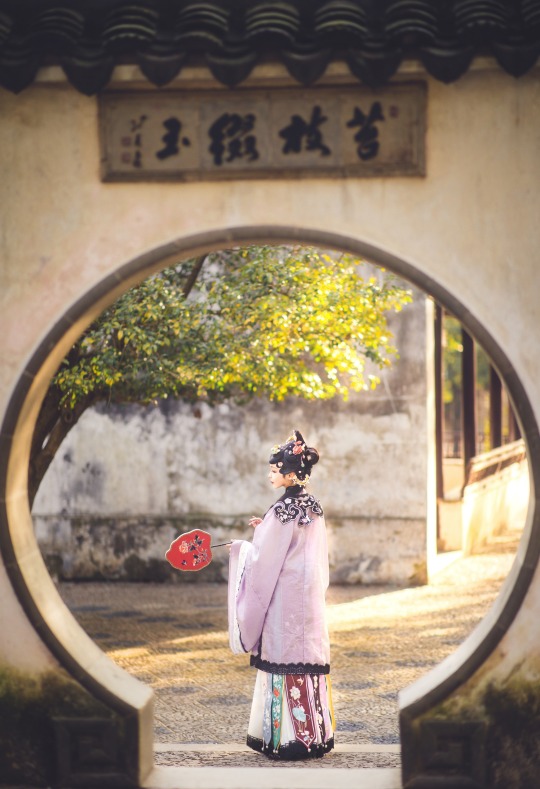









𝒮𝓊𝓃𝓃𝓎𝓊𝒻ℯ𝒾元気姬
#Qing Dynasty#Mamianqun#Qizhuang#Yunjian#Cloud collar#Han women’s clothing of the Qing Dynasty#Manchu Fashion#Chinese Fashion#Fashion
216 notes
·
View notes
Text
oh yeah my roommate said wei wuxian is anakin skywalker if he was a communist not a fascist and they were so right i had to sit there quietly for a sec and digest it. think about it.
#LANWANGHI IS SOOOO PADME TOOOOO ARE YOU SERIOUS#obiwan as jiang cheng. it makes sense#does that make lan qiren yoda. mace windu?#whos liam neeson i cant be bothered to think of that guys name#MAUL IS XUE YANGGGGGGGGGG#guys im kinda on a roll here#i guess wen rouhan or wtvr his name is is palpytine#lmao lan xichenxis jarjar#obv lan suizhui is luke. OBVVVVV#jin ling is leia. lan jingyi is han#ouyang zizhen is lando i except no other options#bc fairy is chewwie. my god im a genius#wen ning is ahsokha? and then wen qing could be rex or cody…..#this needs to stop im gonna go read a time travel fix it au#jace.txt
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
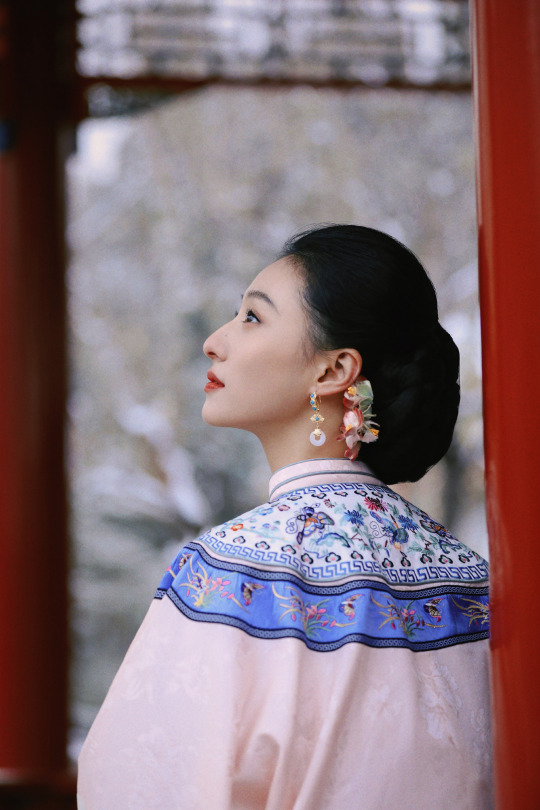
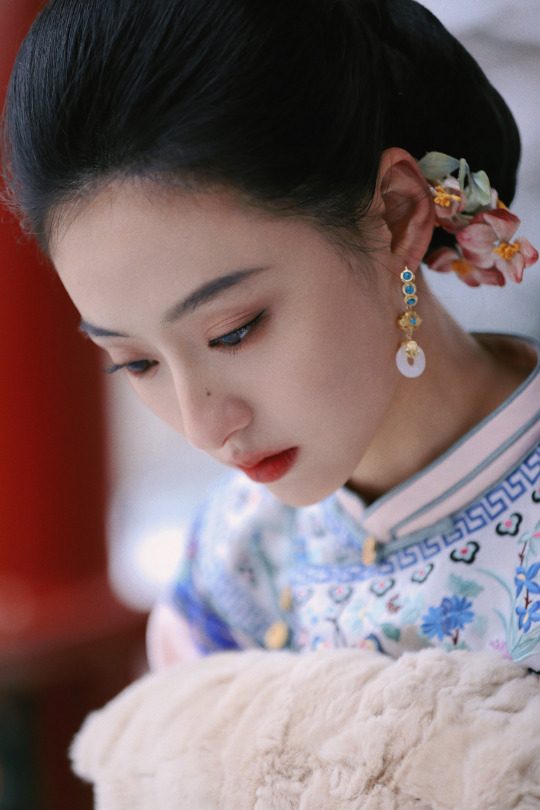






HU LIANXIN 胡连馨 in qing han nv zhuang | winter photoshoot
Hu Lianxin: more photos here
winter photoshoot: more photos here
qing han nv zhuang photoshoot: more photos here
#hu lianxin#胡连馨#chinese actress#chinese fashion#fashion#cnladies#photoshoots#winter photoshoot#winter#winter photos#winter photography#qing han nv zhuang
61 notes
·
View notes
Photo
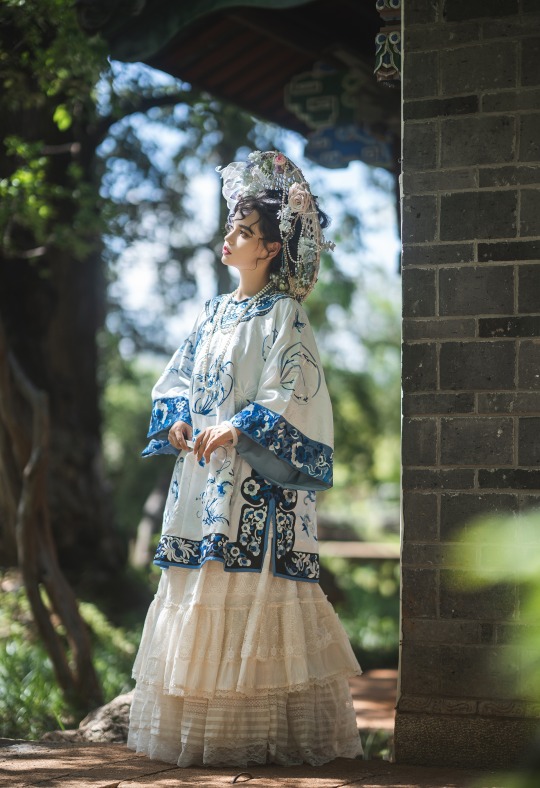
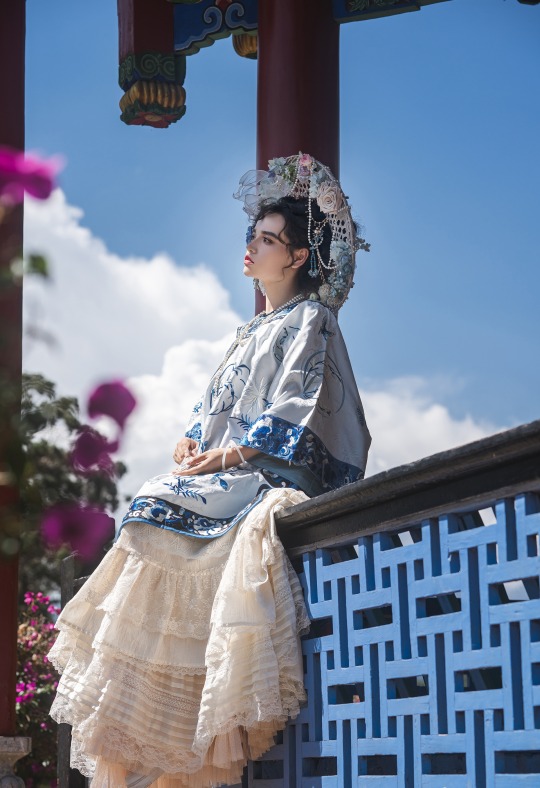
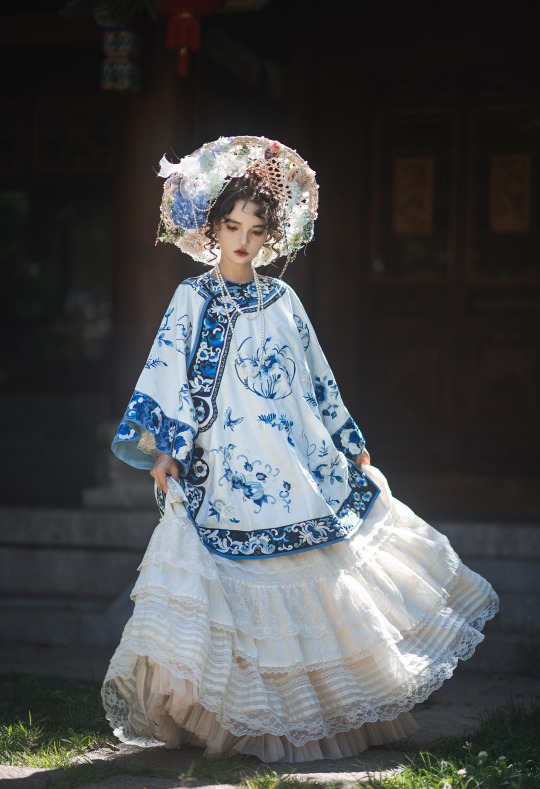
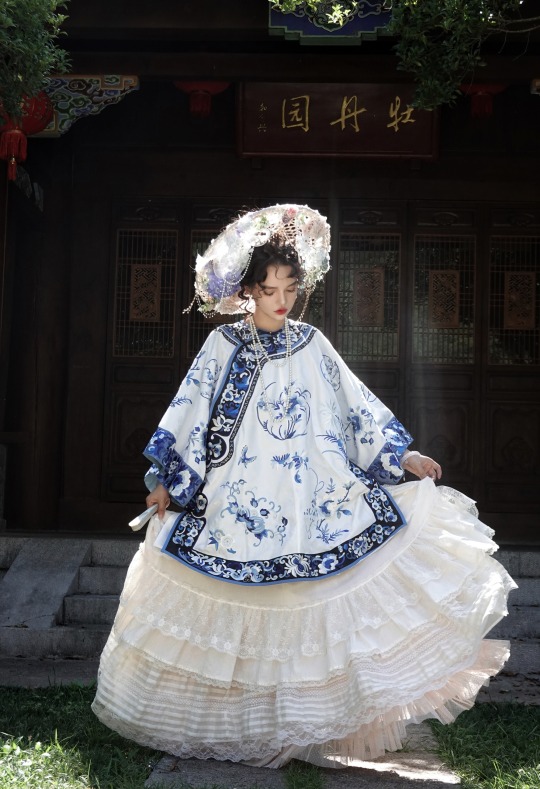








𝒬𝒾𝓏𝒽𝓊𝒶𝓃𝑔/旗装: 花神妙华服
𝑀𝑜𝒹𝑒𝓁: 肉肉馅团子
𝒞𝒶𝓂𝑒𝓇𝒶: 花轮子哥哥
𝑀𝒶𝓀𝑒𝓊𝓅: 蚊𝓌𝓌𝓌桑
150 notes
·
View notes
Text
This post is not an invitation for sinophobia piss off
God hanfu spaces can be so vile 💀 using 'manchu' and 'dog' so interchangeably is crazy, reason 10339405060 why I never look into the comments of Twitter posts abt hanfu
#diary#hater tag#stop oppression complexing we've been at the bottom of the hierarchy for a century and were at the bottom before qing as well#i try to keep this in private but you can only see ur ppl called so many slurs before getting irritated#also han women continued wearing hanfu into qing+ hanfu is better preserved than many ethnic minority clothing histories but whatever#i dont want to incite sinophobia but if i have to see 1 more person pretending theyre so kind for treating us minorities so fucking well#lol#as someone w plenty of experience of racism both back home in the mommyland and in c*nada#oh my god lol i keep quiet and struggle against sinophobia as much as i can but it feels like im defending ppl who see me as dirt sometimes#my tags have spiraled and arent rlly abt manchu anymore ngl 😨 my worst experiences at home have been wrt being hui and muslim lolol#since manchu are sinicized basically only terminally online pplare haters#anyways i might delete this later but ive kept quiet as much as i can for a long time and its getting frustrating#also hui and manchu are aggressively sinicized so the way i know less sinicized minorities have it even worse than my familyand i lol
11 notes
·
View notes
Photo

#cdrama#love between fairy and devil#cdramaedit#night of love with you (2022)#night of love with you#cang lan jue#dong fang qing cang#xiao lan hua#leng ye han#luo qing#qi qi#夜色倾心#苍兰诀#my memes#memes#userstorge
63 notes
·
View notes
Text










Cdrama: Different Princess (2024)
Gifs of Ending of cdrama "Different Princess"
[Different Princess] EP01 | Writer Travels into Her Book | Song Yiren/Sun Zujun/Ding Zeren | YOUKU
Watch this video on Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HFcV251ppto





#Different Princess#花青歌#Flower Green Song#Hua Qing Ge#Fa Cheng Go#2024#youtube#cdrama#chinese drama#episode 1#1st episode#Youku#Web Series#Ireine Song#Ding Ze Ren#Zhu Rong Jun#Sun Zu Jun#Zhang Yue Nan#Chen Ze#Chu Han#Chen Ming
5 notes
·
View notes