#national oceanic and atmospheric administration
Text
Dharna Noor at The Guardian:
Climate experts fear Donald Trump will follow a blueprint created by his allies to gut the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (Noaa), disbanding its work on climate science and tailoring its operations to business interests.
Joe Biden’s presidency has increased the profile of the science-based federal agency but its future has been put in doubt if Trump wins a second term and at a time when climate impacts continue to worsen.
The plan to “break up Noaa is laid out in the Project 2025 document written by more than 350 rightwingers and helmed by the Heritage Foundation. Called the Mandate for Leadership: The Conservative Promise, it is meant to guide the first 180 days of presidency for an incoming Republican president.
The document bears the fingerprints of Trump allies, including Johnny McEntee, who was one of Trump’s closest aides and is a senior adviser to Project 2025. “The National Oceanographic [sic] and Atmospheric Administration (Noaa) should be dismantled and many of its functions eliminated, sent to other agencies, privatized, or placed under the control of states and territories,” the proposal says.
That’s a sign that the far right has “no interest in climate truth”, said Chris Gloninger, who last year left his job as a meteorologist in Iowa after receiving death threats over his spotlighting of global warming.
The guidebook chapter detailing the strategy, which was recently spotlighted by E&E News, describes Noaa as a “colossal operation that has become one of the main drivers of the climate change alarm industry and, as such, is harmful to future US prosperity”. It was written by Thomas Gilman, a former Chrysler executive who during Trump’s presidency was chief financial officer for Noaa’s parent body, the commerce department.
Gilman writes that one of Noaa’s six main offices, the Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research, should be “disbanded” because it issues “theoretical” science and is “the source of much of Noaa’s climate alarmism”. Though he admits it serves “important public safety and business functions as well as academic functions”, Gilman says data from the National Hurricane Center must be “presented neutrally, without adjustments intended to support any one side in the climate debate”.
[...]
Noaa also houses the National Weather Service (NWS), which provides weather and climate forecasts and warnings. Gilman calls for the service to “fully commercialize its forecasting operations”.
He goes on to say that Americans are already reliant on private weather forecasters, specifically naming AccuWeather and citing a PR release issued by the company to claim that “studies have found that the forecasts and warnings provided by the private companies are more reliable” than the public sector’s. (The mention is noteworthy as Trump once tapped the former CEO of AccuWeather to lead Noaa, though his nomination was soon withdrawn.)
The claims come amid years of attempts from US conservatives to help private companies enter the forecasting arena – proposals that are “nonsense”, said Rosenberg.
Right now, all people can access high-quality forecasts for free through the NWS. But if forecasts were conducted only by private companies that have a profit motive, crucial programming might no longer be available to those in whom business executives don’t see value, said Rosenberg.
[...]
Fully privatizing forecasting could also threaten the accuracy of forecasts, said Gloninger, who pointed to AccuWeather’s well-known 30- and 60-day forecasts as one example. Analysts have found that these forecasts are only right about half the time, since peer-reviewed research has found that there is an eight- to 10-day limit on the accuracy of forecasts.
The Trump Administration is delivering a big gift to climate crisis denialism as part of Project 2025 by proposing the dismantling and privatizing the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and National Weather Service (NWS) in his potential 2nd term.
This should frighten people to vote Democratic up and down the ballot if you want the NOAA and NWS to stay intact.
#Project 2025#Climate Change#Climate Crisis#Weather#AccuWeather#National Weather Service#NOAA#NWS#John McEntee#The Heritage Foundation#Donald Trump#Climate Change Denialism#Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research#National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration#Climate Crisis Denial
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
Atlantic Tropical Weather Outlook issued by the National Hurricane Center in Miami, FL, USA
2024-04-24, 20:00 EDT

For the North Atlantic...Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico:
East-Central Subtropical Atlantic: An area of low pressure located about 900 miles northwest of the Cabo Verde Islands has been producing a small but persistent area of showers and thunderstorms to the east of its center since this morning. However, the low is forecast to move southwestward at 10 to 15 mph into an area of stronger upper-level winds tonight and tomorrow, and additional development is not expected.
No additional Special Tropical Weather Outlooks are scheduled for this system unless conditions warrant. Regularly scheduled Tropical Weather Outlooks will resume on May 15, 2024, and Special Tropical Weather Outlooks will be issued as necessary during the remainder of the off-season.
* Formation chance through 48 hours...low...10 percent.
* Formation chance through 7 days...low...10 percent.
$$ Forecaster Berg/Brown
#sorry the beginning of the text was cut off at first! fixed now#the NHC changes the advisory formatting every year ever so slightly so i have to adjust how the bot parses them the first few posts lol#not gonna bother fixing the text timestamp since they sorta just post the special advisories whenever#bot tags:#bot post#meteorology#weather#tropical weather#tropical storm#tropical depression#hurricane#atlantic#atlantic ocean#caribbean#gulf of mexico#noaa#national oceanic and atmospheric administration#nhc#national hurricane center
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
In a week when parts of the state are getting triple-digit temperatures and weather officials urge Texans to stay cool and hydrated, Gov. Greg Abbott gave final approval to a law that will eliminate local rules mandating water breaks for construction workers.
House Bill 2127 was passed by the Texas Legislature during this year’s regular legislative session. Abbott signed it Tuesday. It will go into effect on Sept. 1.
Supporters of the law have said it will eliminate a patchwork of local ordinances across the state that bog down businesses. The law’s scope is broad but ordinances that establish minimum breaks in the workplace are one of the explicit targets. The law will nullify ordinances enacted by Austin in 2010 and Dallas in 2015 that established 10-minute breaks every four hours so that construction workers can drink water and protect themselves from the sun. It also prevents other cities from passing such rules in the future. San Antonio has been considering a similar ordinance.
Texas is the state where the most workers die from high temperatures, government data shows. At least 42 workers died in Texas between 2011 and 2021 from environmental heat exposure, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Workers’ unions claim this data doesn’t fully reflect the magnitude of the problem because heat-related deaths are often recorded under a different primary cause of injury.
This problem particularly affects Latinos because they represent six out of every 10 construction workers, according to U.S. Census Bureau data.
Unions expect heat-related deaths to go up if mandated water breaks go away.
“Construction is a deadly industry. Whatever the minimum protection is, it can save a life. We are talking about a human right,” said Ana Gonzalez, deputy director of policy and politics at the Texas AFL-CIO. “We will see more deaths, especially in Texas’ high temperatures.”
The National Weather Service is forecasting highs over 100 degrees in several Texas cities for at least the next seven days.
Heat waves are extreme weather events, often more dangerous than tornadoes, severe thunderstorms or floods. High temperatures kill people, and not just in the workplace. Last year, there were 279 heat-related deaths in Texas, based on data analysis by The Texas Tribune.
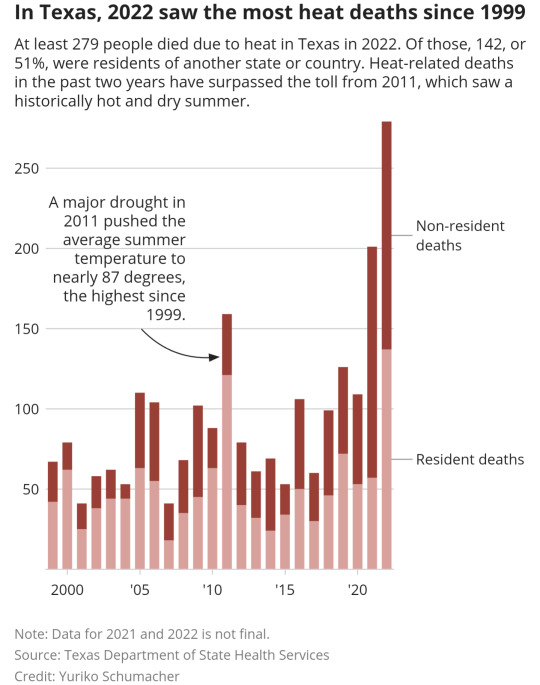
In 2022, Texas saw its second-hottest summer on record, and an extreme drought swept the state. This summer is not expected to be as hot as the weather pattern known as La Niña eases, which typically brings dry conditions to Texas, state climatologist John Nielsen-Gammon said.
Still, climate change amplifies the effects of heat waves, said Hosmay Lopez, an oceanographer at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration who studies heat waves. Climate change causes heat waves to stretch for longer periods of time, reach higher temperatures and occur more often than they would otherwise. The problem is especially pronounced in dry areas of the Southwest due to a lack of vegetation and soil moisture, which in wetter regions produces a cooling effect through evaporation.
At the same time, he added, increased urbanization across the U.S. — especially in places like Texas where cities are expanding — makes more people vulnerable to health dangers from extreme heat due to the “urban island” effect. Essentially, the combination of concrete and buildings, plus a lack of green spaces causes ground-level heat to radiate, increasing the temperature in cities.
“The impact of climate change on extreme heat is not only enhanced [by weather events] but also enhanced through social dynamics as well,” Lopez said.
HB 2127, introduced by state Rep. Dustin Burrows, R-Lubbock, is perhaps Texas Republicans’ most aggressive attempt to curb progressive policies in the state’s largest, liberal-leaning cities. Under the new law, local governments would be unable to create rules that go beyond what state law dictates in broad areas like labor, agriculture, business and natural resources.
Beyond eliminating mandated water breaks for construction workers, opponents of the legislation argue that it will also make it more difficult for cities and counties to protect tenants facing eviction or to combat predatory lending, excessive noise and invasive species. Labor unions and workers’ rights advocates opposed the law, while business organizations supported it, including the National Federation of Independent Business, a lobbying group with more than 20,000 members in Texas. Abbott said it would “provide a new hope to Texas businesses struggling under burdensome local regulations.”
Supporters of HB 2127 say that local regulations on breaks for construction workers are unnecessary because the right to a safe labor environment is already guaranteed through the Occupational Safety and Health Administration.
Water breaks are better solved by OSHA controls, argued Geoffrey Tahuahua, president of Associated Builders and Contractors of Texas. Tahuahua believes local rules impose a rigid scheme that, unlike OSHA guidelines, does not allow the flexibility needed to tailor breaks to individual job site conditions.
“They try to make one size fits all, and that is not how it should work,” he said. “These ordinances just add confusion and encourage people to do the minimum instead of doing the right thing.”
David Michaels, who was head of OSHA from 2009 to 2017, disagreed with the approach of HB 2127 proponents.
“Under OSHA law, it is employers who are responsible to make sure workers are safe,” said Michaels, now a professor at the George Washington University School of Public Health. “And we have compelling evidence that they are doing a very poor job because many workers are injured on the job, especially in Texas.”
Michaels pointed out that OSHA does not have a national standard for heat-related illnesses and issues citations only for over-exposure to heat after an injury or death, but not before that occurs.
“The better solution would be to have a national standard, but since we do not, local ordinances are very important for saving lives,” he said. “Prohibiting these local laws will result in workers being severely hurt or killed.”
Gonzalez, from the Texas AFL-CIO, disagrees with the idea that local regulations hurt businesses.
Mandated water breaks “were passed in 2010 in Austin and construction is still growing, especially in the state’s largest cities,” Gonzalez said. “It is simply false, an excuse to limit local governments’ power and an intrusion into democracy.”
HB 2127 does not impede the enactment of a state law establishing mandatory breaks for construction workers, and during the regular session, two bills were filed to that effect.
House Bill 495, authored by Rep. Thresa Meza, D-Irving, sought to establish 10-minute mandatory breaks every four hours for contractors working for a governmental entity. House Bill 4673, by Rep. Maria Luisa Flores, D-Austin, would have created a statewide advisory board responsible for establishing standards to prevent heat illness in Texas workplaces and set penalties for employers who do not comply with them.
Neither bill made it through the legislative process.
Daniela Hernandez, state legislative coordinator for the Workers Defense Project, said she hopes legislators will push for a state law mandating water breaks for workers. She added that she would not discard the possibility that cities sue to try to keep their water break ordinances.
“Without an ordinance or a law, there is no safeguard. There is no guarantee that the worker will have those water breaks,” he said. “We will keep fighting.”
#us politics#news#the texas tribune#2023#texas#gov. greg abbott#republicans#conservatives#gop policy#gop platform#gop#House Bill 2127#Texas Legislature#heat wave#U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics#worker's rights#union workers#Texas AFL-CIO#Ana Gonzalez#National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration#Dustin Burrows#National Federation of Independent Business#Occupational Safety and Health Administration#Associated Builders and Contractors of Texas#Mandated water breaks#House Bill 495#House Bill 4673#Thresa Meza#Maria Luisa Flores#Workers Defense Project
54 notes
·
View notes
Text
NOAA National Marine Sanctuary Posters
Free for download!








#noaa#national oceanic and atmospheric administration#National marine sanctuary#science art#digital art#art download#free art#science communication
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploration of Deep Waters of Glacier Bay National Park
youtube
Jul 12, 2023
May - September 2023, NOAA Ocean Exploration is conducting a series of expeditions to map and explore deep waters off Alaska. We're still waiting to get underway for our first expedition that will include remotely operated vehicle dives (deep an eye out for some (good) news about that)...while you wait, here's video from a 2016 expedition to explore waters within Glacier Bay National Park, to get you pumped and ready for what we might see (hopefully soon)!
#undescribed video#silent video#deep sea exploration#fishes#sea stars#anemone#sponges#coral#octopus#crab#scallop#seal#human diver#many benefits of being a marine biologist#national oceanic and atmospheric administration#Youtube
5 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Jesus and his disciples are on a boat. It’s evening. Tired from a day of teaching, Jesus falls asleep. But then a massive storm comes up. Waves are breaking into the boat and filling it. Several of Jesus’s disciples were fishermen, and even they are terrified. But Jesus just sleeps on. They wake him up with, “Teacher, do you not care that we are perishing?” (Mark 4:38). What did they expect Jesus to do? Perhaps he’d be an extra pair of hands for bailing out? Or maybe he’d pray to God for the storm to start dying down? But Jesus, fresh from sleep, speaks to the wind and the sea: “Peace!” he says, “Be still!” (Mark 4:39). The wind stops, and there is a great calm. Then Jesus asks, “Why are you so afraid? Have you still no faith?” (Mark 4:40). We might expect the disciples to be relieved. “Phew! The storm is over. Jesus saved the day!” But they’re not. Mark tells us they’re “filled with great fear” and say to one another, “Who then is this that even the wind and the sea obey him?” (Mark 4:41).
In Genesis God spoke the oceans into being. In Exodus, he drove the Red Sea back with a strong east wind and made a path so that his people could walk through on dry ground. Here, Jesus speaks to the wind and the sea, and they obey. This is no gradual calming of a storm. The brakes are crammed on suddenly, and his disciples are jolted from one fear to another...
Once again, he is telling us.
~ Rebecca McLauglin
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
You know how as a kid everyone had that THING they were just obsessed with for awhile? Not necessarily their whole childhood, just a distinct enough phase that it still holds room in memory and at least one birthday party passed during it so they got a bunch of stuff related to the theme? Like for some kids it was bugs, others dinosaurs? Well for me it was the ocean. And you know what, i feel like it was misguided to ever stop. Because have you seen the ocean? It’s fucking huge. We split it up into other oceans but the water is all connected. And WE BARELY KNOW WHAT’s IN IT. THERE IS SO MUCH WEIRD SHIT DOWN THERE, IT’S INSANE. HOW THE FUCK DO WE FUNCTION WHEN WE DON’T KNOW ANYTHING ABOUT IT? LIKE HOOOOOW? AND TSUNAMIS? HURRICANES? I just…. I feel like we should bring all of our childhood obsessions back cuz we were right, the ocean IS cool, and so are bugs, and so are dinosaurs
#childhood#national oceanic and atmospheric administration#Ocean#obsessesion#obsession#sea#bugs#cool bugs#the ocean#the ocean is cool#dinosaurs#science#bill nye
3 notes
·
View notes
Link
This is disturbing. 1930′s (Dust Bowl) meets 2020′s (Drought and wildfires).
youtube
Excerpt from this New York Times story:
The video is mesmerizing: As three whitish-gray geysers gush eastward from the mountains of New Mexico, a sheet of brown spills down from the north like swash on a beach.
What it represents is far more destructive.
The image, a time-lapse captured by a National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration satellite, shows two devastating events happening in the Western United States. The first is a wildfire outbreak in northern New Mexico that started last month and has intensified in the past two weeks, fueled by extreme drought and high winds. The second is a dust storm caused by violent winds in Colorado.
Both are examples of the sorts of natural disasters that are becoming more severe and frequent as a result of climate change.
Seven large fires were burning in New Mexico as of Tuesday, according to the NASA Earth Observatory. The satellite image shows four of them. The westernmost is the Cerro Pelado fire, covering about 27,000 acres near the Los Alamos National Laboratory. The northernmost is the Cooks Peak fire, covering about 59,000 acres near Taos. Just south of that are the Calf Canyon and Hermits Peak fires, which merged around April 22 into one huge, 160,000-acre blaze.
The total land burning in the satellite image is roughly 380 square miles, an area larger than Indianapolis. The Hermits Peak/Calf Canyon fire in particular has forced thousands of people to evacuate their homes, including in Las Vegas, N.M., a town of 13,000 about an hour east of Santa Fe.
High winds were also responsible for the second phenomenon visible in the image NOAA released: the dust storm in Colorado.
“Visibility is dropping to near zero and winds are gusting to 50-60 m.p.h. within this blowing dust,” the National Weather Service in Pueblo, Colo., said on Twitter on Friday, warning of extremely dangerous conditions for drivers.
The satellite imagery underscores how widespread the effects of such disasters can be. While the “brownout” conditions were relatively localized during the dust storm, winds carried the dust particles across hundreds of miles of southeastern Colorado, western Kansas, and the Oklahoma and Texas Panhandles.
Fine particulate matter degrades air quality and poses health hazards, particularly for people with underlying lung or heart diseases. That applies to dust as well as to smoke, soot and other byproducts of wildfires.
11 notes
·
View notes
Link
#Civic and Community Engagement#Federal Government#Northern Mariana Islands#Science and Environment#Contextomy#Emergency Response#guide#islands#marine debris#National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration#Pacific region#preparedness
0 notes
Text

Illustration by João Fazenda
The Burning of Maui
The governor called the fires Hawaii’s “largest natural disaster” ever. They would more accurately be labelled an “unnatural disaster.”
— By Elizabeth Kolbert | August 20, 2023
The ‘alalā, or Hawaiian crow, is a remarkably clever bird. ‘Alalā fashion tools out of sticks, which they use, a bit like skewers, to get at hard-to-reach food. The birds were once abundant, but by the late nineteen-nineties their population had dropped so low that they were facing extinction. Since 2003, all the world’s remaining ‘alalā have been confined to aviaries. In a last-ditch effort to preserve the species, the San Diego Zoo Wildlife Alliance has been breeding the crows in captivity. The alliance keeps about a third of the birds—some forty ‘alalā—at a facility outside the town of Volcano, on the Big Island, and the rest outside the town of Makawao, on Maui. Earlier this month, the Maui population was very nearly wiped out. On the morning of August 8th, flames came within a few hundred feet of the birds’ home and would probably have engulfed it were it not for an enterprising alliance employee, one of her neighbors, and a garden hose.
According to the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, “many factors” contributed to the ‘alalā’s decline, including habitat destruction, invasive species, and the effects of agriculture on the landscape. Owing to these developments, Hawaii’s native fauna in general is in crisis; the state has earned an unfortunate title as “the extinction capital of the world.” Of the nearly hundred and fifty bird species that used to be found in Hawaii and nowhere else, two-thirds are gone. Among the islands’ distinctive native snails, the losses have been even more catastrophic.
Last week, as the death toll from the fires in West Maui continued to mount—late on Friday, the number stood at a hundred and eleven—it became clear that the same “factors” that have decimated Hawaii’s wildlife also contributed to the deadliness of the blazes. Roughly a thousand people have been reported as still missing, and some two thousand homes have been destroyed or damaged. The worst-hit locality, the town of Lahaina, which lies in ruins, was built on what was once a wetland. Starting in the mid-nineteenth century, much of the vegetation surrounding the town was cleared to make way for sugar plantations. Then, when these went out of business, in the late twentieth century, the formerly cultivated acres were taken over by introduced grasses. In contrast to Hawaii’s native plants, the imported grasses have evolved to reseed after fires and, in dry times, they become highly flammable.
“The lands around Lahaina were all sugarcane from the eighteen-sixties to the late nineteen-nineties,” Clay Trauernicht, a specialist in fire ecology at the University of Hawaii at Mānoa, told the Guardian. “Nothing’s been done since then—hence the problem with invasive grasses and fire risk.”
Also contributing to the devastation was climate change. Since the nineteen-fifties, average temperatures in Hawaii have risen by about two degrees, and there has been a sharp uptick in warming in just the past decade. This has made the state more fire-prone and, at the same time, it has fostered the spread of the sorts of plants that provide wildfires with fuel. Hotter summers help invasive shrubs and grasses “outgrow our native tree species,” the state’s official Climate Change Portal notes.
As Hawaii has warmed, it has also dried out. According, again, to the Climate Change Portal, “rainfall and streamflow have declined significantly over the past 30 years.” In the weeks leading up to the fires in West Maui, parts of the region were classified as suffering from “severe drought.” Meanwhile, climate change is shifting storm tracks in the Pacific farther north. Hurricane Dora, which made history as the longest-lasting Category 4 hurricane on record in the Pacific, passed to the south of Maui and helped produce the gusts that spread the Lahaina fire at a speed that’s been estimated to be a mile per minute.
After visiting the wreckage of Lahaina, Hawaii’s governor, Josh Green, called the Maui fires the “largest natural disaster Hawaii has ever experienced.” In fact, the fires would more accurately be labelled an “unnatural disaster.” As David Beilman, a professor of geography and environment at the University of Hawaii at Manoa, recently pointed out, for most of Hawaii’s history fire simply wasn’t part of the islands’ ecology. “This Maui situation is an Anthropocene phenomenon,” he told USA Today.
A great many more unnatural disasters lie ahead. Last month was, by a large margin, the hottest July on record, and 2023 seems likely to become the warmest year on record. Two days after Lahaina burst into flames, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration issued a revised forecast for the current Atlantic hurricane season, which runs through the end of November. The agency had been predicting a “near-normal” season, with between five and nine hurricanes. But, because of record sea-surface temperatures this summer—last month a buoy in Manatee Bay, south of Miami, registered 101.1 degrees, a reading that, as the Washington Post put it, is “more typical of a hot tub than ocean water”—noaa is now projecting that the season will be “above normal,” with up to eleven hurricanes. Rising sea levels and the loss of coastal wetlands mean that any hurricanes that make landfall will be that much more destructive.
A few days after noaa revised its forecast, officials ordered the evacuation of Yellowknife, the capital of Canada’s Northwest Territories. A wildfire burning about ten miles away would, they feared, grow to consume the city. The Canadian Broadcasting Corporation called the evacuation order “extraordinary.” This summer has been Canada’s worst wildfire season on record, and, at times, the smoke has spread all the way to Europe. There are currently something like a thousand active fires in the country.
Two days after the Yellowknife evacuation was ordered, another Pacific hurricane—Hilary—intensified into a Category 4 storm. Hilary was being drawn north by a “heat dome” of high pressure over the central Plains, which was expected to bring record temperatures to parts of the Midwest. The storm’s unusual track put some twenty-six million people in four states—California, Utah, Nevada, and Arizona—under flash-flood watches.
How well humanity will fare on the new planet it is busy creating is an open question. Homo sapiens is a remarkably clever species. So, too, was the ‘alalā. ♦
— Published in the Print Edition of the August 28, 2023, New Yorker Issue, with the Headline “Fire Alarm.”
#Maui#Natural Disaster | Un-natural Disaster#Elizabeth Kolbert#The New Yorker#Alalā | Hawaiian Crow#San Diego Zoo Wildlife Alliance#U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service#Lahaina#Clay Trauernicht | University of Hawaii at Mānoa#Climate Change Portal#Hawaii’s Governor | Josh Green#David Beilman | University of Hawaii at Manoa#Anthropocene Phenomenon#National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration#Atlantic Hurricane 🌀#Manatee Bay | South of Miami#Yellowknife | Canada’s 🇨🇦 Northwest Territories#Europe#Pacific Hurricane 🌀#Mid-West | California | Utah | Nevada | Arizona#Fire 🔥 Alarm 🚨
0 notes
Text
Atlantic Tropical Weather Outlook issued by the National Hurricane Center in Miami, FL, USA
2023-09-03, 02:00 EDT
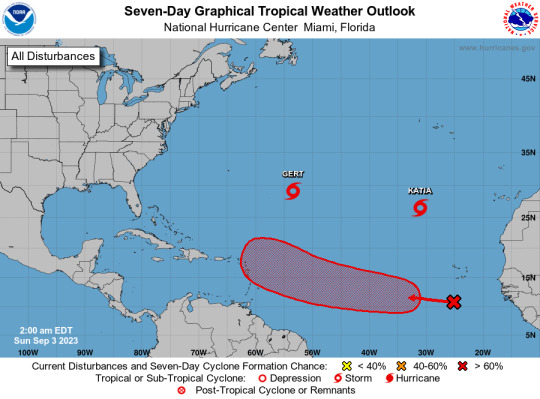
Active Systems: The National Hurricane Center is issuing advisories on Tropical Storm Gert, located about 700 miles east-southeast of Bermuda, and Tropical Storm Katia, located about 850 miles north-northwest of the Cabo Verde Islands. Eastern and Central Tropical Atlantic (AL95): A tropical wave located over the far eastern tropical Atlantic is producing disorganized shower and thunderstorm activity to the south-southwest of the Cabo Verde Islands. Environmental conditions appear conducive for some gradual development of this system by the middle part of this week, and a tropical depression is likely to form while it moves westward to west-northwestward at 15 to 20 mph over the eastern and central portions of the tropical Atlantic.
* Formation chance through 48 hours...low...30 percent.
* Formation chance through 7 days...high...70 percent.
$$ Forecaster Pasch
#bot post#meteorology#weather#tropical weather#tropical storm#tropical depression#hurricane#atlantic#atlantic ocean#caribbean#gulf of mexico#noaa#national oceanic and atmospheric administration#nhc#national hurricane center
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
Climate experts fear Donald Trump will follow a blueprint created by his allies to gut the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), disbanding its work on climate science and tailoring its operations to business interests.
Joe Biden’s presidency has increased the profile of the science-based federal agency but its future has been put in doubt if Trump wins a second term and at a time when climate impacts continue to worsen.
The plan to “break up NOAA” is laid out in the Project 2025 document written by more than 350 rightwingers and helmed by the Heritage Foundation. Called the Mandate for Leadership: The Conservative Promise, it is meant to guide the first 180 days of presidency for an incoming Republican president.
The document bears the fingerprints of Trump allies, including Johnny McEntee, who was one of Trump’s closest aides and is a senior adviser to Project 2025. “The National Oceanographic [sic] and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) should be dismantled and many of its functions eliminated, sent to other agencies, privatized, or placed under the control of states and territories,” the proposal says.
That’s a sign that the far right has “no interest in climate truth”, said Chris Gloninger, who last year left his job as a meteorologist in Iowa after receiving death threats over his spotlighting of global warming.
The guidebook chapter detailing the strategy, which was recently spotlighted by E&E News, describes NOAA as a “colossal operation that has become one of the main drivers of the climate change alarm industry and, as such, is harmful to future US prosperity”. It was written by Thomas Gilman, a former Chrysler executive who during Trump’s presidency was chief financial officer for NOAA’S parent body, the Commerce Department.
Gilman writes that one of NOAA’S six main offices, the Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research, should be “disbanded” because it issues “theoretical” science and is “the source of much of Noaa’s climate alarmism”. Though he admits it serves “important public safety and business functions as well as academic functions”, Gilman says data from the National Hurricane Center must be “presented neutrally, without adjustments intended to support any one side in the climate debate”.
But NOAA’S research and data are “largely neutral right now”, said Andrew Rosenberg, a former NOAA official who is now a fellow at the University of New Hampshire. “It in fact basically reports the science as the scientific evidence accumulates and has been quite cautious about reporting climate effects,” he said. “It’s not pushing some agenda.”
The rhetoric harkens back to the Trump administration’s scrubbing of climate crisis-related webpages from government websites and stifling climate scientists, said Gloninger, who now works at an environmental consulting firm, the Woods Hole Group.
“It’s one of those things where it seems like if you stop talking about climate change, I think that they truly believe it will just go away,” he said. “They say this term ‘climate alarmism’ … and well, the existential crisis of our lifetime is alarming.”
NOAA also houses the National Weather Service (NWS), which provides weather and climate forecasts and warnings. Gilman calls for the service to “fully commercialize its forecasting operations”.
He goes on to say that Americans are already reliant on private weather forecasters, specifically naming AccuWeather and citing a PR release issued by the company to claim that “studies have found that the forecasts and warnings provided by the private companies are more reliable” than the public sector’s. (The mention is noteworthy as Trump once tapped the former CEO of AccuWeather to lead NOAA, though his nomination was soon withdrawn.)
The claims come amid years of attempts from US conservatives to help private companies enter the forecasting arena – proposals that are “nonsense”, said Rosenberg.
Right now, all people can access high-quality forecasts for free through the NWS. But if forecasts were conducted only by private companies that have a profit motive, crucial programming might no longer be available to those in whom business executives don’t see value, said Rosenberg.
“What about air-quality forecasts in underserved communities? What about forecasts available to farmers that aren’t wealthy farmers? Storm-surge forecasts in communities that aren’t wealthy?” he said. “The frontlines of most of climate change are Black and brown communities that have less resources. Are they going to be getting the same service?”
Private companies like Google, thanks to technological advancements in artificial intelligence, may now indeed be producing more accurate forecasts, said Andrew Blum, author of the 2019 book The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the Forecast. Those private forecasts, however, are all built on NOAA’S data and resources.
Fully privatizing forecasting could also threaten the accuracy of forecasts, said Gloninger, who pointed to AccuWeather’s well-known 30- and 60-day forecasts as one example. Analysts have found that these forecasts are only right about half the time, since peer-reviewed research has found that there is an eight- to 10-day limit on the accuracy of forecasts.
“You can say it’s going to be 75 degrees out on May 15, but we’re not at that ability right now in meteorology,” said Gloninger. Privatizing forecasting could incentivize readings even further into the future to increase views and profits, he said.
Commercializing weather forecasts – an “amazing example of intergovernmental, American-led, postwar, technological achievement” – would also betray the very spirit of the endeavor, said Blum.
In the post-second world war era, John F. Kennedy called for a global weather-forecasting system that relied on unprecedented levels of scientific exchange. A privatized system could potentially stymie the exchange of weather data among countries, yielding less accurate results.
The founding of weather forecasting itself showcases the danger of giving profit-driven companies control, said Rosenberg. When British V. Adm Robert FitzRoy first introduced Britain to the concept of forecasts during Victorian times, he was often bitterly attacked by business interests. The reason: workers were unwilling to risk their lives when they knew dangerous weather was on the horizon.
“The ship owners said, well, that means maybe I lost a day’s income because the fishermen wouldn’t go out and risk their lives when there was a forecast that was really bad, so they didn’t want a forecast that would give them a day’s warning,” Rosenberg said. “The profit motive ended up trying to push people to do things that were dangerous … there’s a lesson there.”
#us politics#news#the guardian#2024#project 2025#donald trump#biden administration#National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration#Mandate for Leadership: The Conservative Promise#Johnny McEntee#Chris Gloninger#global warming#climate crisis#climate change#department of commerce#Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research#National Hurricane Center#Andrew Rosenberg#National Weather Service#AccuWeather
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
50-prozentige Chance, dass 2023 das wärmste Jahr seit Beginn der Aufzeichnungen wird: NOAA
Klimaexperten der US-Regierung haben am Montag darauf hingewiesen, dass es eine Wahrscheinlichkeit von fast 50 Prozent gibt, dass 2023 das wärmste Jahr aller Zeiten wird. Sie warnen zudem davor, dass es im nächsten Jahr noch heißer werden könnte. Sarah Kapnick, Chefwissenschaftlerin der National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), erklärte, dass 2023 bisher das drittwärmste Jahr seit…

View On WordPress
#Bill Nelson#El Niño#Gavin Schmidt#Goddard Institute for Space Studies#Grad Fahrenheit#NASA#National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
0 notes
Text







#animals#ocean art#blue sky#glitter#kawaii#cute#aesthetic#first post#marine animals#national oceanic and atmospheric administration#ocean
1 note
·
View note
Text

Today's Is Guru Purnima
0 notes