#climate crisis
Text
Since the 1960s, the world has seen a spike in the number of natural disasters, largely due to rising sea levels and an ever gradually increasing global surface temperature.
The good news? We’re getting better at helping each other when disasters strike.
According to a recent study from Our World In Data, the global toll from natural disasters has dramatically dropped in the last century.
“Low-frequency, high-impact events such as earthquakes and tsunamis are not preventable, but such high losses of human life are,” wrote lead authors Hannah Ritchie and Pablo Rosado.
To conduct their research, Ritchie and Rosado gathered data from all geophysical, meteorological, and climate-related disasters since 1900. That includes earthquakes, volcanic activity, landslides, drought, wildfires, severe storms, and mass floods.
In the early-to-mid 20th century, the average annual death toll from disasters was very high, often climbing to over a million.
For example, the study cites that in 1931, 2.7 million people died from the Yangtze–Huai River floods. In 1943, 1.9 million died from the Bangladeshi famine of 1943. Even low-frequency events had extreme death tolls.
“In recent decades we have seen a substantial decline in deaths,” Ritchie and Rosado observed. “Even in peak years with high-impact events, the death toll has not exceeded 500,000 since the mid-1960s.”
Why has the global death toll from disasters dropped?
There are a number of factors at play in the improvement of disaster aid, but the leading component is that human beings are getting better at predicting and preparing for natural disasters.
“We know from historical data that the world has seen a significant reduction in disaster deaths through earlier prediction, more resilient infrastructure, emergency preparedness, and response systems,” Ritchie and Rosado explained in their study.
On April 6, [2024],a 7.2 magnitude earthquake rocked the city of Hualien in Taiwan. Days later, as search and rescue continues, the death toll currently rests at 16.
Experts have praised Taiwan for their speedy response and recovery, and attributed the low death toll to the measures that Taiwan implemented after an earthquake of similar strength hit the city 25 years earlier. Sadly, on that day in 1999, 2,400 people died and 11,000 were injured.
In an interview with Al Jazeera, Wang Yu — assistant professor at National Taiwan University — said that event, known as the Chi-Chi earthquake, revolutionized the way Taiwan approached natural disasters.
“There were lots of lessons we learned, including the improvement of building codes, understanding earthquake warning signs, the development and implementation of earthquake early warning (EEW) systems and earthquake education,” said Wang.
Those same sensors and monitoring systems allowed authorities to create “shakemaps” during Hualien’s latest earthquake, which helped them direct rescue teams to the regions that were hit the hardest.
This, in conjunction with stronger building codes, regular earthquake drills, and public education campaigns, played a huge role in reducing the number of deaths from the event.
And Taiwan’s safeguards on April 6 are just one example of recent measures against disasters. Similar models in strengthening prediction, preparedness, and recovery time have been employed around the world when it comes to rescuing victims of floods, wildfires, tornados, and so on.
What else can we learn from this study?
When concluding the findings from their study, Ritchie and Rosado emphasized the importance of increasing safety measures for everyone.
Currently, there is still a divide between populations with high gross national income and populations living in extreme poverty.
Even low-income countries that infrequently have natural disasters have a much higher death rate because they are vulnerable to collapse, displacement, and disrepair.
“Those at low incomes are often the most vulnerable to disaster events; improving living standards, infrastructure, and response systems in these regions will be key to preventing deaths from natural disasters in the coming decades,” surmised Ritchie and Rosado.
“Overall development, poverty alleviation, and knowledge-sharing of how to increase resilience to natural disasters will therefore be key to reducing the toll of disasters in the decades to come."
-via GoodGoodGood, April 11, 2024
#good news#hope#climate change#hope posting#climate news#climate crisis#climate anxiety#climate emergency#natural disasters#disasters#earthquake#wildfire#hurricane#cw death#taiwan#tsunamis#building construction#climate action#climate hope
357 notes
·
View notes
Text

#never trump#republican assholes#climate change#ecology#environment#green jobs#sustainability#corporate greed#maga morons#climate crisis#climate activism#climate deniers
279 notes
·
View notes
Text


#politics#democrats#Climate change#climate crisis#Global war#Gop#hill#hillary clinton#trump#donald trump#Carbon emissions
181 notes
·
View notes
Text
REBLOG THIS TO TELL CLIMATE CHANGE DENIERS TO GET THE HECK OFF YOUR BLOG
#reblog#chain post#not forced#hellsite#climate#climate justice#climate crisis#climate change#climate action
143 notes
·
View notes
Text

Imagining Worlds After Climate Disaster, Julie Heffernan Melds Chaos and the Sublime
51 notes
·
View notes
Text

A.2.8 Is it possible to be an anarchist without opposing hierarchy?
No. We have seen that anarchists abhor authoritarianism. But if one is an anti-authoritarian, one must oppose all hierarchical institutions, since they embody the principle of authority. For, as Emma Goldman argued, “it is not only government in the sense of the state which is destructive of every individual value and quality. It is the whole complex authority and institutional domination which strangles life. It is the superstition, myth, pretence, evasions, and subservience which support authority and institutional domination.” [Red Emma Speaks, p. 435] This means that “there is and will always be a need to discover and overcome structures of hierarchy, authority and domination and constraints on freedom: slavery, wage-slavery [i.e. capitalism], racism, sexism, authoritarian schools, etc.” [Noam Chomsky, Language and Politics, p. 364]
Thus the consistent anarchist must oppose hierarchical relationships as well as the state. Whether economic, social or political, to be an anarchist means to oppose hierarchy. The argument for this (if anybody needs one) is as follows:
“All authoritarian institutions are organised as pyramids: the state, the private or public corporation, the army, the police, the church, the university, the hospital: they are all pyramidal structures with a small group of decision-makers at the top and a broad base of people whose decisions are made for them at the bottom. Anarchism does not demand the changing of labels on the layers, it doesn’t want different people on top, it wants us to clamber out from underneath.” [Colin Ward, Anarchy in Action, p. 22]
Hierarchies “share a common feature: they are organised systems of command and obedience” and so anarchists seek “to eliminate hierarchy per se, not simply replace one form of hierarchy with another.” [Bookchin, The Ecology of Freedom, p. 27] A hierarchy is a pyramidally-structured organisation composed of a series of grades, ranks, or offices of increasing power, prestige, and (usually) remuneration. Scholars who have investigated the hierarchical form have found that the two primary principles it embodies are domination and exploitation. For example, in his classic article “What Do Bosses Do?” (Review of Radical Political Economy, Vol. 6, No. 2), a study of the modern factory, Steven Marglin found that the main function of the corporate hierarchy is not greater productive efficiency (as capitalists claim), but greater control over workers, the purpose of such control being more effective exploitation.
Control in a hierarchy is maintained by coercion, that is, by the threat of negative sanctions of one kind or another: physical, economic, psychological, social, etc. Such control, including the repression of dissent and rebellion, therefore necessitates centralisation: a set of power relations in which the greatest control is exercised by the few at the top (particularly the head of the organisation), while those in the middle ranks have much less control and the many at the bottom have virtually none.
Since domination, coercion, and centralisation are essential features of authoritarianism, and as those features are embodied in hierarchies, all hierarchical institutions are authoritarian. Moreover, for anarchists, any organisation marked by hierarchy, centralism and authoritarianism is state-like, or “statist.” And as anarchists oppose both the state and authoritarian relations, anyone who does not seek to dismantle all forms of hierarchy cannot be called an anarchist. This applies to capitalist firms. As Noam Chomsky points out, the structure of the capitalist firm is extremely hierarchical, indeed fascist, in nature:
“a fascist system… [is] absolutist — power goes from top down … the ideal state is top down control with the public essentially following orders.
“Let’s take a look at a corporation… [I]f you look at what they are, power goes strictly top down, from the board of directors to managers to lower managers to ultimately the people on the shop floor, typing messages, and so on. There’s no flow of power or planning from the bottom up. People can disrupt and make suggestions, but the same is true of a slave society. The structure of power is linear, from the top down.” [Keeping the Rabble in Line, p. 237]
David Deleon indicates these similarities between the company and the state well when he writes:
“Most factories are like military dictatorships. Those at the bottom are privates, the supervisors are sergeants, and on up through the hierarchy. The organisation can dictate everything from our clothing and hair style to how we spend a large portion of our lives, during work. It can compel overtime; it can require us to see a company doctor if we have a medical complaint; it can forbid us free time to engage in political activity; it can suppress freedom of speech, press and assembly — it can use ID cards and armed security police, along with closed-circuit TVs to watch us; it can punish dissenters with ‘disciplinary layoffs’ (as GM calls them), or it can fire us. We are forced, by circumstances, to accept much of this, or join the millions of unemployed… In almost every job, we have only the ‘right’ to quit. Major decisions are made at the top and we are expected to obey, whether we work in an ivory tower or a mine shaft.” [“For Democracy Where We Work: A rationale for social self-management”, Reinventing Anarchy, Again, Howard J. Ehrlich (ed.), pp. 193–4]
Thus the consistent anarchist must oppose hierarchy in all its forms, including the capitalist firm. Not to do so is to support archy — which an anarchist, by definition, cannot do. In other words, for anarchists, ”[p]romises to obey, contracts of (wage) slavery, agreements requiring the acceptance of a subordinate status, are all illegitimate because they do restrict and restrain individual autonomy.” [Robert Graham, “The Anarchist Contract, Reinventing Anarchy, Again, Howard J. Ehrlich (ed.), p. 77] Hierarchy, therefore, is against the basic principles which drive anarchism. It denies what makes us human and “divest[s] the personality of its most integral traits; it denies the very notion that the individual is competent to deal not only with the management of his or her personal life but with its most important context: the social context.” [Murray Bookchin, Op. Cit., p. 202]
Some argue that as long as an association is voluntary, whether it has a hierarchical structure is irrelevant. Anarchists disagree. This is for two reasons. Firstly, under capitalism workers are driven by economic necessity to sell their labour (and so liberty) to those who own the means of life. This process re-enforces the economic conditions workers face by creating “massive disparities in wealth … [as] workers… sell their labour to the capitalist at a price which does not reflect its real value.” Therefore:
“To portray the parties to an employment contract, for example, as free and equal to each other is to ignore the serious inequality of bargaining power which exists between the worker and the employer. To then go on to portray the relationship of subordination and exploitation which naturally results as the epitome of freedom is to make a mockery of both individual liberty and social justice.” [Robert Graham, Op. Cit., p. 70]
It is for this reason that anarchists support collective action and organisation: it increases the bargaining power of working people and allows them to assert their autonomy (see section J).
Secondly, if we take the key element as being whether an association is voluntary or not we would have to argue that the current state system must be considered as “anarchy.” In a modern democracy no one forces an individual to live in a specific state. We are free to leave and go somewhere else. By ignoring the hierarchical nature of an association, you can end up supporting organisations based upon the denial of freedom (including capitalist companies, the armed forces, states even) all because they are “voluntary.” As Bob Black argues, ”[t]o demonise state authoritarianism while ignoring identical albeit contract-consecrated subservient arrangements in the large-scale corporations which control the world economy is fetishism at its worst.” [The Libertarian as Conservative, The Abolition of Work and other essays, p. 142] Anarchy is more than being free to pick a master.
Therefore opposition to hierarchy is a key anarchist position, otherwise you just become a “voluntary archist” — which is hardly anarchistic. For more on this see section A.2.14 ( Why is voluntarism not enough?).
Anarchists argue that organisations do not need to be hierarchical, they can be based upon co-operation between equals who manage their own affairs directly. In this way we can do without hierarchical structures (i.e. the delegation of power in the hands of a few). Only when an association is self-managed by its members can it be considered truly anarchistic.
We are sorry to belabour this point, but some capitalist apologists, apparently wanting to appropriate the “anarchist” name because of its association with freedom, have recently claimed that one can be both a capitalist and an anarchist at the same time (as in so-called “anarcho” capitalism). It should now be clear that since capitalism is based on hierarchy (not to mention statism and exploitation), “anarcho”-capitalism is a contradiction in terms. (For more on this, see Section F)
#faq#anarchy faq#revolution#anarchism#daily posts#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#organization#grassroots#grass roots#anarchists#libraries#leftism#social issues#economy#economics#climate change#climate crisis#climate#ecology#anarchy works#environmentalism#environment#solarpunk#anti colonialism#mutual aid#cops#police
26 notes
·
View notes
Text

"No climate justice on occupied land"
#feminist#social justice#free palestine#settler violence#settler colonialism#genocide#climate justice#climate action#climate crisis#climate change#greta thunberg#europe#politics#the hague#netherlands#global news
28K notes
·
View notes
Text

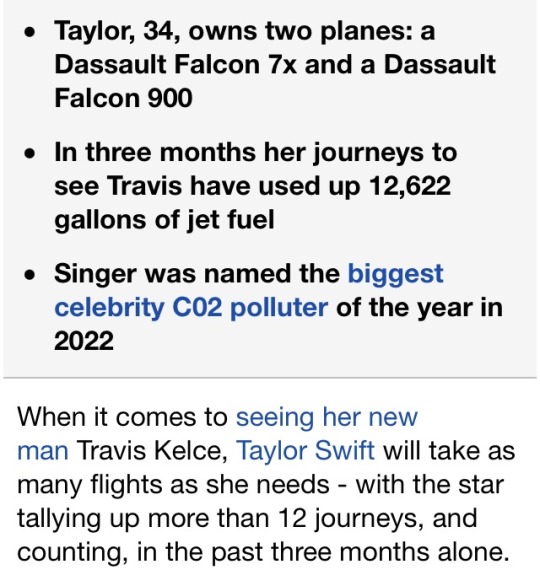







imagine being that fucking rich and that fucking careless.
#anti taylor swift#taylor swift is a climate criminal#taypollution#carbon emissions#co2#the goth punk billionaire#climate change#climate crisis
36K notes
·
View notes
Text
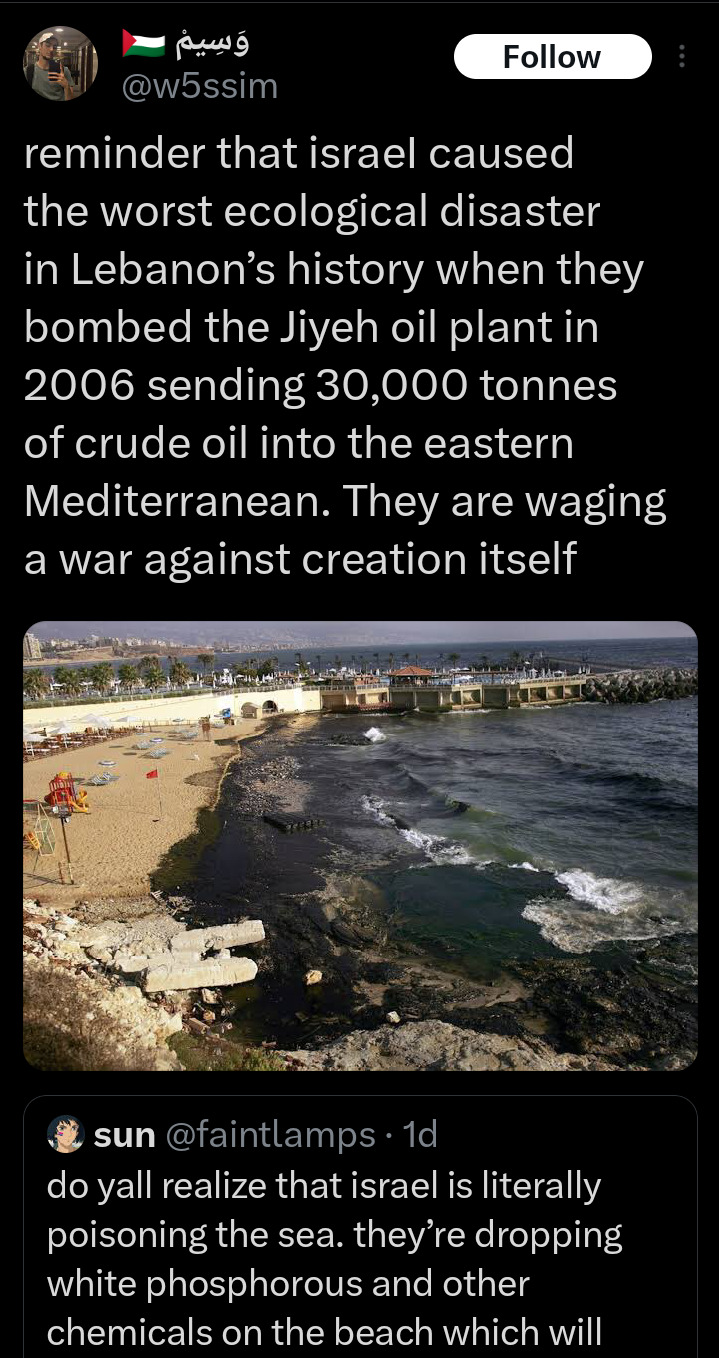
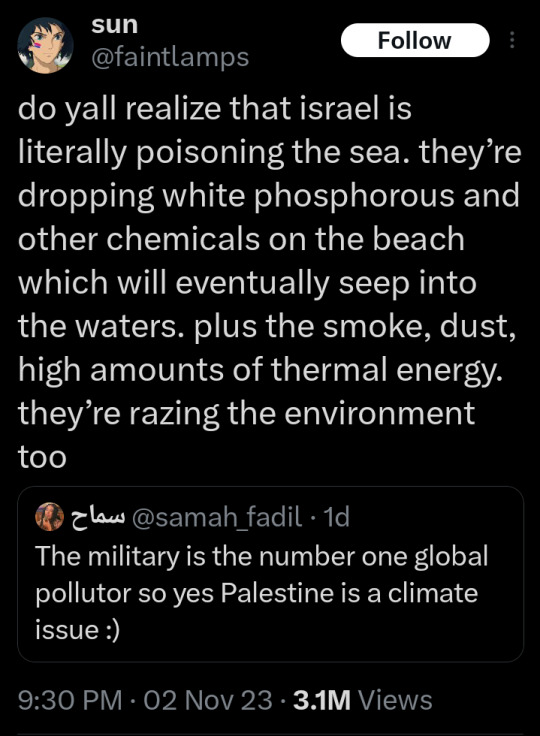
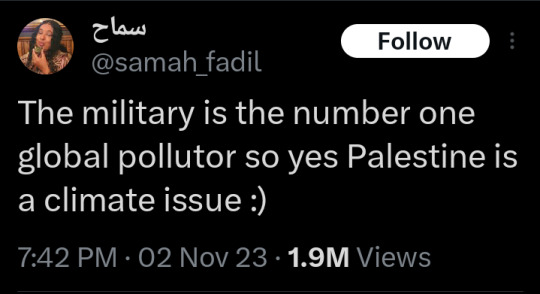

41K notes
·
View notes
Text
We need everyone's help right now to protect the rainforest and Indigenous People
The Amazon Rainforest is under a massive threat. I know you've heard this a million times, but this is different. There is a piece of legislation that will decimate the rights of Indigenous people of Brazil, who have been protecting the rainforest. It's unfathomably bad. It has majority support. And they're voting tomorrow.
As reported here, the Bill allows "the Brazilian government to find energy resources, set up military bases, develop strategic roads, and implement commercial agriculture on protected Indigenous tribal lands, without any prior discussion with the affected peoples."
The thing you can do—and I know this sounds overly simple—is sign this petition—and tell your friends to do the same: SIGN HERE.
As reported here, the Bill allows "the Brazilian government to find energy resources, set up military bases, develop strategic roads, and implement commercial agriculture on protected Indigenous tribal lands, without any prior discussion with the affected peoples."
Again, this bill has majority support. You may be wondering, why will a petition signed by people who don't live in Brazil make any difference? Because it will give those opposing it political air cover. It will show the world is with them.
But we need a LOT of signatures.
Please do this simple act and spread the word.
51K notes
·
View notes
Text
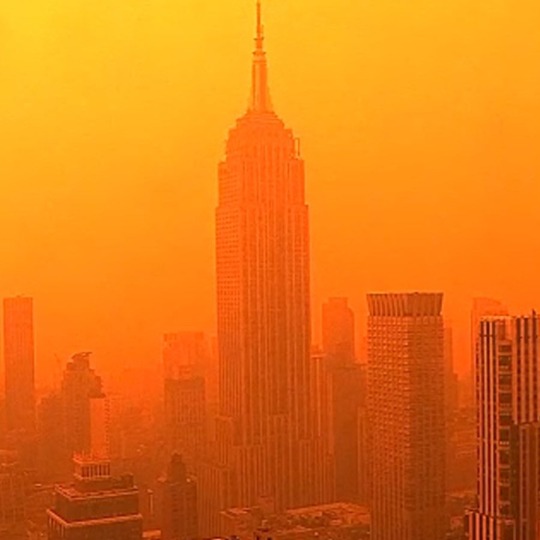
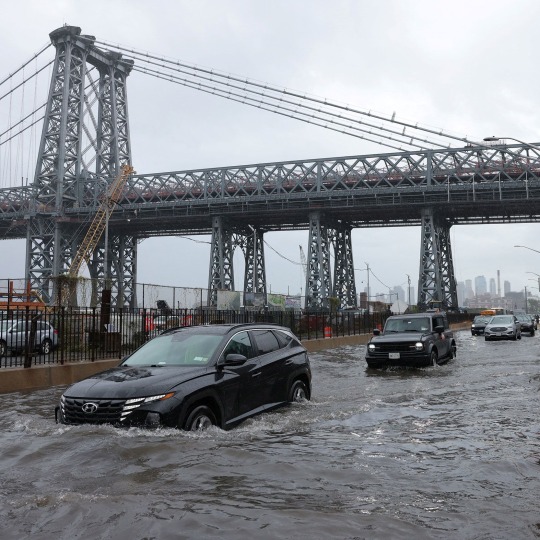








Nothing to see here, just fire + floods + climate change
#politics#climate change#climate crisis#global warming#nyc#nyc flooding#nyc floods#climate collapse#civil engineering
29K notes
·
View notes
Text
No paywall version here.
"Two and a half years ago, when I was asked to help write the most authoritative report on climate change in the United States, I hesitated...
In the end, I said yes, but reluctantly. Frankly, I was sick of admonishing people about how bad things could get. Scientists have raised the alarm over and over again, and still the temperature rises. Extreme events like heat waves, floods and droughts are becoming more severe and frequent, exactly as we predicted they would. We were proved right. It didn’t seem to matter.
Our report, which was released on Tuesday, contains more dire warnings. There are plenty of new reasons for despair. Thanks to recent scientific advances, we can now link climate change to specific extreme weather disasters, and we have a better understanding of how the feedback loops in the climate system can make warming even worse. We can also now more confidently forecast catastrophic outcomes if global emissions continue on their current trajectory.
But to me, the most surprising new finding in the Fifth National Climate Assessment is this: There has been genuine progress, too.
I’m used to mind-boggling numbers, and there are many of them in this report. Human beings have put about 1.6 trillion tons of carbon in the atmosphere since the Industrial Revolution — more than the weight of every living thing on Earth combined. But as we wrote the report, I learned other, even more mind-boggling numbers. In the last decade, the cost of wind energy has declined by 70 percent and solar has declined 90 percent. Renewables now make up 80 percent of new electricity generation capacity. Our country’s greenhouse gas emissions are falling, even as our G.D.P. and population grow.
In the report, we were tasked with projecting future climate change. We showed what the United States would look like if the world warms by 2 degrees Celsius. It wasn’t a pretty picture: more heat waves, more uncomfortably hot nights, more downpours, more droughts. If greenhouse emissions continue to rise, we could reach that point in the next couple of decades. If they fall a little, maybe we can stave it off until the middle of the century. But our findings also offered a glimmer of hope: If emissions fall dramatically, as the report suggested they could, we may never reach 2 degrees Celsius at all.
For the first time in my career, I felt something strange: optimism.
And that simple realization was enough to convince me that releasing yet another climate report was worthwhile.
Something has changed in the United States, and not just the climate. State, local and tribal governments all around the country have begun to take action. Some politicians now actually campaign on climate change, instead of ignoring or lying about it. Congress passed federal climate legislation — something I’d long regarded as impossible — in 2022 as we turned in the first draft.
[Note: She's talking about the Inflation Reduction Act and the Infrastructure Act, which despite the names were the two biggest climate packages passed in US history. And their passage in mid 2022 was a big turning point: that's when, for the first time in decades, a lot of scientists started looking at the numbers - esp the ones that would come from the IRA's funding - and said "Wait, holy shit, we have an actual chance."]
And while the report stresses the urgency of limiting warming to prevent terrible risks, it has a new message, too: We can do this. We now know how to make the dramatic emissions cuts we’d need to limit warming, and it’s very possible to do this in a way that’s sustainable, healthy and fair.
The conversation has moved on, and the role of scientists has changed. We’re not just warning of danger anymore. We’re showing the way to safety.
I was wrong about those previous reports: They did matter, after all. While climate scientists were warning the world of disaster, a small army of scientists, engineers, policymakers and others were getting to work. These first responders have helped move us toward our climate goals. Our warnings did their job.
To limit global warming, we need many more people to get on board... We need to reach those who haven’t yet been moved by our warnings. I’m not talking about the fossil fuel industry here; nor do I particularly care about winning over the small but noisy group of committed climate deniers. But I believe we can reach the many people whose eyes glaze over when they hear yet another dire warning or see another report like the one we just published.
The reason is that now, we have a better story to tell. The evidence is clear: Responding to climate change will not only create a better world for our children and grandchildren, but it will also make the world better for us right now.
Eliminating the sources of greenhouse gas emissions will make our air and water cleaner, our economy stronger and our quality of life better. It could save hundreds of thousands or even millions of lives across the country through air quality benefits alone. Using land more wisely can both limit climate change and protect biodiversity. Climate change most strongly affects communities that get a raw deal in our society: people with low incomes, people of color, children and the elderly. And climate action can be an opportunity to redress legacies of racism, neglect and injustice.
I could still tell you scary stories about a future ravaged by climate change, and they’d be true, at least on the trajectory we’re currently on. But it’s also true that we have a once-in-human-history chance not only to prevent the worst effects but also to make the world better right now. It would be a shame to squander this opportunity. So I don’t just want to talk about the problems anymore. I want to talk about the solutions. Consider this your last warning from me."
-via New York Times. Opinion essay by leading climate scientist Kate Marvel. November 18, 2023.
#WE CAN DO THIS#I SO TRULY BELIEVE THAT WE CAN DO THIS#WE CAN SAVE OURSELVES AND THE WORLD ALONG WITH US#climate crisis#united states#climate change#conservation#hope posting#sustainability#climate news#climate action#climate emergency#fossil fuels#global warming#environmentalism#climate hope#solarpunk#climate optimism#climate policy#earth#science#climate science#meteorology#extreme weather#renewable energy#solar power#wind power#renewables#carbon emissions#climate justice
33K notes
·
View notes
Text
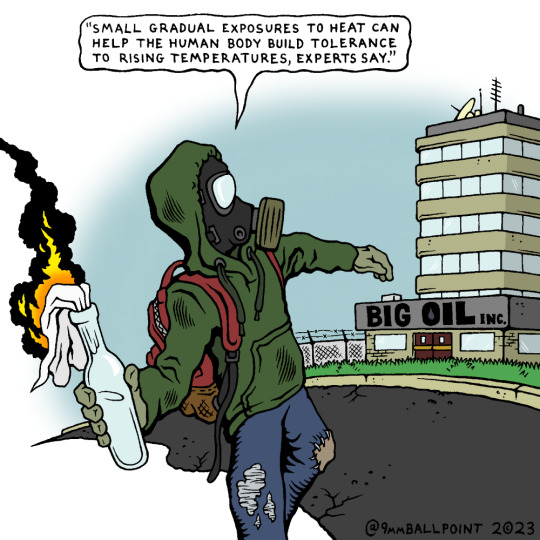

PS: for entertainment purposes only, of course
PPS: actual Washington Post quote
26K notes
·
View notes
Text

DR ADAM LEVY ClimateAdam
ROSEMARY MOSCO
#comic#climate change#climate science#climate action#climate crisis#doom scroll break#radical optimism#hope is a radical act
26K notes
·
View notes
Text




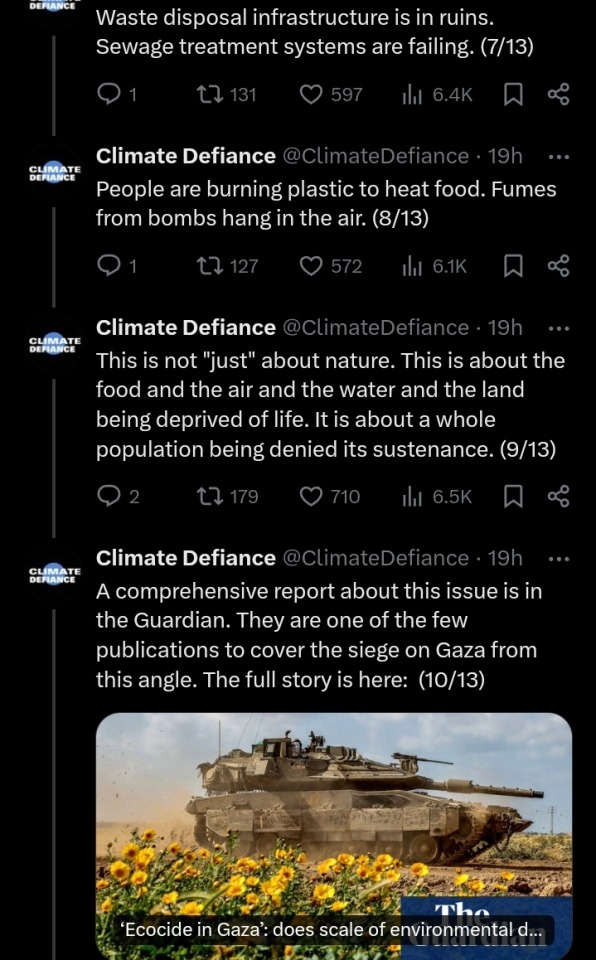
#yemen#jerusalem#tel aviv#current events#palestine#free palestine#gaza#free gaza#news on gaza#palestine news#news update#war news#war on gaza#climate change#climate crisis#climate justice#global warming#environmental justice
6K notes
·
View notes
Text


Climate crisis is coming for all of us. We need to vote for people who are not insulated from reality via donor bribes.
We need a robust EPA. The current Supreme Court wants to end the EPA and Federal power to regulate our air and water. Never forget.
Get involved. Vote.
39K notes
·
View notes