#medical science
Text
The young woman was catatonic, stuck at the nurses’ station — unmoving, unblinking and unknowing of where or who she was.
Her name was April Burrell.
Before she became a patient, April had been an outgoing, straight-A student majoring in accounting at the University of Maryland Eastern Shore. But after a traumatic event when she was 21, April suddenly developed psychosis and became lost in a constant state of visual and auditory hallucinations. The former high school valedictorian could no longer communicate, bathe or take care of herself.
April was diagnosed with a severe form of schizophrenia, an often devastating mental illness that affects approximately 1 percent of the global population and can drastically impair how patients behave and perceive reality.
“She was the first person I ever saw as a patient,” said Sander Markx, director of precision psychiatry at Columbia University, who was still a medical student in 2000 when he first encountered April. “She is, to this day, the sickest patient I’ve ever seen.”
It would be nearly two decades before their paths crossed again. But in 2018, another chance encounter led to several medical discoveries reminiscent of a scene from “Awakenings,” the famous book and movie inspired by the awakening of catatonic patients treated by the late neurologist and writer Oliver Sacks.
Markx and his colleagues discovered that although April’s illness was clinically indistinguishable from schizophrenia, she also had lupus, an underlying and treatable autoimmune condition that was attacking her brain.
After months of targeted treatments — and more than two decades trapped in her mind — April woke up.
The awakening of April — and the successful treatment of other peoplewith similar conditions — now stand to transform care for some of psychiatry’s sickest patients, many of whom are languishing in mental institutions.
Researchers working with the New York state mental health-care system have identified about 200 patients with autoimmune diseases, some institutionalized for years, who may be helped by the discovery.
And scientists around the world, including Germany and Britain, are conducting similar research, finding that underlying autoimmune and inflammatory processes may be more common in patients with a variety of psychiatric syndromes than previously believed.
Although the current research probably will help only a small subset of patients,the impact of the work is already beginning to reshape the practice of psychiatry and the way many cases of mental illness are diagnosed and treated.
“These are the forgotten souls,” said Markx. “We’re not just improving the lives of these people, but we’re bringing them back from a place that I didn’t think they could come back from.”
– A catatonic woman awakened after 20 years. Her story may change psychiatry.
#block JavaScript in site settings if article is paywalled#April burrel#disability#schizophrenia#lupus#mental illness#catatonia#chronic illness#institutionalization#psychiatry#medical science#healthcare#autoimmune disease#Washington post#knee of huss
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Woman Who Can Smell Parkinson’s Helps Develop Test
Joy Milne, 72, from Perth, Scotland, has a hyper-sensitive sense of smell, allowing her to be able to smell Parkinson’s disease, which progressively damages parts of the brain over many years.
She discovered her unusual ability when her late husband, Les, developed a different odour when he was 33. She described it as a ‘musky aroma’. That was 12 years before he was diagnosed with Parkinson’s. Les, who was a doctor, was determined to research the link between odour and Parkinson’s, and contacted Dr Tilo Kunath at the University of Edinburgh, who paired up with Professor Perdita Barran to begin the research. They determined that the reasons for a change in the scent of a person suffering the disease is due to a chemical change of the skin oil (sebum).
In the preliminary sessions, Milne was asked to smell T-shirts worn by people who had Parkinson’s and those who did not. She successfully identified all of the Parkinson’s patients, but told researchers that a member of the control group, a non-Parkinson’s patient, did smell like the disease. 8 months later, they were diagnosed with the disease.
Now, a team of researchers at the University of Manchester have developed a simple test involving a cotton bud swiped down the back of the neck that can identify those with Parkinson’s. The molecules on the cotton bud can be examined using mass spectrometry, which helps the diagnosis. This is a huge leap forward, as there is no definitive test for Parkinson’s, and a diagnosis is based on symptoms and medical history. Currently, there are no cures for Parkinson’s, but an early diagnosis can help begin the treatment early, lessening the speed of the deterioration.
Milne says she can sometimes smell that a person has Parkinson’s when walking down the street, but has been told by medical ethicists that she cannot tell them. She is continuing to work with scientists to see if she can smell other diseases, like cancer or TB, and hopes that one day her talent can be considered normal diagnosis.
Source: the Guardian, written by PA Media
#science#science communication#scicomm#stem#science education#biology#health#medical science#parkinson's disease
9K notes
·
View notes
Text
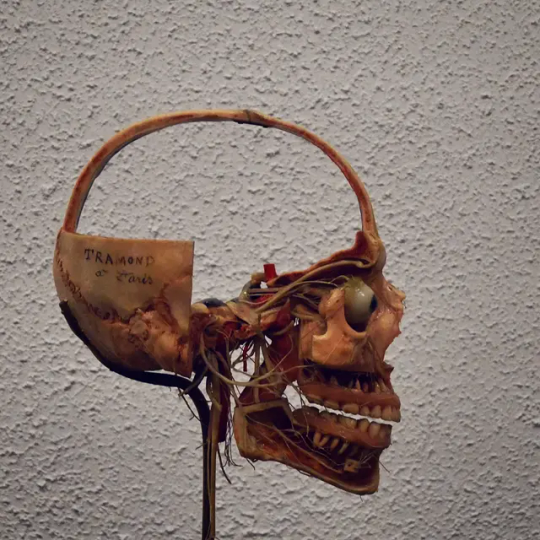


Model bisections of human head- Science Museum, London
#gothic#memento mori#goth#folk horror#skull#dead#folklore#skulls#england#dissection#dissect#bisection#science#science museum#horror#macabre#morbid#anatomy#medical#medicine#medical science#goth aesthetic#goth art#creepy#brain
281 notes
·
View notes
Text

This image shows a decellularized heart, stripped of all native cells, leaving behind an intact vascular system and a scaffold that has been infused with stem cells.
One of the greatest limitations to organ transplantation derives from organ rejection caused by antibodies of the transplant recipient reacting to donor antigens on cell surfaces within the donor organ.
By re-cellularizing an decellularized organ with a patient’s own cells, the adverse immune response is eliminated.
236 notes
·
View notes
Photo
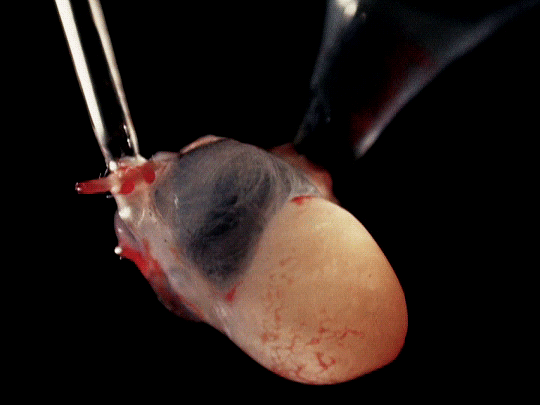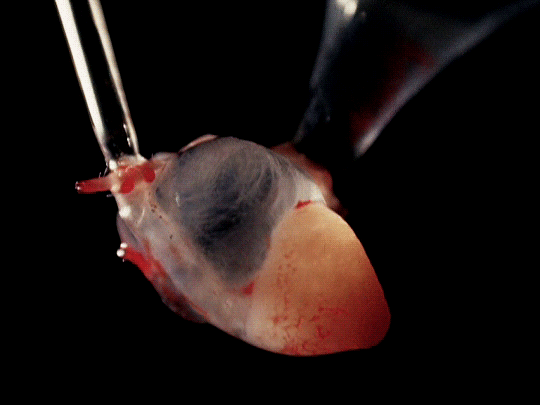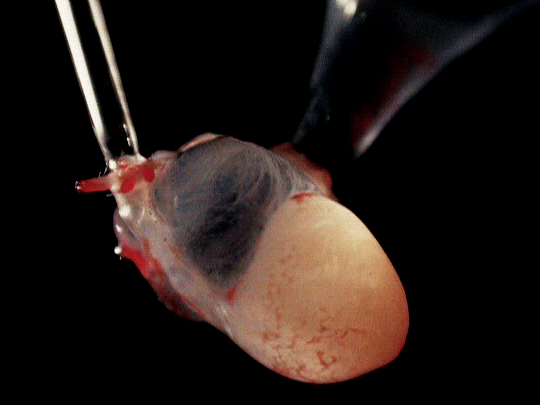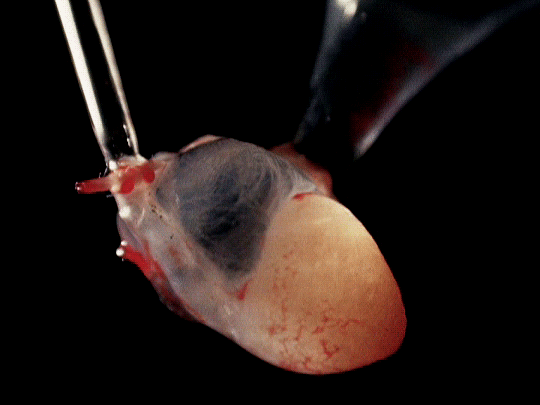
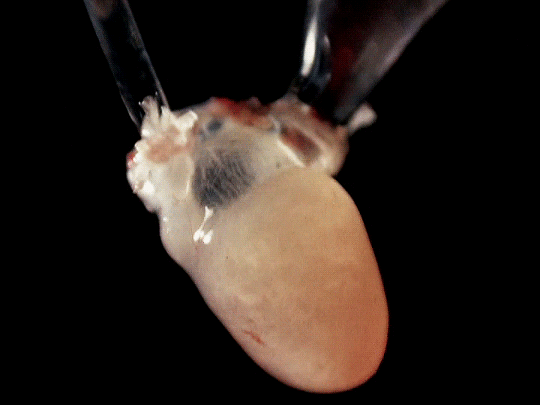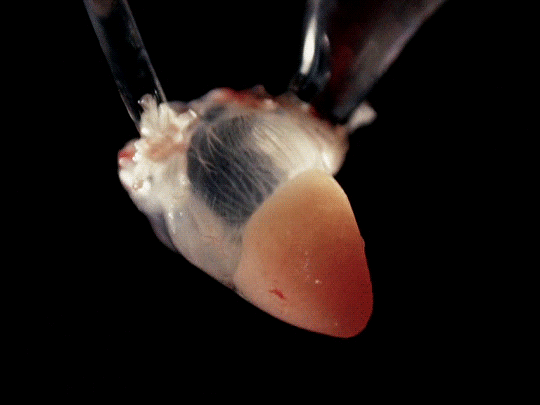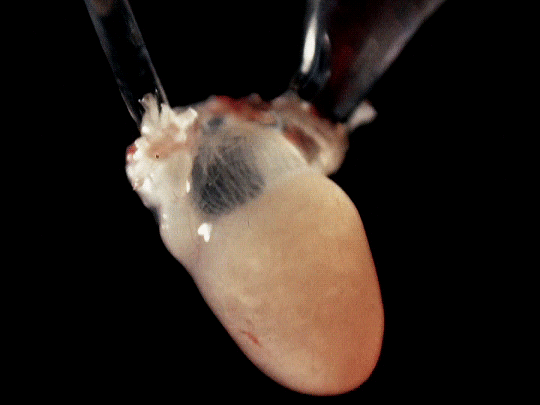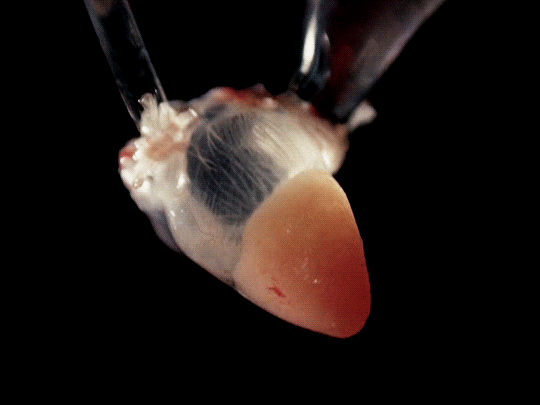
frog hearts (1951)
707 notes
·
View notes
Text
Autism and Bright Lights





The Autistic Teacher
#autism#actually autistic#bright light#medical science#light sensitivity#neurodiversity#feel free to reblog/share#The Autistic Teacher (Facebook)
382 notes
·
View notes
Text
A team of surgeons in New York has performed the world's first transplant of an entire eye in a procedure widely hailed as a medical breakthrough, although it isn't yet known whether the man will ever see through the donated eye.
The groundbreaking surgery involved removing part of the face and the whole left eye – including its blood supply and optic nerve – of a donor and grafting them onto a lineworker from Arkansas who survived a 7,200-volt electric shock in June 2021.
Aaron James, 46, suffered extensive injuries including the loss of his left eye, his dominant left arm above the elbow, his nose and lips, front teeth, left cheek area and chin.
He was referred to NYU Langone Health, a leading medical center for facial transplants, which carried out the procedure on May 27.
Transplanting an entire eye has long been a holy grail of medical science, and though researchers have had some success in animals – where they have restored partial vision – it's never before been performed in a living person.
Continue Reading.
214 notes
·
View notes
Text

What Is the LifeVac Choking Rescue Device? Three Lifesaving Moments with LifeVac
61 notes
·
View notes
Text


Autopsy on the bodies of Chang and Eng Bunker
#medical science#medicalcore#conjoined twins#archive#internet archive#medical illustration#g0re#image#555#the Siamese twins#chang and eng bunker
263 notes
·
View notes
Text


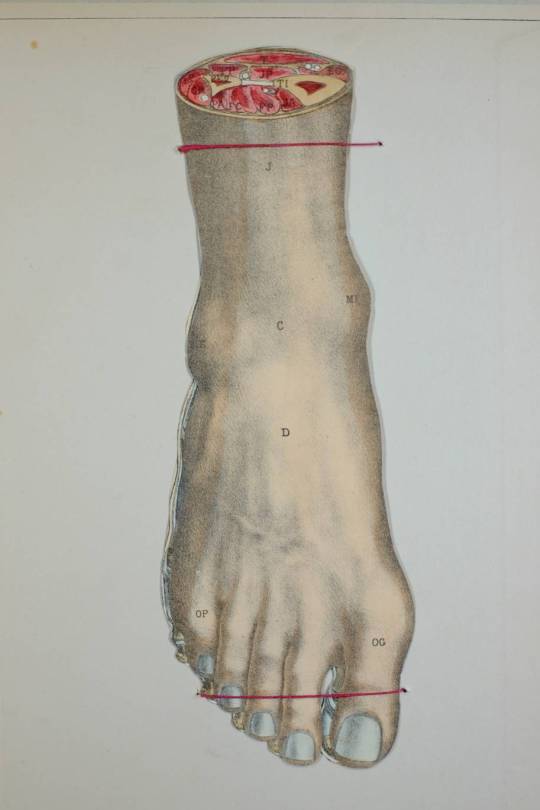
Human Anatomy and Physiology, A Movable Atlas
Gustave-Joseph Witkowski, c. 1880
#art#science#medicine#anatomy#witkowski#gustave joseph witkowski#1880s#skeleton#human anatomy and physiology#medical science#the body#illustration#vintage
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Johnson & Johnson is currently, like right this minute, trying to extend their patent on the TB drug bedaquiline, keeping it out of generic for another four years. TB killed about 30,000 people last week and is the world's deadliest infectious disease.
If this drug does not go generic now it could affect 6 million people in the next four years (the time it would take the "new" patent to run out). Out of those millions of people who get TB, but can't get bedaquiline, most of them will die. From a PREVENTABLE DISEASE.
Why is this happening? Money. But also, because TB is not an issue in countries like the US. We can afford its $1.50 a pill price. But if you live in a poor country, that's too much money to spend on something you need to take for up to four months.
J&J needs to let this drug go public and do its job in places that can't currently afford it. They need to help people, instead of trying to wring the last few drops of money out of one of their many products, at the cost of human lives.
@sizzlingsandwichperfection-blog does a waaaay better job of explaining this than me. Check out the video and the video description for links and ways to help!
#johnson and johnson#j&j#bedaquiline#tuberculosis#preventable diseases#patientsnotpatents#patients not patents#patients#doctors#medical science#medical#medication#science tumblr#health care#health industry#pharmaceutical#TB#healthcare#treatment#medicine#people are dying#help if you can#help plz#do something#booklr#rich people#poor people#Youtube#john green#hank green
112 notes
·
View notes
Text
#science#science communication#scicomm#science education#stem#science blog#biology#physics#medical science#health#medical mystery#medical research#genetics
63 notes
·
View notes
Text
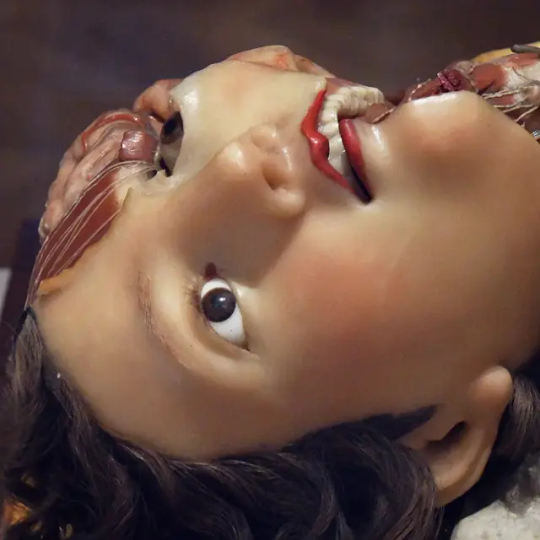


Model depicting internal organs for medical study (1700's)- Science museum, London
#dissection#dissect#anatomy#medical#medical science#medicine#history#science museum#cadaver#mannequin#dead#death#goth#gothic#horror#macabre#morbid#gruesome#goth aesthetic#goth art#eye#evil eye#rotting#decay#internal organs
150 notes
·
View notes
Text
A new drug was able to quickly and temporarily immobilize sperm in male mice, according to a study published Tuesday in Nature Communications, a discovery researchers described as a “game-changer” that could pave the way for a male contraceptive pill and could ultimately allow men to share equal responsibility with women for birth control.
A single oral dose of the drug immobilized mice sperm for up to two and a half hours and was 100% effective in the first two hours, the researchers said.
Treated mice showed normal mating behavior but none impregnated a mate despite 52 different attempts to do so, the researchers said, compared to almost a third of mice impregnating mates after being treated with an inactive control substance.
The drug is fast-acting—Melanie Balbach, one of the study’s authors and a researcher at Weill Cornell Medicine, said it worked within 30 to 60 minutes—and works by inhibiting an enzyme needed for sperm to function.
It is also temporary, with efficacy dropping to 91% at three hours and fertility returning to normal by the next day.
These properties set the drug apart from many of the other efforts to develop a male contraceptive, the researchers said, which often rely on hormones to control fertility and can take weeks or months to be effective or to wear off.
The study demonstrates proof-of-concept for “safe, non-hormonal, on-demand, male contraceptives,” the researchers said, and while it may work in theory any product will be many years and a great deal of testing in the future.
-via Forbes, 2/14/23
And there is ANOTHER breakthrough with a different method from just two months later:
A ground-breaking contraceptive pill for men could be just around the corner after a major genetic breakthrough. Scientists at Washington State University have identified a gene which temporarily renders sperm infertile after they remove it.
The research team discovered a protein encoded by this gene, found solely in the testicular tissue of most mammals, which reduced sperm counts and deformed remaining sperm to make them incapable of fertilizing an egg when altered. The potentially historic breakthrough contraceptive pill would also have no hormonal side-effects and could be additionally help control animal overpopulation — replacing castration.
Crucially, the destabilization of the infertility protein is not permanent, meaning sperm will recover once the person or animal stops taking the treatment. Scientists have hailed the discovery as potentially important for the future of the human race. In their study, researchers identified the expression of a gene called Arrdc5 in the testicular tissue of mice, pigs, cattle, and humans...
However, disrupting the functions of this protein will not require any hormonal interference, a key hurdle considering the multiple roles testosterone plays beyond sperm production in men, including the building of bone mass and muscle strength as well as red blood cell production. The team also says that designing a drug which only targets this protein would further make it easily reversible as a contraceptive.
-via Study Finds, 4/19/23
Note: Please excuse the cissexist language from the sources here, which I have not edited out for accuracy, etc. The Forbes article does respectfully discuss trans and nonbinary people and their birth control needs further down.
#birth control#contraception#reproductive care#reproductive rights#medical science#genetics#sperm#gender equality#good news#hope
181 notes
·
View notes
Photo


Foxgloves in medicine (1951)
#foxglove#digitalis#digitalis purpurea#flowers#nature#history#medical history#medical science#botany#vintage#50's#1950's#*
474 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ok so scientists of Tumblr. Is it worth it to make a professional science Twitter? My current PI suggested I do to find opportunities but Twitter is Twitter and I don't want to touch it with a 10 foot poll. But, I am lacking in marine science opportunities and absolutely need to network.
So, strangers on the internet what's your opinion. Is science Twitter worth it?
#scientists of Tumblr#biology#ecology#environmental science#marine biology#astrophysics#science#physics#medical science#vet studyblr#studyblr#stemblr#chemistry#women in stem#honestly i should just review papers here on Tumblr#start a new trend#veterinary medicine#biochemistry
82 notes
·
View notes