#greek law office for refugees
Text
#greek lawyer for refugees#immigration lawyer#greek lawyer#greek law office for refugees#migration law#migrants#refugees#residence permits#application for political asylum#political asylum#appeals#protection from deportation#protection from administrative detention#passports#pleadings#family reunifications#naturalisation-acquisition de la citoyenneté grecque et accompagnement à toutes les étapes du processus#golden visa
2 notes
·
View notes
Note
this is like, definitely a really weird question to throw your way, but you're the only person i know of who's into it, so- how do you get into the Mechanisms? like. do you just listen to the albums?
Not a weird question at all, anon! The Mechanisms are great but they're also like. A lot and really difficult to get into without some help.
I highly recommend checking out this post for a great general guide on the characters, basic lore, and the main albums.
Basic info from me:
The Mechanisms were a character band where the performers each played a member of a crew of space pirates, made immortal through being "mechanized" (except for The Toy Soldier, which is doing its own thing).
The albums and individual tracks are presented as retellings of events that the mechs witnessed in their travels to different planets, space stations, solar systems, etc. Different mechs play characters in the story (ie: Jonny Sims plays the mech Jonny D'Ville who plays Ulysses in UDAD), presenting their own (self-admittedly biased and inaccurate) accounts of what happened. These albums are heavily based on things like mythos and existing tales, which is explained in-lore as stories just replaying in the universe in different ways.
These stories do not have happy endings. Ever. "So know the void is screaming mad, no happy endings out there, lad." - Tales to be Told.
Since the albums are telling a story, the songs have to be listened to in order to understand them. The general pattern is narration-song-narration-song. The albums themselves can be listened to in any order though; most people recommend Once Upon a Time In Space, then High Noon Over Camelot, then Ulysses Dies at Dawn, then The Bifrost Incident. Personally (don't come at me), I feel like TBI is a poor one to end on because it doesn't have a finale song like the others; I recommend finishing on a really strong note with UDAD or HNOC.
Once Upon a Time In Space: a story of a rebel space faction waging war against an immortal tyrant king, with a heavy focus on a refugee princess trying to save her wife from the king. Inspired by classic Western fairytales like Snow White and Cinderella.
High Noon Over Camelot: a scifi Western taking place on an abandoned space station, with the leaders trying to gain access to the station's controls before it goes hurtling into the sun. One of the songs, Hellfire, is incredible but based heavily on Southern doom preachers in case that's a trigger. Inspired by Arthurian mythos with biblical themes and a tarot theme for the track names?
Ulysses Dies at Dawn: a corrupt world run by people using the brains (and, presumably, souls) of the dead to run the planet and fuel their own immortality, with a main focus on a retired war criminal and their brief stint as the captive of a bunch of criminals trying to access their locked vault. Inspired by Greek and Roman mythos (you can actually figure out "sides" based on the characters' names!)
The Bifrost Incident: a transport officer trying to investigate the decades-old disappearance of a train containing their world's most powerful and influential people, with three captive mechs being their main source of information. Inspired by Norse and Cthulhu mythos.
There's also some incredible side albums like Gunpower Tim vs the Moon Kaiser (GPT's origin story and how he was mechanized), Frankenstein (an extremely trans retelling), and Alice (a side sequel to OUATIS, about a planet where the war continues).
There's also individual tracks and short stories that sometimes stand on their own and are sometimes connected to one of the main albums, just little ways to fill in the lore. Jessica Law, the performer for The Toy Soldier, has a frankly beautiful song called Narcissus Under the Knife that is about a character mentioned in one of the lore stories for UDAD.
Some of the mechanisms have their own individual origin songs. That list includes Gunpowder Tim vs the Moon Kaiser (GPT), One-Eyed Jacks (Jonny D'Vill, debatable, he's said most of it is lies), Lucky Sevens (Ashes O'Reilly), Cyberian Demons (Nastya Rasputina), and Lost in the Cosmos (Drumbot Brian). Kofi Young, the performer for Doctor Baron Marius Von Raum (neither a doctor nor a baron) is working on their own album for Marius' origin titled The Death of Byron von Raum.
Speaking of lore: you can find official fiction for the characters and individual albums (excluding TBI rip) on the official website. Highly recommend reading them if you're interested in engaging with the fandom.
There's more lore but a lot of it is buried in old archived blogspot posts, on twitter, or idly mentioned on either tumblr or on discord servers (Maki's is very active). I'm sure there's some google doc with links floating around tumblr somewhere but a lot of it is just off-hand stuff (like the time Drumbot Brian was briefly replaced as drummer with octokittens, multi-tentacled creatures living on the ship).
The fandom has sooooooo many antis, man, it's not even funny. People will ride your ass for shipping Nastya and Jonny, noncon is a big no-no (goddd), and fans simultaneously want all the mechs to be uwu soft and fluffy found family but also if you give them any personality traits whatsoever then you're trying to erase their horrific crimes. It's a fucking mess so be prepared for that.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text

2022 / 50
Aperçu of the Week:
"Having to go to school should be considered child labor."
(My 14-year-old son)
Bad News of the Week:
In a European country that is also a NATO member, the judiciary has sentenced a citizen to two years and seven months in prison for insulting public officials. Sound harsh? It is. Especially when the convicted man merely spoke of "fools" and did not address anyone personally. Even harder, however, is that the person also got a so-called "political ban". Especially because he is a politician. Stupidly from the opposition. Stupidly in Turkey.
Ekrem Imamoglu is the mayor of Istanbul, by far the largest city in Turkey, a vibrant metropolis located on two continents. He is accused of publicly insulting officials: he is said to have called those who "canceled the (municipal) elections (on March 31, 2019)" idiots. The bottom line is that he has thus denied non-partisanship to the officials. And is right in doing so. Because after two decades of the richly authoritative AKP rule under President Recep Erdogan, Turkey's state agencies, like the judiciary, have degenerated into lackeys.
And just like other critics such as Deniz Yükel, Osman Kavala, Canan Kaftancioglu or even Jan Böhmermann, Ekrem Imamoglu is now suffering the same fate. Anyone who doubts the ruler gets into trouble. Especially if he is considered a promising challenger to Erdogan in the upcoming elections in June 2023. Who obviously thinks little of the rule of law. You can also ask any Kurd. Or, more recently, any Swede or Finn. He denies the former any right to exist. And at least NATO membership for the latter, because he disagrees with their treatment of the - surprise! - Kurds. After all, they are basically terrorists.
But as I said, Turkey is a NATO member. For the U.S., therefore, it is a geopolitically indispensable partner. Because of its location on the southern Black Sea, which controls the access of Russian navy - not only Cuba fan Nikita Crushchov can sing a song about that. And for the EU also geopolitically an indispensable partner. Again, on the Bosphorus and the Dardanelles. In this case as the bridge of countless not only Syrian or Afghan refugees to Europe. As long as Erdogan protects the democracies of others, he may nip this same democracy in the bud in his own country. That is probably also politics. Without any ban at all.
Good News of the Week:
Political Brussels has been rocked by a scandal for a week now: there are allegations of corruption against members of the EU Parliament. And these are so massive that the investigation has led to house searches and even arrests in four cases. At the center is a vice president of the Parliament, the Greek Eva Kaili. Bags full of cash would have been found on her. The accusations are serious. They range from bribery and money laundering to participation in a criminal organization.
Corruption always involves two parties: the bribed party and the bribing party. The latter is allegedly the Gulf state of Qatar. Which is apparently not only willing to buy international sports organizations, but also political goodwill with key partner countries. And it seems fitting, after all, Kaili in particular has recently been a vocal advocate of visa-free travel for Qataris. Her lawyer has so far denied any corruption, but that is his job: "She has nothing to do with money flows from Qatar, nothing at all," and he is not allowed to comment on details.
The reactions at the European level came promptly. Still on the weekend, Kaili was deprived of all powers of the office by the President of the Parliament, the Maltese Roberta Metsola. Then she was expelled from her Greek Pasok party and also from the Socialist group in the European Parliament. And finally, the formal impeachment by the Parliament itself. Already on the second working day of the week! And with only one dissenting vote!
Mind you, the presumption of innocence also applies in Belgium until a legal conviction. And at the moment it seems that Kaili's partner Giorgi is the mastermind. But political hygiene demands action in the case of such serious accusations. Quickly and clearly. That is what happened. The U.S. Republicans, for example, could take a leaf out of their book.
But what also makes this case so unique is just that - its uniqueness. For background: the EU Parliament has existed since 1952, has 705 members from 27 countries in this legislative period, and is the only directly elected supranational institution in the world. And yet this is the first time that a scandal of this magnitude has happened. For me, this means two things: Europe is not a banana republic. And if it is, it knows how to fight back.
Personal happy moment of the week:
Just now the fireplace crackles für the first time this winter. Which pleases me in several ways. The never-ending fascination of the flames. The adorable scent that fills the whole house. The almost therapeutic warmth, which is incomparable. And it was a simple wish I could fulfill for my wife on her birthday.
I couldn't care less...
...about the publicly celebrated royal family therapy of "Harry & Meghan" - now also available as a streaming service. There's really nothing more to say about it.
As I write this...
...I am once again very much in agreement with a position taken by UN Secretary General Antonio Guterres. He had reacted "very disturbed" to the interim blocking of various journalists' accounts on Twitter by Elon Musk. The "arbitrary" move sets a "dangerous precedent" at a time when journalists around the world are facing "censorship, physical danger and even worse." Media should not be "silenced on a platform that declares itself a space for free speech." There is really nothing more to say about this either.
Post Scriptum
U.S. Republicans continue to work to lack respect for the rule of law. The latest highlight was delivered by Marjorie Taylor Greene at the New York Young Republican Club Gala, when she commented on the storming of the Capitol on Jan. 6, 2021, as follows: "I got to tell you something, if Steve Bannon and I had organized that, we would have won. Not to mention, it would've been armed." There was applause. That can only be called a loss of reality. In comparison, the digital trading cards in the style of superheroes of her idol Donald Trump, who considers himself "better than Lincoln, better than Washington," are merely a bad joke. But they also show that the true function of elected politicians - namely to be public servants - has not yet got around in these circles.
#thoughts#aperçu#good news#bad news#news of the week#happy moments#politics#child labor#turkey#nato#erdogan#democracy#brussels#european union#eva kaili#corruption#fireplace#harry & meghan#antonio guterres#elon musk#twitter#republicans#marjorie taylor greene#Post scriptum#donald trump#free press#eu parliament#qatar#refugees#school
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Anonymous asked: I have always appreciated your thoughtful views on the defence of the British monarchy, and as a university historian it’s reassuring to see someone using history to make invalubale insights to a controversial institution. I wonder what are your own thoughts on the passing of Prince Philip and what his legacy might be? Was he a gaffe prone racist and a liability to the Queen?
I know you kindly got in touch and identified yourself when you felt I was ignoring your question. I’m glad we cleared that up via DM. The truth is as I said and I’m saying here is that I had to let some time pass before I felt I could reasonably answer this question. Simply because - as you know as someone who teaches history at university - distance is good to make a sober appraisal rather than knee jerk in the moment judgements.

Contrary to what some might think I’m not really a fan girl when it comes to the royal family. I don’t religiously follow their every movement or utterance especially as I live in Paris and therefore I don’t really care about tabloid tittle tattle. I only get to hear of anything to do with the royal family when I speak to my parents or my great aunts and uncles for whom the subject is closer to their heart because of the services my family has rendered over past generations to the monarchy and the older (and dying) tight knit social circles they travel in.
Like Walter Bagehot, I’m more interested in the monarchy as an institution and its constitutional place within the historical, social, and political fabric of Britain and its continued delicate stabilising importance to that effect. It was Walter Bagehot, the great constitutional scholar and editor the Economist magazine, who said, “The mystic reverence, the religious allegiance, which are essential to a true monarchy, are imaginative sentiments that no legislature can manufacture in any people.” In his view, a politically-inactive monarchy served the best interests of the United Kingdom; by abstaining from direct rule, the monarch levitated above the political fray with dignity, and remained a respected personage to whom all subjects could look to as a guiding light.
Even as a staunch monarchist I freely confess that there has always been this odd nature of the relationship between hereditary monarchy and a society increasingly ambivalent about the institution. To paraphrase Bagehot again, there has been too much ‘daylight’ shone onto the ‘magic’ of the monarchy because we are obsessed with personalities as celebrities.
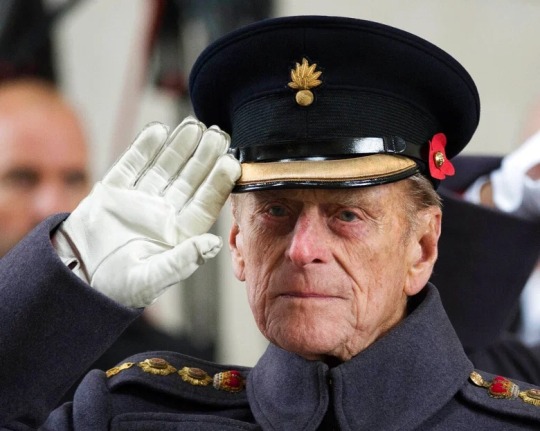

Having said that I did feel saddened by the passing of Prince Philip, the Duke of Edinburgh. After the Queen, he was my favourite royal. Anne, Princess Royal, would come next because she is very much like her father in temperament, humour, and character, so unlike her other brothers.
I have met the late Prince Philip when I was serving in the army in a few regimental meet-and-greet situations - which as you may know is pretty normal given that members of the royal family serve as honorary colonel-in-chiefs (patrons in effect) of all the British army regiments and corps.I also saw him at one or two social events such the annual charitable Royal Caledonian Ball (he’s an expert scottish reeler) and the Guards Polo Club where my older brothers played.
I’ll will freely confess that he was the one royal I could come close to identify with because his personal biography resonated with me a great deal.
Let’s be honest, the core Windsor family members, born to privilege, are conditioned and raised to be dull. Perhaps that’s a a tad harsh. I would prefer the term ‘anonymously self-effacing’, just another way of saying ‘for God’s sake don’t draw attention to yourself by saying or doing anything even mildly scandalous or political lest it invites public opprobrium and scrutiny’. The Queen magnificently succeeds in this but the others from Charles down just haven’t (with the exception of Princess Anne).
However, many people forget this obvious fact that it’s the incoming husbands and wives who marry into the Windsor family who are relied upon to bring colour and even liven things up a little. And long before Kate Middleton, Meghan Markle (very briefly), or Lady Diana Spencer, were the stars of ‘The Firm’- a phrase first coined by King George VI, Queen Elizabeth II's father who ruled from 1936 to 1952, who was thought to have wryly said, "British royals are 'not a family, we're a firm,” - it was Prince Philip who really livened things up and made the greater impact on the monarchy than any of them in the long term.
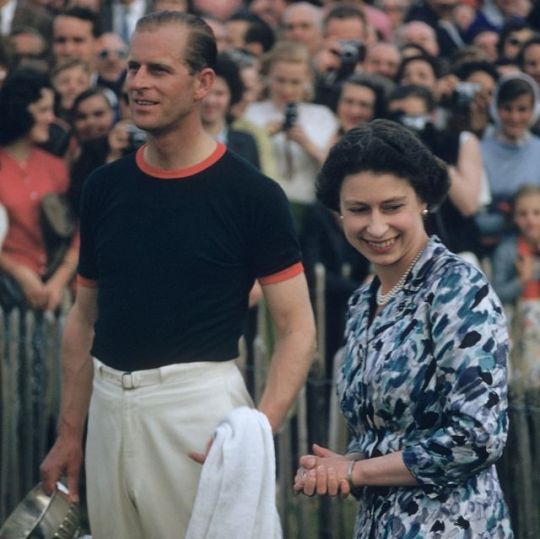

Prince Philip’s passing belied the truth of a far more complex individual: a destitute and penniless refugee Greek-Danish prince with a heart breaking backstory that could have been penned by any 19th Century novelist, and also eagle eyed reformer who tried to drag the royal family into the 20th century. At the core of the man - lost scion of a lost European royal dynasty, a courageous war veteran, and Queen’s consort - were values in which he attempted to transform and yet maintain much older inherited traditions and attitudes. Due to his great longevity, Philip’s life came to span a period of social change that is almost unprecedented, and almost no one in history viewed such a transformation from the front row.
Prince Philip would seem to represent in an acute form the best of the values of that era, which in many ways jar with today’s. He had fought with great courage in the war as a dashing young naval officer; he was regularly rude to foreigners, which was obviously a bonus to all Brits. He liked to ride and sail and shoot things. He was unsentimental almost to a comic degree, which felt reassuring at a time when a new-found emotional incontinence made many feel uncomfortable. Outrageous to some but endearing to others, he was the sort of man you’d want to go for a pint with, perhaps the ultimate compliment that an Englishman can pay to another Englishman. This has its own delicious irony as he wasn’t really an Englishman.
There are 4 takeways I would suggest in my appraisal of Prince Philip that stand out for me. So let me go through each one.

1. Prince Philip’s Internationalism
It may seem odd for me to say that Prince Philip wasn’t English but he wasn’t an Englishman in any real sense. He was a wretch of the world - stateless, homeless, and penniless. That the Prince of Nowhere became the British Monarchy’s figurehead was more than fitting for a great age of migration and transition in which the Royal Family survived and even flourished. That he was able to transform himself into the quintessential Englishman is testimony not just to his personal determination but also to the powerful cultural pull of Britishness.
He was born on a kitchen table in Corfu in June 1921. A year later in 1922, Philip, as the the great-great-grandson of Queen Victoria and nephew of Constantine I of Greece, was forced to flee with his family after the abdication of Constantine. He grew up outside Paris speaking French; ethnically he was mostly German although he considered himself Danish, his family originating from the Schleswig border region. He was in effect, despite his demeanour of Royal Navy officer briskness, a citizen of nowhere in an age of movement. From a very young age he was a stateless person, nationally homeless. Indeed, Philip was an outsider in a way that even Meghan Markle could never be; at his wedding in 1947, his three surviving sisters and two brothers-in-law were not permitted to attend because they were literally Britain’s enemies, having fought for the Germans. A third brother-in-law had even been in the SS, working directly for Himmler, but had been killed in the conflict.

Even his religion was slightly exotic. He was Greek Orthodox until he converted to Anglicanism on marrying Elizabeth - what with his wife due to become supreme head of the Church and everything - but his ties with eastern Christianity remained. His great-aunts Princess Elisabeth of Hesse and by Rhine and Tsarina Alexandra are both martyrs of the Russian Orthodox Church, having been murdered by the Bolsheviks; Philip’s mother went on to become an Orthodox nun and a “Righteous Among the Nations” for saving a Jewish family during the Nazi occupation of Greece, spending much of her time in squalid poverty.
His parents were part of the largely German extended aristocracy who ruled almost all of Europe before it all came crashing down in 1918. When he died, aged 99, it marked a near-century in which all the great ideological struggles had been and gone; he had been born before the Soviet Union but outlived the Cold War, the War on Terror and - almost - Covid-19.
The world that Philip was born into was a far more violent and dangerous place than ours. In the year he was born, Irish rebels were still fighting Black and Tans; over the course of 12 months the Spanish and Japanese prime ministers were assassinated, there was a coup in Portugal and race riots in the United States. Germany was rocked by violence from the far-Left and far-Right, while in Italy a brutal new political movement, the Fascists, secured 30 seats in parliament, led by a trashy journalist called Benito Mussolini.
The worst violence, however, took place in Greece and Turkey. Following the defeat of the Ottoman Empire, what remained of Turkey was marked for permanent enfeeblement by the Allies. But much to everyone’s surprise the country’s force were roused by the brilliant officer Mustafa Kemal, who led the Turks to victory. Constantinople was lost to Christendom for good and thousands of years of Hellenic culture was put to the flames in Smyrna.
The Greek royal family, north German imports shipped in during the 19th century, bore much of the popular anger for this disaster. King Constantine fled to Italy, and his brother Andrew was arrested and only escaped execution through the intervention of his relative Britain’s George V. Andrew’s wife Alice, their four daughters and infant son Philip fled to France, completely impoverished but with the one possession that ensures that aristocrats are never truly poor: connections.
Philip had a traumatic childhood. He was forged by the turmoil of his first decade and then moulded by his schooling. His early years were spent wandering, as his place of birth ejected him, his family disintegrated and he moved from country to country, none of them ever his own. When he was just a year old, he and his family were scooped up by a British destroyer from his home on the Greek island of Corfu after his father had been condemned to death. They were deposited in Italy. One of Philip's first international journeys was spent crawling around on the floor of the train from an Italian port city, "the grubby child on the desolate train pulling out of the Brindisi night," as his older sister Sophia later described it.

In Paris, he lived in a house borrowed from a relative; but it was not destined to become a home. In just one year, while he was at boarding school in Britain, the mental health of his mother, Princess Alice, deteriorated and she went into an asylum; his father, Prince Andrew, went off to Monte Carlo to live with his mistress. "I don't think anybody thinks I had a father," he once said. Andrew would die during the war. Philip went to Monte Carlo to pick up his father's possessions after the Germans had been driven from France; there was almost nothing left, just a couple of clothes brushes and some cuff-links.
Philip’s four sisters were all much older, and were soon all married to German aristocrats (the youngest would soon die in an aeroplane crash, along with her husband and children). His sisters became ever more embroiled in the German regime. In Scotland going to Gordonstoun boarding school, Philip went the opposite direction, becoming ever more British. Following the death of his sister Cecilie in a plane crash in 1937, the gulf widened. As the clouds of conflict gathered, the family simply disintegrated. With a flash of the flinty stoicism that many would later interpret, with no little justification, as self-reliance to the point of dispassion, the prince explained: “It’s simply what happened. The family broke up… I just had to get on with it. You do. One does.”
In the space of 10 years he had gone from a prince of Greece to a wandering, homeless, and virtually penniless boy with no-one to care for him. He got through it by making a joke of everything, and by being practical.
By the time he went to Gordonstoun, a private boarding school on the north coast of Scotland, Philip was tough, independent and able to fend for himself; he'd had to be. Gordonstoun would channel those traits into the school's distinct philosophy of community service, teamwork, responsibility and respect for the individual. And it sparked one of the great passions of Philip's life - his love of the sea. It was Gordonstoun that nurtured that love through the maturation of his character.
Philip adored the school as much as his son Charles would despise it. Not just because the stress it put on physical as well as mental excellence - he was a great sportsman. But because of its ethos, laid down by its founder Kurt Hahn, a Jewish exile from Nazi Germany.
Hahn first met Philip as a boy in Nazi Germany. Through a connection via one of his sister’s husbands, Philip, the poor, lonely boy was first sent off to a new school - in Nazi Germany. Which was as fun as can be imagined. Schloss Salem had been co-founded by stern educator called Kurt Hahn, a tough, discipline-obsessed conservative nationalist who saw civilisation in inexorable decline. But by this stage Hahn, persecuted for being Jewish in Nazi Germany, had fled to Britain, and Philip did not spend long at the school either, where pressure from the authorities was already making things difficult for the teachers. Philip laughed at the Nazis at first, because their salute was the same gesture the boys at his previous school had to make when they wanted to go to the toilet, but within a year he was back in England, a refugee once again.

Philip happily attended Hahn’s new school, Gordonstoun, which the strict disciplinarian had set up in the Scottish Highlands. Inspired by Ancient Sparta, the boys (and then later girls) had to run around barefoot and endure cold showers, even in winter, the whole aim of which was to drive away the inevitable civilisational decay Hahn saw all around him. To 21st century ears it sounds like hell on earth, yet Philip enjoyed it, illustrating just what a totally alien world he came from.
That ethos became a significant, perhaps the significant, part of the way that Philip believed life should be lived. It shines through the speeches he gave later in his life. "The essence of freedom," he would say in Ghana in 1958, "is discipline and self-control." The comforts of the post-war era, he told the British Schools Exploring Society a year earlier, may be important "but it is much more important that the human spirit should not be stifled by easy living". And two years before that, he spoke to the boys of Ipswich School of the moral as well as material imperatives of life, with the "importance of the individual" as the "guiding principle of our society".
It was at Gordonstoun one of the great contradictions of Philip's fascinating life was born. The importance of the individual was what in Kurt Hahn's eyes differentiated Britain and liberal democracies from the kind of totalitarian dictatorship that he had fled. Philip put that centrality of the individual, and individual agency - the ability we have as humans to make our own moral and ethical decisions - at the heart of his philosophy.
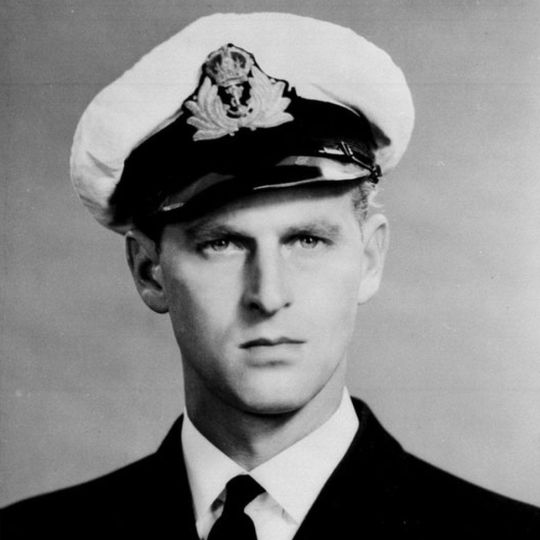

At Dartmouth Naval College in 1939, the two great passions of his life would collide. He had learned to sail at Gordonstoun; he would learn to lead at Dartmouth. And his driving desire to achieve, and to win, would shine through. Despite entering the college far later than most other cadets, he would graduate top of his class in 1940. In further training at Portsmouth, he gained the top grade in four out of five sections of the exam. He became one of the youngest first lieutenants in the Royal Navy.
The navy ran deep in his family. His maternal grandfather had been the First Sea Lord, the commander of the Royal Navy; his uncle, "Dickie" Mountbatten, had command of a destroyer while Philip was in training. In war, he showed not only bravery but guile. It was his natural milieu. "Prince Philip", wrote Gordonstoun headmaster Kurt Hahn admiringly, "will make his mark in any profession where he will have to prove himself in a trial of strength".
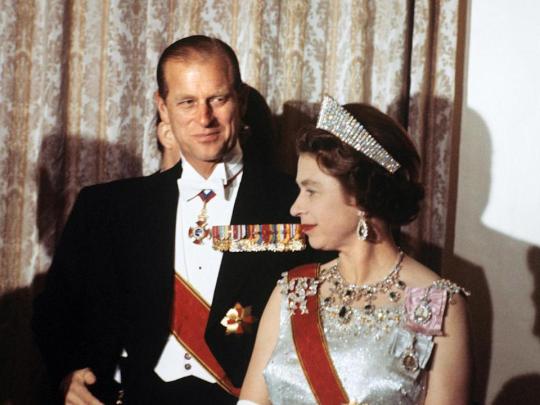

2. Prince Philip and the modernisation of the monarchy
In his own words, the process of defining what it meant to be a royal consort was one of “trial and error.” Speaking with BBC One’s Fiona Bruce in 2011, Philip explained, “There was no precedent. If I asked somebody, 'What do you expect me to do?' they all looked blank. They had no bloody idea, nobody had much idea.” So he forged for himself a role as a moderniser of the monarchy.
He could not have had much idea back in 1939. Back then in Dartmouth in 1939, as war became ever more certain, the navy was his destiny. He had fallen in love with the sea itself. "It is an extraordinary master or mistress," he would say later, "it has such extraordinary moods." But a rival to the sea would come.
When King George VI toured Dartmouth Naval College, accompanied by Philip's uncle, he brought with him his daughter, Princess Elizabeth. Philip was asked to look after her. He showed off to her, vaulting the nets of the tennis court in the grounds of the college. He was confident, outgoing, strikingly handsome, of royal blood if without a throne. She was beautiful, a little sheltered, a little serious, and very smitten by Philip.
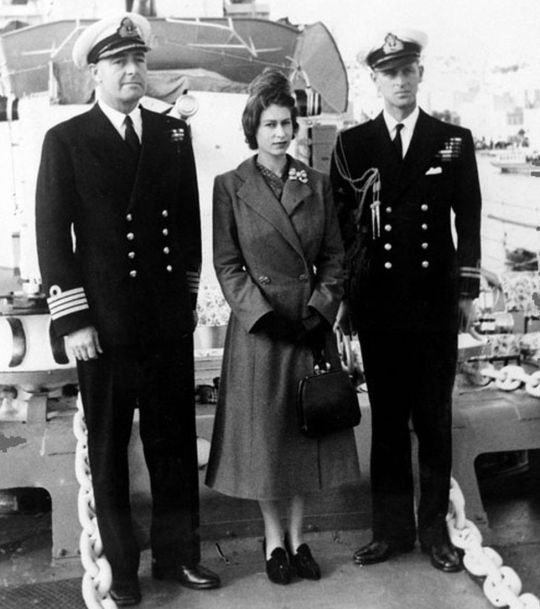

Did he know then that this was a collision of two great passions? That he could not have the sea and the beautiful young woman? For a time after their wedding in 1948, he did have both. As young newlyweds in Malta, he had what he so prized - command of a ship - and they had two idyllic years together. But the illness and then early death of King George VI brought it all to an end.
He knew what it meant, the moment he was told. Up in a lodge in Kenya, touring Africa, with Princess Elizabeth in place of the King, Philip was told first of the monarch's death in February 1952. He looked, said his equerry Mike Parker, "as if a ton of bricks had fallen on him". For some time he sat, slumped in a chair, a newspaper covering his head and chest. His princess had become the Queen. His world had changed irrevocably.
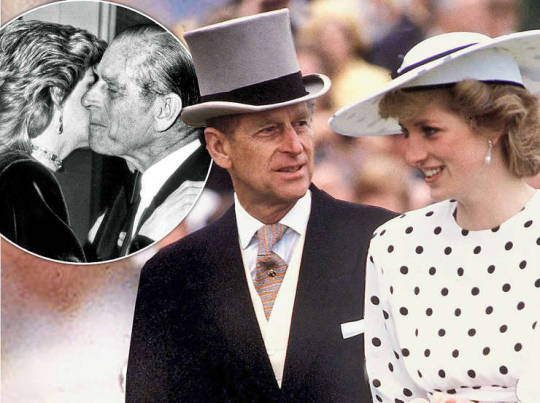

While the late Princess Diana was later to famously claim that there were “three people” in her marriage - herself, Prince Charles and Camilla - there were at least 55 million in Philip and Elizabeth’s. As Elizabeth dedicated her life to her people at Westminster Abbey at the Coronation on June 2, 1953, it sparked something of an existential crisis in Philip. Many people even after his death have never really understood this pivotal moment in Philip’s life. All his dreams of being a naval officer and a life at sea as well as being the primary provider and partner in his marriage were now sacrificed on the altar of duty and love.
With his career was now over, and he was now destined to become the spare part. Philip, very reasonably, asked that his future children and indeed his family be known by his name, Mountbatten. In effect he was asking to change the royal family’s name from the House of Windsor to the House of Mountbatten. But when Prime Minister Winston Churchill got wind of it as well as the more politically agile courtiers behind the Queen, a prolonged battle of wits ensued, and it was one Philip ultimately lost. It was only in 1957 that he accepted the title of “Prince.”

Even though he had almost lost everything dear to him and his role now undefined, he didn’t throw himself a pity party. He just got on with it. Philip tried to forge his own distinct role as second fiddle to the woman who had come to represent Great Britain. He designated himself the First Officer of the Good Ship Windsor. He set about dusting off some of the cobwebs off the throne and letting some daylight unto the workings of the monarchy by advocating reasonable amount of modernisation of the monarchy.
He had ideas about modernising the royal family that might be called “improving optics” today. But in his heart of hearts he didn’t want the monarchy to become a stuffy museum piece. He envisaged a less stuffy and more popular monarchy, relevant to the lives of ordinary people. Progress was always going to be incremental as he had sturdy opposition from the old guard who wanted to keep everything as it was, but nevertheless his stubborn energy resulted in significant changes.
When a commission chaired by Prince Philip proposed broadcasting the 1953 investiture ceremony that formally named Elizabeth II as queen on live television, Prime Minister Winston Churchill reacted with outright horror, declaring, “It would be unfitting that the whole ceremony should be presented as if it were a theatrical performance.” Though the queen had initially voiced similar concerns, she eventually came around to the idea, allowing the broadcast of all but one segment of the coronation. Ultimately, according to the BBC, more than 20 million people tuned in to the televised ceremony - a credit to the foresight of Philip.
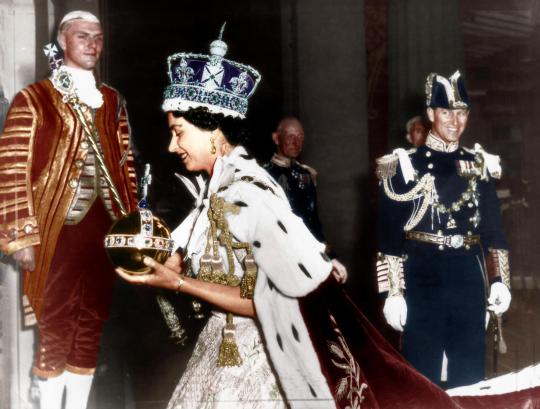

Elizabeth’s coronation marked a watershed moment for a monarchy that has, historically, been very hands off, old-fashioned and slightly invisible. Over the following years, the royals continued to embrace television as a way of connecting with the British people: In 1957, the queen delivered her annual Christmas address during a live broadcast. Again, this was Philip’s doing when he cajoled the Queen to televise her message live. He even helped her in how to use the teleprompter to get over her nerves and be herself on screen.
Four years later, in 1961, Philip became the first family member to sit for a television interview. It is hard for us to imagine now but back then it was huge. For many it was a significant step in modernising the monarchy.
Though not everything went to plan. Toward the end of the decade, the Windsors even invited cameras into their home. A 1969 BBC fly-on-the-wall documentary, instigated by Philip to show life behind the scenes, turned into an unmitigated disaster: “The Windsors” revealed the royals to be a fairly normal, if very rich, British upper-class family who liked barbecues, ice cream, watching television and bickering. The mystery of royalty took a hit below the waterline from their own torpedo, a self-inflicted wound from which they took a long time to recover. Shown once, the documentary was never aired again. But it had an irreversible effect, and not just by revealing the royals to be ordinary. By allowing the cameras in, Philip opened the lid to the prying eyes of the paparazzi who could legitimately argue that since the Royals themselves had sanctioned exposure, anything went. From then on, minor members of the House of Windsor were picked off by the press, like helpless tethered animals on a hunting safari.

Prince Philip also took steps to reorganise and renovate the royal estates in Sandringham and Balmoral such as intercoms, modern dish washers, generally sought to make the royal household and the monarchy less stuffy, not to have so much formality everywhere.
Philip helped modernised the monarchy in other ways to acknowledge that the monarchy could be responsive to changes in society. It was Prince Philip - much to the chagrin of the haughty Princess Margaret and other stuffy old courtiers - who persuaded the Queen to host informal lunches and garden parties designed to engage a broader swath of the British public. Conversely, Prince Philip heartily encouraged the Queen (she was all for it apparently but was still finding her feet as a new monarch) to end the traditional practice of presenting debutantes from aristocratic backgrounds at court in 1952. For Philip and others it felt antiquated and out of touch with society. I know in speaking to my grandmother and others in her generation the decision was received with disbelief at how this foreign penniless upstart could come and stomp on the dreams of mothers left to clutch their pearls at the prospect there would be no shop window for their daughter to attract a suitable gentleman for marriage. One of my great aunts was over the moon happy that she never would have to go through what she saw as a very silly ceremony because she preferred her muddy wellies to high heels.

A former senior member of the royal household, who spent several years working as one of Prince Philip’s aides, and an old family friend, once told us around a family dinner table that the Duke of Edinburgh was undoubtedly given a sense of permanence by his marriage into the Royal Family that was missing from earlier years. But the royal aide would hastily add that Prince Philip, of course, would never see it that way.
Prince Philip’s attitude was to never brood on things or seek excuses. And he did indeed get on with the job in his own way - there should be no doubt that when it came to building and strengthening the Royal Family it was a partnership of equals with the Queen. Indeed contrary to Netflix’s hugely popular series ‘The Crown’ and its depiction of the royal marriage with Philip’s resentment at playing second fiddle, the prince recognised that his “first duty was to serve the Queen in the best way I could,” as he told ITV in 2011. Though this role was somewhat ill-suited to his dynamic, driven, and outspoken temperament, Philip performed it with utter devotion.

3. Prince Philip’s legacy
One could argue rightly that modernising the monarchy was his lasting legacy achievement. But he also tried to modernise a spent and exhausted Britain as it emerged from a ruinous war. When peace came, and with it eventual economic recovery, Philip would throw himself into the construction of a better Britain, urging the country to adopt scientific methods, embracing the ideas of industrial design, planning, education and training. A decade before Harold Wilson talked of the "white heat of the technological revolution", Philip was urging modernity on the nation in speeches and interviews. He was on top of his reading of the latest scientific breakthroughs and well read in break out innovations.
This interest in modernisation was only matched by his love for nature. As the country and the world became richer and consumed ever more, Philip warned of the impact on the environment, well before it was even vaguely fashionable. As president of the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) in the UK for more than 20 years from 1961, he was one of the first high-profile advocates of the cause of conservation and biological diversity at a time when it was considered the preserve of an eccentric few.
For a generation of school children in Britain and the Commonwealth though, his most lasting legacy and achievement will be the Duke of Edinburgh Awards (DofE). He set up the Duke of Edinburgh award, a scheme aimed at getting young people out into nature in search of adventure or be of service to their communities. It was a scheme that could match the legacy of Baden Powell’s scouts movement.

When Prince Philip first outlined his idea of a scheme to harness the values of his education at Gordonstoun by bringing character-building outdoor pursuits to the many rather than the fee-paying few, he received short shrift from the government of the day. The then minister of education, Sir David Eccles responded to the Duke’s proposal by saying: “I hear you’re trying to invent something like the Hitler Youth.” Undeterred he pushed on until it came to fruition.
I’m so glad that he did. I remember how proud I was for getting my DofE Awards while I was at boarding school. With the support of great mentors I managed to achieve my goals: collecting second-hand English books for a literacy programme for orphaned street children in Delhi, India with a close Indian school friend and her family; and completing a 350 mile hike following St. Olav’s Pilgrimmage Trail from Selånger, on the east coast of Sweden, and ending at Nidaros Cathedral in Trondheim, on the west coast of Norway.
It continues to be an enduring legacy. Since its launch in 1956, the Duke of Edinburgh awards have been bestowed upon some 2.5 million youngsters in Britain and some eight million worldwide. For a man who once referred to himself as a “Greek princeling of no consequence”, his pioneering tutelage of these two organisations (alongside some 778 other organisations of which he was either president or a patron) would be sufficient legacy for most.

4. Prince Philip’s character
It may surprise some but what I liked most about Prince Philip was the very thing that helped him achieve so much and leave a lasting legacy: his character.
It is unhelpful to the caricature of Prince Philip as an unwavering but pugnacious consort whose chief talent was a dizzying facility in off-colour one-liners that he was widely read and probably the cleverest member of his family.
His private library at Windsor consists of 11,000 tomes, among them 200 volumes of poetry. He was a fan of Jung, TS Eliot, Shakespeare and the cookery writer Elizabeth David. As well as a lifelong fascination with science, technology and sport, he spoke fairly fluent French, painted and wrote a well received book on birds. It’s maddening to think how many underestimated his genuine intellect and how cultured he was behind the crusty exterior.

He didn’t have an entourage to fawn around him. He was the first to own a computer at Buckingham Palace. He answered his own phone and wrote and responded to his own correspondence. By force of character he fought the old guard courtiers at every turn to modernise the monarchy against their stubborn resistance.
Prince Philip was never given to self-analysis or reflection on the past. Various television interviewers tried without success to coerce him in to commenting on his legacy.But once when his guard was down he asked on the occasion of his 90th birthday what he was more proud of, he replied with characteristic bluntness: “I couldn’t care less. Who cares what I think about it, I mean it’s ridiculous.”
All of which neatly raises the profound aversion to fuss and the proclivity for tetchiness often expressed in withering put-downs that, for better or worse, will be the reflex memory for many of the Duke of Edinburgh. If character is a two edged sword so what of his gaffes?

There is no doubt his cult status partly owed to his so-called legendary gaffes, of which there are enough to fill a book (indeed there is a book). But he was no racist. None of the Commonwealth people or foreign heads of state ever said this about him. Only leftist republicans with too much Twitter time on their hands screamed such a ridiculous accusation. They’re just overly sensitive snowflakes and being devoid of any humour they’re easily triggered.
There was the time that Philip accepted a gift from a local in Kenya, telling her she was a kind woman, and then adding: “You are a woman, aren’t you?” Or the occasion he remarked “You managed not to get eaten, then?” to a student trekking in Papua New Guinea. Then there was his World Wildlife Fund speech in 1986, when he said: “If it has got four legs and it is not a chair, if it has got two wings and it flies but is not an aeroplane, and if it swims and it is not a submarine, the Cantonese will eat it.” Well, he wasn’t wrong.

Philip quickly developed a reputation for what he once defined, to the General Dental Council, as “dentopedology – the science of opening your mouth and putting your foot in it”. Clearly he could laugh at himself as he often did as an ice breaker to put others at ease.
His remarking to the president of Nigeria, who was wearing national dress, “You look like you’re ready for bed”, or advising British students in China not to stay too long or they would end up with “slitty eyes”, is probably best written off as ill-judged humour. Telling a photographer to “just take the fucking picture” or declaring “this thing open, whatever it is”, were expressions of exasperation or weariness with which anyone might sympathise.
Above all, he was also capable of genuine if earthy wit, saying of his horse-loving daughter Princess Anne: “If it doesn’t fart or eat hay she isn’t interested.” Many people might have thought it but few dared say it. If Prince Philip’s famous gaffes provoked as much amusement as anger, it was precisely because they seem to give voice to the bewilderment and pent-up frustrations with which many people viewed the ever-changing modern world.

A former royal protection officer recounts how while on night duty guarding a visiting Queen and consort, he engaged in conversation with colleagues on a passing patrol. It was 2am and the officer had understood the royal couple to be staying elsewhere in the building until a window above his head was abruptly slammed open and an irate Prince Philip stuck his head out of the window to shout: “Would you fuck off!” Without another word, he then shut the window.
The Duke at least recognised from an early age that he was possessed of an abruptness that could all too easily cross the line from the refreshingly salty to crass effrontery.
One of his most perceptive biographers, Philip Eade, recounted how at the age of 21 the prince wrote a letter to a relation whose son had recently been killed in combat. He wrote: “I know you will never think much of me. I am rude and unmannerly and I say things out of turn which I realise afterwards must have hurt someone. Then I am filled with remorse and I try to put matters right.”
In the case of the royal protection officer, the Duke turned up in the room used by the police officers when off duty and said: “Terribly sorry about last night, wasn’t quite feeling myself.”
Aides have also ventured to explain away some of their employer’s more outlandish remarks - from asking Cayman islanders “You are descended from pirates aren’t you?” to enquiring of a female fashion writer if she was wearing mink knickers - as the price of his instinctive desire to prick the pomposity of his presence with a quip to put others at ease.

Indeed many people forget that his ‘gaffes’ were more typical of the clubbish humour of the British officer class – which of course would be less appreciated, sometimes even offensive, to other ears. It’s why he could relate so well to veterans who enjoyed his bonhomie company immensely.
But behind the irascibility, some have argued there also lay a darker nature, unpleasantly distilled in his flinty attitude to his eldest son. One anecdote tells of how, in the aftermath of the murder of the Duke’s uncle and surrogate father, Lord Mountbatten, Philip lectured his son, who was also extremely fond of his “honorary grandfather”, that he was not to succumb to self-pity. Charles left the room in tears and when his father was asked why he had spoken to his son with so little compassion, the Duke replied: “Because if there’s any crying to be done I want it to happen within this house, in front of his family, not in public. He must be toughened up, right now.”
But here I would say that Prince Philip’s intentions were almost always sincere and in no way cruel. He has always tried to protect his family - even from their own worst selves or from those outside the family ‘firm’ who may not have their best interest at heart.

In 1937, a 16-year-old Prince Philip had walked behind his elder sister Cecile’s coffin after she was killed in a plane crash while heavily pregnant. The remains of newly-born infant found in the wreckage suggested the aircraft had perished as the pilot sought to make an emergency landing in fog as the mother entered childbirth. It was an excruciating taste of tragedy which would one day manifest itself in a very princely form of kindness that was deep down that defined Philip’s character.
When about 60 years later Prime Minister Tony Blair’s spin doctors in Downing Street tried to strong arm the Queen and the royal household over the the arrangements for the late Prince Diana’s funeral, it was Philip who stepped in front to protect his family. The Prime Minister and his media savvy spin doctors wanted the two young princes, William and Harry, to walk behind the coffin.
The infamous exchange was on the phone during a conference call between London and Balmoral, and the emotional Philip was reportedly backed by the Queen. The call was witnessed by Anji Hunter, who worked for Mr Blair. She said how surprised she was to hear Prince Philip’s emotion. ‘It’s about the boys,” he cried, “They’ve lost their mother”. Hunter thought to herself, “My God, there’s a bit of suffering going on up there”.’
Sky TV political commentator Adam Boulton (Anji Hunter’s husband) would write in his book Tony’s Ten Years: ‘The Queen relished the moment when Philip bellowed over the speakerphone from Balmoral, “Fuck off. We are talking about two boys who have just lost their mother”. Boulton goes on to say that Philip: ‘…was trying to remind everyone that human feelings were involved. No 10 were trying to help the Royals present things in the best way, but may have seemed insensitive.’

In the end the politicians almost didn’t get their way. Prince Philip stepped in to counsel his grandson, Prince William, after he had expressed a reluctance to follow his mother’s coffin after her death in Paris. Philip told the grieving child: “If you don’t walk, I think you’ll regret it later. If I walk, will you walk with me?”
It’s no wonder he was sought as a counsellor by other senior royals and especially close to his grandchildren, for whom he was a firm favourite. His relationship with Harry was said to have become strained, however, following the younger Prince’s decision to reject his royal inheritance for a life away from the public eye in America with his new American wife, Meghan Markle. For Prince Philip I am quite sure it went against all the elder Prince had lived his life by - self-sacrifice for the greater cause of royalty.
This is the key to Philip’s character and in understanding the man. The ingrained habits of a lifetime of duty and service in one form or another were never far away.

In conclusion then....
After more time passes I am sure historians will make a richer reassessment of Prince Philip’s life and legacy. Because Prince Philip was an extraordinary man who lived an extraordinary life; a life intimately connected with the sweeping changes of our turbulent 20th Century, a life of fascinating contrast and contradiction, of service and some degree of solitude. A complex, clever, eternally restless man that not even the suffocating protocols of royalty and tradition could bind him.
Although he fully accepted the limitations of public royal service, he did not see this as any reason for passive self-abnegation, but actively, if ironically, identified with his potentially undignified role. It is this bold and humorous embrace of fated restriction which many now find irksome: one is no longer supposed to mix public performance with private self-expression in quite this manner.
Yet such a mix is authentically Socratic: the proof that the doing of one’s duty can also be the way of self-fulfilment. The Duke’s sacrifice of career to romance and ceremonial office is all the more impressive for his not hiding some annoyance. The combination of his restless temperament and his deeply felt devotion to duty found fruitful expression; for instance, in the work of Saint George’s House Windsor - a centre and retreat that he created with Revd. Robin Woods - in exploring religious faith, philosophy, and contemporary issues.

Above all he developed a way to be male that was both traditional and modern. He served one woman with chivalric devotion as his main task in life while fulfilling his public engagements in a bold and active spirit. He eventually embraced the opportunity to read and contemplate more. And yet, he remained loyal to the imperatives of his mentor Kurt Hahn in seeking to combine imagination with action and religious devotion with practical involvement.
Prince Philip took more pride in the roles he had accidentally inherited than in the personal gifts which he was never able fully to develop. He put companionship before self-realisation and acceptance of a sacred symbolic destiny before the mere influencing of events. In all these respects he implicitly rebuked our prevailing meritocracy which over-values officially accredited attainment, and our prevailing narcissism which valorises the assertion of discrete identities.

Prince Philip was Britain’s longest-serving consort. He was steadfast, duty driven, and a necessary adjunct to the continuity and stability of the Queen and the monarchy. Of all the institutions that have lost the faith of the British public in this period - the Church, Parliament, the media, the police - the Monarchy itself has surprisingly done better than most at surviving, curiously well-adapted to a period of societal change and moral anarchy. The House of Hanover and later Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (changed to Windsor), since their arrival in this country in 1714, have been noted above all for their ability to adapt. And just as they survived the Victorian age by transforming themselves into the bourgeoise, domestic ideal, so they have survived the new Elizabethan era (Harry-Meghan saga is just a passing blip like the Edward-Wallis Simpson saga of the 1930s).
There was once a time when the Royal’s German blood was a punchline for crude and xenophobic satirists. Now it is the royals who are deeply British while the country itself is increasingly cosmopolitan and globalised. British society has seen a greater demographic change than the preceding four or five thousand years combined, the second Elizabethan age has been characterised more than anything by a transformational movement of people. Prince Philip, the Greek-born, Danish-German persecuted and destitute wanderer who came to become one of the Greatest Britons of the past century, perhaps epitomised that era better than anyone else. And he got through it by making a joke of everything, and by being practical.
I hope I don’t exaggerate when I say that in our troubled times over identity, and our place and purpose in the world, we need to heed his selfless example more than ever.

As Heraclitus wisely said, Ήθος ανθρώπω δαίμων (Character is destiny.)
RIP Prince Philip. You were my prince. God damn you, I miss you already.
Thanks for your question.
#question#ask#prince philip#duke of edinburgh#queen elizabeth II#the queen of spades#monarchy#britain#british#royalty#politics#history#culture#europe#crown#icon#great briton#society
284 notes
·
View notes
Text

A beautiful late April day, seventy-two years after slavery ended in the United States. Claude Anderson parks his car on the side of Holbrook Street in Danville. On the porch of number 513, he rearranges the notepads under his arm. Releasing his breath in a rush of decision, he steps up to the door of the handmade house and knocks.
Danville is on the western edge of the Virginia Piedmont. Back in 1865, it had been the last capital of the Confederacy. Or so Jefferson Davis had proclaimed on April 3, after he fled Richmond. Davis stayed a week, but then he had to keep running. The blue-coated soldiers of the Army of the Potomac were hot on his trail. When they got to Danville, they didn’t find the fugitive rebel. But they did discover hundreds of Union prisoners of war locked in the tobacco warehouses downtown. The bluecoats, rescuers and rescued, formed up and paraded through town. Pouring into the streets around them, dancing and singing, came thousands of African Americans. They had been prisoners for far longer.
In the decades after the jubilee year of 1865, Danville, like many other southern villages, had become a cotton factory town. Anderson, an African-American master’s student from Hampton University, would not have been able to work at the segregated mill. But the Works Progress Administration (WPA), a bureau of the federal government created by President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s New Deal, would hire him. To put people back to work after they had lost their jobs in the Great Depression, the WPA organized thousands of projects, hiring construction workers to build schools and artists to paint murals. And many writers and students were hired to interview older Americans—like Lorenzo Ivy, the man painfully shuffling across the pine board floor to answer Anderson’s knock.
Anderson had found Ivy’s name in the Hampton University archives, two hundred miles east of Danville. Back in 1850, when Lorenzo had been born in Danville, there was neither a university nor a city called Hampton—just an American fort named after a slaveholder president. Fortress Monroe stood on Old Point Comfort, a narrow triangle of land that divided the Chesapeake Bay from the James River. Long before the fort was built, in April 1607, the Susan Constant had sailed past the point with a boatload of English settlers. Anchoring a few miles upriver, they had founded Jamestown, the first perma- nent English-speaking settlement in North America. Twelve years later, the crews of two storm-damaged English privateers also passed, seeking shelter and a place to sell the twenty-odd enslaved Africans (captured from a Portuguese slaver) lying shackled in their holds.
After that first 1619 shipload, some 100,000 more enslaved Africans would sail upriver past Old Point Comfort. Lying in chains in the holds of slave ships, they could not see the land until they were brought up on deck to be sold. After the legal Atlantic slave trade to the United States ended in 1807, hundreds of thousands more enslaved people passed the point. Now they were going the other way, boarding ships at Richmond, the biggest eastern center of the internal slave trade, to go by sea to the Mississippi Valley.
By the time a dark night came in late May 1861, the moon had waxed and waned three thousand times over slavery in the South. To protect slavery, Virginia had just seceded from the United States, choosing a side at last after six months of indecision in the wake of South Carolina’s rude exit from the Union. Fortress Monroe, built to protect the James River from ocean-borne invaders, became the Union’s last toehold in eastern Virginia. Rebel troops entrenched themselves athwart the fort’s landward approaches. Local planters, including one Charles Mallory, detailed enslaved men to build berms to shelter the besiegers’ cannon. But late this night, Union sentries on the fort’s seaward side saw a small skiff emerging slowly from the darkness. Frank Baker and Townshend rowed with muffled oars. Sheppard Mallory held the tiller. They were setting themselves free.
A few days later, Charles Mallory showed up at the gates of the Union fort. He demanded that the commanding federal officer, Benjamin Butler, return his property. Butler, a politician from Massachusetts, was an incompetent battlefield commander, but a clever lawyer. He replied that if the men were Mallory’s property, and he was using them to wage war against the US government, then logically the men were therefore contraband of war.
Those first three “contrabands” struck a crack in slavery’s centuries-old wall. Over the next four years, hundreds of thousands more enslaved people widened the crack into a gaping breach by escaping to Union lines. Their movement weakened the Confederate war effort and made it easier for the United States and its president to avow mass emancipation as a tool of war. Eventually the Union Army began to welcome formerly enslaved men into its ranks, turning refugee camps into recruiting stations—and those African-American soldiers would make the difference between victory and defeat for the North, which by late 1863 was exhausted and uncertain.
After the war, Union officer Samuel Armstrong organized literacy programs that had sprung up in the refugee camp at Old Point Comfort to form Hampton Institute. In 1875, Lorenzo Ivy traveled down to study there, on the ground zero of African-American history. At Hampton, he acquired an education that enabled him to return to Danville as a trained schoolteacher. He educated generations of African-American children. He built the house on Holbrook Street with his own Hampton-trained hands, and there he sheltered his father, his brother, his sister-in-law, and his nieces and nephews. In April 1937, Ivy opened the door he’d made with hands and saw and plane, and it swung clear for Claude Anderson without rubbing the frame.1
Anderson’s notepads, however, were accumulating evidence of two very different stories of the American past—halves that did not fit together neatly. And he was about to hear more. Somewhere in the midst of the notepads was a typed list of questions supplied by the WPA. Questions often reveal the desired answer. By the 1930s, most white Americans had been demanding for decades that they hear only a sanitized version of the past into which Lorenzo Ivy had been born. This might seem strange. In the middle of the nineteenth century, white Americans had gone to war with each other over the future of slavery in their country, and slavery had lost. Indeed, for a few years after 1865, many white northerners celebrated emancipation as one of their collective triumphs. Yet whites’ belief in the emancipation made permanent by the Thirteenth Amendment, much less in the race-neutral citizenship that the Fourteenth and Fifteenth Amendments had written into the Constitution, was never that deep. Many northerners had only supported Benjamin Butler and Abraham Lincoln’s moves against slavery because they hated the arrogance of slaveholders like Charles Mallory. And after 1876, northern allies abandoned southern black voters.
Within half a century after Butler sent Charles Mallory away from Fortress Monroe empty-handed, the children of white Union and Confederate soldiers united against African-American political and civil equality. This compact of white supremacy enabled southern whites to impose Jim Crow segregation on public space, disfranchise African-American citizens by barring them from the polls, and use the lynch-mob noose to enforce black compliance. White Americans imposed increased white supremacy outside the South, too. In non-Confederate states, many restaurants wouldn’t serve black customers. Stores and factories refused to hire African Americans. Hundreds of midwestern communities forcibly evicted African-American residents and became “sundown towns” (“Don’t let the sun set on you in this town”). Most whites, meanwhile, believed that science proved that there were biologically distinct human races, and that Europeans were members of the superior one. Anglo-Americans even believed that they were distinct from and superior to the Jews from Russia, Italians, Greeks, Slavs, and others who flooded Ellis Island and changed the culture of northern urban centers.
By the early twentieth century, America’s first generation of professional historians were justifying the exclusions of Jim Crow and disfranchisement by telling a story about the nation’s past of slavery and civil war that seemed to confirm, for many white Americans, that white supremacy was just and necessary. Above all, the historians of a reunified white nation insisted that slavery was a premodern institution that was not committed to profit-seeking. In so doing, historians were to some extent only repeating pre–Civil War debates: abolitionists had depicted slavery not only as a psychopathic realm of whipping, rape, and family separation, but also as a flawed economic system that was inherently less efficient than the free-labor capitalism developing in the North. Proslavery writers disagreed about the psychopathy, but by the 1850s they agreed that enslavers were first and foremost not profit-seekers. For them, planters were caring masters who considered their slaves to be inferior family members. So although anti- and proslavery conclusions about slavery’s morality were different, their premises about slavery-as-a-business-model matched. Both agreed that slavery was inherently unprofitable. It was an old, static system that belonged to an earlier time. Slave labor was inefficient to begin with, slave productivity did not increase to keep pace with industrialization, and enslavers did not act like modern profit-seeking businessmen. As a system, slavery had never adapted or changed to thrive in the new industrial economy—let alone to play a premier role as a driver of economic expansion—and had been little more than a drag on the explosive growth that had built the modern United States. In fact, during the Civil War, northerners were so convinced of these points that they believed that shifting from slave labor to free labor would dramatically increase cotton productivity.
It didn’t. But even though the data of declining productivity over the ensuing three score and ten years suggested that slavery might have been the most efficient way to produce the world’s most important crop, no one let empirical tests change their minds. Instead, historians of Woodrow Wilson’s generation imprinted the stamp of academic research on the idea that slavery was separate from the great economic and social transformations of the Western world during the nineteenth century. After all, it did not rely upon ever-more efficient machine labor. Its unprofitable economic structures supposedly produced antique social arrangements, and the industrializing, urbanizing world looked back toward them with contempt—or, increasingly, nostalgia. Many whites, now proclaiming that science proved that people of African descent were intellectually inferior and congenitally prone to criminal behavior, looked wistfully to a past when African Americans had been governed with whips and chains. Granted, slavery as an economic system was not modern, they said, and had neither changed to adapt to the modern economy nor contributed to economic expansion. But to an openly racist historical profession—and a white history-reading, history-thinking public obsessed with all kinds of race control—the white South’s desire to white-wash slavery in the past, and maintain segregation now and forever, served the purpose of validating control over supposedly premodern, semi-savage black people.
Such stories about slavery shaped the questions Claude Anderson was to ask in the 1930s, because you could find openly racist versions of it baked into the recipe of every American textbook. You could find it in popular novels, politicians’ speeches, plantation-nostalgia advertising, and even the first blockbuster American film: Birth of a Nation. As president, Woodrow Wilson—a southern-born history professor— called this paean to white supremacy “history written with lightning,” and screened it at the White House. Such ideas became soaked into the way America publicly depicted slavery. Even many of those who believed that they rejected overt racism depicted the era before emancipation as a plantation idyll of happy slaves and paternalist masters. Abolitionists were snakes in the garden, responsible for a Civil War in which hundreds of thousands of white people died. Maybe the end of slavery had to come for the South to achieve economic modernity, but it didn’t have to come that way, they said.
The way that Americans remember slavery has changed dramatically since then. In tandem with widespread desegregation of public spaces and the assertion of black cultural power in the years between World War II and the
1990s came a new understanding of the experience of slavery. No longer did academic historians describe slavery as a school in which patient masters and mistresses trained irresponsible savages for futures of perpetual servitude.
Slavery’s denial of rights now prefigured Jim Crow, while enslaved people’s resistance predicted the collective self-assertion that developed into first the civil rights movement and later, Black Power.
But perhaps the changes were not so great as they seemed on the surface. The focus on showing African Americans as assertive rebels, for instance, implied an uncomfortable corollary. If one should be impressed by those who rebelled, because they resisted, one should not be proud of those who did not. And there were very few rebellions in the history of slavery in the United States. Some scholars tried to backfill against this quandary by arguing that all African Americans together created a culture of resistance, especially in slave quarters and other spaces outside of white observation. Yet the insistence that assertive resistance undermined enslavers’ power, and a focus on the development of an independent black culture, led some to believe that enslaved people actually managed to prevent whites from successfully exploiting their labor. This idea, in turn, created a quasi-symmetry with post– Civil War plantation memoirs that portrayed gentle masters, who maintained slavery as a nonprofit endeavor aimed at civilizing Africans.
Thus, even after historians of the civil rights, Black Power, and multicultural eras rewrote segregationists’ stories about gentlemen and belles and grateful darkies, historians were still telling the half that has ever been told. For some fundamental assumptions about the history of slavery and the history of the United States remain strangely unchanged. The first major assumption is that, as an economic system—a way of producing and trading commodities—American slavery was fundamentally different from the rest of the modern economy and separate from it. Stories about industrialization emphasize white immigrants and clever inventors, but they leave out cotton fields and slave labor. This perspective implies not only that slavery didn’t change, but that slavery and enslaved African Americans had little long-term influence on the rise of the United States during the nineteenth century, a period in which the nation went from being a minor European trading partner to becoming the world’s largest economy—one of the central stories of American history.
The second major assumption is that slavery in the United States was fundamentally in contradiction with the political and economic systems of the liberal republic, and that inevitably that contradiction would be resolved in favor of the free-labor North. Sooner or later, slavery would have ended by the operation of historical forces; thus, slavery is a story without suspense. And a story with a predetermined outcome isn’t a story at all.
Third, the worst thing about slavery as an experience, one is told, was that it denied enslaved African Americans the liberal rights and liberal subjectivity of modern citizens. It did those things as a matter of course, and as injustice, that denial ranks with the greatest in modern history. But slavery also killed people, in large numbers. From those who survived, it stole everything. Yet the massive and cruel engineering required to rip a million people from their homes, brutally drive them to new, disease-ridden places, and make them live in terror and hunger as they continually built and rebuilt a commodity-generating empire—this vanished in the story of a slavery that was supposedly focused primarily not on producing profit but on maintaining its status as a quasi-feudal elite, or producing modern ideas about race in order to maintain white unity and elite power. And once the violence of slavery was minimized, another voice could whisper, saying that African Americans, both before and after emancipation, were denied the rights of citizens because they would not fight for them.
All these assumptions lead to still more implications, ones that shape attitudes, identities, and debates about policy. If slavery was outside of US history, for instance—if indeed it was a drag and not a rocket booster to American economic growth—then slavery was not implicated in US growth, success, power, and wealth. Therefore none of the massive quantities of wealth and treasure piled by that economic growth is owed to African Americans. Ideas about slavery’s history determine the ways in which Americans hope to resolve the long contradiction between the claims of the United States to be a nation of freedom and opportunity, on the one hand, and, on the other, the unfreedom, the unequal treatment, and the opportunity denied that for most of American history have been the reality faced by people of African descent. Surely, if the worst thing about slavery was that it denied African Americans the liberal rights of the citizen, one must merely offer them the title of citizen—even elect one of them president—to make amends. Then the issue will be put to rest forever.
Slavery’s story gets told in ways that reinforce all these assumptions. Textbooks segregate twenty-five decades of enslavement into one chapter, painting a static picture. Millions of people each year visit plantation homes where guides blather on about furniture and silverware. As sites, such homes hide the real purpose of these places, which was to make African Americans toil under the hot sun for the profit of the rest of the world. All this is the “symbolic annihilation” of enslaved people, as two scholars of those weird places put it.2 Meanwhile, at other points we tell slavery’s story by heaping praise on those who escaped it through flight or death in rebellion, leaving the listener to wonder if those who didn’t flee or die somehow “accepted” slavery. And everyone who teaches about slavery knows a little dirty secret that reveals historians’ collective failure: many African-American students struggle with a sense of shame that most of their ancestors could not escape the suffering they experienced.
The truth can set us free, if we can find the right questions. But back in the little house in Danville, Anderson was reading from a list of leading ones, designed by white officials—some well-meaning, some not so well-meaning. He surely felt how the gravity of the questions pulled him toward the planet of plantation nostalgia. “Did slaves mind being called ‘nigger’?” “What did slaves call master or mistress?” “Have you been happier in slavery or free?” “Was the mansion house pretty?” Escaping from chains is very difficult, however, so Anderson dutifully asked the prescribed questions and poised his pencil to take notes.
Ivy listened politely. He sat still. Then he began to speak: “My mother’s master was named William Tunstall. He was a mean man. There was only one good thing he did, and I don’t reckon he intended to do that. He sold our family to my father’s master George H. Gilman.”
Perhaps the wind blowing through the window changed as a cloud moved across the spring sun: “Old Tunstall caught the ‘cotton fever.’ There was a fever going round, leastways it was like a fever. Everyone was dying to get down south and grow cotton to sell. So old Tunstall separated families right and left. He took two of my aunts and left their husbands up here, and he separated altogether seven husbands and wives. One woman had twelve children. Yessir. Took ‘em all down south with him to Georgia and Alabama.”
Pervasive separations. Tears carving lines on faces. Lorenzo remembered his relief at dodging the worst, but he also remembered knowing that it was just a lucky break. Next time it could’ve been his mother. No white person was reliable, because money drove their decisions. No, this wasn’t the story the books told.
So Anderson moved to the next question. Did Ivy know if any slaves had been sold here? Now, perhaps, the room grew darker.
For more than a century, white people in the United States had been singling out slave traders as an exception: unscrupulous lower-class outsiders who pried apart paternalist bonds. Scapegoaters had a noble precedent. In his first draft of the Declaration of Independence, Thomas Jefferson tried to blame King George III for using the Atlantic slave trade to impose slavery on the colonies. In historians’ tellings, the 1808 abolition of the Atlantic trade brought stability to slavery, ringing in the “Old South,” as it has been called since before the Civil War. Of course, one might wonder how something that was brand new, created after a revolution, and growing more rapidly than any other commodity-producing economy in history before then could be considered “old.” But never mind. Historians depicted slave trading after 1808 as irrelevant to what slavery was in the “Old South,” and to how America as a whole was shaped. America’s modernization was about entrepreneurs, creativity, invention, markets, movement, and change. Slavery was not about any of these things—not about slave trading, or moving people away from everyone they knew in order to make them make cotton. Therefore, modern America and slavery had nothing to do with each other.
But Ivy spilled out a rush of very different words. “They sold slaves here and everywhere. I’ve seen droves of Negroes brought in here on foot going South to be sold. Each one of them had an old tow sack on his back with everything he’s got in it. Over the hills they came in lines reaching as far as the eye can see. They walked in double lines chained together by twos. They walk ‘em here to the railroad and shipped ’em south like cattle.”
Then Lorenzo Ivy said this: “Truly, son, the half has never been told.”
To this, day, it still has not. For the other half is the story of how slavery changed and moved and grew over time: Lorenzo Ivy’s time, and that of his parents and grandparents. In the span of a single lifetime after the 1780s, the South grew from a narrow coastal strip of worn-out plantations to a sub-continental empire. Entrepreneurial enslavers moved more than 1 million enslaved people, by force, from the communities that survivors of the slave trade from Africa had built in the South and in the West to vast territories that were seized—also by force—from their Native American inhabitants. From
1783 at the end of the American Revolution to 1861, the number of slaves in the United States increased five times over, and all this expansion produced a powerful nation. For white enslavers were able to force enslaved African-American migrants to pick cotton faster and more efficiently than free people. Their practices rapidly transformed the southern states into the dominant force in the global cotton market, and cotton was the world’s most widely traded commodity at the time, as it was the key raw material during the first century of the industrial revolution. The returns from cotton monopoly powered the modernization of the rest of the American economy, and by the time of the Civil War, the United States had become the second nation to undergo large-scale industrialization. In fact, slavery’s expansion shaped every crucial aspect of the economy and politics of the new nation—not only increasing its power and size, but also, eventually, dividing US politics, differentiating regional identities and interests, and helping to make civil war possible.
The idea that the commodification and suffering and forced labor of African Americans is what made the United States powerful and rich is not an idea that people necessarily are happy to hear. Yet it is the truth. And that truth was the half of the story that survived mostly in the custodianship of those who survived slavery’s expansion—whether they had been taken over the hill, or left behind. Forced migration had shaped their lives, and also had shaped what they thought about their lives and the wider history in which they were enmeshed. Even as they struggled to stay alive in the midst of disruption, they created ways to talk about this half untold. But what survivors experienced, analyzed, and named was a slavery that didn’t fit the comfortable boxes into which other Americans have been trying to fit it ever since it ended.
I read Lorenzo Ivy’s words, and they left me uneasy. I sensed that the true narrative had been left out of history—not only American history in general, but even the history of slavery. I began to look actively for the other half of the story, the one about how slavery constantly grew, changed, and reshaped the modern world. Of how it was both modernizing and modern, and what that meant for the people who lived through its incredible expansion. Once I began to look, I discovered that the traces of the other half were everywhere. The debris of cotton fevers that infected white entrepreneurs and separated man and woman, parent and child, right and left, dusted every set of pre–Civil War letters, newspapers, and court documents. Most of all, the half not told ran like a layer of iridium left by a dinosaur-killing asteroid through every piece of testimony that ex-slaves, such as Lorenzo Ivy, left on the historical record: thousands of stanzas of an epic of forced separations, violence, and new kinds of labor.
For a long time I wasn’t sure how to tell the story of this muscular, dynamic process in a single book. The most difficult challenge was simply the fact that the expansion of slavery in many ways shaped the story of everything in the pre–Civil War United States. Enslavers’ surviving papers showed calculations of returns from slave sales and purchases as well as the costs of establishing new slave labor camps in the cotton states. Newspapers dripped with speculations in land and people and the commodities they produced; dramatic changes in how people made money and how much they made; and the dramatic violence that accompanied these practices. The accounts of northern merchants and bankers and factory owners showed that they invested in slavery, bought from and sold to slaveholders, and took slices of profit out of slavery’s expansion. Scholars and students talked about politics as a battle about states’ rights or republican principles, but viewed in a different light the fights can be seen as a struggle between regions about how the rewards of slavery’s expansion would be allocated and whether that expansion could continue.
The story seemed too big to fit into one framework. Even Ivy had no idea how to count the chained lines he saw going southwest toward the mountains on the horizon and the vast open spaces beyond. From the 1790s to the 1860s, enslavers moved 1 million people from the old slave states to the new. They went from making no cotton to speak of in 1790 to making almost 2 billion pounds of it in 1860. Stretching out beyond the slave South, the story encompassed not only Washington politicians and voters across the United States but also Connecticut factories, London banks, opium addicts in China, and consumers in East Africa. And could one book do Lorenzo Ivy’s insight justice? It would have to avoid the old platitudes, such as the easy temptation to tell the story as a collection of topics—here a chapter on slave resistance, there one on women and slavery, and so on. That kind of abstraction cuts the beating heart out of the story. For the half untold was a narrative, a process of movement and change and suspense. Things happened because of what had been done before them—and what people chose to do in response.
No, this had to be a story, and one couldn’t tell it solely from the perspective of powerful actors. True, politicians and planters and bankers shaped policies, the movement of people, and the growing and selling of cotton, and even remade the land itself. But when one takes Lorenzo Ivy’s words as a starting point, the whole history of the United States comes walking over the hill behind a line of people in chains. Changes that reshaped the entire world began on the auction block where enslaved migrants stood or in the frontier cotton fields where they toiled. Their individual drama was a struggle to survive. Their reward was to endure a brutal transition to new ways of labor that made them reinvent themselves every day. Enslaved people’s creativity enabled their survival, but, stolen from them in the form of ever-growing cotton productivity, their creativity also expanded the slaveholding South at an unprecedented rate. Enslaved African Americans built the modern United States, and indeed the entire modern world, in ways both obvious and hidden.
One day I found a metaphor that helped. It came from the great African-American author Ralph Ellison. You might know his novel Invisible Man. But in the 1950s, Ellison also produced incredible essays. In one of them he wrote, “On the moral level I propose we view the whole of American life as a drama enacted on the body of a Negro giant who, lying trussed up like Gulliver, forms the stage and the scene upon which and within which the action unfolds.”3
The image fit the story that Ivy’s words raised above the watery surface of buried years. The only problem was that Ellison’s image implied a stationary giant. In the old myth, the stationary, quintessentially unchanging plantation was the site and the story of African-American life from the seventeenth century to the twentieth. But Lorenzo Ivy had described a world in motion. After the American Revolution—which seemed at the time to portend slavery’s imminent demise—a metastatic transformation and growth of slavery’s giant body had begun instead. From the exploitation, commodification, and torture of enslaved people’s bodies, enslavers and other free people gained new kinds of modern power. The sweat and blood of the growing system, a network of individuals and families and labor camps that grew bigger with each passing year, fueled massive economic change. Enslaved people, meanwhile, transported and tortured, had to find ways to survive, resist, or endure. And over time the question of their freedom or bondage came to occupy the center of US politics.
This trussed-up giant, stretched out on the rack of America’s torture zone, actually grew, like a person passing through ordeals to new maturity. I have divided the chapters of this book with Ellison’s imagined giant in mind, a structure that has allowed the story to take as its center point the experience of enslaved African Americans themselves. Before we pass through the door that Lorenzo Ivy opened, here are the chapters’ names. The first is “Feet,” for the story begins with unfree movement on paths to enslaved frontiers that were laid down between the end of the American Revolution in 1783 and the early 1800s. “Heads” is the title of the second chapter, which covers America’s acquisition of the key points of the Mississippi Valley by violence, a gain that also consolidated the enslavers’ hold on the frontier. Then come the “Right Hand” and the “Left Hand” (Chapters 3 and 4). They reveal the inner secrets of enslavers’ power, secrets which made the entire world of white people wealthy.
“Tongues” (Chapter 5) and “Breath” (Chapter 6) follow. They describe how, by the mid-1820s, enslavers had not only found ways to silence the tongues of their critics, but had built a system of slave trading that served as expansion’s lungs. Most forms of resistance were impossible to carry out successfully. So a question hung in the air. Would the spirit in the tied-down body die, leaving enslaved people to live on like undead zombies serving their captors? Or would the body live, and rise? Every transported soul, finding his or her old life killed off, faced this question on the individual level as well: whether to work with fellow captives or scrabble against them in a quest for individualistic subsistence. Enslaved African Americans chose many things. But perhaps most importantly, they chose survival, and true survival in such circumstances required solidarity. Solidarity allowed them to see their common experience, to light their own way by building a critique of enslavers’ power that was an alternative story about what things were and what they meant.
This story draws on thousands of personal narratives like the one that Lorenzo Ivy told Claude Anderson. Slavery has existed in many societies, but no other population of formerly enslaved people has been able to record the testimonies of its members like those who survived slavery in the United States. The narratives began with those who escaped slavery’s expansion in the nineteenth century as fugitives. Over one hundred of those survivors published their autobiographies during the nineteenth century. As time went on, such memoirs found a market, in no small part because escapees from southern captivity were changing the minds of some of the northern whites about what the expansion of slavery meant for them. Then, during the 1930s, people like Claude Anderson conducted about 2,300 interviews with the ex-slaves who had lived into that decade. Because the interviews often allowed old people to tell about the things they had seen for themselves and the things they heard from their elders in the years before the Civil War, they take us back into the world of explanation and storytelling that grew up around fires and on porches and between cotton rows. No one autobiography or interview is pure and objective as an account of all that the history books left untold. But read them all, and each one adds to a more detailed, clearer picture of the whole. One story fills in gaps left by another, allowing one to read between the lines.4
Understanding something of what it felt like to suffer, and what it cost to endure that suffering, is crucial to understanding the course of US history. For what enslaved people made together—new ties to each other, new ways of understanding their world—had the potential to help them survive in mind and body. And ultimately, their spirit and their speaking would enable them to call new allies into being in the form of an abolitionist movement that helped to destabilize the mighty enslavers who held millions captive. But the road on which enslaved people were being driven was long. It led through the hell described by “Seed” (Chapter 7), which tells of the horrific near-decade from 1829 to 1837. In these years entrepreneurs ran wild on slavery’s frontier. Their acts created the political and economic dynamics that carried enslavers to their greatest height of power. Facing challenges from other white men who wanted to assert their masculine equality through political democracy, clever entrepreneurs found ways to leverage not just that desire, but other desires as well. With the creation of innovative financial tools, more and more of the Western world was able to invest directly in slavery’s expansion. Such creativity multiplied the incredible productivity and profitability of enslaved people’s labor and allowed enslavers to turn bodies into commodities with which they changed the financial history of the Western world.
Enslavers, along with common white voters, investors, and the enslaved, made the 1830s the hinge of US history. On one side lay the world of the industrial revolution and the initial innovations that launched the modern world. On the other lay modern America. For in 1837, enslavers’ exuberant success led to a massive economic crash. This self-inflicted devastation, covered in Chapter 8, “Blood,” posed new challenges to slaveholders’ power, led to human destruction for the enslaved, and created confusion and discord in white families. When southern political actors tried to use war with Mexico to restart their expansion, they encountered new opposition on the part of increasingly assertive northerners. As Chapter 9, “Backs,” explains, by the 1840s the North had built a complex, industrialized economy on the backs of enslaved people and their highly profitable cotton labor. Yet, although all northern whites had benefited from the deepened exploitation of enslaved people, many northern whites were now willing to use politics to oppose further expansions of slavery. The words that the survivors of slavery’s expansion had carried out from the belly of the nation’s hungriest beast had, in fact, become important tools for galvanizing that opposition.
Of course, in return for the benefits they received from slavery’s expansion, plenty of northerners were still willing to enable enslavers’ disproportionate power. With the help of such allies, as “Arms” (Chapter 10) details, slavery continued to expand in the decade after the Compromise of 1850. For now, however, it had to do so within potentially closed borders. That is why southern whites now launched an aggressive campaign of advocacy, insisting on policies and constitutional interpretations that would commit the entire United States to the further geographic expansion of slavery. The entire country would become slavery’s next frontier. And as they pressed, they generated greater resistance, pushed too hard, and tried to make their allies submit—like slaves, the allies complained. And that is how, at last, whites came to take up arms against each other.
Yet even as southern whites seceded, claiming that they would set up an independent nation, shelling Fort Sumter, and provoking the Union’s president, Abraham Lincoln, to call out 100,000 militia, many white Americans wanted to keep the stakes of this dispute as limited as possible. A majority of northern Unionists opposed emancipation. Perhaps white Americans’ battles with each other were, on one level, not driven by a contest over ideals, but over the best way to keep the stream of cotton and financial revenues flowing: keep slavery within its current borders, or allow it to consume still more geographic frontiers. But the growing roar of cannon promised others a chance to force a more dramatic decision: slavery forever, or nevermore. So it was that as Frank Baker, Townshend, and Sheppard Mallory crept across the dark James River waters that had washed so many hulls bearing human bodies, the future stood poised, uncertain between alternative paths. Yet those three men carried something powerful: the same half of the story that Lorenzo Ivy could tell. All they had learned from it would help to push the future onto a path that led to freedom. Their story can do so for us as well. To hear it, we must stand as Lorenzo Ivy had stood as a boy in Danville—watching the chained lines going over the hills, or as Frank Baker and others had stood, watching the ships going down the James from the Richmond docks, bound for the Mississippi. Then turn and go with the marching feet, and listen for the breath of the half that has never been told.
Excerpted from the book THE HALF HAS NEVER BEEN TOLD by Edward Baptist. Copyright © 2014 by Edward Baptist. Reprinted with permission of Basic Books.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
News on Countries of Asylum
Global
Deadly practice of migrant ‘pushbacks’ must cease: UN Special Rapporteur
How vaccine passports could imperil LGBTQ+ refugees
Africa
Experts call for increased inclusion of refugees in health, education, sports in Africa
BOTSWANA: As universities begin to offer scholarships, refugee students look forward to a more secure future
ETHIOPIA: Ethiopia commended for efforts towards inclusive education policies for refugee children and the youth
MOZAMBIQUE: Grave concerns for forcibly disappeared Rwandan asylum seeker
UGANDA:
Over 950 refugees from DRC cross into Uganda amid rebel activities in North Kivu province
COVID-19 poses a major threat to the life and welfare of refugees in Uganda
Americas
CANADA:
Oversight of Canada Border Services Agency requested in case of Egyptian asylum-seeker facing deportation
Government plans to increase the number of protected persons admitted to Canada from 23,500 to 45,000 in 2021
What the Biden administration can learn from Canada’s private refugee sponsorship program
COLOMBIA: Colombia reopens border with Venezuela after 14 months
USA:
US suspects 4,000 cases of fraud in Iraq refugee resettlement programme, with freeze of refugee programme extended indefinitely
The Biden administration ends former administration’s Migrant Protection Protocols
US ends policy limiting asylum for gang and domestic violence survivors
US border officials are using a new surveillance app to collect and store information on asylum seekers before they enter the US
The 2021 Spring Regulatory Agenda signals major change to immigration, asylum, and border policy
Asia
BANGLADESH:
Rohingya Muslim refugees injured in protests on isolated island during UNHCR visit
Concerning conditions reported on remote island of Bhasan Char, housing thousands of Rohingya refugees
UNHCR improperly collected and shared personal information from ethnic Rohingya refugees with Bangladesh, who relayed to Myanmar
INDIA: Over 50 shanties housing Rohingya refugees destroyed in a fire, leaving hundreds homeless
JAPAN: Government withdraws controversial immigration bill after mounting public criticism, following death of an asylum-seeker in detention facility
Asia Pacific
UN shared Rohingya data without informed consent: HRW
AUSTRALIA:
Immigration detention centres on Christmas Island pose a COVID outbreak risk and should be closed - Australian Human Rights Commission
Asylum seeker family who spent nearly three years in detention on Christmas Island are reunited
130 people still being held in Papua New Guinea’s capital Port Moresby and 110 people on Nauru
Australia's foreign affairs department urged to retract a report, amidst claims of inaccuracy and deportation of Tamil refugees
Anger mounts as Australia declines to fast-track plans to save Afghan translators, who worked with Western troops, from Taliban retribution
Plight of Tamil family fuels concern over Australia asylum rules
NEW ZEALAND: Discussions taking place to resettle refugees from Australia’s offshore regime in New Zealand
Europe
Efforts to stop people from entering the European Union illegally are being ramped up with experimental new digital barriers
DENMARK:
Amendment to Danish law seeks to forcibly transfer asylum-seekers to third countries for processing
Hundreds of Syrian refugees conducted a sit-in demonstration in front of the Danish parliament, protesting measures aimed at returning them to Syria
Denmark’s Syrian refugee residency move reflects shifting policies across Europe
FINLAND: City of Lahti seeks to evict the only reception centre for asylum seekers with mental health problems in Finland
FRANCE: New app launched in southern France to help asylum seekers with their administrative status, accommodation, health and everyday needs
GREECE:
Greece should not consider Turkey 'safe' for asylum seekers, rights organizations say
Greece plans to send back asylum seekers from Somalia, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Syria and Bangladesh who arrive from Turkey
Greek plans for refugee camps, including concrete walls and drones, decried
Draconian prison sentences handed to four Afghan youths found guilty of starting the fire that destroyed the Moria migrant camp on the island of Lesbos
ITALY:
Fishermen in the Sicilian fishing town of Mazara del Vallo targeted by Libyan Coast Guard when rescuing migrant boats
Italy under pressure to reduce arrivals from Mediterranean, as they record a nine-fold increase in arrivals to shore in the past two years
Around 700 people arrived on the Italian island of Lampedusa in one day in June, as reception centre reaches full capacity
IRELAND: Housing policies exclude travellers, migrants and asylum seekers
SPAIN: At least three people are dead and four missing after a migrant boat carrying nearly 50 passengers capsized in Spain's Canary Islands
UK:
Asylum in the UK, by numbers
UK high court strikes down pandemic protections for refused asylum seekers
Plans to impose a ‘good faith’ requirement on immigration lawyers, strongly attacked by Law Society, Bar Council and Immigration Law Practitioners Association
Temporary ban on accepting new asylum seekers into Scotland could last for years
Conservative-run Kent County Council planning to sue government over number of child asylum seekers in the local authority’s care
Problems with new cash cards, issued through the Home Office, leaves thousands of asylum-seekers at risk
MENA
IRAN: Government formalises access to banking services – including debit cards, for Afghan refugees
LEBANON:
Lebanese protesters attack Syrian refugees and demanded they "go home," as voting for Syrian election takes place
Vital aid needed for around 1.5 million Lebanese and 400,000 migrant workers living in increasingly critical conditions
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The area of Essex called Essex Village was originally named Potapoug Point, or Big Point, by the Nahantic tribe. It was laid out as a part of the original Saybrook colony in 1648. It bordered the Connecticut River with two large coves on either side. There were three original families: the Pratts, the Hides, and the Lays. The Lays took the northern parts, the Pratts the middle acres, and the Hides the southern acres. In 1722 the settlers were given the right to form a Congregation Church, which was located in Center-Brooke, the original “social center” of what is now the Town of Essex. Main Street on the "point" was not laid out until 1748, and up to that time only a few people resided here.
By the middle of the 18th century, however, the focus was already moving to Potapoug Point, or Essex Village as we now know it, where shipbuilding was beginning to offer an alternate occupation to farming. The building of the ship “Oliver Cromwell” in 1775/76 by Captain Uriah Hayden could be considered the pivotal change in the local economy. The Oliver Cromwell was the first ship commissioned and financed by the Colony of Connecticut and the largest one launched in the river valley up to that time. The Town of Essex itself was split from Old Saybrook, and was incorporated in 1854, and in 1859, the villages of Centerbrook and Ivoryton were added. Shipbuilding remained a main economic force until the 1870s.

1. The Essex Town Green was originally the site of three homes. The Town Green borders Middle Cove and looks out onto Thatchbed Island.
2. The Gamaliel Conklin House, a center chimney, colonial style home with a steeply pitched roof, was built in 1800. Conklin, along with Jesse Murray, was a supplier of masts, blocks, and gear for the shipbuilding industry. 20 Main Street.
3. Next door is the Jesse Murray house, built in 1805, is in the Federal Style. 22 Main Street.
4. Uriah Hayden House. 24 Main Street. Uriah was the man most responsible for establishing a formal shipbuilding industry in Essex. Meigs Lane was once a pentway. This house was modeled after the new Baptist church, built by Jeremiah Gladding, in the “Egyptian style.” Additions have been added since.
5. 26 Main Street. Cape house on water. 1803.
6. The Noah Pratt house, 28 Main Street. Built in 1805 on land original known as Cornfield point. The house was sold to Uriah Hayden in 1817 and remained in the Hayden family until 1977. It now houses Commercial offices.
7. 30 Main Street, at the corner of Parker Lane, was erected in 1840 for Judge William Phelps. It was later owned by Dr. Charles H. Hubbard (1836-1908), who practiced in Essex for nearly forty-eight years. He also held various town offices and was the executor for the estate of Capt. Isaiah Pratt (1814-1879), who had left money for a new high school. Dr. Hubbard successfully challenged a stipulation in the will that would have limited enrollment to the children of parents who were members of the First Congregational Church. He continued as a trustee and leader of the new school for many years. Hubbard Field in Essex is named for him. The barn in back is newly constructed. Considered Greek Revival.
8. 32 Main Street. 1799. Grover L’Hommedieu (1741-1841) was one of the patriot militiamen who became refugees from Long Island to Connecticut after the Battle of Long Island in 1776 during the Revolutionary War. He settled in Norwich and in 1797 leased land from Samuel Lay in Essex. There he erected the town’s first ropewalk. Around that time he also erected the house at 32 Main Street in Essex. It was later occupied by his son Ezra L’Hommedieu (1772-1860), a ship-carver who invented the double-podded center screw auger, which he patented in 1809. Grover’s daughter Sarah (Sally) married Ebenezer Hayden II, the town’s leading merchant. In 1802, Grover L’Hommedieu sold the ropewalk to his partner, Ebenezer’s son, Jared. In 1815, the L’Hommedieu House was purchased by another member of the Hayden family, John G. Hayden.

9. The L’ Hommedieu Ropewalk. Essex had two ropewalks, in different locations, at different times. L'Hommideau had "lately erected" a frame that was 15' wide by 60 rods (1000') long that ran on the north side of Main Street. This meant it ran from the west side of the current "Glass Basket" building to where Essex Square is today. There was a 20' wide "store" at the west end of this ropewalk, and the land rent was 4 pounds per year. Main Street followed a different path at that time, being located roughly halfway between current Main and Pratt Streets, and there was no Essex Square or North Main Street then. Grover was allowed to have a "copper"(large tar kettle) and a capstan for winding rope on the north side of this structure, although these were on Lay property. This "frame" was said to be "open," indicating it probably had a roof, but no sidewalls. Consequently, it was probably operated on a seasonal basis. It was torn down in 1814.
10. The Griswold Inn, oldest continuously operating Inn in America is at at 36 Main Street. The Griswold Inn is the most famous landmark building in Essex. A sign at the Inn states that the Griswold House was built by Sala Griswold in 1776. It originally stood near the shipyard and was moved to its current location on Main Street to become part of the house constructed by Richard Hayden in 1801. Hayden’s house was the first three-story building in the lower Connecticut River Valley. Around the same time, Richard’s two brothers, John G. and Amasa Hayden, built houses on either side (they are now part of the Griswold Inn complex, the Amasa Hayden House being the Inn’s annex). Hayden sold his house to Ethan Bushnell in 1806, moving to a new brick house nearby. Ethan Bushnell turned his home into a tavern. A former schoolhouse on the property, built in 1738, was attached to the house, possibly to serve as a kitchen (it is now the taproom). After the Burning of the ships in 1812, it notoriously served and housed British soldiers. The Tavern was inherited by Bushnell’s children in 1849 and passed through a variety of owners over the years, probably acquiring the name Griswold House during the period it was owned by Emory Morse of Wallingford in the 1870s and 1880.
The Griswold Inn starred in Halmark’s “Christmas at Pemberley Manor” movie. And had a role in the 70’s Dark Shadows series as the Collinsport Inn. Owned by only six families. Currently owned by Geoff Paul, who lives in Champlin Square.



12. Richard Hayden house/ Hayden rectory. 1806. Richard Hayden, an Essex shipbuilder and merchant, built the first brick house in town in 1806. He had earlier lived in the house which is now the Griswold Inn. Hayden was head of the Hayden Shipyard and he built a ship’s chandlery in 1813, which was later moved across Main Street. During the War of 1812, he built a privateer schooner, the Black Prince, which he advertised in New York. This was one of the causes of the British Raid on Essex in 1814, which led to serious financial losses for Hayden, who died two years later. His widow and children remained in the Federal-style house until 1833, when Richard Hayden’s cousin, Samuel Hayden, bought the house. In 1894, Samuel’s daughter, Mary Tucker, left the house and furniture to St. John’s Episcopal Parish and was the church’s rectory until 2013.
13. Noah Tooker house. 1728. At corner of Novelty Lane. May have faced the river, then turned when the rectory was built. Several other houses in Essex were built to face the river and remain so sited today.
14. The Ebenezer Hayden II (the first Ebenezer Hayden was a brother who was born earlier but had died) probably built his Georgian and Federal style house, located on Main Street in Essex, in stages in the late 1790s. The doorway, featuring a semi-circular fanlight window, may have been added around 1800. The Hayden House was the first home in the lower Connecticut River Valley to have a hipped roof, which may have been constructed by the noted builder Thomas Hayden of Windsor and shipped down the river in sections to be placed on the building. The Ebenezer Hayden House is the third home up from the river and one of many homes built by members of the Hayden family in the vicinity of the Hayden Shipyard. Ebenezer II married Sarah, the daughter of Grover L’Hommideau, who had created the town’s first ropewalk.
15. Foot of Main, the Hayden-Starkey Store, at 48 Main Street in Essex, was only the second brick building in town when it was built in 1809. A warehouse and ships store, or chandlery, it was constructed by Samuel and Ebenezer Hayden, sons of Capt. Uriah Hayden, and was situated between their two residences. Their cousin, Richard Hayden, had recently built his house, Essex’s first brick building, nearby. Timothy Starkey, Jr., the Hayden brothers’ brother-in-law, became their partner in 1810. It is said that the British destroyed ropewalk and took merchandise from this store during their raid on Essex in 1814. Remaining in the Hayden family for many years, the building became a residence in 1856.

16. Uriah and Ann’s Inn. Now the Dauntless Boat Club. Built in 1776, this important structure was the homestead and tavern of shipbuilder Uriah and Ann Hayden. The Oliver Cromwell ship was built in his shipyard to the south of the house in 1776. The front yard has been filled in. To the southeast on Middle cove shore, where the Essex Corinthian Yacht club, Essex Yacht club, and Novelty Lane now stand, was the location of the Old Shoddy Mill, a wood turning factory which burned down in 1900. It was once owned by Thomas Dickinson, who went on to found the Witch Hazel factory.

17. Dickinson Boathouse, built by E.E. Dickinson of Witch hazel factory fame in the 1920’s. It replaced a West Indies warehouse that was built in 1753 and torn down in 1918. The building is now in privately owned.

18. Burning of the ships. The embargo that President Thomas Jefferson passed, followed by the British blockade of the Connecticut River during the War of 1812, impacted the shipbuilding industry of the town. The leading boat builders were converting their merchant ships into privateers in the hope of bringing home some of the spoils of war, but this act backfired. On the morning of April 8, 1814, 137 British marines and sailors, under the command of Captain Richard Coote, raided Potapoug Point and destroyed 28 ships with a value of $200,000. Of which, $60,000 was lost by the Haydens. The disaster, one of the few invasions and occupation of US. soil by a foreign power, is celebrated almost every year in Essex with a parade. It was, after all, the greatest financial loss suffered by the American side during the War of 1812. Why was there no real resistance by the Potapaug Militia, either during the initial attack, or during the British retreat? The head of this force lived in a home on the lefthand side of Main Street, close to the shore. There is strong suspicion that he agreed not to oppose the raiding force, in return for their promise not to harm homes or residents. Recently uncovered minutes of the local Masonic Lodge add greatly to this speculation for George Jewett, the Militia commander, was also Master of the Lodge. Captain Richard Coote, the person in command of the British, who had apparently spared the ships of one Judea Pratt of New City Street, due to Masonic influence, could undoubtedly have "cut a similar deal" with fellow Freemason Jewett.
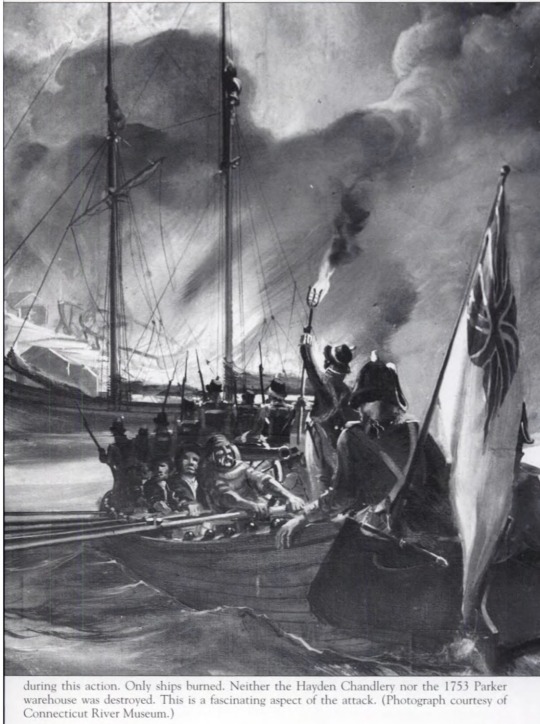

One immediate result of the raid was the demise of the old 1797 ropewalk, and a new larger one built 200 feet to the north. This change set for current street layout and appearance of Essex. Up until then, most commercial activity in Essex Village had centered in Champlin Square, with the Pratt Smithy and Ebenezar Hayden Store.
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

March 7, London - Fortress Europe - A protest outside the Greek Embassy
Join refugees, solidarity campaigners and Syrian activists on Saturday, 7 March out side the Greek Embassy to demand justice for refugees, and end to the EU's backwards policy of closing the borders to those most in need.
Video emerged on Monday of Greek coastguard officers trying to capsize a boat full of refugees at sea, as a crisis mounted over refugees from the Middle East attempting to reach western Europe.
A child was also killed on Monday when the boat they were aboard capsized off the island of Lesbos and a Syrian refugee trying to cross the Greek border was killed by rubber bullets, underscoring the dangers faced by those attempting make the passage west from Turkey.
in the recent months, Assad and his allies have initiated a brutal and unprecedented military campaign on the South East of Idlib province. Hundreds of civilians, including many children, have been killed and Hundreds more injured according to local NGOs and medics operating in Idlib province. This militarily campaign has pushed nearly a million people to flee their homes having no place to go with a closed Turkish border in the north. Idlib is home to nearly three million people, about half of whom were forcibly displaced in large groups from other parts of the country that were retaken by Assad forces.
On 7 March 2016, the European Council met with Turkey in Brussels. The agreement outlined was criticised by UNHCR and many NGOs for violating international law. We protested the deal 4 years ago, and today we call on all nations to respect and honour the rights of refugees.
54 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Story of Split

I recently visited Split, Croatia. It's steeped in history. Wherever you turn, you’re mired in it. When you lean back in your chair in one of the numerous cafes of the old town, your shirt is brushing against 1700-year-old Roman wall. You sip your coffee and can almost hear in your mind the banter of legionnaires who leaned against this same wall with cups of wine during the break from duty. Houses of the downtown Split sprout like unruly hair from within the Roman limestone walls dating from 3rd century A.D. The city’s Cathedral of St. Domnius is consecrated in 7th century. The black granite sphinx guarding the front entrance to the cathedral is estimated to be from 15th century B.C. It is no wonder then that an aspiring scribe who finds himself walking the cobblestone streets of ancient times can’t stop imagination from running wildly back through centuries. Allow me to take you through the time to the very beginning of Split:
The year is 260. We are standing at the seashore in Aspàlathos, a Greek trading outpost in a charming bay on the central coast of Dalmatia. Several ships are tied to the shore, their sails folded like the wings of seagulls lining their masts and the shore. Slaves and sailors bustle over gangplanks, unloading ships and loading the others. At our back, the habitat is not much to look at, just a few rows of stone houses stretching along the shore. Most of them have dual function, as a warehouse and an abode. People who own them are from the Greek colony of Issa on the island of Vis. It’s about half a day sail south-southwest from here. Aspàlathos was built for one purpose: trade. It's trading with Dalmatae and other Illyrian tribes inhabiting the coast and hinterland of the Balkans, and with Romans from Salona, a metropolis of 60,000 souls, the Roman capital of the province of Dalmatia, and a cultural, political and commercial center of the region. It sits less than two-hour walk, or half an hour on a fast horse from Aspàlathos.
Next to us stands a lanky youth. His shoulders are wide and long muscles are taught from military training. His hair is cropped short, revealing high brow and sharp features. He wears a legionnaire's uniform, with leather-strap sandals instead of boots, common for legionnaires on those warm days of spring. He gazes into the distance, dreaming of faraway places, dreaming of seeing Rome one day. He's only 16, eager to leave family's nest. Next to him stands a man with stooped shoulders holding his hands behind his back. Man's fingers are smeared with ink, an unmistakable mark of a scribe. His squints at the youth.
"Diocles, my son," the man speaks, "go with fortune and may Jupiter keep you safe and return you to us. When you can, send us a word, so that we know you're alive and well." The man places a hand on Diocles's shoulder and the youth turns to meet his eyes.
"Remember," the man continues, "when you tire of marching and battles, your home will wait for you. You won't find a better place to rest than this." The man swipes an arm wide over the peaceful bay, the village and rolling green hills behind it.
Diocles smiles at the man. "I know, father. Thank you. It's time to go back to my legion."
They clasp forearms for a long moment, eyes locked on each other's. Then Diocles breaks the hold and walks with long, impatient strides north, across the hills, toward Salona and its garrison. His father returns to the house which is also his office. A scribe is an important part of every trade, the hand that writes contracts, permits, receipts and counts coins. Unfortunately, most of those coins are transferred from one client to another, from a buyer to a seller. A pay for scribe's services will not build him a palace. Diocles's father is doing alright, keeping his family well fed and clothed, with solid roof over their head, and a nice little farm where his wife tends to her cabbages which grow so well in this weather. He hoped to pass all this to Diocles one day, but the youth is eager to see the world, as young men often are. And what better way to do it, but with the mightiest army of the time: Roman legions.

Thirty-five years later, in 295 A.D., the youth who is now a man of over 50, returns to the bay of his youth. He observes the works started to build a large structure that will stretch from the seashore and climb the gentle slope of the hill. His name has changed, as is his appearance; he is stockier now, almost stout. His chestnut hair, streaked with grey throughout, recedes further from his brow, and his jaw and face are covered by neatly trimmed salt-and-pepper beard and moustache. A toga picta died Tyrian purple was draped over his shoulders, marking his stature. He is Gaius Aurelius Valerius Diocletianus, or Diocletian, the emperor of the Roman Empire. The structure whose foundations are just being built is going to be known as Diocletian's Palace.

In the year 305 A.D. Imperator Caesar Gaius Aurelius Valerius Diocletianus - Diocletian for short - took his stroll along the raised promenade atop the southern wall of his new home. Flowerbeds and trees lined the promenade on both sides to offer the emperor shade from the scorching Adriatic sun. A few marble benches were placed in regular intervals to allow a breathtaking view over the Brettia channel at the islands Brettia (today's Brač) and Solentium (today's Šolta). The emperor moved with shuffling steps, leaning on a cane for support. He was gaunt, his cheeks were hollowed, his shoulders stooped and boney. His skin was grey and a size too large for a man he became. Diocletian was fighting an ailment for over a year, a mysterious illness that almost killed him. It left him emaciated and weak. Next to Diocletian walked a stout man with powerful if somewhat stooped shoulders and strong arms clasped leisurely behind his back. He had open round face with eyes perpetually half-closed and eyebrows that climbed a touch too high, giving him a disbelieving, inquisitive expression. The lower half of his face was obscured in bushy dark hair which greyed at the sides, trimmed to follow the line of a strong jaw. His meaty lips were slightly downturned as if in disapproval. He was Maximian Herculius, co-emperor and Diocletian's partner in ruling the empire that grew too big for a single person to rule over. When Diocletian was confirmed as the emperor of Rome, he turned east to secure the eastern borders of the empire. He soon realized that the news from the Gaul and western borders of the empire travelled too long and his imperial decisions and decrees weren't reaching the west in time. To remedy it, Diocletian elevated his friend Maximian to Cesar, and soon after Augustus, making him equal in status, an emperor in the west, although Diocletian's seniority gave him the upper hand in decision-making. The two worked well together, Maximian's military brawn complemented Diocletian's political wisdom and the alliance born of friendship lasted throughout the twenty years of their rein.
Reaching the bench, Diocletian gingerly lowered himself on it and lifted his face toward the healing warmth of Dalmatian sun. The almost forgotten scent of the homeland wafted to his nostrils.
"I think, my friend, that I can get easily used to retirement," he smiled. "I already feel better."
"You'll miss the action when your strength returns," Maximian grunted in response. "Is your wife joining you?"
Diocletian shook his head. "Prisca is staying in Thessalonica with Galerius and Valeria. She may come when my strength returns."
Galerius was Diocletian son-in-law and successor, the Cesar in the East. His wife - Diocletian's daughter Valeria asked her mother Prisca to stay with them.
"Come Maximian," Diocletian reached his hands to his friend who helped him stand up - "let me show you the gardens. I'm going to grow cabbage here, the way my family did." They walked on to the colonnaded gardens accessible from the promenade.
Diocletian's failing health made the other emperors of the tetrarchy convince him and Maximian to retire. Weakened by disease, Diocletian accepted without much objection. Maximian resisted at first, but Diocletian talked him into leaving the post to younger men. Not suffering idleness well, Maximian sailed to visit his friend's retirement home.
It was an imposing fortress built at the place Diocletian called home so many decades earlier. An impressive walled compound had 16 watchtowers along east, west and north land-facing walls. The only unfortified wall was the southern wall, built on the edge of the sea. Its only opening was a small landing for the imperial galley and supply ships. The walls were built of large limestone blocks. An arcaded gallery bearing the tree-lined promenade stretched along the south wall. The imperial palace with private living quarters and audience hall covered the south half of the fortress. A Peristyle with a balcony from which the emperor greeted his subjects was the very center of the compound. The west side of the Peristyle housed the temple of Jupiter with gardens built for worshipers. The emperor attended the round temple of Jupiter on the east side of the square. The main streets traversing the fortress from east to west and north, met at the forum on the north edge of the Peristyle. The north half of the compound held twin military garrisons for the emperor's legions.

Upon Diocletian's death in 312 A.D., the palace was reclaimed as a property of Roman Republic, and was used as a refuge for exiled dignitaries and deposed rulers. In 7th century A.D. the Roman metropolis of Salona was sacked and destroyed by invading Slavs. Refugees fled from the ruins of the city to find refuge within Spalato's fortified walls. Once luxurious palace and garrison compound was taken down. Its stones were used to build many smaller houses. With time, the willy-nilly building continued outside the Roman walls, under different rulers. Venetians built another set of walls to protect the city from the Croatian-Hungarian and later Ottoman threat. Parts of the wall, as well as "Mletačka kula" (The Venetian Tower) have grown into the tissue of modern days Split.


#writing#amwriting#history#historical fiction#travel#split#spalato#croatia#roman empire#diocletian#ancient
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Headlines: Saturday, September 26, 2020
Largest California wildfire threatens marijuana-growing area
(AP) California’s largest wildfire is threatening a marijuana-growing enclave, and authorities said many of the locals have refused to evacuate and abandon their maturing crops even as weather forecasters predict more hot, dry and windy conditions that could fan flames. The wildfire called the August Complex is nearing the small communities of Post Mountain and Trinity Pines, about 200 miles (322 kilometers) northwest of Sacramento, the Los Angeles Times reported. Law enforcement officers went door to door warning of the encroaching fire danger but could not force residents to evacuate, Trinity County Sheriff’s Department Deputy Nate Trujillo said. “It’s mainly growers,” Trujillo said. “And a lot of them, they don’t want to leave because that is their livelihood.” The area is in the Emerald Triangle, a three-county corner of Northern California that by some estimates is the nation’s largest cannabis-producing region. People familiar with Trinity Pines said the community has up to 40 legal farms, with more than 10 times that number in hidden, illegal growing areas. Growers are wary of leaving the plants vulnerable to flames or thieves. Each farm has crops worth half a million dollars or more and many are within days or weeks of harvest.
Things to avoid during your Zoom session
(Reuters) An Argentine lawmaker has resigned after being caught on a live camera caressing his wife before appearing to partially pull down her top and kiss her breast during a virtual session of the country’s lower house of Congress on Thursday. The lower house of deputies said in a statement on Twitter early on Friday that it had voted to accept the resignation of Juan Ameri, a representative from the northern province of Salta in the ruling coalition. Virtual meetings amid the coronavirus pandemic have tripped up lawmakers before. In June, Ireland’s Luke Ming Flanagan appeared to be wearing no trousers as he discussed policy matters with his European Parliament peers.
Queen Elizabeth II to trim costs as COVID-19 hits income
(AP) Britain’s Queen Elizabeth II and her family are facing a 35 million pound ($45 million) hit from the coronavirus pandemic, partly due to a shortage of tourists, the monarch’s money-manager said Friday. Releasing the royal household’s annual accounts, Keeper of the Privy Purse Michael Stevens said a lack of income from visitors to royal buildings was likely to bring a general funding shortfall of 15 million pounds ($19 million) over three years. He said the impact of the pandemic is also likely to cause a 20 million-pound ($25.4 million) shortfall in a 10-year, 369-million-pound program to replace antiquated heating, plumbing and wiring at Buckingham Palace, the queen’s London home. Stevens said the royal household would not ask for more government money but would “look to manage the impact through our own efforts and efficiencies.”
As Virus Cases Surge in Europe, Hospitalizations Lag.
(NYT) In Munich, normally brimming with boisterous crowds for Oktoberfest this month, the authorities just banned gatherings of more than five people. In Marseille, France, all bars and restaurants will be closed next Monday. And in London, where the government spent weeks urging workers to return to the city’s empty skyscrapers, it is now asking them to work from home. Summer ended in Europe this week with a heavy thud amid ominous signs that a spike in coronavirus cases may send another wave of patients into hospitals. But just how imminent is the peril? As they weigh actions to curb a second wave of the virus, European leaders are dealing with a confusing, fast-changing situation, with conflicting evidence on how quickly new cases are translating into hospital admissions—and how severe those cases will end up being. In Spain, where new cases have surged to more than 10,000 a day, hospitals in Madrid are close to capacity and the government said it was preparing to reopen field hospitals in hotels and in the city’s largest exhibition center. Yet in France, which reported 66,000 new cases over the last seven days, hospital admissions and deaths, while also rising, are going up more slowly. There is a similar divergence between infection rates and hospitalizations in Germany and Austria. And in Britain, which reported 6,178 new coronavirus cases on Wednesday—the highest figure since May 1—just 134 patients were admitted to hospitals on Monday, barely a tenth of those admitted in early May.
Pope to UN: Use COVID crisis to come out better, not worse
(Washington Post) Pope Francis urged world leaders Friday to use the coronavirus emergency as an opportunity to reform the injustices of the global economy and the “perverse logic” of the nuclear deterrence doctrine, warning that increased isolationist responses to problems “must not prevail.” Francis laid out his appeal for greater involvement and influence of the United Nations in protecting the poor, migrants and the environment in a videotaped speech Friday to the U.N. General Assembly, held mostly virtually this year because of the pandemic. Francis said the world has a choice to make as it emerges from the COVID-19 crisis and addresses the grave economic impact it has had on the planet’s most vulnerable: greater solidarity, dialogue and multilateralism, or self-retreat into greater nationalism, individualism and elitism. “The pandemic has shown us that we cannot live without one another, or worse still, pitted against one another,” he said. “This is why, at this critical juncture, it is our duty to rethink the future of our common home and our common project.”
Migrants accuse Greece of pushing them back out to sea
(AP) Shortly after reaching the Greek island of Lesbos, a group of Afghan migrants say, their hopes for a new life in Europe were cut short when Greek authorities rounded them up, mistreated them, shoved them into life rafts and abandoned them at sea, where they were rescued by the Turkish coast guard. Turkey, which hosts about 4 million refugees, accuses Greece of large-scale pushbacks—summary deportations without access to asylum procedures, in violation of international law. Greece, which lies on the EU’s southeastern border and has borne the brunt of migration flows from Turkey, denies the allegations and in turn accuses Ankara of weaponizing migrants. In March, Turkey made good on threats to send migrants to Europe, declaring its borders with the EU open. In what appeared to be a government-organized campaign, thousands headed to the Greek border, leading to scenes of chaos and violence. Turkey’s border with EU member Bulgaria was largely unaffected. Greece shut its frontier and controversially suspended asylum applications for a month. Uneasy neighbors Greece and Turkey have been at loggerheads for decades over several territorial issues, and asylum-seekers have found themselves caught up in the geopolitical conflict.
Taliban entrepreneurs
(Foreign Policy) For decades, Afghanistan’s untapped mineral wealth has been touted as the country’s trillion-dollar El Dorado. But while the Afghan government has never been able to monetize mountains of copper, iron ore, gold, and gemstones, the Taliban have—and are ramping up their mining operations as just-started peace talks aim to shape the future of a postwar Afghanistan. In recent years, the Taliban have deliberately moved to secure control over regions of Afghanistan rich in mineral deposits, from lapis lazuli mines in northern Badakhshan to gold, lead, and zinc in Helmand and vast talc and marble deposits in southern Nangarhar. The Taliban, who already control most of the country’s mineral wealth, are banking on further developing the sector to make it the bedrock of the country’s postwar economy—or theirs, at least.
The Indian navy and China
(WSJ) India’s border conflict with China is pushing New Delhi to look for an asymmetric response: flexing its naval might as it deepens cooperation with other democracies that seek to counter Beijing’s global ambitions. India, which operates one of the world’s largest navies, sits astride shipping routes in the Indian Ocean that connect China to its main sources of oil and gas in the Middle East and to its key markets in Europe. Though growing fast, China’s navy still has only limited ability to operate in a region far from its home shores—and has to contend with the U.S. in its own backyard. “On the northern border, the best we can hope for is to achieve a stalemate. But at sea, we have an advantage over the Chinese,” said retired Adm. Arun Prakash, a former head of the Indian navy. “A show of force at sea can send a message to China that you are vulnerable, that we can interfere with your shipping and with Chinese energy supplies. Their economy would be shaken up.”
‘Tis the season for travel in China. But virus fears cast a shadow over festivities.
(Washington Post) Zuo Weiwei has been stuck since February in her hometown Wuhan—yes, that Wuhan—and the problem now is that the city is overflowing with tourists. Wuhan’s government, like many across China, has been offering free tickets to tourist attractions to try to salvage economic growth. For better or worse, it appears to be working, as China approaches its first major holiday season since tamping down the coronavirus. The “Golden Week” holiday is one of the largest annual human migrations, with upward of 700 million people on the move. This year, it will be a crucial test of China’s efforts to regain normalcy and prevent new coronavirus waves. The holiday season begins with China’s National Day on Oct. 1, marking 71 years of Communist Party rule. The period also coincides with this year’s mid-autumn festival, a one-day holiday that falls on the night of the fullest autumn moon. With borders closed around the world, those in China itching to travel have had to look closer to home. Around 408 million highway trips are expected to be made this Golden Week, slightly up from last year, China’s Ministry of Transport said on Thursday. But the flood of travelers will make social distancing difficult and brings the risk of new virus outbreaks that could spread rapidly across the country.
Tunisian migrants
(Washington Post) The economic fallout from the coronavirus pandemic is propelling thousands of Tunisians to make the perilous Mediterranean journey in search of better living conditions, with the largest wave in nearly a decade reaching Italy’s shores. The strict lockdown Tunisia imposed in March was largely successful in containing the outbreak, but the measures devastated the country’s already ailing economy. During the first eight months of this year, nearly 8,000 Tunisians crossed the Mediterranean to Italy, six times as many as last year.
Palestinian elections
(Foreign Policy) Fatah and Hamas, the two largest political factions in the occupied Palestinian territories, have agreed to hold elections for the first time in almost 15 years. The last elections, held in 2006, resulted in a landslide victory for Hamas, leading to bloody clashes between the two sides and a de facto split within Palestine, with Hamas taking control of the Gaza Strip and the Fatah-led Palestinian Authority (PA) retaining control of the West Bank. Leaders said a vote will be held within six months. The move follows an unprecedented show of unity among Palestinians in opposition to recent moves by several Arab states to normalize diplomatic ties with Israel.
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Neo-Bashibasouks


The Janissaries are probably the one thing that comes to mind as an military force associated with the Ottoman Empire - Christian boys taken from their families as part of the devisherme system (jyzia) by the Ottomans, forcibly converted to Islam and indoctrinated to be loyal to the Sultan. They were considered one of the elite forces in Europe, very disciplined and ready to enter in combat anytime. On the flip side, they possessed immense political clout and had the power to depose sultans that did not play along with their interests. When Mahmud II began a series of reforms on the army, the janissaries mutinied and were suppressed them in what is known the Auspicious Event. Despite these reforms, another group emerged in the 17th century known as Bashibasouks.
Their name translating to “crazyheads” or “corrupted heads”, they were irregular forces formed from criminals or homeless of the Empire and belonged to no specific ethnicity (the majority were Turkish, but they employed white Circassians just like black Sudanese), who were completely undisciplined, not salaried like normal soldiers and instead were paid on plunder and loot. During the Crimean War, British and French officers had difficulties working with them because they acted like brigands rather than proper soldiers. Even Ottoman troops were forced to disarm them several times because of their unruly nature. The incident they are most infamous for was the April Uprising when Bulgarians rose up against the Ottoman occupation and in response, bashibasouks were deployed to crush the populace. News of the massacre reached Europe led to outrage because of the vivid descriptions of the atrocities carried out by the brigands:
Let me tell you what we saw at Batak ... The number of children killed in these massacres is something enormous. They were often spitted on bayonets, and we have several stories from eye-witnesses who saw the little babes carried about the streets, both here and at Olluk-Kni, on the points of bayonets. The reason is simple. When a Mohammedan has killed a certain number of infidels he is sure of Paradise, no matter what his sins may be ... It was a heap of skulls, intermingled with bones from all parts of the human body, skeletons nearly entire and rotting, clothing, human hair and putrid flesh lying there in one foul heap, around which the grass was growing luxuriantly. It emitted a sickening odour, like that of a dead horse, and it was here that the dogs had been seeking a hasty repast when our untimely approach interrupted them

(The Bulgarian Martyress by Konstantin Makovsky is one notable representation of the Bashibazouks assaulting two Bulgarian women - one of them dead in the ground)
Even more outrageous was the British Empire’s support of Turkey at the time, which lead to liberal politician William Gladstone denouncing the Prime Minister Benjamin Disraeli for standing with the Sublime Porte. On his manifesto, he attacked the Turks, stressing it wasn’t a matter of Islam, but rather specific to Turkey:
Let me endeavour, very briefly to sketch, in the rudest outline what the Turkish race was and what it is. It is not a question of Mohammedanism simply, but of Mohammedanism compounded with the peculiar character of a race. They are not the mild Mohammedans of India, nor the chivalrous Saladins of Syria, nor the cultured Moors of Spain. They were, upon the whole, from the black day when they first entered Europe, the one great anti-human specimen of humanity. Wherever they went a broad line of blood marked the track behind them, and, as far as their dominion reached, civilization vanished from view. They represented everywhere government by force as opposed to government by law.
Ultimately, their atrocities escalated into a full blown intervention by the Russian Empire, Serbia and Romania in 1877, beginning the 11th Russian-Turkish War, which once again saw the Ottoman Empire as the loser, thousands of Muslims refugees from the Balkans fleeing from ethnic cleansing, Bulgarian gaining autonomy as an principality and the bashibazouks being disused by the Ottomans (however, irregular troops continued to being used to persecute Christian minorities like Greeks, Armenians and Assyrians in the intervening years before the complete ethnic cleansing in Anatolia).
It’s not a surprise that in Erdogan’s nostalgic and revanchist delusions to revive the Ottoman Empire, he would restore the bashibazouks in the form of the Free Syrian Army. It has used them as both shock troops and canon fodder to fight mostly Kurdish forces along the border, but as a ceasefire began last week these units turned to looting attacking civilians and mutilating corpses, according to videos they posted online. The US says human rights violations may be occurring. Kurdish activists wonder why NATO stands behind religious extremists whose statements look little different than ISIS.

Videos showed men waving swords and chanting about "killing the kuffar" or "infidels," terminology often used by ISIS. On October 21, a group calling itself Jaish Islam, calls on its members to treat Christians as second-class citizens in areas that are conquered and to make them pay special taxes in accordance with discriminatory religious laws. More accounts that emerged on October 22 showed a man with a beard and his friends celebrating the killing of what they call "the corpses of pigs." They claim to be from the "mujahideen of Faylaq al-Majd." The man shows off a dead body of a woman and says "this is one of your whores whom you have sent us. This whore is under our feet."

This is an attitude reflected by Erdogan specially in his Arabic twitter where he exploits religion by using terms like “Army of Mohammed” descending on their enemies, which is ironic because they claim to be fighting against terrorists themselves. He is surely breathing a huge sign of relief with the recent death of Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi that he no longer has any rival to leading the potential Caliphate if he feels bold enough to declare it.
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
⚖️ JUDICIAL SUCCESS IN MIGRATION LAW!

⚖️ 🏛️ The Administrative Court of First Instance of Thessaloniki orders the Administration to allow our client's temporary stay in Greece until the decision is issued and to refrain from any action that would result in his forced departure from Greece.
✅ In this way, he is not at risk of arrest and deportation !!!
💼 As a greek law office, we provide legal assistance to refugees and migrants in Greece. Christos M. Terzidis, a Greek migration lawyer with a PhD title from the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki and former legal advisor to the NGO 'ARSIS' on refugee and migrant issues, is greatly experienced and specializes in Migration Law.
⚖️ We protect the human rights of refugees, providing legal assistance to refugees and migrants,undertaking cases that deal with refugee and immigrant residence permits (issuance and renewal) , application for political asylum and support at all stages of the process , appeals , protection from deportation and protection from administrative detention, deposition applications and their presentation and support before the Administrative Courts , presentation and representation before the Appeals Authority and its competent committees , passports (issuance-renewal) , family reunifications, Golden visa cases and so on.
✍ We prepare each case methodically with the outmost care and attention.
🆘 There is a 24-hour service available for emergency cases (like arrests and so on).
📞 You can reach us on 00306977424779 , so that we help you resolve your legal issues!
#refugees#refugees in greece#refugees greece#human rights of refugees#greece refugees#syrian refugees#ukranian refugees#migrants#migration law#migration lawyer#legal assistance to refugees#protect the human rights of refugees#human rights#residence permits#political asylum#protection from deportation#protection from detention#passports#travel documents#golden visa#ukranian refugees in greece#ukraine refugees#how to help refugees#stand with refugees#for refugees#deportation defense lawyer#deportation defense attorney#find a deportation lawyer
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Literature can save a life. Just one life at a time."
Teju Cole on carrying and being carried. Translation, refugees, new words.
New York Books, July 5, 2019

A reproduction of a scene from an ancient Greek vase depicting the flight from Troy, with Aeneas carrying his father Anchises on his back, nineteenth century
The English word translation comes from the Middle English, which originates from the Anglo-French translater. That in turn descends from the Latin translatus: trans, across or over, and latus, which is the past participle of ferre, to carry, related to the English word “ferry.” The translator, then, is the ferry operator, carrying meaning from words on that shore to words on this shore.
Every work of translation carries a text into the literature of another language. Fortunate to have had my work translated into many languages, I am now present as an author in the literature of each of those languages. Dany Laferrière, in his 2008 novel I Am a Japanese Writer, expresses this slightly strange notion more beautifully than I can:
When, years later I myself became a writer and was asked, “Are you a Haitian writer, a Caribbean writer or a Francophone writer?” I would always answer that I took the nationality of my reader, which means that when a Japanese reader reads my books, I immediately became a Japanese writer.
Much is found in translation. There’s the extraordinary pleasure of having readers in languages I don’t know. But there’s also the way translation makes visible some new aspect of the original text, some influence I didn’t realize it had absorbed. When I think about the Italian translation of my work, I can feel the presence of Italo Calvino and Primo Levi, unnerved and delighted that I mysteriously now share their readership. When I’m translated into Turkish, it is Nâzım Hikmet’s political melancholy I think of. Maybe those who like his work will, reading me in Turkish, find something to like in mine as well? In German, perhaps even more than English, I sense the hovering presences of writers who shaped my sensibility—writers like Walter Benjamin, Thomas Mann, Hermann Broch, and W.G. Sebald, among many others. Thanks to translation, I become a German writer.
I trust my translators utterly. Their task is to take my work to a new cohort of my true readers, the same way translation makes me a true reader of Wisława Szymborska, even though I know no Polish, and of Svetlana Alexievich, even though I know no Russian.
Gioia Guerzoni, who has translated four of my books into Italian so far, has worked hard to bring my prose into a polished but idiomatic Italian. Recently, she was translating an essay of mine, “On the Blackness of the Panther,” which ranged on various matters, from race, the color black, and colonialism, to panthers, the history of zoos, and Rainer Maria Rilke. It wasn’t an easy text to translate. In particular, the word “blackness” in my title was a challenge. To translate that word, Gioia considered nerezza or negritudine, both of which suggest “negritude.” But neither quite evoked the layered effect that “blackness” had in my original title. She needed a word that was about race but also about the color black. The word she was looking for couldn’t be oscurità (“darkness”), which went too far in the optical direction, omitting racial connotations. So she invented a word: nerità. Thus, the title became: “La nerità della pantera.” It worked. The word was taken up in reviews, and even adopted by a dictionary. It was a word Italian needed, and it was a word the Italian language—the Italian of Dante and Morante and Ferrante—received through my translator.
Translation, after all, is literary analysis mixed with sympathy, a matter for the brain as well as the heart. My German translator, Christine Richter-Nilsson, and I discussed the epigraph to my novel Open City, the very first line in the book. It reads, in English, “Death is a perfection of the eye.” The literal translation, the one Google Translate might serve up, would be something like “Tod ist eine Perfektion des Auges.” But Christine sensed that this rendering would equate “death” with “perfection of the eye,” rather than understanding that death was being proposed as the route to a kind of visionary fullness. So she first thought of “Vollendung,” which describes a finished state of fullness; then she thought further, and landed on “Vervollkommnung.” Vervollkommnung is a noun that embeds the verb “kommen,” and with that verb, the idea that something is changing and coming into a state of perfection. That was the word she needed.
Christine also knew that what I was calling the eye in my epigraph was not a physical organ (“das Auge”), it was the faculty of vision itself. But I didn’t write “seeing,” so “des Sehens” would not quite have worked. In conversation with my German editor, she decided on something that evoked both the organ and its ability: der Blick. So, after careful consideration, her translation of “Death is a perfection of the eye” was “Der Tod ist eine Vervollkommnung des Blickes.” And that was just the first sentence.
A young woman from Bonn named Pia Klemp is currently facing a long-drawn-out legal battle in Italy. Klemp, a former marine biologist, is accused of rescuing people in the Mediterranean in 2017. If the case comes to trial, as seems likely, she and nine others in the humanitarian group she works with face enormous fines or even up to twenty years in prison for aiding illegal immigration. (Klemp’s plight is strikingly similar to that of another young German woman, Carola Rackete, who was arrested in Italy this week for captaining another rescue boat.) Klemp is unrepentant. She knows that the law is not the highest calling. As captain of a converted fishing boat named Iuventa, she had rescued endangered vessels carrying migrants that had been launched from Libya. The precious human lives were ferried over to the Italian island of Lampedusa. The question Klemp and her colleagues pose is this: Do we believe that the people on those endangered boats on the Mediterranean are human in precisely the same way we are human?
When I visited Sicily a couple of years ago and watched a boat of rescued people with bewildered faces come to shore, there was only one possible answer to that question. And yet we are surrounded by commentary that tempts us to answer it wrongly, or that makes us think our comfort and convenience are more important than human life.
Because Pia Klemp’s holy labor takes place on water, it reminds me of an earlier struggle. In 1943, the Danes received word that the Nazis planned to deport Danish Jews. And so, surreptitiously, at great personal risk, the fishermen of north Zealand began to ferry small groups of Danish Jews across to neutral Sweden. This went on, every day, for three weeks, until more than 7,000 people, the majority of Denmark’s Jewish population, had been taken to safety.
Currently in my own country, hundreds of people die on the border in the name of national security. Children are separated from their parents and thrown in cages. A few years ago, I visited No Más Muertes (No More Deaths), a humanitarian organization in Arizona that provides aid to travelers by leaving water, blankets, and canned food at strategic points in the Sonoran Desert. These are activities that the US government has declared illegal. The organization also conducts searches for missing migrants, and often locates the bodies of those who have died of hunger or thirst in the desert.
A young geographer named Scott Warren, working with No Más Muertes and other groups, has sought to help travelers cross safely. He provides water and, when possible, shelter. For this holy labor, Warren was arrested and charged last year with harboring migrants. Although the case against him recently ended in a mistrial, the US Attorney’s Office in Arizona is seeking a retrial. Warren is far from the only No Más Muertes volunteer to have been arrested as part of the government’s war on those who offer life-saving help to our fellow citizens.
Can we draw a link between the intricate and often modest work of writers and translators, and the bold and costly actions of people like Pia Klemp and Scott Warren? Is the work of literature connected to the risks some people undertake to save others? I believe so—because acts of language can themselves be acts of courage, just as both literature and activism alert us to the arbitrary and essentially conventional nature of borders. I think of Edwidge Danticat’s words in her book Create Dangerously:
Somewhere, if not now, then maybe years in the future, a future that we may have yet to dream of, someone may risk his or her life to read us. Somewhere, if not now, then maybe years in the future, we may also save someone’s life.
And I think of a friend of mine, a filmmaker and professor from Turkey who signed a letter in 2016 condemning the slaughter of Kurds by the Turkish state and calling for a cessation of violence. She was one of more than 1,100 signatories from universities and colleges in Turkey. In response, Recep Tayyip Erdoğan’s government initiated investigations of every Turkish signatory, accusing them all of terrorism. Most, my friend included, now face long trials and prison sentences. Many have been fired from their jobs or hounded by pro-government students. Some have already been jailed.
My friend and the other academics were carrying their fellow citizens. With the stroke of a pen, they attempted to carry them across the desert of indifference, over the waters of persecution. For this, they face consequences similar to those faced by Pia Klemp and Scott Warren: public disrepute, impoverishment, prison time. My friend finds herself in great danger for her stand, and so now it is her turn to be ferried to greater safety, because she did the right thing, and we must, too.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Greece Passenger Locator Form - What You Need To Know
If you are traveling to Greece as a tourist, or as an immigrant, you will need a Greece Passenger Locator form. This form is required for anyone who plans to live and work within Greece. This form is required for consular assistance and non-refugees who receive assistance from the Greek government. It is used to gather information about all aspects of the country including where to eat, lodging, travel, and work.
http://ko.ivisa.com/greece-passenger-locator-form
On receiving the data on the applicant's personal profile and preferences through the electronic system of Greece, the agency sends back a unique qr code which needs to be entered on the Greece passenger locator form. The applicant is then required to enter the qr code at the place designated for processing. This is done by a licensed agent who is sent by the agency.
The applicant can proceed with the application only if he shows proof that his identity is genuine and that he possesses all the legal rights according to the law. The application may be rejected if the facts or figures are not correct. Before you submit the form, make sure that you have entered all required data. There is no room for errors so double-check everything. You might be rejected if you enter Greece using the euro as your currency.
After the application is submitted online, Greece has set a 72-hour deadline for submission. Failure to submit the application on time will result in the validity period being void and you not being allowed to travel unless you have valid reasons. Failure to submit the application in time could result in the applicant being arrested and prosecuted. Contact your nearest travel agent for more information about applying for a Greek visa.
Your name and details will be entered into the electronic database of Greece's immigration office when you enter the country with a visa number. Officials will give you a paper identification card and a photo scan upon arrival. This paper id is also required upon arrival at any airport as identification.
The official language of Greece is Greek, so all communication facilities such as hospitals and banks can be used in Greek. Many vehicles run on greek roads so travelers can take advantage of the free public transportation that runs throughout the country. Athens has two international airports that offer flights to all major cities around the world. The Othello Airport is approximately 40 miles away from the city. For hassle-free travel, it is a good idea to book your tickets in advance.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Yanis Varoufakis on Angela Merkel’s Legacy, European Politics & the “Sordid Arms Race” on the Seas
— September 29, 2021 | Democracy Now
— GUESTS: Yanis Varoufakis, Member of the Greek Parliament and Former Finance Minister of Greece.
The center-left Social Democratic Party in Germany has narrowly claimed victory in an election that marks an end to the 16-year era of Angela Merkel’s conservative chancellorship. We look at what this means for Europe and the world with Yanis Varoufakis, a member of the Greek Parliament and the former finance minister of Greece. The SDP’s narrow victory should be viewed critically, says Varoufakis, noting that the party “ruthlessly” practiced austerity in 2008 and 2009. “Not much has changed,” Varoufakis says. “It’s not as if an opposition party won.”


AMY GOODMAN: This is Democracy Now!, democracynow.org, The War and Peace Report. I’m Amy Goodman, with Juan González, as we turn now to Germany, where the center-left Social Democratic Party narrowly claimed victory Sunday in an election that puts an end to the 16-year era of Angela Merkel’s conservative leadership. Merkel’s party, the Christian Democrats, won the second most votes, with the Green Party coming in third. Social Democrats will now have to form a ruling coalition, which could take weeks or possibly months. The SDP’s candidate for chancellor, Olaf Scholz, who positioned himself as a leader in the vein of Merkel during his campaign, vowed to tackle the climate crisis and modernize industry, he says.
Well, for more on what this means for Europe and the world, we’re joined in Greece by Yanis Varoufakis. He’s a member of the Greek Parliament, former finance minister of Greece who negotiated with Chancellor Merkel and international creditors in 2015, when they demanded harsh new austerity measures for a European bailout of Greece, largely at Merkel’s behest, although at some points Varoufakis was excluded from the negotiations. His latest piece for Jacobin is headlined “Angela Merkel Was Bad for Europe and the World.” His new book is called Another Now.
We welcome you back to Democracy Now!, Yanis. If you can first talk about what’s happened in Germany, what it means for Greece and for the world?
YANIS VAROUFAKIS: Well, it’s good to be back, Amy. Thank you.
Look, not much has changed. Let’s not hyperventilate about the great changes. Point number one: Angela Merkel was not defeated. She’s the first German chancellor in the postwar era that has not been defeated. She resigned. So, she is going home because she’s had enough. Point number one.
Point number two: The previous administrations, at least the last two, were administrations — the so-called grand coalitions between the Christian Democrats and the Social Democrats, who now narrowly beat the Christian Democrats. So, it’s not as if [inaudible] Democrats are coming into government. They went into government. Olaf Scholz, who is going to be chancellor, if this coalition that he’s now concocting comes to fruition, he was finance minister until yesterday. So, let’s, you know, take down a few notches all the hype about the great changes that we’re going to see in Germany.
The other point, which is very important — two points, if I may, Amy, quickly, brief ones. Firstly, the austerity that hit our country here in Greece in 2010 was first practiced in 2009 — not to such an extent, but it was first practiced, put into place in Germany in 2009 — 2008, 2009, by the Social Democrats themselves. So it’s not as if the Social Democrats are an anti-austerity party. They were the inventors of austerity, and they practiced it ruthlessly in Germany.
And finally, the point I need to make is that whoever is in this government and whoever leads this government, this government is going to contain, for the first time since ages, the so-called Free Democratic — the Free Democrats of Germany, the FDP, which is a very strong, austerian, right-wing — libertarian even — party. And they are going to exact a pound of flesh from the Social Democrats or the Christian Democrats or the Greens, whoever joins them up. Their price for joining the government will be business as usual.
JUAN GONZÁLEZ: Well ,Yanis Varoufakis, you have argued, in articles you published in the New Statesman and Jacobin, that Merkel’s austerity policies condemned Europe and Germany to decline. Could you expand on that?
YANIS VAROUFAKIS: Happily. Remember the Lehman Brothers and the great financial meltdown of 2008? Very soon after that, Angela Merkel found out, to her, you know, disbelief, that the German banks were also kaput, bankrupt. And so were the French banks. So were all the banks in the European Union, including the British ones. And they had to actually salvage them, like President Obama did in the United States, except that, unlike President Obama, the Europeans had given up on having a central bank, a national central bank. So they effected a cynical transfer of — instead of printing money, instead of having the Central Bank of Europe, the ECB, print the money, which is what Tim Geithner and Larry Summers and Barack Obama did in the United States — instead of doing that, they transferred their losses onto the shoulders of the weakest taxpayers, who were Greeks, you know, working-class Germans and so on. So you had socialism for the very few, for the bankers, and harsh austerity for everyone else — not just the Greeks, but the German workers, the French workers, the Slovak workers, the Portuguese workers, the Spanish workers.
Now, what happens when you do that? You know, the bankers have been refloated. They are constantly being given money that the Central Bank brings, eventually. And the masses are suffering and laboring under the yoke of austerity. Now, big business looks at the “little people” out there and says, “Oh, well, they will not be able to afford the equivalent of a German Tesla,” let’s say, so they don’t build one. They won’t invest. So investment is very low. Good quality jobs disappear. They are replaced by mini jobs, delivery jobs, you know, the gig economy. So you have discontent across Europe. You have low levels of investment in the places that are the richest, like Germany. And, of course, you have nonexistent investment in places like Greece.
This is what I said when I tried to make the point in the articles that you kindly mentioned, that Angela Merkel leaves the chancellery, the office of prime minister of Germany, much stronger than she inherited it, because of the crisis. She leaves Germany complete and replete and full of economic surpluses, of, you know, surplus money. But she also leaves it with low levels of investment and, effectively, condemned to be falling behind China and the United States when it comes to the things humanity and Europeans will be needing in the next few years, which is green energy, artificial intelligence, high-tech companies that can combine the green transition with some degree of shared prosperity.
JUAN GONZÁLEZ: I wanted to ask you about another issue that marks, I guess, Merkel’s legacy, is the issue of immigration. I mean, we’re seeing new images again, not just in the United States of Haitians and Central Americans at the border, but, once again, in Southern Europe, of 600 asylum seekers yesterday in one boat in Italy, a huge increase in those escaping from Africa and the Middle East, coming to Europe. Greece, obviously, has been dealing with this. But Merkel was distinguished among the leaders by initially welcoming hundreds of thousands of migrants into Germany, when other countries were trying to close their borders. Your sense of her legacy in terms of migration policy and how migration is affecting Europe, given the fact that these imperial powers keep waging wars, disrupting these countries, creating chaos, and then insisting that migrants cannot come into Europe?
YANIS VAROUFAKIS: Yes, you are so right. I mean, it was such a show of hypocrisy recently, when the Taliban moved into Kabul, and the liberal press in the United States, and then, of course, in the European Union, they were horrified by the sight of the Taliban taking over, and all these concerns about the liberal, progressive Afghans, especially women, and then, at the very same time, you know, our great and good leaders, the same ones who were lamenting the success of the Taliban, they started talking about raising the height of the fences that they’re building to turn Europe into fortress Europe — not one mention of letting the Afghan women that are being persecuted by the Taliban come in.
But going back to your question about Merkel’s legacy when it comes to immigration, look, there was a key word in your question. That was “initially.” Her initial response, in 2015, the summer of 2015, when the Syrian refugees came storming in, running away from the civil war in Syria — her initial response was great. I mean, I even tweeted that — and, you know, I’m not a political ally of Angela Merkel. I said in my tweet that I am proud to be European because of Angela Merkel, because she said, “Let them in.” My goodness! And she let 1 million people in. But then, immediately, her pragmatism kicks in. She is the leader of a conservative party that would — was about to eat her up alive, to put it blunt — not too bluntly, I hope. And within two weeks, she reversed course. So, that initial response shows that the woman is probably a very decent person. And, you know, all kudos to her. But within two weeks, she spoke to the Turkish president, Mr. Erdoğan, and together they concocted a travesty of a policy.
Effectively, the European Union, under Merkel’s guidance, bribed, with a few billion euros, the president of Turkey, the Turkish government, to allow the European Union to violate international law, not to allow refugees. You know, refugees, on these ramshackle boats that end up on Lesbos, the Greek islands — right? — here, they really don’t have the right to seek asylum, because Merkel and Erdoğan agreed, years ago, with the approval of my former comrades in this government, after I resigned, the French, the Italians and so on — they agreed that Turkey is a safe country, and therefore, no refugees from Syria, from Afghanistan, from wherever, has the right, the automatic right, to file an application for a refugee status, even if they’ve been tortured. You know, this is absolutely preposterous. So, you have the initial reaction, which was good, and then you have what has been happening over the last few years.
Let me give you some — a piece of information which I think is significant. Last week, two weeks ago, a concentration camp, a prison camp, was built with European Union money, as part of the Merkel legacy, on the island of Samos. Now, on the one hand, you have those who are waxing lyrical about it, because those refugees that used to live in tents, and they would — you know, tents that would be washed away whenever there was a wintery storm or rain, heavy rain falling — you know, suddenly, they had decent dwellings. They even had a restaurant, and they had Wi-Fi. But what they forget to mention is that there is also barbed wire surrounding them. So these people can stay in there for years for having committed the crime of coming to Europe to seek refugee status.
AMY GOODMAN: Very quickly, Yanis Varoufakis, you’re speaking to us from a Greek island, and so we’re having a little trouble with the Skype. But thank you all for bearing with us. You tweeted on Tuesday, “At a time when the US& France are competing on which of the two will undermine Peace in the Pacific more effectively, the Greek PM is pushing Greece further into debt bondage by purchasing French frigates–with a nod from Biden so as to placate Macron. Greece deserves better!” And, of course, talking about AUKUS, this new military alliance to marginalize China, many are asking if it’s Biden who is really creating a new cold war with China. He makes a deal with the U.K. and Australia for — it was a deal, $65 billion, nuclear-powered subs. And this cut France out. They felt stabbed in the back. So now France is making a deal with Greece, further militarizing the world. Your thoughts?
YANIS VAROUFAKIS: I am ever so depressed by this. You know, we are not learning any lessons from the past. You put it quite rightly. There is a sordid arms race, arms deal race, happening in the Pacific. So, you know, the French want to make some money out of the Australians by selling them submarines. The Americans come in, and they cut the French out of the deal. The French get seriously peeved. All this is happening, supposedly, in order to increase security in the Pacific. It is doing exactly the opposite, because the Chinese are simply going to respond to this arms race by just upping the ante, building more of their own nuclear subs.
The nuclear subs are a waste in any case. Now, you know, we live in a technological world where we have transparent oceans. These old-fashioned nuclear submarines are neither here nor there. They are not increasing security. If they increase anything, it is insecurity.
But there’s a lot of money to be made, by the French, who want to sell them, by the American government, who wants to make sure that their mates that are producing these nuclear subs get the deals from Australia. And Macron is stabbed. And then, sadly, President Biden decides to throw him a few morsels of bread in order to pacify him. And that is to give the green light to the Greek prime minister to buy three or four frigates from the French government, which — exactly what are they going to contribute to our security? Yes, we do have a problem with Turkey. We have a recalcitrant Turkey. We have a Turkish regime that traditionally proves imperialist or acts imperialistically when it wants to solidify its own foundering base within Turkey, because it is a dictatorship, and our Turkish comrades, Turkish democratic comrades, are suffering under it. So, whenever the Turkish government feels unsafe, it creates tensions in the Aegean. But how exactly is this going to help? By “this,” I mean a few more high-tech frigates that Greece is going to buy from France — using what? More debt.
You mentioned that, you know, I was a finance minister at the height of the Greek debt crisis. Well, let me restate it for the record, that, back then, when every newspaper in the world, including in the United States, was covered with articles about the Greek crisis, our debt-to-GDP ratio was something like 170%, 150%, 170%. Right? One-and-a-half times our national income. Today it’s more than twice. It’s 210%, 212%. And still they are borrowing more money from the Europeans to buy European frigates to pacify Macron in terms of what he lost in the Pacific, while both the Pacific and the Aegean oceans and seas are becoming less secure and more prone to conflicts that will only have victims amongst the working classes of China, of Australia, of the United States, of Greece, of Turkey, of France and Germany.
AMY GOODMAN: Finally, Yanis, if you can say why you called your new book Another Now?
YANIS VAROUFAKIS: Because I’m a leftist. And we leftists have a problem, Amy, especially those of us who declare to be critical of capitalism or against capitalism, because the obvious question that then comes or is thrown at us is — and it’s a fair question — “Mate, if you don’t like capitalism, what’s the alternative? How could we have organized society — the economy, polity, the whole thing — differently without capitalism?” So I decided to write a novel, a science fiction novel, a political science fiction novel, in which I imagine that the 2008 great financial collapse led to not just Occupy Wall Street, but to a global movement that, with some degree of realism, built another now.
AMY GOODMAN: We want to thank you for being with us. We’re going to ask you to stay so we can have a further conversation about Another Now and post it at democracynow.org. Yanis Varoufakis, member of the Greek Parliament, former finance minister of Greece. His latest piece for Jacobin, we’ll link to, “Angela Merkel Was Bad for Europe and the World.” His new book is titled Another Now.
And that does it for our show. Happy Birthday to Paul Powell!
0 notes
Text

THIS AIN'T LEGAL
Have you ever heard of absolute immunity? Federal officers who violate the Civil Rights of American citizens in an attempt to do harm with recorded video evidence of the violation in action or officers who willingly falsify a police report of a violent attack in order to frame the victim while the antagonist sits before a judge and jury perjuring herself with alligator tears before an all white jury with her blonde locks, and blue eyes, damn devil, and goes free while an innocent child spends 17 months behind bars. To say that Amerikkka is unjust is an understatement. Too many times Black people are dragged into a court that's already biased, having to face a judge, and jury who may have a vested financial interest in the private prison industry, but let's be real. The school to prison pipeline is not a myth, it's a bloody bruise on the face of Lady Liberty. Liberty, and justice for all never applied to the indigenous people of Amerikkka or any of the ADOS, and FBA citizens whose roots are entrenched in the Earth bleeding from a wound the wicked do not want to heal. The above mentioned scenarios actually happened to one of your own Amerikkka, and a child from the Middle East. It's funny that Amerikkkans appear to want peace seemingly always, but you're forever raising hell outside of your jurisdiction? Joe Biden is deporting Haitian refugees out of the country ASAP, while transporting inland, and giving amnesty to Afghan refugees, and South Americans even so far as to offer them free secondary education, and housing. The culture of Amerikkka is against a Black man ever rising up to experience the American Dream in a Taliban like Aristocracy or Totalitarian society that started centuries before Biden became president. He's not the answer to our problems nor is he the root of the issue. Amerikkka is a canker sore, and a blight that impedes the progression of a once dominant, but humble people. No one needs to preach of racial superiority and use terror tactics in order to justify a calloused approach to validate this viral disease that affects everyone with a modicum of common sense, decency, and compassion. Amerikkka was a Nation before Amerigo Vespucci set foot on these shores. Alkebulan was inhabited by some of the most brilliant minds, and still is before Scipio Africanus named the dark continent after himself, an albino. Ohhh the irony, and moral hypocrisy. Timbuktu, and the city of Alexandria were well established kingdoms in Alkebulan where Greek, and Roman scholars went to gather much needed knowledge because they were dumb as hell. Egypt is a mystery that none can determine for now. When the prophecy is fulfilled by the Father whom the Prophet Joel spoke thereof He would pour His Spirit down upon all flesh, the truth will set you and I free. And it shall come to pass afterward, that I will pour out my spirit upon all flesh; and your sons and your daughters shall prophesy, your old men shall dream dreams, your young men shall see visions. What's impeding us from this prophetic word? Keep your thoughts to yourself. That's a luxury I haven't had since the age of stupid. Not wanting to call you out on the sins of your fathers, but you are just like him. I hope, and pray the Father fulfills His will in time before our hearts wax cold, too late. Amerikkka’s public enemy will not be our Black sons or daughters that are trying to follow the rules of man whose lawlessness has revealed itself to be an entire race of people. You create the laws, and break them leaving everyone with a bad taste in their mouth except those who profit from our pain. Chris Rock said this years ago. “The white man is the only one who profits from everyone's pain, especially a Black man’s.” you see how they treat us, and you have no inclination of what your future will hold for your people in the aftermath of the Zombie Apocalypse. I hate this form of pop culture rhetoric. There will be souls inhabiting these bodies that were once dead, and decomposing. God will deliver the dead from the sea, and He will deliver the dead from death, and hell.
Isaiah 26:17-21
17 Like as a woman with child, that draweth near the time of her delivery, is in pain, and crieth out in her pangs; so have we been in thy sight, O Lord.
18 We have been with child, we have been in pain, we have as it were brought forth wind; we have not wrought any deliverance in the earth; neither have the inhabitants of the world fallen.
19 Thy dead men shall live, together with my dead body shall they arise. Awake and sing, ye that dwell in dust: for thy dew is as the dew of herbs, and the earth shall cast out the dead.
20 Come, my people, enter thou into thy chambers, and shut thy doors about thee: hide thyself as it were for a little moment, until the indignation be overpast.
21 For, behold, the Lord cometh out of his place to punish the inhabitants of the earth for their iniquity: the earth also shall disclose her blood, and shall no more cover her slain..
When our Lord Christ Jesus does this work how do you think those who've hated, and betrayed us for a season of sin will react in the oncoming horror set before mankind? God has placed us on the Earth for a purpose, not to suffer. I can't put the blame on Joe Biden or those who came before him for what this nation or planet has done, and is doing to us; psych!!! The God of our fathers will judge you according to your works which has wrought death and destruction. The wrath, and judgment Joe Biden, trump, and their people will incur, and experience is worse than any Stephen King novel or Jordan Peele, and M. Night Shyamalan movies can induce in your alleged, fragile psyche. I've told Jacob, and warned the gentiles of God's incoming judgment, but no ones willing to heed the words of an idiot savant. I'm guilty of many things by way of my woeful condition. I'm compelled to elaborate these truths to you as they become relevant at a particular hour. Watch out for your young children who may be a pain, but they're innocent, and they're yours. The world sees us as prey, a potential payoff for an organ harvest, and fodder for the wickedly unjust. This woman that they have been searching for these last 5 or so days in a National Park has this Nation all a buzz. Who is she? Do you know how many women of Jacob go missing everyday without any press from the media? We can blame them, but are they at fault? Hell yeah!!! Continue to read. Our people have been limited by those who control the information, the social media platforms, infighting within our own tried Black media organizations that have blessed us over the years who are left open to attack by oppressive censorship that purposely restricts what they can, and cannot reveal to the Black masses. I was amazed to find out in 2017 that Coretta Scott King, and her family successfully sued the US government over the assassination of MLK Jr.; that was in 1999. The Atlanta Black Star might have covered the litigation process, but I didn't hear a peep from anyone I knew or even hear about it on any news media platform, especially from the major media news networks. That's how they've Silenced the Lamb with threats, and bullying tactics. We've come too far to go back to Egypt. The only time I wanna hear mention of going to Egypt is if my Church takes a sabbatical to the Motherland, and my Apostle takes the trip with us to seek the truths that have been denied us. Reference Joel 2:28. Those who stay committed to this ministry will see beyond the veil. If you placed all of your faith in me or Apostle Johnson you have overlooked the reasons God led you to this Church, Elders, Evangelists, Prophetesses, Deacons, Ministers, and the entire Church family. He nor I can do anything without the will of the Father, and I’m stuck on dufus. Get yo tail back to Church ASAP!!! We place our faith in men who have let us down many times. Apostle has done much for me, but Jesus has done everything. God will do a good work in all of us. I want every man, woman, and child in this ministry to reap what they have sown; don't leave. When the sky turns black, and the heavens roll back, peeling back the clouds, that's when you will see or hear the Son of God coming for His faithful. Apostle has taught us of the temporal mental mindset many times. Evidently it’s true as many of us have forgotten his teachings. My mind went off on a tangent, excuse me, where was I ? BET is owned by Jews, who used to own us. They run the entertainment industry that Buck breaks our men, and you wouldn't believe what they do to black women, and children who are all looking for a way to display their talents in order to get wealth, and their name up in lights. Leroy has the talent, all Mr. Epstein can offer you is a bogus contract that rips you off in the end leaving you po, broke, and lonely with a busted a-hole. Those who beat the system at their own game wind up 6 feet deep. Why do you think they murdered Michael Jackson, Prince, Sam Cooke, and James Brown? Michael owned half of SONY BMI. Prince owned all of his Masters that his
siblings sold for pennies on the dollar. Sam was going to start his own label, and brother James who had a label, but the IRS falsely audited him several times forcing him to sell his label keeping Soul Brother number 1 from becoming the first billionaire recording artist decades before JZ did. THIS AINT LEGAL. All that glitters isn't gold people. Ask Mr. Goldberg who runs several porn studios in Silicone Valley California. They run the majority of that particular industry as well as recording, movie and TV production studios while controlling the financial institutions. The majority heads of the Department of the Treasury including the current, Janet Yellen have been Jewish. Not trying to be a dissenter, but someone’s getting screwed. It's the middle class, and our fat, Black… ? William Randolph Hearst made the movie Reefer Madness which was a propaganda film not because hemp was a gateway drug to other crap, hell a pack of cigarettes has killed more people than ten thousand blunts. Smoke a blunt, and 30 minutes later you wanna eat. Smoke crack, and 30 minutes later you're sucking d**k. Hemp can be used in a vast amount of ways that would’ve crippled Mr. Hearst’s other industries. You can use it as fabric for clothes that's stronger, and more durable than cotton. The hemp plant had more useful potential than the soybean, and peanut combined!!! Marijuana isn't a drug at all, it's an herb. The Egyptians used it to cure many ailments including cancer. If I were still on Instagram Mark Suckerberg would personally shut my page down himself… again. That's why I no longer use white run social media websites. Mr. Hearst's only interest in getting the government to make hemp illegal was to keep his financial, investment interests ever increasing. In the end it turned out to do more harm than good. Now that the government has managed to tax the herb, they've made it legal. Why in the hell are Black men, and women still serving draconian, archaic prison sentences for minor marijuana drug offenses that don't make sense to a mongoloid retard?!! Like I said: “THIS AINT LEGAL.” Babylon the Damned will fall on its pancaked derriere soon enough. Pray to God the Zombie Apocalypse runs right past your abode or get some pads from your son's football uniform in order to appease the dead in Christ who may want a ham sandwich or your daughter Becky. This too shall pass. Try lamb's blood? The closer I get to death or that visitation with someone I've been wanting to see for a long time because I can't see, the more these things come back to my remembrance. This is enough for today. Whatever God reveals to me in the next few days hopefully I’ll relate some of that information to you. I thank those for judging me as a simp, punk b**ch, p**sy a** n**gah, punk a** n**gah, sorry a** n**gah, faggot, and everything you project or judge according to your flesh. I have no secrets so what am I trying to hide? Get your house in order Jeff, your life may be required of you, and ya boy in the wheelchair. Still someone else's identity Yippie Yai Kai Yay mother!@#$%& 9/21/2021
1 note
·
View note