#grassland mammals
Text
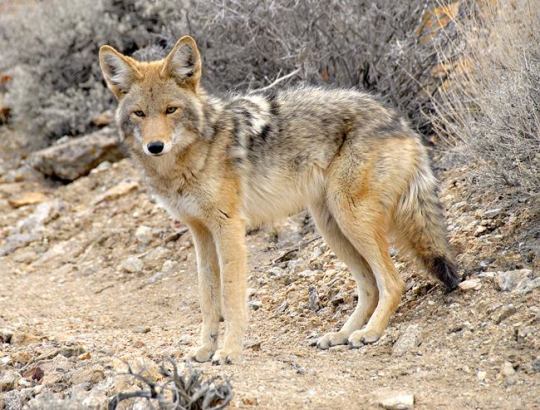




Close Up with Coyotes
Often confused with wolves, foxes, or even stray dogs, the coyote (Canis latrans) is a species of canid found only in Central and North America, from Panama to central Canada. Historically, the coyote mainly occupied grasslands, scrubland, and deserts; however, in the past few centuries the species has expanded its range to include deciduous and evergreen forests, mountains, swamps, and even cities. Generally individuals and groups keep to one home territory, but they will move when resources become lacking.
Among the canines, coyotes are rather small, weighing only 8 to 20 kg (18 to 44 lb), and males tend to be larger than females. Generally coyotes sport a light gray, red, or brownish coat with a lighter underside; however, regional populations may differ wildly. This species may be identified from other canids by its large pointed ears, whitish facial markings, and narrow snout.
Though C. latrans does occasionally form packs, it is more likely to hunt individually or in small family groups. Nonfamily packs, usually made of bachelors, are rare. In addition, coyotes have been known to form mutualistic hunting relationships with other species like badgers. It is primarily carnivorous, hunting mainly at dawn and dusk for rabbits and hares, squirrels, mice, lizards, and occasionally larger targets such as deer or pronghorn. This species will also readily consume carrion, as well as produce and human food waste, making it highly adaptable to urban areas. Traditionally, the species has been limited via both competition and direct predation by wolves and cougars; in its expanded range, coyotes may also be predated upon by bears, alligators, lynx, and golden eagles.
Though reproduction typically takes place in the spring, from January to March, temporary pair bonds may form as early as November. Mates prepare dens, which may be dug out or selected from tree hollows or pre-existing burrows, and establishes a territory up to 19 square km (11 square miles). During this time, daughters from a females previous litter, or her sisters, may join the group. Pregnancy typically lasts just over 60 days, during which time the male and any assisting females do most of the hunting. Litters average 6 pups, and weaning takes about a month. During this time, the male continues to provide for the mother and pups, but will abandon the den if the mother goes missing. By the age of four or five weeks the pups develop a hierarchy through play-fighting. After about 6 months, the male pups will leave, while females will typically stay with their mothers until at least the next mating season, at which time they reach sexual maturity. In the wild, individuals may live as long as 10 years.
Conservation status: Due to its large range and adaptability to human habitats, the C. latrans is considered Least Concern by the IUCN. In urban areas, coyotes are regularly hunted as a nuisance species due to their predation on free-roaming pets and, occasionally, livestock.
In traditional Indigenous American stories, the coyote was seen as a trickster or anti-hero (here is an interesting paper about the 'Coyote' character in traditional stories versus western interpretations). The European colonization of North America and the eradication of large predators like wolves and cougars has allowed coyotes to spread far beyond their original geographic range and become a 'nuisance species' in urban areas.
If you like what I do, consider leaving a tip or buying me a ko-fi!
Photos
Neil Nurmi
Carlos Porrata
Natrice Miller
Tom Koerner
#coyote#Carnivora#Canidae#canines#canids#carnivores#mammals#generalist fauna#generalist mammals#grasslands#grassland mammals#scrubland#scrubland mammals#deserts#desert mammals#north america
169 notes
·
View notes
Text


Oct 2023, pen & inks. Grass is not all the same.
Many people don't know that grasslands have fall colors. This is partly because over 75% of the prairie habitat on the North American continent has been destroyed by agriculture, systematic destruction, and more recently by urban sprawl. We have less than 1% of historic tallgrass prairie remaining. Please learn about these beautiful and rare spaces to help them, and if you get the chance, go see a prairie in national grassland or in a state or national park.
Aside from the sparkly ink, this illustration has a narrower color range than the Red Hills mixedgrass prairie it represents.
Species: Little bluestem (S. scoparium), big bluestem (A. gerardii), maidenhair (Sporobolus sp.), sideoats grama (B. curtipendula), blooming prairie blazing star (Liatris sp.), and the late season remnants of basketflower (Centaurea americana) and dwarf four-nerve daisy (Tetraneuris linearifolius).
#my art#inktober#ink#prairie#nature illustration#grassland#little bluestem#big bluestem#plant blindness#that one comic about the english language words for grassland being inherently agricultural lives rent free in my mind#do I fully agree? not necessarily. but I do think about it a lot#shimmer ink#fountain pen#freehand#by systematic destruction I mean genocide of its human residents and mass slaughter of its keystone mammal species#[insert Dr Kimmerer's essay about Do you think the land loves you back]#you've heard of 'go touch grass' now get ready for- go touch NATIVE grass#undescribed for now sorry sdkfjlg
42 notes
·
View notes
Text
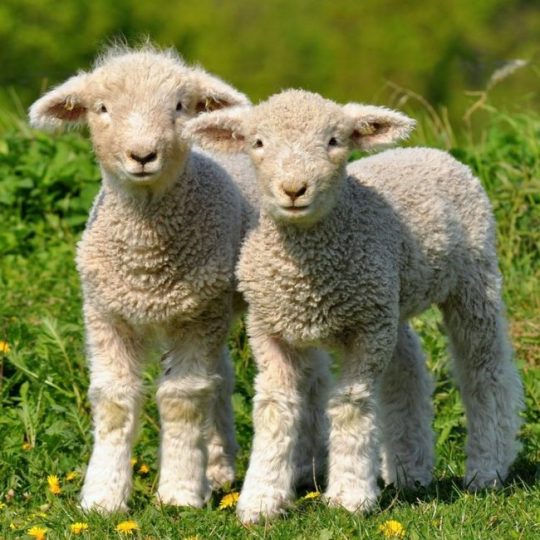
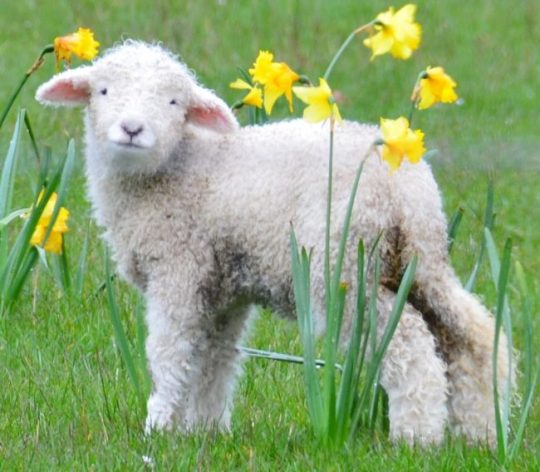





Charming kind sheeps walking in the field🐑🍀
#sheep#cutie#wildlife#animal#farm animals#grassland#mammal#farm#lamb#field#nature#photography on tumblr
39 notes
·
View notes
Text

Instead of starting a whole new speculative biology project like I tend to do, I decided to continue one I already have. The one I selected is my Pangea Ultima project which speculates life on Earth 250 million years from now when all the continents have reformed into a super continent like they did 250 million years ago. Where I left off on this project I was exploring the grasslands/plains on Pangea Ultima and in this post I'll showcase the (comparatively) smaller herbivores of this environment.
Plains Loper: Large descendants of crickets reaching 17 in in total body length, the Plains Lopers evolved elongated heads for reaching grasses as the wildebeest and antelope of the distant past have. Their exoskeletons have become beetle-like to provide some protection from predators but will use their powerful hind legs to escape danger.
Grass Roach: Rivaling the largest roaches of today (at 4 in.), the Grass Roach evolved extra long legs positioned below there bodies to achieve great speeds and coloration that helps them blend in with the grasses that they feed on.
Armadillopod: Giant descendants of isopods (aka pill bugs/roly-polies), these heavily armored scavengers feed on decaying plant matter, roots, and even carcases left behind by predators. If they feel threatened they will partially submerge themselves in the ground using their hook-like legs and barbed rim of their shells to hold themselves in place leaving only their remarkably durable shells exposed.
Prairie Ashbreather: Filling the ecological niche once filled by long extinct gophers and prairie dogs, the Prairie Ashbreathers dig elaborate tunnels below the grasslands with powerful claws feeding primarily on root systems though they will occasionally snag a Grass Roach if it's able to catch one.
As always, comments and critiques are welcome.
#speculative biology#speculative evolution#speculative zoology#ecology#creature design#insect#arthropods#isopods#roach#cockroach#mammals#mammal#rodent#pangea ultima#my art#digital color#digital illustration#digital art#grasslands#prairie#plains#grass#future evolution
13 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Winter Bighorn III
In order to find Bighorn Rams one need to hike up and into the high elevation grasslands and hopefully you meet up with the Bighorn Rams. Tough hiking but worth it.
Photographer: Bruce Turnbull
61 notes
·
View notes
Note
Do you have any cool bird facts
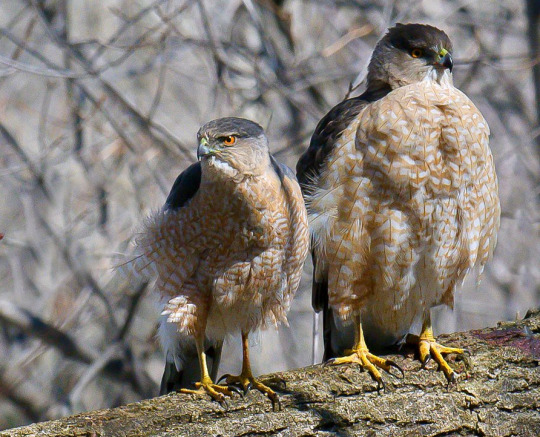
female raptors (eagles, hawks, falcons, etc) are larger than male raptors in pretty much all species. this happens even in groups not closely related to each other (ex: hawks and falcons), so its beneficial enough in their niche that its evolved independently a few times, though its unsure exactly what that benefit is atm (bc unlike males being larger in a lot of mammals, female raptors dont make a habit of fighting each other or using size to attract mates as far as we know). ex: heres a male and female Cooper's Hawk

somewhat mentioned above but falcons are more closely related to parrots than they are to hawks
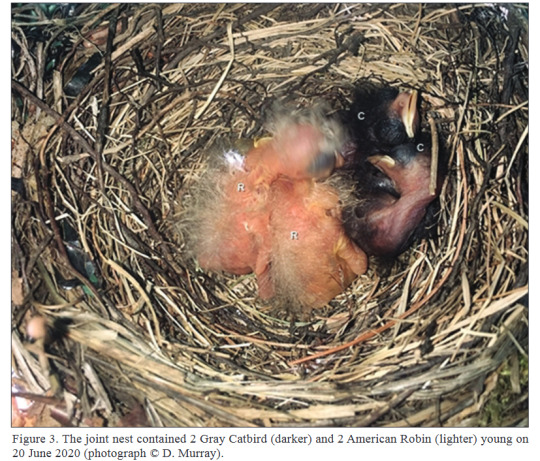
Gray Catbirds and American Robins have been witnessed raising young in the same nest at the same time. In one instance (reported by Mulvihill and Murray), they were recorded caring for the young of both species in the nest, and when the Catbird young fledged, the adult Catbirds continued to provide food for the not-yet-fledged Robins. heres a pic of the nest from the report

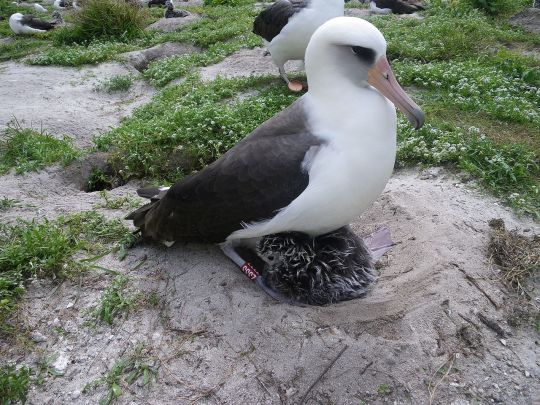
the worlds oldest known bird as of 2024 is a wild Laysan Albatross named Wisdom who's 72-73 years old (at minimum, we dont actually know her birth date, just that she was at least 5 years old when she was banded in the 50s) and still raising chicks. here's her with one of her chicks

also Albatrosses have wingspans of up to 3.5m/11.5ft and have been recorded flying 49,700 miles without touching land (they do land in the water to eat tho)
this is from personal experience but if you walk around in a north american grassland for long enough, you Will get jumpscared by a Mourning Dove bc they make their nests on the ground in the grass and like to hang out on the ground in the grass and they also like to wait until youre right overtop of them to freak out and fly away from you
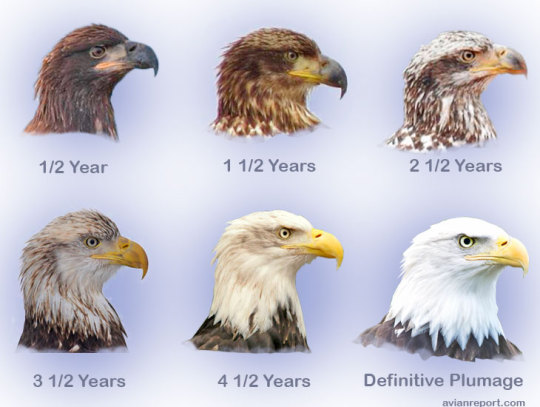
Bald Eagles don't get their fully white heads and tails until theyre about 5 years old

A lot of birds have been observed incorporating cigarette butts into their nests, and a study in Mexico on House Finches found that this actually results in drastic decreases in parasites affecting young compared to nests without them
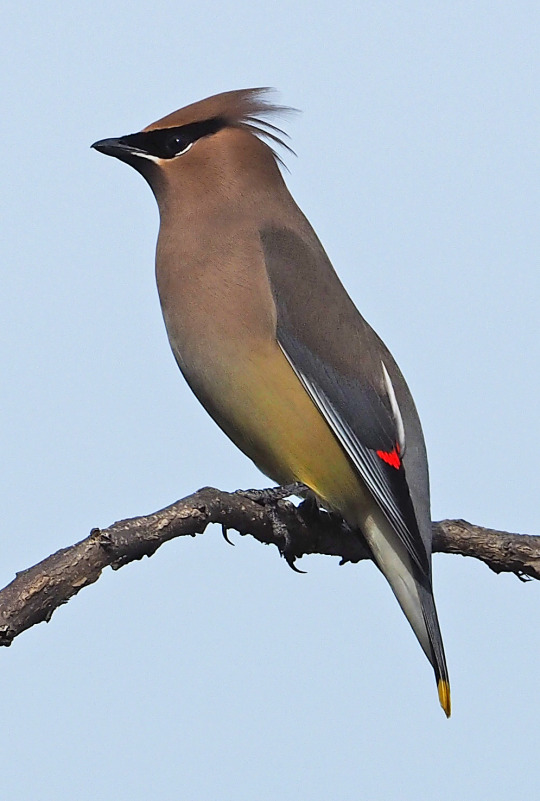
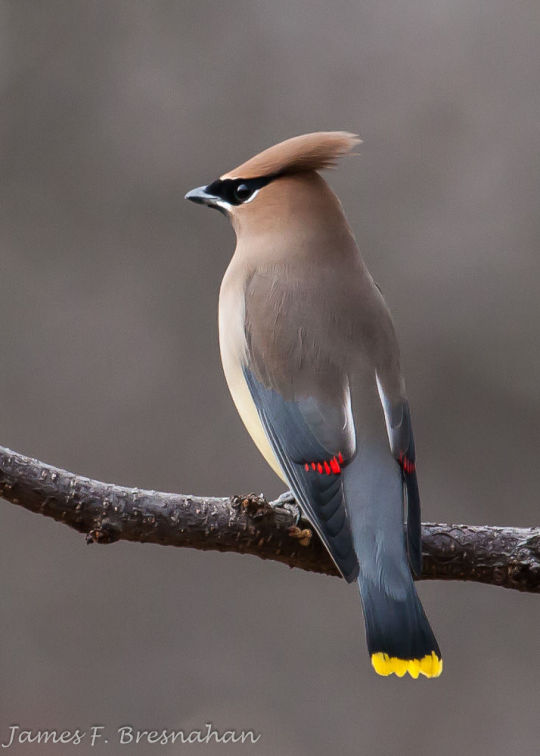
Cedar Waxwings (and Waxwings in general) just look so smooth. they look like someone airbrushed them. look at this shit


in Jacanas, females lay eggs in multiple males' nests, and then the males raise the young by themself. Also they carry their babies under their wings like this

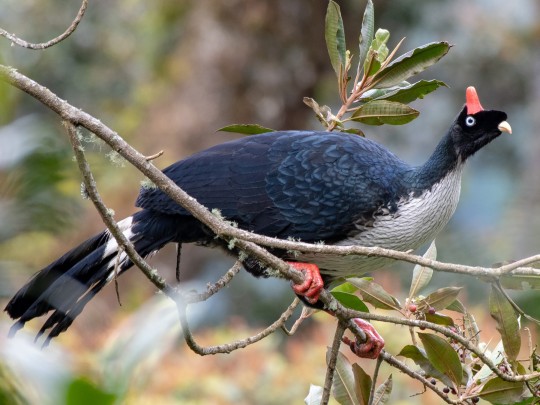
Horned Guan. Theyre endangered and live in a small area of central america. both the males and females have the little horn fez, the males just have taller ones

6K notes
·
View notes
Text
you have everything you need to survive and you will get through the trip and come home safely
for the purposes of "polls can only have ten things", your options are limited to land ecosystems
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Happy Earth Day!

We share this beautiful planet with over two million other species, from wasps the size of a grain of dust to whales larger than an office building. Yet, many of these species now face extinction due to the ways in which we humans have modified the planet to suit our needs. According to the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN), 13% of birds, 21% of reptiles, 27% of mammals, 37% of sharks, and 41% of amphibians are currently endangered, and some estimates suggest that 28% of all species on Earth are at risk of extinction in the near future. Imagine you woke up tomorrow and more than a quarter of every plant, animal, and fungus, from the elephants at the zoo to the earthworms beneath the soil, simply vanished, never to be seen ever again. If we choose to continue treating our planet so poorly, this will become a reality.
Here at Consider Nature, we believe the best way to protect our planet is to arm ourselves with knowledge! Over the years, we have written many articles on some of Earth’s coolest, weirdest, and most-endangered species, in the hope of inspiring readers to step up to the plate and protect biodiversity. I hope you will spend a few minutes of your Earth Day today reading about some of the species we believe are worth saving.
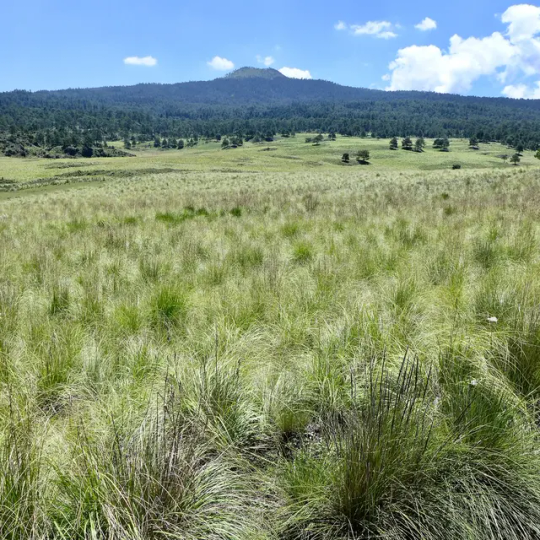

Zacaton grasslands in central Mexico, home to the Zacatuche, or volcano rabbit. Image credit: Jurgen Hoth
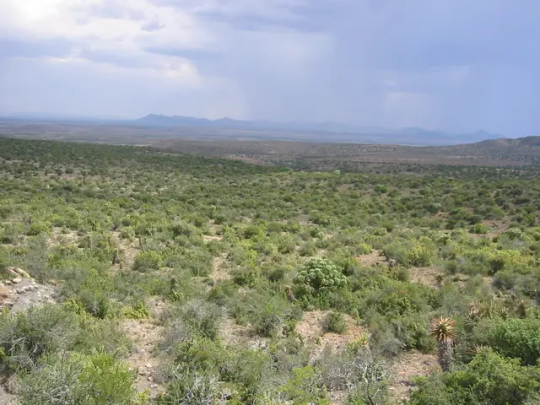

The Succulent Karoo, one of the most biodiverse ecosystems on Earth and home to the Karoo Padloper. Image credit: Tjeerd Wiersma under CC BY-SA 2.0.

The Gulf of California, home of the critically endangered Vaquita. Image credit: Natural World Heritage Sites.
658 notes
·
View notes
Text
The World is Amazing, Actually (Part 11 or 12, I lost count)
It's been awhile since I made a post about how fucking rad the world actually is, and amidst all the pandemics and climate change and economic troubles, I felt the need.
So:
Today’s Wild Place (The Earth is An Alien Planet):
The Danakil Depression, Ethiopia:

The Danakil Depression is probably the closest you'll ever be able to come to standing on the surface of Venus (without the crushing atmosphere, of course). Choking sulphuric acid and chlorine gases fill the air, while acid ponds and geysers pepper the landscape.
- Daisy Dobrijevic, published July 4, 2022
(BTW scientists recently discovered microbes capable of surviving in this toxic, extremely hot environment, which means...well, even if we kick the bucket, life will continue. There's something comforting in knowing that no matter how bad we screw up...life will go on.)
Today’s Incredible Feat of Engineering (look! at what! we made!):
Ouarzazate Solar Power Station in Morocco, which has gone solar in a big way.

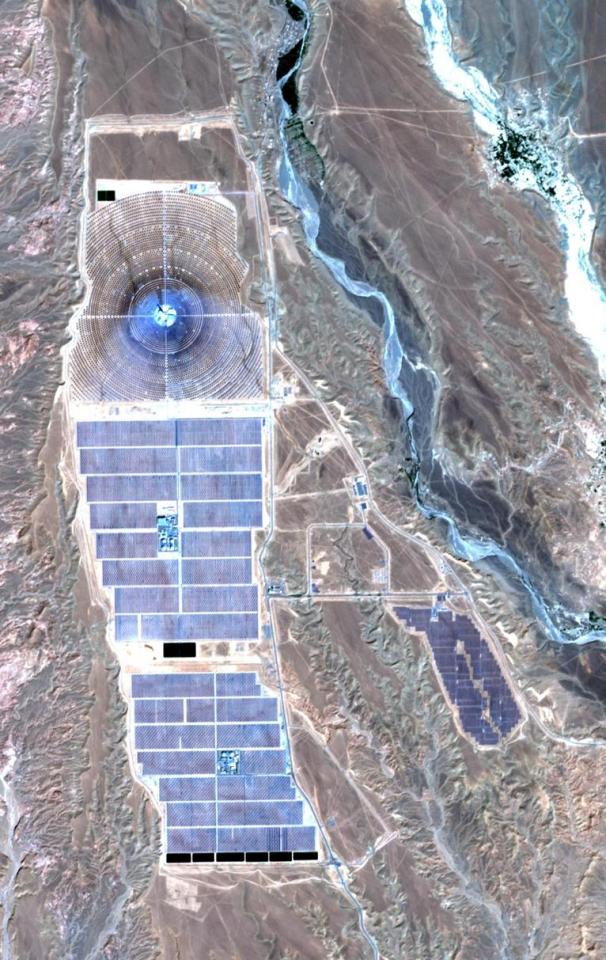
(Which means they are making a huge contribution to helping fight toxic pollution, noise pollution, water use, land destruction, and carbon emissions. No really, there are charts. Reducing carbon emissions charts. Reducing irresponsible land use charts. Charts! Graphs! Data samples!)
Today’s Cool Life Form (the rare, the weird, the beautiful):
The Hispaniolan Solenodon.
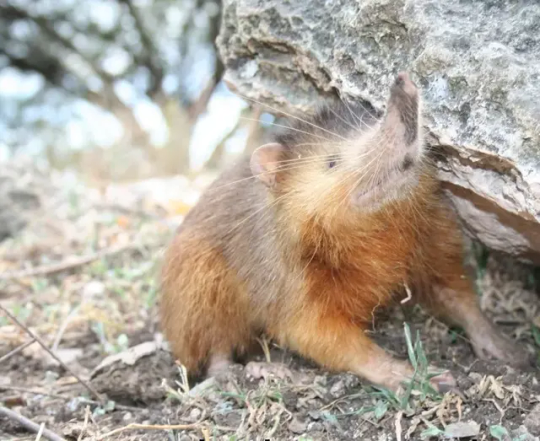

A very rare, nocturnal, shrew-like creature that is one of the few mammals able to produce venom. Look at him! Look at his snout! He's just a little guy! He will bite you and run away on his back legs! He's rare, and endangered, but not gone! Not gone yet, bitches!

(Bonus: 10 Fun Facts About the Solenodon)
Today’s Bizarre Mystery (no, seriously, wtf?):
The Great Unconformity.
Hey, remember the Grand Canyon? Remember how we can see the passage of time through each layer, going back hundreds of thousands of years?

Did you know that apparently, on this massive record of earth's geological history, there's a chunk of time missing? Science has some hypotheses about how and why this happens (and yes, it's been found in more than one place), but they are really only hypotheses, and no one's really sure what happened to, oh, 1.6 billion years, give or take.
Today’s Act of Humanity (yes, we are worth the effort):
After fleeing a war, Ukrainians rush to help Mississippi tornado victims.
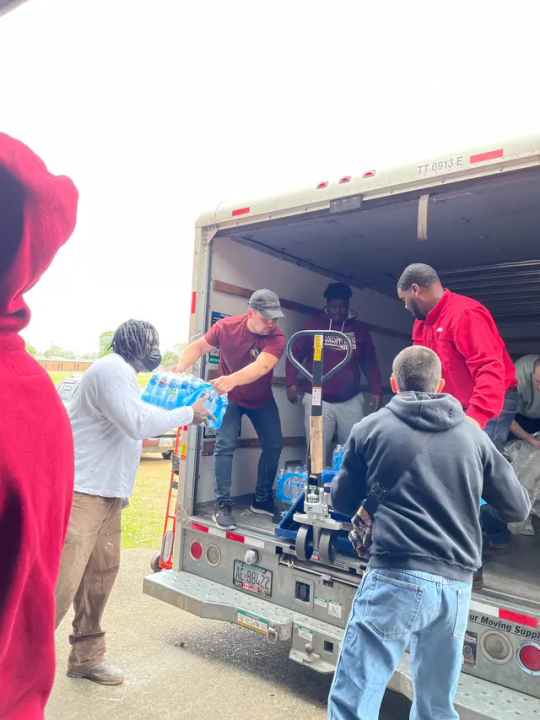

"They made the 16-hour drive south to donate bottled water and volunteer with aid workers, buoyed by the idea that they could help a community facing a similar struggle to theirs.
“We had to leave our home,” Pavliuk told The Washington Post in Ukrainian, in an interview interpreted by Hrebenyk. “And they don’t have a place to go back, either.”"
NEW CATEGORY:
Today's Good News About The Future (No, It's Not Too Late and Anyone Who Says Otherwise is Selling Something):

The Saiga Antelope, a species critical to the continued survival of huge swathes of grassland, that in 2003 was down to 6% of it's population and already extinct in it's natural habitat of China and Ukraine, has rebounded back to almost 2 million strong thanks to conservation efforts.

Previous | Next
#the world is amazing#planet earth#nature#good news#animals#danakil depression#Ouarzazate Solar Power Station#morocco#Hispaniolan Solenodon#little creature#saiga antelope#climate change#climate conservation#hope#ukraine immigrants#people are okay#mississippi tornado#look for the helpers#I'm so tired of being worried about the world#but it's not all bad
211 notes
·
View notes
Text
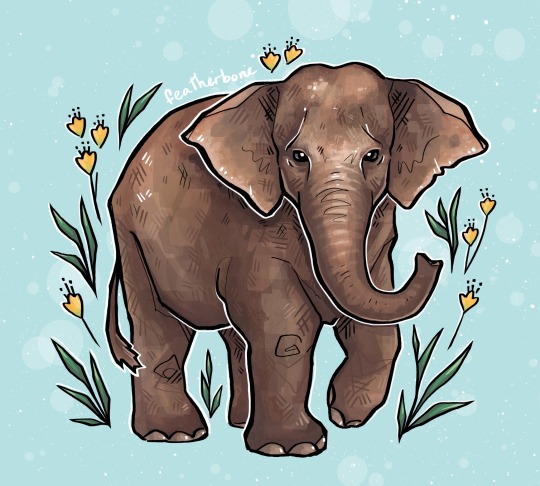

[ID: an illustration of a grayish brown elephant facing forward and to the right, with one front foot raised. It is on a blue background with yellow flowers and green leaves. End.]
Asian elephant! Largest land mammal on the continent, at around 11,000lbs. They’re threatened by habitat loss and fragmentation, and by poaching. If their forest and grassland habitats can no longer support their nutritional needs they may graze in agricultural fields, resulting in dangerous human-elephant conflicts.
163 notes
·
View notes
Text
Animal of the Day!
Pampas Cat (Leopardus colocola)

(Photo in public domain)
Conservation Status- Near Threatened
Habitat- Andes Mountain range
Size (Weight/Length)- 60 cm
Diet- Small mammals; Bird eggs
Cool Facts- Due to the Pampas cat’s elusive behavior and hard to traverse habitat, little is known about these small felines. They thrive in their grassland home, using their coloration to blend in with the thick grass. Pampas cats are found on mountain plateaus up to 5,000 meters tall. Their preferred food are viscachas and guinea pigs. Some scientists believe the Pampas cat to be fully nocturnal while others believe the complete opposite. Hopefully, as technology increases, there will be more opportunities to study this elusive feline.
Rating- 11/10 (Different fur coloration based on where they’re born.)
#animal of the day#animals#mammals#cats#feline#sunday#september 10#pampas cat#biology#science#conservation#the more you know
358 notes
·
View notes
Text
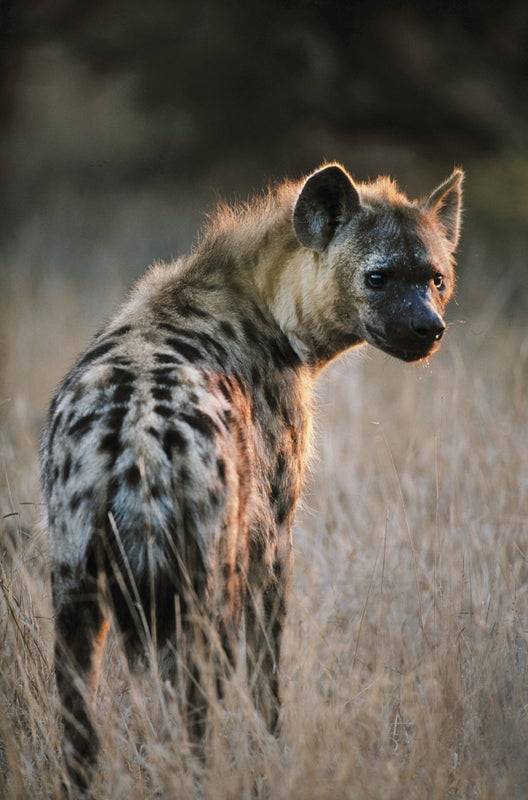




Say Hi to the Spotted Hyena
The spotted hyena is also known, perhaps most famously, as the laughing hyena (Crocuta crocuta). This species once ranged throughout Eurasia, but following the end of the Ice Age was restricted to sub-Saharan Africa. Today they can be found in many types of dry, open habitat, including savannah, semi-desert, and mountain forests. At times, the spotted hyena may also enter urban areas in search of food.
Unlike other hyenas, Crocuta crotuta is a predator, not a scavenger. They most commonly prey on wildebeast, but they may also hunt zebra, gazelles, Cape buffalo, and warthog. In addition, desperate times may cause packs to hunt on more dangerous prey such as young hippopotamus, giraffe, and rhinoceros. Spotted hyenas have incredible endurance, reaching speeds of 60 km/hr (37 mph); a single chase can last over 24 km (14 miles). When live prey is scarce, the laughing hyena can also turn to carrion, as well as snakes and ostrich eggs. In turn, this species may be killed by lions, though this may be motivated more by competition than prey drive.
Spotted hyena females are typically larger than males, weighing 44.5–67.6 kg (98–149 lb) to the males' 40.5–69.2 kg (89.3–153 lb). The height range for both sexes lies between 70–91.5 cm (27.6–36.0 in). In addition, female laughing hyena are somewhat famous for their masculinated genetalia; the clitoris is enlarged, resembling a penis, and is accompanied by sacs filled with fibrous tissue that resemble a scrotum. As the name implies, the coat is light brown with darker spots over most of the body. Because the species has such a wide diet, it has was is considered to be the strongest in relation to size of any mammal. The bite force is stronger than that of a brown bear, and can exert a force of 4,500 newtons-- enough to crush bone.
The laughing hyena is a highly social animal, and individuals live in communities up to 80 strong; size largely depends on prey availability and whether or not the group migrates. A clan territory can be anywhere from 40 km (24 mi) to 1000 (621mi) squared. Females dominate the males, and a pack is usually led by a matriarch. Hierarchies are strictly enforced, and positions are primarily inherited through birth and transferred through death. In addition, one's rank is maintained and recognized through social alliances and their contributions to the clan rather than size or dominance displays. The entirety of the clan comes together most often when defending a territory, gathering at the communal den, or at a kill; however, these kills are more commonly produced from smaller offshoots of the clan.
Crocuta crotuta can breed year-round, though mating is at its peak during the wet season from April to June. Members of both sexes pair indiscriminately with multiple mates, both within their clan and without. To offer himself, the male performs a mating ritual in which he lowers himself to the ground before the female, and retreats if any aggression is shown. Once impregnated, the female carries for about 110 days before giving birth to two cubs-- three is fairly rare. Weaning takes another 14 to 18 months, during which time cubs learn to hunt and defend the clan, as well as establish their place in the social hierarchy. Sootted hyenas reach maturity at about 3 years old, and can live an average of 12 years in the wild, though individuals as old as 25 have been recorded.
Conservation status: The spotted hyena has been determined Least Concern by the IUCN. However, outside protected areas the population is declining due to deforestation and hunting as a nuisance species.
If you like what I do, consider leaving a tip or buying me a ko-fi!
Photos
Augusto Bila
Elise Pianegonda
Evie Davidian
Art Wolfe
#spotted hyena#Carnivora#Hyaenidae#hyenas#carnivores#mammals#savannahs#savannah mammals#grasslands#grassland mammals#scrubland#scrubland mammals#africa#sub saharan africa#animal facts#biology#zoology#requested
175 notes
·
View notes
Text

Two popular classics! But who is the Superb Owl?
The most widely distributed owl in the Americas, the great horned owl ranges throughout North America and much of Central and South America. They can be found in almost any habitat. These owls mostly prey on rodents and lagomorphs, but are opportunistic hunters and will take anything they can catch, including smaller owls. They hunt by watching from a perch. Regarding their ecological niche, they are sometimes described as the nocturnal equivalent of red-tailed hawks. Great horned owls nest earlier in the year than most other raptors. These owls are very long-lived, with a typical lifespan of around 13 years in the wild (with a record of 28) and up to 50 in captivity!
Western barn owls live throughout Europe as well as much of Africa and the Arabian peninsula in a wide variety of habitats, but most especially favoring open woodland and grasslands. These owls mostly eat small mammals such as rodents and shrews, but will also eat birds, amphibians, lizards, and insects. They hunt by flying slowly over ground and pouncing when movement is detected. Western barn owls are usually monogamous, mating for life. After fledging, young remain with their parents for only about a month. Since barn owls have relatively high metabolic rates, they eat proportionally more rodents than other owls and are thereby appreciated by farmers as effective pest control.
509 notes
·
View notes
Text
Textbooks on biology and forestry make it clear that large parts of Europe would naturally be covered by dense forests.
The textbook narrative is that our ancestors felled the forests, drained the swamps and cultivated the heathland. In other words, they created the varied landscapes of meadows, heaths and grasslands that characterized our cultural landscapes before the advent of modern agriculture.
But new research from Aarhus University suggests that this is not the case. Elena Pearce, postdoc at the Department of Biology at Aarhus University, and the lead author of the study explains.
“The idea that the landscape was covered by dense forest across most of the continent is simply not right. Our results show that we need to reassess our view of what European nature is," she says, and her colleague and co-author Professor Jens-Christian Svenning continues:
“Nature during the last interglacial period – a period with a mild climate similar to today, but before modern humans arrived - was full of variation. Importantly, the landscapes harboured large amounts of open and semi-open vegetation with shrubs, light-demanding trees and herbs alongside stands of tall-growing shade trees.”
[...]
According to calculations from the new study, somewhere between 50 and 75 per cent of the landscape was covered by open or semi-open vegetation. And this is most likely due to the large mammals that lived at that time, explains Jens-Christian Svenning.
"We know that a lot of large animals lived in Europe at that time. Aurochs, horses, bison, elephants and rhinos. They must have consumed large amounts of plant biomass and thereby had the capacity to keep the tree-growth in check," he says and continues:
"Of course, it’s also likely that other factors such as floods and forest fires also played a part. But there’s no evidence to suggest that this caused enough disturbance. For example, forest fires encourage pine trees, but mostly we did not find pine as a dominant species.”
Although the research group cannot be 100 percent certain about the extent to which large animals were behind the open areas, there are strong indications that they were. Firstly, large animals such as bison have exactly that effect in areas where they are still found in European forests. Furthermore, beetle fossils from the last interglacial period also show that many large animals lived at that time.
“We have looked at a number of finds of beetle fossils from that time in the UK. Although there are beetle species that thrive in forests with frequent forest fires, we found none of them in the fossil data. Instead, we found large quantities dung beetles, and this shows that parts of the landscape have been densely populated by large herbivores," he says.
#trees#forest#wood pasture#ecology#prehistory#more evidence against the closed canopy hypothesis#emphasis added
142 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Salii’Qi - Saliinthia’s Sophonts
The primary sophont species residing on the warm, Earth-like world of Saliinthia are the Salii’Qi, a race of strange mammalian-insect creatures. They have dispersed into four main subspecies, two sedentary groups who live in the forests and islands respectively, and the two nomadic groups who call the grasslands and deserts home. Through this blog I will delve deep into their various cultures, religions, technology, and day to day lives living on Saliinthia!
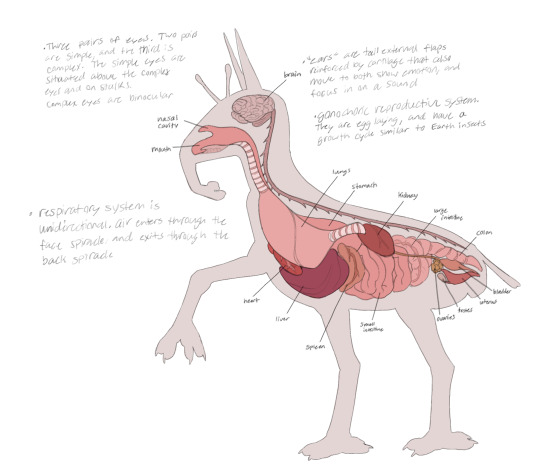
Basic Biology
The Salii’Qi evolved from intelligent, largely carnivorous pack hunters, with the grassland subspecies being the oldest ones. They have intelligence equivalent to that of human beings, though tending to be better at problem solving. Their mammal-like biology gives them warm blood and dense bones, though their skeleton is derived from a graphite filled exoskeleton similar to that of insects, that was slowly internalized over the course of millions of years. They are egg layers, and have a complex life cycle not unlike that of an Earth caterpillar or beetle.
Salii’Qi have three sets of eyes, two are simple and detect movement and light only, while the third pair is complex and has an expanding and contracting pupil like Earth’s vertebrates. They hear through bright colored ear flaps held up by cartilage, able to swivel and pin to show emotion or focus in on certain sounds.
Salli’Qi have four pairs of limbs, two are used for walking while the other two are used for physical manipulation. One pair of limbs are attached to the skull. These “arms” evolved from pedipalps, now used for eating and handling weapons or other objects. The pedipalps are weaker than their forearms, so they usually use those for heavier work like lifting large objects. With the evolution of centaurism in these creatures, they lost a lot of flexibility in their backs, and so can no longer keep their forearms on the ground for long periods of time.

The skeleton of the Salii’Qi have a dark color due to the high amount of graphite present in their bones, with black teeth stronger than ours. Their bones are dense and very similar to ours, although the ribs are free floating and connected with cartilage. Some of the vertebrae located near the end of the body are fused, which aid in supporting the back. Ancient relatives had a connected skeleton below the skin, which resembled that of insects. To allow for more flexibility and dexterity, those bones have now been reduced to cover less area.

Salii’Qi have organs very similar to ours, but have a unidirectional respiratory system. They breathe in through two spiracles beneath their eyes, and after passing through the lungs, it is exhaled through the two spiracles placed behind the first pair of leg’s shoulders. This allows faster replacement of oxygen in the bloodstream, fueling their insect-like biology.
Their digestive system extremely similar to ours, the only notable difference being the tiered stomach, which allows for tough protein rich plant matter to be digested.
Salii’Qi have a gonochoric reproductive system, meaning they have two sexes. Both sexes have bright colored ear flaps and antennae, but during the spring the male coloration deepens for mating. Females are slightly larger than males, and have duller colors. Depending on the culture, females may take multiple male partners during the mating season, or only keep one partner for their whole life.
Subspecies
The Salii’Qi are spread over four main subspecies, and are regional variants. As mentioned before, the nomadic grasslanders were the first successful variants, which then radiated into the forest, desert, and island subspecies. As the names imply, they live in settlements and groups around specific biomes they are best adapted to.

The foresters are mostly a sedentary group, and also physically the largest. They eat the most fruit and plant matter out of any other , and have learned how to farm and selectively breed crops. They have long, thin limbs for reaching up into the vegetation, and upturned simple eyes to see differences in the shadows above. They are skittish and try too keep to themselves, but enjoy trading their crops with other groups.
Grasslanders are nomadic, but have specific areas they return to during nesting season. They follow the herds of large grazers who roam the grasslands, using their good stamina to their advantage. They are a proud and strong group, seen as kind and humorous. They are artisans, creating unique goods and clothing out of hides and pelts for trading with other groups.
Desert dwellers live in smaller groups, and instead of hunting, they primarily ranch and travel with herds of domesticated livestock. Desert Salii'Qi forage desert fruits, roots, and other plant matter before a harvest. They travel to feeding grounds during the fall and winter, but return to fertile river communities during the spring and summer where plants for livestock flourish along the banks. During this time, the desert Salii-Qi raise their children to take on their next journey.
Islanders are small, social Salii'Qi who settled on an archipelago millions of years ago. They are the most well adapted group and the second oldest subspecies. Islanders have partially webbed feet, seal-like fur, powerful limbs, and higher back spiracles which makes it easier to spend time in the water. They primarily feed on fish and island fruit which they've selectively bred. Islanders mainly spearfish, but also use boats for fishing and trade. They routinely voyage to the mainland to trade goods, and some have even settled on the mainland shores.
#salii'qi#saliinthia#spec bio#speculative biology#biology#xenobiology#alien#speculative fiction#speculative ecology#aliens#sci fi#evolution
198 notes
·
View notes
Text

Conservationists are working to reintroduce the Scottish wildcat but face a massive numerical deficit and challenge. Lessons can be learned from its near demise, such as not waiting to conserve species until its nearly too late, the Scottish Rewilding Alliance’s Richard Bunting says.
Image by Charlie Marshall via Flickr (CC BY 2.0).
Small cats face big threats: Reasons to save these elusive endangered species

Researcher Philip Muruthi believes the serval (Leptailurus serval) could be an ambassador for African grasslands. With the ability to jump up to 1.5 meters (5 feet) in the air, it helps control small mammal populations in its habitat. “Serval cat ecotourism is another possibility,” Muruthi says. “They can be hard to spot, but when you see one in the wild, you never forget it."
Image courtesy of Nancy Lewis/African Wildlife Foundation.

Like their big cat cousins, small cat species can have strong cultural ties to human communities. Anthony Gerardo Pino Charaja of the Andean Cat Alliance explains that in countries like Peru, the Andean cat was long closely linked spiritually to the protection of livestock such as alpacas and llamas and was also designated as a deity of water.
Image courtesy of Andean Cat Alliance.

Clouded leopards prey upon a range of species including wild pigs and ungulates, helping control forest populations.
Image by Charlie Marshall via Flickr (CC BY 2.0).
#charlie marshall#photographer#flickr#cats#scottish wildcat#mammal#animal#wildlife#scottish rewilding allance#nancy lewis#african wildlife foundation#leptailurus serval#servals#andean cat alliance#andean cat#clouded leopard
117 notes
·
View notes