#generalist mammals
Text
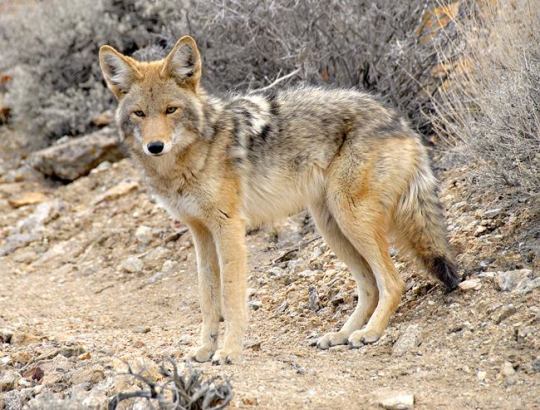




Close Up with Coyotes
Often confused with wolves, foxes, or even stray dogs, the coyote (Canis latrans) is a species of canid found only in Central and North America, from Panama to central Canada. Historically, the coyote mainly occupied grasslands, scrubland, and deserts; however, in the past few centuries the species has expanded its range to include deciduous and evergreen forests, mountains, swamps, and even cities. Generally individuals and groups keep to one home territory, but they will move when resources become lacking.
Among the canines, coyotes are rather small, weighing only 8 to 20 kg (18 to 44 lb), and males tend to be larger than females. Generally coyotes sport a light gray, red, or brownish coat with a lighter underside; however, regional populations may differ wildly. This species may be identified from other canids by its large pointed ears, whitish facial markings, and narrow snout.
Though C. latrans does occasionally form packs, it is more likely to hunt individually or in small family groups. Nonfamily packs, usually made of bachelors, are rare. In addition, coyotes have been known to form mutualistic hunting relationships with other species like badgers. It is primarily carnivorous, hunting mainly at dawn and dusk for rabbits and hares, squirrels, mice, lizards, and occasionally larger targets such as deer or pronghorn. This species will also readily consume carrion, as well as produce and human food waste, making it highly adaptable to urban areas. Traditionally, the species has been limited via both competition and direct predation by wolves and cougars; in its expanded range, coyotes may also be predated upon by bears, alligators, lynx, and golden eagles.
Though reproduction typically takes place in the spring, from January to March, temporary pair bonds may form as early as November. Mates prepare dens, which may be dug out or selected from tree hollows or pre-existing burrows, and establishes a territory up to 19 square km (11 square miles). During this time, daughters from a females previous litter, or her sisters, may join the group. Pregnancy typically lasts just over 60 days, during which time the male and any assisting females do most of the hunting. Litters average 6 pups, and weaning takes about a month. During this time, the male continues to provide for the mother and pups, but will abandon the den if the mother goes missing. By the age of four or five weeks the pups develop a hierarchy through play-fighting. After about 6 months, the male pups will leave, while females will typically stay with their mothers until at least the next mating season, at which time they reach sexual maturity. In the wild, individuals may live as long as 10 years.
Conservation status: Due to its large range and adaptability to human habitats, the C. latrans is considered Least Concern by the IUCN. In urban areas, coyotes are regularly hunted as a nuisance species due to their predation on free-roaming pets and, occasionally, livestock.
In traditional Indigenous American stories, the coyote was seen as a trickster or anti-hero (here is an interesting paper about the 'Coyote' character in traditional stories versus western interpretations). The European colonization of North America and the eradication of large predators like wolves and cougars has allowed coyotes to spread far beyond their original geographic range and become a 'nuisance species' in urban areas.
If you like what I do, consider leaving a tip or buying me a ko-fi!
Photos
Neil Nurmi
Carlos Porrata
Natrice Miller
Tom Koerner
#coyote#Carnivora#Canidae#canines#canids#carnivores#mammals#generalist fauna#generalist mammals#grasslands#grassland mammals#scrubland#scrubland mammals#deserts#desert mammals#north america
169 notes
·
View notes
Photo
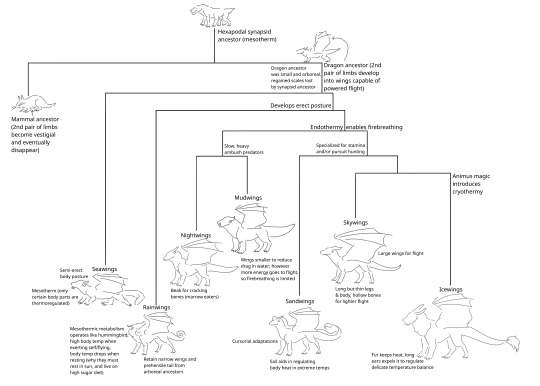
dragon family tree. cladograms my beloved
#its not really realistic that a clade of non-generalist animals would diversify this much#and its definitely not realistic that theyd be able to hybridize#but hey. its dragons!#icewings are so so so fucked up tho there's no way to make them real animals#and ig in this world vertebrates are hexapodal originally instead of tetrapods#i like the idea of dragons being descended from non-mammal synapsids though. not reptiles but not mammals either! theyre their own thing#i also like the idea of nightwings being marrow eaters/scavengers and stopping bc it becomes impolite/gross in their culture#but then on the volcano they go back to it by necessity and it works for them#ALSO. if theres anything confusing here dont be afraid to send an ask i would love to explain my processes#wof#wings of fire#worldbuilding#wof worldbuilding#speculative biology#my art
229 notes
·
View notes
Text

hello it is wip wednesday my dudes. i am always a huge fan of humans being the Scary Weird Monsters of different worlds and Sasha would especially have a pretty mean reputation preceding her i think.
#amphibia is a death world but humans are the worlds most xtreme generalists and also mammals in a place where mammals are very rare#amphibia#marball au#also hey remember brian? the ex accountant from the Mauraders? i’m so glad i don’t need to make a throwaway oc for outsider pov lmao#he is my current victim of ‘throwing sasha with violent intent at people’#writing action/fight stuff simply makes me sane <3 like getting zoomies out
67 notes
·
View notes
Text
Selected recurrent patterns or "laws" of evolution, of potential use for speculative biology. List compiled by Neocene's Pavel Volkov, who in turn credits its content to Nikolay Rejmers (original presumably in Russian). These are guidelines, and not necessarily scientifically rigorous.
Dollo's Law, or irreversibility of evolution: organisms do not evolve back into their own ancestors. When mammals returned to the sea, they did not develop gills and dermal scales and change back into fish: they became whales or seals or manatees, who retain mammalian traits and show marks of land-dwelling ancestry.
Roulliet's law, or increase of complexity: both organisms and ecosystems tend to become more complex over time, with subparts that are increasingly differentiated and integrated. This one is dodgier: there are many examples of simplification over time when it is selected for, for example in parasites. At least, over very large time scales, the maximum achievable complexity seems to increase.
Law of unlimited change: there is no point at which a species or system is complete and has finished evolving. Stasis only occurs when there is strong selective pressure in favor of it, and organism can always adapt to chaging conditions if they are not beyond the limits of survival.
Law of pre-adaptation or exaptation: new structures do not appear ex novo. When a new organ or behavior is developed, it is a modification or a re-purposing of something that already existed. Bone tissue probably evolved as reserves of energy before it was suitable to build an internal skeleton from, and feathers most likely evolved for thermal isolation and display before they were refined enough for flight.
Law of increasing variety: diversity at all levels tends to increase over time. While some forms originate from hybridization, most importantly the Eukaryotic cells, generally one ancestor species tends to leave many descendants, if it has any at all.
Law of Severtsov or of Eldredge-Gould or of punctuated equilibrium: while evolution is always slow from the human standpoint, there are moments of relatively rapid change and diversification when some especily fertile innovation appears (e.g. eyes and shells in the Cambrian), or new environments become inhabitable (e.g. continental surface in the Devonian), or disaster clears out space (e.g. at the end of the Permian or Cretaceous), followed by relative stability once all low-hanging fruit has been picked.
Law of environmental conformity: changes in the structure and functions of organisms follow the features or their environment, but the specifics of those changes depend on the structural and developmental constraints of the organisms. Squids and dolphins both have spindle-shaped bodies because physics make it necessary to move quickly through water, but water is broken by the anterior end of the skull in dolphins and by the posterior end of the mantle in squids. Superficial similarity is due to shared environment, deep structural similarity to shared ancestry.
Cope's and Marsh's laws: the most highly specialized members of a group (which often includes the physically largest) tend to go extinct first when conditions change. It is the generalist, least specialized members that usually survive and give rise to the next generations of specialists.
Deperet's law of increasing specialization: once a lineage has started to specialize for a particular niche, lifestyle, or resource, it will keep specializing in the same direction, as any deviation would be outcompeted by the rest. In contrast, their generalist ancestors can survive with a marginal presence in multiple niches.
Osborn's law, or adaptive radiation: as the previous takes place, different lines of descent from a common ancestor become increasingly different in form and specializations.
Shmalhausen's law, or increasing integration: over time, complex systems also tend to become increasingly integrated, with components (e.g. organs of an organism, or species in a symbiotic relationship) being increasingly indispensable to the whole, and increasingly tightly controlled.
202 notes
·
View notes
Text

Neolicaphrium recens here might look like some sort of early horse, but this little mammal was actually something else entirely.
Known from southern South America during the late Pleistocene to early Holocene, between about 1 million and 11,000 years ago, Neolicaphrium was the last known member of the proterotheriids, a group of South American native ungulates that were only very distantly related to horses, tapirs, and rhinos. Instead these animals evolved their remarkably horse-like body plan completely independently, adapting for high-speed running with a single weight-bearing hoof on each foot.
Neolicaphrium was a mid-sized proterotheriid, standing around 45cm tall at the shoulder (~1'6"), and unlike some of its more specialized relatives it still had two small vestigial toes on each foot along with its main hoof. Tooth microwear studies suggest it had a browsing diet, mainly feeding on soft leaves, stems, and buds in its savannah woodland habitat.
It was one of the few South American native ungulates to survive through the Great American Biotic Interchange, when the formation of the Isthmus of Panama allowed North and South American animals to disperse into each other's native ranges. While many of its relatives had already gone extinct in the wake of the massive ecological changes this caused, Neolicaphrium seems to have been enough of a generalist to hold on, living alongside a fairly modern-looking selection of northern immigrant mammals such as deer, peccaries, tapirs, foxes, jaguars… and also actual horses.
Some of the earliest human inhabitants of South America would have seen Neolicaphirum alive before its extinction. We don't know whether they had any direct impact on its disappearance – but since the horses it lived alongside were hunted by humans and also went extinct, it's possible that a combination of shifting climate and hunting pressure pushed the last of the little not-horses over the edge, too.
———
NixIllustration.com | Tumblr | Twitter | Patreon
#science illustration#paleontology#paleoart#palaeoblr#neolicaphrium#proterotheriidae#litopterna#meridiungulata#south american native ungulates#panperissodactyla#ungulate#mammal#art#convergent evolution#not-horse#a phony pony#quaternary extinction
478 notes
·
View notes
Note
my mom recently read in a novel that some larger praying mantis species have been known to kill and eat hummingbirds. I know about bird-eating tarantulas, but I was curious if you knew of other insects who prey on birds, mammals, etc.? I know most will scavenge anything, but what abt critters who hunt? the idea of insects who hunt large prey is fascinating to me
large generalist predatory insects like mantises and katydids predominantly eat other insects, but the majority of the vertebrate prey they take is probably frogs and lizards, and typically ones smaller than themselves. hummingbirds might not be too representative of typical vertebrate prey because (I believe I heard a mantis researcher say) their metabolism is so tightly wound that the stress of being caught is enough to kill them, and all the mantis has to do is hang on, which they definitely can do. still, vertebrate predation is pretty impressive for orthopterans and mantodeans, since they’ve got to do it all without venom!
army ants of various types are also famous for their ability to catch vertebrates, but most army ants are actually specialists on other social insects (ants, wasps, termites), and the few generalist predator army ants still predominantly prey on invertebrates (and don’t skeletonize cows and horses like they do in cartoons).
diving beetles will hunt fish and aquatic amphibians—there’s a reason their larvae are called “water tigers!” belostomatid water bugs are probably the most impressive aquatic vertebrate-eaters though, and use powerful venom to subdue surprisingly large fish, tadpoles, and even other vertebrates:
outside of insects, there’s a lot of spiders that can feed on herptiles, either by overpowering them with strength like huntsmen and tarantulas, or by snaring them in webs like widows, the most successful snake eaters:
plus, there’s always the famous Nephila orbweavers whose sturdy webs can catch avian prey, but this is probably a fairly rare occurrence.
going over to centipedes, giant scolopendrids are quite successful predators of vertebrates, with any species large enough likely preying on herptiles, and occasionally on some far larger than they are!
Scolopendra venom is evolved to take down large prey, so it’s no surprise they’re some of the most prolific vertebrate-eaters in the arthropod world. some very large Scolopendra (gigantea, maybe galapagoensis, viridicornis, heros) will hunt bats, sometimes by hanging to catch them in flight. other predation on mammals and birds seems to occur opportunistically, especially where the prey is helpless: S. galapagoensis was recorded feeding on baby rodents in the Galapagos; other island species like Cormocephalus coynei will feed on seabird chicks (enough with the “fluffy” avian favoritism, Nature! ‘pedes gotta eat).
oh, speaking of nestling-devouring, there’s also some freaky observations of slugs munching on soft mushy songbird babies! someone on Twitter had their nest camera record some chicks getting eaten by a large Carabus ground beetle, but I can’t find it again.
but I think the most shocking example of vertebrate predation by an invertebrate is probably Epomis, another ground beetle. as larvae, they feed on frogs far larger than they are by letting themselves get attacked, latching onto the would-be predator, and munching on it until it perishes. adult beetles also prey on amphibians, but just run them down instead of luring prey.
youtube
(there’s also video of the adult beetles preying on frogs, but they seem to all be stolen by some weird content scraper YT channels, so I’ll not post them here.)
let me know if I missed any good examples of vertebrate predation by bugs!
308 notes
·
View notes
Text

Survival of the newest: The mammals that survive mass extinctions aren't as 'boring' as scientists thought
via: Field Museum
When an asteroid hit the Earth 66 million years ago, it set off a devastating mass extinction. The dinosaurs (except for a few birds) all died out, along with lots of the mammals. But some small mammals survived, laying the groundwork for all the mammals alive today.
For decades, scientists have assumed that mammals and their relatives that survived challenging times (like those during mass extinctions) made it because they were generalists that were able to eat just about anything and adapt to whatever life threw at them.
A new study into the mammal family tree through multiple mass extinctions revealed that the species that survived aren't as generic as scientists had thought: instead, having new and different traits can be the key to succeeding in the aftermath of a catastrophe...
Read more: https://phys.org/news/2023-10-survival-mammals-survive-mass-extinctions.html
#extinction#extinction events#catastrophes#evolution#mammal#mammals#mammal evolution#prehistoric#fossils#nature#science
71 notes
·
View notes
Text
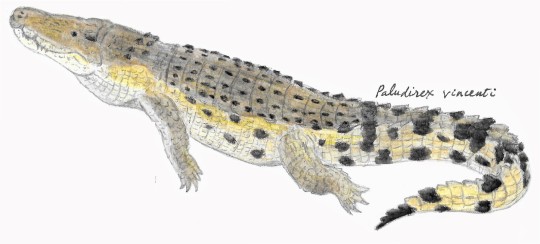
Paludirex: Life of the Swamp King
Having gotten the long taxonomic history of Pallimnarchus and Paludirex out of the way (see here), lets talk more about the animal itself.
As far as we know at this point in time, Paludirex was the last of the large semi-aquatic mekosuchines and the largest members of this group had ever gotten. Whereas the cleaver-headed Baru dominated the waterways of the Oligocene and Miocene, Paludirex lived from the Pliocene and Pleistocene. There is some division between the species tho as it appears. Given the ambiguity around the origin of some Paludirex vincenti specimens, this species is currently only known from the Pliocene, whereas Paludirex gracilis is currently only known from the Pleistocene. There may also be a third species from the same region as Paludirex vincenti.
Comparisson between Paludirex gracilis (left) and Paludirex vincenti (right)

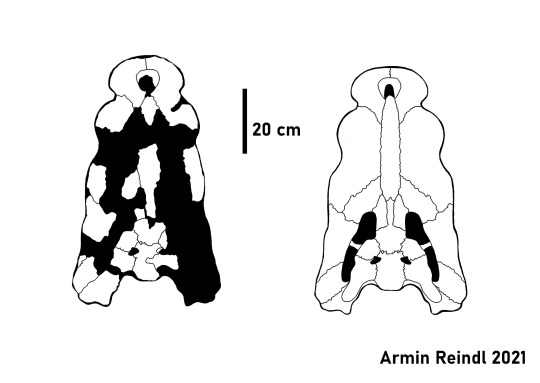
Anatomically, Paludirex has a pretty easily recognizable animal. Unlike Baru, with its short, triangular skull, Paludirex had a head that was almost rectangular when viewed from above, about half as wide as long and comparably flat. Mind you the skull can still be pretty deep, especially in Paludirex vincenti, but the proportions still highlight how wide it is most of all. In both robustness and skull width, Paludirex far exceeds what is known in modern saltwater crocodiles, which likely fill a similar niche.
Left: Skull reconstruction of Paludirex vincenti.
Right: Life reconstruction of Paludirex (Nellie Pease)

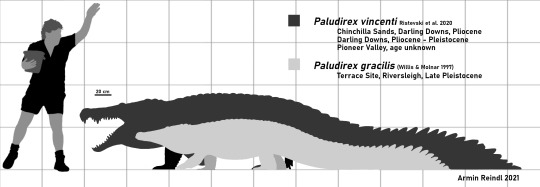
As said before, Paludirex represents the biggest mekosuchine. At a minimum length of 4 meters, it already rivals many of today's crocodiles and Baru, and that's just the smaller ones. Large individuals of Paludirex vincenti probably got much larger, 5 meters and more further drawing parallels to todays salties.
A size comparisson between Steve Irwin and both species of Paludirex
Now while the description is pretty sound on account of recent work by Ristevski and co., the ecology is a different matter. A lot of work was published back when Pallimnarchus was still a thing, so trying to separate what and what isn't applicable these days is a bit of a challenge.
On the most simple level, Paludirex was a generalist semi-aquatic ambush hunter. It's skull, tho incredibly robust and wide, shows no peculiar adaptations like long slender jaws so its obviously not a specialist. It's semi-aquatic because the nostrils and eyes face up so that they would peer out from the water while the rest of the body remained submerged. And these last two together basically suggest ambush-hunting.
Willis and Molnar also made comparissons between Paludirex skulls (or rather skulls now recognized as such) and Mugger crocodiles. All in all this suggests that its diet could have ranged from turtles to aquatic birds to large mammals (so the typical croc range really). They also infer that it may have had similar habitat preferences, being found in marshes, swamps, rivers, lakes, anywhere theres freshwater really. One exception may be that some researchers have argued that Paludirex was avoiding saltwater and brackish water, which eventually could have factored into its extinction once inland waterways in Queensland dissappeared.
Top: Eastern Sahul megafauna, the foreground features Paludirex about to ambush a giant kangaroo (Ryan Bargiel, Vlad Konstantinov, Andrey Atuchin & Scott Hocknull)
Bottom left: Paludirex vincenti (Diego Ortega Anatol)
Bottom right: An unforunate Paludirex being attacked by a marsupial lion (Joschua Knüppe)


As with many crocs, its pretty likely that individuals were hostile towards each other at certain times, perhaps during territorial disputes or in the mating season. Now this one's a bit of a more ambiguous one regarding the assignment of the fossils. Fossils of leg material show clear bite marks, HOWEVER, the fossils were assigned to Pallimnarchus purely on the basis that they don't appear to have belonged to a terrestrial animal (as often inferred for Quinkana) nor to a modern croc. Based on this, the material was assumed to have been that of Pallimnarchus without much else to back it up. Now that Pallimnarchus is no more, it is reasonable to assume that it may be Paludirex but then again, it could also be an entirely different animal. Only way to tell would be to find Paludirex fossils with leg fossils attached.
This does bring up the interesting discussion, what crocs did coexist with Paludirex? Well there's a couple. As just mentioned, there's Quinkana, which I'll research more in depth later, but for now it's commonly assumed to be more terrestrial than other mekosuchines. There's the Darling Downs form, which lived around the same time as Paludirex vincenti in Queensland and may be a third species of this taxon. Gunggamarandu is another animal from this region, tho much as with Paludirex its not entirely clear if its Pliocene or Pleistocene. More certain is the fact that during the Pleiostocene, Paludirex gracilis coexisted with freshwater crocodiles in the Riversleigh WHA. Finally, there's indetermined species of crocodiles that date as far back as the Pliocene. Historically, they've been regarded as salties, but more recently it's though that they were a different species entirely and that salties only moved in recently, possibly after Paludirex went extinct and the niche of large semi-aquatic predator was free.
Top left: Quinkana faces off against Megalania (Hodari Nundu)
Top right: A freshwater crocodile running (Brandon Sideleau)
Bottom: Gunggamarandu, a relative of today's gharials (Eleanor Pease)



By this point I've basically already given away the reason why Paludirex is no more. With mekosuchines already taking a massive hit during the late Miocene, the group was not at its peak when Paludirex came around. And things were not getting any better as Australia grew more and more arid, river systems disappearing, freshwater drying up and the habitat of these animals shrinking bit by bit. Paludirex, presumably staying clear of coastal waters, was hit hard by these events and eventually it was just too much. And once it was out, saltwater crocodiles moved in, leading into the modern day.
#paludirex#pallimnarchus#palaeoblr#pliocene#pleistocene#australia#paleontology#prehistory#crocodile#croc#crocodilia#mekosuchinae#gunggamarandu#paludirex vincenti#paludirex gracilis#quinkana
117 notes
·
View notes
Text
Moth of the Week
Garden Tiger Moth
Arctia caja

The garden tiger moth or great tiger moth is a moth of the family Erebidae. They were first described in 1758 by Charles Linnaeus. The caterpillars are known as “woolly bears.”
Description The forewings of this moth are brown with white patterning. This white pattern can be missing entirely. The hindwings are orange with black dots which also may vary from moth to moth due to chance and artificial reasons. French entomologist Charles Oberthür discovered about 500 different variation in patterns.
The patterns on the moth’s wings warn predators that they are toxic. The toxin in this species in part contains neurotoxic choline esters which interfere with the acetylcholine receptor.
The head is lined with red over dark brown and has white antennae while the thorax is a matching dark brown. The abdomen matches the hindwings with bright orange fur and black stripes.
Wingspan Range: 45 - 65 mm (1.8 to 2.6 in)
Diet and Habitat This species are called generalists, meaning they eat a wide variety of plants. That are known to eat plants in the Digitalis and Plantago genuses. These plants produce pyrrolizidine alkaloids, a common chemical that causes toxicity in moths. Adult moths eat nectar from flowers and have no observed preference.
They range from the northern United States and Canada to Europe and Northern and Central Asia. In Europe, it goes north until Lapland. They prefer cold, temperate climates and are found in the mountains of Tien Shan (up to an elevation of 3,000 m (9,800 ft)), grasslands, sand dunes, meadows, woodland edges, hedgerows, gardens, and forests. Because this species are generalists in diet, they are not confined to one habitat due to host plant locations.
Mating Females lay around 50 eggs on the underside of host plant leaves. Eggs hatch from August to September when the former generation has died. It has been observed that generations do not overlap.
Predators Adult moths use their wing patterns and colors to warn predators that they are inedible. Their diet allows them to gain toxins including neurotoxic choline esters which interfere with the acetylcholine receptor. The full effects of the toxins are not known. The adults are mostly preyed on by birds and bats. Another way the adults protect themselves from bats is to make noise with their wings which interferes with the bats’ behaviors.
However, several species of endoparasitic flies prey on the species as larva. These include: Carcelia gnava, Carcelia lucorum, Carcelia tibialis, Compsilura concinnata, Exorista fasciatax Exorista grandis, Hubneria affinis, Pales pavida, Thelaira leucozona, Thelaira nigripes, and Thelymorpha marmorata.
The larvas’ defense against outside forces is stinging hairs that cause hives and irritation in mammals, including humans. These hairs are not fatal.
Fun Fact The garden tiger moth has been a protected species since 2007 by the Biodiversity Action Plan in the United Kingdom.
(Source: Wikipedia, Butterfly Conservation, Moth Identification)
#libraryofmoths#animals#bugs#facts#insects#moth#mothoftheweek#lepidoptera#Erebidae#garden tiger moth#great tiger moth#Arctia caja
141 notes
·
View notes
Text
Two of the biggest islands on our planet have had their fair share of challenges during their transition from the Anthropocene to the Anectyocene, dealing with extinctions, invasive species and loss of diversity.

One of them, New Zealand, at our time ravaged by invasive cats, stoats, deers and mice, has now managed to go through it. While now having a much more mammal-heavy biota, with the invasive species having adapted similar forms to their continental relatives, the birds were still able to remain important players in these ecosystems, both as small generalists and scavengers, like the ever present kiwis, and as large specialists, like the Southern Rakaumanu, the biggest land animal on the island, that roams the inland and eastern grasslands of South Island.

The other island, Madagascar, suffered much less the damages of the invasive fauna, with only lemurs suffering the heaviest losses. Currently the invasive cats and dogs have been able to only take over similar niches to their Holocene ones, remaining small tree hunters and medium-sized pack hunters and scavengers. The abscence of a bigger tree dwelling hunter allowed the fossa to not lose its niche and get outcompeted, but it won’t be able to become the true Malagasy apex predator as crocodiles would get there first.
Lemurs will reclaim much of their former diversity, even adapting similar forms to the African and South American simians, with land dwelling browsers and semi-terrestrial almost baboon-like generalists. The largest herbivores there, tho, would become geese and ducks, that would become flightless and the most prolific herbivores on the island.
#speculative evolution#speculative biology#spec evo#spec bio#worldbuilding#artwork#digital art#epigene period#future earth
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
Round 3, Poll 13
Wedge-tailed Eagle vs Short-tailed Pygmy-tyrant


sources under cut
Wedge-tailed Eagle
“they’re friggin’ huge, they can have a wingspan of over 9 feet, I’m always just completely in awe when I see them. also, great legs.”
As a true generalist, anything is on the menu for this eagle. They seem to prefer mammals, especially the invasive European rabbit, but will also hunt native marsupials, including larger macropods (kangaroo). Because of this wide diet they’ve got a range that encompasses all of Australia and Tasmania.
Wedge-tailed Eagle have been noted to attack hang gliders and paragliders, though they are mostly targeting the sail itself and not the human. They’ve also been known to attack unmanned aerial vehicles used for survey operations. This is likely territorial defense, with the eagles mistaking these objects as another eagle.
Short-tailed Pygmy-tyrant
“small. hilarious name-bird combo”
“the smallest bird in the world after several species of hummingbirds. Naming this beast a "tyrant” is the funniest thing ever. Also I’m tail-shaming it" (for reference: tyrant refers to the family this bird belongs to- tyrant flycatchers, which are named after kingbirds)
“Although its plumage is similar to some other tyrant flycatchers, in the field the bird is more often mistaken for a large beetle or insect, especially while in flight… Its flight movements have a mechanical-feel that enhances the insect comparison.” - Wiki
Images: Eagle (Luke Shelley); Flycatcher (Anselmo d'Affonseca)
#hipster bird main bracket#round 3#quarterfinals#bird poll#animal poll#Wedge-tailed Eagle#Short-tailed Pygmy-tyrant
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
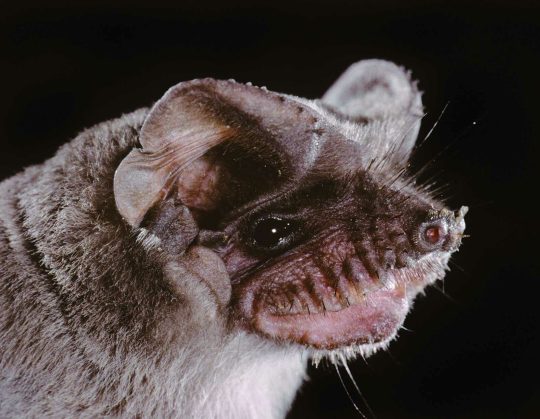



Fly Free with the Mexican Free-tailed Bat
Also known as the Brazilian free-tailed bat, guano bat, or Tadarida brasiliensis, this member of the order Chiroptera is one of the most widely-distributed New World bat species. They are common throughout the southern United States, Central America, and western South America. In many parts of the southern United States, the species is migratory and moves to Central America for the winter. They roost primarily in caves, but can also build nests in buildings; because of this, they can be found in a range of habitats including tropical and deciduous forests, mountains, deserts, and urban areas.
Like most bats, the Mexican free-tailed bat is nocturnal, emerging at sunset to hunt. They are primarily insectivores, and will travel great over 31 km (50 mi) to find food. In fact, this species holds the record for both the highest recorded flight altitude-- at 3.3 km (2 mi) high-- and the fastest flight speed-- an astounding 160 kph (99.4 mph)! That makes the Brazilian free-tailed bat the fastest mammal on Earth, although they can only achieve those top speeds in short bursts and with a good tail wind. Moving that fast can be useful, not only for covering great distances or catching insects, but for avoiding predators like raptors and owls. Young bats that can't fly may also be susceptible to opossums, skunks, and snakes.
The roosts of T. brasiliensis can be quite large; many contain several thousand individuals, while some have been recorded as housing more than a million. For this reason, communication is very important. Mexican free-tailed bats use echolocation to navigate and, for mothers, to locate their young. This species has over 15 distinct calls just for socialization. In addition, they can use their vocalizations to 'jam' the echolocation of other rival species and steal their prey.
Mating for the Brazilian free-tailed bat occurs once a year in the spring. Females gather in large maternity groups, while males mark out a territory by urinating and emitting loud vocalizations. Once a pair mates, the two separate- often to seek out another partner. Gestation lasts 11-12 weeks, and once females give birth they leave their offspring in a group of pups known as a creche, that is cared for communally. The pups take 4-7 weeks to be weaned, and after they learn to fly they join the larger roost as independent adults. However, females take up to 9 months to become sexually mature, while males may take as long as 2 years. In the wild, an individual may live as long as 8 years.
Size-wise, T. brasiliensis is on the smaller side of the bat group. Most individuals are around 9 cm (3.5 in) in length and weigh around 7–12 g (0.25–0.42 oz), with a wingspan of 28 cm (11 in). Females tend to be slightly heavier, but not larger otherwise. The tail of the Mexican free-tailed bat accounts for nearly half its total body length, and is unconnected by the thin membrane that makes up its wings (the uropatagium)-- hence the name 'free-tailed'. The ears are large and rounded, to assist with echolocation, and the muzzle is heavily wrinkled to give them a wider gape when catching bugs in mid-air. The Brazilian free-tailed bat's fur is dark brown or gray, with no distinguishing features save the long, white bristles around their feet.
Conservation status: The IUCN has classified the Mexican free-tailed bat as Near Threatened. However, populations are declining due to habitat destruction and susceptibility to a fungus known as white nose syndrome. Governments in the southern United States and Mexico, as well as private NGOs like Bat Conservation International, have established laws and conservation areas to protect the species.
If you like what I do, consider leaving a tip or buying me a kofi!
Photos
Michael Durham
Merlin D. Tuttle
Carlos Russi
#mexican free-tailed bat#Chiroptera#Molossidae#free-tailed bats#bats#mammals#generalist mammals#tropical forest mammals#deciduous forest mammals#wetland mammals#desert mammals#north america#southern north america#central america#south america#western south america
118 notes
·
View notes
Text
Asteriornis vs Panraogallus
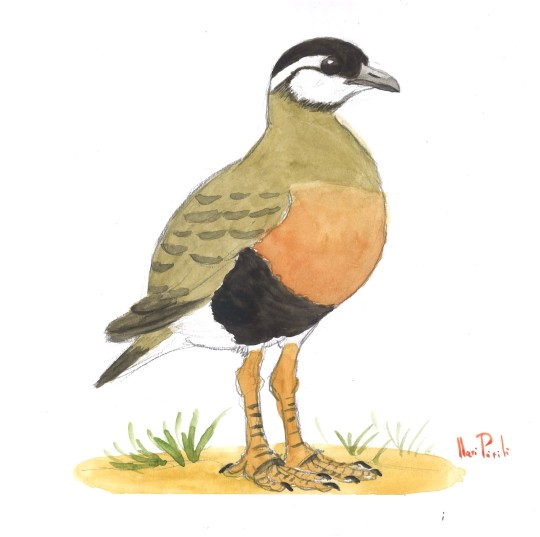


Factfiles:
Asteriornis maastrichtensis

Artwork by @otussketching, written by @zygodactylus
Name Meaning: Asteria’s Maastrichtian Bird
Time: 66.8 million years ago (Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous_
Location: Maastricht Formation, Eben-Emael, Belgium
Say hello to the Wonderchicken! While we know that modern dinosaurs - birds - had to have evolved in the Mesozoic, and diversified somewhat during it, actual fossil representatives of Mesozoic modern birds are quite rare, with only a few duck-related taxa (Vegavis and Teviornis) known. Asteriornis finally adds a stem-chicken to that group, which we knew had to have been around since we had stem-ducks! (They diverged at the same time, so the presence of stem-ducks requires the presence of stem-chickens). A small, long-legged bird, Asteriornis had a lot of characteristics similar to both chickens and ducks, indicating it may have evolved right after that initial divergence. It had a slightly down-curved beak without specializations, allowing it to have a generalist diet. It had wings similar to living ground birds, and that combined with its long legs indicates a terrestrial lifestyle. Living along the coast, Asteriornis would have eaten whatever it could forage for, possibly wading into the water or trekking through high vegetation when necessary. It lived near the ocean, along the coast, and as such it shared its habitat with many types of invertebrates, including corals and echinoderms and crustaceans, as well as ammonites. Surrounded by grasses, palms, and shrubs, Asteriornis also lived alongside other vertebrates such as a wide variety of sharks, tons of mosasaurs, turtles, elasmosaurs, marsupials, and other dinosaurs such as Orthomerus, Janavis, large theropods, an unknown opposite-bird, and other potential Ornithurans.
Panraogallus hezhengensis

Artwork by @otussketching, written by @zygodactylus
Name Meaning: Coiled Chicken from Hezheng
Time: 7.25 to 11.1 million years old (Tortonian stage of the Miocene epoch, Neogene period)
Location: Liushu Formation, Gansu Province, China
Panraogallus was a weird early chicken that differed from others by one notable feature: a very long neck, much longer than other pheasants. This is only seen in a handful of related birds today. Panraogallus seemed to follow the zigzag pattern present in some grouse rather than a loop like that seen in a cracid or guineafowl. This gave it a low, loud call, distinct from those of other pheasants. It was quite large, around 2.5 kilograms on average. The calls of these species, which would have traveled extremely long distances in its habitat, were probably used in communication - to attract mates, warn of danger, and gather flocks. In the temperate savannah habitat, Panraogallus would have been able to reach each other over large distances, very easily coverable in single days of walking in such an open area. Other birds in the area included the diurnal hawk-owl Miosurnia, kestrels, old world vultures, ostriches, sandgrouse, and the weird Ergilornithids. Mammal neighbors included Gomphotherium, Chilotherium, Chalicotheres, weird horses, bizarre giraffids, and giant hyena mimics.
DMM Round One Masterpost
#dmm#dinosaur march madness#dinosaurs#dmm round one#dmm rising stars#palaeoblr#paleontology#bracket#march madness#polls#asteriornis#panraogallus
95 notes
·
View notes
Text
Weretober 2022: The Great Werebeast Clades


Set in the same world as my Merfolk pieces, for this October, my theme is basically biology inspired Werebeasts. These are the dominant people of the land, and can be divided in into five major clades:
Were-Mammals: The generalists of the setting, basically the equivalent of humans in other fantasy setting. The dominant clade of Beast Fables.
Were-Reptiles: The pragmatic and patient people of the setting (usually). They seem sluggish, but when they need to, they can do what they’re assigned to with great gusto.
Were-Amphibians: Loud and extroverted, were-amphibians like to give a big show and talk themselves up... but you gotta be honest about those achievements.
Were-Birds: A people of song, dance, arts and culture... and violence. Lots of it. After all, combat can be considered a form of art, no?
Were-Arthropods: A peoples that few themselves in how much they can contribute as part of a whole collective, so they tend to be VERY specific in their roles.
#weretober#weretober 2022#beast fables#werebeast#reptiles#amphibians#mammals#arthropods#birds#tazmanian devil#shrike#rattlesnake#creature design#character design#nazrigart#my art
215 notes
·
View notes
Note
Oooo now you’re really getting me into Clanmew. What are the names for birds and bird species in Clanmew?
The simple word for "Bird" evolved from Old Tribemew, at the Dawn of the Clans. A "Bird" is any two-winged flying animal with bones.
Bird (and bats) = Hafefyl
The major types of birds that the Clan cats recognize are as follows;
Raptor = Yassga
A large, dangerous bird. Any avian perceived to pose a threat is in this category, including swans, ravens, and herons. Not just birds of prey.
Fowl = Eyawoon
Large prey birds, the same level of danger as any other large quarry. Ducks, pheasants, gulls, cormorants, a chicken or peacock would also be in this category.
Game = Biyaw
These are the birds that are eaten regularly, without much other consideration. It's where most of the 'odd' birds that don't fit other categories go. Pigeons, sparrows, quails.
Fancy = Pyrrya
Any bird that would be a shameful thing to kill. That usually means songbirds with pleasing songs, but also colorful ones with pleasing patterns and behaviors, and even bats as they bring sickness when eaten.
Examples of "Yassga";
Golden Eagle (Aquila chrysaetos) = Nyieu
A species only encountered in the Tribe mountain, before re-contact it was considered a legendary animal. The most dangerous flying species, capable of attacking small deer.
Sparrow Hawk (Accipiter nisus) = Yi'i
When hawks are being noted for their speed, it's this species. They primarily hunt other birds, but not cats.
Red Kite (Milvus milvus) = Eeao
This is the species that is both large and bold enough to take kittens. The vast majority of the time when hawks are mentioned in a dangerous context, it is a kite. Goshawks are not as numerous in this area as canon implies.
Kestrel (Falco tinnunculus) = Ipip
Acrobatic, agile bird able to seemingly 'hover' in the air.
Marsh Harrier (Circus aeruginosus) = Yeepi
Skilled attentive hunters that tend to hunt small mammals in open areas, especially wetlands. RiverClan and ShadowClan see these a lot.
Merlin (Falco columbarius) = Mweelili
A small, generalist hunter that likes low-density areas like moorland, sparse woods, and brush. Known for being friendly with Harriers and eating just about anything.
Osprey (Pandion haliaetus) = Pyip
Not actually a dangerous species; but the perception of danger will make Clan cats avoid this creature. Most commonly found by the sea.
Swan (Cygnus olor) = Hchom
Large and quiet, these birds are so large they can drown a foolish warrior or break a bone.
Raven (Corvus corax) = Nyok
A raven is considered a very dangerous bird not only for its size and ferocious beak, but because of how vengeful an unkindness can be. They remember Clan cats and seemingly mess with them on purpose.
Gray Heron (Ardea cinerea) = Krekek
With their habit of spearing, bludgeoning, and even brutally drowning their prey, herons are feared and avoided. There are stories of herons picking off wayward kittens, but it's unknown if it's true or just a tale to stop them from wandering.
Eagle owl (Bubo bubo) = Huo
The biggest, largest, most dangerous owl. Cats are a desired prey. No other owl will attack an adult warrior, and eagle owls are most often found in ThunderClan territory where there's thick forest and a nearby rocky cliff.
Tawny owl (Strix aluco) = Hrrua'u
A loud, sonorous owl. Known best for being the species roosting in the old Owl Tree.
Barn owl (Tyto alba) = Weear
This owl does not hoot, it screeches.
Examples of "Eyawoon";
Duck (Anas platyrhynchos) = Kwek
There are several species of ducks they encounter occasionally-- but this one, the mallard duck, is the most common. ThunderClan liked to try and hunt them when they had Sunningrocks, sometimes inflaming tensions between clans.
Ring-necked Pheasant (Phasianus colchicus) = Rauqa
Named for the territorial cry of a male pheasant, the most impressive prize that a ThunderClan warrior can catch.
Black-headed Gull (Chroicocephalus ridibundus) = Rewp
Not just a seabird; found further in-land and will make do with just about any body of water. This is a species regularly found and hunted at Sanctuary Lake, and also the type that Gullswoop is named for.
Herring Gull (Larus argentatus) = Eeyar
The Clan cats haven't been doing salt patrols long enough yet to know that this is absolutely not an Eyawoon, but in fact, a Yassga. Sandwhich-stealing BASTARDS. They're the ones with the gray back, yellow beak, little red mark on the lip, and feral Grinch-looking eyes. If you live by the ocean you know. (There is another species that looks similar but Clan cats think they are the same animal)
Cormorant (Phalacrocorax carbo) = Waer
A large, black fishing bird that dives underwater to catch its prey. Revered by RiverClan.
Carrion crow (Corvus corone) = Rawk
This is the species being referred to when "crowfood" is mentioned. Rawkwoo.
Magpie (Pica pica) = Ke'ek
Glossy, beautiful blue, black, and white bird. Very intelligent and a difficult catch; like crows and ravens they are smart enough to have a concept of social learning.
Egret (Egretta garzetta) = Bwawa
Though they have many of the same 'brutal' behaviors as herons, they're too small to cause damage and hence are sorted into 'eyawoon'
There is currently no word for Chicken but Ravenpaw is probably using the term Barley likes best. Except the rooster which he immediately named "Urkaroona."
Examples of "Biyaw";
Wood Pigeon (Columba palumbus) = Huwoohoo
Big, fat, common, a popular meal bird.
Dove (Columba livia) = Hrru
Funfact: In TPB, there is a moment where Fireheart scolds Cloudpaw for calling a pigeon a 'dove.' In English, pigeons and doves are synonyms, but in Clanmew, Cloudtail had killed a Huwoohoo, but called it a Hrru.
Sparrow (Passer domesticus and Passer montanus) = Qee
Though there's a difference in plumage between these species, Clan cats think they are the same species because their songs are nearly identical. Passer montanus (Eurasian Tree Sparrow) is just considered what a sparrow looks like when it lives deep in the woods.
Quail (Coturnix coturnix) = Wipiwik
A round little ground bird that's very fast.
Jackdaw (Coloeus monedula) = Miaw
A black-and gray bird with a mewling call.
Song Thrush (Turdus philomelos) = Errari
This bird has many songs, which is taken by Clan cats as intentionally trying to hide its true name. They may even be changing their appearances to look like a Mistle Thrush; clearly they're something much more intelligent, since they use stones to smash open snail shells.
Mistle Thrush (Turdus viscivorus) = Charrech
Much larger than a Song Thrush. Brave, one of the few birds that sings even in terrible weather, but named for the angry sound it makes when it's guarding berry bushes in winter.
Fieldfare (Turdus pilaris) = Apapach
A very important winter prey bird which travels in large flocks. Bullied by Mistle Thrushes for good food sources.
Redwing (Turdus iliacus) = Eean
Similar to a fieldfare, but smaller and usually in tinier groups. The call is very different, so these birds are not usually confused by Clan cats unless they're seen first. Apapach are the preferred prey of the two.
Blackbird (Turdus merula) = Oohee
Males are blue-black with a yellow ring around the eye, and females are a ruddy dappled brown.
Eurasian jay (Garrulus glandarius) = Arkr
Loud, aggressive medium-sized birds. Pale with blue wings.
Examples of "Pyrrya"
Bat (4 SPECIES) = Fip
This refers to the sound of their wings mid-flight. No species of bat is consumed. If eaten they can bring horrible sickness, seen as a punishment for killing an holy night-loving animal with such a beautiful voice and great hunting skill. Clan cats are able to hear bat songs out of range of human hearing!
Pipistrelle (Pipistrellus pipistrellus) = Popep
A very small, common bat species that usually eats mosquitoes and midges in wet areas.
Soprano Pipistrelle (Pipistrellus pygmaeus) = Ipi'ip
Humans can barely tell the difference between these two, but Clan cats recognize that the song of a Soprano is much faster, higher-pitched, and absolutely sonorous. Considered the night version of a wren and held in high esteem.
Long-eared Brown Bat (Plecotus auritus) = Fepfr
A very quiet, low-flying bat with a habit for doing some ground-hunting. This is usually the first bat that an apprentice sees instead of hears, and the one which is used to teach them to not hunt bats. It has a very modest song, which Clan cats explain as mourning for every bat accidentally killed and discarded. Rarely called the "Fip Hhass;" the Whisper Bat.
Noctule (Nyctalus noctula) = Shi'po
The largest bat, has huge teeth and a broad face. Females both migrate and hibernate, but males stay awake all year and sing with a very distinctive tune hard to put into a word.
Songbird (SEVERAL SPECIES) = Pigu
Note: Most songbirds are down here in this category, but some, like Song Thrushes, are only here conditionally. Usually if there's enough food to go around.
Wren (Troglodytes troglodytes) = Pi'ie
The song of this tiny bird is so fast and beautiful that Clan cats have a hard time putting it into words; these birds are not killed except by fiends and rogues.
Robin (Erithacus rubecula) = Birri
This is a small, gray-and-brown bird with a bright orange face. They're not very filling, pretty, and sing a delightful song, so like the other species in this category they aren't taken unless there's a serious need.
Woodcock (Scolopax rusticola) = Mweep
Though large and delicious, these birds are so enjoyed that killing them is dishonorable without approval. They're the only bird that can fly away with its young, it dances and puts on air shows as mating rituals, and they're quite rare.
There are more species than this found in the area but this should be more than enough for now. Here's the most significant "bird" species they experience on a regular basis!
68 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hello fellow synapsid! φ(゜▽゜*)♪
For an Easter joke, I was going to do a cartoon-esque illustration of Kollikodon. It's a Cenomanian (~99-96 MYA) monotreme with "bun like molars". There isn't much material, so I was going to go with a "well, if NO ONE ELSE was going to suggest this common ecological and phylogenetic attributes" approach.
Thing is, I haven't done an independent paleo reconstruction before, and all the material that's known is the right maxillary. Also, as committed to the joke as I am at this point, mammals aren't really my strongest of interest.
I'm worried that, since it's an obscure genus with few illustrations, my depiction might give people the wrong impression of what the animal was like... But I don't like being TOO conservative, especially when a gut feeling is telling me that certain approaches in speculation are viable, but unexplored.
Do you have any advice? Common mistakes, pitfalls I should avoid, how many pages a day should I speed read Witton's paleoartist's handbook, other folks to asks for advice? Things that'll help me be a better paleoartist.
I also know you don't specialise in paleoart, but since this is a case for a synapsid, you were the first person I thought of to ask for advice.
First step is starting with what we know. Thing with Kollikodon is that all we have is this:

It seems to be a stem-monotreme, decently close to the monotreme crown. Based on all other monotremes (including the extinct Kryoryctes and Steropodon), we can guess that its body was relatively stocky and short-limbed. It's outside the clade that we know had the beaks present in platypi and echidna, though we don't have enough to say for certain that it didn't have one. Should also be noted, though, that its teeth imply a different ecology from either of them. Its molars are bunodont (flat, quadrangular, multicusped), and bunodont molars are common in generalist omnivores (humans have somewhat bunodont molars), but the unusual morphology of Kollikodon's molars implies that it might have been doing more crushing than the average generalist.
The thing about something as fragmentary and enigmatic as this is that lots of speculation is necessary to portray it at all. But the flipside is, there are many ways to do it that aren't wrong. So a lot of it's up to you. If you want to avoid giving people the wrong impression of what it's like, then try to avoid features that are "out of left field" so to speak. Things that we don't see in monotremes or that we wouldn't expect in a generalist omnivore are less likely to be present in Kollikodon based on the data we have. For example, all known monotremes have relatively short limbs, and you don't necessarily need particularly long legs if you're a generalist, so it's safest to give it relatively short limbs. So keep in mind what it's related to and what life it was probably living, and have fun with it from there, is what I'd say.
And if you want some more paleoart-focused advice, there are a whole bunch of paleoartists on Tumblr! @i-draws-dinosaurs, @knuppitalism-with-ue, @aberrantologist, @ppaleoartistgallery, @alphynix, @dinodanicus, and @usik-paleo-illust are just a few, and you can find many more are in the #paleoart tag. I'm not an artist, so I recommend reaching out to some of them if you want some more experienced tips!
16 notes
·
View notes