#defensive medicine
Text
Put Republicans in power nationally and dystopian pregnancy care in "MAGA Mike" Johnson's Louisiana will become the norm from sea to shining sea. Republicans won't be happy unless there's a virtual MAGA overseer in every doctor's office.
In Louisiana, MAGA Republican state abortion restrictions are causing OB-GYNs to practice an extreme form of defensive medicine to avoid arrest.
(emphasis added)
In the wake of Louisiana's abortion ban, pregnant women have been given risky, unnecessary surgeries, denied swift treatment for miscarriages and ectopic pregnancies, and forced to wait until their life is at risk before getting an abortion, according to a new report first made available to NPR.
It found doctors are using extreme caution to avoid even the appearance of providing an abortion procedure.
"We were stunned by just how much regular medical practice for pregnant people has been disrupted," said Michele Heisler, the medical director of Physicians for Human Rights and one of the report's authors.
[ ... ]
In one of the most extreme examples of how pregnancy care has changed, doctors described cases of women who experienced preterm premature rupture of membranes (when the "water breaks" early in pregnancy, before the fetus is viable). Some of these women were forced to undergo Cesarean section surgeries to empty their uterus and avoid infection, instead of receiving an abortion procedure or medication.
"Which is ludicrous, absolutely ludicrous," said Freehill. "The least safe thing that we do, no matter if it's early in pregnancy or full-term at your due date, is a C-section."
[ ... ]
In what doctors described as another serious deviation from standard medical practice, OB-GYNs in Louisiana are now delaying routine prenatal care until patients reach 12 weeks of pregnancy — the point at which the risk of miscarriage drops significantly.
One patient interviewed in the report said several different doctors' offices wouldn't see her before 12 weeks.
[ ... ]
Physicians are also delaying treatment of miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy out of fear of breaking the law, the report found — as previously reported in news stories from states operating under abortion bans. Ectopic pregnancies — when the embryo implants outside of the uterus — are never viable, and they can even be deadly.
[ ... ]
Some hospitals have even told physicians that they can't give patients any information on how to get an abortion outside of Louisiana — because that advice could be construed as "providing" an abortion.
Believe it or not, things could get even worse in the state. There have already been reports at other news sources of OB-GYNs leaving Louisiana.
Louisiana already suffers from some of the highest rates of maternal mortality and morbidity in the nation. Black women in the state are more than twice as likely to die as a result of their pregnancy as white women.
Nearly two-thirds of maternal deaths in Louisiana are among low-income women on Medicaid.
Some doctors in the report said they have considered leaving Louisiana. Others warned that a possible exodus of OB-GYNs would exacerbate the state's existing shortage of obstetricians.
Considering how MAGA Republicans regard women as little more than baby-making machines, their assault on reproductive freedom ironically discourages pregnancies in the first place.

#reproductive freedom#louisiana#pregnancy care#ob-gyn#defensive medicine#c-sections#abortion#maternal mortality#physicians for human rights#roe v. wade#dobbs v. jackson women's health organization#a woman's right to choose#republicans hate freedom#restore roe#election 2024#vote blue no matter who
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
got a new laptop case so that means new stickers :]

#got a lot of new vegas on there#with a tasteful sprinkle of 3 and 4#and of course. criminal defense and cats#i made the text bubbles + books stickers myself!!!#the books say 'i like medicine and reading books about failed prewar socioeconomic policies'#fallout#fo4#fnv#fo3#oldworld.posting
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
On May 28, 1914, the Institut für Schiffs-und Tropenkrankheiten (Institute for Maritime and Tropical Diseases, ISTK) in Hamburg began operations in a complex of new brick buildings on the bank of the Elb. The buildings were designed by Fritz Schumacher, who had become the Head of Hamburg’s building department (Leiter des Hochbauamtes) in 1909 after a “flood of architectural projects” accumulated following the industrialization of the harbor in the 1880s and the “new housing and working conditions” that followed. The ISTK was one of these projects, connected to the port by its [...] mission: to research and heal tropical illnesses; [...] to support the Hamburg Port [...]; and to support endeavors of the German Empire overseas.
First established in 1900 by Bernhard Nocht, chief of the Port Medical Service, the ISTK originally operated out of an existing building, but by 1909, when the Hamburg Colonial Institute became its parent organization (and Schumacher was hired by the Hamburg Senate), the operations of the ISTK had outgrown [...]. [I]ts commission by the city was an opportunity for Schumacher to show how he could contribute to guiding the city’s economic and architectural growth in tandem, and for Nocht, an opportunity to establish an unprecedented spatial paradigm for the field of Tropical Medicine that anchored the new frontier of science in the German Empire. [...]
[There was a] shared drive to contribute to the [...] wealth of Hamburg within the context of its expanding global network [...]. [E]ach discipline [...] architecture and medicine were participating in a shared [...] discursive operation. [...]
---
The brick used on the ISTK façades was key to Schumacher’s larger Städtebau plan for Hamburg, which envisioned the city as a vehicle for a “harmonious” synthesis between aesthetics and economy. [...] For Schumacher, brick [was significantly preferable] [...]. Used by [...] Hamburg architects [over the past few decades], who acquired their penchant for neo-gothic brickwork at the Hanover school, brick had both a historical presence and aesthetic pedigree in Hamburg [...]. [T]his material had already been used in Die Speicherstadt, a warehouse district in Hamburg where unequal social conditions had only grown more exacerbated [...]. Die Speicherstadt was constructed in three phases [beginning] in 1883 [...]. By serving the port, the warehouses facilitated the expansion and security of Hamburg’s wealth. [...] Yet the collective profits accrued to the city by these buildings [...] did not increase economic prosperity and social equity for all. [...] [A] residential area for harbor workers was demolished to make way for the warehouses. After the contract for the port expansion was negotiated in 1881, over 20,000 people were pushed out of their homes and into adjacent areas of the city, which soon became overcrowded [...]. In turn, these [...] areas of the city [...] were the worst hit by the Hamburg cholera epidemic of 1892, the most devastating in Europe that year. The 1892 cholera epidemic [...] articulated the growing inability of the Hamburg Senate, comprising the city’s elite, to manage class relationships [...] [in such] a city that was explicitly run by and for the merchant class [...].
In Hamburg, the response to such an ugly disease of the masses was the enforcement of quarantine methods that pushed the working class into the suburbs, isolated immigrants on an island, and separated the sick according to racial identity.
In partnership with the German Empire, Hamburg established new hygiene institutions in the city, including the Port Medical Service (a progenitor of the ISTK). [...] [T]he discourse of [creating the school for tropical medicine] centered around city building and nation building, brick by brick, mark by mark.
---
Just as the exterior condition of the building was, for Schumacher, part of a much larger plan for the city, the program of the building and its interior were part of the German Empire and Tropical Medicine’s much larger interest in controlling the health and wealth of its nation and colonies. [...]
Yet the establishment of the ISTK marked a critical shift in medical thinking [...]. And while the ISTK was not the only institution in Europe to form around the conception and perceived threat of tropical diseases, it was the first to build a facility specifically to support their “exploration and combat” in lockstep, as Nocht described it.
The field of Tropical Medicine had been established in Germany by the very same journal Nocht published his overview of the ISTK. The Archiv für Schiffs- und Tropen-Hygiene unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Pathologie und Therapie was first published in 1897, the same year that the German Empire claimed Kiaochow (northeast China) and about two years after it claimed Southwest Africa (Namibia), Cameroon, Togo, East Africa (Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda), New Guinea (today the northern part of Papua New Guinea), and the Marshall Islands; two years later, it would also claim the Caroline Islands, Palau, Mariana Islands (today Micronesia), and Samoa (today Western Samoa).
---
The inaugural journal [...] marked a paradigm shift [...]. In his opening letter, the editor stated that the aim of Tropical Medicine is to “provide the white race with a home in the tropics.” [...]
As part of the institute’s agenda to support the expansion of the Empire through teaching and development [...], members of the ISTK contributed to the Deutsches Kolonial Lexikon, a three-volume series completed in 1914 (in the same year as the new ISTK buildings) and published in 1920. The three volumes contained maps of the colonies coded to show the areas that were considered “healthy” for Europeans, along with recommended building guidelines for hospitals in the tropics. [...] "Natives" were given separate facilities [...]. The hospital at the ISTK was similarly divided according to identity. An essentializing belief in “intrinsic factors” determined by skin color, constitutive to Tropical Medicine, materialized in the building’s circulation. Potential patients were assessed in the main building to determine their next destination in the hospital. A room labeled “Farbige” (colored) - visible in both Nocht and Schumacher’s publications - shows that the hospital segregated people of color from whites. [...]
---
Despite belonging to two different disciplines [medicine and architecture], both Nocht and Schumacher’s publications articulate an understanding of health [...] that is linked to concepts of identity separating white upper-class German Europeans from others. [In] Hamburg [...] recent growth of the shipping industry and overt engagement of the German Empire in colonialism brought even more distant global connections to its port. For Schumacher, Hamburg’s presence in a global network meant it needed to strengthen its local identity and economy [by purposefully seeking to showcase "traditional" northern German neo-gothic brickwork while elevating local brick industry] lest it grow too far from its roots. In the case of Tropical Medicine at the ISTK, the “tropics” seemed to act as a foil for the European identity - a constructed category through which the European identity could redescribe itself by exclusion [...].
What it meant to be sick or healthy was taken up by both medicine and architecture - [...] neither in a vacuum.
---
All text above by: Carrie Bly. "Mediums of Medicine: The Institute for Maritime and Tropical Diseases in Hamburg". Sick Architecture series published by e-flux Architecture. November 2020. [Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me. Text within brackets added by me for clarity. Presented here for commentary, teaching, criticism purposes.]
#abolition#ecology#sorry i know its long ive been looking at this in my drafts for a long long time trying to condense#but its such a rich comparison that i didnt wanna lessen the impact of blys work here#bly in 2022 did dissertation defense in architecture history and theory on political economy of steel in US in 20s and 30#add this to our conversations about brazilian eugenics in 1930s explicitly conflating hygiene modernist architecture and white supremacy#and british tropical medicine establishment in colonial india#and US sanitation and antimosquito campaigns in 1910s panama using jim crow laws and segregation and forcibly testing local women#see chakrabartis work on tropical medicine and empire in south asia and fahim amirs cloudy swords#and greg mitmans work on connections between#US tropical medicine schools and fruit plantations in central america and US military occupation of philippines and rubber in west africa
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
some magma pages from the past few days <333
@polyphonial, @2sc4rghost, @seasonalberries and @eternal-moss (oh yeah my brother also contributed a bit)








💞💖💕💓💗💘💝❤🧡💛💚💙💜🤎🖤🤍
#hope its cool with everyone that im posting these ✌#they make me grin like an idiot <3#need more of this in my life#besties i would point out every little thing i love about these but my notes would be longer than i can comprehend in my sleepy state#just know these are the last things i think about before falling asleep at night and the first things i think about when i wake up in the m#orning#🥺 <333333#i am not tagging characters or media bc i dont actively hate myself like that 😎👍#in all of these except that last one i started drawing in the bottom right corner and i dont know why#the medicine seller page is so unhinged#in my defense it was berries that drew him first so#yesterday morning was a solo except my brother pasting in a photo of alex jones#i have... (checks downloads) ...26 versions of WWWWWWWEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEE saved......#i would write more here but i cannot process thoughts rn im bout to fall asleep and have been the entire day :-)))#buddy daddies#tbhk#hmc#tgcf#moomin#omori#tbna#trigun#adventure time#mononoke#mdzs#drawfee#csm#pokemon#ok yea#magma
85 notes
·
View notes
Text
"reblog for a larger sample size!!!!" is rly giving "stem student cramming their thesis 2 months before defense"
97 notes
·
View notes
Text
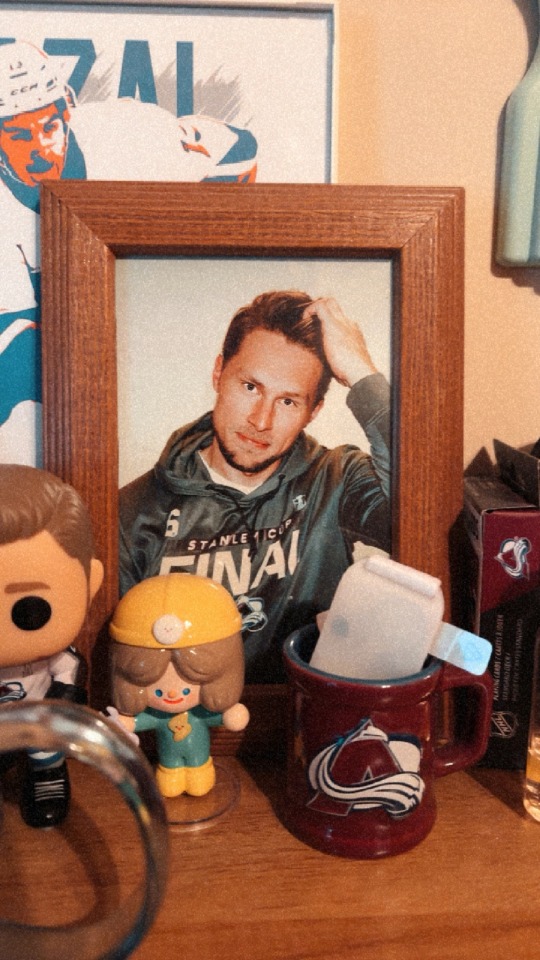

@jostystyles reminded me it was ej’s birthday. in conclusion, i am horrible. how could i forget my man?! anyways here’s a photo of him framed on my desk 🤭🩵
#in my defense#i worked#and had a migraine so took a migraine medicine induced nap immediately after#in my defense i have none#erik johnson#happy birthday my toothless king i adore you
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ok before I continue, hi, I survived! Good morning!!
#i had a fever for like 2-3 hours after i logged off it was hell but it wasnt anything dangerous#and now i took my medicines on time#LOOK I KNOW I EAS ONLY HEALTHY FOR LIKE 2 WEEKS BUT I PROMISE I DONT GET SICK THIS OFTEN#IM NOT A VICTORIAN CHILD THAT HAS NO DEFENSES I PROMISE#I JUST HAD A ROCKY END/START OF THE YEAR!!!!
8 notes
·
View notes
Note
Do you watch this lakorn? https://mydramalist.com/759431-my-stand-in
not yet sadly, but i've actually been meaning to start it!!!!!! it's just that between work, obligations, and now getting sick, i keep end up postponing it ;;;;;;;;;
im also trying to understand from the gifsets im seeing on my dash if the relationship between ming and joe is the kind of messed up that makes me go rabid, or the kind of messed up that just frustrates me to no end, but more to be ready on what to expect rather than to decide whether to watch it or not. i just enjoy up, poon, and mek as actors too much not to give this a chance tbh
so yeah, hopefully i'll be able to get around to watching it soon!!!!!!
#THERE ARE JUST SOOOOO MANY SHOWS AND SO LITTLE TIME#and yeah okay technically both yesterday and today i spent my entire time rewatching vice versa when i could have watched something new#(i still have to watch the first ep of my marvellous dream is you)#BUT IN MY DEFENSE. vice versa is like medicine to me it helps me heal#ANYWAY. if you're watching the show and wanna let me know how you're liking it i would love to hear your thoughts about it anon!!!!!!#sorry for the late reply and i hope you're having a wonderful day!!!!!! 💜#my stand in#m: ask
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Sometimes you just gotta be stupid" <- me right before i chug a glass of chocolate milk after taking medicine i should absolutely not be drinking milk with
#in my defense i had a mouthful of milk before i even remembered i had taken my medicine 5 minutes earlier#and i really wanted chocolate milk:)#if my tummy hurts later it was all for love#I'm pretty sure milk only makes the medicine not absorb as well but surely once won't kill me#howw talks
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
hot girl problems (wants to write a sickfic but has a special interest on the three plagues. you can probably guess where this is going)
#the only reason I haven’t written this is because it feels weird#worse is I want to write it w/ percy#in my defense: he does wear a plague doctor mask and doesn’t have modern medicine
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
.
#only been awake for 45 minutes and shit was peaceful until he came home#I go to plug up my switch on one of the counters and I accidentally knocked a packet of medicine off because he started asking me questions#about shit and so I was trying to focus on what I’m doing (trying to keep from knocking stuff over)#and trying to answer his questions at the same time- then cause I knocked the medicine off he starts talking about how I’m always knocking#stuff over and how clumsy I am and it hurts my feeling because he’s always talked to me about how I’m always ‘fucking shit up’#so I become defensive when he starts in on that shit and then on top of all of that he tries to make me feel like I’m crazy for having a#a reaction to what he’s saying 🤦🏻♀️#*sigh*#vent#sorry#I’m just so tired of it
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
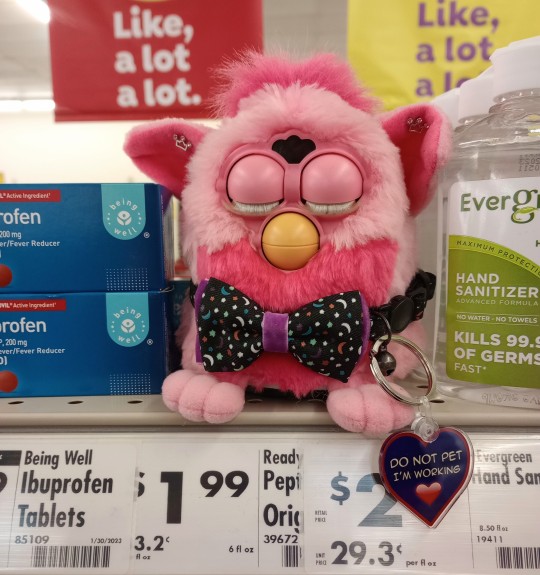

A Furby is the best kind of medicine!*
*Please do not take this as actual medical advice. Take your meds when needed and remember to use your aids!
[Image description: Princey is a 1999 two-tone pink Flamingo Furby sitting on a shelf, surrounded by over-the-counter medications. She is wearing a black collar decorated with various colorful moons and stars and a bowtie. A purple heart tag hangs from his collar that reads, in all caps, "Do not pet. I'm working". End ID.]
#tj taulks#furby#furby fandom#furby community#furblr#allfurby#f: princey#medicine#< for blacklist#just to be safe#i was feeling more anxious than usual (thank you hormonal imbalances) so i brought princey with me#silly name i know. in my defense i was listening to a lot of prince and the revolution#she also goes by he/she pronouns!
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Just learned today my dad has been trusting chat gpt for medical advice. i cannot emphasize this enough we as a species are on our last legs and we are not gonna make it to 2060
#and he got all grumpy when i told him chat gpt doesnt know anything its just saying literally whatever the fuck it wants#he was fine asking it about medicine and taking whatever it said at face value with NO sources like HELLO ARE U CRAZY??#at least on google u can tell if it a blurb is written by thesame compeny trying to sell u the supplements#im way more worried about parents being phone short form content addicted than babies like they have no natural defense against it#they didnt grow up expecting everything online to be a lie or someone trying to sell u shit they just believe whatever#last year my dad sent us a video of fireworks that was so clearly badly edited and he was like wow i cent believe they can do this now#sidney talks shit
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
kane is the only person who truly cares about my woes
#deity dialogue#kane has been dealing with my whining all day#in my defense I actually have good reason to be whining I’m in pain and we don’t have pain medicine#anyways kane makes silly offers to make me feel better and it’s very sweet
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
im not very far in so stop me if this is a premature take, but i think it's fun that an unintentional(?) consequence of mordremoth being eeeeeevil nature is that its "greening" of the desert is framed as unambiguously bad. The high fantasy desert fever dream / "inhospitable wasteland"? Defended to the death against an encroaching forest? disorienting. i feel like im on the other side of the great green wall. "mainstream fantasy game accidentally stumbles towards thoughtful take on desert ecology" was not on my bingo board. now we just need to take all of the sand out of maguuma
#guild wars 2 tag#in other news im also rotating mordremoth and its domain over plants and the mind#something something plants as the first chemists had to create a variety of phytochemical defenses against Being Eaten#leading to all variety of poisons and medicines and hallucinogens and Spicy.#modern medicine still stands on the shoulders of giants#again. probably not intentional. but i do all my own work over here filling in the blanks.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Happy International Women’s Day to women who prioritize women, especially today.

This site gives the deeper dive about the Trans Identified Male who transitioned after his career in the military was over instead of a woman in medicine or a woman in science on International Women’s Day off all days? Fuck that.

Selma Fraiberg (March 8, 1918–1981) was an American child psychoanalyst, author and social worker. She studied infants with congenital blindness in the 1970s. She found that blind babies had three problems to overcome: learning to recognize parents from sound alone, learning about permanence of objects, acquiring a typical or healthy self-image. She also found that vision acts as a way of pulling other sensory modalities together and without sight babies are delayed. In addition to her work with blind babies, she also was one of the founders of the field of infant mental health and developed mental health treatment approaches for infants, toddlers and their families. Her work on intergenerational transmission of trauma such as described in her landmark paper entitled "Ghosts in the Nursery"[1] has had an important influence on the work of living psychoanalysts and clinical researchers such as Alicia Lieberman and Daniel Schechter Her seminal contribution to childhood development, "The Magic Years", is still in use by students of childhood development and early childhood education throughout the United States. The Magic Years, which deals with early childhood and has been translated into 11 languages, was written when she was teaching at the Tulane Medical School in New Orleans.
At the time of her death, Selma Fraiberg was a professor of child psychoanalysis at the University of California, San Francisco and a clinician who devoted her career to helping troubled children. She was also professor emeritus of child psychoanalysis at the University of Michigan Medical School, where she had taught from 1963 to 1979, and had also been director of the Child Developmental Project in Washtenaw County, Mich., for children with emotional problems.
Fraiberg's work is said to have paralleled that of Anna Freud, a pioneer in child psychoanalysis. Both were keenly interested in young blind people. For 15 years Professor Fraiberg studied the development of children who were blind from birth, and this led to her writing Insights From the Blind: Comparative Studies of Blind and Sighted Infants, published in 1977. In the same year, she wrote Every Child's Birthright: In Defense of Mothering, a study of the early mother-child relationship in which she argued that all subsequent development is based on the quality of the child's first attachments.

Lilia Ann Abron (born March 8, 1945[1]) is an entrepreneur and chemical engineer. In 1972, Abron became the first African American woman to earn a PhD in chemical engineering.
Abron was born in Memphis, Tennessee,was the second of four daughters.[5]She was born prematurely, at home, and had to be rushed to the hospital by her aunt in a cab, as ambulances were not available for African Americans at the time.[5]
Her parents were both educators who had attended LeMoyne College (now LeMoyne-Owen College). Her father, Ernest Buford Abron, had sustained an injury playing football in college, and was thus unable to serve during World War II. He worked as a Pullman porter and later was a teacher. Abron's mother, Bernice Wise Abron, was a typist from Arkansas. She typed briefs for Wiley Branton, the Little Rock Nine's defense attorney.
Abron's parents were Baptists and she was baptized at the age of 9. She participated in Girl Scouts and in the junior choir at her church.
Abron attended a public school and was placed in the school's math and science track. After graduating from Memphis High School, she decided to study medicine.
Abron was assistant professor of civil engineering at Tennessee State University from 1971. She was also an assistant professor of environmental engineering Vanderbilt University from 1973. In 1975, she moved Howard University as assistant professor of civil and environmental engineering, simultaneously working at Washington Technical Institute (now part of the University of the District of Columbia).[8][5]
Dr. Abron is a registered professional engineer, and a member of the Water Environmental Federation, the American Society of Civil Engineers, the American Water Works Association, the Society of Sigma Xi, and the American Association of University Women.[5][9] She also serves on the Engineering Advisory Board for the National Sciences Foundation.[5]
In 2004, she was elected fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences.[10] She was elected to the National Academy of Engineering in 2020, for "leadership in providing technology-driven sustainable housing and environmental engineering solutions in the United States and South Africa".[11] She was inducted into Tau Beta Pi, DC Alpha Chapter as an Eminent Engineer, and she is a History Maker®.
She has been bestowed the highest honor - Distinguished Member, Class of 2021 - of the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE). As of January 2021, she became President of The American Academy of Environmental Engineers and Scientists (AAEES).
PEER Consultants, P.C.[edit]
In 1978, Abron founded and became President and CEO of PEER Consultants, P.C. [3][5][12][13] She was the first African-American to start an engineering consulting firm focused on environmental issues and concerns relating to the physical and human environments. [14] PEER offers engineering and construction management services, environmental management and sustainability services, and advisory/consulting services.[15] With headquarters in Washington, DC and additional offices in Baltimore, MD, Burlington, MA, and Clearwater, FL, PEER is strategically located to serve its clients throughout the U.S. Since 1978, the firm is focused on providing transformative, appropriate, and sustainable solutions for its clients’ challenging environmental problems.
With this consulting firm, Abron succeeded in proving that by enacting sustainable practices in poverty-stricken parts of the world, living conditions there can drastically improve.[16] In 1995, Abron co-founded PEER Africa Pty. (Ltd.), with the mission of building energy-efficient homes in post-apartheid South Africa.[8] Abron was presented with a United Nations award for her work in developing low-cost energy-efficient housing.[5] The company carried out projects all over Africa, including in Mali, Uganda and Nigeria.
Personal life
Abron is a member of Delta Sigma Theta sorority.[9] She gives talks and presentations related to energy and the environment.[17][18] She is particularly active in promoting science education, and through her company, offers financial support to science fair participants. PEER staff are encouraged to work with students in their neighborhood schools, and Abron herself mentors students.[5]
She cites the book Silent Spring by Rachel Carson as an inspiration for entering the environmental movement.[2]
Abron is a Christian who began her three-year term serving as deacon at The First Baptist Church of the City of Washington, D.C. on June 17, 2018.[6] She previously served as president of the Washington D.C. chapter of Jack and Jill for America.[5] She also plays the hand bells in the Angelus church choir.[
Honors
William W. Grimes Award for Excellence in Chemical Engineering from the American Institute of Chemical Engineers, 1993[5]
Admission to the Engineering Distinguished Alumni Academy at the University of Iowa, 1996[5]
Hancher-Finkbine Alumni Medallion from the Finkbine Society of the University of Iowa, awarded for learning, leadership and loyalty to the university, 1999[5][8]
Induction into the National Black College Alumni Hall of Fame, 1999[5]
Magic Hands Award by LeMoyne-Owen College, May 2001[8]
Alumni Achievement Award, Washington University School of Engineering and Applied Science, 2001[5]
American Academy of Arts and Sciences, 2004[8][19]
Superior Achievement from American Academy of Environmental Engineers & Scientists, 2012[20]
#Todayinwomenshistory.org is liberal feminism#Selma Fraiberg#Women in medicine#Books by women#Ghosts in the Nursery#The Magic Years#Insights From the Blind: Comparative Studies of Blind and Sighted Infants#Every Child's Birthright: In Defense of Mothering#Lilia Ann Abron#March 8 1945#Women in science#African American women in science#Lilia Ann Abron received a lot of awards and honors for her work in science
4 notes
·
View notes