#Kilonova
Text

A simulated image of NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope’s future observations toward the center of our galaxy, spanning less than 1 percent of the total area of Roman’s Galactic Bulge Time-Domain Survey. The simulated stars were drawn from the Besançon Galactic Model.
Exploring the Changing Universe with the Roman Space Telescope
The view from your backyard might paint the universe as an unchanging realm, where only twinkling stars and nearby objects, like satellites and meteors, stray from the apparent constancy. But stargazing through NASA’s upcoming Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will offer a front row seat to a dazzling display of cosmic fireworks sparkling across the sky.
Roman will view extremely faint infrared light, which has longer wavelengths than our eyes can see. Two of the mission’s core observing programs will monitor specific patches of the sky. Stitching the results together like stop-motion animation will create movies that reveal changing objects and fleeting events that would otherwise be hidden from our view.
youtube
Watch this video to learn about time-domain astronomy and how time will be a key element in NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope’s galactic bulge survey. Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
This type of science, called time-domain astronomy, is difficult for telescopes that have smaller views of space. Roman’s large field of view will help us see huge swaths of the universe. Instead of always looking at specific things and events astronomers have already identified, Roman will be able to repeatedly observe large areas of the sky to catch phenomena scientists can't predict. Then astronomers can find things no one knew were there!
One of Roman’s main surveys, the Galactic Bulge Time-Domain Survey, will monitor hundreds of millions of stars toward the center of our Milky Way galaxy. Astronomers will see many of the stars appear to flash or flicker over time.
youtube
This animation illustrates the concept of gravitational microlensing. When one star in the sky appears to pass nearly in front of another, the light rays of the background source star are bent due to the warped space-time around the foreground star. The closer star is then a virtual magnifying glass, amplifying the brightness of the background source star, so we refer to the foreground star as the lens star. If the lens star harbors a planetary system, then those planets can also act as lenses, each one producing a short change in the brightness of the source. Thus, we discover the presence of each exoplanet, and measure its mass and how far it is from its star. Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center Conceptual Image Lab
That can happen when something like a star or planet moves in front of a background star from our point of view. Because anything with mass warps the fabric of space-time, light from the distant star bends around the nearer object as it passes by. That makes the nearer object act as a natural magnifying glass, creating a temporary spike in the brightness of the background star’s light. That signal lets astronomers know there’s an intervening object, even if they can’t see it directly.

This artist’s concept shows the region of the Milky Way NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope’s Galactic Bulge Time-Domain Survey will cover – relatively uncharted territory when it comes to planet-finding. That’s important because the way planets form and evolve may be different depending on where in the galaxy they’re located. Our solar system is situated near the outskirts of the Milky Way, about halfway out on one of the galaxy’s spiral arms. A recent Kepler Space Telescope study showed that stars on the fringes of the Milky Way possess fewer of the most common planet types that have been detected so far. Roman will search in the opposite direction, toward the center of the galaxy, and could find differences in that galactic neighborhood, too.
Using this method, called microlensing, Roman will likely set a new record for the farthest-known exoplanet. That would offer a glimpse of a different galactic neighborhood that could be home to worlds quite unlike the more than 5,500 that are currently known. Roman’s microlensing observations will also find starless planets, black holes, neutron stars, and more!
youtube
This animation shows a planet crossing in front of, or transiting, its host star and the corresponding light curve astronomers would see. Using this technique, scientists anticipate NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope could find 100,000 new worlds. Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center/Chris Smith (USRA/GESTAR)
Stars Roman sees may also appear to flicker when a planet crosses in front of, or transits, its host star as it orbits. Roman could find 100,000 planets this way! Small icy objects that haunt the outskirts of our own solar system, known as Kuiper belt objects, may occasionally pass in front of faraway stars Roman sees, too. Astronomers will be able to see how much water the Kuiper belt objects have because the ice absorbs specific wavelengths of infrared light, providing a “fingerprint” of its presence. This will give us a window into our solar system’s early days.
This animation visualizes a type Ia supernova.
Roman’s High Latitude Time-Domain Survey will look beyond our galaxy to hunt for type Ia supernovas. These exploding stars originate from some binary star systems that contain at least one white dwarf – the small, hot core remnant of a Sun-like star. In some cases, the dwarf may siphon material from its companion. This triggers a runaway reaction that ultimately detonates the thief once it reaches a specific point where it has gained so much mass that it becomes unstable.
youtube
NASA’s upcoming Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will see thousands of exploding stars called supernovae across vast stretches of time and space. Using these observations, astronomers aim to shine a light on several cosmic mysteries, providing a window onto the universe’s distant past. Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Since these rare explosions each peak at a similar, known intrinsic brightness, astronomers can use them to determine how far away they are by simply measuring how bright they appear. Astronomers will use Roman to study the light of these supernovas to find out how quickly they appear to be moving away from us.
By comparing how fast they’re receding at different distances, scientists can trace cosmic expansion over time. This will help us understand whether and how dark energy – the unexplained pressure thought to speed up the universe’s expansion – has changed throughout the history of the universe.

NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will survey the same areas of the sky every few days. Researchers will mine this data to identify kilonovas – explosions that happen when two neutron stars or a neutron star and a black hole collide and merge. When these collisions happen, a fraction of the resulting debris is ejected as jets, which move near the speed of light. The remaining debris produces hot, glowing, neutron-rich clouds that forge heavy elements, like gold and platinum. Roman’s extensive data will help astronomers better identify how often these events occur, how much energy they give off, and how near or far they are.
And since this survey will repeatedly observe the same large vista of space, scientists will also see sporadic events like neutron stars colliding and stars being swept into black holes. Roman could even find new types of objects and events that astronomers have never seen before!
Learn more about the exciting science Roman will investigate on X and Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
#NASA#astronomy#telescope#Roman Space Telescope#dark energy#galaxies#cosmology#astrophysics#stars#galaxy#space images#time#supernova#Nancy Grace Roman#black holes#neutron stars#kilonova#rogue planets#exoplanets#space#science#tech#technology#Youtube
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
The long awaited trailer to Kilonova is here! I've been working on this project since fall of last year, and with a team of 20 other students we've brought it to life!
I did the creature designs for two of the enemies, Stellupi and Eversor, created all the rigs, did some proxy models and modeled the collars and stars inside them. I was also the lead animator and did many of the creature animations, especially the ones shown here in the trailer! I also provided the sounds for the stellupi which you can hear a little of in the trailer.
This past semester I stepped into the role of art director and I'm absolutely ecstatic about what our team managed to put together. Kilonova will be coming to Steam sometime next year, and I couldn't be more proud to have been part of this project.
129 notes
·
View notes
Text
@jazz-bazz Live Photo of me right now enjoying the greatest things life has to offer me also waffles readers did I get the tags right?

#this is so dumb I’m sorry#self portrait#midnight moth draws#<- yup putting my art tag on this#kilonova#waffles
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
Supernovae are some of the most powerful explosions in the Universe, occurring in the final death throes of massive stars.
#my writing#supernova#hypernova#kilonova#astroblr#astrophotography#astronomy#astronomia#astrophysics#physics#women in stem#astro observations#science#space
24 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Kilonova in Ellipse
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
Discovery Alert! In a new discovery released on October 25, 2023, Webb Telescope Discovers Tellurium, a Rare Cosmic Element from Star Merger. Read full article here

Discover how Webb and a collaboration of telescopes observed an incredibly bright gamma-ray burst, GRB 230307A, and revealed the secrets of a neutron star merger that produced a cosmic explosion called a kilonova. But that's not all! Webb's keen eye also detected the presence of tellurium, an element even rarer on Earth than platinum. 🌌💫
🔍 Unlock the mysteries of the cosmos, learn about neutron star mergers, and dive into the thrilling world of space exploration. 🪙✨
Read the full article here.
Join us on this cosmic journey as we delve into the depths of the universe and unravel its most profound secrets. 🌠🔮 Don't miss out on this awe-inspiring discovery! 🚀 #NASA #WebbTelescope #SpaceExploration #CosmicDiscovery #Astronomy #Tellurium #Kilonova
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Blood (Echo) wakes up everyday and chooses “shitpost”. This is the consequence of that choice.
#oc#security breach au#robot#security breach#fnaf oc#sundrop#azil#free runner au#jenn&co#Bloodmoon#Kilonova#echo chamber#free runner sun#free runner Bloodmoon#Azil Sun#Azil Bloodmoon#shitpost#whiskers on kittens#rotisserie chickens
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Best regards
Refutations For Some Physics Theories
First Theory
Planet creation data is created by random process, initial condition and historical unknown factors – this idea is told by the physics book-
It's a wrong idea – the paper tests my planet diameter equation proves that the planet diameter is created based on exact equation and can be concluded theoretically and proves NO random process caused to create any planet diameter (or any creation data)
Second Theory
No Planet Moves By The Sun Gravity – Newton is wrong
The planet creation and motion should be done by one force only – because – if two forces have effect on the same one planet this planet will be broken.
The planet safe motion necessitates one force to cause the planet creation and motion
The sun created no planet and caused no planet to move
Also no proof for the sun massive gravity where its rotation period is (25.4 days for equator) and (34.4 days for pole) proving the sun has No massive gravity
The point is - The planets order contradicts the gravitation equation but the equation is accepted spite of that (regardless the planets data)
Third Theory
The mass gravity force definition is wrong also
Suppose the moon moves by the Earth mass gravity
The moon moves and produces motion energy- now – from what source this motion energy will be paid? From the Earth mass itself!
That tells- If the Earth causes the moon to move that will cause to decrease the Earth mass itself to pay the moon motion energy – it's wrong definition for the mass gravity
The mass gravity is a bond between 2 masses –
The Earth and the moon are connected together with the mass gravity - They are similar to a lorry and its trailer – If a force causes the Earth to move this same force will cause the moon to move – the two planets move together- this is the effect of the mass gravity but the motor is neither the Earth nor the moon – it's outer force – and this outer force will pay the motion energy for the Earth and for the moon
The mass gravity creates the bond between the two planets but can't cause any motion
(the conclusion- The Mass Gravity Can't Cause Any Motion)
Again Newton is wrong.
Fourth Theory
Why does the moon rotation period = the moon orbital period =27.3 days?
The book tells because of (The Tidal Locking)
This is a wrong idea –
It's the effect of Venus motion on the moon motion
In fact the planet diameter equation uses the moon motion because the moon rotation period = its orbital period =27.3 days – this feature caused the factor (s) to be =1 in the planet diameter equation and without this factor the equation can't work
It's the direct effect of Venus motion on the moon motion –
Let's summarize this fact in following
The equation needs the factor (s) to be =1 otherwise the equation can't work
In the past Venus rotation period was = Venus orbital period =243 days by that Venus motion is used by the planet diameter equation and all planets diameters are defined based on Venus motion (we know that the Earth moon is created after all planets)
But later a great event caused Venus orbital period to be =224.7 days and by that the factor (s) NOT = 1 that causes a serious problem for the planet diameter equation – for that Venus motion created an effect on the moon motion and caused its rotation period to be = its orbital period =27.3 days and by that the factor (s) be= 1 and the planet diameter equation could work again - this fact is proved in details in point no. (7) - Shortly - (NO Tidal Locking Causes The Periods Equality)
Fifth Theory
Giant-impact hypothesis tells us a planet in Mars size has collided with the Earth and caused the moon creation- (Can Mars Itself Did That? the theory tells NO Impossible)
The fact is that-
Mars original orbit was between Mercury and Venus and Mars had migrated from its original orbit to its current one
In details– Mars original orbital distance was 84 million km –and Mars had migrated from it to its current one (228 million km) – in its migration motion Mars had collided with Venus and then with the Earth and caused the moon creation- Mars Itself Did That-
This idea answer the question (Why Does Venus Have No Moon?) because Mars had pushed all collision debris with it in its motion direction- Venus had found no debris around and for that Venus couldn't create its own moon
This theory is proved in details in (Mars Migration Theory) Point no. (14)
Sixth Theory
The gravitational waves are discovered recently and called as (gravitational waves) based on the idea tells (The Waves Are Created By The Gravitational Field Energy)
BUT
The planet motion energy analysis forces us to suppose the motion energy is stored in the space in waves form – because
The planet can't store its motion energy in its own body otherwise its temperature would be raised –
Means- the planet motion energy storing in the space in waves form is an idea more trustee and has more good proves than the gravitational field existence-
Shortly
The discovered waves are produced by the planets motions energies but they called them as (gravitational waves) to refer to the gravitational field based on the belief tells (Planet Moves By The Sun Gravity which Is NOT Fact)
The paper proves that these waves are created by the planets motions energies and no any proof is found for the gravitational field existence
Seventh Theory
The Sun Is Not Doing Nuclear Fusion To Produce Its Rays
The Sun Rays Are Produced By The Planets Motions Energies Total
The sun is a phenomenon created by the planets motions –
It's noticeable, No one sees the solar system massive motion energy and they created this artificial idea (the nuclear fusion) to create the sun rays and left the planet motion energy without using!
The paper proves this fact in the paper part Two in details with many powerful proves
Thanks a lot – please read
Can The Gravitational Waves Produce A Light Beam?
or
or
or
or
Gerges Francis Tawdrous +201022532292
Physics Department- Physics & Mathematics Faculty
Peoples' Friendship university of Russia – Moscow (2010-2013)
Curriculum Vitae https://www.academia.edu/s/b88b0ecb7c
E-mail [email protected], [email protected]
ORCID https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1041-7147
Facebook https://www.facebook.com/gergis.tawadrous
VK https://vk.com/id696655587
Tumblr https://www.tumblr.com/blog/itsgerges
Researcherid https://publons.com/researcher/3510834/gerges-tawadrous/
Google https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=2Y4ZdTUAAAAJ&hl=en
Livejournal https://gerges2022.livejournal.com/profile
Pocket https://getpocket.com/@646g8dZ0p3aX5Ad1bsTr4d9THjA5p6a5b2fX99zd54g221E4bs76eBdtf6aJw5d0?src=navbar
PUBLICATIONS
box https://app.box.com/s/47fwd0gshir636xt0i3wpso8lvvl8vnv
Academia https://rudn.academia.edu/GergesTawadrous
List of publications http://vixra.org/author/gerges_francis_tawdrous
Slideshare https://www.slideshare.net/Gergesfrancis
#astronomie#astrophysique#étoile#effondrement#gravitation#gamow#hoyle#nucléosynthèse#nucléosynthèse primordiale#nucléosynthèse stellaire#nucléosynthèse explosive#proton#neutron#géante rouge#étoile à neutrons#fusion#énergie de liaison#alpher#bethe#kilonova#hdastro#hdcosmo#ligo#физика#астрофизика#ukrall#sonnensystem#himmel#heinrich himmler#schloss einstein
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo


First Kilonova Progenitor System identified Astronomers using the SMARTS 1.5-meter Telescope at Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory in Chile, a Program of NSF's NOIRLab, have uncovered the first example of a phenomenally rare type of binary star system, one that has all the right conditions to eventually trigger a kilonova — the ultra-powerful, gold-producing explosion created by colliding neutron stars. Such an arrangement is so vanishingly rare that only about 10 such systems are thought to exist in the entire Milky Way Galaxy. The findings are published today in the journal Nature. This unusual system, known as CPD-29 2176, is located about 11,400 light-years from Earth. It was first identified by NASA’s Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory. Later observations with the SMARTS 1.5-meter Telescope allowed astronomers to deduce the orbital characteristics and types of stars that make up this system — a neutron star created by an ultra-stripped supernova and a closely orbiting massive star that is in the process of becoming an ultra-stripped supernova itself. An ultra-stripped supernova is the end-of-life explosion of a massive star that has had much of its outer atmosphere stripped away by a companion star. This class of supernova lacks the explosive force of a traditional supernova, which would otherwise “kick” a nearby companion star out of the system. “The current neutron star would have to form without ejecting its companion from the system. An ultra-stripped supernova is the best explanation for why these companion stars are in such a tight orbit,” said Noel D. Richardson at Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University and lead author of the paper. “To one day create a kilonova, the other star would also need to explode as an ultra-stripped supernova so the two neutron stars could eventually collide and merge.” As well as representing the discovery of an incredibly rare cosmic oddity, finding and studying kilonova progenitor systems such as this can help astronomers unravel the mystery of how kilonovae form, shedding light on the origin of the heaviest elements in the Universe. “For quite some time, astronomers speculated about the exact conditions that could eventually lead to a kilonova,” said NOIRLab astronomer and co-author André-Nicolas Chené. “These new results demonstrate that, in at least some cases, two sibling neutron stars can merge when one of them was created without a classical supernova explosion.” Producing such an unusual system, however, is a long and unlikely process. “We know that the Milky Way contains at least 100 billion stars and likely hundreds of billions more. This remarkable binary system is essentially a one-in-ten-billion system,” said Chené. “Prior to our study, the estimate was that only one or two such systems should exist in a spiral galaxy like the Milky Way.” Though this system has all the right stuff to eventually form a kilonova, it will be up to future astronomers to study that event. It will take at least one million years for the massive star to end its life as a titanic supernova explosion and leave behind a second neutron star. This new stellar remnant and the pre-existing neutron star will then need to gradually draw together in a cosmic ballet, slowly losing their orbital energy as gravitational radiation. When they eventually merge, the resulting kilonova explosion will produce much more powerful gravitational waves and leave behind in its wake a large amount of heavy elements, including silver and gold. “This system reveals that some neutron stars are formed with only a small supernova kick,” concluded Richardson. “As we understand the growing population of systems like CPD-29 2176 we will gain insight into how calm some stellar deaths may be and if these stars can die without traditional supernovae.” This research was presented in the paper “A high-mass X-ray binary descended from an ultra-stripped supernova” to appear in the journal Nature. TOP IMAGE....This is an artist’s impression of the first confirmed detection of a star system that will one day form a kilonova — the ultra-powerful, gold-producing explosion created by merging neutron stars. These systems are so phenomenally rare that only about 10 such systems are thought to exist in the entire Milky Way. CREDIT CTIO/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/J. da Silva/Spaceengine/M. Zamani LOWER IMAGE....This infographic illustrates the evolution of the star system CPD-29 2176, the first confirmed kilonova progenitor. Stage 1, two massive blue stars form in a binary star system. Stage 2, the larger of the two stars nears the end of its life. Stage 3, the smaller of the two stars siphons off material from its larger, more mature companion, stripping it of much of its outer atmosphere. Stage 4, the larger star forms an ultra-stripped supernova, the end-of-life explosion of a star with less of a “kick” than a more normal supernova. Stage 5, as currently observed by astronomers, the resulting neutron star from the earlier supernova begins to siphon off material from its companion, turning the tables on the binary pair. Stage 7, with the loss of much of its outer atmosphere, the companion star also undergoes an ultra-stripped supernova. This stage will happen in about one million years. Stage 7, a pair of neutron stars in close mutual orbit now remain where once there were two massive stars. Stage 8, the two neutron stars spiral into toward each other, giving up their orbital energy as faint gravitational radiation. Stage 9, the final stage of this system as both neutron stars collide, producing a powerful kilonova, the cosmic factory of heavy elements in our Universe. CREDIT CTIO/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/P. Marenfeld
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
16 Feb 2023.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Bug fixing in the game is always so fun and as an artist I have less than no idea why some bugs occur. But my absolute favorite so far is one grunt just pops up in the final arena in a T pose

There’s actual grunts running around fighting, but this one stands there invincible. Unmoving. Eternal.
#ramblies#funny#game project#they might have fixed him now but we’ll see#another of my babies spasms halfway into the ground which is funny but not as funny as the t poser#kilonova
46 notes
·
View notes
Text
I love my PA wife, she spoils me. No but really, it’s not so much the material objects, but it’s so nice to know someone thinks of you and cares about your well-being and stuff. It helps with the dumpster goo feelings. Also obviously I love ghost and Halloween and I like when they come together. ALSO - she printed out waffles for me so I can start planning where to add things and edit etc. look at it! This is printed double sided. It is literally a book! A big book! Because these are 8x10 pages. It’s 337 double sided pages. And it’s not done. Considering what a fucking train wreck I am, I am kind of proud of that. I also got my lil guy signed by the queen goddess Lucy herself. He’s very excited to become a Canadian citizen. Anyways that’s it for now I guess.




#mina appreciation post#having this will give me the motivation to finish it#like it feels like an accomplishment#I don’t care if it’s fanfic I wrote a book#and also I’m going to write two more#kilonova#waffles#the band ghost#also I bought the ghildo#obviously#wrist reveal?
29 notes
·
View notes
Note
Thank you so much for your super sweet comment on Kilonova 🖤🖤🖤 I really appreciate it!
Of course!! It was such a beautiful story, I laughed, I cried, I felt uhhhhhh other things. It was just incredible, and it'll be on my mind for a long time!
I was jamming on my drive home and Choke by The Warning came on and it has such Kilonova vibes -
Don't cry
Just let me drown
Let me drown
Let me dive in
Sink in deeper
Push my head
Choke me 'til I drown
Let me drown
Ugh, them 🤍
Thank you again for sharing such a beautiful work!!
1 note
·
View note
Photo

Kilonova
35 notes
·
View notes
Link
The Space News Podcast. SpaceTime Series 26 Episode 132 *Rare heavy element discovered in stellar collision Astronomers have discovered the rare heavy element tellurium being produced in the kilonova collision of a pair of neutron stars. *Planetary defence mission update The European Space Agency’s Hera spacecraft has arrived at ESA’s ESTEC test centre in the Netherlands as it continues preparations for next October’s launch on its planetary defence mission to the asteroid Didymos and its small moon Dimorphos. *Moscow threatens star wars As Moscow continues its war against Ukraine, the Kremlin is also continuing to ratchet up its threats against the west. *The Science Report Tai Chi could slow the progression of Parkinson's disease. Lead exposure is likely to blame for 5.5 million adult deaths from heart disease, and the loss of 765 million IQ points in kids under five globally every year. Just 20-25 minutes of exercise a day may be enough to offset the heightened risk of death. Skeptics guide to why there are no new ghosts And our regular guest: Tim Mendham from Australian Skeptics Listen to SpaceTime on your favorite podcast app with our universal listen link: https://spacetimewithstuartgary.com/listen and access show links via https://linktr.ee/biteszHQ Additionally, listeners can support the podcast and gain access to bonus content by becoming a SpaceTime crew member through www.bitesz.supercast.com or through premium versions on Spotify and Apple Podcasts. Details on our website at https://spacetimewithstuartgary.com For more SpaceTime and show links: https://linktr.ee/biteszHQ If you love this podcast, please get someone else to listen to. Thank you… To become a SpaceTime supporter and unlock commercial free editions of the show, gain early access and bonus content, please visit https://bitesz.supercast.com/ . Premium version now available via Spotify and Apple Podcasts. For more podcasts visit our HQ at https://bitesz.com
#astronomical#collision#defense#discovery#esa#estec#hera#kilonova#launch#mission#netherlands#neutron#phenomenon#planetary#research#spacecraft#stars#stellar#tellurium#testing
0 notes
Text
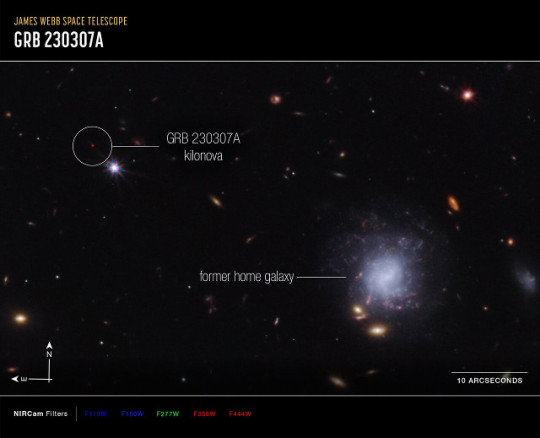
An article published in the journal "Nature" reports the detection of heavy elements including tellurium ejected from a kilonova, the merger between two neutron stars. A team of researchers started from the gamma-ray burst cataloged as GRB 230307A to examine data collected by ground-based and space telescopes which made it possible to identify the characteristics of a kilonova at the origin of that very powerful explosion, which lasted about 200 seconds in the second brightest gamma-ray burst detected so far.
The James Webb Space Telescope made it possible to examine the environment around the kilonova with its NIRCam and NIRSpec instruments, detecting the spectroscopic traces left in the emissions from materials ejected at high speed. For the first time, tellurium, a very rare element on Earth, was detected. Webb also made it possible to ascertain that the pair of neutron stars that merged was ejected from its home galaxy hundreds of millions of years ago.
1 note
·
View note