#whig party
Photo

I’m starting Whigblr
#whiggism#whig#whig party#william henry harrison#whh#tippecanoe and tyler too#1840#whigs#will harrison#henry clay#the american system#internal improvements#anti-jacksonianism#parliamentism#tariff policy#protective tariffs#my post
251 notes
·
View notes
Note
Is it true there's only been one Whig President?
And did he get anything done before his death?
No, technically, there were four Whig Presidents: William Henry Harrison, John Tyler, Zachary Taylor, and Millard Fillmore. But it was more like three-ish because Tyler was nominally a Whig when he was elected as Harrison's Vice President in 1840, but when he assumed the Presidency following President Harrison's death, Tyler clashed with his fellow Whigs in Congress and was booted from the party just a few months into his term after more issues and the resignation of practically his entire Cabinet.
Whig Presidents definitely had a rough time, though. And the man who was arguably the most famous Whig of his time, Henry Clay, lost all of his bids for the White House -- even in 1844 against the first dark horse, James K. Polk. Harrison and Taylor were the only Whigs who were ever actually elected President. Harrison died just a month into his term, and was succeeded by Tyler who, as I previously mentioned, wasn't exactly winning any Whig-of-the-Year contests or being picked to be on the cover of the Whig video game. Taylor lasted a bit longer than Harrison did, but he also died in office, and Fillmore -- the last Whig President -- succeeded him. Fillmore was probably the "best" of the Whig Presidents, but that's kind of like being the most “dignified” Trump.
But...Whigs can also claim some credit for Abraham Lincoln! Lincoln was a ardent Whig for most of his political career prior to the formation of the Republican Party in the mid-1850s.
#Whig Party#Whigs#Presidents#History#William Henry Harrison#John Tyler#Zachary Taylor#Millard Fillmore#Abraham Lincoln#Politics#Presidential Politics
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
what if we brought back the whig party
#manuscriptsdontburnoriginal#whig party#me saying some shit#just to see what happens#i just said this in the actual world and my friend told me to tweet it but i dont have twitter so this is the next best thing
1 note
·
View note
Text
In the 2016 U.S.A. Election, Jennifer Laurent (W-CA) won a narrow victory over Frank O'Ryan (D-IL)

#politics#elections#2016#alt history#alternate history#alternate election map#election map#map#2016 election#whig#whig party#alex jones#Charlie Baker
1 note
·
View note
Text
I swear I actually am trying to promote my ocs more + share more information abt them (mostly on my other blog. still) it's just so difficult because most of what I write is out of a desire to play around with the concepts I learn about while studying the historical period the stories are set in and so I always have to preface nearly every single thing I say about my ocs with 67 paragraphs of real life background information if I want the average reader to have any idea what I'm fucking talking about
#like charles doesn't make any sense as a character if u don't know abt the politics of the whig party circa the mid 1790s how am I meant#to talk about him without referencing a million pieces of niche drama from that time. horrid#ocs#jory.txt
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Indiana's actually a really funny state where several executive cabinet positions are elected, the governor doesn't appoint the attourney general, secretary of state, etc.
1 note
·
View note
Text
« Trump won’t just go away; he'll have to be defeated. And Haley can’t defeat him because she has no answer for the central problem: She needs the support of a group of voters who are religiously devoted to him.
However, I do believe that the longer she stays in the race, the more damage she’ll do to Trump’s bid.
[ … ]
It's probably not her intention, but Haley is providing a service to the nation: a soft launch of reminding voters that Trump is a chaos agent of the highest order who put the nation through a dizzying series of unnecessary crucibles that tested the very durability of our institutions and our ability to withstand his anti-democratic onslaught.
Haley has begun to do the work that Biden and his campaign team will greatly expand on — if they're smart. »
— Charles M. Blow writing in the New York Times.
For some bizarre reason, candidates for the GOP presidential nomination thought they could make headway without criticizing the deeply flawed frontrunner.
When Nikki Haley belatedly started slamming Trump, the public attention devoted to her campaign shot up. It's certainly too late to do her much good, but her attacks on Trump do increase the possibility of him responding in such a way that women voters would find offensive.
If Trump loses this year, the GOP will be in shambles. If the party doesn't disintegrate like the Whigs, it will be looking to somebody who was not tied too closely to Trump. By publicly creating some space between herself and The Orange One, Nikki Haley could be looking ahead to 2028.
In the meantime, the more people attacking Trump from different directions – the better. There's already some indication that Biden, or at least his surrogates, are stepping up attacks on Trump's economic record. Reminding voters that Trump's fumbling of the early pandemic response led to economic meltdown should get more emphasis.
112 notes
·
View notes
Text
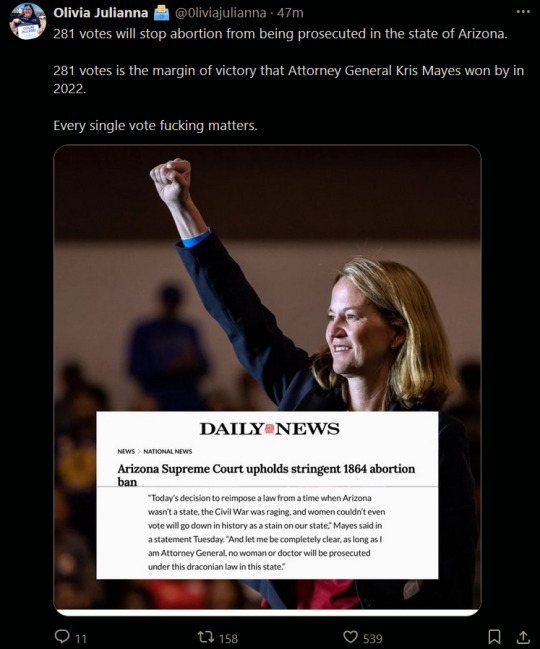

Once again, this is why voting matters, voting will always matter.
A group also already got enough signatures before this ruling to put abortion rights on the ballot in AZ this november.
Abortion, Birth Control, IVF, Surrogacy, the Civil Rights Act and more, its all on the line this year. At the local, state and national level we have to send the Republican Party to the same place the Whigs went: Oblivion.
I have been beating this drum since the 2010 midterm disaster and the Tea Party, and they've only gotten worse since then. They're only going to get worse from here on out.
47 notes
·
View notes
Text
Because @maltheniel has enabled me, I'm going to tell you about William Henry Seward.
If you had the American history education that I had, you might have heard of a thing called Seward's Folly--also known as Alaska. Seward was the Secretary of State who was mocked for buying America territory in what appeared to be a barren wasteland, until he was vindicated by the discovery of oil and gold and a jillion other useful natural resources. If you had the education that I had, this is the only thing you heard about him, but the more I look into the Civil War, the more baffling this is, because this guy is everywhere in the political scene of the time.
Seward was an extremely vocal anti-slavery Whig from New York. He started as a US Senator in 1849, and he became part of President Zachary Taylor's inner circle, influencing him to support measures to keep slavery out of the new territories. After Taylor died, the question of slavery in the territories dominated politics for the next decade, with the conflict getting more heated and the positions getting more polarized. The Whig Party fell apart because of disagreements over the issue; Seward held on for as long as he could, but eventually joined the newly-forming Republican Party, and became well-known for his eloquent speeches against slavery.
When it came time to choose the Republican nominee for the 1860 presidential election, Seward was by far the top candidate. All but a shoe-in. Unfortunately, some of his anti-slavery speeches were a bit too eloquent, and gave him a reputation for being much more radically anti-slavery than he was. A significant portion of the party doubted he could win a nationwide election when slavery was such a divisive issue. This gave Lincoln's team a chance to pitch him as a less-radical option, which allowed him to come from behind and win the nomination.
Seward was extremely gracious about the loss, immediately publishing letters announcing his full support of Lincoln as candidate, and putting his own campaign manager to work getting Lincoln elected. Privately, though, he was seething. He had been in politics for decades, helped to build the party, and then lost his chance at the presidency to a guy who'd been working as a backwoods lawyer for the last twelve years.
But he knew his politics, and knew it was better to support the party's candidate than to oppose him. Lincoln offered Seward the prime Cabinet position of Secretary of State--he was qualified for it and deserved it--and Seward accepted. Seward hoped that he'd be able to help select the other Cabinet members, so he could pick people from his own faction who he'd work well with. Then he, with his extensive connections and political experience, could be the real head of the administration, with Lincoln as a compliant figurehead.
Lincoln was having none of it. He listened to Seward's suggestions, but he'd basically already chosen the people he wanted for his Cabinet, across all factions of the party. While he made use of Seward's expertise and trusted him as Secretary of State, he was going to be head of his own administration and be the one making all the final decisions. After a rocky start, Seward came to recognize that Lincoln had a shrewd mind and good judgement, and he became Lincoln's loyal supporter and a good friend.
But there was a persistent idea that Seward was the real power behind the throne, sparked partly by the prominent role he took in Washington between the election and the inauguration. States started seceding almost as soon aa Lincoln was elected, and Seward was the one who had to hold things together in Washington while Lincoln was tying things up in Illinois. He was getting reports from informants, watching out for Southern spies, and keeping Lincoln abreast of what was going on. He gave a stirring speech to Congress urging the Southern states to keep the Union together, offering all sorts of concessions to mollify them, such as amendments preventing the federal government from interfering with slavery. It was a highly controversial speech, and his wife, Frances, raked him over the coals for it. She understood, earlier than almost anybody, that this crisis would turn into a long war about slavery, and that they couldn't afford to bend on that issue, even to keep the Union together. (Lincoln privately approved of several measures Seward talked about, but publicly said little, preferring to see the public's response to Seward before taking official positions.)
Seward was a little bit like a Civil War version of Evil Chancellor Traytor. Under both Lincoln and Johnson, rumors persisted that Seward was the shadowy figure who was really in charge, secretly manipulating the president into making unpopular decisions, even though most of the time, Seward had nothing to do those decisions, and often disagreed at least partially with what the president chose to do.
Best example of the effects of this misconception is the time Seward came under attack during the middle of the war. The war was going badly, and since people couldn't directly attack the president, they started going after Seward. Chase, the Treasury Secretary, told some members of Congress that Seward was the reason the Cabinet couldn't get along, and that he was always trying to take control. These senators wanted to meet with the president and force him to get rid of Seward. When Seward heard about this, he gave Lincoln his letter of resignation, not wanting to cause problems for the administration. Lincoln responded by allowing the senators to join in a Sewardless Cabinet meeting. When confronted with both the senators and the Cabinet, Chase was forced to admit that his stories had been exaggerated, and the other Cabinet members rallied to Seward's defense, resenting Congress' meddling. Lincoln refused to accept Seward's resignation, and Seward returned to the Cabinet, having been saved by Lincoln's political acumen.
I'm going to skip ahead so I can tell you the craziest part of the story. Four days before the Civil War officially ended, Seward got into a carriage accident that left him bedridden with a broken jaw and a bunch of other injuries. When told of Lee's surrender on April 9th, Seward said (through a broken jaw, after barely surviving a painful accident), "For the first time in my life, you've made me cry." (Which is both touching and an incredibly badass claim, given what he's just suffered.)
Five days later, John Wilkes Booth shot the president at Ford's Theater. Everyone knows (or should know) that part of the story. What I didn't know was that his conspiracy also called for Seward's assassination. Booth knew his Shakespeare and didn't want to leave Seward alive as a Marc Antony to eulogize the dead tyrant. (He also wanted to kill Andrew Johnson, but that assassin chickened out, and it's not really important to this story).
While Booth was at the theater, his co-conspirator went to Seward's house under the pretense of delivering medication. When Seward's son wouldn't let him go upstairs, the assassin tried to shoot him and broke his skull with the gun. The assassin then made his way to Seward's bedroom--where, I need you to remember, Seward was still bed-ridden--and stabbed him five times in the face and neck. Like, sliced away flaps of flesh. The only reason Seward didn't die was because the splint for his broken jaw deflected the blade away from his jugular vein. And because his other son and bodyguard made it into the room and forced the assassin to flee.
Chalk this one up in the "Parts of American History I'm Furious No One Told Me About" column.
While Seward was recovering, they hid the president's death from him, thinking he wouldn't survive the shock. But he figured it out three days later when he saw the flags at half-staff through his bedroom window, and realized that if Lincoln were alive, he'd have been the first to come see Seward after the attack.
Of course, Seward survived (badly scarred) and went on to buy Alaska. Which is an interesting story. But not half so interesting as all the stuff that came before it.
#history is awesome#presidential talk#answered asks#maltheniel#i really tried to keep this short#but there's just too much that i find interesting about this guy#like i said he was involved in everything political at the time#and you've got to talk about a lot of it to get across just how involved he was#like i had the whole post written out and then realized i hadn't even talked about the between-administrations thing#i can't leave that out!#so even though no one wants to read that much about william seward i want to tell you that much about him and it's my blog so there#i also have to add that it was very satisfying to head to wikipedia#and find out that his first political party was specifically an anti-mason party#and that he got criticized for his support of catholics#he's a career politician so there's a lot to disapprove of but i very much like both of those things about him
187 notes
·
View notes
Note
Who do you consider to have been some of the most important / formative mayors of New York?
This is a great question, and actually rather difficult to answer, because for the longest time both Tammany Hall and the Whig/Republican machine tended to prefer mayors who were dull but reliable non-entities. Starting in 1824, NYC was divided into wards that elected Aldermen and Assistant Aldermen to the Board of Aldermen and the Board of Assistants, who together made up the bicameral Common Council. This led to a system whereby the real political action was shunted to the local level, where the ward's Aldermen and the ward boss (and his precinct bosses) ran the show.
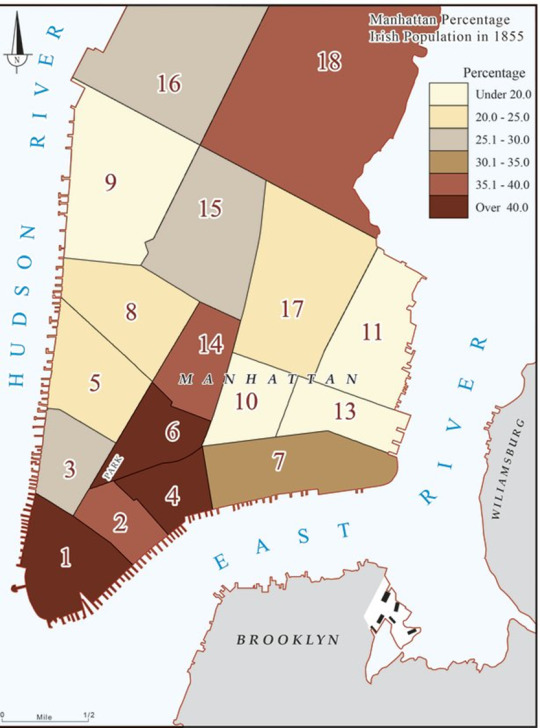
The downfall of Boss Tweed led to some reforms, with the bicameral Common Council replaced by a unicameral Board of Aldermen who were elected from larger State Senate districts or at-large, as part of the Whig Party's drive to dilute the power of Tammany's Irish Catholic voting base. This would change somewhat when the five boroughs were consolidated into Greater New York in 1898, which added the borough presidents and the Board of Estimate into the mix, and then again in 1901 and so forth.
However, the overall trend was a weak mayor system where real political power was fairly evenly distributed between aldermen (who were not only the city's legislatures but were also represented on the Board of Estimate through their President), the borough presidents, the mayor, and the comptroller.
So the major players in NYC politics tended not to be mayors:

Dewitt Clinton was incredibly transformational, but despite serving three terms as mayor his real mark on New York was as governor where he was the driving force behind the construction of the Erie Canal.
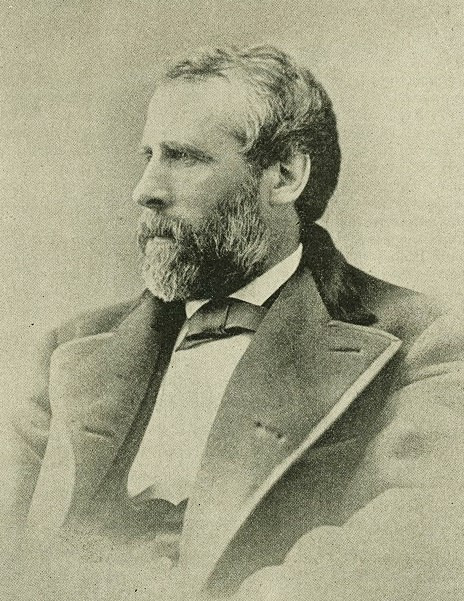

Andrew Haswell Green, the "Father of Greater New York," was responsible for the creation of Central Park, the New York Public Library, the Bronx Zoo, The Museum of Natural History, the Metropolitan Museum of Art, Riverside, Morningside, and Fort Washington Parks, Columbus Circle, and the consolidation of Greater New York - but he never served as mayor. The original Robert Moses, Green's political power came from his leadership of the Central Park Commission, the Greater New York Commission, a six-year stint in the Comptroller's office, and his position on a number of NGOs.
But if we're talking transformative mayors, there is one name that rises above all the rest: Fiorello goddamn LaGuardia.

There had been other reform mayors before him - Seth Low had established the Civil Service, John P. Mitchel brought scientific management to city government - but none of them had ever been able to get re-elected. Unlike the wealthy WASP reformers, LaGuardia knew how to beat Tammany at the ethnic politics game. Tammany's strength had always been in the Irish wards of the city, and while they had tried to divide-and-rule by promoting the naturalization of Russian and Polish Jews in return for them voting for Irish-American politicians in the Lower East Side while noticably neglecting the naturalization of Italians, the emergence of second-generation Jewish and Italian voters meant that this strategy had run its course.
Born to a Sephardic mother from Trieste and a lapsed Catholic father from southern Italy, Fiorello had an astonishing knack for transcending ethnic political boundaries in New York City - he spoke Italian, German, Yiddish, and Croatian, but he was also a progressive Republican and Episcopalian (which meant he could speak middle-class WASP too). LaGuardia won the 1933 mayoral election by bringing together a Fusion coalition that brought middle class German-American Republicans together with Italians and Jews, a coalition that he would expand in 1936 by bringing socialists, unions, and black voters together into the American Labor Party.
Over his twelve years as Mayor, LaGuardia was almost pathologically active (in a way that's oddly reminiscent of Henry II), transforming almost every aspect of New York City:
Jobs for the Unemployed:
LaGuardia's immediate mission as mayor was to fight the Great Depression that had had left a third of the City unemployed. He did this by forming an enduring alliance with FDR in which the New Deal would provide NYC with unpredecented level of federal support in exchange for NYC becoming the New Deal's model city - the first of the "Little New Deals." In his first hundred days in office, LaGuardia convinced FDR to give New York City a full 20% of the Civil Works Administration's work relief budget. This put 200,000 New Yorkers back to work - and this would only be the beginning of New York City's experiments with direct job creation.
As part of Fiorello LaGuardia's "Little New Deal," LaGuardia's new Parks Department employed 70,000 workers - paid for by CWA and later WPA money - to rebuild New York City's parks, constructing the Central Park Zoo and 60 playgrounds in the first year.
When the New Deal created the Works Progress Administration in 1935, LaGuardia once again lobbied FDR to put NYC first in line. This culminated in some 700,000 New Yorkers - a tenth of the city's entire population - getting jobs through the WPA and other New Deal programs. Together with the Parks Department, LaGuardia and Robert Moses would mobilize this workforce to completely transform the city.
Public Works:
This is where we have to discuss Fiorello LaGuardia's fateful decision to make Robert Moses his master builder. While Moses was in the process of becoming the "Power Broker" before LaGuardia - he had already been made president of the Long Island State Park Commission and chairman of the New York State Council of Parks - LaGuardia enabled his ascent to the heights of power by making him Parks Commissioner, Commissioner and then Chairman of the Triborough Bridge Authority, Commissioner of the NYC Planning Commission, and Chairman of the Emergency Public Works Commission.
The pact between them was simple: LaGuardia would give Moses the public appointments he needed to consolidate public works across the city and would steer New Deal public works money through Moses' agencies, and in exchange Moses would be LaGuardia's master builder with a mandate to "build it quickly and build it well." This was not an easy task, because Robert Moses was a political enemy of FDR and FDR tried to bar him from being given any WPA or PWA funding, but the mayor was able to persuade Roosevelt that it was more important that LaGuardia's proposed $1 billion public works program for NYC be carried at speed and administered efficiently.
As LaGuardia's workhorse, Moses would oversee almost all of NYC's public works, including the West Side Highway, the future FDR Drive, the Brooklyn Battery Tunnel, the Triborough Bridge, the LaGuardia and future JFK Airports, and Jones Beach Park, among others. LaGuardia would also construct the Sixth Avenue Subway line, the Queens-Midtown Tunnel and the Lincoln Tunnel without Moses (who was completely uninterested in mass transit and who always preferred bridges to tunnels).
In addition to these major projects, LaGuardia with and without Moses built the city's first municipal power plants, 37 sewage treatment plants, 9 fire houses, 142 elementary schools and 22 high schools, half of NYC's then-23 municipal hospitals, eight District Health Centers to provide preventative, specialized, and public health immunization care, and the first 14 of the City's public housing projects.
City Government:
To dismantle Tammany's patronage system, he began to massively expand the civil service to eliminate patronage jobs, and then when Tammany beat him on a government reform bill in 1934, he simply kept pushing. He pushed through the LaGuardia Reform Charter of 1938 that abolished the Tammany-dominated Board of Aldermen and replaced it with a City Council elected by Single Transferrable Vote, established the Board of Estimate as a central administrative body with powers over the city budget, public contracts, franchises, and land use - crippling Tammany's ability to raise money through graft and kickbacks.
To transform New York City into a "strong mayor" model, he undertook a campaign of transforming independent agencies scattered across the five boroughs into a system of unified citywide departments or public authorities that answered directly to the mayor and gave him unprecedented state capacity. In 1934, he formed the Parks Department and the New York City Housing Authority; in 1936 he formed the Department of Buildings and the City Planning Commission; in 1938, he restructured the Department of Welfare to run the city's social welfare programs and a massively expanded public hospital system; in 1940, he took over the IRT (operating the 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6), and the BMT and IND (operating the A, B, C, D, E, F, G, J, L, M, N, Q, R, W, and Z lines), unifying the NYC subway system for the first time.
To deal with police corruption, LaGuardia appointed Lewis Valentine to purge the NYPD so that the mayor could use it (and Thomas Dewey) in a crusade against the mafia's gambling, racketeering, and vice operations. This marked a rare period of honesty and effectiveness in the NYPD, although after WWII the system of protection rackets and mafia corruption would eventually re-establish itself.
Ironically, this exhaustive list of accomplishments really made it hard for later mayors to distinguish themselves, because mostly their task was completing, managing, or mis-managing the system that LaGuardia had built. After LaGuardia I would say that Robert Wagner Jr. (established public sector collective bargaining, created CUNY, Lincoln Center, Shakespeare in the Park, and dealt the killing blow to Tammany) and John Lindsay (see my previous post, but chiefly scatter-site housing, the civilian complaint review board, and the Knapp Commission on police corruption) are on my list of formative mayors.
After them, there have been long-serving mayors and good mayors, but unfortunately not the two combined.
#history#historical analysis#nyc history#nyc mayor#fiorello laguardia#tammany hall#urban history#urban studies#urban politics#political machines#new deal#robert moses#infrastructure
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
You guys! So I am on the website for the Youth America Grand Prix - which is toting itself as the world’s largest student ballet scholarship competition. And firstly, I’m astounded at the way the Master Ballet Academy swept this competition. 😆 Like I would be so salty if I had to compete against this school.
But anyway what jumped out to me is this: Each Season culminates in the week-long Season Finals where more than 1500 of the world’s most promising dancers recieve in-depth mentoring, greater scholarship and performance opportunities. The Season Finals closing night Gala, “Stars of Today meet The Stars of Tomorrow” , features the world’s most exciting young dance talent alongside the stars of today’s leading dance companies.
All I hear is Billy & Steve are going to a gala. Oh what drama might that involve. There can only be one winner. Did one of them win. How does the other one feel. Imagine poor Billy squeezed into a tux, trying to act like he doesn’t care about the stupid after party and the big whigs. But then getting star struck when Madam H. introduces him to some legend in the field who may or may not have been his first crush lol. Imagine Steve teasing him about it. “Is that a blush? Are you blushing right now?”
Imagine Billy wanting to dance with Steve, but being too afraid to. Until he sees a couple of guys take to the floor together and NOBODY says anything! Everybody’s admiring how graceful they are and having fun with it, like it’s the most natural thing in the world. That’s when it hits Billy that they don’t care. He can take his boyfriend’s hand and they can dance and no one is going to see anything but two classmates having fun.
#harringrove#ballet au#plot bunnies#but seriously imagine Harringrove at the gala#Slow dancing!!!#They’re still on the down low up until that moment#And by on the down low I mean litterally everyone has guessed that they’re fucking lol but it’s the 80s so the politely pretend
17 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hello! How are you?
I am reading about political parties during the Regency era and I have a question. Which of Austen's characters do you think are Whigs and which are Tories?
You really going to force me to relearn what Whigs and Tories were? Cruel, cruel nonnie. I'm going to cheat, this is from my favourite thesis on Jane Austen, Above the Vulgar Economy:
As Josephine Ross in Jane Austen: A Companion maintains,
The clear-cut distinctions of modern parliamentary politics had yet to emerge; and while the Whigs in the House of Commons tended to represent the interests of the aristocracy and upper classes, as well as expressing liberal ideals, the Tories – with their broad adherence to the more traditionally middle-class principles of upholding the Crown and keeping disaffection in check – were more identified with the landed gentry, and educated, but modestly situated, families such as the Austens.
At the time, the two party system was still evolving, and there was a great deal of dissention in the ranks. There were reactionaries, reformers and radical members in both parties. There were conservative, moderate and liberal Tories, and the Whig party was factionalized into Portland Whigs, Rockingham Whigs, Benthamites and Foxites to name a few.
Also, I have gotten the impression from reading other novels (eg. Wives & Daughters by Elizabeth Gaskell) from the time that often people knew which party their family voted for, but knew almost nothing else. Something that totally still happens today!
Here is another great passage:
In fact, when Pride & Prejudice was originally written as First Impressions in 1796 and 1797, Austen‟s novel appears to have been taking a stand in favor of two controversial economic proposals being debated in the House of Commons and in the press, a national minimum wage and Poor Law reform, thus Pride & Prejudice was
much more than a satire of manners but was also a political critique of Jane Austen's society. Both proposals were championed at the time by Tory Prime Minister William Pitt, the Younger and supported by liberal Tories and moderate Whigs. Both proposals were vehemently opposed by reactionary Tories and radical Whigs. The eligible bachelors in Pride & Prejudice are all associated with the Whig party, as is Lady Catherine de Bourgh, but the characters, like the Whigs in the House of Commons, have very different attitudes towards money and the working class.
Additionally, Austen's contemporaries would have known that Elizabeth Bennet's agricultural county, Hertfordshire, was, at least for the working class, the poorest county in England, just as Fitzwilliam Darcy's Derbyshire, financially stimulated by the Industrial Revolution, was the richest county, and Lady Catherine de Bourgh‟s Kent was a mixed county that varied enormously, from parish to parish, in prevailing wages and in treatment of the poor. The admirable Whig characters, like Fitzwilliam Darcy and Charles Bingley, are kindly and generous, while the radical Whig, Lady Catherine de Bourgh, is selfish and stingy, and George Wickham is simply an opportunist and a scoundrel. By its presentation of the different Whig characters, the text appears to be appealing to Whigs to be generous to the working class and encouraging Tories to look approvingly on those Whigs who are willing to financially support the poor.
Pride and Prejudice also includes a large number of characters who are servants, many identified by name. As most of them have no dialogue and do nothing to forward the plot, their presence in the novel at all may seem curious, but the depiction of the working class in Pride and Prejudice is more subtle to the modern reader than it would have been to Austen‟s original readers. The servants in Pride and Prejudice refute the assumptions of prominent Whig economists and politicians, Edmund Burke, Frederic Eden and Patrick Colquhoun, who depicted the lower class as ignorant, wasteful and immoral. Lady Catherine‟s financial neglect of the poor in Kent conforms to the economists‟ advice based on their assumptions that the working class was already adequately compensated for its labor and that poverty was the result of the irresponsible behavior of the poor. In stark contrast, Fitzwilliam Darcy‟s generosity to the poor in Derbyshire serves as a model response to poverty, and the general prosperity of Darcy‟s home county suggests that the solution to poverty is a combination of higher wages and liberal charity, exactly what the Prime Minister was proposing in 1797.
The general impression that I have gotten is that both Whigs and Tories were relatively ineffective. Anyway, a pretty clear answer for one character:
Pride and Prejudice‟s hero is almost certainly a Whig as well since the choice of the name, Fitzwilliam Darcy, is highly suggestive. Lord Fitzwilliam, later Earl Fitzwilliam, was from the north of England and, as historian William Hague describes him, one of the “Three great Earls of the Whig aristocracy”
Anywho, I'm not going to go through and sort them all since it seems fairly ambiguous who would be affiliated with which party. Also, almost everyone on earth holds some views that are extremely contradictory, so it's impossible to tell.
#question response#whigs vs. tories#someone with a better grasp on politics can answer this if they wish#I encourage everyone to read the extremely long thesis I'm quoting#It's amazing
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
Things I have asked my English boyfriend and he's said "what the fuck are you talking about" to:
1. Do you guys still use sovereigns? [No, apparently they stopped using them in ww1]
2. Do you guys still just have the whigs the tories, or do you have more political parties now? [Turns out the whigs haven't existed since 1859]
He just asked me if I'm secretly hundreds of years old
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
god the tory party just truly is absolutely fucking disgusting. a fetid heap of bigotry stitched together with the guiding policy of “if we can’t cancel it we can just make it really, really, shit.” a scourge on these nations. a party of people so overflowing with self importance that they believe all their ideas must be excellent, all their prejudices justified, because they were predestined to lead! they were meant to write these laws and give these speeches! ordained for it! they must be right! i hope they get so badly destroyed at the next election that they become a cautionary tale of political failure. i hope one day kids in history classes learn the word tory like they learn the word whig. “what a strange nickname for a party. i wonder what happened to them?”
#and for that matter i hope they all get bedbugs#lucys ramblings#i apologise for the rant it’s conference season and also i went campaigning yesterday and some guy shouted at me with his young son#next to him about the ‘’evils’’ of immigration#tories cw#uk politics#tags for ppl who don’t wanna see this stuff#most of all i hope there’s enough of the state left functioning that we can fix most of their mess. and that we don’t forget what they’ve#ruined beyond repair
23 notes
·
View notes
Note
Propaganda for George IV: Prinny hated Napoleon too! Prinny hated Napoleon so much he kept his father's Tory government instead of bringing in the Whigs who would have ended the war in 1812. Prinny made his maiden speech in the House of Lords wearing pink high heels and spangles. Did Madame de Staël throw a banquet with a stream full of live fish running down the table? Did she design her own clothes? Did she remodel London and turn Buck House into Buckingham Palace? How many beautiful public parks did she create? Prinny cared so much about fashion he once bought thirty-two walking sticks in one day! He made kilts cool again. He once wore so many rings he couldn’t sign papers. He played the cello. Madame de Staël? Boring. You like the Lawrence portraits of the heads of the coalition forces? You like the fact that Wellington had a giant statue of Napoleon in his hall? You like high cravats? Lover's eye miniatures? You like parties and bling? You like fun? Vote for George IV!
.
17 notes
·
View notes
Note
Is Trump the first person to run for president three different times?
No, there have been numerous people through the history of the United States who have run for President three or more times, but most of them didn't get their party's nomination.
Interestingly, a lot of people forget that the 2024 election is actually Joe Biden's fourth, full-fledged, formal Presidential campaign, in addition to Trump's third campaign. Biden unsuccessfully sought the Democratic nomination in 1988 and 2008 before finally winning the nomination and general election in 2020. Ronald Reagan first ran for President in 1968 when he jumped into the race for the Republican nomination as an alternative to Richard Nixon, but it was kind of a half-hearted, late bid and Reagan later admitted that he wasn't quite ready to run for President at that point, which was only about a year into his tenure as Governor of California. Reagan challenged incumbent President Ford for the Republican nomination in 1976 and very nearly pulled off a rare intraparty defeat of a sitting President from his own party. And of course, Reagan ran and won in 1980 and 1984.
It's not just a relatively recent phenomenon, either; candidates have been running for President three or more times for as long as the Presidency has existed. Thomas Jefferson sought the Presidency in 1796 , 1800, and 1804, and there are many more examples, including Ulysses S. Grant, who was the first former President to make a serious attempt at breaking George Washington's tradition of serving two terms and then retiring. Grant won Presidential elections in 1868 and 1872, and allowed his supporters to actively work for his nomination at the 1880 Republican National Convention after President Hayes retired without seeking a second term. Grant was the frontrunner for the nomination, but once the balloting for the nominee started, the convention became deadlocked between Grant and James G. Blaine -- another person who ran for President multiple times: 1876, 1880, and 1884 (when he was nominated, but lost the general election). On the thirty-sixth ballot, the Republicans finally nominated James Garfield, who had emerged as a compromise candidate.
It is less common for someone to be a major party nominee for President on three or more occasions, which Trump has a shot of being in 2024 if he's not in prison. However, it is still not unprecedented. Obviously, Franklin D. Roosevelt won four Presidential elections (1932, 1936, 1940, and 1944), which had never happened before and will never happen again unless the Constitution is amended. William Jennings Bryan was the Democratic nominee in 1896, 1900, and 1908, and lost all three times. Grover Cleveland won the Democratic nomination in three straight elections: 1884 (which he won), 1888 (which he lost), and 1892 (which he won). Trump is hoping to join Cleveland as the only Presidents to serve two non-consecutive terms. Henry Clay was his party's nominee on three different occasions, and lost all three times. In an odd quirk of the times, because the major political parties were still in the process of forming in the first half of the 19th Century, Clay was technically the Presidential nominee for three different political parties: Democratic-Republican in 1824, National Republican in 1832, and Whig in 1844. Martin Van Buren was elected President as the Democratic nominee in 1836 and renominated in 1840, but lost the general election, After breaking with his party over the spread of slavery to new American territories, former President Van Buren ran as the Free Soil nominee in 1848, but came in third in the general election behind Zachary Taylor and Lewis Cass. And, one more recent example would be Richard Nixon, who was the 1960 Republican Presidential nominee and narrowly lost the general election in John F. Kennedy. Despite the belief that his political career was finished -- particularly after a humiliating loss in the 1962 campaign for Governor of California -- Nixon won the Republican nomination again in 1968 and 1972 and went on to win the general election both times (as well as winning 49 out of 50 states in 1972).
(I'm sorry...I understand that was a long-winded, overly-detailed way of answering your question when I also could have just said, "No.")
#Presidents#Presidential Elections#Presidential Politics#Presidential Nominees#Presidential Campaigns#History#Politics#Political History#Presidential History#Campaigns#Elections
26 notes
·
View notes