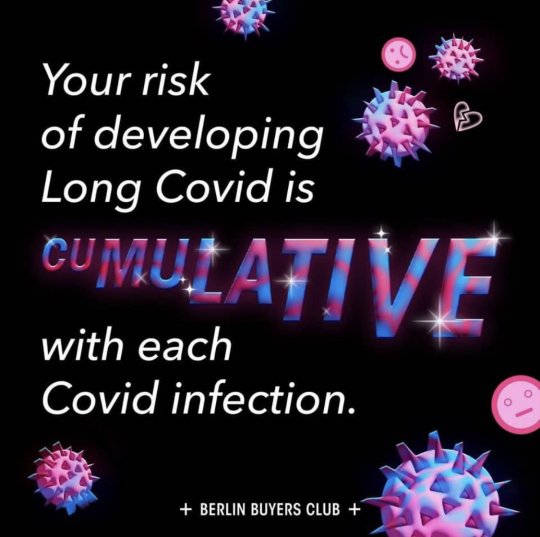
#sars cov 2
Text
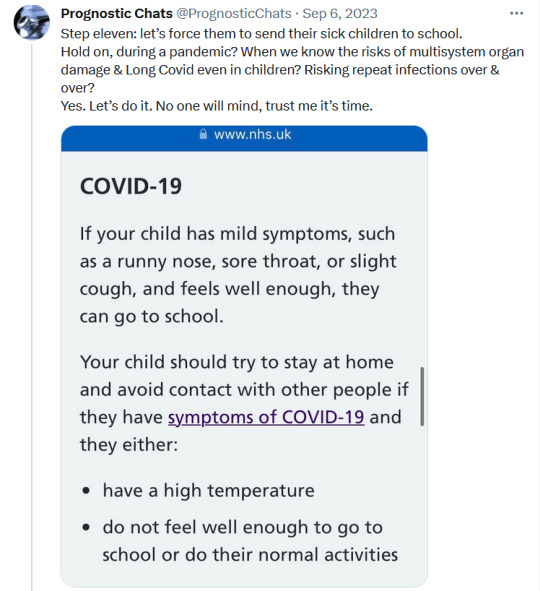
If you have a cold and test negative for COVID you are not in the clear. Tests take a while to turn positive. Meanwhile you are spreading COVID to family and friends. Mask up if you have any symptoms. This virus is just evil.
20K notes
·
View notes
Text
tumblr just nuked @milf-adjacent's blog with zero warning, no explanation from staff or e-mail whatsoever. her blog has been a vital resource for documenting COVID-19, and she did nothing ban worthy. she seems to be another target of the transmisogyny being carried out by staff.
#covid 19#covid pandemic#mask up#sars cov 2#covid isn't over#tags for spreading the word#please get it out there!!#milf-adjacent
6K notes
·
View notes
Text




Futurama S11E07
#sigh.#sars cov 2#covid 19#futurama#gotta love how they are once again downplaying the seriousness of the developing h5n1 situation too#definitely not concerning that many mammals in the wild are being infected by birds#and definitely not concerning that cows and chickens are being infected now#and about 3 detected cases in humans (so far)#it's nothing serious anyway - it's not like viruses can keep spreading and mutating if left to spread without appropriate mitigations!#that's never happened before! it's definitely not happening with anything else right now!#''ABC'' right????#so weird and ''random'' that cases of rsv flu tuberculosis mpox measles are popping up constantly everywhere these days right??#love this new normal!!!#ppl continue killing and disabling themselves and other ppl and FOR WHAT#FOR FUCKING WHAT
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
disabled people: we are still dying, can you please just wear a mask to the grocery store and doctor’s offices so we can live
conservatives: no, die or stay inside all day, no one cares
leftists: no 🏳️🌈✨💖
#wear a mask#covid#sars cov 2#disability rights#eugenics#disability pride month#lgbt#it really is like this :')#queer#pandemic#ableism#disabled queer#auspol#me not ever being able to share the same air with anyone ever really does something to your mental health#trying not to die in the ongoing pandemic#wear a fucking mask#we would actually like to access third spaces too#we just lost 100 years of disease prevention bc govt propaganda worked a little too well and gave every single medical person brain rot#they went from 'do no harm' to 'actually i think you should quit complaining and allow me to kill you with airborn aids'#which is happening EVERYWHERE BTW and it made it to the media that an aust hospital COVERED IT UP like this is what we're dealing with#this is what modern day eugenics looks like and no one gives a shit#Ableism#HAPPY NEW YEAR#pride#LGBTQIA#activism#acab
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Covid minimzers be like "where's the wealth of evidence that covid is getting worse" while being completely ignorant of the absolute wealth of covid studies being published each day, none of them saying "covid is like the flu now."
#covid#pandemic#covid 19#covid isn't over#mask up#covid conscious#covid19#wear a mask#long covid#covid-19#sars cov 2
969 notes
·
View notes
Text

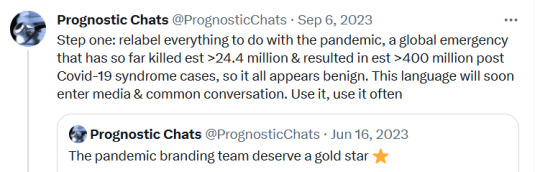

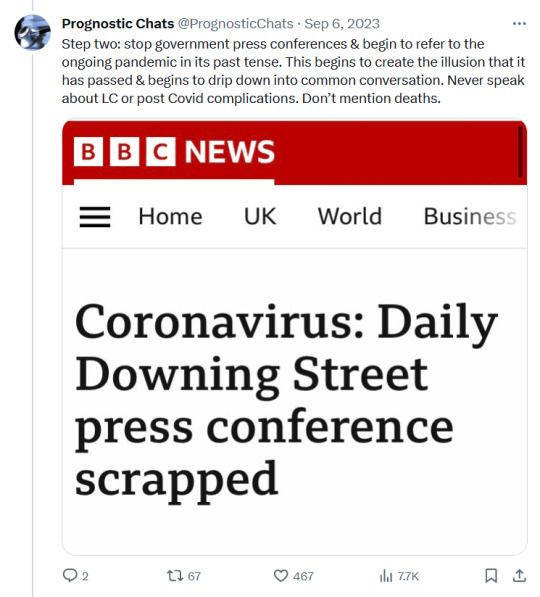


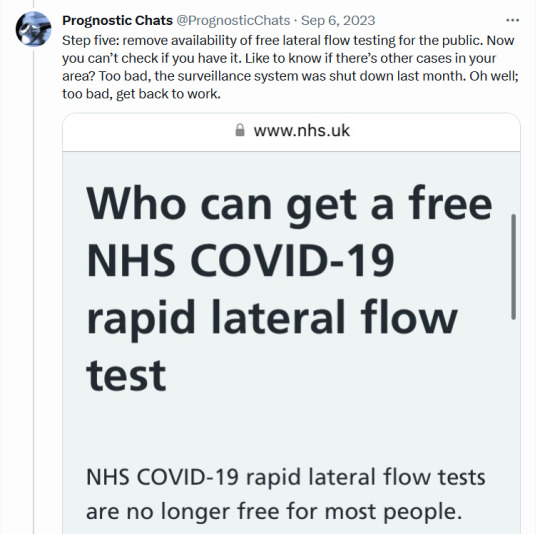


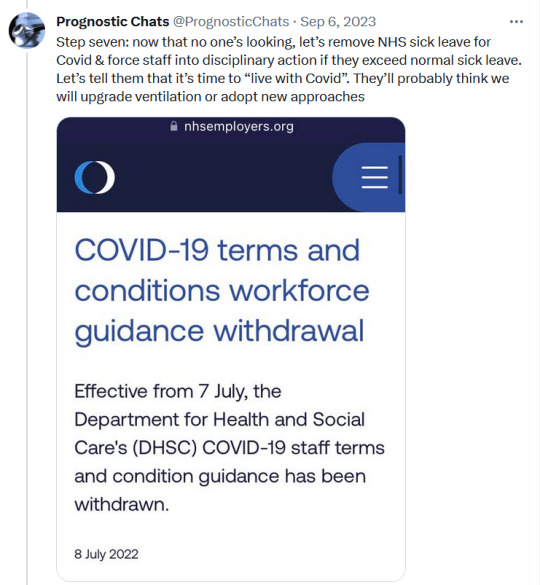
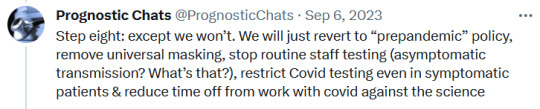

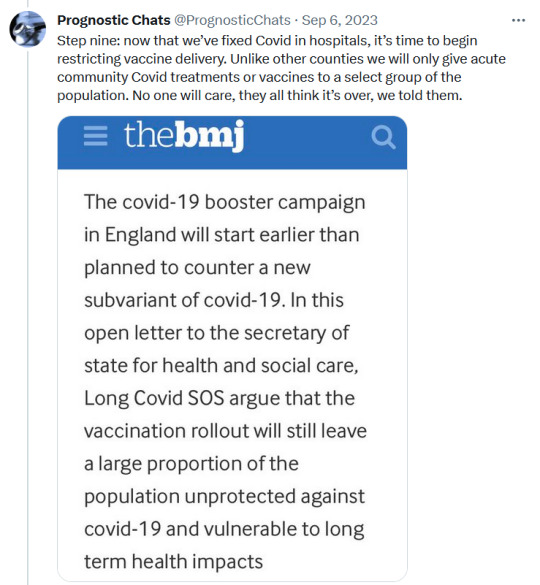
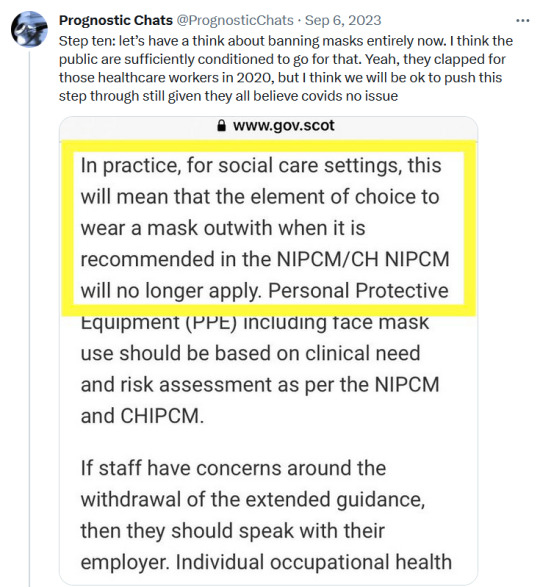



#sars cov 2#covid isnt over#pandemic isnt over#wear a mask#wear a fucking mask#alt text covid#world issues#disability rights#disability justice#important#nonfiction
937 notes
·
View notes
Text

#covid 19#covid#covid isn't over#communism#anti capitalism#socialism#anarchy#leftism#sars cov 2#long covid#i think i hauve covid#mask up#pandemic#hood#mask girl#mask kink#mask k!nk#mask k1nk#covid masks#cdc#paxlovid#covid19#covid pandemic#covid is not over
258 notes
·
View notes
Text
Now we know how COVID attacks your heart
Even patients with mild COVID symptoms could face a higher risk of developing heart disease and stroke
By Sanjay Mishra Nov 07, 2023 04:08 PM 5 min. read
Scientists have noticed that COVID-19 can trigger serious cardiovascular problems, especially among older people who have a buildup of fatty material in their blood vessels. But now a new study has revealed why and shown that SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, directly infects the arteries of the heart.
The study also found that the virus can survive and grow inside the cells that form plaque—the buildup of fat-filled cells that narrow and stiffen the arteries leading to atherosclerosis. If the plaque breaks, it can block blood flow and cause a heart attack or a stroke. The SARS-CoV-2 infection makes the situation worse by inflaming the plaque and increasing the chance that it breaks free.
This can explain long-term cardiovascular effects seen in some, if not all, COVID-19 patients.
SARS-CoV-2 virus has already been found to infect many organs outside the respiratory system. But until now it hadn't been shown to attack the arteries.
"No one was really looking if there was a direct effect of the virus on the arterial wall," says Chiara Giannarelli, a cardiologist at NYU Langone Health, in New York, who led the study. Giannarelli noted that her team detected viral RNA—the genetic material in the virus—in the coronary arteries. “You would not expect to see [this] several months after recovering from COVID.”
Mounting evidence now shows that SARS-CoV-2 is not only a respiratory virus, but it can also affect the heart and many other organ systems, says Ziyad Al-Aly, a clinical epidemiologist at Washington University in St. Louis. Al-Aly's research has shown that the risk of developing heart and cardiovascular diseases, including heart failure, stroke, irregular heart rhythms, cardiac arrest, and blood clots increases two to five times within a year of COVID-19, even when the person wasn't hospitalized.
"This important study links, for the first time, directly the SARS-CoV-2 virus with atherosclerotic plaque inflammation," says Charalambos Antoniades, chair of cardiovascular medicine at the University of Oxford, United Kingdom.
Virus triggers the inflammation in plaque
A recent study of more than 800,000 people led by Fabio Angeli, a cardiologist at University of Insubria in Varese, Italy, has shown that COVID-19 patients develop high blood pressure twice as often as others. More worrying is that the risk of cardiac diseases can also rise for patients who suffered only mild COVID symptoms.
"I saw a patient who now has a defibrillator, and she didn't even have a severe [COVID] illness," says Bernard Gersh, a cardiologist at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota.
Wondering whether the cardiovascular damage during COVID was due to the virus directly attacking the blood vessels, the NYU team analyzed autopsied tissue from the coronary arteries and plaque of older people who had died from COVID-19. They found the virus was present in the arteries regardless of whether the fatty plaques were big or small.
"The original finding in this study is that the virus was convincingly found in the plaque in the coronary artery," says Juan Carlos Kaski, a cardiovascular specialist at St George's, University of London, who was not involved in the study.
The NYU team found that in the arteries, the virus predominantly colonized the white blood cells called macrophages. Macrophages are immune cells that are mobilized to fight off an infection, but these same cells also absorb excess fats—including cholesterol from blood. When microphages load too much fat, they change into foam cells, which can increase plaque formation.
To confirm that the virus was indeed infecting and growing in the cells of the blood vessels, scientists obtained arterial and plaque cells—including macrophages and foam cells—from healthy volunteers. Then they grew these cells in the lab in petri dishes and infected them with SARS-CoV-2.
Giannarelli found that although virus infected macrophages at a higher rate than other arterial cells, it did not replicate in them to form new infectious particles. But when the macrophages had become loaded with cholesterol and transformed into foam cells, the virus could grow, replicate, and survive longer.
"We found that the virus tended to persist longer in foam cells," says Giannarelli. That suggests that foam cells might act as a reservoir of SARS-CoV-2. Since more fatty buildup would mean a greater number of foam cells, plaque can increase the persistence of the virus or the severity of COVID-19.
Scientists found that when macrophages and foam cells were infected with SARS-CoV-2 they released a surge of small proteins known as cytokines, which signal the immune system to mount a response against a bacterial or viral infection. In arteries, however, cytokines boost inflammation and formation of even more plaque.
"We saw that there was a degree of inflammation [caused] by the virus that could aggravate atherosclerosis and cardiovascular events," says Giannarelli.
These findings also confirm previous reports that measuring inflammation in the blood vessel wall can diagnose the extent of long-term cardiovascular complications after COVID-19, says Antoniades.
"What this study has found is that plaque rupture can be accelerated and magnified by the presence of the virus," says Kaski.
Understanding heart diseases after COVID
While this new research clearly shows that SARS-CoV-2 can infect, grow, and persist in the macrophages of plaques and arterial cells, more studies are needed to fully understand the many ways COVID-19 can alter cardiac health.
"The NYU study identifies one potential mechanism, especially the viral reservoir, to explain the possible effects" says Gersh. "But It's not going to be the only mechanism."
This study only analyzed 27 samples from eight elderly deceased patients, all of whom already had coronary artery disease and were infected with the original strains of virus. So, the results of this study do not necessarily apply to younger people without coronary artery disease; or to new variants of the virus, which cause somewhat milder disease, says Angeli.
"We do not know if this will happen in people who have been vaccinated," says Kaski. "There are lots of unknowns."
It is also not clear whether and to what extent the high inflammatory reaction observed in the arteries of patients within six months after the infection, as shown in the new study, will last long-enough to trigger new plaque formation. "New studies are needed to show the time-course of the resolution of vascular inflammation after the infection," says Antoniades.
COVID patients should watch for any new incidence of shortness of breath with exertion, chest discomfort, usually with exertion, palpitations, loss of consciousness; and talk to their physician about possible heart disease.
374 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Weather
In the US, 41 out of 54 states and territories are at high or very high COVID wastewater levels as of 1/18/2024. Ten states and territories have no data available. It’s important to note that levels of “moderate,” “low,” or “minimal” do not necessarily indicate a low risk of COVID exposure in our daily lives. Viral spread is still ongoing even if at lower levels, and precautions are warranted to protect ourselves and others.

Looking at the CDC’s national and regional wastewater data over time, we continue to see “Very High” levels nationally. It’s important to note that the last two weeks are provisional data, indicated by a gray shaded area on the graph, meaning that those values can change as additional wastewater sites report data.
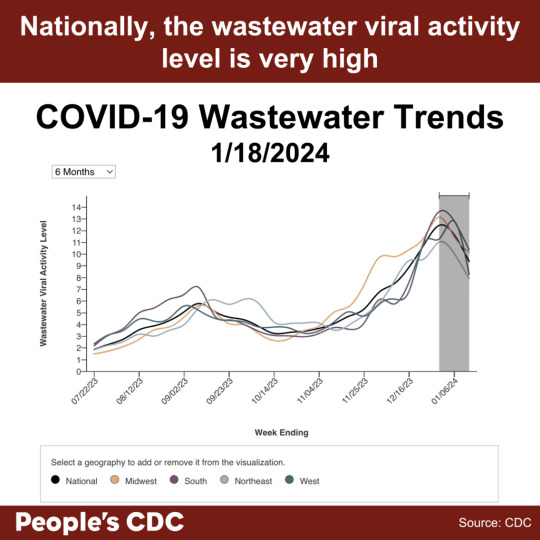
Although wastewater data does not provide the same level of detail as previous PCR-based testing data, wastewater monitoring is an important ongoing resource to inform us about the current COVID situation. While the provisional data tentatively shows a downward trend this week, time will tell whether this is a true decrease in the final data. A downward trend does not mean continued decreases are guaranteed or that protections should be relaxed. Multilayered protections help drive COVID spread lower, and relaxing protections can lead to a resurgence of viral spread.
Visit the CDC’s State and Territory Trends page to see available wastewater testing near you, including the number of wastewater sites reporting. Write your elected officials to let them know you want to keep and expand wastewater testing in your area and nationally.
Wins
In November 2023, the CDC’s Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee (HICPAC) passed a series of draft proposals that will further weaken already insufficient protocols employed within healthcare settings. HICPAC refuses to reckon with the airborne nature of infectious diseases such as SARS-CoV-2, and does not propose crucial measures such as universal masking with well-fitted respirators, isolation periods, and ventilation. The People’s CDC has penned a letter to the ACLU alerting them of HICPAC’s irresponsible decisions, and the ramifications associated with them. We hope that by working together with the ACLU, we can implement public advocacy and legal actions in order to tackle this critical issue.
You can read the full letter here.
Johns Hopkins reinstated healthcare masking on 1/12/2024, in response to high respiratory virus levels. As with many other healthcare systems and public health departments that have restored healthcare masking when facing public pressure, we hope that universal masking can become a standard of care rather than a short term response to a surge. See “Take Action” below for more information.
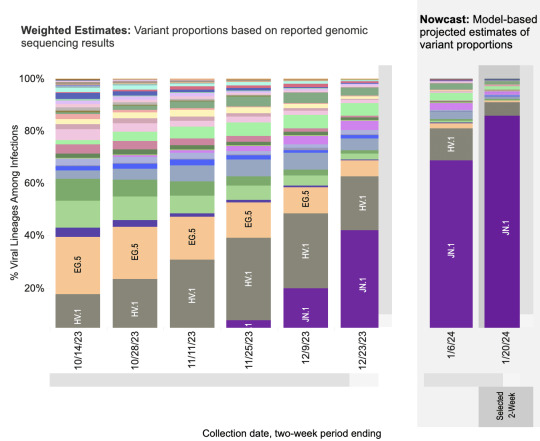
Variants
JN.1, now the most prominent variant in the United States, is estimated to account for 85.7% of circulating variants by 1/20/2024. HV.1 is expected to drop to 5.3%, and all other variants are estimated to make up less than 2% each. Although ongoing viral spread allows opportunities for new variants to emerge, the latest 2023-2024 COVID vaccine boosters, COVID tests, and COVID treatments are still expected to be effective for JN.1.
Current updated booster uptake is low (as of January 19, 2024, the CDC reports that only 21.5% of adults and 11% of children have received it). It is not too late to get the updated booster, and to protect yourself against the latest variant!
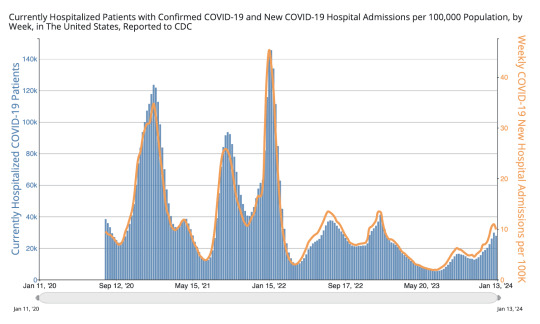
Hospitalizations
In the most recent week (ending January 13, 2024), we see a slight downward trend in new hospital admissions, currently at 32,861. We see a similar slight downtick in currently hospitalized patients with COVID , at 27,879. This most recent week shows a slight decrease in hospitalizations, although it is too soon to say whether hospitalizations for the current surge have passed their peak. Hospitals continue to be overwhelmed. The data also lacks information on hospital-acquired infections. We urge you to continue taking stringent precautions, such as donning a well-fitting respirator (e.g., N95, KN95) in all indoor spaces–and especially in healthcare settings.
Long COVID
Amid ongoing advocacy by Long COVID groups, the US Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions (HELP) held a committee hearing on “Addressing Long COVID: Advancing Research and Improving Patient Care.” The hearing included testimony from three Long COVID patients and four Long COVID physicians and researchers, bringing much-needed attention to the urgent need for funding for Long COVID research and treatments, and to the need for improved access to care for Long COVID patients. We recognize the community care modeled by some of the panelists and attendees who wore masks for the hearing, and we wish the senators on the committee would mask up as well.
Take Action
Write your elected officials to let them know that Long COVID impacts all of us, and that we need ongoing support for Long COVID research and clinical care. Ask Senators to support bill S.2560, the Long COVID Support Act. Ask Representatives to support bills HR.1114 (Long COVID RECOVERY NOW Act) and HR.3258 (TREAT Long COVID Act).
Although some healthcare settings have reinstated masking in response to high COVID levels along with high respiratory virus activity, ongoing pressure is needed to restore, keep, and expand masking broadly. Use our letter template and toolkit to call or write your elected officials in support of healthcare masking.
Want to do more to support healthcare masking? Consider starting, sharing, or joining a local campaign. Check out work in Illinois, Maryland, and Wisconsin, just to name a few. Also, sign and share our letter to the ACLU asking them to join us in supporting safe and equitable access to healthcare. Sign on is open until 2/1/2024.
#op#covid#covid pandemic#covid news#covid 19#covid-19#covid isn't over#covid19#mask up#coronavirus#pandemic#people's cdc#pcdc#long covid#sars cov 2#sars-cov-2#coronavirus pandemic#wear a mask#covid variant#covid variants#covid vaccine#get vaccinated#covid vaccines#medical#disability#uspol#img#links#to read#described in alt text
184 notes
·
View notes
Text
Respiratory distress in SARS-CoV-2 exposed uninfected neonates followed in the COVID Outcomes in Mother-Infant Pairs (COMP) Study
Top 5 Takeaways
High Rates of Respiratory Distress in Exposed Uninfected Neonates: The study found unusually high rates (17%) of respiratory distress (RD) in SARS-CoV-2 exposed uninfected (SEU) term neonates.
Maternal COVID-19 Vaccination Reduces Neonatal RD: Maternal vaccination against COVID-19 significantly reduced the frequency of neonatal RD, with a 67% decline in the odds of RD in neonates born to vaccinated mothers compared to those born to unvaccinated mothers.
Proteomic Analysis Reveals Inflammatory Response: Proteomic analysis indicated a robust inflammatory response in SEU neonates with RD, involving pathways like ciliary dysregulation and enhanced IgE production.
Demographic and Clinical Factors: The study enrolled 221 pregnant persons with COVID-19 and 227 exposed fetuses. It highlighted the correlation of RD with factors like maternal disease severity, prematurity, and the absence of maternal COVID-19 immunization.
Th2-Skewed Immune Response in SEU Neonates: SEU preterm infants with RD showed a Th2-skewed immune response, indicated by elevated levels of certain cytokines and the inhibition of FC gamma receptors.
Original Article Author and Citation
Olivia M. Man, Tamiris Azamor, Mary Catherine Cambou, Trevon L. Fuller, Tara Kerin, Sophia G. Paiola, Jessica S. Cranston, Thalia Mok, Rashmi Rao, Weiqiang Chen, Jae U. Jung, Viviana Fajardo Martinez, Suan-Sin Foo, Karin Nielsen-Saines
Suggested Citation
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-44549-5
Summary
The study aimed to understand the impact of prenatal COVID-19 exposure on neonatal respiratory distress (RD). A high incidence of RD was observed in SEU neonates, and maternal vaccination notably reduced this risk. Proteomic analysis suggested a strong inflammatory response in these neonates.
Methods
The research employed a longitudinal cohort study approach, enrolling mothers with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 during pregnancy and their exposed fetuses. Various demographic, clinical, and proteomic analyses were used to understand the complex relationship between maternal COVID-19 parameters and infant RD.
Discussion
The findings highlight the protective role of maternal COVID-19 vaccination in reducing neonatal RD. The study also revealed a Th2-skewed immune response in SEU neonates with RD, suggesting potential long-term implications, including the development of allergic processes and pulmonary fibrosis.
Conclusion
Maternal vaccination against COVID-19 significantly decreases the risk of neonatal RD in SEU infants. The study underscores the importance of maternal vaccination for reducing neonatal morbidity and improving long-term infant health.
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
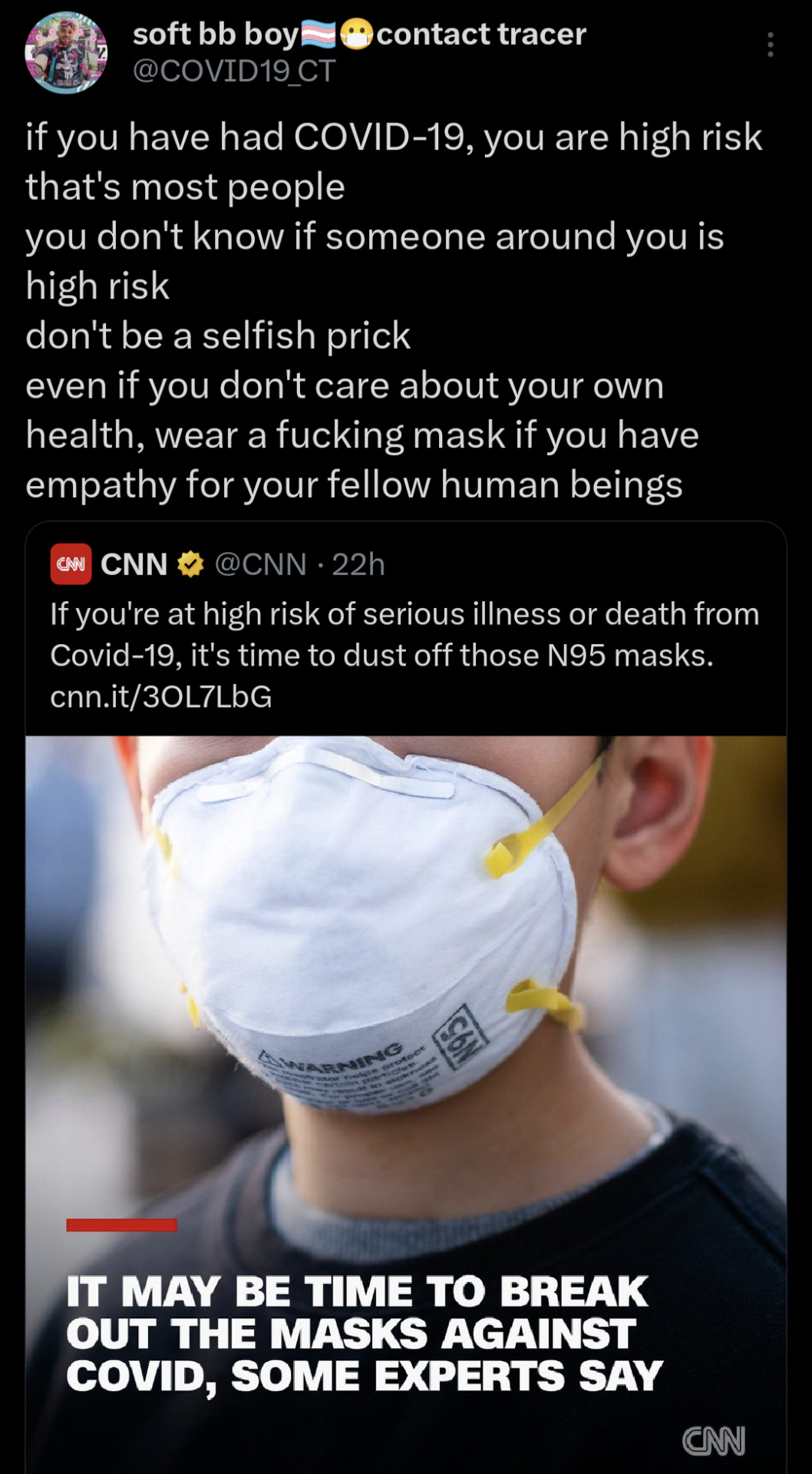
newsflash dipshits: you should have been wearing a n95 mask this whole fucking time!!!!!!
if you didn't, you either didn't care about high risk people or lied to yourself saying that you were never in danger from the level 3 airborne biohazard that you have been huffing since 2020
#wear a mask#mask up#gas mask#mask#masks#face mask#covid#covid19#sars cov 2#coronavirus#airborne#biohazard
63 notes
·
View notes
Text


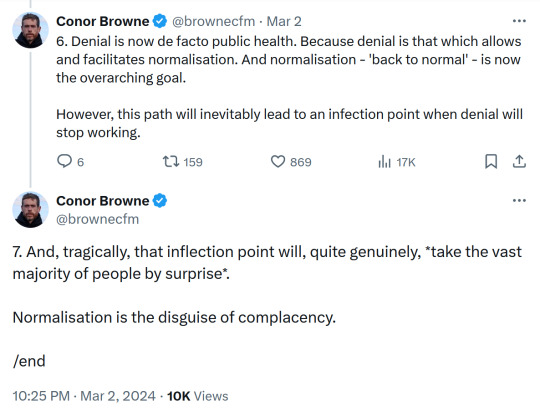
"The long-term effects of [the covid-19 pandemic]... are accumulating slowly enough to be normalised."
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

Solidarity = True Love
Wearing a Mask = True Love
Resisting Mass Death = True Love
#wear a mask#covid#pandemic#sars cov 2#disability justice#disability rights#eugenics#community care#community solidarity#antifa#n95#protect yourself and the ones you love by not disabling or killing them with SARS#there's no cure for long covid#chronic illness#wear a fucking mask#lgbtq community#disabled queer
49 notes
·
View notes
Text

"pandemic era" "during covid" etc. etc. what do you mean. WHAT DO YOU MEAN.
#sars cov 2#now? do you mean NOW??????#golly gee i wonder what was happening in between March '22 and '23 that made that number TRIPLE
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
hiiiiii covid tumblr😷
some of my very close friends in our local mask bloc are working with ~30 other mask blocs across the US to raise money to purchase 360,000 masks to give away to our communities for FREE! (more details under the cut if you’re interested)
so far they’re raised $10,265 out of the $18,000 goal!! If you’re able to contribute, please do so at gofundme and please share with your friends!! any $ amount is hugely appreciated!!
this purchase will be coming from a large government surplus sale, as part of the pattern of governments getting rid of their Covid protection supplies because they don’t care enough to have precautions anymore! gov surplus sales provide a huuuge deal bc of the quantity & desire to get rid of stuff as soon as possible, BUT this also means there’s only so many surplus sales left since governments are no longer buying more masks. and that’s a big part of why this purchase is so important, because there may not be many more large surplus deals after this one!!
#covid#covid 19#covid conscious#covid is airborne#covid pandemic#covid isn't over#mask up#sars cov 2#pandemic#mask bloc#mutual aid#disability justice
18 notes
·
View notes