#lobbyists
Text

We need to end lobbyism as we know it. Corporate bribery is the worst way to provide a human right like health care.
Sad that $800 million/year in bribes costs us $650 billion/year in savings.
22K notes
·
View notes
Text

2K notes
·
View notes
Text


THIS WEEK, WASHINGTON’S top Israel lobby is rallying its supporters to go to Capitol Hill and falsely claim to lawmakers that people aren’t starving in Gaza and Israel isn’t blocking aid shipments, according to talking points obtained by the American Prospect.
Israel has led a brutal siege on Gaza since Oct. 7, when Hamas killed 1,139 Israelis and kidnapped more than 200. More than 31,000 Palestinians have been killed, 2 million have been internally displaced, and hundreds of thousands are at imminent risk of famine, according to the United Nations.
The powerful lobbying group American Israel Public Affairs Committee, or AIPAC, is working to maintain support for Israel’s war, amid increased protests and public outcry. This week, AIPAC convened in Maryland for its annual policy conference, which it uses to marshal its donors and supporters to serve as a grassroots lobbying army in the halls of Congress.
The Prospect obtained a copy of AIPAC’s talking points for supporters heading to the Hill — and they are extreme, to say the least. The documents instruct supporters to claim that “reports that people are starving in Gaza are false,” and say that “Israel is not blocking the delivery of aid to Gaza.”
The AIPAC talking points additionally claim that Hamas wants people to believe Gazans are starving in order to “exert pressure” on Israel, and argues the “United States must not fall into Hamas’ trap.”

These claims from AIPAC are false. Gazans are starving on a massive, unprecedented scale. According to the United Nations, 2.2 million Palestinians in Gaza — almost the entire population of the region — are facing “crisis or worse levels of food insecurity.” Half a million of those included in that figure face “catastrophic” levels of food insecurity.
The Integrated Food Security Phase Classification (IPC) — a leading food security analysis and advocacy group — classifies the Gaza Strip as being in Phase 4 “Emergency” status food insecurity, with a high risk of imminent famine conditions.
(continue reading)
439 notes
·
View notes
Text
The NDP alone are opposing proposed changes to federal rules around lobbying, which would allow lobbyists to raise funds for a politicians campaign, while lobbying that politician at the same time.
“This is one of the most unethical things that MPs have done in the past 30 years, and it will allow favour-trading between lobbyists and politicians that will corrupt all future federal policy-making processes,” Duff Conacher, Co-founder of Demeocracy Watch. Democracy Watch is a national non-profit organization dedicated to government accountability and democratic reform.
[...]
Other than the NDP, all parties approved the Commissioner’s proposed new Lobbyists’ Code that will allow lobbyists to influence politicians and party leaders soon after fundraising or campaigning for them.
Full article
Tagging: @politicsofcanada
#cdnpoli#canadian politics#canadian news#canadian#canada#lobbyists#political fundraising#ethics#corruption#NDP
318 notes
·
View notes
Text



x
#401(k)#savings#tax-advantaged retirement#bipartisan legislation#wealth gap#federal budget#financial industry#lobbying#retirement security#tax law#retirement savings#bipartisan#wealth disparities#federal deficit#financial services industry#tax-advantaged accounts#tax breaks#Congress#lobbyists#Social Security#Medicare
15 notes
·
View notes
Text

#us politics#2022#twitter#tweet#republicans#conservatives#gop#us supreme court#scotus#ginni thomas#justice clarence thomas#national defense authorization act#state secrets#lobbyists#jane mayer
207 notes
·
View notes
Text

Are capitalists and their lobbies doing actual work?
#Are capitalists and their lobbies doing actual work?#capitalism#anti capitalist#lobbies#lobbying#lobbyists#capitalist hell#capitalist dystopia#capitalist bullshit#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government#wage slavery#slavery#slave wages#slaves#slave#employment#employees#employers#eat the rich#eat the fucking rich#class war
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
#i love this person they are honestly the only one whos managed to explain this properly#dnc#democrats#republicans#politics#tiktoks#capitalism#lobbying#lobbyists
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
A beef industry group is running a campaign to influence science teachers and other educators in the US. Over the past eight years, the American Farm Bureau Foundation for Agriculture (AFBFA) has produced industry-backed lesson plans, learning resources, in-person events, and webinars as part of a program to boost the cattle industry’s reputation.
Beef has one of the highest carbon footprints of any food, but AFBFA funding documents reveal that the industry fears that science teachers are exposed to “misinformation,” “propaganda,” and “one-sided or inaccurate” information. The campaign from the AFBFA—a farming-industry-backed group that "educates" Americans about agriculture—is an attempt to fight back and leave school teachers with a “more positive perception” of the beef industry, the funding documents reveal.
According to survey data included in these documents, educators who attended at least one of the AFBFA’s programs were 8 percent more likely to trust positive statements about the beef industry. Some 82 percent of educators who participated in a program had a positive perception of how cattle are raised, and 85 percent believed that the beef industry is “very important” to society.
The beef industry “knows it has a trust issue,” says Jennifer Jacquet, a professor of environmental science and policy at the University of Miami. The industry is attempting to influence public opinion by starting with children, says Jan Dutkiewicz at the Pratt Institute’s Department of Social Science and Cultural Studies. Dutkiewicz points out that one of the AFBFA’s objectives outlined in its most recent funding document is to run events that “engage educators and students … to increase their understanding and positive perceptions of the beef industry.”
...
The AFBFA is a contractor to Beef Checkoff, a US-wide program in which beef producers and importers pay a per-animal fee that funds programs to boost beef demand in the US and abroad. In 2024, Beef Checkoff has approximately $42 million to disperse across its initiatives, and a funding request reveals that the AFBFA’s campaign for 2024 is projected to cost $800,000. The allocation of Beef Checkoff funding to programs like this is approved by members of the Cattlemen’s Beef Board and the Federation of State Beef Councils, two groups that represent the cattle industry in the US.
One lesson plan provided as part of the program directs students to beef industry resources to help devise a school menu. In another lesson plan students are directed to create a presentation for a conservation agency regarding the introduction of cattle into their ecological preserve. A worksheet aimed at younger students has them practice their sums by adding up the acreage of cow pastures. Another worksheet based around a bingo game aimed at 8- to 11-year-olds asks teachers to “remind students that lean beef is a nutritions source of protein that can be incorporated in daily meals.”
Science teachers in many states are currently updating their lessons to incorporate the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS)—a set of teaching guidelines that encourage educators to place more emphasis on how science is used in the real world. AFBFA funding documents show that the foundation intends to use the adoption of the NGSS as an opportunity to provide teachers with learning materials that relate to the beef industry.
“Furthermore, NGSS requires teachers to approach challenging topics such as climate change and sustainability,” reads an AFBFA funding authorization request for its education program. It continues: “Teachers and students are receiving information from educationally trusted sources that do not represent agriculture accurately or in a balanced way, and beef production is often the target of "misinformation". To achieve balance and to ensure the accuracy of information, a concerted effort must be made to engage teachers in the conversation around these topics.”
Dutkiewicz says that food production should be taught in US schools but that industry-funded material is unlikely to provide objective information about the impact of beef production. “I worry that clearly partial resources that are strategically designed to achieve a corporate messaging are being provided by a Checkoff program,” he says.
#enviromentalism#ecology#Beef industry#cattle#livestock industry#meat industry#livestock#lobbyists#corporate lobbying#American farm Bureau Foundation for agriculture#AFBFA#Cattle industry#Cattlemen Beef Board#Beef lobby
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

Capitalism kills. Lobbyists kill.
Using DEI and 'woke' to describe decades of short-sighted and greedy capitalism is perverse.
Lobbyism is bribery.
422 notes
·
View notes
Text
For many cooks, waiters and bartenders, it is an annoying entrance fee to the food-service business: Before starting a new job, they pay around $15 to a company called ServSafe for an online class in food safety.
That course is basic, with lessons like “bathe daily” and “strawberries aren’t supposed to be white and fuzzy, that’s mold.” In four of the largest states, this kind of training is required by law, and it is taken by workers nationwide.
But in taking the class, the workers — largely unbeknown to them — are also helping to fund a nationwide lobbying campaign to keep their own wages from increasing.
The company they are paying, ServSafe, doubles as a fund-raising arm of the National Restaurant Association — the largest lobbying group for the food-service industry, claiming to represent more than 500,000 restaurant businesses. The association has spent decades fighting increases to the minimum wage at the federal and state levels, as well as the subminimum wage paid to tipped workers like waiters.
The federal minimum wage has risen just once since 1996, to $7.25 from $5.15, while the minimum hourly wage for tipped workers has been $2.13 since 1991. Minimums are higher in many states, but still below what labor groups consider a living wage.
For years, the restaurant association and its affiliates have used ServSafe to create an arrangement with few parallels in Washington, where labor unwittingly helps to pay for management’s lobbying. First, in 2007, the restaurant owners took control of a training business. Then they helped lobby states to mandate the kind of training they already provided — producing a flood of paying customers.
More than 3.6 million workers have taken this training, providing about $25 million in revenue to the restaurant industry’s lobbying arm since 2010. That was more than the National Restaurant Association spent on lobbying in the same period, according to filings with the Internal Revenue Service.
That $25 million represented about 2% of the National Restaurant Association’s total revenues over that same period, but more than half of the amount its members paid in dues. Most industry groups are much more reliant on big-dollar donors or membership support to meet their expenses. Most of the association’s revenues come from trade shows and other classes.
Tax-law experts say this arrangement, which has helped fuel a resurgence in the political influence of restaurants, appears legal.
But activists for raising minimum wages — and even some restaurant owners — say the arrangement is hidden from the workers it relies on.
“I’m sitting up here working hard, paying this money so that I can work this job, so I can provide for my family,” said Mysheka Ronquillo, 40, a line cook who works at a Carl’s Jr. hamburger restaurant and at a private school cafeteria in Westchester, Calif. “And I’m giving y’all money so y’all can go against me?”
Ms. Ronquillo is also a labor organizer in California. She said that she had taken the class every three years, as required, and that she never knew ServSafe funded the other side of that fight.
As workers have become more aware of how their payments to ServSafe are used, something of a backlash is developing. Looking ahead to coming battles over minimum wages in as many as nine states run by Democrats, including New York, Saru Jayaraman of the labor-advocacy group One Fair Wage said she was encouraging workers to avoid ServSafe.
“We’ll be telling them to use any possible alternatives,” Ms. Jayaraman said.
The kind of class that these workers pay for, called “food handler” training, is offered by ServSafe or its affiliates in all 50 states and the District of Columbia. But an online database maintained by the National Restaurant Association show the vast majority of its classes are taken in four large states where food-handler classes are mandatory for most workers: Texas, California, Illinois and Florida.
Other companies also offer this training. But restaurant industry veterans say that ServSafe is the dominant force in the market — to the point that some restaurant owners said they did not realize there were alternatives.
“ServSafe is very much the Kleenex” of the industry — a brand that defines the business, said Nick Eastwood, who runs a competitor called Always Food Safe. “We believe they’ve got at least 70%+ of the market. Maybe higher.”
The president of the National Restaurant Association, Michelle Korsmo, declined to be interviewed. In a written statement, she said the group had sought to protect both public health and the financial health of the industry.
“The association’s advocacy work keeps restaurants open; it keeps workers employed, it finds pathways for worker opportunity, and it keeps our communities healthy,” Ms. Korsmo wrote. Her group declined to say how much of the training market it captures.
As money flowed in from the National Restaurant Association’s training programs, its overall spending on politics and lobbying more than doubled from 2007 to 2021, tax filings show. The national association donated to Democrats, Republicans and conservative-leaning think tanks, and sent hundreds of thousands of dollars to state restaurant associations to beef up their lobbying.
During the Clinton and Obama administrations, the association was a major force in limiting employer-provided health care benefits. And though pressure from liberal groups has grown and workers’ wages have fallen for decades when adjusted for inflation, the group helped assemble enough bipartisan opposition to scuttle a bill in 2021 to raise the federal minimum wage for all workers to $15 per hour over five years.
The association had also won a series of battles over state-level wage minimums, though its fortunes reversed last year. Both the District of Columbia and Michigan moved to eliminate the “tip credit” system — where restaurants are allowed to pay waiters a salary below the minimum wage, on the expectation that tips from customers will make up the rest. That was the first time any state had eliminated the tip-credit system in more than 10 years.
Legally, the National Restaurant Association and its state-level affiliates are a species of nonprofit called a “business league,” with more freedom to lobby than a traditional charity.
Since the 1960s, their lobbying has focused heavily on the minimum wage — arguing that labor-intensive operations like restaurants, which employ more workers at or near the minimum wage than any other industry, could be put out of business by any significant increase in employee costs.
Fifteen years ago, they had just lost a battle in that fight.
Over the association’s objections, Congress had raised the minimum wage to $7.25 an hour. Former board members said they were searching for a new source of revenue — without asking members to pay more in dues.
“That’s when the decision was contemplated, of buying the ServSafe program,” said Burton “Skip” Sack, a former chairman of the association’s board. “Because it was profitable.”
At the time, the ServSafe program was run by a charity affiliated with the restaurant association. The association bought the operation, transforming it into an indirect fund-raising vehicle.
After that, state restaurant associations in California, Texas and Illinois lobbied for changes in state law.
Previously, those states had required food-safety training for restaurant managers, which typically was paid for by restaurants themselves. After the association’s takeover of ServSafe, lobbying records show, the state affiliates pushed for a broader and less-common type of mandate, covering all food “handlers” like cooks, waiters, bartenders and those who bus tables.
The three state legislatures agreed, in lopsided votes.
In written statements, the state restaurant associations said they were not trying to raise money. Instead, they said they worked with other groups seeking to reduce food-borne disease.
“This law was happening with or without our participation in the process,” said the president of the California Restaurant Association, Jot Condie. California legislative records show his association was the sponsor of the bill that imposed the mandate.
ServSafe soon had waves of new customers, which in turn generated more money for the association and its lobbying efforts. Today, Florida, California, Texas, Illinois and Utah all have similar requirements. John Bluemke, a senior vice president for sales at ServSafe from 2002 to 2010, said there was little need to pursue mandates in smaller states: “Once you did the big states, who cares about Nebraska?”
“If you’ve got a million people going through that thing, do the math,” Mr. Bluemke said. The National Restaurant Association does not release figures about the cost of offering food-handler classes, but Mr. Bluemke said that — because they are generally offered online — the costs are low and the profits high.
“We always said the first course costs you a million dollars,” Mr. Bluemke said, for making the video. “And the rest are free.”
When managers take mandatory training, restaurant veterans say, the employer usually pays. But state websites say that restaurant employees should expect to pay for these classes themselves, and restaurant workers interviewed by The New York Times said that was their experience.
The restaurant association notes that some employers have covered the costs of getting certified and that employees are given lower rates in certain circumstances. So not all 3.6 million workers paid $15 each.
“The N.R.A. is different from most traditional trade associations in our business model,” Dawn Sweeney, the National Restaurant Association’s chief executive at the time, wrote to members in 2014 — reminding them of what a good deal they had.
Business leagues, which are tax-exempt, are generally allowed to run a for-profit business, as long as it advances the common interest of their broader trade. The National Restaurant Association contends that its business cleanly fits this standard.
“The rules the I.R.S. has passed are not always clear as to what is and is not allowed,” said Anna Massoglia, an investigations manager at OpenSecrets, a nonpartisan group that tracks the flow of money in politics. “This makes it easier for groups to exploit that lack of clarity. I’m not familiar with another group that has done it to this scale.”
The Internal Revenue Service declined to comment, citing taxpayer-privacy rules.
For restaurant workers, there is little clue that money paid to ServSafe supports lobbying — much less lobbying that tries to keep workers’ pay low. The only hint is a line on ServSafe’s website, saying it “reinvests proceeds from programs back into the industry.”
Even some members of the restaurant association — the beneficiaries of this arrangement — said they did not know how it worked.
Johnny Martinez, a Georgia restaurateur, said he supports a $15 minimum wage and pays at least that much in a state where it is still $7.25 per hour. And he describes his association membership as “the price of entry” for navigating the industry, “even though I disagree with them on a lot of things.”
But he expressed frustration upon discovering the connections between ServSafe and lobbying efforts, saying “it feels very wrong” to him.
“This is a certification that’s also wrapped up inside of a lobbyist,” Mr. Martinez said. “It is weird that the tests that they require the workers to pay for are being run by the same company that’s fighting to make sure those people don’t make more money.”
#us politics#news#2023#the new york times#food service industry#worker's rights#workers#working class#ServSafe#National Restaurant Association#lobbyists#corporate lobbying#corporate lobbyists#wages#raise the minimum wage#poverty wages#minimum wage#living wage#One Fair Wage#internal revenue service#texas#California#Florida#illinois#Always Food Safe#utah#California Restaurant Association#Business leagues
61 notes
·
View notes
Text

AIPAC, a rightwing conservative, quasi-religious, foreign organization, is interfering with U.S. elections and shaping who is and who isn’t a member of Congress.
AIPAC is currently targeting progressives like Ilhan Omar, Rashida Tlaib, Summer Lee, Jamaal Bowman, Greg Casar, Delia Ramirez, Maxwell Frost, Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez, and others who do not feel beholden to Israel and are sympathetic to Palestinians.

If AIPAC was a super PAC funded by North Korea, or China, or Russia, or Iran—and interfering in elections by financing the campaigns of specific candidates—almost every member of Congress would be freaking out. And rightly so. This is no different.
#politics#aipac#palestine#israel#foreign agents#citizens united#cori bush#jamaal bowman#rashida tlaib#summer lee#ilhan omar#alexandria ocasio cortez#the squad#foreign lobbyists#lobbyists#election interference#election integrity#bribery
134 notes
·
View notes
Text
The NDP has a lobbyist problem.
Many of the party’s top officials shuffle between employment at lobbying firms and work on provincial and federal elections—and the priorities and perspectives of their day jobs are a key reason why the party runs such uninspiring campaigns.
In the most recent provincial election in Alberta, the NDP—including Rachel Notley’s brain trust, campaign managers, and high-profile volunteers—was stacked with party insiders who lobby for corporate clients.
Only one got any attention: the campaign’s manager, Nathan Rotman, who is a registered lobbyist for Airbnb. But others include Cheryl Oates, a campaign advisor who as recently as February was leading a lobbying push in British Columbia for Uber, as well as a U.S. coal company.
Brian Topp, a senior campaign advisor and former chief of staff to Notley, runs the firm where Oates works. The firm has recently also lobbied for Bank of Montreal, McCain Foods, railway giant CN, and one of Canada’s largest cannabis corporations.
Other important roles—like Notley’s press secretary, and campaign managers in multiple ridings—were filled by lobbyists. [...]
Continue Reading.
Tagging: @politicsofcanada, @abpoli
105 notes
·
View notes
Text
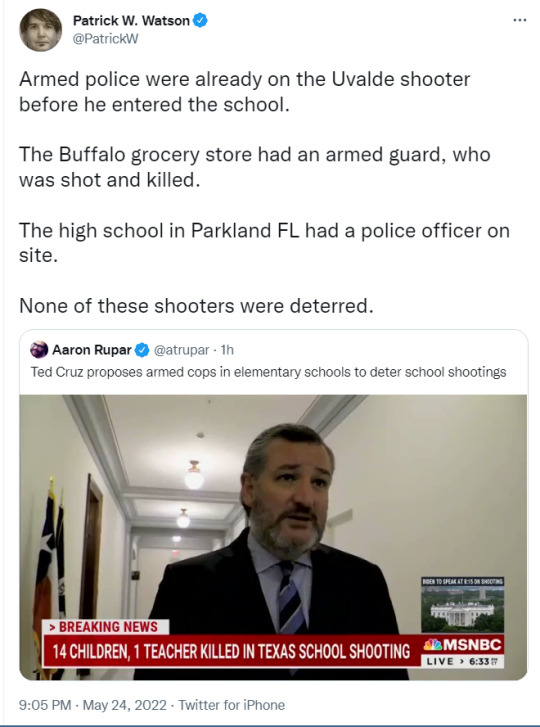
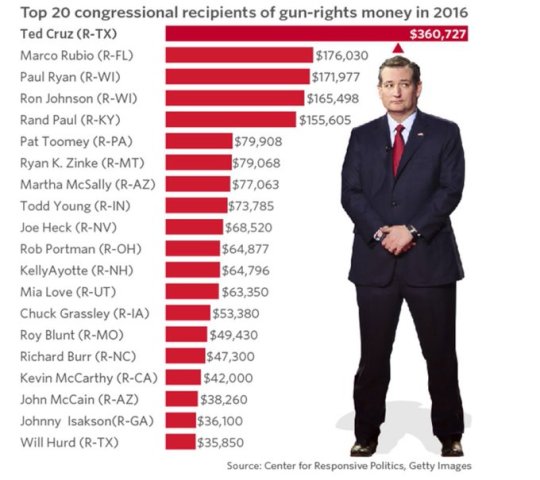
393 notes
·
View notes
Text


Worthwhile listen from Pitchfork Economics. Also written about here.
#politics#us politics#progressive#history#capitalism#class war#child labor#child labor laws#exploitation#reform#economics#lobbyists#lobbying#labor rights#labor#worker protections#education#public education#jennifer sherer#nina mast
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
The government asks for our trust. As though we did not walk blindly with them for decades. While they sought to poison us at every opportunity. Greed & Lobbyist are truly the Devil Incarnate
Theata
#government#poetry#inspiring quotes#life quote#book quote#quotes#quoteoftheday#personal growth#writing#thoughts of the day#today on tumblr#devil#corporate greed#lobbyists#philosophy
13 notes
·
View notes