#joseph schildkraut
Text


Propaganda
Joseph Schildkraut (Cleopatra, The Life of Emile Zola)—no propaganda submitted
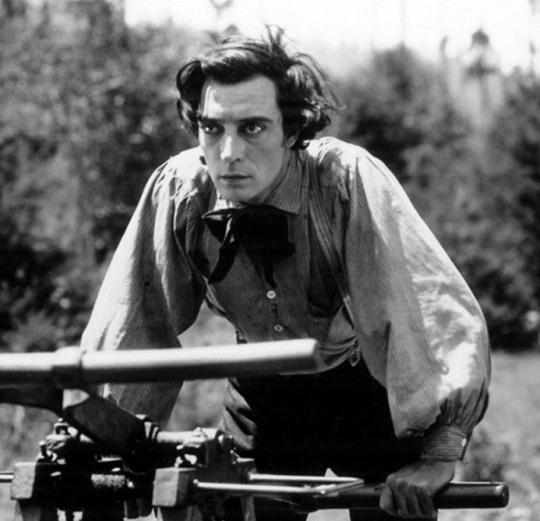
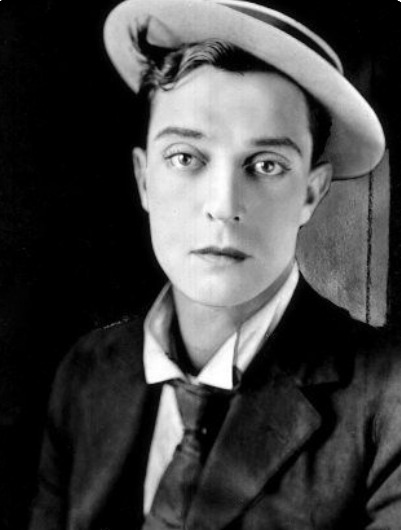
Buster Keaton (The General, The Navigator, Sherlock Jr.)—Just look at his freaking face...
This is round 1 of the bracket. All other polls in this bracket can be found here. Please reblog with further support of your beloved hot sexy vintage man.
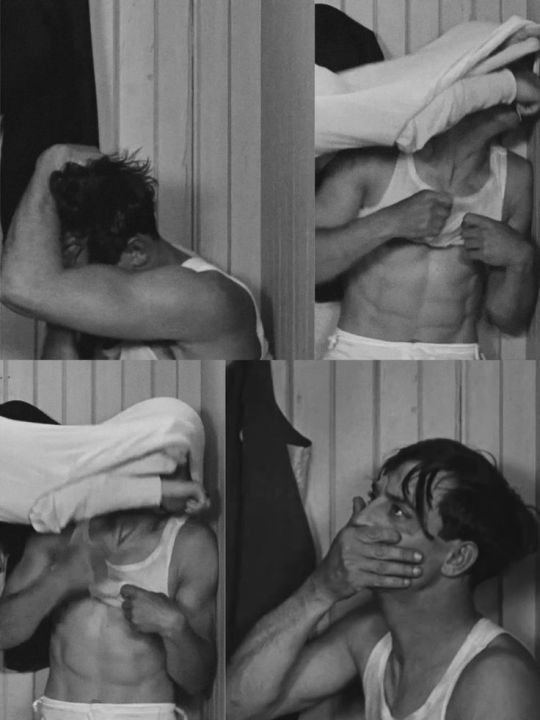
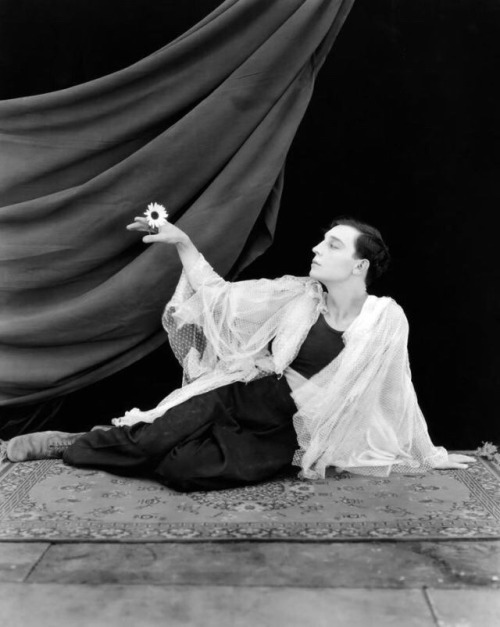
[additional propaganda and propaganda photos submitted under the cut—mildly NSFW]
Schildkraut propaganda photos:


Keaton additional propaganda + photos:


This entire Tumblr page was submitted
This post

"Ripped body, gorgeous unique face, beautiful personality too"



497 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Tell-Tale Heart (1941)
#the tell tale heart 1941#joseph schildkraut#roman bohnen#1941#1940s movies#jules dassin#short film#edgar allan poe#hidden gem#movie poster
65 notes
·
View notes
Text











THE TWILIGHT ZONE | 3.31 The Trade-Ins
#thetwilightzone#ttz#ttzedit#thetwilightzoneedit#1960's#1960's tv#tvedit#tvgifs#retrotv#retrotvedit#1962#the trade-ins#3.31#3x31#season 3#rod serling#joseph schildkraut#noah keen#alma platt#theodore marcuse#edson stroll#terence de marney
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

#The Shop Around the Corner#Margaret Sullavan#James Stewart#Frank Morgan#Joseph Schildkraut#Ernst Lubitsch#1940
11 notes
·
View notes
Photo

#Marlene Dietrich#charles boyer#movie poster#basil rathbone#c aubrey smith#tilly losch#joseph schildkraut#john carradine#alan marshal#david o selznick#technicolor#film#movie posters#films#poster
15 notes
·
View notes
Text

“Rebel?” Marie Antoinette, 1938
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo


Films Watched in 2022:
67. The Man in the Iron Mask (1939) - Dir. James Whale
#The Man in the Iron Mask#James Whale#Louis Hayward#Joan Bennett#Warren William#Joseph Schildkraut#Alan Hale#Walter Kingsford#Miles Mander#Bert Roach#Marion Martin#Montagu Love#Doris Kenyon#Albert Dekker#Nigel de Bruiler#Dwight Frye#Peter Cushing#Alexander Dumas#Films Watched in 2022#My Edits#My Post
14 notes
·
View notes
Text

Joseph Schildkraut-Katherine DeMille "Las cruzadas" (The crusades) 1925, de Cecil B. DeMille.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text

Dann informierte ich mich mal über die Kreuzzüge. Nachdem ungläubige Sarazene die Heilige Stadt erobern, ruft ein rühriger Eremit die total gläubigen europäischen Könige auf, sich zu einem Kreuzzug zusammenzutun, um sie zurückzuerobern. Der unsolide englische König Richard Löwenherz kommt bloß mit, um einer arrangierten Ehe mit der Schwester der französischen Königs zu entgehen. Unerwartet heiratet er dann doch relativ schnell, und zwar Loretta Young, was sich als kluger Zug herausstellt, da es ihr schließlich gelingt, die Kampfhandlungen zu beenden. Allein durch ihre Schönheit! Alles ist genau so passiert.
#The Crusades#Loretta Young#Henry Wilcoxon#Ian Keith#Katherine DeMille#C. Aubrey Smith#Joseph Schildkraut#Film gesehen#Cecil B. DeMille
1 note
·
View note
Video
youtube
The Diary of Anne Frank (1959) 2.0
(FULL MOVIE)
Director: George Stevens
Anne Frank played by Millie Perkins
Language: English
Won 3 Oscars
IMDb link
#anne frank#the diary of anne frank#film#movie#1959#hollywood#old hollywood#diary of anne frank#diary of a young girl#George Stevens#millie perkins#Shelley Winters#Joseph Schildkraut#ana frank#The Diary of a Young Girl#anne frank diary#Anne Frank House#anne frank huis#Amsterdam#The Netherlands#USA#world war II#World War Two#world war 2#holocaust#history#oscars#Academy Awards
1 note
·
View note
Text
Congrats to the ultimate winner of the Hot & Vintage Movie Men Tournament, Mr. Toshiro Mifune! May he live happily and well where the sun always shines, enjoying the glories of a battle hard fought.
A loving farewell to all of our previous contestants, who are now banished to the shadow realm and all its dark joys and whispered horrors—I hear there's a picnic on the village green today. If you want to remember the fallen heroes, you can find them all beneath the cut.
What happens next? I'll be taking a break of two weeks to rest from this and prep for the Hot & Vintage Ladies Tournament. I'll still be around but only minimally, posting a few last odes to the hot men before transitioning into a little early ladies content, just like I did with this last tournament. The submission form for the Hot & Vintage Ladies tournament will remain up for one more week (closing February 21st), so get your submissions in for that asap! Once the form closes, there will be one more week of break. The first round of the Hot & Vintage Ladies Tournament will be posted on February 29th, as Leap Year Day seems like a fitting allusion to leaping into these ladies' arms.
Thanks for being here! Enjoy the two weeks off, and send me some great propaganda.
In order of the last round they survived—
ROUND ONE HOTTIES:
Richard Burton
Tony Curtis
Red Skelton
Keir Dullea
Jack Lemmon
Kirk Douglas
Marcello Mastroianni
Jean-Pierre Cassel
Robert Wagner
James Garner
James Coburn
Rex Harrison
George Chakiris
Dean Martin
Sean Connery
Tab Hunter
Howard Keel
James Mason
Steve McQueen
George Peppard
Elvis Presley
Rudolph Valentino
Joseph Schildkraut
Ray Milland
Claude Rains
John Wayne
William Holden
Douglas Fairbanks Sr.
Harold Lloyd
Charlie Chaplin
John Gilbert
Ramon Novarro
Slim Thompson
John Barrymore
Edward G. Robinson
William Powell
Leslie Howard
Peter Lawford
Mel Ferrer
Joseph Cotten
Keye Luke
Ivan Mosjoukine
Spencer Tracy
Felix Bressart
Ronald Reagan (here to be dunked on)
Peter Lorre
Bob Hope
Paul Muni
Cornel Wilde
John Garfield
Cantinflas
Henry Fonda
Robert Mitchum
Van Johnson
José Ferrer
Robert Preston
Jack Benny
Fredric March
Gene Autry
Alec Guinness
Fayard Nicholas
Ray Bolger
Orson Welles
Mickey Rooney
Glenn Ford
James Cagney
ROUND TWO SWOONERS:
Dick Van Dyke
James Edwards
Sammy Davis Jr.
Alain Delon
Peter O'Toole
Robert Redford
Charlton Heston
Cesar Romero
Noble Johnson
Lex Barker
David Niven
Robert Earl Jones
Turhan Bey
Bela Lugosi
Donald O'Connor
Carman Newsome
Oscar Micheaux
Benson Fong
Clint Eastwood
Sabu Dastagir
Rex Ingram
Burt Lancaster
Paul Newman
Montgomery Clift
Fred Astaire
Boris Karloff
Gilbert Roland
Peter Cushing
Frank Sinatra
Harold Nicholas
Guy Madison
Danny Kaye
John Carradine
Ricardo Montalbán
Bing Crosby
ROUND THREE SMOKESHOWS:
Marlon Brando
Anthony Perkins
Michael Redgrave
Gary Cooper
Conrad Veidt
Ronald Colman
Rock Hudson
Basil Rathbone
Laurence Olivier
Christopher Plummer
Johnny Weismuller
Clark Gable
Fernando Lamas
Errol Flynn
Tyrone Power
Humphrey Bogart
ROUND 4 STUNGUNS:
James Dean
Cary Grant
Gregory Peck
Sessue Hayakawa
Harry Belafonte
James Stewart
Gene Kelly
Peter Falk
QUARTERFINALIST VOLCANIC TOWERS OF LUST:
Jeremy Brett
Vincent Price
James Shigeta
Buster Keaton
SEMIFINALIST SUPERMEN:
Omar Sharif
Paul Robeson
FINALIST FANTASIES:
Sidney Poitier
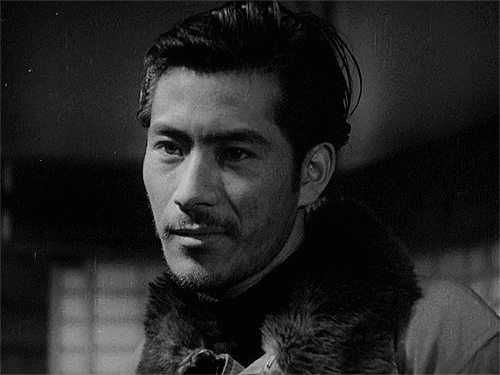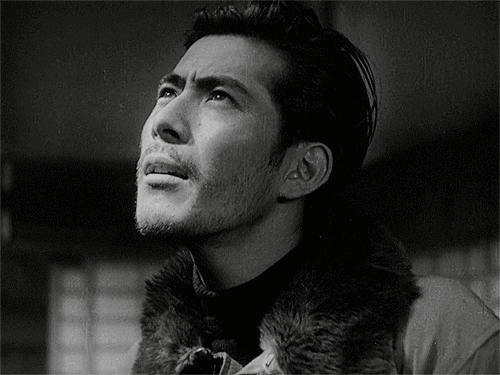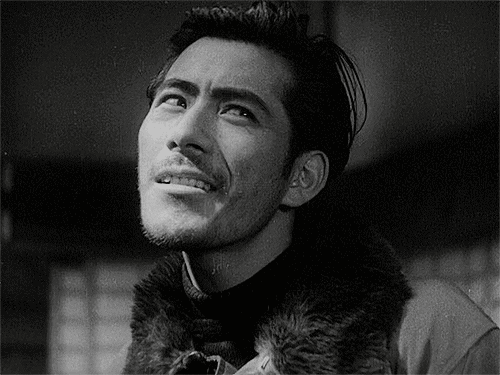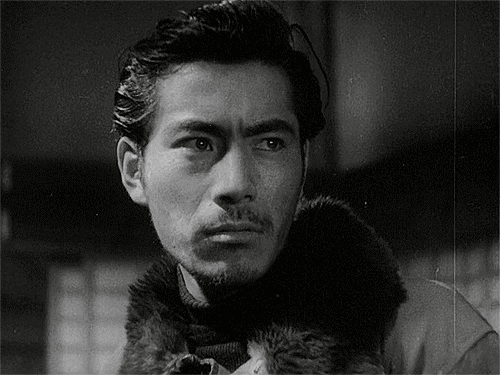
Toshiro Mifune
and ok, sure, here's the shadow-bracket-style winner's portrait of Toshiro Mifune.
#hotvintagepoll#hot men finals#a winner crowned!#fuck that old man (requiem)#shadow bracket#toshiro mifune
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
Masterpost of Hot Old Man Round 1 Polls
Paul Newman v Richard Burton
Omar Sharif v Tony Curtis
Red Skelton v Burt Lancaster
Christopher Plummer v Keir Dullea
Anthony Perkins vJack Lemmon
Kirk Douglas v Alain Delon
James Dean v Marcello Mastroianni
Harry Belafonte v Jean-Pierre Cassel
Marlon Brando v Robert Wagner
Sammy Davis Jr. v James Garner
James Coburn v Rock Hudson
Peter Cushing v Rex Harrison
George Chakiris v Sidney Poitier
Dean Martin v Sean Connery v Jeremy Brett
Tab Hunter v Toshiro Mifune
Howard Keel v Peter O'Toole
Robert Redford v James Mason
Steve McQueen v Charlton Heston
Dick Van Dyke v George Peppard
Elvis Presley v Peter Falk
Oscar Micheaux v Rudolph Valentino
Joseph Schildkraut v Buster Keaton
Jimmy Stewart v Ray Milland
Cary Grant v Claude Rains
John Wayne v Errol Flynn
Clint Eastwood v William Holden
Douglas Fairbanks Sr. v Sessue Hayakawa
Carman Newsome v Harold Lloyd
Noble Johnson v Charlie Chaplin
John Gilbert v Conrad Veidt
Ramon Novarro v Robert Earl Jones
Slim Thompson v Gary Cooper
John Barrymore v Paul Robeson
Edward G. Robinson v Clark Gable
Humphrey Bogart v William Powell
Leslie Howard v Ronald Colman
Peter Lawford v Vincent Price
Harold Nicholas v Mel Ferrer
Joseph Cotten v Danny Kaye
John Carradine v Keye Luke
Ivan Mosjoukine v Gilbert Roland
Benson Fong v Spencer Tracy
Guy Madison v Felix Bressart
James Shigeta v Ronald Reagan
Montgomery Clift v Ricardo Montalbon
Peter Lorre v Frank Sinatra
Bob Hope v Gregory Peck
Fred Astaire v Paul Muni
Bela Lugosi v Cornel Wilde
Cesar Romero v John Garfield
Basil Rathbone v Cantinflas
Henry Fonda v Turhan Bey
Boris Karloff v Robert Mitchum
David Niven v Van Johnson
Gene Kelly v José Ferrer
Robert Preston v Tyrone Power
Jack Benny v Donald O'Connor
Fredric March v Lex Barker
Michael Redgrave v Gene Autry
James Edwards v Alec Guinness
Fayard Nicholas v Fernando Lamas
Ray Bolger v Johnny Weismuller
Orson Welles v Sabu Dastigir
Mickey Rooney v Laurence Olivier
Rex Ingram v Glenn Ford
Bing Crosby v James Cagney
@hotvintagepoll
380 notes
·
View notes
Text

Robert Morley and Norma Shearer in Marie Antoinette (W.S. Van Dyke, 1938)
Cast: Norma Shearer, Tyrone Power, John Barrymore, Robert Morley, Anita Louise, Joseph Schildkraut, Gladys George, Henry Stephenson. Screenplay: Claudine West, Donald Ogden Stewart, Ernest Vajda. Cinematography: William H. Daniels. Art direction: Cedric Gibbons, Henry Grace. Film editing: Robert Kern. Costume design: Adrian, Gile Steele. Music: Herbert Stothart.
Hollywood historical hokum, W.S. Van Dyke's Marie Antoinette was a vehicle for Norma Shearer that had been planned for her by her husband, Irving G. Thalberg, who died in 1936. MGM stuck with it because as Thalberg's heir, Shearer had control of a large chunk of stock. It also gave her a part that ran the gamut from the fresh and bubbly teenage Austrian archduchess thrilled at the arranged marriage to the future Louis XVI, to the drab, worn figure riding in a tumbril to the guillotine. Considering that it takes place in one of the most interesting periods in history, it could have been a true epic if screenwriters Claudine West, Donald Ogden Stewart, and Ernest Vajda (with uncredited help from several other hands, including F. Scott Fitzgerald) hadn't been pressured to turn it into a love story between Marie and the Swedish Count Axel Fersen. But the portrayal of their affair was stifled by the Production Code's squeamishness about sex, and the long period in which Marie and Louis fail to consummate their marriage lurks unexplained in the background. MGM threw lots of money at the film: Shearer sashays around in Adrian gowns with panniers out to here, with wigs up to there, and on sets designed and decorated by Cedric Gibbons and Henry Grace that make the real Versailles look puny. The problem is that nothing like a genuine human emotion appears on the screen, and the perceived necessity of glamorizing the aristocrats turns the French Revolution on its head. The cast of thousands includes John Barrymore as Louis XV, Gladys George as Madame du Barry, and Joseph Schildkraut (made up with what looks like Jean Harlow's eyebrows and Joan Crawford's lipstick) as the foppish Duke of Orléans. The best performance in the movie comes from Morley, who took the role after the first choice, Charles Laughton, proved unavailable; Morley earned a supporting actor Oscar nomination for his film debut. With the exception of��The Women (George Cukor, 1939), in which she is upstaged by her old rival Joan Crawford, this is Shearer's last film of consequence. When she turned 40 in 1942, she retired from the movies and lived in increasing seclusion until her death, 41 years later. It says something about Shearer's status in Hollywood that Greta Garbo, who retired at about the same time, and who also sought to be left alone, was the more legendary figure and was more ardently pursued by gossips and paparazzi.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Found media!
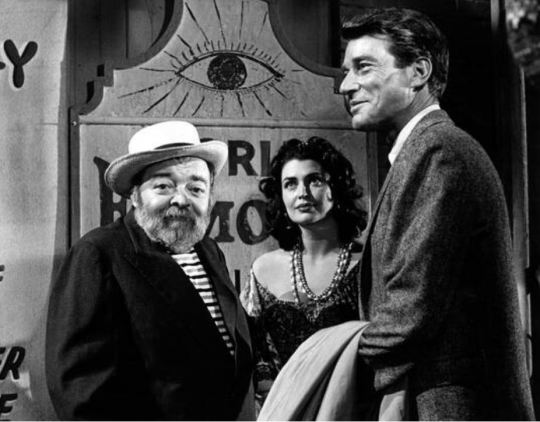

77 Sunset Strip (TV series), "5, Part 1": Peter Lorre as The Gypsy, with Laurette Luez and Efrem Zimbalist Jr. | September 20, 1963.
Damn, everybody's in this (there are 5 parts in total). Herbert Marshall ❤ , Wally Cox, Burgess Meredith, Joseph Schildkraut, Ed Wynn, William Shatner - ! Plot



Watch it here:
Or if you prefer archive.org, it's listed under "601_5P1.mp4" in this collection. There are more "parts" but I believe Peter Lorre is only in that first one.
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
joseph schildkraut in the shop around the corner? a snack!
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Posted July 19, 2022
By Christopher Lane, Ph.D; reviewed by Vanessa Lancaster
Key points
Surveys indicate that 85-90 percent of the public believes low serotonin or a chemical imbalance causes depression.
Among 237 psychology students interviewed, 46 percent had heard the chemical imbalance explanation from a physician.
The serotonin hypothesis has been challenged repeatedly and found wanting, even as it remains popular and influential.
A comprehensive, well-powered, high-quality umbrella review now determines that the theory is “not empirically substantiated.”
Almost as soon as it was floated in 1965 by Harvard psychiatrist Joseph Schildkraut, the serotonin hypothesis of depression—reduced and simplified by pharma marketing to the “chemical imbalance” theory of depression and anxiety—has been subject to critical research and found wanting.
The poor standing of the hypothesis in the scientific literature, however, barely dented its afterlife in textbooks, across clinical and treatment settings, and on mental health apps and websites. Nor has it dispelled the continued use of the phrase as “shorthand” between doctors and patients and in everyday settings, including for quite different mental states and conditions.
The “Chemical Imbalance” Metaphor Takes Root
Revisiting the history of this controversy raises several still-relevant details. In December 2005, as advertising for SSRI antidepressants flooded American magazines, talk shows, and network TV, the result of multibillion-dollar campaigns pitched in this case directly to consumers, Florida-based professors and researchers Jeffrey Lacasse and Jonathan Leo asked pointedly in PLoS Medicine, “Are the claims made in SSRI advertising congruent with the scientific evidence?”
The answer in “Serotonin and Depression: A Disconnect Between the Advertisements and the Scientific Literature,” their well-researched article, was a resounding no. The resulting “incongruence,” they determined, was “remarkable and possibly unparalleled.”
Lacasse and Leo found repeated evidence that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration had approved the marketing of SSRIs with two phrases still heavily in the subjunctive—that depression “may be due to a serotonin deficiency” and that SSRI efficacy, “modestly” outcompeting placebo, was “presumed to be linked to potentiation of serotonergic activity.” However, the research itself could not identify the precise mechanism.
The FDA had accepted aspirational language that the drugs “help to restore the brain’s chemical balance” and “bring serotonin levels closer to normal,” even though both claims were, and remain, scientifically meaningless.
“There is no such thing as a scientifically established correct ‘balance’ of serotonin,” Lacasse and Leo cautioned more than a decade ago, joining numerous other experts then and now. Additionally, both aspirational claims rest on a hypothesis that follow-up studies would end up contradicting repeatedly. In short, both the hypothesis and the expensive marketing that pushed it into American living rooms rested on a hedge: “Scientists believe that it could be linked with an imbalance of a chemical in the brain called serotonin.”
A Multibillion-Dollar Error
The hedge proved highly effective, even though, as David Healy explained in 2015 in “Serotonin and Depression,” in the BMJ, in practice, it entailed embracing or tacitly accepting “the marketing of a myth.” Through further oversimplification, a revised metaphor of a “chemical imbalance” took root as folk wisdom for multiple, dissimilar conditions listed in the DSM.
Returning to the controversy in “Antidepressants and the Chemical Imbalance Theory of Depression” (2015), Lacasse and Leo found that while the marketing had shifted emphasis from “correcting imbalances” to “‘adjusting’ or ‘affecting’ neurotransmitter levels,” leading psychiatrists were if anything, more wedded to the “chemical imbalance” metaphor than before.
Some had taken to the airwaves to say that it simplified communication with their patients. Daniel Carlat, the editor of The Carlat Psychiatry Report, explained on National Public Radio when asked what we know about psychiatric medication:
We don’t know how the medications actually work in the brain…. I’ll often say something like the way Zoloft works, is, it increases the level of serotonin in your brain (or synapses, neurons) and, presumably, the reason you’re depressed or anxious is that you have some sort of a deficiency. And I say that [chuckles] not because I really believe it, because I know the evidence really isn’t there for us to understand the mechanism—I think I say that because patients want to know something. And they want to know that we as physicians have some basic understanding of what we’re doing when we’re prescribing medications. They certainly don’t want to know that a psychiatrist essentially has no idea how these medications work (Qtd. in Lacasse and Leo).
The point in reproducing Carlat (who has made several such admissions on national media) was not to single him out but to stress how widespread the thinking and practice he shared so candidly. In 2007, as Lacasse and Leo pointed out, Frances, Lysaker, and Robinson found that among 237 psychology students interviewed, “46 percent had heard the chemical imbalance explanation from a physician.”
Inevitably, the problem of spreading false scientific information dovetails with that of medical ethics and the risk of enabling medically-induced harms. Because physicians swear to uphold the Hippocratic oath Primum non nocere (“First Do No Harm”), Lacasse and Leo questioned “the ethics of telling a falsehood to patients because you think it is good for them.”
They asked more broadly of those repeating the discredited hypothesis, whether as metaphor or oversimplification: “Do you believe it is ethical to present a falsified scientific theory as a fact to a patient? What are the possible negative effects of doing so?”
A significant consequence they anticipated at the time was that patients would realistically “conclude that they have been misled.”
Cut to the Present-day
A major new review of the research—the first of its kind exhaustively reviewing the evidence, published today in the journal Molecular Psychiatry—reaches a strikingly similar conclusion. In “The Serotonin Theory of Depression: A Systematic Umbrella Review of the Evidence,” University College London Psychiatry Professor Joanna Moncrieff and a team of five other top European researchers found “there is no evidence of a connection between reduced serotonin levels or activity and depression.”
The peer-reviewed umbrella review—representing one of the highest forms of evidence in scientific research—was extrapolated from meta-analyses and systematic reviews on depression and serotonin levels, receptors, and transporters involving tens of thousands of participants.
Although “the serotonin hypothesis of depression is still influential,” Moncrieff and coauthors noted, citing widely adopted textbooks published as recently as 2020 and surveys indicating that “85-90 percent of the public believes that depression is caused by low serotonin or a chemical imbalance,” the primary research indicates there is “no support for the hypothesis that depression is caused by lowered serotonin activity or concentrations.”
Among other key findings:
“Research on serotonin receptors and the serotonin transporter, the protein targeted by most antidepressants, found weak and inconclusive evidence suggestive of higher levels of serotonin activity in people with depression.” Widespread use of antidepressants is seen as the likely cause.
The researchers also looked at studies where serotonin levels had been “artificially lowered in hundreds of people” (by depriving their diets of the necessary amino acid that makes serotonin) and found that “lowering serotonin in this way did not produce depression in hundreds of healthy volunteers,” according to a 2007 meta-analysis and several recent studies.
Numerous other reviews on re-examination were found to provide weak, inconsistent, or nonexistent evidence of a connection between serotonin and depression.
The researchers also probed well-powered studies involving tens of thousands of patients that focused on gene variation, including the gene for the serotonin transporter. These found “no difference in the genes between people with depression and healthy controls.” As such, “high-quality genetic studies effectively exclude an association between genotypes related to the serotonin system and depression, including a proposed interaction with stress.”
The researchers also looked at “the effects of stressful life events and found that these exerted a strong effect on people’s risk of becoming depressed—the more of these a person had experienced, the more likely they were to be depressed.”
Legacy Effects of a Discredited Theory
“The popularity of the chemical imbalance idea of depression has coincided with a huge increase in the use of antidepressants,” note Moncrieff and coauthor Mark A. Horowitz in the study’s press release. “Prescriptions for antidepressants have sky-rocketed since the 1990s, going from being rare to a situation now where one in six adults in England and 2 percent of teenagers are prescribed an antidepressant in a given year.”
The practical ramifications of the umbrella review are thus vast and consequential, involving millions of people across multiple countries because the findings are tied to a discredited theory that is still fueling mass prescribing on a global basis.
Moncrieff explained in the press release:
Patients should not be told that depression is caused by low serotonin or by a chemical imbalance and they should not be led to believe that antidepressants work by targeting these hypothetical and unproven abnormalities. In particular, the idea that antidepressants work in the same way as insulin for diabetes is completely misleading. We do not understand what antidepressants are doing to the brain exactly, and giving people this sort of misinformation prevents them from making an informed decision about whether to take antidepressants or not.
Invited to extrapolate the review’s findings for Psychology Today, Moncrieff added:
Antidepressant use has reached epidemic proportions across the world and is still rising, especially among young people. Many people who take them suffer side effects and withdrawal problems that can be really severe and debilitating. A major driver of this situation is the false belief that depression is due to a chemical imbalance. It is high time to inform the public that this belief is not grounded in science.
End of article.
Also:
Joanna Moncrieff et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2022.
Abstract
The serotonin hypothesis of depression is still influential. We aimed to synthesise and evaluate evidence on whether depression is associated with lowered serotonin concentration or activity in a systematic umbrella review of the principal relevant areas of research. PubMed, EMBASE and PsycINFO were searched using terms appropriate to each area of research, from their inception until December 2020. Systematic reviews, meta-analyses and large data-set analyses in the following areas were identified: serotonin and serotonin metabolite, 5-HIAA, concentrations in body fluids; serotonin 5-HT1A receptor binding; serotonin transporter (SERT) levels measured by imaging or at post-mortem; tryptophan depletion studies; SERT gene associations and SERT gene-environment interactions. Studies of depression associated with physical conditions and specific subtypes of depression (e.g. bipolar depression) were excluded. Two independent reviewers extracted the data and assessed the quality of included studies using the AMSTAR-2, an adapted AMSTAR-2, or the STREGA for a large genetic study. The certainty of study results was assessed using a modified version of the GRADE. We did not synthesise results of individual meta-analyses because they included overlapping studies. The review was registered with PROSPERO (CRD42020207203). 17 studies were included: 12 systematic reviews and meta-analyses, 1 collaborative meta-analysis, 1 meta-analysis of large cohort studies, 1 systematic review and narrative synthesis, 1 genetic association study and 1 umbrella review. Quality of reviews was variable with some genetic studies of high quality. Two meta-analyses of overlapping studies examining the serotonin metabolite, 5-HIAA, showed no association with depression (largest n = 1002). One meta-analysis of cohort studies of plasma serotonin showed no relationship with depression, and evidence that lowered serotonin concentration was associated with antidepressant use (n = 1869). Two meta-analyses of overlapping studies examining the 5-HT1A receptor (largest n = 561), and three meta-analyses of overlapping studies examining SERT binding (largest n = 1845) showed weak and inconsistent evidence of reduced binding in some areas, which would be consistent with increased synaptic availability of serotonin in people with depression, if this was the original, causal abnormaly. However, effects of prior antidepressant use were not reliably excluded. One meta-analysis of tryptophan depletion studies found no effect in most healthy volunteers (n = 566), but weak evidence of an effect in those with a family history of depression (n = 75). Another systematic review (n = 342) and a sample of ten subsequent studies (n = 407) found no effect in volunteers. No systematic review of tryptophan depletion studies has been performed since 2007. The two largest and highest quality studies of the SERT gene, one genetic association study (n = 115,257) and one collaborative meta-analysis (n = 43,165), revealed no evidence of an association with depression, or of an interaction between genotype, stress and depression. The main areas of serotonin research provide no consistent evidence of there being an association between serotonin and depression, and no support for the hypothesis that depression is caused by lowered serotonin activity or concentrations. Some evidence was consistent with the possibility that long-term antidepressant use reduces serotonin concentration.
#fascinating#my friend taupe sent these to me#and i was talking about how when i was in therapy for OCD my doctor told me how SSRIs work (supposedly) but that no one...#...actually knows what all OCD does in the brain or how SSRIs interact with a brain that has OCD. we just know these drugs often help.#and they do! Sertraline (generic Zoloft) saved my life -- literally. i would not have lived this long if i hadn't been put on it AND had...#...rigorous therapy like i did. i needed BOTH to survive and i am very lucky to still be here.#i'm still on an SSRI (a different one) and it helps with my OCD and depressive periods and PTSD. it helps a LOT.#what exactly is it doing to my brain? i don't know. and neither does my doctor. but we DO know that it's better for me than not being on it#and honestly? i've looked up the long term effects and i'm willing to deal with them because they are SO MUCH BETTER than...#...the alternative. i will likely be on an SSRI for my entire life. and that is fine. i can FUNCTION now.#i'm not constantly miserable. i can LIVE. and that is EVERYTHING to me.#and i also know that antidepressants aren't for everyone. they work for ME and that's great. but they don't work for everyone.#personal#medical#depression#ssri#antidepressants#modern science#taupe sent me this
28 notes
·
View notes