#european anthropology
Text






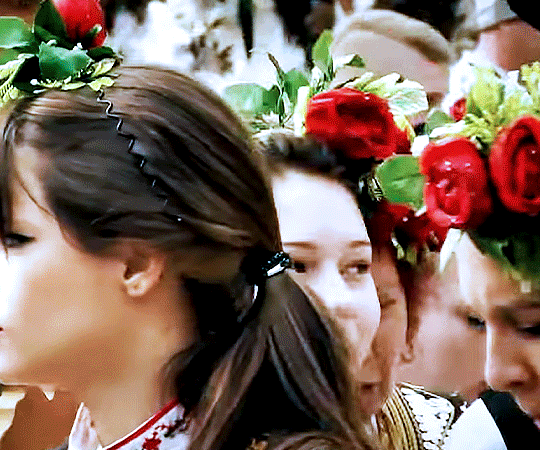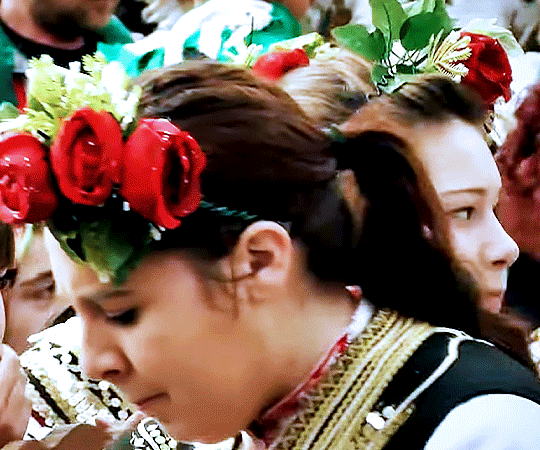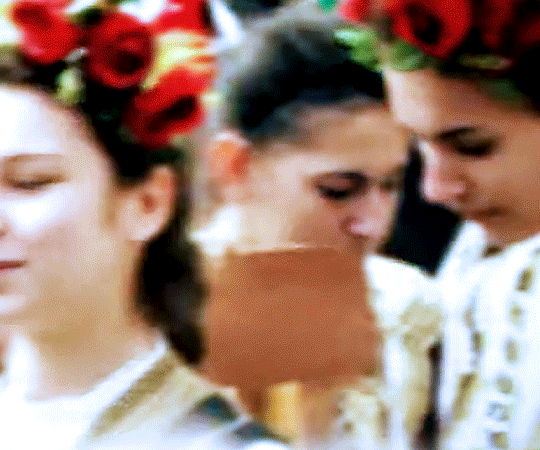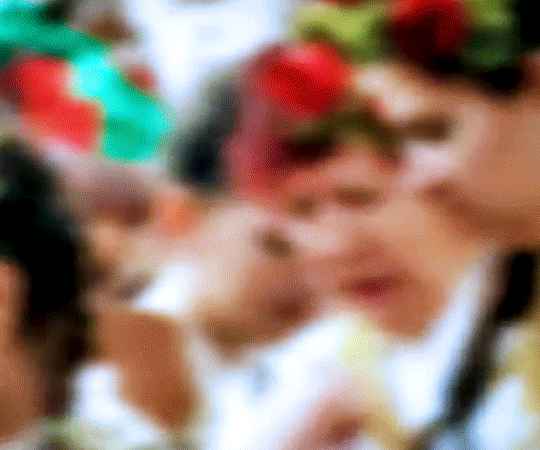



Kukeri - originates from the old Slavic word "kuka," which means an evil spirit. The pagan festival is a centuries-old Bulgarian tradition where people dance through the streets in scary masks, animal skins and loud bells.
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
EG Colloquium 2022 - Opening of the Conference with Marc ABÉLÈS & Pascal LAMY
The European General Studies programme of the College organised this end-of-the-year colloquium entitled “30 years after the anthropological report on the European Commission: Where does anthropology stand and what does it tell us about the European institutions?” on 20 & 21 June 2022.
This is a talk between Marc Abélès and Pascal Lamy on European Anthropology. Marc Abélès presents the report he wrote 30 years ago, reflect on the different methods and processes used for the report and will put into perspective the key conclusions from this report within current context. Pascal Lamy also explains in a video why this report was ordered and the impact it had on the institutions.
0 notes
Text
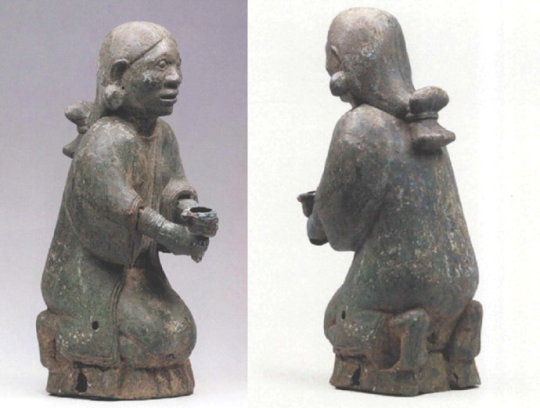
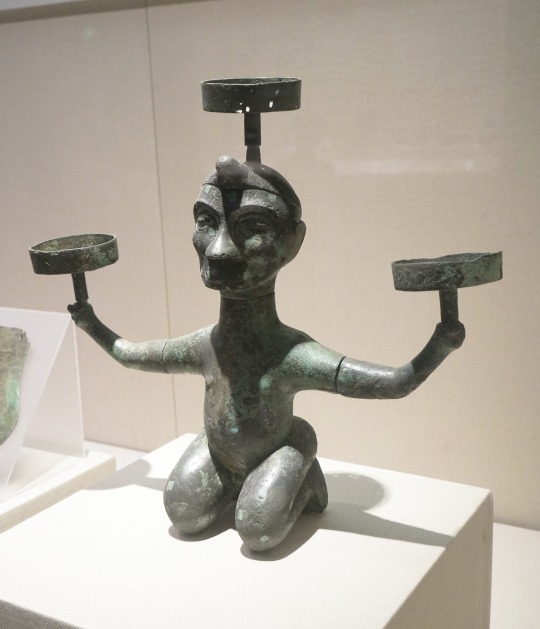
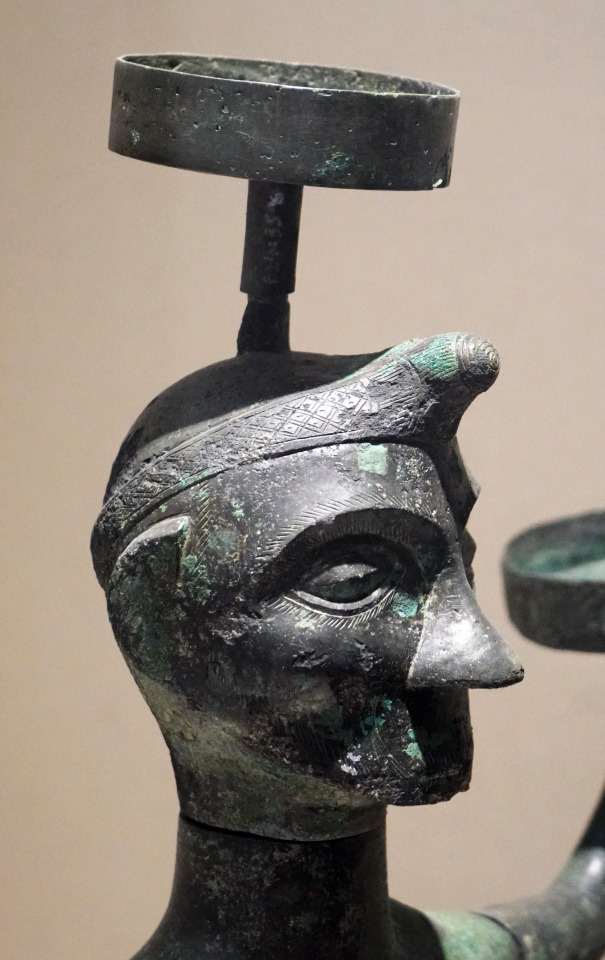
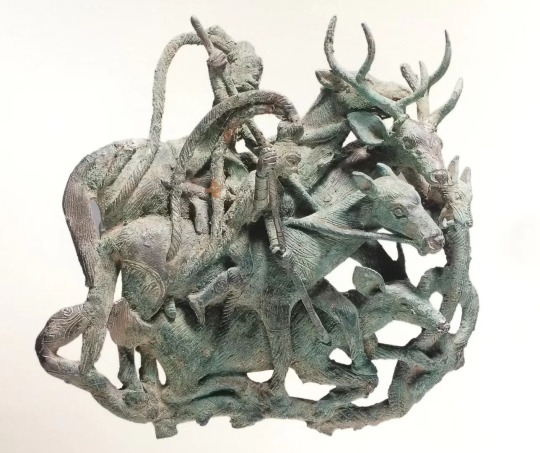
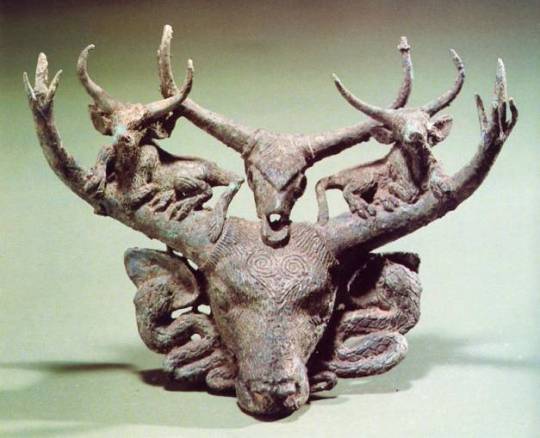


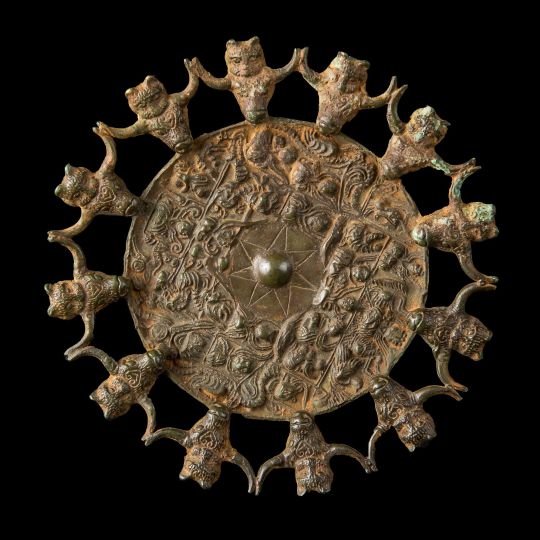

















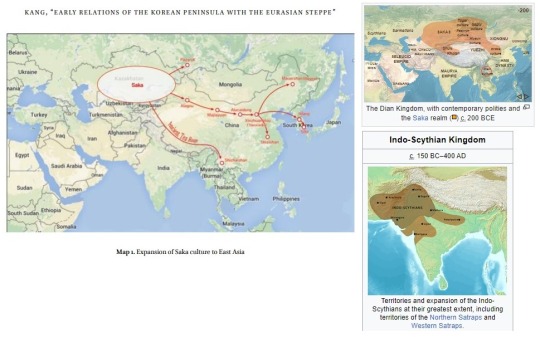









Dian Kingdom 8th-1st C. BCE. Meant to post this one a long time ago but it took me forever to put together. I'm just going to post 30 images here, I got about 100 total on my blog. Link at bottom.
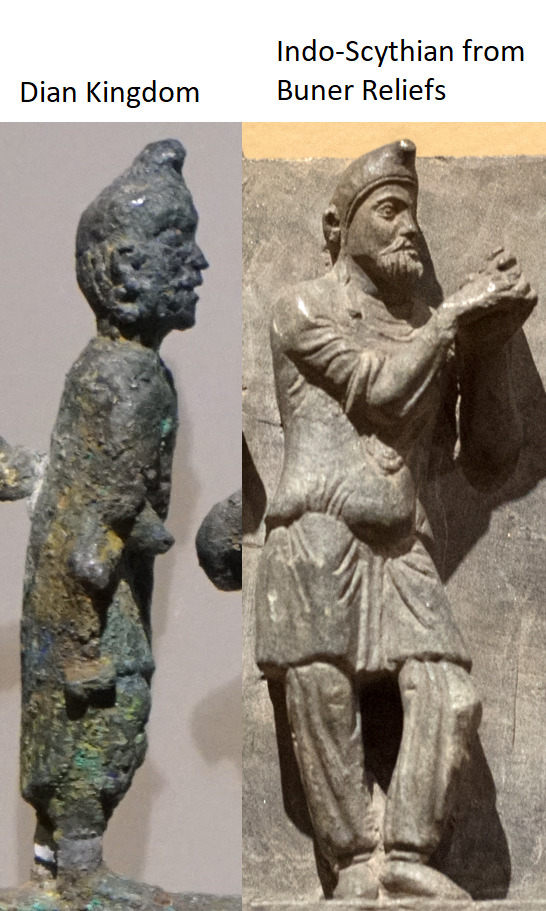
The Dian Kingdom was an advanced civilization in what is modern-day southwest China. It was occupied by the Han Dynasty and incorporated into China after that. From what I've gathered, the people of the Dian Kingdom were probably closely related to the Baiyue people from southern China and northern Vietnam. Wikipedia says they may have spoke a Tibeto-Burman language. I found it interesting that some of these people look Caucasoid though and were wearing clothing similar to Scythians. The image I compared of the Dian man to the Indo-Scythian has a similar facial structure, hat, and even the same type of pants (sorry, I don't have time to tidy up the comparison photos more).
The Dian art theme of the four tigers attacking an ox is found in the same pre-Han period among the Xiongnu at Aluchaideng, and a similar motif appears at Tillya Tepe a couple centuries later. The theme is the same but the style is very different, still it indicates a connection to these places of the world through trade and exposure.
Some of the scenes with soldiers show a variety of different equipment styles and certain subjects have distinct fashion styles (like the people wearing the items that make their ears look huge). I watched a couple documentaries on genetics of the Dian and they were only able to find genetic info for one person, who was identified as similar to the Baiyue people. I'll link those youtube videos in sources below. I assume these people were primarily related to modern day Vietnamese and southern Chinese (or other people nearby) but may have had close interactions with (and even immigrants from) Scythian cultures despite their distance from them, which is interesting.
From the videos: "According to the final count, the amount of bronze ware excavated from Lijia Mountain is almost half the amount of the Shang Dynasty bronze ware excavated in Yinxu, Henan."
youtube
youtube
#ancient history#history#museums#art history#art#sculpture#statue#ancient china#china#vietnam#scythian#artifacts#antiquities#anthropology#archaeology#indo european#Youtube
268 notes
·
View notes
Photo

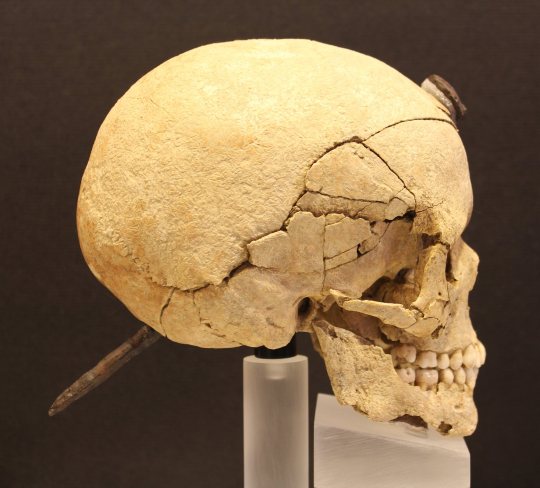
In various cities of the Ancient Iberians (Ancient Iberians were the indigenous cultures that lived in the Eastern coast of the Iberian peninsula before they got conquered by the Roman empire), archaeologists have often found skulls perforated by a nail. All of them have been found in the cities located in what nowadays is the Northern half of Catalonia (Ancient Iberian cultures, though related to each other, varied a lot area to area).
These are believed to be the skulls of their enemies, who were captured and beheaded. The enemy’s heads were nailed to the city walls or above the entrance door to houses, together with their weapons. Most of these heads belonged to individuals of the male sex, though some are female and a few belonged to children.
The Ancient Iberian language hasn’t been deciphered and their contemporaries didn’t write much about them, thus many aspects of their culture aren’t known for certain. Archaeologists have the hypothesis that this practice could be related to the way Celts exhibited the heads and hands of their enemies as war trophies, or related to a belief present in the ancient Mediterranean according to which cutting someone’s head off stopped them from reaching immortality. The Gauls even passed down the beheaded heads of their enemies to their children, as a prized possession that brought prestige. It’s a possibility that Northern Iberians were in touch with this practice.
Photos from the Ancient Iberian site Ullastret (Comarques Gironines, Catalonia) posted on National Geographic. Information from Rovirà i Hortalà, 1998 and MAC Ullastret.
#història#arqueologia#ullastret#catalunya#ancient iberians#antiquity#ancient history#ancient#archaeology#archeology#protohistory#war history#historical#historical artifacts#artifacts#anthropology#bones#european history#europe
117 notes
·
View notes
Text
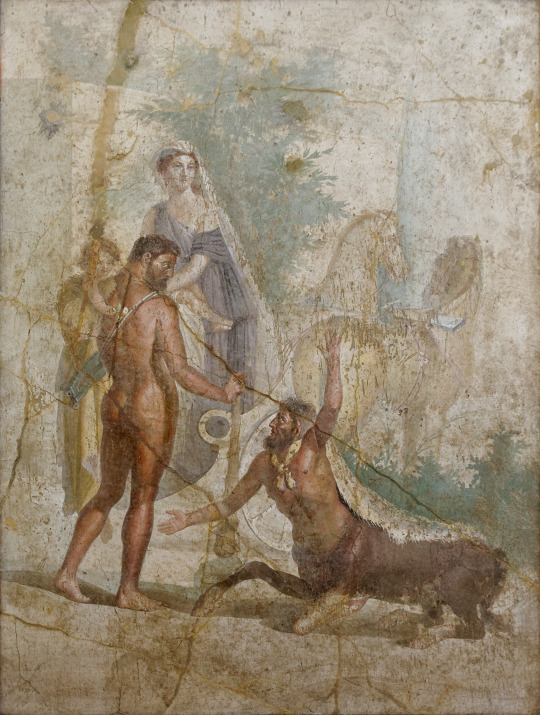

Hercules carrying his son Hyllus looks at the centaur Nessus, who is about to carry Deianira across the river on his back, 1st century AD
Naples National Archaeological Museum
#fresco#hercules#art#hyllus#greek mythology#cradle of civilization#southern europe#ancient#anthropology#archaeology#fine arts#fine art#nessus#centaur#civilization#western civilization#deianira#european art#classical art#europe#european#oil painting#mediterranean#europa#naples#greece#rome
238 notes
·
View notes
Text
Review of The Horse, the Wheel, and Language: How Bronze-Age Riders from the Eurasian Steppes Shaped the Modern World by David W. Anthony

I will be upfront, it is a very technical book. If you are not well versed in the anthropological categorizing of cultures and time periods of the areas being discussed it can be very difficult to keep up with the more finite points the author is making. That being said, I had never heard of any of the specific cultures being discussed in the Danube Valley and was still able to enjoy this book and its well put together analysis of various aspects of language, culture, technological developments and shifts in behaviors and place.
If you are especially interested in any of the major themes this book discusses (which is in all honesty is an extensive list including but not limited to; the development of Indo-European language, the time periods and locations as well as likely motivation for domestication of various livestock types, the cultural effects of technological developments on the peoples of the Eurasian Steppes and their migration/trading patterns) I do highly recommend. It is heavy reading but extremely illuminating.
#The horse the wheel and language#David W Anthony#historical anthropology#anthropologist#anthropology#ancient languages#language#historical linguistics#linguistics#proto indo european#indo european#steppes#eurasian#eurasian steppe#horse#horses#husbandry#burials#Cattle#sheep#book review
159 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hello! I used to have this domain as a studyblr but since finishing my masters, I saw little point in continuing that route so I decided to start from scratch. So consider this a little introduction back into this site that feels completely strange to me despite growing up in the Tumblr golden era.
My name is Lis, I'm a PhD student in Scientific Archaeology focusing on the effects of animal domestication in Central Europe. I'm currently struggling to find a passion for a subject that I genuinely love so I'm hoping that coming back to this little corner of the internet will reignite my love for history and learning.
#studyblr#archaeology#history#ancient history#culture#anthropology#european history#ancient culture#genomics#genetics#phd diaries
76 notes
·
View notes
Text
I love how much of a universal human constant it is to fear The Woods. what happens in The Woods is none of our business. if you see or hear something in The Woods after dark, No You Fucking Didn’t and you should leave immediately.
#something something huge swathes of our planet were once covered in dense forrest and jungles full of predators#something something generational memory of survival tips passed on as myths and stories#this thought was sparked after i watched a funny reel by a native man talking about skin walkers#and it reminded me of the same way older european folk tales would talk about The Wolf in the The Woods#i’m sure someone has already done an anthropology about this but anyway i love people and i love how we share mythos across time <3#humanity#anthropology#the woods are lovely dark and deep
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

This goes quadruple for anything related to medicine
#it's always like#and here is the unit where the professor says they definitely do not want to harm children#and knows we shouldn't desecrate corpses just bc they aren't european#psychology#biology#anthropology#archeology#sociology
15 notes
·
View notes
Text









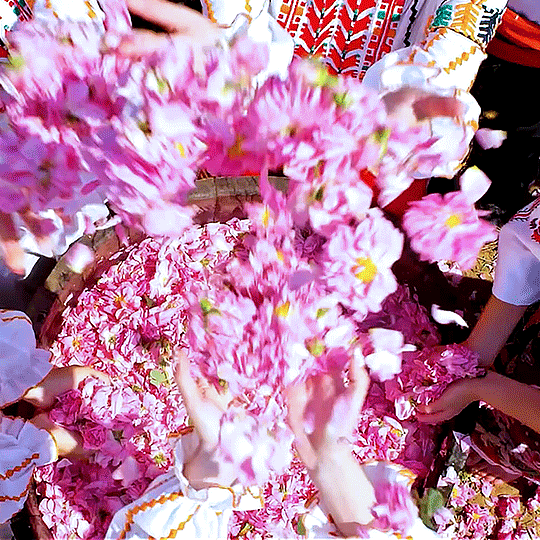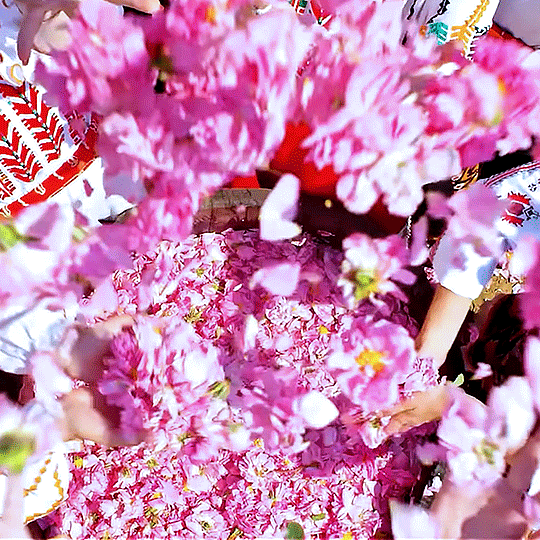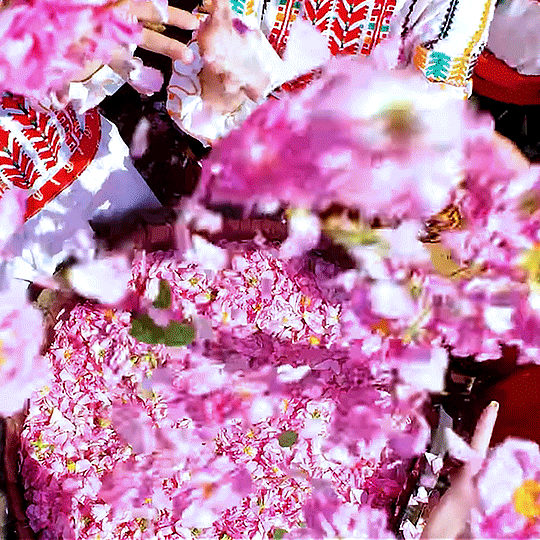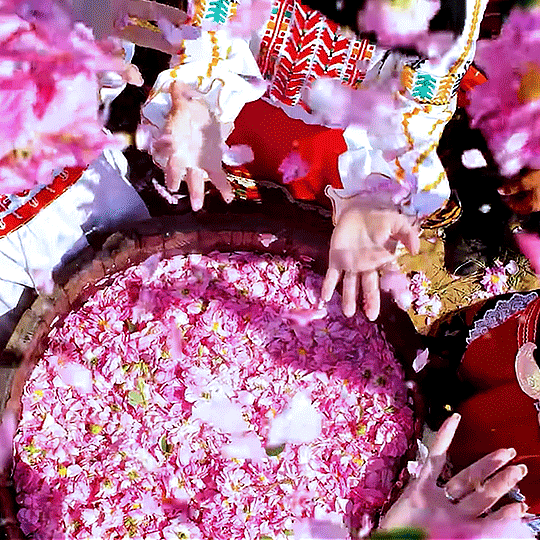
Bulgaria’s Rose Valley & Rosa Damascena: On February 14th, Bulgarians celebrate St Trifon Zarezan (an ancient Thracian holiday rite). Dressed in their traditional best, vine growers prune and sprinkle Bulgarian wine for a good harvest. Then, they gather for a delicious meal.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
it is fascinating to me that the majority of people it seems have never considered that borders are just lines on a map? its just a piece of paper? not to have anarchic tendencies but like. it’s just words
#tried to type and retype this sentiment in prev but it kind of negates the premise of the post (which i agree with)#because like. yeah borders are just lines#but like re prev jannik IS italian since thats what he identifies with#even though people call him german/austrian because of his background#which is weird to say right? its weird. like idk man he plays for team italy sooo#so i didnt want to be like well borders are fake. true but not the point#and now unrelated to prev post but back to the topic of borders#they do fascinate me. guy who’s obsessed with colonial history#something i think about a lot is like. ppl r always talking about how tiny european countries are etc#and its like yeah. due to the diversity of ethnic groups in the continent (yeah yeah multiple cultures in a country too)#and then comparing that to north america like if we considered indigenous bands and nations in the same way its the same thing#but no one ever talks about it. like damn theres a great diversity of people groups worldwide and only europe gets to carve out areas#<- although like again. not that im pro ethnicstate or pro border but like theres a reason why europe is small and other countries arent#idk. i heart political science and history and anthropology and culture god bless
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Colonial appropriation of indigenous lands often began with some blanket assertion that foraging peoples really were living in a State of Nature – which meant that they were deemed to be part of the land but had no legal claims to own it. The entire basis for dispossession, in turn, was premised on the idea that the current inhabitants of those lands weren’t really working. The argument goes back to John Locke’s Second Treatise of Government (1690), in which he argued that property rights are necessarily derived from labour. In working the land, one ‘mixes one’s labour’ with it; in this way it becomes, in a sense, an extension of oneself. Lazy natives, according to Locke’s disciples, didn’t do that. They were not, Lockeans claimed, ‘improving landlords’ but simply made use of the land to satisfy their basic needs with the minimum of effort. James Tully, an authority on indigenous rights, spells out the historical implications: land used for hunting and gathering was considered vacant, and ‘if the Aboriginal peoples attempt to subject the Europeans to their laws and customs or to defend the territories that they have mistakenly believed to be their property for thousands of years, then it is they who violate natural law and may be punished or “destroyed” like savage beasts.’ In a similar way, the stereotype of the carefree, lazy native, coasting through a life free from material ambition, was deployed by thousands of European conquerors, plantation overseers and colonial officials in Asia, Africa, Latin America and Oceania as a pretext for the use of bureaucratic terror to force local people into work: everything from outright enslavement to punitive tax regimes, corvée labour and debt peonage.
From The Dawn of Everything: A New History of Humanity (2021), by anthropologist David Graeber and archaeologist David Wengrow
#the dawn of everything#david graeber#david wengrow#history#world history#colonialism#settler colonialism#imperialism#genocide#european colonialism#john locke#locke#archaeology#anthropology#quote#book quotes#native american
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

Comparison of Minoan, Mycenaean, Sogdian, & Khwarazm artworks 17th C. BCE - 4th C. CE
When I came across the Khwarazm (aka Chorasmian) murals I remembered this red-eared priestess from Thera. Their large eyebrows, red-painted ears, extremely light skin tone, and general facial features look very similar to each other despite being over 1,000 years apart and in different regions of the world. Other than that their clothing, jewelry, and hairstyle are quite different. I couldn't figure out what the significance of the red ears were, though Jason Earle speculates it might be an artistic depiction of a person hearing something divine from a deity (Cosmetics and Cult Practices in the Bronze Age Aegean? A Case Study of Women with Red Ears). These are the only images I've come across, that I can recall, of people with their ears painted red so I felt like comparing them.
The Erkurgan fragment has red solar symbols very similar to the Mycenaean plaster head. Again these two pieces of art are over 1,000 years apart and in different geographic locations. I don't know who the Erkurgan fragment should be attributed to, but this was a place in the heart of Sogdiana. I assume it represents a Sogdian because of location and time period, but that's just my assumption. Solar symbols appear in basically all civilizations, but I've never come across these specific red styled ones (that I can recall) except in these two instances. In both instances they appear on the cheeks, forehead, and probably the chin (the Erkurgan fragment's chin is damaged but seems to have some red paint). Again, seeing this unique symbol made me feel I should compare the two. From what I've read all the images here are generally thought to be depictions of females with religious significance.
#minoan#mycenaean#art history#ancient history#ancient#art#antiquities#history#paganism#pagan#goddess#priestess#indo european#ancient art#archaeology#anthropology#sogdiana#ancient greece
275 notes
·
View notes
Text
having jewish family from n iraq general area is very strange. n iraq area is a bit of an outlier from its neighbors people group-wise because it’s often kurd = muslim; arab = muslim also; assyrian = christian (or at least an overwhelming amount of christians are assyrian); yazidi = yazidi; but jews are called ‘kurdish jews’? they probably just got that label because they were in the area (some have ‘tribal’ last names if they were from the literal towns the tribes got their names from), but for example syrian jews who lived in aleppo/damascus and spoke arabic are called syrian jews, some people use “arab jew” but afaik most don’t
in that context “kurdish jew” seems a little...misleading? “assyrian jew” is too, they were both religious minorities and spoke aramaic but jews have a separate history (and due to current politics it feels insensitive but idk.) and both of those can be used by israeli govt stuff for propaganda purposes, so looking into sources for this is nigh impossible. tbh i prefer ‘mesopotamian jew’
#strange situation overall that i don't think can be solved anytimne soon#*srael pretty much fucked up jewish history research that isnt european#ultimately small potatoes compared to what palestinians are going through#weird pan-’mizrahi’ ethno-anthropology ultimately relates back to it. colonialism & all that#both 'kurdish jew' and 'assyrian jew' sources i managed to find were zionist propaganda. sobs#not to mention it was a very small community and there aren't a ton of descendants in the world in comparison to like. moroccan jews#ironically the most reputable + objective historical account w/ interviews from people who lived it#was compiled by someone currently head of netanyahu's 'ministry of arab affairs'#such is the state of mizrahi jewish history research#there’s also historical records referring to them both as ‘kurdish jews’ and ‘assyrian jews’#but 'kurdish jews' could've been location-based and probably wasn't in the modern context of 'a people'#('kurdish christians' was often used to refer to assyrians for example)#and 'assyrian jews' was also used to refer to s. iraq general area jews and syrian jews#i’d complain about how it’s annoying that jews are ‘their own thing’ unless they’re bene israel/’kurdish’/yemenite etc but#ill uh. explain this in a reblog
22 notes
·
View notes
Text

There's a poem here but I'm too unmedicated to sculpt it out.
How beautiful is it that "To Have" and "To Give" have been, in a way, mistaken for each other? The act of Having and the act of Giving being interconnected.
Sharing a meaning, if you will.
#ignore the pretentiousness. it's incurable.#humanity is beautiful#linguistics#anthropology#proto-indo european
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
2022 Reading Log pt. 21

101. The Rise and Reign of the Mammals by Steve Brusatte. This book covers mammalian evolution throughout synapsid history, starting in the Carboniferous and ending in the present day. There’s a lot of good information in here, both about the species themselves and the history of their discovery and discoverers. But I found the authorial voice consistently off-putting. Brusatte writes about evolution alternately like a war or a poker game, and there are constant references to dominating, beating or tricking other lineages, particularly dinosaurs. After crowing about how mammals survived and thrived in the Mesozoic by exploiting small body sizes and niches like eating seeds and insects, he dismisses all of bird evolution (which in the Cenozoic did the same thing) in a paragraph, and never talks about Cenozoic animals other than mammals at all. What’s weird is I don’t remember his previous book, The Rise and Fall of Dinosaurs, being so mercilessly jingoistic about its focus clade. Maybe the publisher told him to write more enthusiastically about a “less exciting” group; maybe it’s the zeal of the newly converted (Brusatte was primarily a dinosaur paleontologist until relatively recently); maybe the first book was this annoyingly written and I have forgotten.

102. The Accidental Ecosystem by Peter S. Alagona. This book is a short overview about how wild animals have moved into American cities, why American cities developed into places where animals can thrive, how humans are reacting to these and how we should in the future. The tone is generally optimistic but realistic—that cities can serve as oases of biodiversity during climate change and extinction events, but a world with only rats, crows and sparrows would be a depauperate one. Most of the book is organized around an incident of some charismatic megafauna making the news (like Pedals the bipedal bear of New Jersey, or a nesting pair of bald eagles blithely feeding their chicks fresh kitten), and then talking about that species in greater context. I’ve read several other books recently about human/animal interactions, and this one did the best job at being inclusive, talking about how parks can and have been used as agents of gentrification, the impact of economic decisions on the fate of cities and animals alike, and existing biases within ecology and evolutionary studies. Highly recommended.

103. Travels to the Otherworld and other Fantastic Realms, edited by Claude and Corinne Lecouteux, translated by Jon E. Graham. This is a collection of medieval European fantastic literature, although not all of it is necessarily fantasy in the modern sense. Some are religious visions, others historical fantasies, others excerpts from novels and folk tales. All of them are wild. Both as a look into the medieval mindset and for their various bizarre creatures and occurrences. Some highlights include multiple versions of the adventures of Alexander the Great, the Vision of Tundale, a German journey through Hell that’s much gnarlier than anything in Dante, and the adventures of Marcolf, the Sherlock Holmes to King Solomon’s Watson (!). Also highly recommended; this might be the most fun I’ve had with a book this year.

104. Empire of the Scalpel: The History of Surgery by Ira Rutkow. Just what it says on the cover. The book starts with trepanations of cavemen and progresses to the modern era. Rutkow follows the Great Man school of history, and many of the chapters are biographical sketches of a surgeon who was important in developing the field. It feels somewhat incomplete—not only are non-surgical advances in medicine basically ignored, the development of the modern American insurance state is glossed over, even as the book discusses how hospitals became prestigious institutions and surgeons very wealthy. The book also uses weird kennings, as if it were written by an Icelandic skald—surgeons are “scalpel wielders” or “students of the knife”, etc, as often as they’re just surgeons. I definitely learned stuff from this book (like the quack “orifical surgery”, which posed that all diseases could be cured by cutting out irregular shapes from the mouth, nose, anus and genital openings!), but found the book rather less than the sum of its parts.

105. Monster Anthropology, edited by Yasmine Musharbash and GH Presterudstuen. This is a collection of academic essays about monsters as cultural signifiers and participants. After a very good introduction (the Works Cited of which will keep me busy a long while), the bulk of the book looks at particular cultures and particular monsters. The book was published in Australia, and several of the essays are on the same group of Indigenous Australians, the Warlpiri, and their monsters (most of which have not penetrated Western consciousness, but the pankarlangu is starting to make some inroads). One minor note I found interesting—there’s an actual folkloric monster that fits the D&D concept of a rakshasa! The tepun of the Eastern Penan people in Borneo is a shapeshifting hedonist that has aspects of humans and tigers.

106. Scent: A Natural History of Fragrance by Elise Vernon Pearlstine. Gave up on 50 pages in. The book purports to be a natural history—what molecules are made by what plants, why, and how those plants live. The actual contents contain some of that, but much more cultural histories. I’ve read and enjoyed several books about the cultural history of plants recently, so I’m not inherently opposed to the concept. But the book is incredibly poorly organized. The narrative skips back and forth through time and space and species, words are used and then defined several pages later as if it’s the first time we’re seeing them, concepts will be repeated multiple times to the point of redundancy, and the preface and introduction contain the exact same sentences, twice! The fact that this book was published in this state is frankly embarrassing.
#reading log#bad books#botany#cultural history#paleontology#stem mammals#prehistoric mammals#anthropology#monster books#surgery#medical history#european folklore#medieval folklore#ecology#urban ecology
91 notes
·
View notes