#early qing dynasty
Photo
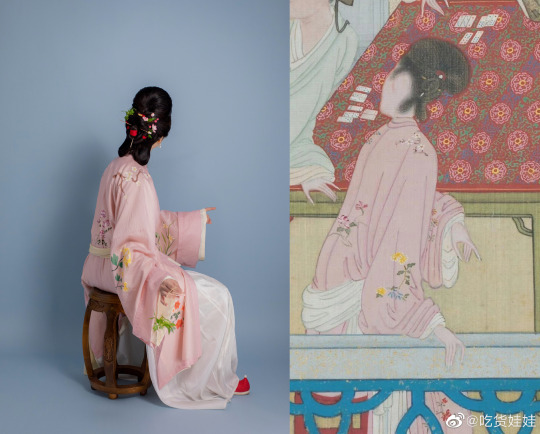
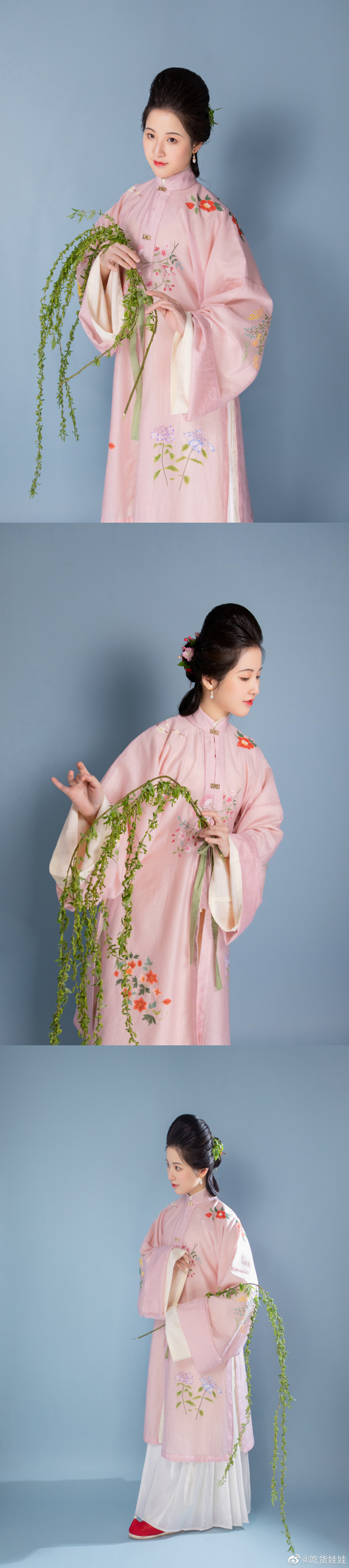
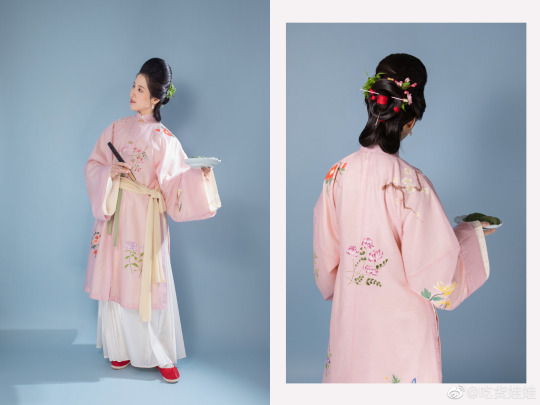
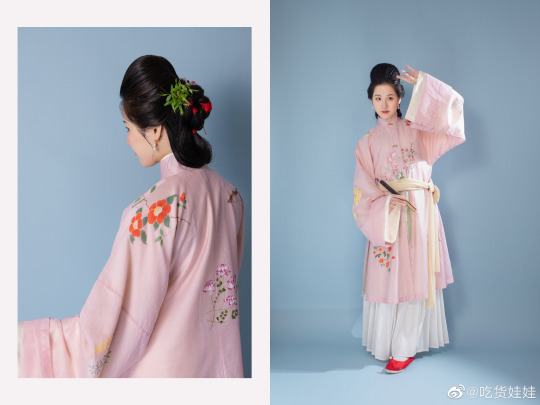









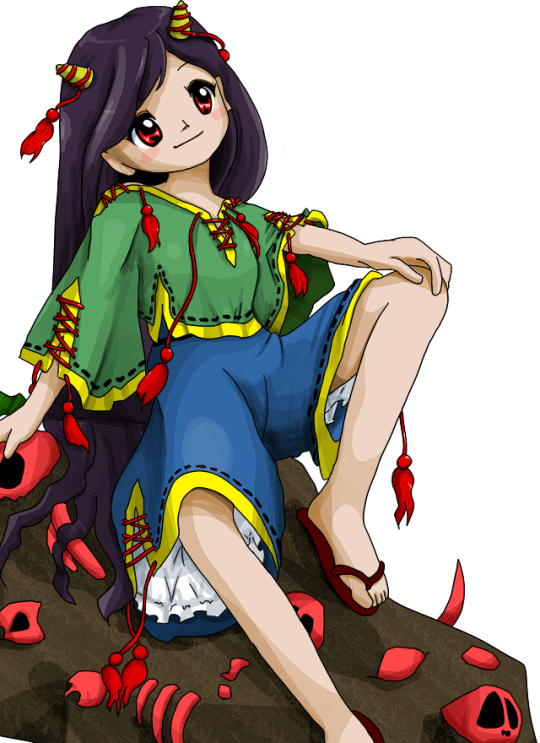
[Hanfu · 漢服]Chinese Early Qing Dynasty Traditional Clothing & Qingming Festival/清明節
————————
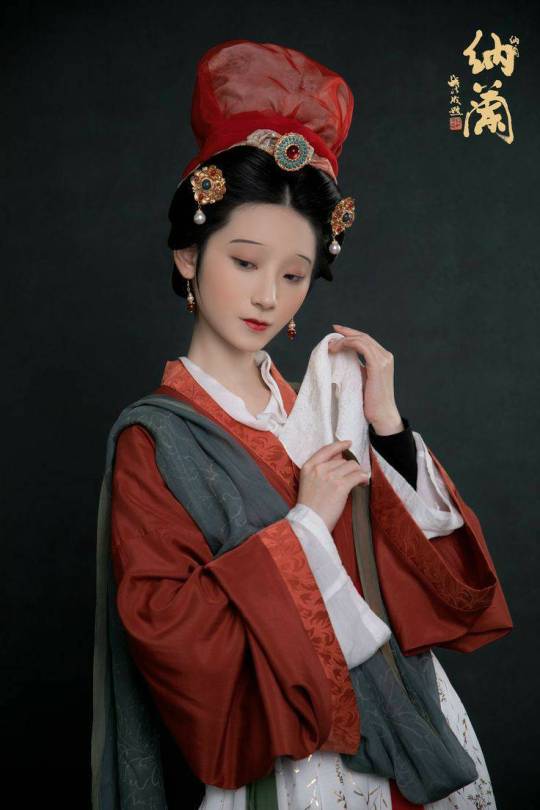
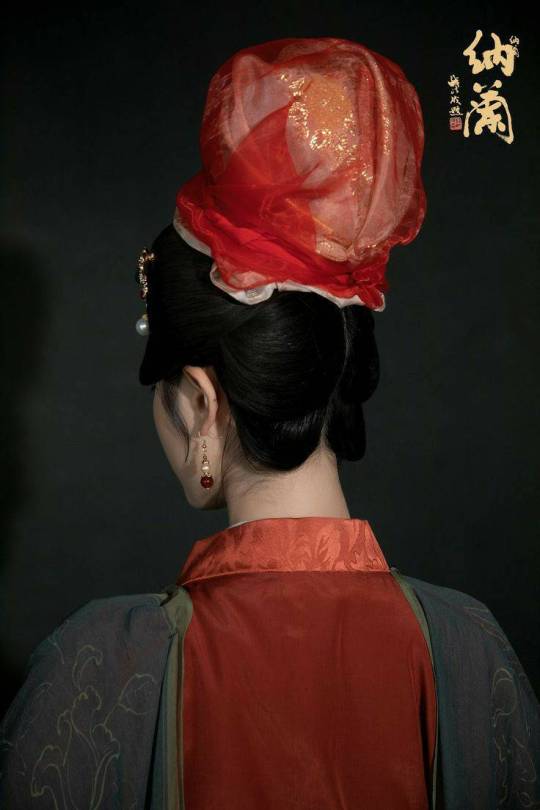
Han ethnic Women's attire & Hairstyle ”Peony Head (牡丹头) in the Early Qing Dynasty
Han ethnic Women's attire and hairstyle in the early Qing Dynasty was not like men that force to change by the Qing government. Women's attire and hairstyle were not particularly different from late Ming Dynasty.
————————
【Qingming Festival/清明節】
The Qingming festival or Ching Ming Festival,also known as Tomb-Sweeping Day in English (sometimes also called Chinese Memorial Day, Ancestors' Day, the Clear Brightness Festival, or the Pure Brightness Festival), is a traditional Chinese festival observed by ethnic Chinese in mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan, Malaysia, Singapore, Cambodia, Indonesia, Philippines, Thailand, and Vietnam.
During Qingming, Chinese families visit the tombs of their ancestors to clean the gravesites and make ritual offerings to their ancestors. Offerings would typically include traditional food dishes and the burning of joss sticks and joss paper.The holiday recognizes the traditional reverence of one's ancestors in Chinese culture.
The origins of the Qingming Festival go back more than 2500 years, although the observance has changed significantly. It became a public holiday in mainland China in 2008, where it is associated with the consumption of qingtuan,green dumplings made of glutinous rice and Chinese mugwort or barley grass.
--------
【Qingming Festival Customs: 插柳/戴柳 put willow/wearing willow 】
“清明不插柳,红颜变皓首”:
As the saying goes, it means in Qingming Festival, in the first ten days of March of the lunisolar calendar every year, is the day when traditional customs go to graves to worship ancestors. According to the old custom, when returning from worshiping ancestors during the Qingming Festival, people have to break off willow branches and wear them on head.It is said that if people don’t do this, young people will become old people with white hair.
According to the "Qing Jialu/清嘉录" written by Gu Lu of the Qing Dynasty:
「清明日,滿街叫賣楊柳,人家買之插於門上,農人以插柳日晴雨佔水旱,若雨,主水。」
every Qingming Festival, "willows are sold all over the street, and people buy them and put them on the door.
Q:why wearing willow or put willow on the door?
Jia Sixie(贾思勰)of the Northern Wei Dynasty(386-535) said in "Qi Min Yao Shu/齐民要术": “取柳枝著户上,百鬼不入家。”
“Take the willow and put it on the door/house, and a hundred ghosts will not enter the house”
It is said that a hundred spirits come out on Qingming Festival, and people need to worship their ancestors while carefully keep a certain distance from other spirits and keep them out of house. Willow has become a weapon for people to avoid evil spirits and protect people from them.
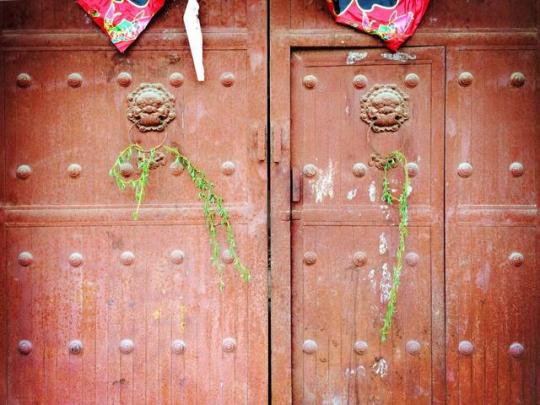

The custom is still widespread in parts of China especially Wudi(吴地) area: area in the south of the Yangtze River
----
In ancient times, there were many interesting Qingming Festival customs. Apart from visit the tombs of their ancestors to clean the gravesites and make ritual offerings to their ancestors, there were also a series of custom sports activities such as spring outing, swinging, Cuju (蹴鞠:is an ancient Chinese ball game) , playing polo etc.
_______
🧚🏻Recreation Work:@吃货娃娃
🔗Weibo:https://weibo.com/1868003212/MAyid6Mtv
_______
#Chinese Hanfu#hanfu#early qing dynasty#Ming Dynasty#Late Ming Period#Qingming Festival/清明節#Chinese Culture#chinese customs#hanfu accessories#chinese traditional clothing#chinese#chinese historical fashion#historical fashion#吃货娃娃#插柳/戴柳
142 notes
·
View notes
Photo



Puyi, last emperor of China, with his consort Wan Rong, early 20th century
#mdpchina#costume#20th c. china#chinese dress#chinese costume#qing dynasty#early 20th century#china#20th Century#vintage#vintage style#photography
98 notes
·
View notes
Text
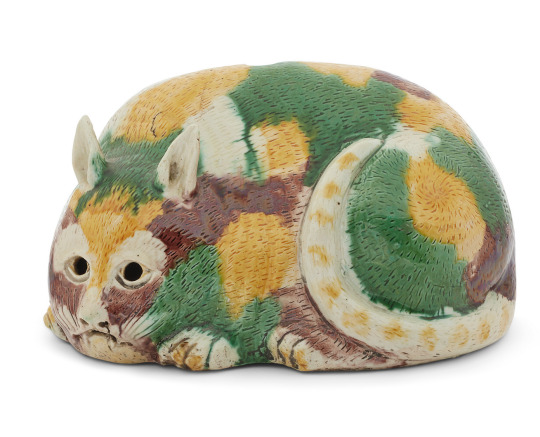
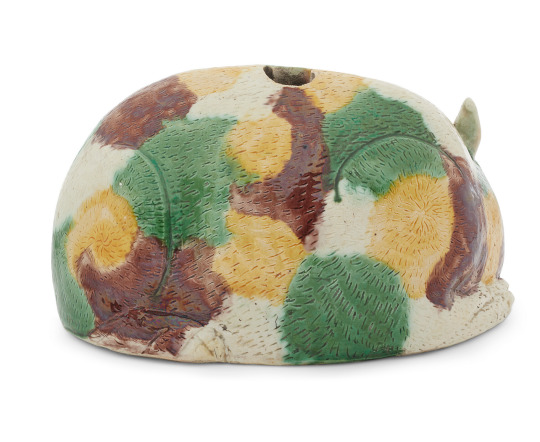


A night lantern in the form of a cat with egg and spinach glaze, Qing Dynasty, 18th - 19th Century
Christie's
#ceramics#cat#lighting design#china#qing dynasty#18th century#early 19th century#chinese art#egg and spinach
75 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hello Audrey, hope you are well!
This is regarding the recently aired Kangxi-era drama The Long River. It has very few scenes featuring women, I didnt complete it yet but gathered some pictures because I was curious about the fashion. I'd love to hear what do you think about these?
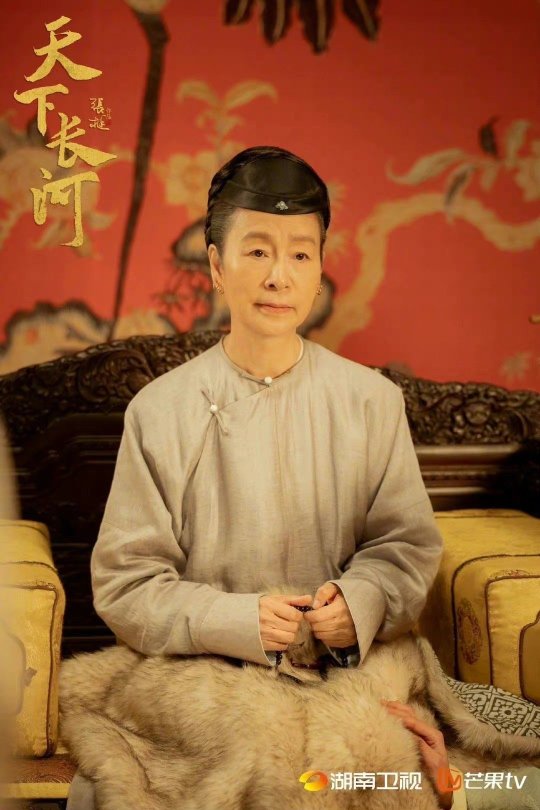
Styling of Empress Dowager Xiaozhuang, grandmother of Kangxi Emperor.
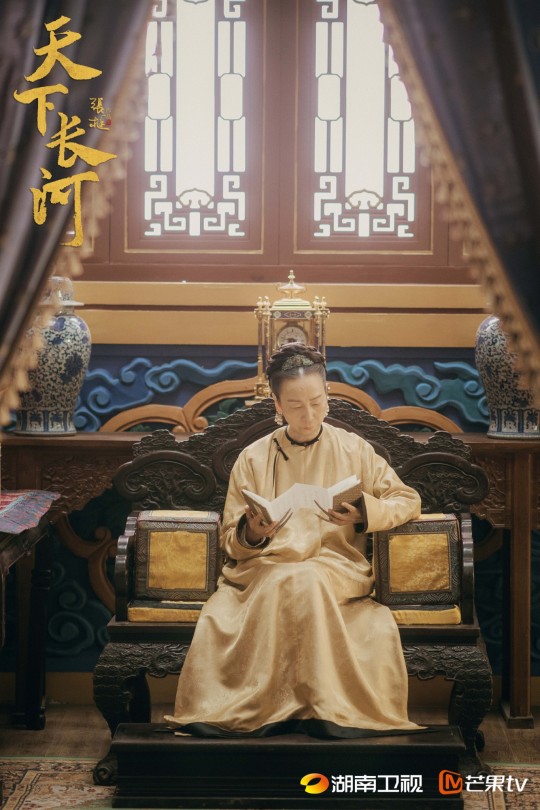
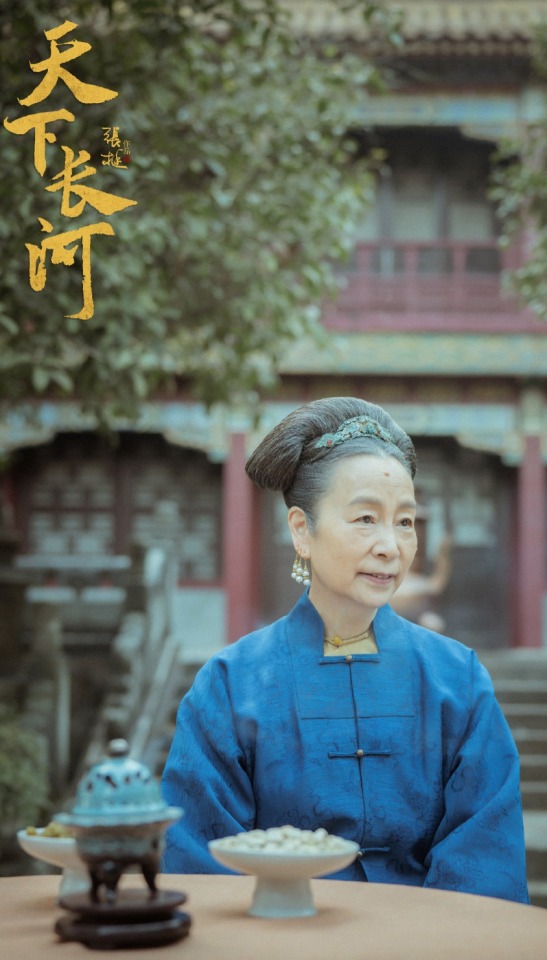






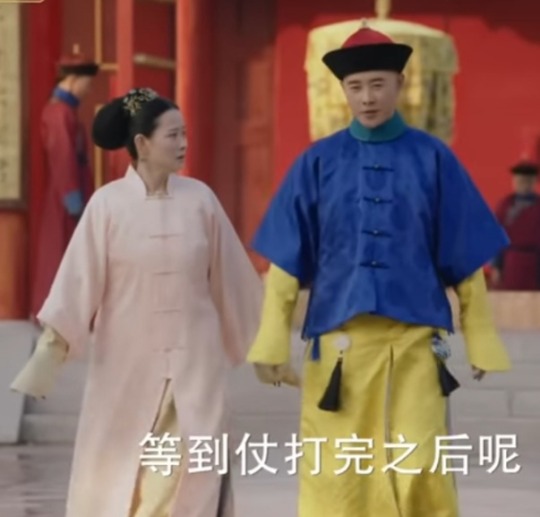
Styling of Kangxi's mom


Some servants (left) and a middle class (probably) woman (right)


Thank you very much for your time!
These look pretty solid! Maybe the first time I've seen 17th century Manchu clothing represented with honesty. The costumes in the second and third last images look like rented guzhuang costumes, I'm not sure why there is a discrepancy in the quality of costumes?

Portrait of Empress Xiaozhuang (1613-88). I think this is the reference they used for the plain collarless robes, which are quite well tailored and true to history.

Another similar styling from the 17th century.

Portrait of Empress Xiaozhaoren (1609-89), showing the square collar jacket.
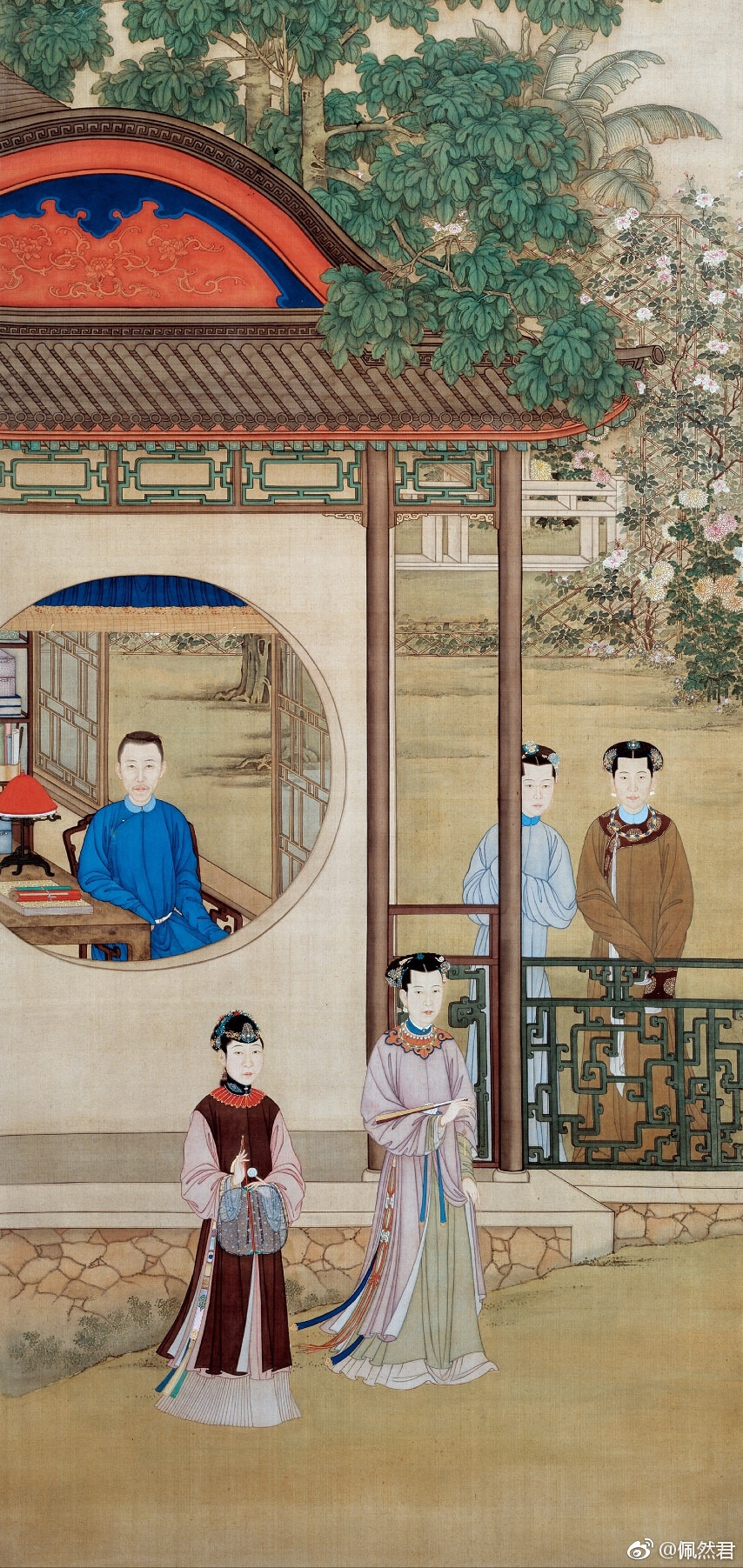

The guzhuang looking costumes might be a reference to this sort of stuff (the two ladies in the top right), but this is from the Qianlong era and 18th century. Not sure if something similar would have been done in the 17th, but either way the sleeves of the drama costumes look too short and a bit awkward.
88 notes
·
View notes
Text
Qing Dynasty mandarin winter robes, from the Beijing Palace Museum collection:
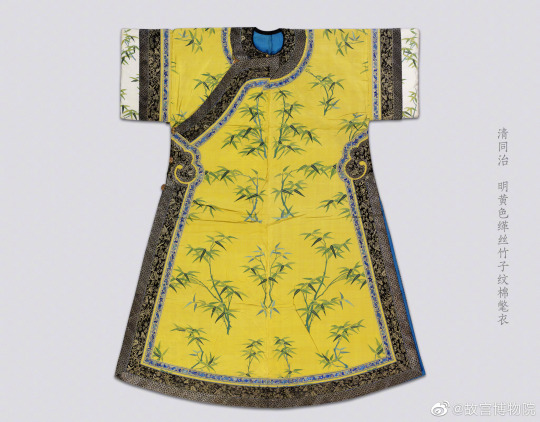
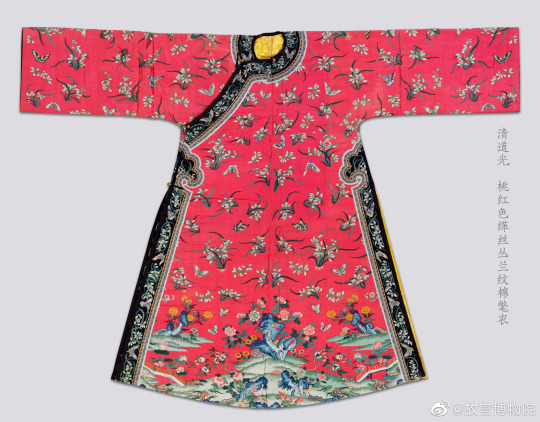
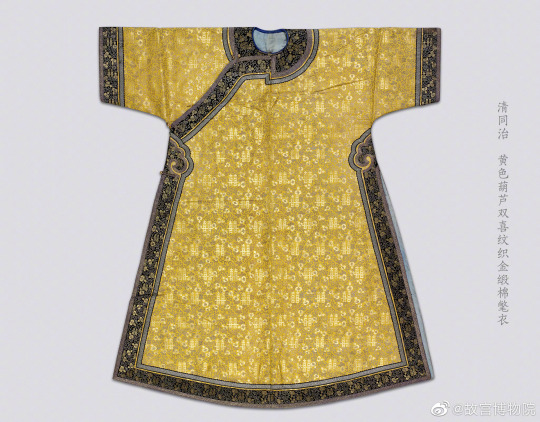









#china#qing dynasty#historical fashion#early modern history#winter clothing#forbidden city#beijing palace museum#artefacts#chinese fashion#manchu fashion#daicing gurun#textile#asian costume#silk#satin#mink#history
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
I get the sense that most of the time periods I was interested in as a kid are pretty niche which huh
#like my impression of what's popular is like three kingdoms + song dynasty* + qing dynasty + maybe chu-han contention and maaaaybe-#-spring and autumn/warring states?#whereas me it's like early shang + zhou + spring and autumn/warring states broadly but the wu-yue stuff in specific-#+ han dynasty specifically the time from gaozu to emperor wu/emperor zhao +scattered bits of northern and southern dynasties#+ the conflicts wrt jiedushi and eunuchs in late tang#my rambles#it's weird for a lot of these it's been so long I can't really tell you any of the specifics anymore even when I still have a strong-#-association of it with fondness/fascination#I should really reread stuff I've been meaning to for so long I just never have time ackkk
1 note
·
View note
Text
打鐵花 (da2tie3hua1; struck iron fireworks) is a traditional folk firework that began in Henan and Shanxi, first arising in Queshan county, Henan and later circulating through the whole country. It had first appeared during the Northern Song dynasty, and was most popular during the Ming and Qing dynasties.
For Queshan struck iron fireworks, a two-layer pergola is built and covered with willow branches for performances, under which the molten iron is struck up with two willow sticks to create a rain of fire.
[eng by me + edited an ad out]
(On top of the information in the video, I have some more about its recent history under the cut.)
*Also, a note about one of the subtitles: I realized later that "going into battle without a shield" actually just meant going shirtless. I was only confused about this phrasing while translating because she didn't go shirtless, although that is for obvious reasons
Queshan struck iron fireworks had almost been lost before Yang Jianjun unearthed it again in 1988. It had almost died out in the early years of the Republic of China being established, after which there had only been three performances until 1988: 1952, 1956, 1962. Yang Jianjun had seen the 1956 performance as a 7-8 year old and later on as the director of a cultural centre, began digging up the skill and its history. In the process, he became an apprentice to Li Wanfa, who had been the last head of the Queshan Struck Iron Fireworks Society. He practised with sand and water, learning of its historical origin, its ancestral inheritors, craftsmanship and performance arts, but didn't touch the real thing until 1988. Through Yang Jianjun's efforts and investment, the first struck iron fireworks performance in more than 25 years took place in Nanshan Square (then a deserted area) in Queshan county.
Queshan struck iron fireworks are different from other struck iron fireworks in that it requires a wide area to perform, whereas others only needed a wall or could be hit straight up into the air, and it costs much more money to set up.
The names of inheritors are difficult to trace, and can only be traced back to the Qing dynasty during the Qianlong period, making Yang Jianjun a sixth-generation inheritor, and Jiang Xunqian (OP) the first woman and a seventh-generation inheritor.
#douyin#arts#imparting culture#struck iron fireworks#creator: 江寻千(九月)#personal fav#i spent wayyyy too much time on this#def the most time i've ever spent on a post#i'm v v excited to post this#also i originally tl'd 打铁花 as blacksmith's fireworks and then i realised that wouldn't work
8K notes
·
View notes
Note
hey (culture ask incoming) im wondering about weddings in china and whether people generally wear more western style wedding clothes or traditional chinese style?
(Long-winded answer incoming)
Depends.
I would say Chinese/hanfu style wedding attire has been making a big comeback (so to speak) in recent years as a side effect of the hanfu revival movement, but there is also Chinese wedding attire that is distinctly it's own genre of clothing, i.e, bridal/groom wear. When you look at it, you know (if you know) that it's wedding attire. More on this in a second.
Still, for those who can afford it, it is popular these days to wear both western style wedding attire and Chinese wedding attire. Most people who I've seen wear both change into the Chinese attire for the wedding banquet. If they wear a western wedding dress, it will be at the ceremony/walking down the aisle. Likewise, if they wear both hanfu and Chinese wedding attire, they will wear the hanfu for the ceremony. Another thing to keep in mind is that in China, it is quite popular to take wedding photos in a myriad of outfits, not just the one you will be wearing on the occasion. So people nowadays may take photos in all the different kinds of wedding attire (via clothing rentals), whether they are going to wear it at their wedding or not. In that spirit, they still technically wear both western and Chinese style wedding clothes.
Hopefully that answers your question there. I have a #chinese wedding that covers a lot of videos but in which you can see the types of gowns and all that which I will briefly go into below.
So: when it comes to "traditional Chinese style" wedding attire, what does that really mean?
To me, three main types of clothing come to mind: 1) Chinese Wedding Attire™ , 2) Chinese style wedding attire, 3) Wedding hanfu
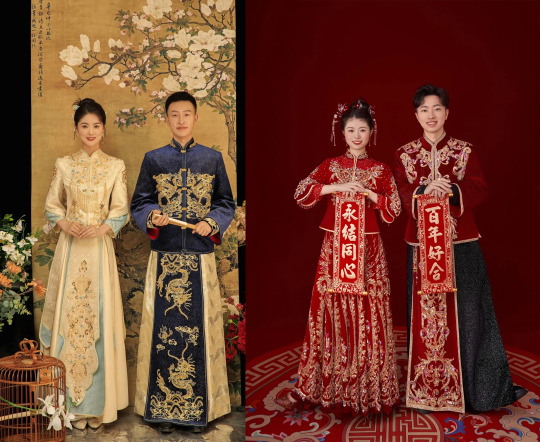
1) Chinese Wedding Attire™, AKA 秀禾服 Xiùhé
Visually distinct, it is not really hanfu nor qizhuang but a secret third thing.... In this case, it is a blend of Qing dynasty and Republican era styles dubbed "xiuhe". As bridal wear specifically, it is actually a rather recent trend (21st century), but it's become a fixture in Chinese wedding wear. While the colors can vary wildly and magnificently, the classic colors here are gold and red.
The style that exists today shows Qing dynasty influence in its construction and at its core consists of both bride and groom wearing embroidered tang suit tops and a matching silk skirt. The bride usually wears hair ornaments/pins in place of a veil. Since there are pins in the hair, brides may wear a xiapei/cape with a long train instead.
A few bridal styles (keep in mind that these are just the classic cuts and colors—there are other styles/colors that contain recognisable elements of bridal wear but are made of different fabrics, have different draping, have more tassels, have a softer look, etc):
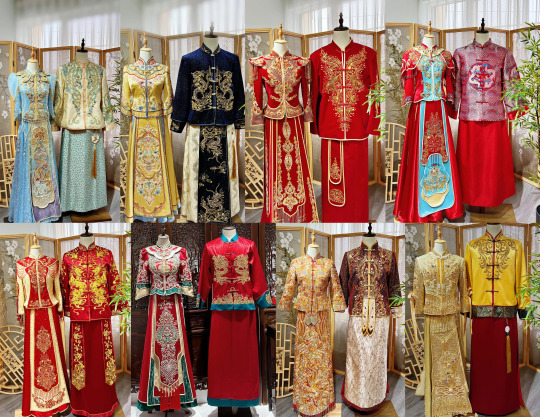



2) Chinese style wedding attire
This is admittedly somewhat of the same thing as Wedding Attire™, just toned down as it was more popular/commonplace in the last century, when it was what was most affordable for most, but it's a style that nonetheless comes to mind. With this, the key is simply that the bride wears a mostly all red dress/top+skirt and the groom wears a suit. Bride and groom will also often wear a red flower/ribbon pinned to their top or worn around them gift-wrapped style, haha. My mom just wore a red top and bottom to her wedding dinner (that's as much detail as I've ever gotten out of her lol) when she got married in the early 80s. Another thing is, since white is a funerary color/color of death in Asian cultures, some people also just wear Western style wedding dresses that are red.


3) Wedding hanfu
As you can imagine, this is ornate hanfu that is worn for weddings. Song/Ming style hanfu is particularly popular here.This clothing is traditional in the sense that it has historical basis and is what those who could afford to word for weddings historically. Historical wedding colors varied but color pairings like red & blue and red & green are traditional (man wears red, woman wears blue/green; 红男绿女). Wearing hanfu for weddings is a trend that has become popular with the hanfu revival movement and is, as you might guess, a trend for Han Chinese people



Chinese ethnic minorities have their own wedding attire that they may choose to wear/wear as well (if they do a banquet, etc). Or they might just wear red/xiuhe/western style dresses, too—this is another area where wedding photos let you basically wear everything.
(just a few examples:)


#text#answered ask#chinese wedding#hanfu#long post#少数民族#LMAO I just noticed I accidentally included the same couple twice in the hanfu section 💀#…it’s ok her makeup and hairpiece is slightly different
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Amazing fanart by Joanacchi! Posted here on tumblr with their blessing. Each one is based on a style that reflects a particular ancient culture's art history. (See below for descriptions provided by the artist!)
Store (buy these prints!) Twitter Instagram




Aang: Tibetan Thangka
"Thangkas are traditional Tibetan tapestries that have been used for religious and educational purposes since ancient times! The techniques applied can vary greatly, but they usually use silk or cotton fabrics to paint or embroider on. What you can depict in a Thangka is really versatile, and I wanted to represent things that make up Aang as a character."
Zuko and Azula: Japanese Ukiyo-e
"Ukiyo-e is a style that has been around Japan between the 17th and 19th century, and focused mainly in representing daily life, theater(kabuki), natural landscapes, and sometimes historical characters or legends!
Ukiyo-e was developed to be more of a fast and commercial type of art, so many drawings we see are actually woodblock prints, so the artist could do many copies of the same art!
I based my Zuko and Azula pieces on the work of Utagawa Kuniyoshi (1798-1861) one of the last ukiyo-e masters in Japan! He has a specific piece which featured a fire demon fighting a lord that fought back with lighting, and that really matched Zuko and Azula's main techniques!”
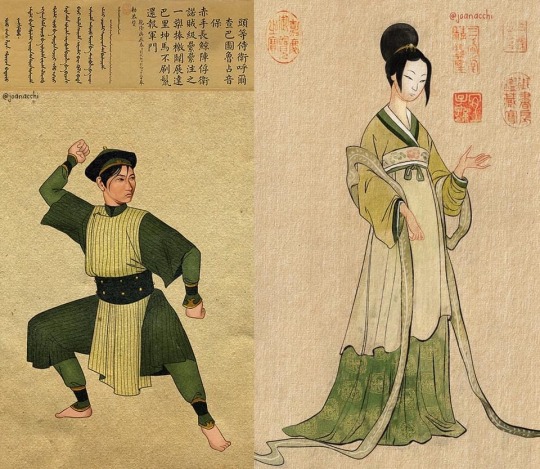
Toph: Chinese Portraiture from Ming and Qing Dynasties
"Ming Dynasty (1368-1644) was one of the longest in China! It was also a period where lots of artistic evolutions were happening, especially when it comes to use of colour! There was not a predilection for portraits during this time, but there are a lot of pieces depicting idealized women and goddesses from the standards of the time. For this portrait of Toph, I imagined something that maybe their parents commissioned, depicting a soft and delicate Toph which we know is not what she is about ♥️
Qing Dynasty (1644-1912) was the last Chinese Dynasty to reign before the Revolution. One of the most famous emperors of this period was Qianlong, and he really liked Western art! He commissioned a lot of portraits of his subordinates, and I chose a portrait of one of his bodyguards as a reference for the second Toph portrait, which I believe is much more like how she would want to be represented! The poem on top talks about the bodyguards' achievements during a specific war. I had no time to come up with a poem for Toph, so I just used the same one for the composition!”
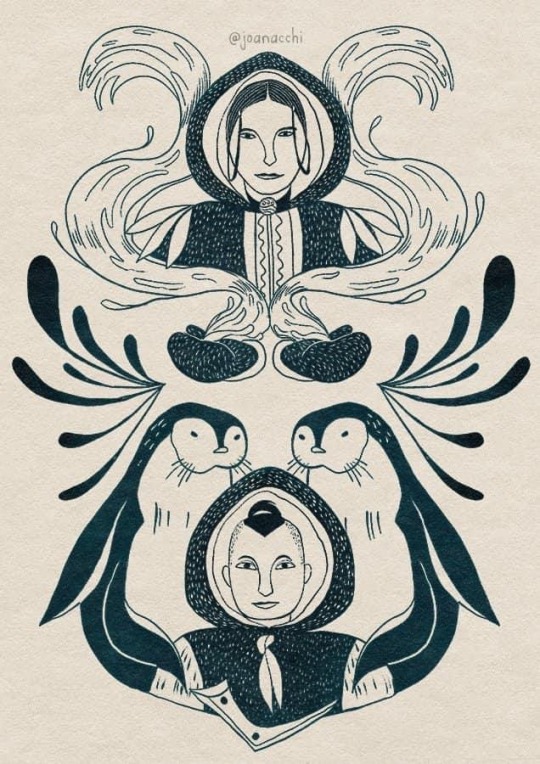
Sokka and Katara: Inuit Lithograph
"For a long time, Inuit art expressed itself in utilitarian ways. The Nomadic lifestyle of early Inuit tribes played a huge part in that: most art pieces are carved in useful tools, clothing, or children's toys, small and easy to be transported, and depicted scenes and patterns representing their daily lives!
That changed a lot during the colonization. Since the settling of the Inuit tribes, many art pieces began to be created in order to be exported to foreigns, so they started to sculpt bigger and more decorative pieces.
Lithography, which is a type of printmaking, was introduced to Inuit people by James Houston, that learned the technique from the japanese. The art form was quickly embraced by the inuit, as part of the process is very similar to carving. Prints that are produced by inuit artists are still being sold today!
As lithography is not an old art style and it's still commercially relevant to the Inuit communities, since creating these in 2021 I have been donating regularly to the Inuit Art Foundation, not only all the money I get from selling some prints of these but a bit more, at least once a year. Hopefully, I can increase donations this year!”
663 notes
·
View notes
Text

A Chinese Russet White Jade Dragon Plaque, early Qing Dynasty (1644–1911). Carved in high relief and reticulated with a dragon pursuing a flaming pearl, amongst lotus bloom and scrolling foliage.
529 notes
·
View notes
Text
The breast binding trend that young women are doing now has already been done by young women 100 years ago.
Read this excerpt from this paper about qipao fashion by Adrienne Cox:
The changes in qipao fashion began with the trend of breast binding in the early 1910s. Breast binding became more popular toward the end of the Qing dynasty, especially among young female students, who sought to hide their feminine figures by binding their breasts and wearing the early qipao that was stylistically similar to their male counterpart’s changpao style.
Breast binding provided young women with a slim boyish figure and allowed them to show off a more androgynous body as they began to move into the public sphere, which allowed them to preserve a sense of modesty. By hiding their feminine figures, they were able to enter the public sphere without drawing the attention of the male gaze as sexually promiscuous women. In the late 1910s, the trend of breast binding for political reasons quickly spread around urban China, and by the 1920s women of each province sported their own versions of breast binding devices. In the north near Beijing, the laoshi moxiong or old-style breast cover was popular and bound the breasts tight to the chest. In the south the xinshi moxiong or new-style breast cover was more popular and provided a slightly looser fit. From this trend of breast binding, we can also understand how women’s outer clothing changed to fit the new style of feminine form, as qipao styles became tighter to conform to the boyish figures.
The general practice of breast binding also points toward women’s desire to take control of their bodies as they are increasingly visible in the public eye. Women chose to bind their breasts as a way to make their body more suitable to the public eye, which then allowed them to take advantage of education and job opportunities that would bring them directly within the gaze of a society that had functioned by hiding female bodies for centuries. During this time period, who was in control of women’s bodies was the serious question. The changes in both breast binding and qipao styles provided women the opportunity to enter the public sphere without drawing the criticism of conservatives who felt women should stay within their traditional gender roles at home.
By the early to mid-1920s, another movement was beginning to gain traction that completely changed the way that women would display their bodies in public, as well as how the Nationalist government would respond to women’s political needs and demands. This movement began as some urban women sought to free their bodies from the constrains of their clothing as well as the constrains of traditional gender norms. These women sought to literally free their bodies from the historical bindings that had deformed women’s bodies. In this movement, breast binding became closely linked with rhetoric surrounding foot binding, which linked it to the feudal and restrictive past. Feminists across China called this the ‘natural curves’ movement, and it sought to completely eradicate breast binding and focused on women’s physical health. The movement was later supported by the Nationalist government after 1927, and women’s health was encouraged for the benefit of the state—healthy women could produce healthy children—but the way women dressed and presented their healthy bodies came under attack from the Nationalist government for being too provocative.
When the ‘natural curves’ movement began, the women involved focused primarily on celebrating women’s ‘natural’ curves and bringing the ‘natural’ female form more fully into the public eye. This would both literally free women from hiding their figures using harmful tactics such as breast binding, as well as figuratively freeing women from the traditional expectations that drove women to hide themselves from men. In the past, women had either been in the home or so overburdened by loose layered clothing that the physical form was ultimately hidden away from sight. The focus of the natural curves movement quickly became the breasts, hips, and legs of women, and women’s magazines such as Linglong devoted centerspreads and articles to showing off and celebrating the physical health of athletic women. In 1933, the editors of Linglong even published an entire issue dedicated to showing healthy and athletic women. Linglong was largely influenced by the readers, and it wasn’t uncommon for a reader’s letter or personal article to be published in the magazine. This is important to note, because the 1933 sports issue that showed women engaged in sports also included images of healthy young children and mothers holding their babies, which shows that women around China supported the movement for a variety of reasons.
The emphasis on healthy and robust bodies became the forefront of the natural curves movement, and this focus was embodied in the two keywords of the movement, ziran mei and jian mei which mean ‘natural beauty’ and ‘healthy beauty.’ Under the principles of ziran mei and jian mei, Chinese women began to abandon their xiongyi entirely to show off the full shape of their breasts. Others began to adopt the western style brassieres, which would cover the breasts without pushing them into the chest. Politically active women throughout urban China could decide how they wanted to express their liberation simply by how they chose to present their bodies, and qipao styles were changed once again, this time to show off women’s full figures. Once again, the qipao was used as a way to show the political stance of the women wearing them.
In the late 1920s the Nationalist government, as well as some conservative civilians supported ‘natural breasts’ and fashion that followed not out of a desire to liberate women, but out of concern for their reproductive health and creating a clear divide between genders. A popular magazine called The Women’s Monthly published an article that openly admonished young women who still bound their breasts, and other women’s magazines published articles encouraging women to abandon their old binders in favor of the western bra, that would support the breasts without constraining them. Breast binding was said to be a major detriment to a woman’s ability to raise her child, as it was widely accepted that breast binding caused women to be unable to produce milk. These groups linked what was supposed to be a form of female liberation back to the traditional gender roles that many women were trying to escape.
–
First there's a breast binding trend among young women who want to avoid being sexualized by male peers.
Then there's a feminist rejection of this trend as feminists promote the importance of women's health and fitness.
And finally, conservatives co-opt the feminist rejection and twist it into a promotion of traditional reproductive duties.
All of this happened 100 years ago.
And all of it is happening again today.
339 notes
·
View notes
Text
[Hanfu · 漢服]Chinese Song Dynasty (960–1279 AD)Traditional Clothing Hanfu Reference to Song Dynasty Sculpture
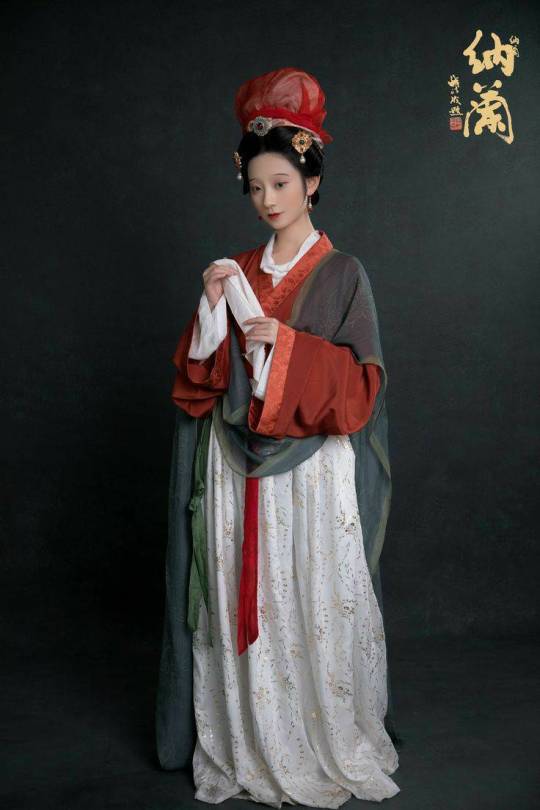






【Historical Reference Artifacts】:
China Song Dynasty Painted Sculpture from【Jin Temple】晋祠宋代彩塑

▶️【About Hairstyle“包髻/Bao Ji”】:
It is one of the hairstyles of ancient Han women.
包髻/Bao Ji is a hairstyles that use rectangular headscarf to cover the hair. When worn, it is folded diagonally, wrapped from the front to the back, and then wrapped around the corner of the scarf to the front of the forehead to tie a knot.
As early as the Tang Dynasty(618-907 AD), there was a prototype of this hairstyle, and it became popular in the Song Dynasty.
Women in the Ming Dynasty(1368-1644 AD) liked to use black gauze to make this hairstyle and this kind of hairstyle survived until the last dynasty of China: the Qing Dynasty.
#chinese hanfu#Song Dynasty (960–1279 AD)#hanfu#hanfu accessories#hanfu_challenge#chinese traditional clothing#china#chinese#chinese history'#chinese fashion history#chinese historical hairstyle#chinese art#漢服#汉服#中華風#包髻/Bao Ji#Jin Temple
208 notes
·
View notes
Text
The real life inspirations behind new characters in Touhou 19 (Unfinished Dream of All Living Ghost)
While I haven’t been posting much about Touhou as of late, I felt obliged to put together the customary post about the inspirations behind the new characters. The new game genuinely renewed my interest. In contrast with similar write-ups pertaining to previous games the research is not entirely mine - some of the sections are a result of cooperation between me and @just9art.
Without further ado, let’s delve into the secrets of the new cast. Find out if Biten is the first “Wukong impersonator” ever, when a tanuki is actually a badger, and why Hisami both is and isn’t an oni. Naturally, the post is full of spoilers. Also, fair warning, it's long.
1. Biten Son - sarugami + Sun Wukong

Sarugami means “monkey kami”, the monkey in mention being the Japanese macaque.To my best knowledge, the term is actually not used commonly in English - the results on jstor and De Gruyter are in the low single digits, Brill outright has nothing to offer. Translations are much more common.

Sarugami are particularly strongly associated with Mount Hiei. You might have heard of it because of its association with Matarajin, though in this case he’s not exactly relevant. Instead, it is believed the monkeys act as messengers of Sanno (the “mountain king”), Sekizan Myojin and Juzenji. Sanno himself could take the form of a monkey according to medieval texts, while Juzenji can be accompanied by a deity depicted as a man with a monkey’s head, Daigyoji, known from the Hie mandala. Sarutahiko is also associated with monkeys based on the similarity between his name and the word saru.
Bernard Faure notes that despite the clearly positive portrayal of monkeys as semi-divine beings in service of these deities, their perception in folklore and mythology can nonetheless be considered ambivalent, because they could be viewed as aggressive. There are even examples of sarugami being portrayed as monstrous antagonists to be defeated by a hero. The best known tale of this variety is known simply as Sarugami taiji. It is preserved in the Konjaku monogatari. Here the sarugami is a fearsome monster who terrorizes a village and demands the offering of one young woman each year.
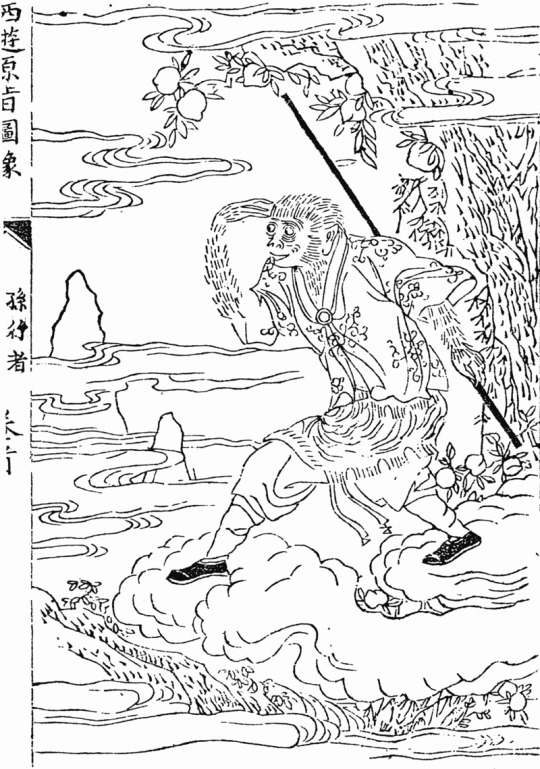

In contrast with the sarugami, I do not think Sun Wukong, one of the protagonists of the classic Chinese novel Journey to the West, needs much of an introduction. We reached the point where even in the west he is recognizable enough to warrant toys based on him (there’s a Lego Wukong on my desk right now). Biten's design has many callbacks to traditional portrayals of Wukong, including the staff (which in the novel is a pillar stolen from the undersea palace of a dragon emperor) and a very distinctive diadem (in the novel making it possible to pressure the unruly Wukong into obeying the monk he is meant to protect).
As a curiosity it’s worth noting that “fake Wukong” is not a brand new idea - in the novel itself, one of the enemies of the heroes, Six-Eared Macaque, actually impersonates him for a time.
Wukong is effectively himself a “divine monkey”, seeing as despite his origin as a literary character he actually came to be worshiped as a deity in mainland China, Taiwan and various areas with a large Chinese diaspora. The topic of Wukong worship itself came to be an inspiration for literature, starting with the excellent The Great Sage, Heaven’s Equal by Pu Songling, a writer active during the reign of the Qing dynasty, in the early eighteenth century.
2. Enoko Mitsugashira - “immortal yamainu” + Cerberus

Enoko gets the least coverage here, because there really isn’t much to say. Yamainu, “mountain dog”, isn’t really a supernatural creature, it’s an old term for either the extinct Japanese wolf, a type of feral dog, or a hybrid between these. It can also be used as a synonym of okuri-inu, a youkai wolf believed to accompany travelers at night.

There’s actually a distinctly Journey to the West-esque component to Enoko’s backstory, but I have no clue if this is intentional. In the aforementioned novel, many of the antagonists, who are generally demonic animals, are motivated by the desire to devour the flesh of the protagonist, the Buddhist monk Tang Sanzang, because it is said to grant immortality. Granted, given the obscurity of the figure Zanmu is based on - more on that later - perhaps this is an allusion to something else we have yet to uncover.
Cerberus, being probably one of the most famous mythical monsters in the world, does not really need to be discussed here. The illustration is included mostly because I like Edmund Dulac and any opportunity is suitable for sharing his illustrations. I do not think it needs to be pointed out that Enoko's bear trap weapons are meant to evoke Cerberus' extra heads.

3. Chiyari Tenkajin - tenkaijin (+ mujina) + chupacabra

While my favorite animal youkai not yet featured in Touhou is easily the kawauso (otter), I was very pleased to learn we sort of got a mujina since I wanted to cover this topic since forever, but never got much of a chance. Technically Chiyari is actually meant to be a tenkaijin, which is not a mujina but a slightly different youkai (a will-o-wisp or St. Elmo’s fire-like creature, specifically) who in the single tale dealing with it takes the form of a mujina after dying, but as there is not much to say about it beyond that you will get a crash course in mujina folklore instead.

Today the word mujina is pretty firmly a synonym of anaguma - in other words, the Japanese badger. The animal does not substantially differ from other badgers, so I do not think much needs to be said about its ecology. However, historically the term could be used to refer to the tanuki regionally, or interchangeably to both animals, so in some cases if insufficient detail is provided it is hard to tell which one is meant.
This ambiguity extends to the folklore surrounding them, and generally if you know what to expect from tanuki tales, which I’m sure most people reading this do, you will instantly recognize many of the plot elements typical for mujina ones. In other words, it is yet another yokai which typically takes the role of a shapeshifting trickster. Some supernatural phenomena could be basically interchangeably attributed to mujina, tanuki, kitsune or kawauso. Mujina are commonly described taking the form of Buddhist monks, which is one of the many similarities between them and tanuki.

The most famous depiction of a shapeshifting mujina comes from Toriyama Sekien’s Konjaku Gazu Zoku Hyakki (The Illustrated One Hundred Demons from the Present and the Past). The accompanying text compares the creature to the supernatural versions of kitsune and tanuki, and states that the artist relied on a tale according to which a mujina was able to successfully impersonate a Buddhist monk until accidentally revealing its tail.
What makes the mujina special is that it is actually the oldest recorded example of a youkai of this sort. A mujina tale already appears in the early Japanese chronicle Nihon Shoki, dated to 627. It reports an incident of a mujina transforming into a human and singing somewhere in the Michinoku Province. I feel like this alone is a good example of why you should be wary of people who seek to present Nihon Shoki or Kojiki as historical truth.
Western audiences as far as I know were first introduced to mujina by Lafcadio Hearn. To my best knowledge, the fabulous shapeshifting badgers however failed to gain the popcultural recognition enjoyed by tanuki and kitsune. They did appear in Shigeru Mizuki's stories every now and then, and I found a mascot character based on them, but overall there isn't all that much beyond that.

Naturally, there isn't much mujina in Chiyari's design, and she instead most likely owes her distinctly spiky appearance to the other inspiration behind her character, the chupacabra. Mujina are not really portrayed as bloodthirsty, but the poorly documented tenkajin apparently is, which is presumably why ZUN decided to connect Chiyari with the chupacabra, the best known modern blood-drinking creature, who first appeared in tall tales from 1995 and subsequently took popculture by storm after spreading from Puerto Rico to mainland USA and Mexico. I am not a chupacabra aficionado so I have little to offer here, sadly.
4. Hisami Yomotsu - yomotsu-shikome

Judging from what I’ve seen on social media and on pixiv, Hisami is shaping up to be one of the most popular new characters (she’s my fave too). In sharp contrast with that, her basis is pretty obscure. So obscure that there isn’t even any historical art to showcase, as far as I can tell (note that this blog claims night parade scrolls might have something to offer, though - I was unable to verify this claim for now, sadly). As we learn from her bio, she is supposed to be a yomotsu-shikome. They’re called the “hags of Yomi” of Yomi in Donald L. Philippi’s Kojiki translation. The term shikome can be literally translated as “ugly woman”. Nothing about them really implies femme fatale leanings we are evidently seeing in Touhou but I’m not going to complain about that.
Yomotsu-shikome appear only in the Kojiki and the Nihon Shoki, and in both of these early chronicles they are portrayed as servants of Izanami after she died and came to reside in Yomi, the land of the dead. Nihon Shoki states there are only eight of them.
The distinct grape vine motif present on Hisami’s clothes seems like an obvious reference to Izanagi’s escape from Yomi following his meeting with Izanami, portrayed in the myth recorded in both of these sources. When the yomotsu-shikome started to pursue him, he threw a vine he used to hold his hair at them. The plant instantly bore fruit, which the entities started to eat. They later resumed the chase, but were once again held back, this time by a bamboo shot. According to the Nihon Shoki, they eventually give up after he creates a river from his piss (sic) to keep them away.

Yomotsu-shikome are sometimes compared to oni by modern researchers. Noriko T. Reider in her monograph about oni argues that alongside hashihime and yamanba (pictured above) they can be effectively grouped with them. Another researcher, Michael D. Foster, is more cautious, and states that despite clear similarities it’s best to avoid conflating oni-like female demons with female oni proper, especially since the latter have a distinct iconography and a distinct set of traits. Norinaga Motoori, the founder of kokugaku or “national learning”, a nationalist intellectual movement in Edo and Meiji period Japan, claimed that oni were based on yomotsu-shikome, which is a pretty dubious claim. It is ultimately not certain when the term oni started to be used, but it is safe to say it has continental origin. And, of course, oni permeate Japanese culture in a way yomotsu-shikome do not.
5. Zanmu Nippaku - Zanmu

This was the toughest mystery to solve, and I am fully indebted to 9 here, since they figured it out, I am merely depending on what they directed me to. Research is still ongoing, and it feels like we just started to untangle this mystery, so you can safely expect further updates.
Zanmu appears to be based on the Buddhist monk… well, Zanmu. You can learn a bit about him here or on Japanese wikipedia; it seems there are quite literally 0 sources pertaining to him in English, and even in Japanese there is actually very little. Their names are not written the same, ZUN swapped the sign for “dream” from the original name for one which can be read as “nothingness”. If the unsourced quote on wikipedia is genuine, the reason might be tied to the personal views of the irl Zanmu. What little we’ve been able to gather about him is that he was active in the Sengoku period, and apparently was regarded as unorthodox and eccentric. This lines up with Zanmu’s omake bio pretty well. Seems the real Zanmu was also unusually long lived, and was able to recall events from distant past in great detail, though obviously the figure of 139 years attributed to him in a few places online has to be an exaggeration.

Yet more puzzling is the reference to Zanmu’s familiarity with Ikkyo you might spot in the linked article. Whether the famous Ikkyo who you may know from the tale of Jigoku Dayu is meant is difficult to determine. The chronology does not really add up; on the other hand the logic behind associating one eccentric semi-legendary monk with another in later legends isn’t particularly convoluted. As 9 pointed out to me, if ZUN was aware of this link, and the same Ikkyo really was meant, it is not impossible the connection between Zanmu and Hisami is meant to in some way mirror that between Ikkyo and Jigoku Dayu.
As you can easily notice, it’s pretty clear the historical Zanmu was male. It does not seem his Touhou counterpart is, obviously. I would say we should wait for more info until declaring that we have a second Miko situation on our hands, with a male historical figure directly reimagined as a female character without any indication we are dealing with a relative rather than the real deal. There’s still relatively little info to go by so I would remain cautious (though naturally this is not meant to discourage you from having headcanons).
Neither me nor 9 were able to find any connection between the historical Zanmu and oni… so far, at least. Therefore, what motivated ZUN to make Zanmu an oni remains to be discovered.
As a final curiosity, on a semi-related note it might be worth pointing out that while not as common as their male peers, female oni are not a modern invention, and already appear in setsuwa from the 13th century. A particularly common motif are tales describing a woman turning into oni due to jealousy or anger.
Further reading:
Jason Colavito, The Secret Prehistory of El Chupacabra (2011)
Bernard Faure, Gods of Medieval Japan vol. 1-3 (2015-2022)
Michael Daniel Foster, The Book of Yokai. Mysterious Creatures of Japanese Folklore (2015)
John Knight, Waiting for Wolves in Japan. An Anthropological Study of People-wildlife Relations (2003)
Noriko T. Reider, Japanese Demon Lore (2010)
272 notes
·
View notes
Text

ROCKING LOCKS FROM 35,000 BC!
These are African Chinese, known as the Jomon people, and it is assumed that the original inhabitants of China were black. They arrived 100,000 years ago and were still living in the country during the Qing Dynasty. Rocking their natural hair way back in the early 20th century!
At about 35,000 B.C. some of these people took this route and entered Japan. They became the first Humans to inhabit the Japanese Islands. Later, another group, known to us as the Ainu, followed.Today, their genes can still be found in 40% of modern Japanese, as well as Mongolians and Tibetans- Past and Present Kings & Queens.
www.ourAfrica.com.ng
192 notes
·
View notes
Text
Note about periodization
I am going to start describing time periods in Chinese history with European historical terms like medieval, Renaissance, early modern, Georgian and Victorian and so on, alongside the standard dynastic terms like Song, Ming and Qing I usually use. So like something about the Ming Dynasty I will tag Ming Dynasty and Renaissance. I already do it sometimes but not consistently. Here’s why.
A common criticism levied against this practice is that periodization is geographically specific and that it’s wrong and eurocentric to refer to, say, late Ming China as Renaissance China. It is a valid criticism, but in my experience the result of not using European periodization is that people default to ‘ancient’ when describing any period in Chinese history before the 20th century, which does conjure up specific images of European antiquity that do not align temporally with the Chinese period in question. I have talked about my issue with ‘ancient China’ before but I want to elaborate. People already consciously or subconsciously consider European periodizations of history to be universal, because of the legacy of colonialism and how eurocentric modern human culture generally is. By not using European historical terms for non-European places, people will simply think those places exist outside of history altogether, or at least exist within an early, primitive stage of European history. It’s a recipe for the denial of coevalness. I think there is a certain dangerous naivete among scholars who believe that if they refrain from using European periodization for non-European places, people will switch to the periodization appropriate for those places in question and challenge eurocentric history writing; in practice I’ve never seen it happen. The general public is not literate enough about history to do these conversions in situ. I have accumulated a fairly large pool of examples just from the number of people spamming ‘ancient China’ in my askbox despite repeatedly specifying the time periods I’m interested in (not antiquity!). If I say ‘Ming China’ instead of ‘Renaissance China’ people will take it as something on the same temporal plane as classical Greece instead of Tudor England. How many people would be surprised if I say that Emperor Qianlong of the Qing was a contemporary of George Washington and Frederick the Great? I’ve seen people talk about him as if he was some tribal leader in the time of Tacitus. European periodization is something I want to embrace ‘under erasure’ so to say, using something strategically for certain advantages while acknowledging its problems. Now there is a history of how the idea of ‘ancient China’ became so entrenched in popular media and I think it goes a bit deeper than just Orientalism, but that’s topic for another post. Right now I’m only concerned with my decision to add European periodization terms.
In order to compensate for the use of eurocentric periodization, I have carried out some experiments in the reverse direction in my daily life, by using Chinese reign years to describe European history. The responses are entertaining. I live in a Georgian tenement in the UK but I like to confuse friends and family by calling it a ‘Jiaqing era flat’. A friend of mine (Chinese) lives in an 1880s flat and she burst out in laughter when I called it ‘Guangxu era’, claiming that it sounded like something from court. But why is it funny? The temporal description is correct, the 1880s were indeed in the Guangxu era. And ‘Guangxu’ shouldn’t invoke royal imagery anymore than ‘Victorian’ (though said friend does indulge in more Qing court dramas than is probably healthy). It is because Chinese (and I’m sure many other non-white peoples) have been trained to believe that our histories are particular and distant, confined to a geographical location, and that they somehow cannot be mapped onto European history, which unfolded parallel to the history of the rest of the world, until we had been colonized. We have been taught that European history is history, but our history is ethnography.
It should also be noted that periodization for European history is not something essentialist and intrinsic either, period terms are created by historians and arbitrarily imposed onto the past to begin with. I was reading a book about medievalism studies and it talked about how the entire concept of the Middle Ages was manufactured in the Renaissance to create a temporal other for Europeans at the time to project undesired traits onto, to distance themselves from a supposedly ‘dark’ past. People living in the European Middle Ages likely did not think of themselves as living in a ‘middle’ age between something and something, so there is absolutely no natural basis for calling the period roughly between the 6th and 16th centuries ‘medieval’. Despite questionable origins, periodization of European history has become more or less standard in history writing throughout the 19th and 20th centuries, whereas around the same time colonial anthropological narratives framed non-European and non-white societies, including China, as existing outside of history altogether. Periodization of European history was geographically specific partially because it was conceived with Europe in mind and Europe only, since any other place may as well be in some primordial time.
Perhaps in the future there will develop global periodizations that consider how interconnected human history is. There probably are already attempts but they’re just not prominent enough to reach me yet. Until that point, I feel absolutely no moral baggage in describing, say, the Song Dynasty as ‘medieval’ because people in 12th century Europe did not think of themselves as ‘medieval’ either. I am the historian, I do whatever I want, basically.
#I was watching an unrelated video about dnd worldbuilding#and out of nowhere someone in the comment section called 1300s chinese people 'ancient asians'#*facepalm*#so I was reminded of this again#rant#colonialism#orientalism#chinese history#historiography
927 notes
·
View notes
Note
there was Chinese interest in the Out Of Asia theory, in both the Republic, Chiang Republic and People’s Republic periods before the Out Of Africa theory became commonly accepted. Was the 1954 Yeti expedition done just from the Nepalese-Indian side or were the American agents and “anthropologists” given access on the Sino-Tibetan side of the Himalayan border?
During the early part of this century, it was absolutely believed for a long time that the deserts of Western China were the most likely place of human origins, as seen in this migration map from 1944, made from the best available knowledge of the time:
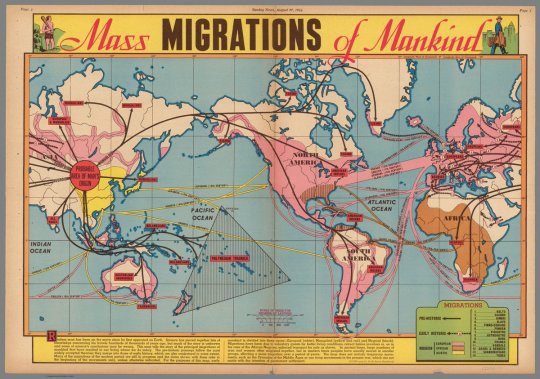
Remember, the oldest fossil remains at this point were in China, where Homo erectus was discovered (originally known by his initial place of discovery in Chungkotien Cave, nicknamed "Peking Man"). The discovery of Australopithecus and Homo habilis in Olduvai Gorge and South Africa, which place human origins in Africa, were not until the 50s and 60s, so it seemed entirely reasonable that Homo sapiens evolved in Western China.

The idea that China's desert regions were the origin of modern humans and culture is seen a lot in pop culture from 1900-1950, mainly because there were tremendous explorations in the region, especially Aurel Stein's expedition of 1908, who ventured into the Taklamakan Desert to find the Dunhuang Caves and Khara-Khoto, a city destroyed completely by Genghis Khan and vanished in the desert.

If you've ever heard of Roy Chapman Andrews and his famous expeditions in the 1920s, it's worth noting that he ventured into the Gobi Desert looking for human remains....not dinosaurs, and the discovery of dinosaur eggs was an unexpected surprise.


For that reason, there was a short lived Silk Road Mania that seemed to be a smaller scale predecessor to the pop culture dominating Egyptomania of the 1920s. It's bizarre to read adventure and fantasy fiction of the 1910s-1920s that features mentions of Silk Road peoples like the Kyrgyz, Sogdians, Tajik, Uigurians, and Tuvans. The best example I can think of would be the Khlit the Kossack stories of Harold Lamb (who also wrote a biography of Tamerlane), which together with Tarzan and Tros of Samothrace, formed the core inspiration for Robert E. Howard's Conan the Barbarian.

The most interesting example of this would be A. Merritt's Dwellers in the Mirage, which featured a lost city in Xinjiang that was the home of the Nordic race, who worshipped their original religion, the kraken-like squid devil god Khalkru. It was widely believed in this era that Nordics emerged from Central Asia originally, and while it's easy to write this off as turn of the century racialist claptrap pseudohistory (along with Hyperborea legends), in this case, it is actually true: a branch of the Indo-European family lived in West China, and 5,000 year old redheaded mummies have been found in the region. As usual, A. Merritt was right on the money with his archeology, more so than other 1920s authors. After all, his "Moon Pool" was set around the just discovered ruins of Nan Madol, the Venice of Micronesia.

Jack Williamson's still chilling Darker Than You Think in 1948 was also set in the Silk Road/Central Asian region, as the place the race of shapeshifters emerged from, Homo magi, who await the coming of their evil messiah, the Night King, who will give them power over the human race.

H. Rider Haggard set "Ayesha: the Return of She" (1905) in Xinjiang, among a lost Greek colony in Central Asia (no doubt based on Alexandria on the Indus, a Greek colony in modern Pakistan that was the furthest bastion of Greek Culture). This was also two years after the Younghusband Thibetan Expedition of 1903, where the British invaded Tibet. At the time, the Qing Dynasty was completely declining and lost control of the frontier regions, and the power vacuum was filled by religious authority by default (this is something you also saw in Xinjiang, where for example, the leader of the city was the Imam of Kashgar).

This is one of the many British invasions they have attempted to cram down the memory hole, but if you ever see a Himalayan art piece that was "obtained in 1903-1904" ....well, you know where it came from.
Incidentally, there's one really funny recent conspiracy theory about paleontology, fossils, and China that I find incredibly interesting: the idea that dinosaurs having feathers is a lie and a sinister plot spread by the Communist Chinese (who else?) to make American youth into sissy fancylads, like Jessie "the Body" Ventura. How? By lying to us and making up that the manly and vigorous Tyrannosaurus, a beast with off the charts heterosexuality and a model for boys everywhere, might have been feathered like a debutante's dress. What next - lipstick on a Great White Shark? The long term goal is to make Americans effeminate C. Nelson Reilly types unable to defend against invasion. This is a theory that is getting steam among the kind of people who used to read Soldier of Fortune magazine, and among abusive stepfathers the world over.

...okay, are you done laughing? Yeah, this is obvious crackpottery and transparent sexual pathology, on the level of the John Birch Society in the 60s saying the Beatles were a Communist mind control plot. Mostly because animals just look how they look, and if it turned out that the ferocious Tyrannosaurus had feathers and looked like a fancylad Jessie Ventura to you, well, that's your problem and mental baggage, really.
I was left scratching my head over this one. But there is (kind of) something to this, and that is that a huge chunk of recent dinosaur discoveries have been in China. I don't think it has anything to do with a Communist plot to turn American boys into fancylads, but more to do with a major push in internal public investment in sciences in that country, and an explosion of Chinese dinosaur discoveries. If you want to see a great undervisited dinosaur museum, go to the Zigong Dinosaur Museum in Sichuan.

Pop quiz: what living scientist has named more dinosaur discoveries? It's not Bakker or Horner. The greatest living paleontologist, Xu Xing, which is why a lot of recently found dinosaurs are named things like Shangtungasaurus.
241 notes
·
View notes