#class politics
Text
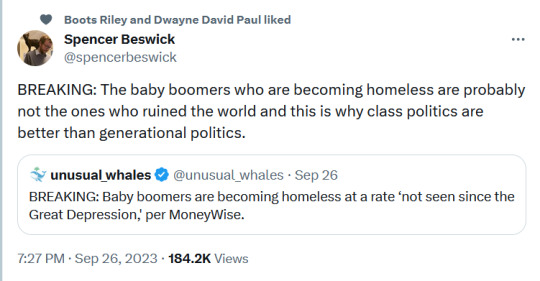
#twitter#tweet#tweets#boomers#economics#economy#homeless#class politics#generational politics#class#inequality#wealth inequality
42K notes
·
View notes
Text
WoT Meta: Feudalism, Class, And The Politics of The Wheel of Time
One of my long standing personal annoyances with the fantasy genre is that it often falls into the trap of simplifying feudal class systems, stripping out the interesting parts and the nuance to make something that’s either a lot more cardboard cut-out, or has our modern ideas about class imposed onto it.
Ironically the principal exception is also the series that set the bar for me. As is so often the case, Robert Jordan’s Wheel of Time is unique in how much it works to understand and convey a realistic approach to power, politics, government, rulership, and the world in general–colored neither by cynicism or idealism. How Jordan works the feudal system into his world building is no exception–weaving in the weaknesses, the strengths, and the banal realities of what it means to have a Lord or Lady, a sovereign Queen or King, and to exist in a state held together by interpersonal relationships between them–while still conveying themes and ideas that are, at their heart, relevant to our modern world.
So, I thought I’d talk a little bit about how he does that.
Defining the Structure
First, since we’re talking about feudal class systems, let's define what that means– what classes actually existed, how they related to each other, and how that is represented in Jordan’s world.
But before that, a quick disclaimer. To avoid getting too deep into the historical weeds, I am going to be making some pretty wide generalizations. The phrases ‘most often’, ‘usually’, and ‘in general’ are going to be doing a lot of heavy lifting. While the strata I’m describing is broadly true across the majority medieval and early Renaissance feudal states these things were obviously heavily influenced by the culture, religion, geography, and economics of their country–all of which varied widely and could shift dramatically over a surprisingly small amount of time (sometimes less than a single generation). Almost nothing I am going to say is universally applicable to all feudal states, but all states will have large swathes of it true for them, and it will be widely applicable.
The other thing I would ask you to keep in mind is that a lot of our conceptions of class have been heavily changed by industrialization. It’s impossible to overstate how completely the steam engine altered the landscape of socio-politics the world over, in ways both good and bad. This is already one of those things that Jordan is incredibly good at remembering, and that most fantasy authors are very good at forgetting.
The disparity between your average medieval monarch’s standard of living and their peasants was pretty wide, but it was nothing compared to the distance between your average minimum wage worker and any billionaire; the monarch and the peasant had far more in common with each other than you or I do with Jeff Bezos or Mike Zuckerberg. The disparity between most people’s local country lord and their peasants was even smaller. It was only when the steam engine made the mass production of consumer goods possible that the wealth gap started to become a chasm–and that was in fact one of the forces that lead to the end of the feudal system and the collapse of many (though by no means all) of the ruling monarchies in Europe.
I bring this up because the idea of a class system not predicated on the accumulation of capital seems pretty alien to our modern sensibilities, but it was the norm for most of history. Descent and birth mattered far more than the riches you could acquire–and the act of accumulating wealth was itself often seen as something vulgar and in many countries actively sinful.
So with that in mind, what exactly were the classes of feudalism, and how do they connect to the Wheel of Time?
The Monarch and their immediate family unsurprisingly occupied the top of the societal pyramid (at least, in feudal states that had a monarch and royal family- which wasn’t all of them). The Monarch was head of the government and was responsible for administering the nation: collecting taxes, seeing them spent, enforcing law, defending the country’s borders and vassals in the event of war, etc. Contrary to popular belief, relatively few monarchs had absolute power during the medieval period. But how much power the monarch did have varied widely- some monarchs were little more than figureheads, others were able to centralize enough power on themselves to dictate the majority of state business- and that balance could shift back and forth over a single generation, or even a single reign depending on the competence of the monarch.
The royal family usually held power in relation to their monarch, but also at the monarch’s discretion. The more power a monarch had, the more likely they were to delegate it to trusted family members in order to aid with the administration of the realm. This was in both official and unofficial capacities: princes were often required to do military service as a right of passage, and to act as diplomats or officials, and princesses (especially those married into foreign powers) were often used as spies for their home state, or played roles in managing court affairs and business on behalf of the ruler.
Beneath the monarch and their family you get the noble aristocracy, and I could write a whole separate essay just on the delineations and strata within this group, but suffice to say the aristocracy covers individuals and families with a wide range of power and wealth. Again, starting from that country lord whose power and wealth in the grand scheme of things is not much bigger than his peasants, all the way to people as powerful, or sometimes more powerful, than the monarch.
Nobles in a feudal system ruled over sections of land (the size and quality usually related sharply to their power) setting taxes, enforcing laws, providing protection to the peasants, hearing petitions, etc. within their domains. These nobles were sometimes independent, but more often would swear fealty to more powerful nobles (or monarchs) in exchange for greater protection and membership in a nation state. Doing so meant agreeing to pay taxes, obey (and enforce) the laws of the kingdom, and to provide soldiers to their liege in the event of war. The amount of actual power and autonomy nobles had varied pretty widely, and the general rule of thumb is that the more powerful the monarch is, the less power and autonomy the nobles have, and vice versa. Nobles generally were expected to be well educated (or at least to be able to pretend they were) and usually provided the pool from which important government officials were drawn–generals, council members, envoys, etc–with some kingdoms having laws that prevented anyone not of noble descent from occupying these positions.
Beneath the nobles you get the wealthy financial class–major merchants, bankers, and the heads of large trade guilds. Those Marx referred to generally as the bourgeoisie because they either own means of production or manage capital. In a feudal system this class tended to have a good bit of soft power, since their fortunes could buy them access to circles of the powerful, but very little institutional power, since the accumulation and pursuit of riches, if anything, was seen to have negative moral worth. An underlying presumption of greediness was attached to this class, and with it the sense that they should be kept out of direct power.
That was possible, in part, because there weren't that many means of production to actually own, or that much capital to manage, in a pre-industrial society. Most goods were produced without the aid of equipment that required significant capital investment (a weaver owned their own loom, a blacksmith owned their own tools, etc), and most citizens did not have enough wealth to make use of banking services. This is the class of merchants who owned, but generally didn’t directly operate, multiple trading ships or caravans, guild leaders for craftsfolk who required large scale equipment to do their work (copper and iron foundries for the making of bells, for example), and bankers who mainly served the nobility and other wealthy individuals through the loaning and borrowing of money. This usually (but not always) represented the ceiling of what those not born aristocrats could achieve in society.
After that you get middling merchants, master craftsfolk and specialty artisans, in particular of luxury goods. Merchants in this class usually still directly manage their expeditions and operations, while the craftsfolk and artisans are those with specialty skill sets that can not be easily replicated without a lifetime of training. Master silversmiths, dressmakers, lacquer workers, hairdressers, and clockmakers are all found in this class. How much social clout individuals in this class have usually relates strongly to how much value is placed on their skill or product by their society (think how the Seanchan have an insatiable appetite for lacquer work and how Seanchan nobles make several Ebou Dari lacquer workers very rich) as well as the actual quality of the product. But even an unskilled artisan is still probably comfortable (as Thom says, even a bad clockmaker is still a wealthy man). Apprenticeships, where children are taught these crafts, are thus highly desired by those in lower classes,as it guaranteed at least some level of financial security in life.
Bellow that class you find minor merchants (single ship or wagon types), the owners of small businesses (inns, taverns, millers etc), some educated posts (clerks, scribes, accountants, tutors) and most craftsfolk (blacksmiths, carpenters, bootmakers, etc). These are people who can usually support themselves and their families through their own labor, or who, in the words of Jin Di, ‘work with their hands’. Most of those who occupy this class are found in cities and larger towns, where the flow of trade allows so many non-food producers to congregate and still (mostly) make ends meet. This is why there is only one inn, one miller, one blacksmith (with a single apprentice) in places like Emond’s Field: most smaller villages can not sustain more than a handful of non-food producers. This is also where you start to get the possibility of serious financial instability; in times of chaos it is people at this tier (and below) that are the first to be forced into poverty, flight, or other desperate actions to survive.
Finally, there is the group often collectively called ‘peasants’ (though that term is also sometimes used to mean anyone not noble born). Farmers, manual laborers, peddlers, fishers- anyone who is unlikely to be able to support more than themselves with their labor, and often had to depend on the combined labor of their spouse and families to get by. Servants also generally fit into this tier socially, but it’s important to understand that a servant in say, a palace, is going to be significantly better paid and respected than a maid in a merchant's house. This class is the largest, making up the majority of the population in a given country, and with a majority of its own number being food-producers specifically. Without the aid of the steam engine, most of a country’s populace needs to be producing food, and a great deal of it, in order to remain a functional nation. Most of the population as a result live in smaller spread out agrarian communities, loosely organized around single towns and villages. Since these communities will almost always lack access to certain goods or amenities (Emond’s Field has a bootmaker, but no candlemaker, for example) they depend on smalltime traders, called peddlers, to provide them with everyday things, who might travel from town to town with no more than a single wagon, or even just a large pack.
The only groups lower than peasants on the social hierarchy are beggars, the destitute, and (in societies that practice slavery) slaves. People who can not (or are not allowed to) support themselves, and instead must either eke out a day to day existence from scraps, or must be supported by others. Slaves can perform labor of any kind, but they are regarded legally as a means of production rather than a laborer, and the value is awarded to their owner instead.
It’s also worth noting that slavery has varied wildly across history in how exactly it was carried out and ran the gamut from the trans-Atlantic chattel slavery to more caste or punitive-based slavery systems where slaves could achieve freedom, social mobility, or even some degree of power within their societies. But those realities (as with servants) had more to do with who their owners were than the slave’s own merit, and the majority of slaves (who are almost always seen as less than a freedman even when they are doing the same work) were performing the same common labor as the ‘peasant’ class, and so viewed as inferior.
Viewing The Wheel of Time Through This Lens
So what does all this have to do with Robert Jordan’s Wheel of Time? A lot actually, especially compared to his contemporaries in fantasy writing. Whereas most fantasy taking place in feudal systems succumbs to the urge to simplify matters (sometimes as far down to their only being two classes, ‘peasant’ and ‘royalty’) Jordan much more closely models real feudalism in his world.
The majority of the nations we encounter are feudal monarchies, and a majority of each of their populations are agrarian farming communities overseen by a local lord or other official. How large a nation’s other classes are is directly tied to how prosperous the kingdom is, which is strongly connected to how much food and how many goods the kingdom can produce on the available land within it. This in turn, is tightly interdependent on how stable the kingdom is and how effective its government is.
Andor is the prime example: a very large, very prosperous kingdom, which is both self-sufficient in feeding itself via its large swathes of farmland (so much so that they can afford to feed Cairhien through selling their surplus almost certainly at next to no profit) and rich in mineral wealth from mines in the west. It is capable of supporting several fairly large cities even on its outskirts, as well as the very well-developed and cosmopolitan Caemlyn as its capital. This allows Andor to maintain a pretty robust class of educated workers, craftsfolk, artisans, etc, which in turn furthers the realm’s prosperity. At the top of things, the Queen presides over the entire realm with largely centralized power to set laws and taxes. Beneath her are the ‘great houses’–the only Houses in Andor besides the royal house who are strong enough that other nobles ‘follow where they lead’ making them the equivalent of Duchesses and Dukes, with any minor nobles not sworn directly to the Queen being sworn to these ten.
And that ties into something very important about the feudal system and the impact it had on our world and the impact it has on Jordan's. To quote Youtuber Jack Rackham, feudalism is what those in the science biz would call an unstable equilibrium. The monarch and their vassals are constantly in conflict with each other; the vassals desiring more power and autonomy, as the monarch works to centralize power on themselves. In feudalism there isn’t really a state army. Instead the monarch and the nobles all have personal armies, and while the monarch’s might be stronger than anyone else’s army, it’s never going to be stronger than everybody else’s.
To maintain peace and stability in this situation everyone has to essentially play Game of Thrones (or as Jordan called it years before Martin wrote GoT, Daes Dae’mar) using political maneuvering, alliances, and scheming in order to pursue their goals without the swords coming out, and depending on the relative skill of those involved, this can go on for centuries at a time….or break apart completely over the course of a single bad summer, and plunge the country into civil war.
Cairhien is a great example of this problem. After losing the Aiel War and being left in ruins, the monarch who ultimately secured the throne of Cairhien, Galldrian Riatin, started from a place of profound weakness. He inherited a bankrupt, war torn and starving country, parts of which were still actively on fire at the time. As Thom discusses in the Great Hunt, Galddrian's failure to resettle the farmers displaced by the war left Cairhien dependent on foreign powers to feed the populace (the grain exports from Tear and Andor) and in order to prevent riots in his own capital, Galldrian choose bread and circuses to keep the people pacified rather then trying to substantially improve their situation. Meanwhile, the nobles, with no effective check on them, began to flex their power, seeing how much strength they could take away from each other and the King, further limiting the throne’s options in how to deal with the crisis, and forcing the King to compete with his most powerful vassals in order to just stay on the throne. This state of affairs ultimately resulted, unsurprisingly, in one of Galladrin’s schemes backfiring, him ending up dead, and the country plunging into civil war, every aristocrat fighting to replace him and more concerned with securing their own power then with restoring the country that was now fully plunged into ruin.
When Dyelin is supporting Elayne in the Andoran Succession, it is this outcome (or one very much like it) that she is attempting to prevent. She says as much outright to Elayne in Knife of Dreams–a direct succession is more stable, and should only be prevented in a situation where the Daughter Heir is unfit–through either incompetence or malice–to become Queen. On the flip side, Arymilla and her lot are trying to push their own agendas, using the war as an excuse to further enrich their Houses or empower themselves and their allies. Rhavin’s machinations had very neatly destabilized Andor, emboldening nobles such as Arymilla (who normally would never dream of putting forward a serious claim for the throne) by making them believe Morgase and Trakand were weak and thus easy to take advantage of.
We also see this conflict crop up as a central reason Murandy and Altara are in their current state as well. Both are countries where their noble classes have almost complete autonomy, and the monarch is a figurehead without significantly more power than their vassals (Tylin can only keep order in Ebou Dar and its immediate surrounding area, and from what she says her father started with an even worse deal,with parts of the capital more under the control of his vassals than him). Their main unifying force is that they wish to avoid invasion and domination by another larger power (Andor for Murandy, Illian and Amadica for Altara) and the threat of that is the only thing capable of bringing either country into anything close to unity.
Meanwhile a lack of centralization has its trade offs; people enjoy more relative freedoms and social mobility (both depend heavily on trade, which means more wealth flowing into their countries but not necessarily accumulating at the top, due to the lack of stability), and Altara specifically has a very robust ‘middle class’ (or as near as you can get pre-industrialization) of middling to minor merchants, business and craftsfolk, etc. Mat’s time in Ebou Dar (and his friendship with Satelle Anan) gets into a lot of this. Think of the many many guilds that call Altara home, and how the husband of an inn owner can do a successful enough business fishing that he comes to own several crafts by his own merit.
On the flip side both countries have problems with violence and lawlessness due to the lack of any enforced uniformity in terms of justice. You might ride a day and end up in land ruled by a Lord or Lady with a completely different idea of what constitutes, say, a capital offense, than the Lord or Lady you were under yesterday. This is also probably why Altara has such an ingrained culture of duels to resolve disputes, among both nobles and common folk. Why appeal to a higher authority when that authority can barely keep the streets clean? Instead you and the person you are in conflict with, on anything from the last cup of wine to who cheated who in a business deal, can just settle it with your knives and not have to bother with a hearing or a petition. It’s not like you could trust it anyways; as Mat informs us, most of the magistrates in Altara do the bidding of whoever is paying their bribes.
But neither Altara nor Murandy represents the extreme of how much power and autonomy nobles can manage to wrangle for themselves. That honor goes to Tear, where the nobles have done away with the monarch entirely to instead establish what amounts to an aristocratic confederacy. Their ruling council (The High Lords of Tear) share power roughly equally among themselves, and rule via compromise and consensus. This approach also has its tradeoffs: unlike Murandy and Altara, Tear is still able to effectively administer the realm and create uniformity even without a monarch, and they are able to be remarkably flexible in terms of their politics and foreign policy, maintaining trade relationships even with bitter enemies like Tar Valon or Illian. On the flipside, the interests of individual nobles are able to shape policy and law to a much greater extent, with no monarch to play arbiter or hold them accountable. This is the source of many of the social problems in Tear: a higher sense of justice, good, or even just plain fairness all take a back seat to the whims and interest of nobles. Tear is the only country where Jordan goes out of his way, repeatedly, to point out wealth inequality and injustice. They are present in other countries, but Jordan drives home that it is much worse in Tear, and much more obscene.
This is at least in part because there is no one to serve as a check to the nobles, not even each other. A monarch is (at least in theory) beholden to the country as a whole, but each High Lord is beholden only to their specific people, house and interests, and there is no force present that can even attempt to keep the ambitions and desires of the High Lords from dictating everything. So while Satelle Anan's husband can work his way up from a single fishing boat to the owner of multiple vessels, most fisherman and farmers in Tear scrape by on subsistence, as taxes are used to siphon off their wealth and enrich the High Lords. While in Andor ‘even the Queen most obey the law she makes or there is no law’ (to quote Morgase), Tairen Lords can commit murder, rape, or theft without any expectation of consequences, because the law dosen’t treat those acts as crimes when done to their ‘lessers’, and any chance someone might get their own justice back (as they would in Altara) is quashed, since the common folk are not even allowed to own weapons in Tear. As we’re told in the Dragon Reborn, when an innkeeper is troubled by a Lord cheating at dice in the common room, the Civil Watch will do nothing about it and citizens in Tear are banned from owning weapons so there is nothing he can do about it. The best that can be hoped for is that he will ‘get bored and go away’.
On the opposite end, you have the very very centralized Seanchan Empire as a counter example to Tear, so centralized it’s almost (though not quite) managed to transcend feudalism. In Seanchan the aristocratic class has largely been neutered by the monarchy, their ambitions and plots kept in check by a secret police (the Seekers of Truth) and their private armies dwarfed by a state army that is rigorously kept and maintained. It’s likely that the levies of the noble houses, if they all united together, would still be enough to topple the Empress, but the Crystal Throne expends a great deal of effort to ensure that doesn't happen,playing the nobles against each other and taking advantage of natural divisions in order to keep them from uniting.
Again, this has pros and cons. The Seanchan Empire is unquestionably prosperous; able to support a ridiculous food surplus and the accompanying flow of wealth throughout its society, and it has a level of equity in its legal administration that we don’t see anywhere else in Randland. Mat spots the heads of at least two Seanchan nobles decorating the gates over Ebou Dar when he enters, their crimes being rape and theft, which is a far cry from the consequence-free lives of the Tairen nobles. Meanwhile a vast state-sponsored bureaucracy works to oversee the distribution of resources and effective governance in the Empress’s name. No one, Tuon tells us proudly, has to beg or go hungry in the Empire. But that is not without cost.
Because for all its prosperity, Seanchan society is also incredibly rigid and controlling. One of the guiding philosophies of the Seanchan is ‘the pattern has a place for everything and everything’s place should be obvious on sight’. The classes are more distinct and more regimented than anywhere else we see in Randland. The freedoms and rights of everyone from High Lords to common folk are curtailed–and what you can say or do is sharply limited by both social convention and law. The Throne (and its proxies) are also permitted to deprive you of those rights on nothing more than suspicion. To paraphrase Egeanin from TSR: Disobeying a Seeker (and presumably any other proxy of the Empress) is a crime. Flight from a Seeker is a crime. Failure to cooperate fully with a Seeker is a crime. A Seeker could order a suspected criminal to go fetch the rope for their own binding, and the suspected criminal would be expected to do it–and likely would because failure to do anything else would make them a criminal anyway, whatever their guilt or innocence in any other matter.
Meanwhile that food surplus and the resulting wealth of the Empire is built on its imperialism and its caste-based slavery system, and both of those are inherently unsustainable engines. What social mobility there is, is tied to the Empire’s constant cycle of expand, consolidate, assimilate, repeat–Egeanin raises that very point early on, that the Corenne would mean ‘new names given and the chance to rise high’. But that cycle also creates an endless slew of problems and burning resentments, as conquered populations resist assimilation, the resistance explodes into violence that the Seanchan must constantly deal with–the ‘near constant rebellions since the Conquest finished’ that Mat mentions when musing on how the Seanchan army has stayed sharp.
The Seanchan also practice a form of punitive and caste-based slavery for non-channelers, and chattel slavery for channelers. As with the real-life Ottoman Empire, some da’covale enjoy incredible power and privilege in their society, but they (the Deathwatch Guard, the so’jhin, the Seekers) are the exception, not the rule. The majority of the slaves we encounter are nameless servants, laborers, or damane. While non-channelers have some enshrined legal protections in how they can be treated by their masters and society as a whole, we are told that emancipation is incredibly rare, and the slave status is inherited from parent to child as well as used as a legal punishment–which of course would have the natural effect of discouraging most da’covale from reproducing by choice until after (or if) they are emancipated–so the primary source for most of the laborers and servants in Seanchan society is going to be either people who are being punished or who choose to sell themselves into slavery rather then beg or face other desperate circumstances.
This keeps the enslaved population in proportion with the rest of society only because of the Empire’s imperialism- that same cycle of expand, consolidate, assimilate, repeat, has the side effect of breeding instability, which breeds desperation and thus provides a wide pool to draw on of both those willing to go into slavery to avoid starvation, and those who are being punished with slavery for wronging the state in some manner. It’s likely the only reason the Empire’s production can keep pace with its constant war efforts: conquered nations (and subdued rebellions) eventually yield up not just the necessary resources, but also the necessary laborers to cultivate them in the name of the state, and if that engine stalls for any sustained length of time (like say a three hundred year peace enforced by a treaty), it would mean a labor collapse the likes of which the Empire has never seen before.
A note on damane here: the damane system is undoubtedly one of chattel slavery, where human beings are deprived of basic rights and person hood under the law for the enrichment of those that claim ownership over them. Like in real life this state of affairs is maintained by a set of ingrained cultural prejudices, carefully constructed lies, and simple ignorance of the truly horrific state of affairs that the masses enjoy. The longevity of channelers insulates the damane from some of the problems of how slavery can be unsustainable, but in the long run it also suffers from the same structural problem: when the endless expansion stops, so too will the flow of new damane, and the resulting cratering of power the Empire will face will put it in jeopardy like nothing has before. There is also the problem that, as with real life chattel slavery, if any one piece of the combination of ignorance, lies, and prejudice starts to fall apart, an abolition movement becomes inevitable–and several characters are setting the stage for just that via the careful spreading of the truth about the sul’dam. Even if the Seanchan successfully put down an abolition movement, doing so will profoundly weaken them in a way that will necessitate fundamental transformation, or ensure collapse.
How Jordan Depicts The Relationships Between Classes
As someone who is very conscious in how he depicts class in his works, it makes sense that Jordan frequently focuses on characters interacting through the barriers of their various classes in different ways. New Spring in particular is a gold mine for this kind of insight.
Take, for example, Moiraine and Siuan’s visit to the master seamstress. A lesser writer would not think more deeply on the matter than ‘Moiraine is nobly born so obviously she’s going to be snobby and demanding, while down-to-earth Siuan is likely to be build a natural rapport and have better relationship her fellow commoner, the seamstress Tamore Alkohima’. But Jordan correctly writes it as the reverse: Tamore Alkohima might not be nobly born, but she is not really a peasant either–rather she belongs to that class of speciality artisans, who via the value placed on her labor and skill, is able to live quite comfortably. Moiraine is much more adept at maneuvering this kind of possibly fraught relationship than Siuan is. Yes, she is at the top of the social structure (all the more so since becoming Aes Sedai) but that does not release her from a need to observe formalities and courtesies with someone who, afterall, is doing something for Moiraine that she can not do for herself, even with the Power. If Moiraine wants the services of a master dressmaker, the finest in Tar Valon, she must show respect for both Tamore Alkohima and her craft, which means submitting to her artistic decisions, as well as paying whatever price, without complaint.
Siuan, who comes from the poor Maule district in Tear, is not used to navigating this kind of situation. Most of those she has dealt with before coming to the Tower were either her equals or only slightly above her in terms of class. She tries to treat Tamore Alkohima initially like she most likely treated vendors in the Maule where everyone is concerned with price, since so many are constantly on the edge of poverty, and she wants to know exactly what she is buying and have complete say over the final product, which is the practical mentality of someone to whom those factors had a huge impact on her survival. Coin wasted on fish a day from going bad, or netting that isn’t the right kind, might have meant the difference between eating that week or not, for a young Siuan and her father.
Yet this this reads as an insult to Tamore Alkohima, who takes it as being treated with mockery, and leads to Moiraine needing to step in to try and smooth things over, and explain to Siuan-
“Listen to me, Siuan and do not argue.” she whispered in a rush. “We must not keep Tamore waiting long. Do not ask after prices: she will tell us after we make our selections. Nothing you buy here will be cheap, but the dresses Tamore sews for you will make you look Aes Sedai as much as the shawl does. And it is Tamore, not Mistress Alkohima. You must observe the properties or she will believe you are mocking her. But try thinking of her as a sister who stands just a little above you. A touch of deference is necessary. Just a touch, but she will tell you what to wear as much as she asks.”
“And will the bloody shoe maker tell us what kind of slippers to buy and charge us enough to buy fifty new sets of nets?”
“No.” Moiraine said impatiently. Tamore was only arching one eyebrow but her face may as well have been a thunderhead. The meaning of that eyebrow was clear as the finest crystal. They had already made the seamstress wait too long, and there was going to be a price for it. And that scowl! She hurried on, whispering as fast as she could. “The shoemaker will make us what we want and we will bargain the price with him, but not too hard if we want his best work. The same with the glovemaker, the stockingmaker, the shiftmaker, and all the rest. Just be glad neither of us needs a hairdresser. The best hairdressers are true tyrants, and nearly as bad as perfumers.”
-New Spring, Chapter 13: Business in the City.
Navigating the relationship between characters of a different class is something a of a running theme throughout New Spring–from Moiraine’s dealing with the discretion of her banker (‘Another woman who knew well her place in the world’ as Moiraine puts it), to having to meet with peasants during her search for the Dragon Reborn (and bungling several of those interactions), to wading through the roughest criminal parts of Chachin in search of an inn, and frequently needing to resort to the Power to avoid or resolve conflict. Moiraine’s ability to handle these situations is tightly tied to her experience with the people involved prior to her time as a Novice, but all hold up and give color to the class system Jordan presents. It also serves as set up so that when Moraine breaks the properties with a different seamstress near the end of the book, it can be a sign of the rising tension and the complex machinations she and Siuan find themselves in.
Notably, Moiraine and Siuan’s relative skill with working with people is strongly related to their backgrounds: the more Moiraine encounters people outside her lived experience as a noble daughter in Cairhien, the more she struggles to navigate those situations while Siuan is much more effective at dealing with the soldiers during the name-taking sequence (who are drawn mostly from the same class as her–common laborers, farmers, etc), and the people in Chachin, where she secures an lodging and local contacts to help in the search with relative ease.
Trying to navigate these waters is also something that frequently trips up characters in the main series as well, especially with the Two Rivers folk who are, ultimately, from a relatively classless society that does not subscribe to feudal norms (more on that below). All of them react to both moving through a society that does follow those norms, and later, being incorporated into its power structures in different, frequently disastrous ways.
Rand, who is not used to the complicated balance between vassal and monarch (which is all the more complicated as he is constantly adding more and more realms under his banner) finds imposing his will and leading the aristocrats who swear fealty to him incredibly difficult. While his reforms are undoubtedly good for the common folk and the general welfare of the nations he takes over, he is most often left to enforce them with threats and violence, which ultimately fuel resistance, rebellion, and more opposition to him throughout the nations he rules, and has down-the-line bad ripple effects on how he treats others, both noble and not, who disagree with him.
Rand also struggles even with those who sincerely wish to serve and aid him in this context: he is awkward with servants, distant with the soldiers and warriors who swear their lives to him, and even struggles with many of his advisors and allies. Part of that is distrust that plagues him in general, but a big element to it is also his own outsider perspective. The Aiel frequently complain that Rand tries to lead them like a King, but that’s because they assume a wetlander King always leads by edict and command. Yet Rand’s efforts to do that with the Westland nations he takes over almost always backfire or have lasting consequences. Rand is frequently trying to frequently play act at what he thinks a King is and does–and when he succeeds it’s almost always a result of Moiraine or Elayne’s advice on the subject, not his own instincts or preconceptions.
Perrin, meanwhile, is unable to hide his contempt for aristocracy and those that willingly follow them, which leads to him both being frequently derelict in his duties as a Lord, and not treating his followers with a great deal of respect. Nynaeve has a similar problem, where she often tries to ‘instill backbone’ into those lower in the class system then her, then comes to regret it when that backbone ends up turned on her, and her leadership rejected or her position disrespected by those she had encouraged to reject leadership or not show respect to people in higher positions.
Interestingly, it’s Mat that most effectively manages to navigate various inter-class relationships, and who via the Band of the Red Hand builds a pretty equitable, merit-based army. He does this by following a simple rule: treating people how they wish to be treated. He accepts deference when it’s offered, but never demands it. He pushes back on the notion he’s a Lord often, but only makes it a serious bone with people who hold the aristocracy in contempt. He’s earnest in his dealings, fair minded, and good at reading social situations to adapt to how folks expect him to act, and when he breaches those expectations it’s usually a deliberate tactical choice.
This lets him maintain strong friendships with people of all backgrounds and classes– from Princes like Beslan to horse thieves like Chel Vanin. More importantly, it makes everyone under his command feel included, respected, and valued for what they are. Mat has Strong Ideas About Class (and about most things really), but he’s the only Two Rivers character who doesn't seem to be working from an assumption that everyone else ought to live by his ideals. He thinks anyone that buys into the feudal system is mad, but he doesn't actually let that impact how he treats anyone–probably from the knowledge that they think he’s just as mad.
Getting Creative With the Structure
The other thing I want to dig into is the ways in which Jordan, via his understanding of the feudal system, is able to play with it in creative and interesting ways that match his world. Succession is the big one; who rules after the current monarch dies is a massively important matter since it determines the flow of power in a country from one leader to the next. The reason so many European monarchies had primogeniture (eldest child inherits all titles) succession is not because everyone just hated second children, it’s because primogeniture is remarkably stable. Being able to point to the eldest child of the monarch and say them, that one, and their younger sibling if they're not around, and so on is very good for the transition of power, since it establishes a framework that is both easy to understand and very very hard to subvert. Pretty much the only way, historically, to subvert a primogeniture succession is for either the heir’s blood relationship to the monarch or the legitimacy of their parent’s marriage to be called into question.
And yet despite that, few of the countries in Jordan's world actually use primogeniture succession. Andor does, as do some of the Borderlands, but the majority of monarchies in Randland use elective succession, where the monarch is elected from among the aristocratic class by some kind of deliberative body. This is the way things are in Tarabon, Arad Doman,Ghealdan, Illian, and Malkier, who all elect the monarchs (or diarchs in the case of Tarabon- where two rulers, the Panarch and the King, share power) via either special council or some other assembly of aristocrats.
There are three countries where we don’t know the succession type (Arafel, Murandy, and Amadicia) but also one we know for sure doesn't use primogeniture succession: Cairhien. We know this because Moiraine’s claim to the Sun Throne as a member of House Damodred is seen as as legitimate enough for the White Tower to view putting her on the Sun Throne as a viable possibility, despite the fact that she has two older sisters whose claims would be considered superior to her own under primogeniture succession. We never find out for sure in the books what the succession law actually is (the country never stabilizes for a long enough period that it becomes important), but if I had to guess I would guess that it’s designated,where the monarch chooses their successor prior to their death, and that the civil war that followed the Aiel War was the result of both Laman and his designated heir(s) dying at the Bloodsnows (we are told by Moiraine that Laman and both his brothers are killed; likely one of them was the next in line).
One country that we know for sure uses designated succession is Seanchan, where the prospective heir is still chosen from among the children of the Empress, but they are made to compete with each other (usually via murder and plotting) for the monarch’s favor, the ‘best’ being then chosen to become the heir. This very closely models how the Ottoman Empire did succession (state sanctioned fratricide) and while it has the potential to ensure competence (by certain metrics, anyways) it also sows the seeds of potential instability by ensuring that the monarch is surrounded by a whole lot of people with bad will to them and feelings of being cheated or snubbed in the succession, or else out for vengeance for their favored and felled candidate. Of course, from the Seanchan’s point of view this is a feature not a bug: if you can’t win a civil war or prevent yourself from being assassinated, then you shouldn’t have the throne anyways.
Succession is far from the only way that Jordan plays with the feudal structure either. Population is something else that is very present in the world building, even though it’s only drawn attention to a handful of times. In our world, the global population steadily and consistently rose throughout the middle ages and the Renaissance (with only small dips for things like the plague and the Mongol Invasion), then exploded with the Industrial Revolution and has seen been on a meteoric climb year over year (something that may just now be stabilizing into an equilibrium again, only time will tell). This is one of the pressures that led to the collapse of feudalism in the real world, as a growing aristocratic class was confronted with finite land and titles, while at the same time the growing (and increasingly powerful) wealthy financial class of various countries were beginning to challenge the traditions and laws that kept them out of direct power. If you’ve ever read a Jane Austen novel (or really anything from the Georgian/Regency/Victorian eras) this tension is on display. The aristocratic class had never been as secure as people think, but the potential to fall into poverty and ruin had never been a greater threat, which had ripple effects for the stability of a nation, and in particular a monarch who derived much of their power from the fealty of their now-destabilized vassals.
In Jordan’s world however, we are told as early as The Great Hunt that the global population is steadily falling, and has been since the Hundred Years’ War (at least). No kingdom is able to actually control all the territory it has on a map, the size of armies have in particular shrunk consistently (to the point where it’s repeatedly commented on that the armies Rand puts together, some of no more than a few thousand, are larger than any ‘since Artur Hawkwing's day’), large swathes of land lay ungoverned and even more uninhabited or settled. Entire kingdoms have collapsed due to the inability of their increasingly small populations to hold together. This is the fate of many of the kingdoms Ingtar talks about in the Great Hunt: Almoth, Gabon, Hardan, Moredo, Caralain, to name just a few. They came apart due to a combination of ineffective leadership, low population, and a lack of strong neighbors willing or able to extend their power and stability over the area.
All of this means that there is actually more land than there are aristocrats to govern it; so much so that in places like Baerlon power is held by a crown-appointed governor because no noble house has been able to effectively entrench in the area. This has several interesting effects on the society and politics of Randland: people in general are far more aware of the fragility of the nation state as a idea then they would be otherwise, and institutions (even the intractable and mysterious White Tower) are not viewed by even their biggest partisans as invulnerable or perpetual. Even the most powerful leaders are aware, gazing out constantly, as they do, at the ruins of the hundreds of kingdoms that have risen and fallen since the Breaking of the World (itself nothing more, to their understanding, then the death of the ultimate kingdom) that there are no guarantees, no promises that it all won’t fall apart.
This conflict reflects on different characters in different ways, drawing out selfishness and cowardice from some, courage and strength from others. This is a factor in Andor’s surprisingly egalitarian social climate: Elayne and Morgase both boast that Andorans are able to speak their minds freely to their leaders about the state of things, and be listened to, and even the most selfish of leaders like Elenia Sarand are painfully aware that they stand on a tower built from ‘the bricks of the common folk’, and make a concentrated effort to ensure their followers feel included and heard. Conversely it also reflects on the extremely regimented culture of the Borderlands, were dereliction of duty can mean not just the loss of your life, but the loss of a village, a town, a city, to Trolloc raids (another pressure likely responsible for slow and steady decline of the global population).
The Borderlanders value duty, honor, and responsibility above all else, because those are the cornerstones holding their various nations together against both the march of time and the Blight. All classes place a high value on the social contract; the idea that everyone must fulfill their duty to keep society safe is a lot less abstract when the stakes are made obvious every winter through monsters raiding your towns. This is most obvious in both Hurin and Ingtar’s behavior throughout The Great Hunt: Hurin (and the rest of the non-noble class) lean on the assurance that the noble class will be responsible for the greater scale problems and issues in order to endure otherwise unendurable realities, and that Rand, Ingtar, Aglemar, Lan (all of whom he believes to be nobly born) have been raised with the necessary training and tools to take charge and lead others through impossible situations and are giving over their entire lives in service to the people. In exchange Hurin pays in respect, obedience, and (presumably) taxes. This frees Hurin up to focus on the things that are decidedly within his ken: tracking, thief taking, sword breaking, etc, trusting that Ingtar, and later Rand, will take care of everything else.
When Hurin comes up against the feudal system in Cairhien, where the failures of everyone involved have lead to a culture of endless backstabbing and scheming, forced deference, entitlement, and mutual contempt between the parties, he at first attempts to show the Cairhienin ‘proper’ behavior through example, in the hopes of drawing out some shame in them. But upon realizing that no one in Cairhien truly believes in the system any longer after it has failed the country so thoroughly (hence the willingness of vassals to betray their masters, and nobles to abandon their oaths–something unthinkable in the Borderlands) he reverts to his more normal shows of deference to Rand and Ingtar, abandoning excessive courtesy in favor of true fealty.
Ingtar (and later Rand) feel the reverse side of this: the pressure to be the one with the answers, to hold it all together, to be as much icon and object as living person, a figure who people can believe in and draw strength from when they have none of their own remaining, and knowing at the same time that their choices will decide the fates and lives of others. It’s no mistake that Rand first meets Hurin and begins this arc in the remains of Hardan, one of those swept-away nations that Ingtar talks about having been left nothing more than ‘the greatest stone quarry for a hundred miles’. The stakes of what can happen if they fail in this duty are made painfully clear from the start, and for Rand the stakes will only grow ever higher throughout the course of the series, as number of those ‘under his charge’ slides to become ‘a nation’ then ‘several nations’ and finally ‘all the world’. And that leads into one of the problems at the heart of Rand’s character arc.
This emphasis on the feudal contract and duty helps the Borderlands survive the impossible, but almost all of them (with the exception of Saldaea) practice cultures of emotional repression and control,spurning displays of emotion as a lack of self-control, and viewing it as weakness to address the pains and psychological traumas of their day to day lives. ‘Duty is heavier than a mountain, death lighter than a feather’, ‘There will be time to sleep when you’re dead’, ‘You can care for the living or mourn the dead, you cannot do both’: all common sayings in the Borderlands. On the one hand, all of these emphasize the importance of fulfilling your duty and obligations…but on the other, all also implicitly imply the only true release from the sorrows and wounds taken in the course of that duty is death. It is this, in part, that breaks Ingtar: the belief that only the Borderlands truly understand the existential threat, and that he and those like him are suffering and dying for ‘soft southlanders’ whose kingdoms are destined to go to ruin anyways. It’s also why he reveals his suffering to Rand only after he has decided to die in a last stand–he is putting down the mountain of his trauma at last. This is also one of those moments in the books that is a particular building block on the road to Rand’s own problems with not expressing his feelings or being willing to work through his trauma, that will swing back around to endanger the same world he is duty-bound to protect.
I also suspect strongly that this is the source of the otherwise baffling Saldean practice of….what we will call dedicated emotional release. One of the core cultural Saldean traits (and something that is constantly tripping up Perrin in his interactions with Faile) is that Saldeans are the only Borderlanders to reject the notion that showing emotion is weakness. In fact, Saldeans in general believe that shows of anger, passion, sorrow, ardor–you name it–are a sign of both strength and respect. Your feelings are strong and they matter, and being willing to inflict them on another person is not a burden or a betrayal of duty, it’s knowing that they will be strong enough to bear whatever you are feeling. I would hesitate to call even the Saldaens well-adjusted (I don’t know that there is a way to be well-adjusted in a society at constant war), but I do think there is merit to their apparent belief in catharsis, and their resistance to emotional repression as a sign of strength. Of course, that doesn't make their culture naturally better at communication (as Faile and Perrin’s relationship problems prove) but I do think it plays a part in why Bashere is such a good influence on Rand, helping push him away from a lot of the stoic restraint Rand has internalized from Lan, Ingtar, Moiraine, et al.
It also demonstrates that a functioning feudal society is not dependent on absolute emotional repression, or perfect obedience. Only mutual respect and trust between the parties are necessary–trust that the noble (or monarch) will do their best in the execution of their duties, and trust that the common folk in society will in turn fulfill their roles to the best of their ability. Faile’s effectiveness as Perrin’s co-leader/second in command is never hindered or even implied to be hindered by her temperament or her refusal to hide/repress her emotions. She is arguably the one who is doing most of the actual work of governing the Two Rivers after she and Perrin are acclaimed their lord and lady: seeing to public works projects, settling disputes, maintaining relationships with various official groups of their subjects.
The prologue from Lord of Chaos (a favorite scene of mine of the books) where Faile is holding public audience while Perrin is off sulking ‘again’ is a great great example of this; Faile is the quintessential Borderland noble heir, raised all her life in the skills necessary to run a feudal domain, and those skills are on prime display as she holds court. But that is not hindered by her willingness to show her true feelings, from contempt of those she thinks are wasting her time, to compassion and empathy to the Wisdoms who come to her for reassurance about the weather. This is one of those things that Perrin has to learn from her over the course of the series–that simply burying his emotions for fear they might hurt others is not a healthy way to go about life, and it isn’t necessary to rule or lead either. His prejudices about what constitutes a ‘good’ Lord (Lan, Agelmar, Ingtar) and a ‘bad’ one (literally everyone else) are blinding him, showing his lack of understanding of the system that his people are adopting, and his role in it.
Which is a nice dovetail with my next bit–
Outsiders And the Non-Feudal State
Another way Jordan effectively depicts the Feudal system is by having groups who decidedly do not practice it be prominent throughout the series–which is again accurate to real life history, where feudalism was the mode of government for much of (but by no means all) of Medieval and Renaissance Europe, but even in Europe their were always societies doing their own thing, and outside of it, different systems of government flourished in response to their environments and cultures; some with parallels to Feudalism, many completely distinct.
The obvious here are the Aiel who draw on several different non-feudal societies (the Scottish Highland Clans, the Iroquois Confederation, the Mongols, and the Zulu to name just a few) and the Seafolk (whose are a combination of the Maori and the Republic of Piracy of all things), but also firmly in these categories are groups like the communities in the Black Hills, Almoth Plain, and the Two Rivers.
Even though it’s an agrarian farming community made up primarily of small villages, the Two Rivers is not a feudal state or system. We tend to forget this because it looks a lot like our notion of a classic medieval European village, which our biases inherently equate to feudal, but Jordan is very good at remembering this is not the case, and that the Two Rivers folk are just as much outsiders to these systems as the Aiel, or the Seafolk.
Consider how often the refrain of ‘don’t even know they’re part of the Kingdom of Andor’ is repeated in regards to the Two Rivers, and how much the knowledge of Our Heroes about how things like Kingdoms, courts, war, etc, are little more than fairy tales to the likes of those Two Rivers, while even places unaffected directly by things like the Trakand Succession or the Aiel War are still strongly culturally, economically, and politically impacted.
Instead of deriving power and justice from a noble or even a code of law, power is maintained by two distinct groups of village elders (The Village Council and the Women’s Circle) who are awarded seats based on their standing within the community. These groups provide the day-to-day ordering of business and resolving of conflicts, aiding those in need and doing what they can for problems that impact the entire community. The Wisdom serves as the community physician, spiritual advisor, and judge (in a role that resembles what we know of pre-Christian celtic druids), and the Women’s Circle manages most social ceremonies from marriages to betrothals to funerals, as well as presiding over criminal trials (insofar as they even have them). The Mayor manages the village economics, maintaining relationships and arbitrating deals with outsider merchants and peddlers, collecting and spending public funds (through a volunteer collection when necessary, which is how we’re told the new sick house was built and presumably was how the village paid for things like fireworks and gleeman for public festivals), while the Council oversees civil matters like property disputes.
On the surface this seems like an ideal community: idyllic, agrarian, decentralized, where everyone cares more about good food and good company and good harvests than matters of power, politics, or wealth, and without the need for any broader power-structure beyond the local town leaders. It’s the kind of place that luddites Tolkien and Thomas Jefferson envisioned as a utopia (and indeed the Two Rivers it the most Tolkien-y place in Randland after the Ogier stedding, of which we see relatively little), but I think Jordan does an excellent job of not romanticizing this way of life the way Tolkien often did. Because while the Two Rivers has many virtues and a great deal to recommend it, it also has many flaws.
The people in the Two Rivers are largely narrow minded and bigoted, especially to outsiders; The day after Moiraine saves the lives of the entire village from a Trolloc attack, a mob turns up to try and burn her out, driven by their own xenophobia and fear of that which they don’t understand. Their society is also heavily repressed and regressive in its sex norms and gender relations: the personal lives of everyone are considered public business, and anyone living in a fashion the Women’s Circle deems unsuitable (such as widower and single father Tam al’Thor) is subject to intense pressure to ‘correct’ their ways (remarry and find a mother for Rand). There is also no uniformity in terms of law or government, no codified legal code, and no real public infrastructure (largely the result of the region’s lack of taxes). This is made possible by the geographic isolation and food stability–two factors that insulate the Two Rivers from many of the problems that cause the formation or joining of a nation state. It’s only after the repeated emergence of problems that their existing systems can not handle (Trolloc raids, martial law under the White Cloaks, the Endless Summer, etc) that the Two Rivers folk begin adopting feudalism, and even then it’s not an instantaneous process, as everyone involved must navigate not just how they are going to adopt this alien form of government, but how they are going to make it match to their culture and history as well.
This plays neatly with the societies that, very pointedly, do not adopt feudalism over the course of the series. The Aiel reject the notion entirely, thinking it as barbaric and backward as the Westerlanders think their culture is–and Jordan is very good at showing neither as really right. The Aiel as a society have many strengths the fandom likes to focus on (a commitment to community care, a strong sense of collective responsibility, a flexible social order that is more capable of accounting for non-traditional platonic and romantic relationships, as well as a general lack of repressive sex norms) but this comes at a serious cost as well. The Aiel broadly share the Borderlander’s response of emotional suppression as a way of dealing with the violence of their daily life, as well as serious problems with institutionalized violence, xenophobia, and a lack of respect for individual rights and agency. Of these, the xenophobia is probably the most outright destructive, and is one of the major factors Rand has to account for when leading the Aiel into Cairhien, as well a huge motivating factor in the Shaido going renegade, and many Aiel breaking clan to join them–and even before Rand’s arrival it manifested as killing all outsiders who entered their land, except for Cairhienin, whom they sold as slaves in Shara.
And yet, despite these problems Jordan never really suggests that the Aiel would be better off as town-or-castle dwelling society, and several characters (most notably the Maidens) explicitly reject the idea that they should abandon their culture, values, and history as a response to the revelations at Rhuidean. Charting a unique course forward for the Aiel is one of the most persistent problems that weighs on the Wise Ones throughout the second half of the series, and Aviendha in particular. Unlike many of the feudal states faced with Tarmon Gai’don, the Aiel when confronted with the end of days and the sure knowledge of the destruction of their way of life are mostly disinterested in ignoring, running from, or rejecting that revelation (those that do, defect to the Shaido). Their unique government and cultural structure gives them the necessary flexibility to pivot quickly to facing the reality of the Last Battle, and to focus on both helping the world defeat the Shadow, and what will become of them afterwards. This ironically, leaves them in one of the best positions post-series, as the keepers of the Dragon’s Peace, which will allow them to hold on to many of their core cultural values even as they make the transition to a new way of life, without having to succumb to the pressures to either assimilate into Westlands, or return to their xenophobic isolationism.
The Seafolk provide the other contrast, being a maritime society where the majority of the people spend their time shipboard. Their culture is one of strong self-discipline and control, where rank, experience, and rules are valued heavily, agreements are considered the next thing to sacred, and material prosperity is valued. Though we don’t spend quite as much time with them as the Aiel, we get a good sense of their culture throughout the mid-series. They share the Aiel’s contempt for the feudal ‘shorebound’, but don’t share their xenophobia, instead maintaining strong trade relationships with every nation on navigable water, though outside of the context of those trade relationships, they are at best frosty to non-Seafolk.
They are not society without problems–the implication of their strong anti-corruption and anti-nepotism policies is that it’s a serious issue in their culture, and their lack of a centralized power structure outside of their handful of island homes means that they suffer a similar problem to the likes of Murandy and Altara, where life on one ship might be radically different then life on another, in terms of the justice or treatment you might face, especially as an outsider. But the trade off is that they have more social mobility then basically any other society we see in Randland. Even the Aiel tend to have strongly entrenched and managed circles of power, with little mobility not managed by the Wise Ones or the chiefs. But anyone can rise high in Sea Folk society, to become a leader in their clan, or even Mistress of the Ships or Master of the Blades– and they can fall just as easily, for shows of incompetence, or failures to execute their duties.
They are also another society who is able to adapt to circumstances of Tamon Gai’don relatively painlessly, having a very effective plan in place to deal with the fallout and realities of the Last Battle. The execution gets tripped up frequently by various factors, but again, I don’t think it’s a mistake that they are one of the groups that comes out the other side of the Last Battle in a strong position, especially given the need that will now exist to move supplies and personnel for rebuilding post-Last Battle. The Seafolk have already begun working out embassies in every nation on navigable water, an important step to modernizing national relationships.
How does all this relate to feudalism and class? It’s Jordan digging into a fundamental truth about the world and people–at no point in our own history have we ever found a truly ‘perfect’ model for society. That’s something he’s constantly trying to show with feudalism–it is neither an ideal nor an abomination, it just is. Conversely, the Two Rivers, Aiel, Seafolk, and Ogier (who I don’t get into to much here for space, but who also have their own big problems with suffrage and independence, and their virtues in terms of environmental stability and social harmony) all exist in largely classes societies, but that doesn't exempt them from having problems or make them a utopia, and it certainly doesn't make them lesser or backwards either–Jordan expends a lot of energy to show them as complex, nuanced and flawed, in the same way he does for his pseudo-Europe.
Conclusion
To restate my premise: one of Jordan’s profound gifts as a writer is his capacity to set aside his own biases and write anything from his villains to his world with an honest, empathetic cast that defies simplification. Feudalism and monarchy more generally have a bad rep in our society, for good reasons. But I think either whitewashing or vilifying the feudal system is a mistake, which Jordan’s writing naturally reflects. Jordan is good at asking complicating questions of simple premises. He presents you with the Kingdom of Andor, prosperous and vast and under the rule of a regal much loved Queen and he asks ‘where does its wealth come from? How does it maintain law and order? How does the Queen exert influence and maintain her rule even in far-flung corners of the realm? How did she come to power in the first place and does that have an impact on the politics surrounding her current reign?’. And he does this with every country, every corner of his world–shining interesting lights on familiar tropes, and exploring the humanity of these grand ideas in a way that feels very real as a result.
The question of, is this an inherently just system is never really raised because it’s a simplifying question, not a complicating one. Whatever you answer–yes or no–does not add to the depiction of these systems or the people within them, it takes away. You make someone flat–be it a glorious just revolutionary opposing a cackling wicked King, or a virtuous and dutiful King suppressing dangerous radical dissidents, and you make the world flatter as a result.
I often think about how, when I began studying European history, I was shocked to learn that the majority of the royalists who rose up against the Jacobins were provincial peasants, marching against what they perceived to be disgruntled, greedy academic and financial elites. These were, after all, the same people that the Jacobins’ revolution claimed to serve and be doing the will of. Many of the French aristocrats were undeniably corrupt, indolent, and detached from their subjects, but when you look closer at the motives of many of the Jacobins you discover that motives were frequently more complex then history tends to remember or their propaganda tried to claim, and many were bitterly divided against each other on matters of tactics, or ideals, or simple personality difference. The simple version of the French Revolution assigns all the blame to the likes of Robespierre going mad with power, and losing sight of the revolutions’ higher ideals, but the truth was the Jacobins could never properly agree on many of their supposed core ideals, and Robespierre, while powerful, was still one voice in a Republic–and every person executed by guillotine was decreed guilty by a majority vote.
This is the sort of nuance lost so often in fantasy stories, but not in Jordan’s books. The story could be simpler–Morgase could just be a just and good high Queen archetype who is driven by love of her people, but Jordan depicts her from the beginning as human–with virtues and flaws, doing the best she can in the word she has found herself. Trying to be a just and good Queen and often succeeding, and sometimes falling short of the mark. The Tairen and Cairhienin nobility could just all be greedy, corrupt, out-of-touch monsters who cannot care for anything beyond their own pleasures–but for every Laman, Weairamon, or Colavaere, you have Dobraine, Moiraine, or Darlin. And that is one of the core tenets of Jordan’s storytelling: that there is no system wholly without merit or completely without flaw, and no group of people is ever wholly good or evil.
By taking this approach, Jordan’s story feels real. None of his characters or world come across like caricature or parody. The heinous acts are sharper and more distinct, the heroic choices more earned and powerful. Nothing is assumed–not the divine right of kings, or the glorious virtue of the common man. This, combined with a willingness to draw on the real complex histories of our own world, and work through how the unique quirks of fantasy impact them, is what renders The Wheel Of Time such a standout as a fantasy series, past even more classic seminal examples of the genre, and why its themes of class, duty, power, and politics resonate with its modern audiences.
#Wheel of Time#WoT#WoT Meta#Wheel of time Meta#Feudalism#Class Politics#Worldbuilding#Wot Book Spoilers#AMOL Spoilers#No one has ever done it like Robert Jordan and no one may ever do it like him again#Their is no earthly way I can tag all the characters refrenced in this#so I'll hit those I talk about more then three times#Rand al'Thor#Moiraine Damodred#Elayne Trakand#Mat Cauthon#Perrin Aybara#faile bashere#Morgase Trakand#ingtar shinowa#Hurin#tuon athaem kore paendrag#I invite pepole to discuss/respond if they want#but a reminder that I assume good faith whenever possible#and ignore bad faith when apparent
150 notes
·
View notes
Text
‘Get rid of the cleaners, rubbish collectors, bus drivers, supermarket checkout staff and secretaries, for example, and society will very quickly grind to a halt. On the other hand, if we woke up one morning to find that all the highly paid advertising executives, management consultants and private equity directors had disappeared, society would go on much as it did before: in a lot of cases, probably quite a bit better. So to begin with, workers need to reclaim a sense of pride and social worth. Doing so would be a big step forward in making the case that the wages and conditions of low-paid jobs must be improved in order to reflect the importance they have in all our lives.’
– Owen Jones, Chavs: The Demonization of the Working Class (2020)
#class politics#socialism#workers rights#union strong#unionize#british politics#uk politics#owen jones#there were a lot of good sections from this book i could have quoted#its very good and very relevant today#(it was originally published in 2011)
140 notes
·
View notes
Text
if you think that only white masc men count as working class then you're a nazi btw. If you think masculinity and the working class are even corrolated then you are homophobic, sexist, and INCREDIBLY susceptible to fascism. Appalachian coal miners are a dying breed and they are part of a working class coelition but they're not the face of it. In the US they are outnumbered by flamboyantly gay baristas, as specific as that is. The working class is the service industry it's elder and disability care it's sex workers its package delivery and uber drivers. Nonwhite people are over represented in the working class in proportion to their percentage of the population, most trans people are working class, women make up half the working class. You don't even know what the working class is you need to read Marx yesterday
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
""Moreover, it turns out that the United States is not all that tightfisted when it comes to social spending. “If you count all public benefits offered by the federal government, America’s welfare state (as a share of its gross domestic product) is the second biggest in the world, after France’s,” Desmond tells us. Why doesn’t this largesse accomplish more?
For one thing, it unduly assists the affluent. That statistic about the U.S. spending almost as much as France on social welfare, he explains, is accurate only “if you include things like government-subsidized retirement benefits provided by employers, student loans and 529 college savings plans, child tax credits, and homeowner subsidies: benefits disproportionately flowing to Americans well above the poverty line.” To enjoy most of these, you need to have a well-paying job, a home that you own, and probably an accountant (and, if you’re really in clover, a money manager).
“The American government gives the most help to those who need it least,” Desmond argues. “This is the true nature of our welfare state, and it has far-reaching implications, not only for our bank accounts and poverty levels, but also for our psychology and civic spirit.” Americans who benefit from social spending in the form of, say, a mortgage-interest tax deduction don’t see themselves as recipients of governmental generosity. The boon it offers them may be as hard for them to recognize and acknowledge as the persistence of poverty once was to Harrington’s suburban housewives and professional men. These Americans may be anti-government and vote that way. They may picture other people, poor people, as weak and dependent and themselves as hardworking and upstanding. Desmond allows that one reason for this is that tax breaks don’t feel the same as direct payments. Although they may amount to the same thing for household incomes and for the federal budget—“You can benefit a family by lowering its tax burden or by increasing its benefits, same difference”—they are associated with an obligation and a procedure that Americans, in particular, find onerous. Tax-cutting Republican lawmakers want the process to be both difficult and Swiss-cheesed with loopholes. (“Taxes should hurt,” Ronald Reagan once said.) But that’s not the only reason. What Desmond calls the “rudest explanation” is that if, for whatever reason, we get a tax break, most of us like it. That’s the case for people affluent and lucky enough to take advantage of the legitimate breaks designed for their benefit, and for the wily super-rich who game the system with expensive lawyering and ingenious use of tax shelters.
And there are other ways, Desmond points out, that government help gets thwarted or misdirected. When President Clinton instituted welfare reform, in 1996, pledging to “transform a broken system that traps too many people in a cycle of dependence,” an older model, Aid to Families with Dependent Children, or A.F.D.C., was replaced by Temporary Assistance for Needy Families, or TANF. Where most funds administered by A.F.D.C. went straight to families in the form of cash aid, TANF gave grants to states with the added directive to promote two-parent families and discourage out-of-wedlock childbirth, and let the states fund programs to achieve those goals as they saw fit. As a result, “states have come up with rather creative ways to spend TANF dollars,” Desmond writes. “Nationwide, for every dollar budgeted for TANF in 2020, poor families directly received just 22 cents. Only Kentucky and the District of Columbia spent over half of their TANF funds on basic cash assistance.” Between 1999 and 2016, Oklahoma directed more than seventy million dollars toward initiatives to promote marriage, offering couples counselling and workshops that were mostly open to people of all income levels. Arizona used some of the funds to pay for abstinence education; Pennsylvania gave some of its TANF money to anti-abortion programs. Mississippi treated its TANF funds as an unexpected Christmas present, hiring a Christian-rock singer to perform at concerts, for instance, and a former professional wrestler—the author of an autobiography titled “Every Man Has His Price”—to deliver inspirational speeches. (Much of this was revealed by assiduous investigative reporters, and by a 2020 audit of Mississippi’s Department of Human Services.) Moreover, because states don’t have to spend all their TANF funds each year, many carry over big sums. In 2020, Tennessee, which has one of the highest child-poverty rates in the nation, left seven hundred and ninety million dollars in TANF funds unspent."
- The New Yorker: "How America Manufactures Poverty" by Margaret Talbot (review of Matthew Desmond's Poverty by America).
195 notes
·
View notes
Text

why do i have things like this in my drafts
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Assimilation is violence, not just the violence of cultural erasure, but the violence of stepping on anyone who might get in the way of your upward mobility. Gay (and lesbian!) landlords evict people with AIDS to increase property values, gay bar owners arrest homeless queers so they don't get in the way of business, and gay political consultants mastermind the election of pro-development, antipoor candidates"
-Mattilda Bernstein Sycamore, "There's more to life than platinum: challenging the tyranny of sweatshop-produced rainbow flags and participatory patriarchy" for "That's Revolting!: Queer Strategies for Resisting Assimilation"
#babble babble#mattilda bernstein sycamore#anti assimilation#assimilation#queer assimilation#class politics#intersectionality
41 notes
·
View notes
Photo


hate the veil of gentility masking the horrors unleashed on the world by the english aristocracy
#communism#socialism#perioddramaedit#downton abbey#downtonabbeyedit#i would like to see the earl of grantham's voting record in the house of lords#bet it perfectly mirrors every other hereditary peer#always voting to keep the poor poor and poorer im sure#out here pretending he's isn't conservative of a most brutal class system ever devised#thank god for thomas - yes i said thomas NOT branson! branson is THAT guy yall kno whom im tamlbout#rich people#inverted totalitarianism#war on the poor#anti capitalism explained#class warfare#class politics#history#anti capitalism#propaganda#economic violence#poverty#income inequality#mental health#downtonedit#dynasts#period drama#british empire
145 notes
·
View notes
Text
These days I mostly avoid being around art spaces and the dwindling population of people that frequent them. This is for the same reason you might duck an old friend who’s been transformed by time and circumstance into a thing that you scarcely recognize. Sometimes it’s better to remember them as they were.
I broke my rule the other night to attend the closing of a theater I built long ago, and it was every bit as sad and disappointing as I would have expected. Hardly anyone came to send her off, and the ones that did could muster nothing better than a couple of beers and off to bed. The whole thing was over by 11.
“Who are you voting for,” a pudgy, bearded, graying Xer, asked me before I left. He was wearing a kind of middle-aged bohemian get-up, right down to the hipster hat, that made him look like he’d just stepped out of a commercial for a new Type II diabetes drug. I’m down to talk my doctor about . . .
“I’m writing in Dave Chappelle,” I said.
He opened and closed his mouth a few times, trying to find the part of his brain that knew how to process a dissenting opinion. Not finding one he sputtered, “But you’re not for Trump.”
“No.”
Then a skinny, wan, pale guy with sunken eyes, and long, greasy black hair, sober as a judge, like someone who’d acquired all the physical attributes of heroin addiction, without ever having had any of the fun, said, “Then you have to vote for Biden, or Trump wins.”
“So what,” I said.
And that was when they both shit themselves and I had to do the whole red-pill/blue-pill thing. By the time that was over, everyone else had gone and I followed suit. Leaving the building for the last time, I thought of livelier days when the whole place, the whole block, the whole city, was full of life and crazy energy.
How did this happen? How did we get here?
This is an article I’ve started, abandoned, and started again a few times over the years. That’s partly because I still had some hope when I began that I might one day be able to return to my craft as a theater director without revealing my opinions. But that was before Due Dissidence had a YouTube show. Now I very visibly express ideas 3-4 times a week that would get me professionally and socially cancelled in about 5 minutes as soon as anyone from that crowd took the time to check out the channel, which of course they would.
Another thing that’s kept this one at the bottom of the digital drawer is lingering affection for a lot of people who are still making the music, lighting the lights, and all that. I have dear friends in the arts and this is going to hurt some of their feelings. Except for the ones who regularly DM to thank me for saying what they can’t without risking career suicide. Those will be greatly cheered by this piece, in the way of a bullied child watching their tormentor take a hard fist to the nose, so I guess in the end that part’s a wash. Here goes.
In the 8 years since the election of doom that transformed me from the kind of guy who wanted to have a beer with Rachael Maddow, to the kind of guy who would protest her book reading, I’ve had lots of debates with lots of people. Enough to notice a distinct pattern
Conservatives will generally keep it on the issues; they may not agree with you, but as a rule they aren’t going to go right to ad hominem attacks on your character. Liberals can go either way: they may debate the issues with you, but they’re just as likely to attack you personally as a closet Republican, a Russian plant, or if you happen to be a white man, that’s kind of their go-to. But the absolute worst people you can find yourself engaging with are members of the arts community. I know this because I’ve been a member of it since at the tender age of 19, I bullshitted my way into a directing gig at the still extant 13th Street Repertory Theater.
The artists I worked with then as a kid from Queens dazzled by the bohemian world I had infiltrated wouldn’t recognize the artists of today, and I suspect they wouldn’t like them all that much. Heirs to a 60’s counter-culture ethos of distrust for authority and institutions, and to an older tradition of the artist-intellectual, they generally thought of all politicians as dishonest psychopaths, and spent more time discussing Kafka than the evils of Soviet Russia, which occupied the same position of public enemy #1 that its successor state does today. And lest the wokeratti immediately jump to its aforementioned go-to, the scene was far more substantively diverse than what you might find at a theater or a gallery today. They were gay and straight, old and young, black and white and brown, and in a major departure from the current moment, both penniless and well to do. There were artists living rent free in the loft above the theater, others renting $250 apartments in pre-hipster Williamsburg who had to walk across the bridge to get to rehearsals for lack of train fare, and still others living comfortably on the Upper West Side. If there was a failing it was in a tendency towards pretentiousness: when a middle-aged woman pronounced confidently at a post-rehearsal dinner that the principal crisis of the modern age was the “post-Nietzschean vacuum,” I almost laughed in her face. No one had that problem in my native Flushing, and I suspected that was true most places. But the problem wasn’t racism, sexism, or homophobia-expressing those sorts of views would have been just about the only thing that could have gotten you ejected in an atmosphere where pretty much anything went, and it was that way in the arts community for as long as I was a part of it.
Generally, I like to heavily source everything I write, ‘cause when you’re offering controversial opinions, you had better cross all your t’s and such. But because the arts are such a distinct subculture and the kinds of institutions that have the means to conduct a wide survey on questions like: what class background do artists usually come from, or, when did artists start to favor censorship, never would, I must of necessity rely on my personal observations and speculations. Which makes this, by definition, a personal essay, so take it as you will.
I’m starting from the premise that something has gone very wrong when you have an American arts community that tends to be politically conservative in the sense of being to the right of general sentiment in the Western world on class and economics; that mindlessly supports politicians like Joe Biden and Hillary Clinton who’s records are at odds with even the identitarian issues that they claim to care about, and that sees de-platforming and cancelling figures like Joe Rogan as a legitimate tactic, never considering the idea that once you let that genie out of the bottle, no one will be more vulnerable to having it turned against them than artists. I’ve given a lot of thought to how a bohemian scene of intellectuals and misfits turned into something resembling a PTA meeting in Scarsdale. This is what I came up with:
I will concede this to the painfully woke white people that dominate the arts even as they lately denounce their own position: rich white people are the crux of the problem, with the emphasis being on “rich” rather than “white,” as some would have it. The low to no pay circumstances of most creatives are beside the point, even though many of them will point to this as evidence of their moral authority to speak on matters of poverty and marginalization. If “artist” isn’t a Professional Managerial Class job, what is it? It sure ain’t factory work. The pretense of artists to social disenfranchisement calls to mind John Goodman’s line in Barton Fink, where his serial killing salesman tells John Turturro’s slumming writer, “You’re just a tourist with a typewriter, Barton. I live here.”
Most of these folks are just playing dress up for a while before they pack it in for Grad School and take up residence in the same sedate suburban enclaves from whence they came. Just as in every other sphere of American society, the arts are, and always have been, dominated by these kinds of middle and upper-middle class, mostly white people, whose sensibilities reflect that reality. The higher up the food chain you go, the more evident that becomes. The same exact advantages of money and connections that favor people in every other industry, favor those who attempt a career in the arts. Perhaps even more so because the standards are so nebulous. If you’re a doctor, or an attorney, you either do your job well, or you don’t. If you’re an artist, the quality of your work is subjective which leaves a lot of room for just hooking up the people you relate to, which in the arts is going to mean a lot of rich white people, hooking up other rich white people. The net effect of that is, if a lot of bad ideas are coming out of the suburbs, that’s going to be reflected in the work.
When the PMC’s were more rooted in the New Deal, with its focus on class and economics, as was the case when I first entered the scene, so were the arts. Now that they’ve turned to neoliberalism in their economics, and the post-modern turn has unmoored their social activism from observable reality, we have an arts community that has nothing to say about the current moment that strays an inch from what you might hear on MSNBC. This is why, as just one example, in a moment of social strife and economic dislocation, the Artistic Director of Connecticut’s Long Wharf Theater recently seized on the idea of a Black Trans Women at the Center festival as the best use of his platform and resources. The company lost their home of 55 years shortly thereafter.
Whereas in the 30’s a good many artists responded to the Depression by adopting a Marxist-Leninist posture and playwrights like Clifford Odets, (the writer being satirized by the Cohens in Barton Fink), and later Arthur Miller and Rod Serling, began writing plays for the first time that placed working class people “at the center,” this generation of artists greets the moment with only contempt for the struggles of working people, seeing them as reactionary Trumpers who sadly lack the education and sophistication to realize that the economy is great, incremental change is the best we can hope for, and getting all bent out of shape about books full of graphic cocksucking in your child’s middle-school library is totally uncool. Rather than to represent the struggles of average people, these artists offer them nothing but derision and when they do bother to acknowledge them, it is only to portray them as wrong-think culture war enemies.
Adding to the problem, poor people who manage to get to college usually don’t decide to major in something that’s going to almost guarantee that they end up poor. Being an artist is a luxury most people from economically disadvantaged environments just don’t think they can afford. You’re a lot more likely to choose it if you have a trust fund to fall back on. So, essentially you end up with a scene dominated by trust fund babies, no matter what identity group they align with. Their politics proceed from there. All these artists going on about white privilege is partly a case of, to use a phrase with which any theater aficionado will be familiar, “Methinks thou dost protest too much.” And as with Diversity Equity and Inclusion efforts in other sectors, this results in pretenses at promoting “representation” amounting to nothing more than trying to find more black and brown people from similar backgrounds to the whites that are already there, and who consequently share the same attitudes. Barracks and Michelles are always welcome, but the Hueys and Assatas make these folks deeply uncomfortable. The theater party I walked into last week, was no more racially diverse than the scene I knew in the 80’s (perhaps a bit less), but it was palpably less wide-ranging in class perspectives.
Another reason the censorious Victorian lady in high dudgeon pose that has become the liberal class default setting over the past 10 years or so, has had so much appeal to this group in particular, probably has to do with the psychological afflictions common to artists, combined with the insecurities inherent in the profession. This is something else I’d love to see a study on: common psychological illnesses in artists, but lacking such a study, I can only tell you what I’ve observed. Most people don’t choose a career in the arts because they’re very secure, contented and happy sorts. The level of personal psychological torment that’s driven them to such an irrational career choice varies, but deep neurosis, emotional neediness, and pervasive self-doubt are kind of a base line. I do not except myself from this analysis: my head is the kind of snake pit that Indiana Jones has nightmares about. Proceeding from there, you’ll find a fair amount of narcissism, borderline personality disorder, manic-depression, and just plain old depression-depression. These qualities are not at all ameliorated by constant rejection and criticism, which is kind of the nature of the beast. In some ways the people who are attracted to the arts are the least capable of enduring its vicissitudes without severe psychological damage. So, you have a bunch of deeply insecure, neurotic people, trying to make their way in a profession where the rules are vague and the agreed upon standards of successful work are non-existent, and then you hand them a secular religion that gives them not only rules and standards, but a weapon with which to bludgeon their critics as -ists, phobes, and reactionary heathens. That’s like throwing crackers at a starving man. Naturally they jumped on it en masse, without ever thinking through the consequences. Critical Social Justice gave artists something they haven’t had since Duchamp signed a urinal and called it a sculpture: certainty. And this group is far too ignorant of the past to know why their forbears rejected the kind of formalism that these standards impose, and what the price paid in quality, creativity and individual expression will be in the long run. Insofar as they embrace Duchamp’s lesson, it is only in using the precedent set by his famous prank to avoid being interrogated on the basis of quality, talent and craftsmanship.
Which brings us to my final observation.
I’m going to let you in on a secret, although if you’ve ever been dragged to a “new interpretation” of Hamlet on the Lower East Side, back when we still did that sort of thing, you probably already know: talent is rare. That’s why we call it talent. If it was common, we’d call it something else. I’ll give you a breakdown from something I have a fair amount of expertise in-auditioning actors. If you audition 100 actors, it’s going to go something like this: about 10% will be so God-awful you have to wonder where they got the encouragement; around 60% will be passable in the way of people who have had a lot of training; 20% will be very good; 8% will be excellent; a final 2% will be exceptional-in other words, talented. So, based on my admittedly subjective observations, only about 30% of the people who call themselves “artists” have any business pursuing it. And only 2% of those are really gifted. So, the scene is, and always has been, mostly populated by hangers-on who are only one 30th Birthday away from packing it in and getting a Masters in Social Work. The appeal of a set of standards that remove the basis of evaluating work from its quality to its adherence to a set of clearly defined political beliefs is obvious. If you can’t out-talent people, you can at least out-woke them.
None of this is to say that representation in the arts isn’t a problem or wasn’t a problem until these meddling kids started performing their virtue for likes and clicks. It’s always been a problem, particularly at the level of management and project leadership, in the arts as in every other sector of society. I would posit that DEI efforts are a solution in search of a problem, only in that part of the reason for that lack of representation, has always been a lack of artists of color walking in the door, which in turn has to do with the economic realities I’ve mentioned. There aren’t a lot of poor white people walking in the door either; I’ve owned 5 theaters in NYC across three decades, and I never met another theater owner or director, who grew up on welfare. In my experience, that lack of representation never had to do with virulent racism in the arts community. It always had to do with class realities and broader issues of structural racism society-wide that stop POC from ever making it to the door to be considered. If you were paying any kind of attention, that lack of diversity was always an embarrassment, but you can’t work with people who simply aren’t there because of societal problems that reach far beyond the arts. If we really want to do something about this, we need to go out into impoverished and marginalized communities, provide training and encouragement to young people in particular, then offer them jobs in our theaters and galleries, instead of only looking for POC from similar backgrounds to the people who are already there in order to assuage their white guilt. Until we see arts institutions doing that, we will know DEI efforts in the arts for what they are: one more example of rich white people protecting the privileges of their class, even if they have to outwardly denounce them in order to do it.
In the end, the arts scene as it exists today and the institutions that support it may have simply become too sclerotic, out of touch, and irrelevant for saving. The future is with activist-artists grown naturally from their communities, using new technologies and platforms to draw attention to concerns and realities that no gatekeeping clique of PMC’s will ever understand or think to explore. As our self-appointed creators of culture have abandoned us, it may be time that we abandon them in turn, leaving their venues to close as they should, leaving their 501c’s to go bankrupt, as they are doing, and taking the space their collapse opens up to create something new of our own.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Y'know, I don't really care about whether or not any given billionaire is a good person or malicious. I care that they are in positions to excercise mass cruelty in order to horde wealth that could help save and improve lives just to play an inconsequential numbers game for purely vain reasons. Maybe some billionaire out there is a nice person, but they are still benefitting from a cruel system that exploits workers and withholds resources from the people that need them.
Is 1 good billionaire really worth the suffering of millions?
125 notes
·
View notes
Note
If Davos would be so thoroughly screwed in a court environment, why were Littlefinger and Septon Barth able to thrive then?
I didn't say he'd be screwed, just that he'd face a lot of opposition from the incumbent nobility. But as with any commoner in that position, the answer was to combine superior ability with royal favor to get shit done, ruthlessly stomping on the fingers of anyone who gets in your way.
Littlefinger thrives because no one sees him as a threat, and because he's lending everyone money and spying on everyone, but mostly because no one sees him as a threat. Also, he is technically a member of the nobility, so he gets more of a pass.
Septon Barth thrived because he had the absolute support of Jaehaerys. Also he was a goddamn wizard, so I imagine that brought a certain amount of fear and respect with it. Don't fuck with Septon Barth unless you want to wake up with firewyrm parasites crawling under your skin.
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
The GOP appeals to the white working class not through class issues, but through racism. Because the white working class in the United States is, by and large, racist.
There's definitely a Horseshoe Effect when it comes to the racial politics between wealthy white Republicans and white working class Republicans. It's arguably their biggest common ground.
It's not that the white working class doesn't care about being underpaid and exploited for their labor. It's not that they're unaware of how much bosses and the capitalist system screw them over. On the contrary, they're quite cognizant of those issues. It's just that they are much more fearful of competing with immigrants over jobs or minorities fighting for racial equality, and they vote accordingly.
Some anecdotal evidence on my part: I'm a white woman born and raised in the South where my mom, dad, and stepdad's sides are all economically diverse but solidly Republican. I've heard pretty much every racist talking point across this large class gamut that doesn't include overt, KKK racism. A very close family member, a woman who grew up working class (and became middle class by marriage), cited the aforementioned fear of immigrants and minorities on why she voted for Trump, more than any other issue. The white working class kids I went to school with were also solidly Republican, and you bet your ass they had racist views!
There's a popular narrative that the white working class started voting Republican because the Democratic Party abandoned class issues. That narrative implies that the Republican Party has made class issues a large part of their platform, but that couldn't be further from the truth, as their embrace of Trickle Down Economics proves. Instead, the Democratic Party started emphasizing racial equality, which turned off the white working class by and large.
There's another popular but just as inaccurate narrative that the white working class are voting against their interests. From a class perspective, that's true. But once again, the white working class greatly prioritizes their racial politics over their class politics, so in reality, they actually are voting for their interests. Maintaining white supremacy - whether they want to admit it or not - interests them more than addressing wealth inequality.
As long as all of these factors hold true, the Republican Party will continue to court the white working class vote with Race Panic ad infinitum.
#my posts#text post#us politics#class politics#race relations#sociology#politics#i'm sure none of this will be controversial on tumblr dot com
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
There’s a reposted tweet making the rounds, of how a world where humans do the hard workthrough low-paid jobs while robots make art and literature wasn’t the future they imagined, and it’s getting under my skin. I really don’t think it’s meant the way I’m reading it. There’s probably a bit of tonedeafness excused by being in pain from the people sharing it, or me imposing my own thoughts on it. Probably a bit of both. Still, it’s bothering me, and better out than in I think.
See, there are quite a lot of working class people, white men in particular, who’ve found a lot of purpose and dignity in doing physically hard jobs; and suffered from the loss of that purpose and dignity when those jobs were mechanized. Manual labor like mining and lumbering trees, factory jobs, even menial jobs at big box stores.
Subjective dignity, I mean: they felt dignified by doing good honest work that required strength, or, more recently, persevering through whatever the boss-man threw at you. At being able to provide for their families, or the illusion of that as the actual wages made it harder and harder to do just that. I don’t think it’s particularly good dignity, and I wish the found that purpose in building communities and actually loving and raising their kids and supporting their friends and what-not. (Not that working-class people don’t do that, too.) I personally think any job that can be done by a robot should, so long as we find a way to share society’s resources so those not needed to do mechanizable labor can still live a good life. (And that’s the tricky bit, isn’t it?) But the fact I disagree with where they found that dignity doesn’t change the fact that they’re experiencing a loss through mechanization and automation. Loss of purpose, of power and control over their lives, of pride at accomplishing something hard and being able to make life easier for the people they love.
What I hear in things like that tweet is people saying that hard word those people took such pride and purpose from is garbage work, fit only for machines, whereas art is the proper work of humans. Which feels dismissive toward the pain of people not like them, who never assumed art could be a career, or a full-time endeavor. Mostly they were too tired to do much of it at all. It seems classist if I was going to put an -ist label on it. And that stings, because I remember being a doctoral student in a program with people who grew up with a lot more money than I had, who had this sort of confidence that sitting around and thinking about theory was their assumed and rightful place. I had to scrounge to fund my education, and most of my family and friends and neighbors were much more likely to work their asses off in factories or at Walmart than they were to be disappointed they had to work as baristas while they waited on their art or writing or music to make them enough money they didn’t have to do that anymore.
As I said, I really don’t think this kind of talk was meant this way. I feel silly even putting it into words, and I certainly don’t mean to be flippant toward folks who do create art professionally or hope to. But seeing the work a lot of people around me found purpose in as the kind of job fit only for machines? That’s hit a bit close to home.
The meaning I’m taking from the whole AI shitstorm is that people need something meaningful to work for, and ideally they need to find it in a place that’s actually worthy of giving them meaning, something authentically dignifying; and that being told, no, this thing you thought let you be worthy of respect and dignity is actually easily done by machines and people only care about the output and not what you put into it? Well, that hurts, no matter who you are. Unity and mutual support between blue-collars and creative-types, and maybe (dare we dream) finding a way to put bread on all our plates so we’re free to invest in the stuff that matters. Not making yourself feel better because really you’re better than those people who are rightly replaceable by robots, no matter what the boss tries to do.
I don’t know. Probably I’m reading too much into this attitude; or writing over it with my own insecurities that really don’t have anything to do with what’s being said. Still: it’s pressing a nerve, and that nerve’s aching quite badly, no doubt about it.
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
twitter is so funny. like, it's instantly obvious who wants a better world and will brick a cop car, and who's some middle classer who never had to risk a damn thing to save a life, let alone their own
like...do they know everyone who Came From Someplace can tell they'd go home the minute it got hard
probably not
#politics#be gay do crimes#twitter#leftist#anti capitalism#class politics#inclusion#privilege#social justice
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
"12.1 MILLION tons of furniture waste went to landfills in the us in 2018*
That’s over 24.2 billion pounds (add in carpets and rugs for another almost 5 billion pounds) discarded to sit in landfills in 2018 alone.
For perspective, when we furnish a home, a one-bedroom apartment requires about 1.1 tons of furniture, so (for some quick math) 11 MILLION one-bedroom apartments are getting tossed into the trash each year.
Meanwhile, 37.9 million people, or 11.6% of the U.S. population, are living in poverty (2021 U.S. Census) and lack the basic necessities to make a house a home.
We solve two problems at the same time, collecting, repurposing, and curating gently-used furnishings and household goods (saving them from landfill) AND giving them to people in need."
"Requesting furniture from Make It Home requires a social worker, caseworker or case manager to make any requests.
If you need furniture, please contact your social worker or if you do not have a social worker, we can recommend some agencies that may be able to help you."
USAmericancharityandwelfaresystems.txt.
#class politics#my family is poor and may need some new furniture and we heard of this and checked out their website and EEEWWW#viscerally revolting#if somebody doesn't take it it's going in the landfill but they're putting the free sofa or whatever behind bureaucratic gatekeeping anyway#big “Poverty by America” vibes#their website is clearly more aimed at potential donors and volunteers than potential aid recipients too#even if this could be justified on utilitarian grounds I'm angry that they chose a framing this insulting#“this stuff is literal garbage but to get it you need a vetted regime-loyal minder to vouch that you're one of the Worthy Poor” fuck you!#bet this is really about reassuring potential donors that their donations won't go to someone they don't sympathize with#which itself says a lot about whose priorities are being catered to (not the people this program is ostensibly for)
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sonnet to the Country Club Ladies at Madison Park Cafe
"Every job is dignified" is easy
to say to someone sweeping up your breadcrumbs.
Mere tolerance scrubs from sight the labor
that complicates your latte. The night-shift's
stars burnish skies for no one, such as me.
I know how wiping a stained sink basin
and scouring a public toilet's wide mouth
will draw a person's eyes down like a monk
who smolders over a lit match. I once
heard a sage from China folded maxims
into cranes to float them down the river.
He knew the porous paper made them sink.
Tonight, I'll sign my name with a wet mop
until I make the floor below us shine.
—Paul Hlava Ceballos (x)
#poetry#paul hlava ceballos#sonnet#work#class politics#recently read#actually i first heard this poem when he read it at the woodland pattern poetry marathon#and i just went#!!!
2 notes
·
View notes