#National Geographic Explorer
Text


By Erin Blakemore
October 25, 2023
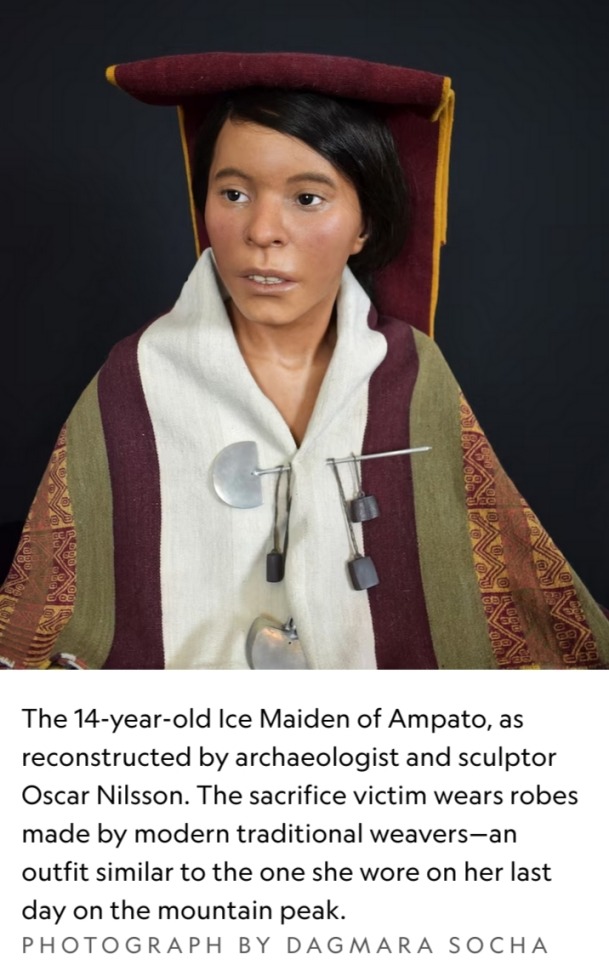
More than 500 years ago, a 14-year-old girl was escorted up an Andean peak and sacrificed to Inca gods.
Buried on the mountain with a variety of offerings, the young woman’s body naturally mummified over time, preserving her hair, her fingernails, the colorful robes she wore on her last day.
But at some point across the centuries, her face became exposed to the elements, her features slowly vanishing over seasons of sunlight and snowfall.
Now, that long-lost face has been recovered thanks to painstaking archaeological analysis and forensic reconstruction.
A striking 3-D bust of the young woman, known today as the Ice Maiden of Ampato, is the centerpiece of a new exhibit in Peru and part of an ongoing effort to understand the drama of human sacrifice practiced in the Andes half a millennium ago.

A sacrificial offering
When National Geographic Explorer Johan Reinhard encountered the mummy, also known as Juanita, atop 21,000-foot Mount Ampato during a 1995 expedition, he knew he had discovered something spectacular.
“At first it looked like one big bundle of textiles,” Reinhard recalls. Then he saw the wizened face amid the folds of fabric.
Here was a young victim of the elusive Inca ritual known as capacocha.
Capacocha mostly involved the sacrifice of children and animals who were offered to the gods in response to natural disasters — to consolidate state power in far-flung provinces of the Inca Empire, or simply to please the deities.
The ritual played an important part in sustaining the Inca Empire. It would involve feasts and grand processions to accompany the children, who appear to have been chosen for their beauty and physical perfection.
Being selected for sacrifice, researchers believe, would have considered a deep honor by the child’s family and community.

Most of the information we have on capacocha, however, is second hand, notes Dagmara Socha, an archaeologist with the Center for Andean Studies at the University of Warsaw who studies the ritual and commissioned the facial reconstruction of the Ice Maiden of Ampato.
“No European colonist ever saw the ceremony,” she explains.
Despite gaps in the historical record, the high-altitude archaeological finds of more than a dozen Inca children on Ampato and other mountains point provide critical evidence for what happened during these rituals.
The means of sacrifice varied, perhaps due to customs related to specific gods. Some children were buried alive or strangled; others had their hearts removed.
The Ice Maiden’s life ended with a single blunt-force blow to the back of the skull.
In search of the Ice Maiden
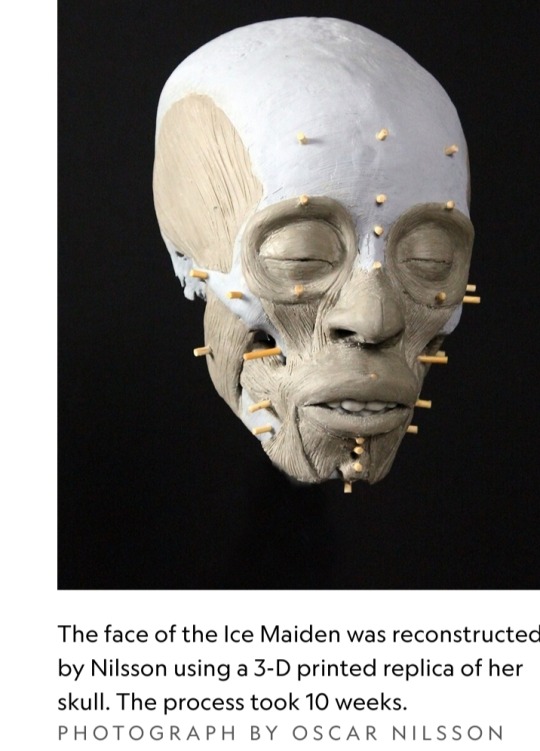
Oscar Nilsson knows that skull intimately: He spent months with a replica of it in his Stockholm studio, eventually fashioning a sculpture of the 14-old-girl that, glimpsed from afar, almost seems alive.

It’s a two-step process, says the Swedish archaeologist and sculptor.
First, Nilsson immerses himself in the world of his subject with an archaeologist’s eye for detail, digesting as much data as possible to understand what she might have looked like.
Even without a mummified face, he can extrapolate the likely depth of the facial tissue that once draped over those bones, using everything from CT scans to DNA analyses to information about diet and disease to make educated guesses about the individual’s face.
Then came the handiwork. Nilsson printed a 3-D replica of the Ice Maiden’s skull, plugging wooden pegs into its surface to guide the depth and placement of each hand-crafted, plasticine clay muscle.
Eerie eyes, masseter muscles, a nose, the delicate rope-like tissues that constitute a human face: each was added in turn.
After making a silicone mold of the bust, he added hundreds of individual hairs and pores in shades of brown and pink.
It took ten weeks.
Following the Inca Gods
The result, wrapped in robes woven by local women from Peru's Centro de Textiles Tradicionales, is the main attraction at “Capacocha: Following the Inca Gods” at the Museo Santuarios Andinos in Arequipa, Peru through November 18.
The reconstruction will be displayed alongside the Ice Maiden’s mummy, accompanied by the stories of 15 other children selected for capacocha atop Ampato and other Andean peaks.
Their ages range from 3 to about 13. The mummies and skeletal remains of several are featured as 3-D models at the exhibition, which also showcases holographs of some of the sacred items buried alongside them.
These natural mummies offer scientists tantalizing clues about their last days.
When Socha and colleagues conducted toxicological and forensic analyses of the remains of a toddler and four six-to-seven-year-old victims featured in the exhibition, they found they were well cared for in the months before their sacrifice.
They were fed a steady diet of coca leaves, ayahuasca vine, and alcohol in the weeks before their deaths — not as much to intoxicate them as to keep them sedated and anxiety-free as the timeline hurtled toward their sacrifice.
“We were really surprised by the toxicology results,” says Socha.
“It wasn’t only a brutal sacrifice. The Inca also wanted the children to be in a good mood. It was important to them that they go happily to the gods.”
High altitude, psychogenic substances, the spectacular view, the knowledge the afterlife was near — all must have made for an astonishing ceremony, says Reinhard.
“The whole phenomenon must have been overpowering.”
During the last phase of his reconstruction, Nilsson spent hours contemplating and attempting to capture the young girl’s presence 500 years after her death.
The result is both unsettlingly realistic and jarringly personal.
“She was an individual,” the forensic reconstructionist says.
“She must have understood her life would end on the mountaintop in a couple of weeks. We can only hope that she believed in the afterworld herself.”
For Reinhard, finally seeing the face of the girl he carried down the mountain on his back decades ago brought the Ice Maiden’s story full circle.
“It brings her back to life,” he says. The reconstruction brings the focus as much to her culture and daily life as to her spectacular death.
But Nilsson never forgot the way the Ice Maiden died, even as he brought her to life through his reconstruction.
More than anything, he says, he wanted to capture a sense of being frozen — a nod not just to her icy, mummified future but to a girl teetering on the edge of eternity, though still very much alive.
“She knew she was supposed to smile, to express pride,” he says. “Proud to be chosen. But still very, very afraid.”
#Ice Maiden of Ampato#Inca Girl#archaeological analysis#forensic reconstruction#human sacrifice#Peru#3-D bust#Juanita#Johan Reinhard#Mount Ampato#National Geographic#National Geographic Explorer#expedition#1990s#20th century#capacocha#Inca ritual#Inca Empire#Dagmara Socha#facial reconstruction#archaeology#archaeologists#Oscar Nilsson#sculptor#Centro de Textiles Tradicionales#Capacocha: Following the Inca Gods#Museo Santuarios Andinos#natural mummies#culture#forensic reconstructionist
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
At Long Last, The American Buffalo Has Come Home
A conservation effort has returned bison to Blackfeet Nation tribal lands more than a century after the animal was nearly slaughtered to extinction.
— Photographs By Louise Johns | By Lailani Upham | Sunday July 09, 2023

“Nititawahsi” is the Blackfeet name for our land—the land where the iinnii (buffalo) live. Our people are Niitawahsin-nanni: the people of the land where the iinnii live.
As colonizers moved west, millions of buffalo were killed and brought to the edge of extinction. Millions more Native peoples were murdered, displaced, and forced to assimilate. By the end of the 19th century, only 300 buffalo were left in the wild and Native populations dropped to less than 300,000.
Now, after more than 150 years, iinnii have finally returned to their homeland, the Amskapi Pikuni (Blackfeet Nation) tribal lands, to roam free.

Forty-nine buffalo run out of their temporary enclosure towards Chief Mountain on the Blackfeet Reservation. The rest of the herd (about 70 buffalo) will join them at the end of the summer. Chief Mountain is not only prime buffalo habitat, but also a sacred place for Native people in both the U.S. and Canada.
“I can’t hardly describe the feeling that I have. I have this jittery feeling, goosebumps,” says Ervin Carlson, director of the Blackfeet Nation Buffalo Program. “It just feels so good to finally see them here in this place where we want them to be.”
On June 26, 49 iinnii were released into the wild at the base of our sacred Ninaistako (Chief Mountain), a Strong Miistaaki (Mountain) that stands tall like the warbonnets of Blackfeet warriors. This miistaaki towers along the border of the Blackfeet Nation, Glacier National Park in Montana, and Waterton National Park in Canada.
Our people, the Siksikaitsitapi (Blackfoot Confederacy) always believed the land we came from was a gift of the Creator, Ihtsi-pai-tapi-yopa. Our stories tell us that iinnii was created as a gift for our people as our life source. The iinnii were and still are our staff of life.
The iinnii coming back and being free on Blackfoot lands again is the beginning of reconciliation, says Cristina Mormorunni, director of Indigenous Led, the organization that leads cultural restoration and conservation of buffalo on Blackfoot lands. “This is the beginning of the truth being told about what happened, and they’re the best ambassadors,” she says.


Helen Augare, a Blackfeet knowledge keeper and director of the Blackfeet Community College Native Science Field Center, has been an integral voice in the return of buffalo to Chief Mountain for the past 15 years.
Now that the buffalo are free, she says “there’s so much still to reconnect to and learn from them.”
“What does that future look like and what [do] our children and grandchildren need to know to be able to help iinnii live a full and prosperous life with us again?” Augare says. “It entailed everything from healthy people, healthy land, healthy water, and most of all healthy relationships. That in itself requires a lot of healing, growth.”

Buffalo are corralled and sorted (calves from adults, and males from females) at the tribal-owned Buffalo Spirit Hills Ranch on June 25, 2023. The herd, originally from Canada’s Elk Island National Park, have been living on the ranch since 2016. The herd descends from the last remaining wild buffalo before they were nearly extirpated.

Blackfeet tribal member Wyett Wippert takes a photo of his daughter, Ruby, in front of the buffalo in their soft release pen at Chief Mountain. “We put so much of our hearts into getting them here,” he says. “It’s a very good feeling knowing that they are under Chief Mountain. People know what they’re going to be doing for their environment and for us as Blackfeet people.” The buffalo are held here for several hours to settle into their surroundings before being released into the wild.

Racine, Monroe, and director Ervin Carlson of the Blackfeet Buffalo Program, on June 25, 2023, after a long day of preparing buffalo to be released at Chief Mountain. “It’s a lot of work to get these animals to this point… they are wild buffalo,” Racine says. “Nobody can do it by themselves. It’s a real honor to be able to have the Iinnii here and to be doing this.”

Blackfeet tribal members Wyett Wippert and Christen Falcon work together to stretch their bison hide onto their handmade wooden frame, the first step in tanning the hide by hand at their home in East Glacier, Montana. on April 9, 2023.

“Bison are a keystone species, they are ecosystem drivers and engineers. They were here for thousands of years,” says Brandon Kittson, wildlife biologist for Blackfeet Fish and Wildlife. “Now having them back on this landscape is a good thing. It’s going to help revitalize some systems and help drive diversity among the different vegetation and communities found in this area.”

Children collect and examine clumps of buffalo fur from the corral at Buffalo Spirit Hills Ranch on June 25, 2023. The fur is integral to the health of the grassland ecosystem, as certain species of birds use it to line and insulate their nests.
— Photojournalist Louise Johns is a National Geographic Explorer. Her National Geographic Society-funded Project, "Buffalo Renaissance," is about Native American efforts to restore Bison to build cultural resiliency and ecological integrity.
#The National Geographic#American Buffalo#Photojournalist#Louise Johns#Buffalo Renaissance#Amskapi Pikuni (Blackfeet Nation)#Niitawahsin-Nanni#Chief Mountain#Ninaistako (Chief Mountain)#Glacier National Park in Montana#Waterton National Park in Canada#The Siksikaitsitapi (Blackfoot Confederacy)#Cristina Mormorunni#Helen Augare#Montana USA 🇺🇸#Canada 🇨🇦#Brandon Kittson Wildlife Biologist#National Geographic Explorer
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

Ian Mcallister - An Acclaimed Filmmaker
Ian McAllister, an acclaimed filmmaker, and National Geographic Explorer, has dedicated his career to capturing the intricate web of life within the Great Bear Rainforest. Through his visually stunning documentaries like "Great Bear Rainforest'' and "Clayoquot Sound," he has shed light on the urgent need for conservation and sustainable practices. McAllister's powerful storytelling and cinematic artistry have succeeded in captivating audiences worldwide, inspiring them to recognize their role as custodians of our planet's natural treasures.
1 note
·
View note
Text
DANCING IN ANTARCTICA (PART II)
Ten years ago I was in Antarctica, the place of my dreams, stark and cold as it was. This past week, I’ve watched my trip DVD a couple of times and been wanting to go back. It is a place which possesses a mystical lure that can’t be explained or understood…unless you feel it too.
A couple years after that trip, I took a chance and submitted a name proposal to the United States Geological Survey…

View On WordPress
#antarc#Dancing#Hey Hey Hey#Lindblad Expeditions#Michael Franti#National Geographic#National Geographic Explorer#Pet loss#Turtle
0 notes
Text

Day 551 of posting pictures of elephants.
Source: National Geographic
#national geographic#elephants#cute animals#cuteness#elephant#image of the day#not my image#cuteness overload#nature#wildlife#adorable#photography#explore#awww#baby#baby animal#baby elephant
259 notes
·
View notes
Text




Anime cafe in Tokyo!
#anime#anime cafe#the kardashians#AI art#visual development#tokyo#sunset#cityscape#asia#disney#pixar#fotor app#national geographic#vacation#tourist#travel agency#explore#artists on tumblr#artists on instagram#sakura#tofu#vegan food#beauty and the beast#gaming#lulusketches#animation#wong fu#aapi#japanese culture#japan
76 notes
·
View notes
Text

Some members of the National Geographic Society make breakfast outside a chow tent.
Willow Tanks, Utah
1967
#vintage camping#campfire light#willow tanks#utah#60s#national geographic society#exploring#history#camping
446 notes
·
View notes
Text
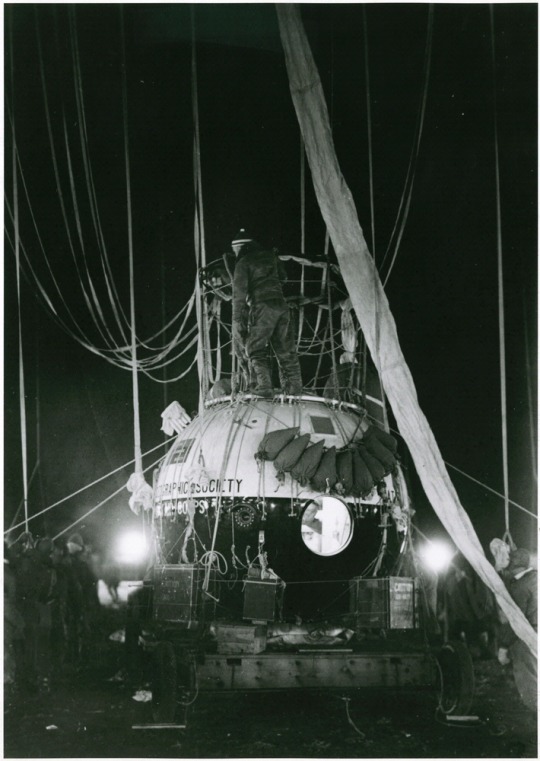
Vista Aérea do Centro do Recife Em 1932.
Foto Capitão Albert William Stevens Feita do Seu Balão Explorer II/Acervo National Geographic Society.


#Vista Aérea do Recife#Ilha de Antônio Vaz#Centro do Recife#recife pe#Recife City#Capitão Albert William Stevens#Ballon Explore II#centro do Recife#Pernambuco#Nordeste#national geographic#Photography#Photo#Old Photography#Old photo#Fotografia Antiga#Fotografias#Fotografia#Antigamente#circa 1932#1930s#Efemérides#Vintage#Vintage Photography#Recife
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

"The thirst was so overwhelming that she couldn't focus her thoughts. In her mind, all she could visualize was a glass filled to the brim with water. She clenched her teeth tightly against her parched, cracked lips. 'This is a city, there must be stores here, and inside those stores, there have to be some drinks.'
With that unwavering determination, she set off in search of stores. There were many in the area, their neon signs advertising long-forgotten 1980s beverages. Yet, they remained tantalizingly closed, their contents just out of reach. Even her attempts to hurl heavy objects found on the desolate streets at the shop windows were met with eerie silence, as if they were repelled by an invisible force.
Then, something caught her eye – a blue city map hanging on one of the doors. It provided a glimmer of hope. She examined it closely and discovered the words 'You are here' with a marked X. 'Alright,' she thought, 'let's see what's around that X.' Her heart quickened as she noticed a fountain marked on the map. 'Well, I hope that one isn't closed.'
She ripped the paper from the door and headed in the direction indicated by the map. Along the way, she stripped clothing from the first mannequin she encountered and muttered to herself, 'Okay, now I'll blend in better with my surroundings. Not that there's anyone to fool around here.' She chuckled, wondering if these were the early signs of madness.
The journey was short, and as she turned the corner, she came upon a large, round fountain. 'What the…?' she exclaimed. The water within the fountain appeared to be suspended in time, its splashes and froth frozen in mid-air, a haunting testament to the unnatural state of this world. Yet her thirst allowed her no hesitation. She bent down and dipped her fingers into the liquid, which clung to her skin like transparent gelatin, a substance from a reality unknown to her. She took a cautious sip, her taste buds discovering an almond-like flavor as the enigmatic liquid quenched her thirst, albeit temporarily."
#nature#80s aesthetic#national geographic#urban jungle#urban exploration#vhs aesthetic#polaroid girl#retrowave#model shoot#model sexy
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

#boho#nature#aesthetic#explore#camping#self healing#protection oil#travel#boho fashion#hippie aesthetic#vintage#national geographic#love#beauty#hippie#earthpix
16 notes
·
View notes
Text

Apollo 11 moon landing issue of National Geographic, published in December of 1969, with bound-in 'flexi-disc' record of space race related sound clips.
#apollo 11#moon landing#national geographic#1969#flexi disc#sounds of the space age#space race#space exploration#astronaut#history
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Last Flower At The Top of The World—and The Perilous Journey To Reach It
Scientists Journeyed to a Stretch of Gravel Off The Coast of Greenland—The Farthest North You Can Go and Still Walk on Land. These Photos Show What They Found There.
— By Sarah Gibbens | Photographs byJeff Kerby | May 08, 2024

An Arctic Poppy thrives on the Northern Coast of Greenland. Among the plant life in this region, these hardy Flowers are like Giants. Some, like this one, grow in clumps that protect themselves from harsh weather. Like a satellite dish, they will slowly turn to follow the sun. On an expedition to understand what lives at this latitude, an Arctic Poppy like this was found about 20 inches south of the World's Northernmost Plant.
At the top of the Earth, the northernmost stretch of land a person can stand on is Inuit Qeqertaat, also named Kaffeklubben Island by early 20th Century Danish Explorers. The region is a dark gray stretch of gravel on the northern coast of Greenland where land slowly gives way to frozen sea ice.
To find what lives amid these rocky soils, climate change researchers and National Geographic Explorers Brian Buma and Jeff Kerby and their team embarked on a journey to survey the region. There, they found a common species of moss (Tortula Mucronifolia), the world's northernmost plant, and a yellow and lime-green Arctic poppy (Papaver Radicatum), growing just a few inches south of the moss.
On the nearby mainland, Greenlandic archaeologist Aka Simonsen discovered a ring of roughly 700-Year-Old Inuit Stones, which may be the northernmost archaeological remains.
Growing in Extremes: The Northernmost Stretch of land in the World, Inuit Qeqertaat, sits off the coast of Johannes V. Jensen Land, a Peninsula in Far Northern Greenland. National Geographic Explorer Brian Buma traveled there to find the northernmost plant-a common moss—and the northernmost flower a few inches south-an Arctic poppy.
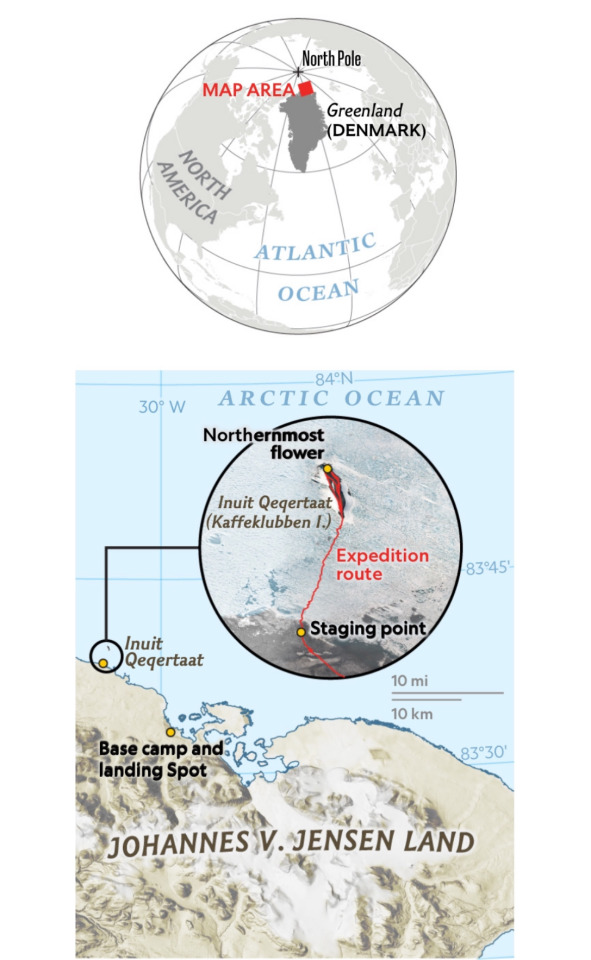
Rosemary Wardley, NGM Staff; Martin Gamache, National Geographic Society Sources: Jeff Kerby, Scott Polar Research Institute; Brian Buma, Environmental Defense Fund; SkySat imagery from July 13, 2023, Planet Labs PBC; ArcticDEM, Version 4.1
The research team left their own mark on the mainland coast, staking plots and recording the vegetation they contained to create a highly detailed digital map of the area they surveyed. Information collected from this trip will be the first data logs in what Buma and Kerby hope will be a long timeline of research in the far northern region.
Here, above the Arctic Circle, the planet is warming four times faster than anywhere else on Earth. Changes here will have ripple effects across the globe, which is why the team braved harsh conditions to find what lives on the edge.

The expedition team was led by climate scientist and National Geographic Explorer Brian Buma. The north coast of Greenland was used as a staging point while shuttling gear across sea ice to Inuit Qeqertaat (Kaffeklubben Island).

Brian Buma collected samples from different layers of this snow glacier to understand the unique properties of water in this rarely visited region. This part of the world is a polar desert, and precipitation is scant, so the samples in this glacier represent many years of snow.

From above, the northern coast of Inuit Qeqertaat—and thus the northernmost stretch of land on Earth—is visible. It was near this shoreline that the team found the edge of terrestrial life, including a common species of moss, officially the farthest north, and the northernmost flower on earth—found about 20 inches south of the moss. The small, gravelly island is about a mile north of mainland Greenland.

This is the northernmost flower on earth, a lone and somewhat ragged Arctic Poppy, sitting near the shoreline of Inuit Qeqertaat. Poppies dotted the northern edge, with a few purple mountain saxifrage (Saxifraga oppositifolia) only slightly farther up the slope. In the background, Brian Buma surveys various contenders for northernmost plant before a final survey determines this flower to be the official runner-up. Seen just behind the flower, a tuft of ‘Mucronate screw moss’ (Tortula mucronifolia) claims that title.

Identifying mosses and other tiny Arctic flora requires a hand lens and careful attention to detail. Up close, Brian Buma examines their adaptations to cold weather, such as small hairs coating a plant's exterior.

Aka Simonsen, a Greenlandic archeologist, prepares to leave camp with Brian Buma, just as the weather begins to turn. After just a few hours the northernmost island, the team left, intending to return the next day. The window to return quickly closed after a few days when bad weather turned into a storm that brought strong winds and heavy precipitation. The July storm dumped nearly a foot of snow and drifts reached several feet. Harsh conditions trapped the team at their base camp for a week.

Aka Simonsen measures a ring of large stones that may have been used to anchor a tent. The stones are roughly 700 years old and likely left by the Thule people. These artifacts were found on the mainland, near the team's base camp and could be the northernmost documented archeological site on Earth.

When the plane returning to retrieve the team landed, it got stuck in snow, and a makeshift runway had to be constructed by scooping snow with snow shoes. Gravel was placed by hand so the plane's tires wouldn't slip on ice or stick in snow during takeoff. Scientists who return to this northernmost region will be able to use the team's detailed digital map to chart how the ecosystem is changing as the planet warms.
#Environment#Environmental#Last Flower 🌺#Top of the World 🌎#The Perilous Journey#Scientists Journeyed | Coat of Greenland 🇬🇱#Arctic Poppy#Giant Flowers 🌺 🌸 💐#National Geographic Explorers Brian Buma | Jeff Kerby#(Tortula Mucronifolia)#Arctic poppy (Papaver Radicatum)#Inuit Qeqertaat#Kaffeklubben#20th Century Danish 🇩🇰 Explorers 🧭#700-Year-Old Inuit Stones#Johannes V. Jensen Land
14 notes
·
View notes
Photo
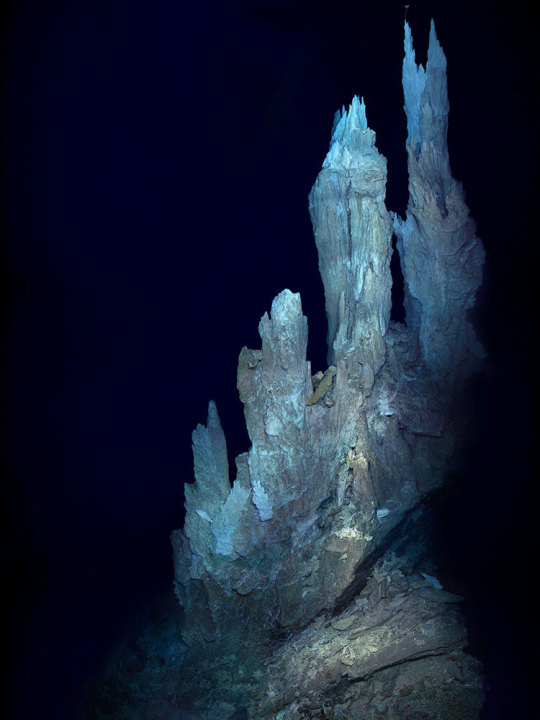

‘Impossible chemistry’: That’s one description of the activity on the ocean floor. Active vents on the seafloor, such as this roughly 100-foot-tall chimney in the Atlantic’s Lost City Hydrothermal Field, rapidly produce simple organic molecules that could have been key to the emergence of life on Earth.
PHOTOGRAPH BY D. KELLEY & M. ELEND, UNIV. WASHINGTON INST. FOR EXPLORATION/
URI-IAO/NOAA/THE LOST CITY SCIENCE TEAM
#d. kelley#m. elend#university of washington institute for exploration#photographers#national geographic#landscape#nature#ocean floor#atlantic's lost city hydrothermal field
16 notes
·
View notes
Text

Day 493 of posting pictures of elephants.
Baby elephants have to learn how to use their trunks after they're born, and until then, they faceplant in water to drink.
Source: National Geographic Kids
#elephants#cute animals#cuteness#elephant#image of the day#not my image#cuteness overload#nature#wildlife#adorable#photography#explore#awww#national geographic#baby#baby animal#baby elephant
181 notes
·
View notes
Text

#hawaii#iphoneography#mobile photography#islands#national geographic#explore#nature travel#beautiful#landscape#ocean#nature pictures#scenic#mountains
4 notes
·
View notes
Photo

American Aviatrix Amelia Earhart (1897-1937)
In 2010, female NASA astronaut Shannon Walker carried one of Earhart's wrist watches for 163 days onboard the International Space Station.This 35 mm Longines is on display in the Ninety-Nines Women's aviation museum in Oklahoma City.
85 years ago, 6 weeks into their Eastward near-equator around the world flight, American Amelia Earhart & her navigator Fred Noonan disappeared above the vast Pacific Ocean.
On July 1, 1937 Earhart's twin engined Lockheed Electra departed Lae - New Guinea aiming towards the tiny Howland island, where she could land & refuel with US Navy support ship USCGC Itasca.
However, on July 2, 1937 the aircraft ran out of fuel and was lost... did they miss Howland island and were marooned on the shores of Nikumaroro?
Certainly the most intruiging aviation mystery, which I would like to see resolved in my lifetime!
(Photo/Slide: MoonwatchUniverse)
#Aviation#Aviatrix#ICAO#Lockheed#Electra#Radionavigation#Radio#NASA#Pacific#WorldTour#Sunrise#MoonwatchUniverse#Amelia Earhart#us navy#itasca#National Geographic#Explorer#pilot#montres#Zulu time
2 notes
·
View notes