#Byzantinists
Text
Benedict XVI and today's Muslims opposite Manuel II Palaeologus and his Turkic Interlocutor
Or why I defended Pope Benedict XVI in 2006 against the thoughtlessly irascible Muslims
When a Muslim writes an Obituary for the Catholic Church's sole Pope Emeritus…

Table of Contents
I. From Joseph Ratzinger to Pope Benedict XVI
II. The theoretical concerns of an intellectual Pope
III. Benedict XVI: A Pope against violence and wars
IV. Manuel II Palaeologus and the Eastern Roman Empire between the Muslim Ottoman brethren and the Anti-Christian Roman enemies
V. The unknown (?) Turkic mystic interlocutor and the Islamic centers of science and reason that Benedict XVI ignored
VI. Excerpt from Benedict XVI's lecture given on the 12th September at the University of Regensburg under title 'Faith, Reason and the University–Memories and Reflections'
VII. The problems of the academic-theological background of Benedict XVI's lecture
VIII. Benedict XVI's biased approach, theological mistakes, intellectual oversights and historical misinterpretations
IX. The lecture's most controversial point
X. The educational-academic-intellectual misery and the political ordeal of today's Muslim states
Of all the Roman popes who resigned the only to be called 'Pope Emeritus' was Joseph Ratzinger Pope Benedict XVI (also known in German as Prof. Dr. Papst), who passed away on 31st December 2022, thus sealing the circle of world figures and heads of states whose life ended last year. As a matter of fact, although being a head state, a pope does not abdicate; he renounces to his ministry (renuntiatio).
Due to lack of documentation, conflicting sources or confusing circumstances, we do not have conclusive evidence as regards the purported resignations of the popes St. Pontian (235), Marcellinus (304), Liberius (366), John XVIII (1009) and Sylvester (105). That is why historical certainty exists only with respect to the 'papal renunciation' of six pontiffs; three of them bore the papal name of 'Benedict'. The brief list includes therefore the following bishops of Rome: Benedict V (964), Benedict IX (deposed in 1044, bribed to resign in 1045, and resigned in 1048), Gregory VI (1046), St Celestine (1294), Gregory XII (1415) and Benedict XVI (2013).
I. From Joseph Ratzinger to Pope Benedict XVI
Benedict XVI (18 April 1927 – 31 December 2022) was seven (7) years younger than his predecessor John Paul II (1920-2005), but passed away seventeen (17) years after the Polish pope's death; already on the 4th September 2020, Benedict XVI would have been declared as the oldest pope in history, had he not resigned seven (7) years earlier. Only Leo XIII died 93, back in 1903. As a matter of fact, Benedict XVI outlived all the people who were elected to the Roman See.
Benedict XVI's papacy lasted slightly less than eight (8) years (19 April 2005 – 28 February 2013). Before being elected as pope, Cardinal Ratzinger was for almost a quarter century (1981-2005) the prefect of the Congregation for the Doctrine of the Faith, which was the formal continuation of the Office of the Holy Inquisition, and therefore one of the most important sections ('dicasteries'; from the Ancient Greek term 'dikasterion', i.e. 'court of law') of the Roman administration ('Curia').
A major step toward this position was his appointment as archbishop of Munich for four years (1977-1981); Bavaria has always been a Catholic heavyweight, and in this regard, it is easy to recall the earlier example of Eugenio Pacelli (the later pope Pius XII), who was nuncio to Bavaria (and therefore to the German Empire), in Munich, from 1917 to 1920, and then to Germany, before being elected to the Roman See (in 1939). Before having a meteoric rise in the Catholic hierarchy, Ratzinger made an excellent scholar and a distinct professor of dogmatic theology, while also being a priest. His philosophical dissertation was about St. Augustine and his habilitation concerned Bonaventure, a Franciscan scholastic theologian and cardinal of the 13th c.
II. The theoretical concerns of an intellectual Pope
During his ministry, very early, Benedict XVI stood up and showed his teeth; when I noticed his formidable outburst against the 'dictatorship of relativism', I realized that the German pope would be essentially superior to his Polish predecessor. Only in June 2005, so just two months after his election, he defined relativism as "the main obstacle to the task of education", directing a tremendous attack against the evilness of ego and portraying selfishness as a "self-limitation of reason".
In fact, there cannot be more devastating attack from a supreme religious authority against the evilness of Anglo-Zionism and the rotten, putrefied society that these criminals diffuse worldwide by means of infiltration, corruption, mendacity, and simulation. Soon afterwards, while speaking in Marienfeld (Cologne), Benedict XVI attacked ferociously all the pathetic ideologies which indiscriminately enslave humans from all spiritual and cultural backgrounds. He said: "absolutizing what is not absolute but relative is called totalitarianism". This is a detrimental rejection of Talmudic Judaism, Zohar Kabbalah, and Anglo-Zionism.
It was in the summer 2005 that I first realized that I should study closer the pre-papal past of the Roman Pontiff whom St Malachy's illustrious Prophecy of the Popes (12th c.) described as 'Gloria olivae' (the Glory of the olive). I contacted several friends in Germany, who extensively updated me as regards his academic publications, also dispatching to me some of them. At the time, I noticed that my Christian friends already used to question a certain number of Cardinal Ratzinger's positions.
But, contrarily to them, I personally found his prediction about the eventuality of Buddhism becoming the principal 'enemy' of the Catholic Church as quite plausible. My friends were absolutely astounded, and then I had to narrate and explain to them the deliberately concealed story of the Christian-Islamic-Confucian alliance against the Buddhist terrorism of the Dzungar Khanate (1634-1755); actually, it took many Kazakh-Dzungar wars (1643-1756), successive wars between Qing China and the Dzungar Khanate (1687-1757), and even an alliance with the Russian Empire in order to successfully oppose the ferocious Buddhist extremist threat.
Finally, the extraordinary ordeal of North Asia {a vast area comprising lands of today's Eastern Kazakhstan, Russia (Central Siberia), Northwestern and Western China (Eastern Turkestan/Xinjiang and Tibet) and Western Mongolia} ended up with the systematic genocide of the extremist Buddhist Dzungars (1755-1758) that the Chinese had to undertake because there was no other way to terminate once forever the most fanatic regime that ever existed in Asia.
Disoriented, ignorant, confused and gullible, most of the people today fail to clearly understand how easily Buddhism can turn a peaceful society into a fanatic realm of lunatic extremists. The hypothetically innocent adhesion of several fake Freemasonic lodges of the West to Buddhism and the seemingly harmless acceptance of Buddhist principles and values by these ignorant fools can end up in the formation of vicious and terrorist organizations that will give to their members and initiates the absurd order and task to indiscriminately kill all of their opponents. But Cardinal Ratzinger had prudently discerned the existence of a dangerous source of spiritual narcissism in Buddhism.
III. Benedict XVI: A Pope against violence and wars
To me, this foresight was a convincing proof that Benedict XVI was truly 'Gloria olivae'; but this would be troublesome news! In a period of proxy wars, unrestrained iniquity, and outrageous inhumanity, a perspicacious, cordial, and benevolent pope in Rome would surely be an encumbering person to many villainous rascals, i.e. the likes of Tony Blair, George W. Bush, Nicolas Sarkozy, and many others so-called 'leaders'. The reason for this assessment of the situation is simple: no one wants a powerful pacifier at a time more wars are planned.
At the time, it was ostensible to all that a fake confrontation between the world's Muslims and Christians was underway (notably after the notorious 9/11 events); for this reason, I expected Benedict XVI to make a rather benevolent statement that evil forces would immediately misinterpret, while also falsely accusing the pacifist Pope and absurdly turning the uneducated and ignorant mob of many countries against the Catholic Church.
This is the foolish plan of the Anglo-Zionist lobby, which has long served as puppets of the Jesuits, corrupting the entire Muslim world over the past 250 years by means of intellectual, educational, academic, scientific, cultural, economic, military and political colonialism. These idiotic puppets, which have no idea who their true and real masters are, imagine that, by creating an unprecedented havoc in Europe, they harm the worldwide interests of the Jesuits; but they fail to properly realize that this evil society, which early turned against Benedict XVI, has already shifted its focus onto China. Why the apostate Anglo-Zionist Freemasonic lodge would act in this manner against Benedict XVI is easy to assess; the Roman pontiff whose episcopal motto was 'Cooperatores Veritatis' ('Co-workers of the Truth') would apparently try to prevent the long-prepared fake war between the Muslims and the Christians.
IV. Manuel II Palaeologus and the Eastern Roman Empire between the Muslim Ottoman brethren and the Anti-Christian Roman enemies
And this is what truly happened in the middle of September 2006; on the 12th September, Benedict XVI delivered a lecture at the University of Regensburg in Germany; the title was 'Glaube, Vernunft und Universität – Erinnerungen und Reflexionen' ('Faith, Reason and the University – Memories and Reflections'). In the beginning of the lecture, Prof. Dr. Ratzinger eclipsed Pope Benedict XVI, as the one-time professor persisted on his concept of 'faith', "which theologians seek to correlate with reason as a whole", as he said. In a most rationalistic approach (for which he had been known for several decades as a renowned Catholic theologian), in an argumentation reflecting views certainly typical of Francis of Assisi and of Aristotle but emphatically alien to Jesus, Benedict XVI attempted to portray an ahistorical Christianity and to describe the Catholic faith as the religion of the Reason.
At an early point of the lecture, Benedict XVI referred to a discussion that the Eastern Roman Emperor Manuel II Palaeologus (or Palaiologos; Μανουήλ Παλαιολόγος; 1350-1425; reigned after 1391) had with an erudite Turkic scholar (indiscriminately but mistakenly called by all Eastern Roman authors at the time as 'Persian') most probably around the end of 1390 or the first months of 1391, when he was hostage at the Ottoman court of Bayezid I. In the historical text, it is stated that the location was 'Ancyra of Galatia' (i.e. Ankara).
This Eastern Roman Emperor was indeed a very controversial historical figure; although undeniably an erudite ruler, a bold diplomat, and a reputable soldier, he first made agreements with the Ottomans and delivered to them the last Eastern Roman city in Anatolia (Philadelphia; today's Alaşehir, ca. 140 km east of Izmir / Smyrna) and then, after he took control of his ailing kingdom thanks to the sultan, he escaped the protracted siege of Constantinople (1391-1402) only to travel to various Western European kingdoms and ask the help of those rather reluctant monarchs (1399-1403).
At the time, all the Christian Orthodox populations, either living in the Ottoman sultanate or residing in the declined Eastern Roman Empire, were deeply divided into two groups, namely those who preferred to be ruled by Muslims (because they rejected the pseudo-Christian fallacy, evilness and iniquity of the Roman pope) and the fervent supporters of a Latin (: Western European) control over Constantinople (viewed as the only way for them to prevent the Ottoman rule); the former formed the majority and were called Anthenotikoi, i.e. 'against the union' (: of the Orthodox Church with the Catholics), whereas the latter constituted a minority group and were named 'Enotikoi' ('those in favor of the union of the two churches').
V. The unknown (?) Turkic mystic interlocutor and the Islamic centers of science and reason that Benedict XVI ignored
Manuel II Palaeologus' text has little theological value in itself; however, its historical value is great. It reveals how weak both interlocutors were at the intellectual, cultural and spiritual levels, how little they knew one another, and how poorly informed they were about their own and their interlocutor's past, heritage, religion and spirituality. If we have even a brief look at it, we will immediately realize that the level is far lower than that attested during similar encounters in 8th- 9th c. Baghdad, 10th c. Umayyad Andalusia, Fatimid Cairo, 13th c. Maragheh (where the world's leading observatory was built) or 14th c. Samarqand, the Timurid capital.
It was absolutely clear at the time of Manuel II Palaeologus and Bayezid I that neither Constantinople nor Bursa (Προύσα / Prousa; not anymore the Ottoman capital after 1363, but still the most important city of the sultanate) could compete with the great centers of Islamic science civilization which were located in Iran and Central Asia. That's why Gregory Chioniades, the illustrious Eastern Roman bishop, astronomer, and erudite scholar who was the head of the Orthodox diocese of Tabriz, studied in Maragheh under the guidance of his tutor and mentor, Shamsaddin al Bukhari (one of the most illustrious students of Nasir el-Din al Tusi, who was the founder of the Maragheh Observatory), before building an observatory in Trabzon (Trebizond) and becoming the teacher of Manuel Bryennios, another famous Eastern Roman scholar.
The text of the Dialogues must have been written several years after the conversation took place, most probably when the traveling emperor and diplomat spent four years in Western Europe. For reasons unknown to us, the erudite emperor did not mention the name of his interlocutor, although this was certainly known to him; if we take into consideration that he was traveling to other kingdoms, we can somehow guess a plausible reason. His courtiers and royal scribes may have translated the text partly into Latin and given copies of the 'dialogues' to various kings, marshals, chroniclers, and other dignitaries. If this was the case, the traveling emperor would not probably want to offer insights into the Ottoman court and the influential religious authorities around the sultan.
Alternatively, the 'unknown' interlocutor may well have been Amir Sultan (born as Mohamed bin Ali; also known as Shamsuddin Al-Bukhari; 1368-1429) himself, i.e. none else than an important Turanian mystic from Vobkent (near Bukhara in today's Uzbekistan), who got married with Bayezid I's daughter Hundi Fatema Sultan Hatun. Amir Sultan had advised the sultan not to turn against Timur; had the foolish sultan heeded to his son-in-law's wise advice, he would not have been defeated so shamefully.
Benedict XVI made a very biased use of the historical text; he selected an excerpt of Manuel II Palaeologus' response to his interlocutor in order to differentiate between Christianity as the religion of Reason and Islam as the religion of Violence. Even worse, he referred to a controversial, biased and rancorous historian of Lebanese origin, the notorious Prof. Theodore Khoury (born in 1930), who spent his useless life to write sophisticated diatribes, mildly formulated forgeries, and deliberate distortions of the historical truth in order to satisfy his rancor and depict the historical past according to his absurd political analysis. Almost every sentence written Prof. Khoury about the Eastern Roman Empire and the Islamic Caliphate is maliciously false.
All the same, it was certainly Benedict XVI's absolute right to be academically, intellectually and historically wrong. The main problem was that the paranoid reaction against him was not expressed at the academic and intellectual levels, but at the profane ground of international politics. Even worse, it was not started by Muslims but by the criminal Anglo-Zionist mafia and the disreputable mainstream mass media, the likes of the BBC, Al Jazeera (Qatari is only the façade of it), etc.
I will now republish (in bold and italics) a sizeable (600-word) excerpt of the papal lecture that contains the contentious excerpt, also adding the notes to the text. The link to the Vatican's website page is available below. I will comment first on the lecture and the selected part of Manuel II Palaeologus' text and then on the absurd Muslim reaction.
VI. Excerpt from Benedict XVI's lecture given on the 12th September at the University of Regensburg under title 'Faith, Reason and the University–Memories and Reflections'
I was reminded of all this recently, when I read the edition by Professor Theodore Khoury (Münster) of part of the dialogue carried on - perhaps in 1391 in the winter barracks near Ankara - by the erudite Byzantine emperor Manuel II Paleologus and an educated Persian on the subject of Christianity and Islam, and the truth of both.[1] It was presumably the emperor himself who set down this dialogue, during the siege of Constantinople between 1394 and 1402; and this would explain why his arguments are given in greater detail than those of his Persian interlocutor.[2] The dialogue ranges widely over the structures of faith contained in the Bible and in the Qur'an, and deals especially with the image of God and of man, while necessarily returning repeatedly to the relationship between - as they were called - three "Laws" or "rules of life": the Old Testament, the New Testament and the Qur'an. It is not my intention to discuss this question in the present lecture; here I would like to discuss only one point - itself rather marginal to the dialogue as a whole - which, in the context of the issue of "faith and reason", I found interesting and which can serve as the starting-point for my reflections on this issue.
In the seventh conversation (διάλεξις - controversy) edited by Professor Khoury, the emperor touches on the theme of the holy war. The emperor must have known that surah 2, 256 reads: "There is no compulsion in religion". According to some of the experts, this is probably one of the suras of the early period, when Mohammed was still powerless and under threat. But naturally the emperor also knew the instructions, developed later and recorded in the Qur'an, concerning holy war. Without descending to details, such as the difference in treatment accorded to those who have the "Book" and the "infidels", he addresses his interlocutor with a startling brusqueness, a brusqueness that we find unacceptable, on the central question about the relationship between religion and violence in general, saying: "Show me just what Mohammed brought that was new, and there you will find things only evil and inhuman, such as his command to spread by the sword the faith he preached.”[3] The emperor, after having expressed himself so forcefully, goes on to explain in detail the reasons why spreading the faith through violence is something unreasonable. Violence is incompatible with the nature of God and the nature of the soul. "God", he says, "is not pleased by blood - and not acting reasonably (σὺν λόγω) is contrary to God's nature. Faith is born of the soul, not the body. Whoever would lead someone to faith needs the ability to speak well and to reason properly, without violence and threats... To convince a reasonable soul, one does not need a strong arm, or weapons of any kind, or any other means of threatening a person with death...".[4]
The decisive statement in this argument against violent conversion is this: not to act in accordance with reason is contrary to God's nature.[5] The editor, Theodore Khoury, observes: For the emperor, as a Byzantine shaped by Greek philosophy, this statement is self-evident. But for Muslim teaching, God is absolutely transcendent. His will is not bound up with any of our categories, even that of rationality.[6] Here Khoury quotes a work of the noted French Islamist R. Arnaldez, who points out that Ibn Hazm went so far as to state that God is not bound even by his own word, and that nothing would oblige him to reveal the truth to us. Were it God's will, we would even have to practice idolatry.[7]
Notes 1 to 7 (out of 13)
[1] Of the total number of 26 conversations (διάλεξις – Khoury translates this as “controversy”) in the dialogue (“Entretien”), T. Khoury published the 7th “controversy” with footnotes and an extensive introduction on the origin of the text, on the manuscript tradition and on the structure of the dialogue, together with brief summaries of the “controversies” not included in the edition; the Greek text is accompanied by a French translation: “Manuel II Paléologue, Entretiens avec un Musulman. 7e Controverse”, Sources Chrétiennes n. 115, Paris 1966. In the meantime, Karl Förstel published in Corpus Islamico-Christianum (Series Graeca ed. A. T. Khoury and R. Glei) an edition of the text in Greek and German with commentary: “Manuel II. Palaiologus, Dialoge mit einem Muslim”, 3 vols., Würzburg-Altenberge 1993-1996. As early as 1966, E. Trapp had published the Greek text with an introduction as vol. II of Wiener byzantinische Studien. I shall be quoting from Khoury’s edition.
[2] On the origin and redaction of the dialogue, cf. Khoury, pp. 22-29; extensive comments in this regard can also be found in the editions of Förstel and Trapp.
[3] Controversy VII, 2 c: Khoury, pp. 142-143; Förstel, vol. I, VII. Dialog 1.5, pp. 240-241. In the Muslim world, this quotation has unfortunately been taken as an expression of my personal position, thus arousing understandable indignation. I hope that the reader of my text can see immediately that this sentence does not express my personal view of the Qur’an, for which I have the respect due to the holy book of a great religion. In quoting the text of the Emperor Manuel II, I intended solely to draw out the essential relationship between faith and reason. On this point I am in agreement with Manuel II, but without endorsing his polemic.
[4] Controversy VII, 3 b–c: Khoury, pp. 144-145; Förstel vol. I, VII. Dialog 1.6, pp. 240-243.
[5] It was purely for the sake of this statement that I quoted the dialogue between Manuel and his Persian interlocutor. In this statement the theme of my subsequent reflections emerges.
[6] Cf. Khoury, p. 144, n. 1.
[7] R. Arnaldez, Grammaire et théologie chez Ibn Hazm de Cordoue, Paris 1956, p. 13; cf. Khoury, p. 144. The fact that comparable positions exist in the theology of the late Middle Ages will appear later in my discourse.
VII. The problems of the academic-theological background of Benedict XVI's lecture
It is my conviction that Benedict XVI fell victim to the quite typical theological assumptions that Prof. Dr. Ratzinger had studied and taught for decades. However, the problem is not limited to the circle of the faculties of Theology and to Christian Theology as a modern discipline; it is far wider. The same troublesome situation permeates all the disciplines of Humanities and, even worse, the quasi-totality of the modern sciences as they started in Renaissance. The problem goes well beyond the limits of academic research and intellectual consideration; it has to do with the degenerate, rotten and useless mental abilities and capacities of the Western so-called scholars, researchers and academics. The description of the problem is rather brief, but its nature is truly ominous.
Instead of perceiving, understanding, analyzing and representing the 'Other' in its own terms, conditions and essence and as per its own values, virtues and world conceptualization, the modern Western European scholars, researchers, explorers and specialists view, perceive, attempt to understand, and seek to analyze the 'Other' in their own terms, conditions and essence and as per their own values, virtues and world conceptualization. Due to this sick effort and unprecedented aberration, the Western so-called scholars and researchers view the 'Other' through their eyes, thus projecting onto the 'Other' their view of it. Consequently, they do not and actually they cannot learn it, let alone know, understand and represent it. Their attitude is inane, autistic and degenerate. It is however quite interesting and truly bizarre that the Western European natural scientists do not proceed in this manner, but fully assess the condition of the object of their study in a rather objective manner.
In fact, the Western disciplines of the Humanities, despite the enormous collection and publication of study materials, sources and overall documentation, are a useless distortion. Considered objectively, the Western scientific endeavor in its entirety is a monumental nothingness; it is not only a preconceived conclusion. It is a resolute determination not to 'see' the 'Other' as it truly exists, as its constituent parts obviously encapsulate its contents, and as the available documentation reveals it. In other words, it consists in a premeditated and resolute rejection of the Truth; it is intellectually barren, morally evil, and spiritually nihilist. The topic obviously exceeds by far the limits of the present obituary, but I had to mention it in order to offer the proper context.
It is therefore difficult to identify the real reason for the magnitude of the Western scholarly endeavor, since the conclusions existed in the minds of the explorers and the academics already before the documentation was gathered, analyzed, studied, and represented. How important is it therefore to publish the unpublished material (totaling more than 100000 manuscripts of Islamic times and more than one million of cuneiform tablets from Ancient Mesopotamia, Iran, Canaan and Anatolia – only to give an idea to the non-specialized readers), if the evil Western scholars and the gullible foreign students enrolled in Western institutions (to the detriment of their own countries and nations) are going to repeat and reproduce the same absurd Western mentality of viewing an Ancient Sumerian, an Ancient Assyrian, an Ancient Egyptian or a Muslim author through their own eyes and of projecting onto the ancient author the invalid and useless measures, values, terms and world views of the modern Western world?
As it can be easily understood, the problem is not with Christian Theology, but with all the disciplines of the Humanities. So, the problem is not only that a great Muslim scholar and erudite mystic like Ibn Hazm was viewed by Benedict XVI and Western theologians through the distorting lenses of their 'science', being not evaluated as per the correct measures, values and terms of his own Islamic environment, background and civilization. The same problem appears in an even worse form, when Ancient Egyptian, Sumerian, Assyrian-Babylonian, Hittite, Iranian and other high priests, spiritual masters, transcendental potentates, sacerdotal writers, and unequaled scientists are again evaluated as per the invalid and useless criteria of Benedict XVI, of all the Western theologians, and of all the modern European and American academics.
What post-Renaissance popes, theologians, academics, scholars and intellectuals fail to understand is very simple; their 'world' ( i.e. the world of the Western Intellect and Science, which was first fabricated in the 15th and the 16th c. and later enhanced progressively down to our days) in not Christian, is not human, and is not real. It is their own delusion, their own invalid abstraction, their abject paranoia, and their own sin for which first they will atrociously disappear from the surface of the Earth (like every anomalous entity) and then flagrantly perish in Hell.
Their dangling system does not hold; they produced it in blood and in blood it will end. Modern sciences constitute a counter-productive endeavor and an aberration that will terminally absorb the entire world into the absolute nothingness, because these evil systems were instituted out of arbitrary bogus-interpretations of the past, peremptory self-identification, deliberate and prejudicial ignorance, as well as an unprecedented ulcerous hatred of the 'Other', i.e. of every 'Other'.
The foolish Western European academic-intellectual establishment failed to realize that it is absolutely preposterous to extrapolate later and corrupt standards to earlier and superior civilizations; in fact, it is impossible. By trying to do it, you depart from the real world only to live in your delusion, which sooner or later will inevitably have a tragic end. Consequently, the Western European scholars' 'classics' are not classics; their reason is an obsession; their language and jargon are hallucinatory, whereas their notions are conjectural. Their abstract concepts are the manifestation of Non-Being.
VIII. Benedict XVI's biased approach, theological mistakes, intellectual oversights and historical misinterpretations
Benedict XVI's understanding of the Eastern Roman Empire was fictional. When examining the sources, he retained what he liked, what pleased him, and what was beneficial to his preconceived ideas and thoughts. In fact, Prof. Dr. Papst did not truly understand what Manuel II Palaeologus said to his Turkic interlocutor, and even worse, he failed to assess the enormous distance that separated the early 15th c. Eastern Roman (not 'Byzantine': this is a fake appellation too) Emperor from his illustrious predecessors before 800 or 900 years (the likes of Heraclius and Justinian I) in terms of Christian Roman imperial ideology, theological acumen, jurisprudential perspicacity, intellectual resourcefulness, and spiritual forcefulness. Benedict XVI did not want to accept that with time the Christian doctrine, theology and spirituality had weakened.
What was Ratzinger's mistake? First, he erroneously viewed Manuel II Palaeologus as 'his' (as identical with the papal doctrine), by projecting his modern Catholic mindset and convictions onto the Christian Orthodox Eastern Roman Emperor's mind, mentality and faith. He took the 'Dialogues' at face value whereas the text may have been written not as a declaration of faith but as a diplomatic document in order to convince the rather uneducated Western European monarchs that the traveling 'basileus' (βασιλεύς) visited during the period 1399-1403.
Second, he distorted the 'dialogue', presenting it in a polarized form. Benedict XVI actually depicted a fraternal conversation as a frontal opposition; unfortunately, there is nothing in the historical text to insinuate this possibility. As I already said, it is quite possible that the moderate, wise, but desperate Eastern Roman Emperor may have discussed with someone married to a female descendant of the great mystic Jalal al-Din Rumi (namely Bayezid's son-in-law, adviser and mystic Emir Sultan). Why on Earth did the renowned theologian Ratzinger attempt to stage manage a theological conflict in the place of a most peaceful, friendly and fraternal exchange of ideas?
This is easy to explain; it has to do with the absolutely Manichaean structure of thought that was first diffused among the Western Fathers of the Christian Church by St Augustine (in the early 5th c.). As method of theological argumentation, it was first effectively contained, and it remained rather marginal within the Roman Church as long as the practice introduced by Justinian I (537) lasted (until 752) and all the popes of Rome had to be selected and approved personally by the Eastern Roman Emperor. After this moment and, more particularly, after the two Schisms (867 and 1054), the Manichaean system of thinking prevailed in Rome; finally, it culminated after the Renaissance.
Third, Benedict XVI tried to depict the early 15th c. erudite interlocutor of the then hostage Manuel II Palaeologus as a modern Muslim and a Jihadist. This is the repetition of the same mistakes that he made as regards the intellectual Eastern Roman Emperor. In other words, he projected onto the 'unknown', 15th c. Muslim mystic his own personal view of an Islamist or Islamic fundamentalist. Similarly, by bulldozing time in order to impose his wrong perception of Islam, he fully misled the audience. As a matter of fact, Islam constitutes a vast universe that Prof. Dr. Papst never studied, never understood, and never fathomed in its true dimensions.
In fact, as it happened in the case of the Eastern Roman Emperor, his interlocutor was intellectually weaker and spiritually lower than the great figures of Islamic spirituality, science, wisdom, literature and intuition, the likes of Nasir al-Din al-Tusi, Al Qurtubi, Mohyi el-Din Ibn Arabi, Ahmed Yasawi, Al Biruni, Ferdowsi, Al Farabi, Tabari, etc., who preceded him by 150 to 500 years. But Benedict XVI did not want to accept that with time the Islamic doctrine, theology and spirituality had weakened.
The reason for this distortion is easy to grasp; the Manichaean system of thinking needs terminal, crystallized forms of items that do not change; then, it is convenient for the Western European abusers of the Manichaean spirit to fully implement the deceitful setting of fake contrasts and false dilemmas. But the 15th c. decayed Eastern Roman Orthodoxy and decadent Islam are real historical entities that enable every explorer to encounter the multitude of forms, the ups and downs, the evolution of cults, the transformation of faiths, and the gradual loss of the initially genuine Moral and vibrant Spirituality. This reality is very embarrassing to those who want to teach their unfortunate students on a calamitous black & white background (or floor).
All the books and articles of his friend, Prof. Theodore Khoury, proved to be totally useless and worthless for the Catholic theologian Ratzinger, exactly because the Lebanese specialist never wrote a sentence in order to truly represent the historical truth about Islam, but he always elaborated his texts in a way to justify and confirm his preconceived ideas. Prof. Khoury's Islam is a delusional entity, something like the artificial humans of our times. Unfortunately, not one Western Islamologist realized that Islam, at the antipodes of the Roman Catholic doctrine, has an extremely limited dogmatic part, a minimal cult, and no heresies. Any opposite opinion belongs to liars, forgers and falsifiers. As a matter of fact, today's distorted representation of Islam is simply the result of Western colonialism. All over the world, whatever people hear or believe about the religion preached by Prophet Muhammad is not the true, historical, religion of Islam, but the colonially, academically-intellectually, produced Christianization of Islam.
Fourth, in striking contrast to what the theologian Ratzinger pretended through use of this example or case study (i.e. the 'discussion'), if Benedict XVI shifted his focus to the East, he would find Maragheh in NW Iran (Iranian Azerbaijan) and Samarqand in Central Asia. In those locations (and always for the period concerned), he would certainly find great centers of learning, universities, vast libraries, and enormous observatories, which could make every 15th c. Western European astronomer and mathematician dream. But there he would also find, as I already said, many Muslim, Christian, Buddhist and other scholars working one next to the other without caring about their religious (theological) differences. This situation is very well known to modern Western scholarship, but they viciously and criminally try to permanently conceal it.
This situation was due to the cultural, intellectual, academic, mental and spiritual unity that prevailed among all those erudite scholars. Numerous Western European scholars have published much about Nasir el-Din al Tusi (about whom I already spoke briefly) and also about Ulugh Beg, the world's greatest astronomer of his time (middle of the 15th c.), who was the grandson of Timur (Tamerlane) and, at the same time, the World History's most erudite emperor of the last 2500 years. However, post-Renaissance Catholic sectarianism and Western European/North American racism prevented the German pope from being truthful at least once, and also from choosing the right paradigm.
IX. The lecture's most controversial point
Fifth, if we now go straight to the lecture's most controversial point and to the quotation's most fascinating sentence, we will find the question addressed by Manuel II Palaeologus to his erudite Turkic interlocutor; actually, it is rather an exclamation:
- «Show me just what Mohammed brought that was new, and there you will find things only evil and inhuman, such as his command to spread by the sword the faith he preached»!
This interesting excerpt provides indeed the complete confirmation of my earlier assessments as regards the intellectual decay of both, Christian Orthodoxy and Islam, at the time. Apparently, it was not theological acumen what both interlocutors were lacking at the time; it was historical knowledge. Furthermore, historical continuity, religious consciousness, and moral command were also absent in the discussion.
The first series of points that Manuel II Palaeologus' Muslim interlocutor could have made answering the aforementioned statement would be that Prophet Muhammad, before his death, summoned Ali ibn Abu Taleb and asked him to promise that he would never diffuse the true faith by undertaking wars; furthermore, Islam was diffused peacefully in many lands outside Arabia (Hejaz), notably Yemen, Oman, Somalia, and the Eastern Coast of Africa. In addition, there were many Muslims, who rejected the absurd idea of the Islamic conquests launched by Umar ibn al-Khattab and actually did not participate.
We have also to take into consideration the fact that, in spite of the undeniable reality of the early spread of Islam through invasions, there has always been well-known and sufficient documentation to clearly prove that the Aramaeans of Mesopotamia, Syria and Palestine, the Copts of Egypt, and the Berbers of Africa, although fully preserving their Christian faith, preferred to live under the rule of the Caliphates and overwhelmingly rejected the Eastern Roman imperial administration, because they had been long persecuted by the Constantinopolitan guards due to their Miaphysite (Monophysitic) and/or Nestorian faiths.
On another note, the Eastern Roman Emperor's Muslim interlocutor could have questioned the overall approach of Manuel II Palaeologus to the topic. In other words, he could have expressed the following objection:
- «What is it good for someone to pretend that he is a follower of Jesus and evoke his mildness, while at the same time violently imposing by the sword the faith that Jesus preached? And what is it more evil and more inhuman than the imposition of a faith in Jesus' name within the Roman Empire, after so much bloodshed and persecution took place and so many wars were undertaken»?
Last, one must admit that the sentence «Show me just what Mohammed brought that was new!» would have been easily answered by an earlier Muslim mystic of the Golden Era of Islam. Actually, this statement is islamically correct and pertinent. The apparent absence of a spectacular response from the part of Manuel II Palaeologus' Muslim interlocutor rather generates doubts as regards the true nature of the text. This is so because he could have immediately replied to Bayezid I's hostage that not one prophet or messenger was sent by God with the purpose of 'bringing something new'; in fact, all the prophets from Noah to Jonah, from Abraham to Jonah, from Moses to Muhammad, and from Adam to Jesus were dispatched in order to deliver the same message to the humans, namely to return to the correct path and live according to the Will of God.
Related to this point is the following well-known verse of the Quran (ch. 3 - Al Imran, 67): "Abraham was neither a Jew nor a Christian but he was (an) upright (man), a Muslim, and he was not one of the polytheists". It is therefore odd that a response in this regard is missing at this point.
It is also strange that, at a time of major divisions within Christianity and more particularly among the Christian Orthodox Eastern Romans, the 'unknown' imperial interlocutor did not mention the existing divisions among Christians as already stated very clearly, explicitly and repeatedly in the Quran. Examples:
"You are the best community ever raised for humanity—you encourage good, forbid evil, and believe in Allah. Had the People of the Book believed, it would have been better for them. Some of them are faithful, but most are rebellious". (ch. 3 - Al Imran, 110)
"Yet they are not all alike: there are some among the People of the Book who are upright, who recite Allah’s revelations throughout the night, prostrating in prayer".
(ch. 3 - Al Imran, 113):
To conclude I would add that elementary knowledge of Roman History, Late Antiquity, and Patristic Philology would be enough for Benedict XVI to know that
- in its effort to impose Christianity on the Roman Empire,
- in its determination to fully eradicate earlier religions, opposite religious sects like the Gnostics, and theological 'heresies' like Arianism,
- in its resolve to exterminate other Christian Churches such as the Nestorians and the Miaphysites (Monophysites),
- in its obsession to uproot Christian theological doctrines like Iconoclasm and Paulicianism, and
- in its witch hunt against Manichaeism, …
… the 'official' Roman and Constantinopolitan churches committed innumerable crimes and killed a far greater number of victims than those massacred by Muslim invaders on several occurrences during the early Islamic conquests.
So, when did the Christian Church encounter Reason and when did it cease to be 'unreasonable' according to the theologian Pope Ratzinger?
One must be very sarcastic to duly respond to those questions: most probably, the Roman Church discovered 'Reason' after having killed all of their opponents and the so-called 'heretics' whose sole sin was simply to consider and denounce the Roman Church as heretic!
If Benedict XVI forgot to find in the Quran the reason for the Turkic interlocutor's mild attitude toward the hostage Manuel II Palaeologus, this is a serious oversight for the professor of theology; he should have mentioned the excerpts. In the surah al-Ankabut ('the Spider'; ch. 29, verse 46), it is stated: "And do not argue with the followers of earlier revelation otherwise than in a most kindly manner".
Similarly, the German pope failed to delve in Assyriology and in Egyptology to better understand that the Hebrew Bible (just like the New Testament and the Quran) did not bring anything 'new' either; before Moses in Egypt and before Abraham in Mesopotamia, there were monotheistic and aniconic trends and traits in the respective religions. The concept of the Messiah is attested in Egypt, in Assyria, and among the Hittites many centuries or rather more than a millennium before Isaiah contextualized it within the small Hebrew kingdom. Both Egypt and Babylon were holy lands long before Moses promised South Canaan to the Ancient Hebrew tribes, whereas the Assyrians were the historically first Chosen People of the Only God and the Assyrian imperial ideology reflected this fact in detail. The Akkadian - Assyrian-Babylonian kings were 'emperors of the universe' and their rule reflected the 'kingdom of Heaven'.
If Etana and Ninurta reveal aspects of Assyrian eschatology, Horus was clearly the Egyptian Messiah, who would ultimately vanquish Seth (Satan/Antichrist) at the End of Time in an unprecedented cosmic battle that would usher the mankind into a new era which would be the reconstitution of the originally ideal world and Well-Being (Wser), i.e. Osiris. There is no Cosmogony without Eschatology or Soteriology, and nothing was invented and envisioned by the Hebrews, the Greeks and the Romans that had not previously been better and more solemnly formulated among the Sumerians, the Akkadians - Assyrian-Babylonians, and the Egyptians. There is no such thing as 'Greco-Roman' or 'Greco-Christian' or' Greco-Judaic' civilization. Both, Islam and Christianity are the children of Mesopotamia and Egypt.
And this concludes the case of today's Catholic theologians, i.e. the likes of Pope Benedict XVI or Theodore Khoury; they have to restart from scratch in order to duly assess the origins and the nature of Christianity before the serpent casts "forth out of his mouth water as a river after the woman, that he may cause her to be carried away by the river". All the same, it was certainly Prof. Ratzinger's full right to make as many mistakes as he wanted and to distort any textual reference he happened to mention.
X. The educational-academic-intellectual misery and the political ordeal of today's Muslim states
Quite contrarily, it was not the right of those who accused him of doing so, because they expanded rather at the political and not at the academic level; this was very hypocritical and shameful. If these politicians, statesmen and diplomats dared speak at the academic level, they would reveal their own ignorance, obscurantism, obsolete educational system, miserable universities, nonexistent intellectual life, and last but not least, disreputable scientific institutions.
The reason for this is simple: not one Muslim country has properly organized departments and faculties endowed with experts capable of reading historical sources in the original texts and specializing in the History of the Eastern Roman Empire, Orthodox Christianity, Christological disputes and Patristic Literature. If a Muslim country had an educational, academic and intellectual establishment similar to that of Spain or Poland, there would surely be serious academic-level objection to Benedict XVI's lecture. It would take a series of articles to reveal, refute and utterly denounce (not just the mistakes and the oversights but) the distorted approach which is not proper only to the defunct Pope Emeritus but to the entire Western academic establishment; these people would however be academics and intellectuals of a certain caliber. Unfortunately, such specialists do not exist in any Muslim country.
Then, the unrepresentative criminal crooks and gangsters, who rule all the countries of the Muslim world, reacted against Pope Benedict XVI at a very low, political level about a topic that was not political of nature and about which they knew absolutely nothing. In this manner, they humiliated all the Muslims, defamed Islam, ridiculed their own countries, and revealed that they rule failed states. Even worse, they made it very clear that they are the disreputable puppets of their colonial masters, who have systematically forced all the Muslim countries to exactly accept as theirs the fallacy that the Western Orientalists have produced and projected onto them (and in this case, the entirely fake representation of Islam that theologians like Ratzinger, Khoury and many others have fabricated).
If Ratzinger gave this lecture, this is also due to the fact that he knew that he would not face any academic or intellectual level opposition from the concerned countries. This is so because all the execrable puppets, who govern the Muslim world, were put in place by the representatives of the colonial powers. They do not defend their local interests but execute specific orders in order not to allow
- bold explorers, dynamic professors, and impulsive intellectuals to take the lead,
- proper secular education, unbiased scientific methodology, intellectual self-criticism, free judgment, and thinking out of the box to grow,
- faculties and research centers to be established as per the norms of educationally advanced states, and
- intellectual anti-colonial pioneers and anti-Western scholars to demolish the racist Greco-centric dogma that post-Renaissance European universities have intentionally diffused worldwide.
That is why for a Muslim today in Prof. Ratzinger's lecture the real problem is not his approach or his mistake, but the impermissible bogus academic life and pseudo-educational system of all the Muslim countries. In fact, before fully transforming and duly enhancing their educational and academic systems, Muslim heads of states, prime ministers, ministers and ambassadors have no right to speak. They must first go back to their countries and abolish the darkness of their ridiculous universities; their so-called professors are not professors.
Here you have all the articles that I published at the time in favor of Benedict XVI; the first article was published on the 16th September 2006, only four days after the notorious lecture and only one day after the notorious BBC report, which called the Muslim ambassadors to shout loud:
-----------------------------
Download the obituary in PDF:
#Bayezid I#Benedict XVI#Benedict XVI Obituary#Benedict XVI's speech on Islam#Byzantine Empire#Byzantine Papacy#Byzantinists#Catholic Church#Constantinople#Constantinopolitan Popes#Manuel II Palaeologus#Manuel II Paleologus#Maragheh#Megalommatis#Orthodox Christianity#Ottoman Empire#Regensburg lecture#relativism#Renaissance#renuntiatio#Rome
1 note
·
View note
Text
seeing red and strangling a pillow. my highly anticipated class on "the first millennium of Christianity," so I'd assume 0-1000 AD give or take a century on either side, apparently uses the first seven-eighths getting to Constantine, then the final lesson is "Collapse of the Western Empire, Charlemagne, Eastern Christianity, and the Rise of Islam". that's like three centuries in 90 minutes. where are my fucking Byzantines?
#the only byzantinist at this university only teaches upper level grad seminars but maybe i'll email her anyway for advice#byzantium
37 notes
·
View notes
Note
sorry if you've already answered this but i just read your post about whipping girl and found it so so so insightful!! i was wondering if you have any other recommendations for books/articles/etc. about transmisogyny and the lives of tma people. thank you in advance!!
I'm glad it was helpful! this is the second ask on the subject I've let pile up, because I want to do my best with it but I'm also far from an expert. I think half the work of answering "transmisogyny syllabus" questions is explaining why it's so hard to do so in the first place.
one of the tools of hegemony is the epistemic violence it works against its subjects; this is essential to transmisogyny, thru which we have historically been rendered unable to so much as record our existence, let alone theorize from it. it is incredibly difficult for a tma person to access the institutional devices of knowledge-making, most of all the university. even when we do it is typically for the institutions we work under to shoehorn our work into the hegemonic model, stymieing actual progress. so theories and histories of transmisogyny have had to progress in a patchwork, often informal fashion, upstream and at personal risk. I am not going to be able to give you books that I would recommend without criticism, because the epistemic violence of transmisogyny has made it virtually impossible to write such a book. but with that said, here are some recommendations:
- this post multiplied my understanding of transmisogyny manifold, and was one of the most clarifying things I've read on the subject
- hands off our lives, our stories, and our bodies, is imo essential to anyone interested in a theory of transmisogyny that actually engages with its manifestations in the global south
- I enjoyed My Words to Victor Frankenstein above the Village of Chamounix: Performing Transgender Rage by Susan Stryker for the vibes
- two historical excavations of transmisogyny: Trans Misogyny in the Colonial Archive: Re-Membering Trans Feminine Life and Death in New Spain, 1604–1821 by Jamey Jesperson and ‘Selective Historians’: The Construction of Cisness in Byzantine and Byzantinist Texts by Ilya Maude
- Romancing the Transgender Native is good for learning the trappings of ahistorical and idealist "third gender" attributions
- especially (but not exclusively) if you are yourself a trans woman/transfem/tma, consider reading Serious Weakness by Porpentine Charity Heartscape. just make sure you look up CWs first
- Jules Gill-Peterson's A Short History of Trans Misogyny is great for some case studies in global transmisogyny, and a decent materialist approach. but I think she makes the same mistake serano made re: equivocation of transmisogyny with the oppression of femininity, and she would have done well to read the second article on this list. I've heard her histories of the transgender child is also good—but I can't say for sure until I read it
- follow @ bloomfilters on twitter
if this looks like a hodgepodge that's because it is on account of what I said in the first two paragraphs. I am really not an expert and I am sure there are others who could give you much more. but to echo a friend, you may be just as likely to get something out of a game or a song written by a tma person as you are an essay. every medium can be an opportunity to plunge the roots of our theorizing deeper.
#ask answer#transmisogyny#just finished a short history today maybe i will post a short review at some point#when my makes you sleepy meds stop making me sleepy
274 notes
·
View notes
Text
Book Review 13 – A Memory Called Empire by Arkady Martine

Okay, getting back into writing these reviews before I fall so far behind that catching up is just impossible. Memory is the first book this year that I’ve actually read before; I’m rereading as the first choice for a theoretical book club with some friends. Honestly quite enjoyed the experience, if only because trying to jot down some things to say when discussing it forced me to take it a little slower this time.
To get the technical details out of the way – the book won the Hugo, and did basically deserve it. The writing’s lovely and occasionally downright poetics, the two leads are both insanely compelling, and the court intrigue is appropriately convoluted and byzantine for what is obviously Constantinople IN SPACE. It’s just overall a joyous read.
So Martine’s clearly very fascinated by the experience of having your standards of aesthetics, and sophistication, and civilization defined by a culture which has never even bothered to notice your existence. The simultaneous rapture at being in the heart of the universe that you’ve read about your entire life, and deep alienation knowing you’ll never actually be a part of it. How ever most of the people trying to be friendly and compliment you don’t even notice how patronizing they’re being. And so on and etc. Mahit’s internal monologue does a really good job of selling the ambivalence of it, especially in the party scene.
The book does an excellent job of actually selling the palace district as a site of imperial grandeur, too, every building buried in symbolic aesthetics and ritual significance. But also just, like, actually impressive and grand to read about. All the contrasts between the oveflowing abundance in the city and life on Lsel are fascinating too – Martine makes really good use of the little worldbuilding quotes at the start of chapters to sell the difference. The one that really stuck in my head was a quote from a tourism
guide explaining all the myriad fine dining choices for tourists visiting the City followed directly by a Lseli agricultural report about how new hydrophonic techniques had increased rice yield sufficiently to support a whole hundred non-replacement births in the next generation (it helps that all the Teixicalaanli food legitimately sounds pretty amazing). Though the time where Mahit’s internal monologue short circuited over the idea of carrying a pregnancy to term in your own body – wasteful! Depriving the station of a necessary laborer for months and months when perfectly good artificial wombs are right there! So decadent – is a close second.
Martine is, as I understand it, a Byzantinist, and oh boy can you tell. The city’s a little bit Tenochtitlan in the aesthetics and the religion, but it really is overwhelmingly space Constantinople. The theoretically absolute emperor dealing with mobs in the streets willing and potentially able to acclaim a usurper, the constant risk of legions doing the same, the basic fact that there’s a vast empire which is viewed as nothing but an adjunct or extension of the capital city which is the entirety of all political life and the place everyone whose anyone needs to be, and so on.
In a way, the obvious Byzantine-ness of the Teixicalaanli makes them seem less imperialist than just imperial, at least from Mahit’s perspective. Which is to say, well, first of all that ‘empire’ has far too many meanings and distinguishing them is hard, but the Teixicalaanli don’t expand like the British or French, in constant competition over captive markets and strategic locations, they don’t feel some glorious burden of manifest destination or a mission civilisatrice that requires universal dominion. They already are the universe, or at least everything worthwhile in it, they go to war like medieval kings or Roman princeps – to win glorious victories and so show the empire they have the right to rule it.
The relation between Lsel and Teixicalaan – well, if suffers from the standard space opera lack of scale, first of all. The stationers number in the tens of thousands – the empire must be in the hundreds of billions, minimum. ‘Realistically’ Six Directions would never have found out about the imago device because relations with them would have been handled by some mid-ranking provincial governor, only showing up in travelogues and fanciful ethnographies. But leaving that aside, Teixicalaanli myopia also means that the cultural imperialism that the book’s so fascinated by is oddly...blameless? Teixicalaan presumably has brutal campaigns dedicated to stamping out native cultures and integrating them into the empire, but there’s hardly one directed at Lsel. The general sense you get is one of vaguely tragic inevitability – that the mismatch in size and wealth is such that of course any sort of even slightly free exchange of media and ideas will lead to Stationer culture being overwhelmed. Makes me think about arguments around CanCon regulations.
(The whole Roman, medieval feel of the empire means it all kind of calls to mind various Germanic elites actively reaching for Roman iconography and institutions to legitimize themselves as much as anything, though of course that’s not really right.)
The book’s politics are, I think, a bit limited by the degree it’s laser-focused on the very uppermost tip of imperial society – the book seems to know this too, given the thirty page digression into cyberpunk two thirds of the way through (speaking of which, I absolutely adore the fact that the elegant, ritually harmonious and utterly aesthetic architecture lasts about three metro stops away from the palace before everything starts turning into economical concrete blocks). Which isn’t really a knock on the book, but I do think some of the praise of it does get a bit overblown; there’s a limit to how much insight you can really have on imperialism when you’re so focused on the stories an empire tells about itself in its most rarified and luxurious heart.
In much the same way there’s something very, I don’t know, ‘written in America in the late 2010s’ about the political imagination the book allows itself. There are people who don’t want the world to be the world, and maybe they can help a bit, but the actual players in the game of thrones are corrupt oligarchs and populist warmongers, you know?
All that said, the book sure does portray a city that views itself as synonymous with civilization. I only realized there was a Teixicalaanli word for foreigner that wasn’t ‘barbarian’ when one of the probably-terrorists made a point of using it during the whole cyberpunk interlude. Which retroactively makes, like, every single other Teixicalaanli character in the book waaaaay more of an asshole. (fanfic thought - Teixicalaanli attempts to talk even vaguely respectfully to/about foreigners as analogous to people trying to be gender neutral or talk about nonbinary people in really strongly genedered languages, right down to the awkward neologisms that the ‘average citizens’ rolls their eyes at. What’s the Teixicalaanli term for ‘the woke plague.’?)
Also – not really a better place to put this in, but something I really do like about the worldbuilding is that no one has anything like the same ideas of what constitutes political legitimacy as the contemporary liberal default? Lsel is a corporatist state, where political power is divided between what are basically guilds who seem to have wide remit to make policy within their jurisdiction, with only one seat on the council seeming to have any sort of election. And Teixicalaan is, of course, a bureacratic-verging-on-stratocratic monarchy, with a strong sense of popular involvement in government, but through demonstrations and rioting instead of any formal process. It’s enjoyable that neither place is actually, like, familiar.
The motor of the book’s plot is byzantine (or Byzantine, I suppose) court intrigue, and as someone who loves polite conversations and poetic allusions followed directly by assassination attempts, I adored it. That said, I’m going to be a slob demanding everything be hand fed to me for a minute and saying that it all got positively opaque by the end. Which is, I suppose, entirely realistic, given Mahit’s position and role in everything, but still I wanted an Agathe Christie drawing room denouncement so bad. Was Ten Pearl actively backing the coup? If not, what was up with the Sunlit? And the Cityshocks? Why was the Information Ministry so politically passive and uninvolved in a literal coup attempt? How was Eight Loop involved in the whole final resolution, given it was her people keeping the emperor safe but it was Nineteen Adze who was with him on camera? All these questions and more, unanswered and, probably, irrelevant! But like, inquiring minds want to know.
Though speaking of the coup, I really did absolutely adore how, like,incompetent and amateurish both coup attempts were? Which seems like it would be a plot hole, but actually it’s probably the strongest argument the book can make for Six Direction’s immortality plan – the empire has been peaceful for so long no one remembers how to do a coup.
Anyway, yes! Extremely good book, Mahit and Seagrass are absolutely great protagonists. Not at all sorry I’m peer pressuring people into reading it.
189 notes
·
View notes
Note
i need to hear more about these byzantine french classes you go to and and the beef you have with their men
it's silly beef but in any medieval studies program there is always that one guy who is like. a weaponry guy or a byzantinist or an old church slavonic guy, etc, who aaaaaalways has something to say about his area of study in any conversation no matter how much it is entirely not related to the topics we're discussing (like, for instance, talking about byzantium alllllll the time in an old french course or talking about old church slavonic allll the time in an late medieval lit survey course, etc)
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
I'm furious and I need to vent.

Last year I was hired on to Invicta as a researcher. A Byzantinist, specifically. I say hired on but I was never given an employee contract and I didn't file a W-2. I instead have to pay all my taxes out of pocket because my boss refuses to honor his promises (contract, healthcare)

I quickly discovered that my writing was not respected and was only used to glorify war. I discovered that the vast majority of the people who consumed my work would despise me personally and I, in turn, don't like them. But my work was successful. My topics, my writing, my art design, and my direction produced videos that ranged between 'successful' and 'wildly successful.' Around my string of successes the channel rotted. My boss adopted a corner-cutting do-it-cheap-and-shitty attitude which disrespected his viewers and failed to recognize the inherent worth of written and visual mediums as art.




My work continued to hit the mark while my boss continued to deliberately kneecap his staff with constant micromanagement combined with an unwillingness to listen to us (me) when we (I) pointed out that his strategies were failing and that he was setting up a member of his team to fail by giving her (the only other woman on the team) a video series that had already proved itself to be failed format (How They Did It).
Last April, I was given my own series to direct. I managed art design, I managed the research, I managed R&D, I managed the 2D storyboard and I was solely responsible for the 3D storyboard. The results of my project exceeded my wildest dreams.



My boss, predictably, tried to turn the format that I pioneered into a collection of cheap shitty cashgrabs that relied on the words '3D' and an interesting thumbnail.
It didn't work.

And now here we are, at my latest project. It was, once again, a smash hit. This video alone has nearly the same amount of views as all of the videos we've put out in the past month put together.
I was pleased, and I had hoped that this demonstration of my ability would make my boss trust me to run the series as I see fit. Instead all it has done is make him attempt to micromanage even harder.
I've had 3 hour-long arguments with him this week. All of them were to prevent him from taking steps to make the series worse in all quantifiable ways.
I'm so fucking tired.
He called me on my fucking lunch break and I had to argue with him while I had a hunger headache.
I just want some goddamn recognition for all of the work I've put in.
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
where are my byzantinists at
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Experiencing Istanbul Through Photography
Maréva U, GABAM-ANAMED Post-Doctoral Fellow (2022–2023)

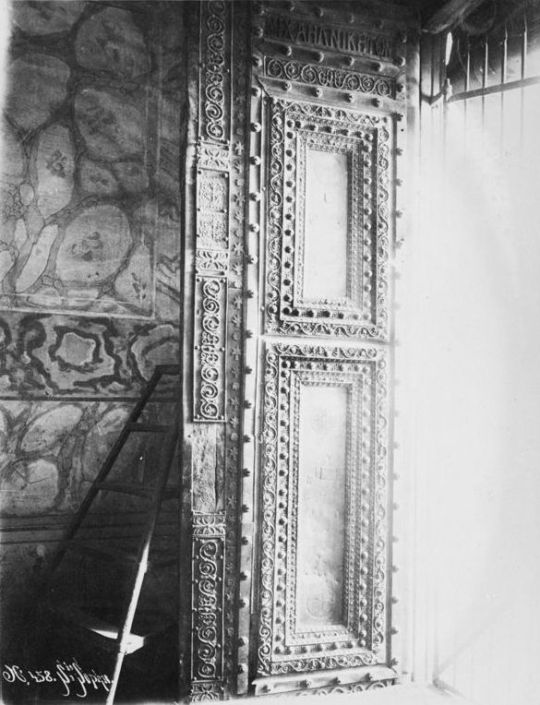
Fig. 1. Istanbul, street leading up to the Galata Tower (photo by Albert Kahn, 1913, No. A2307S, Albert Kahn Museum).
Fig. 2. Istanbul, Hagia Sophia, bronze door (photo by Gabriel Millet, Photo Archives, EPHE).
Photography is a technical and mechanical means of preserving a graphic representation of places, monuments, objects, people, and moments. It can be used as a historical testimony—an approach taken, for example, by the French banker and philanthropist Albert Kahn in his attempt to create the Archives of the Planet between 1908 and 1931[1]—or as a research and documentation tool—an approach we adopt in the humanities and social sciences, as evidenced by the photographs of monuments taken by the Byzantinist Gabriel Millet in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries.[2] Photography is also a means of expression that bears the signature of its author and whose objectivity is equal to any artistic work.
However, for several decades, photography has become, in the words of the sociologist Pierre Bourdieu, a “popular art.”[3] Film cameras and the slow and complex process of developing photographs have given way to digital cameras and smartphones capable of capturing, in high definition, fixed images of our private lives and our travels. These digital tools allow for easy and instantaneous snapshots. They lead us, in a consumerist way, to take an unlimited number of images, most of which are stored indefinitely in our smartphones or computers, without much consideration.
Photography is today overexploited and tends to be conditioned by the dominant visual discourses conveyed by the vast media landscape. These discourses construct cultural codes that define the value of a place, transforming a specific site into an appreciable, visitable, or unmissable and “instagrammable” place. The same places and monuments of Istanbul, as in any tourist city, become the subject of countless photographs, or rather the background in front of which people pose in their best light. These stereotypical photographs, whose colors are often oversaturated by smartphone filters that alter our perception of reality, flood the internet and social media. Unconsciously, these discourses and images influence the way we perceive, experience, and photograph places.
Since my arrival at ANAMED, I have wanted to build my own experience and perception of Istanbul, trying to detach myself from these visual dictates (the choice of black and white photography is partly a result of this intention). My research on the experience of the architectural space of Byzantine monuments has undoubtedly influenced my relationship to the city and to photography. Of course, the architecture of the Byzantine buildings attracted most of my attention.


Fig. 3. Vefa Kilise Camii, western façade (photo by the author). Fig. 4: Küçük Ayasofya Camii (St. Sergius and Bacchus), columns and capitals (photo by the author).
Beyond photographic documentation, it is possible to look at and photograph the monuments we visit and study in a different way, especially by examining how they are integrated into the modern cityscape and how people use their spaces today. In doing so, details such as the contrast between the recently restored Tekfur Sarayı and the nearby pile of rubble, the calmness of a man praying in Fenari Isa Camii (Constantine Lips Monastery), or the movement of a child playing ball in front of Zeyrek Camii (Pantokrator Monastery) can attract our attention.

Fig. 5. Tekfur Sarayı (photo by the author).


Fig. 6. Man in Fenari Isa Camii (Constantine Lips Monastery) (photo by the author). Fig. 7. Child in front of Zeyrek Camii (Pantokrator Monastery) (photo by the author).
Besides Byzantine and Ottoman architectural heritage, Istanbul’s vibrant and colorful urban space deserves more attention. Istiklal Caddesi, which is difficult to avoid if you live in ANAMED, is passed by thousands of people every day. Many of them take selfies and pictures of each other or walk around with their smartphones in hand, continuously filming the hustle and bustle of the street, probably without really paying attention to the urban space. To experience it and to photograph it, it is necessary to slow down, to stop, to turn around, and to look up above the sometimes-oppressive crowd to observe and capture, for example, some architectural details or a man discreetly watching urban life from his window.


Fig. 8. Istiklal Caddesi (photo by the author). Fig. 9. Istiklal Caddesi (photo by the author).

Fig. 10. Sıraselviler Caddesi (photo by the author).
To experience Istanbul through photography, it is necessary to voluntarily lose oneself in the city and to be open to possibilities, opportunities, unexpected events, and encounters. In this way, it is possible to observe space, architecture, scenes of everyday life, people’s attitudes, spontaneous movements, effects of light and shadow. In short, the practice of photography allows us to see what is attractive and visible but also to pay attention to what is ordinary and sometimes hidden or invisible. Such an approach to the city can sometimes be uncomfortable, as it puts us in a contradictory position: between a voyeur, eager for aesthetic visuals, and a detached onlooker, aware of the various aspects of a place and its atmosphere. By unknowingly photographing children playing in the street, a man painfully carrying a washing machine, or a woman sitting on a bench focused on her phone, I experienced this ambivalent situation myself. Photography can thus lead us to question our relationships with others and sometimes to overcome our fears of rejection when we ask permission to take someone’s picture.


Fig. 11. Tünel, Istiklal Caddesi (photo by the author). Fig. 12. Children, Balat (photo by the author).


Fig. 13. House, Fatih (photo by the author). Fig. 14. House, Fatih (photo by the author).

Fig. 15. Man, Fatih (photo by the author).
The act of photography, in my opinion, has other effects on the person who practices it. It teaches us patience in order to capture the desired image, a quality we often lack in our productivity-driven society. Experiencing urban space through photography can allow us to take a break from the frenetic pace of our academic lives, as it leads us to develop an alternative conception of space and time.


Fig. 16. Cat, Fatih (photo by the author). Fig. 17. Woman, Taksim (photo by the author).
Therefore, photography is not just a matter of pressing a button to mechanically fix a part of the urban space and its inhabitants in an image. By walking around, looking for photographable objects and framing them, we appropriate the space and try to give a meaning to what we see. Photography can then be used by anyone (with a camera or a smartphone) to record their own experience of space, to visualize their perceptions and engagements with the place, or to explore their aesthetic and expressive capacities.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[1] https://albert-kahn.hauts-de-seine.fr/en/collections/presentation/a-documentation-project-for-the-world/the-archives-de-la-planete.
[2] https://explore.psl.eu/fr/ressources-et-savoirs-psl/projets-psl-explore/la-phototheque-gabriel-millet-ecole-pratique-des.
[3] Bourdieu, Pierre, ed., Un art moyen : essai sur les usages sociaux de la photographie (Paris: Les Editions de Minuit, 1965).
6 notes
·
View notes
Photo










Elizabeth Blackadder (1931 - 1921 , UK)- Celebrated artist admired for her paintings of flowers and the first woman to be elected to both the Royal and Royal Scottish academies, a long interesting article by Charles Darwent, which gives great insights in her seemingly dated art.
"In 1994, the year that Damien Hirst made his first vitrined sheep, Away from the Flock, pickled in formaldehyde, the artist Elizabeth Blackadder, who has died aged 89, finished a work called Still Life With Cats. The cats were painted in oil on canvas, joining many others in Blackadder’s oeuvre, alongside arum lilies, Japanese fans and tins of sweets.
Mere difference of age does not explain the gap between Blackadder’s art and Hirst’s. Painters of her own generation – Bridget Riley was born in the same year, 1931 – worked in a style that was insistently modern. This was not Blackadder’s way. When she and her husband, the artist John Houston, visited New York in 1969 on the way to paint the Wyoming landscape, they made trips to the Museum of Modern Art to see Picasso and Matisse, not Pollock and Warhol. Modern art institutions returned the compliment: there are only half a dozen or so Blackadders in the Tate, all but one of them lithographs, few ever on show and none more recent than 1963. The British Council Collection holds only two Blackadders, the Arts Council’s none at all. And yet, there is more to the story than meets the eye.
At first glance, a painting such as Iris Oncocylus (1996), in the collection of the National Gallery of Scotland, is not so much unapologetically outdated as defiantly so. Where Georgia O’Keeffe defeminised flower-painting by making oils of lilies that looked like vulvas, Blackadder’s watercolour irises might have been painted by an unusually adept aunt. A second look shows something more complex. Blackadder’s eye is not so much meticulous as engineered: this is botanical painting rather than flower painting. The disposition of her flowers on the paper is just that, a disposition rather than an arrangement.
In an untypically expansive moment, Blackadder hazarded that “the space between flowers [in her work] is as important as the flowers themselves”, adding that her pictures invented themselves as they went along. The two-dimensional sculpturalism of her irises owes more to Matisse than it does to, say, the flower painter Mary Butler. If Blackadder’s flowers are representational, the voids they create are abstract.
Daughter of Thomas and Violet Blackadder, she came from a family of Falkirk engineers. Her father’s factory in the town, Blackadder Brothers’ Garrison Foundry and Engine Works, had been built by Thomas’s own grandfather in 1851. Elizabeth was born in its shadow, in a sandstone villa at 6 Weir Street.
In later life, she refused to talk about her art. If forced to do so, she spoke in the kind of commonsensical terms that would have had conceptualists such as Hirst in tears – “I paint the centre of my flowers black,” Blackadder might say, adding, in a rare confessional burst, “Well, a kind of bluey-black.” She did, however, admit to having had an early teacher. “My father was an engineer, but he drew a lot, mostly boats,” she recalled in a BBC interview to mark her 80th birthday. “From a young age, he helped me to draw.” Blackadder’s father died when she was 10.
Another childhood influence was also familial. During wartime German bombing of Clydebank, Falkirk being on the bombers’ flight path, the young Elizabeth was dispatched by her mother to her grandmother’s house on Holy Loch. “I got sent out as a gardener for all [her] friends,” Blackadder would wryly recall. By her teens, she knew the Linnaean names of all the local wildflowers, and had pressed most in an album. This dual inheritance was to appear in her work as an artist.
After leaving Falkirk high school, she joined the new joint fine-and-applied arts course at Edinburgh University in September 1949, where the Byzantinist David Talbot Rice was her tutor. Blackadder found herself exposed to the Byzantine obsession with pattern, a taste at once formal and decorative. Another discovery was the Italian primitives, particularly Piero della Francesca. In her final year, spent at the Edinburgh College of Art, she met Houston, a fellow student. When Blackadder won a travel scholarship with her first-class degree, the pair set off for Italy. They were married in Edinburgh the following year, 1956, a partnership that was to last until Houston’s death in 2008.
21 notes
·
View notes
Text

Respected and celebrated Byzantinist Sir John Julius Norwich Fail Moments
8 notes
·
View notes
Note
How historically accurate is Steven Ruciman crusades book?
Hey,
I will write in French, because my writing english is not that good.
Steven Runciman est une référence quand on parle des croisades, comme René Grousset, le fut à une époque en France. De formation, byzantiniste, il fut l'un des premiers à dépouiller des sources grecques, latines et arabes. Sans compter que le monsieur parlait ou en tout cas lisait le persan, l'hébreu, le français ancien (oc et aïl) et moderne, l'anglais ancien et moderne, le grec ancien, le latin, l'arabe et le syriaque. De ce fait, ses travaux sont encore une référence dans le monde entier, bien qu'ils aient été écrits entre 1951 et 1953, en trois tomes. Toutefois, certains travaux récents permettent d'approfondir son travail et de mettre en perspective des points flous ou de remettre en question certaines hypothèses qu'il a formulées.
I hope i answer your question. If you have another, don't' hesitate, i will be happy to respond.
0 notes
Text
Working with Maps: An Introduction to GIS, Spatial Data, and Geospatial Resources for Byzantinists, workshop by Ryan Horne (UCLA) and Becky Seifred (UMass Amherst), Zoom, May 15–18, 2023, 11:00 AM–4:00 PM EDT with a break from 1:00–2:00 PM
https://themanfrommensa.com/category/shop/
https://maryjahariscenter.org/events/working-with-maps
This online workshop will offer Byzantinists an introduction to Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and its potential applications in Byzantine studies. Participants will learn how to work with geospatial data, how to organize it, where to find it, and how to create their own. Working in QGIS, a…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Note
Greetings comrade. Any good history books/articles/yt channel recommendations? I would really appreciate it :)
Ur blog is amazing ❤️
Beginner:
Genghis Khan and the Making of the Modern World by Jack Weatherford (great read; given its importance, the details and internal story of the Mongol Empire are often ignored. but they are riveting! accessible style.)
anything by Tom Holland (he’s pretty surface-level and really annoying to read if you know more about the period than him—but if you know less than he does, he’s a very effective communicator. and if you're not sure, give him a try! I think his Roman history books are the best, because that's where his expertise is.)
Intermediate:
History of Rome podcast (disclosure that it was made by a non-expert, and thus has some minor inaccuracies that make it unsuitable for academic research, but if you're not citing it in an essay, it's great. fairly accessible, straightforward linear history, and very thorough. you can listen to it on long walks, drives, or chores, which makes it easy to get through.)
anything by Anthony Kaldellis (somehow both a Byzantinist and a good communicator. he has a huge history of the whole empire coming out this fall, but also a variety of narrative histories (Streams of Gold, Rivers of Blood is the one I have) that are well written and very well researched. and a podcast.)
Grant by Ron Chernow. good read on a man who is interesting for somehow being both excellent and completely ordinary, which is a pretty rare combination for a biography. plus the Civil War was filled with weird people who wrote colorful letters and saved them all, so there is very little guesswork and a lot of first-person testimony, which is a welcome change from the rest of this list. also John Rawlins is in it, and I think he's neat.
Advanced:
any of the famous ancient historians. Livy is my favorite, because he writes very vivid battles, but Herodotus, Thucydides, Tacitus, Suetonius, and the like are all good. are they correct? no, not necessarily. but they're interesting for sure. and all these guys have well-annotated English translations too, so you get guidance through the incredible or confusing parts.
genuinely, just google something you're interested in, and read an paper about it. that's where some of the weirdest, most interesting information is.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Stuff I Read in November 2023
Stuff I Extra Liked is Bold
Books
Three Body Problem, Cixin Liu
System Collapse, Martha Wells
Radical Islam: The Iranian Mojahedin, Ervand Abrahamian
How Europe Underdeveloped Africa, Walter Rodney
Volodya, Selected Works, Vladimir Mayakovsky (ed. Rosy Carrick)
Yuri/GL
Pulse, Ratana Satis
Sabishisugite Lesbian Fuzoku ni Ikimashita Report / My Lesbian Experience with Loneliness, Kabi Nagata
Serenade, Kyesoo Keum
Even Though We’re Adults / Otona ni Nattemo (Vols. 1-6), Takako Shimura
Heaven Will Be Mine [itch]
Short Fiction (SF/F)
Rabbit Test, Samantha Mills [uncanny]
Story of Your Life, Ted Chiang
Mr. Death, Alix E. Harrow [apex]
The Secret Lives of the Nine Negro Teeth of George Washington, Phenderson Djèlí Clark [fireside]
The Mermaid Astronaut, Yoon Ha Lee [bcs]
Paper Menagerie, Ken Liu [archive]
History & Contemporary
Stalin, Soviet Agriculture, And Collectivisation, Mark B. Tauger [DOI]
Natural Disaster and Human Actions in the Soviet Famine of 1931-1933, Mark B. Tauger
Armed Struggle: Strategy and Tactic, Masoud Ahmadzadeh [marxists dot org]
An Analysis of One Year of Urban and Mountain Guerrilla Warfare, Hamid Ashraf [marxists dot org]
Sartre, European Intellectuals and Zionism, Joseph Massad [link]
‘Selective Historians’: The Construction of Cisness in Byzantine and Byzantinist Texts, Ilya Maude [DOI]
Special Interview With Khaled Barakat: Gaza Demands End of Genocide, Not ‘Ceasefire’ [link]
Philosophy and Related
The Emergence of Classes in a Multi-Agent Bargaining Model, Robert Axtell, Joshua M. Epstein, H. Peyton Young
The Evolution of Conventions, H. Peyton Young [JSTOR]
Cognitive Psychology and Neo-Phrenology, Gibbonstrength [link]
The Runabout Inference-Ticket, A. N. Prior [JSTOR]
Monster Culture (Seven Theses), Jeffrey Jerome Cohen
Who Owns Frantz Fanon’s Legacy?, Bashir Abu-Manneh [jacobin]
#reading prog#groupings this month are kinda silly#had multiple category 2 Health Events so it's been tiring#technically have one hwbm route left but yeh
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
i am loosing my mind over this 1940s french dude (apparently a priest and byzantinist what a combo) calling this flaming object on an early 12th century seal ‘a flaming grenade’ (the original french is “une grenade allumée”) and saying ‘the object is actually summarily represented’ to which another scholar (german and from this century) i am reading says ‘whatever he may have imagined it to be, in any case, it is not a scepter, which is correct’ both me and the german scholar essentially went: well it’s definitely not a scepter that’s right but whatever Laurent thought it was it’s also likely not a hand grenade so no that’s not “summarily represented” i have never thought about the effect of ww2 on scholarly terminology until now when i had to verify there wasn’t another definition of grenade that i was missing
#medieval history#i think he’s imagining a three leaf flaming ornament#not sure why he called it a grenade specifically#but it did make me laugh somewhat hysterically#i am putting this commentary in my thesis somehow
1 note
·
View note
Note
Buzz-word n. Colloq. Fashionable technical or specialist word; catchword.
By —prep. 1 near, beside (sit by me; path by the river). 2 through the agency or means of (by proxy; poem by donne; by bus; by cheating; divide by two; killed by robbers). 3 not later than (by next week). 4 a past, beyond (drove by the church). B through; via (went by paris). 5 during (by day; by daylight). 6 to the extent of (missed by a foot; better by far). 7 according to; using as a standard or unit (judge by appearances; paid by the hour). 8 with the succession of (worse by the minute; day by day). 9 concerning; in respect of (did our duty by them; smith by name). 10 used in mild oaths (by god). 11 expressing dimensions of an area etc. (three feet by two). 12 avoiding, ignoring (passed us by). 13 inclining to (north by north-west). —adv. 1 near (sat by). 2 aside; in reserve (put £5 by). 3 past (marched by). —n. (pl. Byes) = *bye1. by and by before long; eventually. By and large on the whole. By the by (or bye) incidentally. By oneself 1 a unaided. B unprompted. 2 alone. [old english]
By- prefix subordinate, incidental (by-effect; byroad).
Bye1 n. 1 cricket run scored from a ball that passes the batsman without being hit. 2 status of an unpaired competitor in a sport, who proceeds to the next round by default. [from *by as a noun]
Bye2 int. (also bye-bye) colloq. = *goodbye. [abbreviation]
By-election n. Election to fill a vacancy arising between general elections.
Byelorussian (also belorussian) —n. Native or language of byelorussia in eastern europe. —adj. Of byelorussia, its people, or language. [russian from belyi white, russiya russia]
Bygone —adj. Past, antiquated. —n. (in phr. Let bygones be bygones) forgive and forget past quarrels.
By-law n. Regulation made by a local authority or corporation. [obsolete by town]
Byline n. 1 line naming the writer of a newspaper article etc. 2 secondary line of work. 3 goal-line or touch-line.
Bypass —n. 1 main road passing round a town or its centre. 2 a secondary channel or pipe etc. Used in emergencies. B alternative passage for the circulation of blood through the heart. —v. Avoid, go round (a town, difficulty, etc.).
Byplay n. Secondary action, esp. In a play.
By-product n. 1 incidental product made in the manufacture of something else. 2 secondary result.
Byre n. Cowshed. [old english]
Byroad n. Minor road.
Byroad n. Minor road.
Byssinosis n. Lung disease caused by textile fibre dust. [greek bussinos made of linen]
Bystander n. Person present but not taking part; onlooker.
Byte n. Computing group of eight binary digits, often representing one character. [origin uncertain]
Byway n. 1 byroad or secluded path. 2 minor activity.
Byword n. 1 person or thing as a notable example (is a byword for luxury). 2 familiar saying.
Byzantine —adj. 1 of byzantium or the e. Roman empire. 2 of its highly decorated style of architecture. 3 (of a political situation etc.) Complex, inflexible, or underhand. —n. Citizen of byzantium or the e. Roman empire. byzantinism n. Byzantinist n. [latin byzantium, now istanbul]
C
C1 n. (pl. Cs or c's) 1 (also c) third letter of the alphabet. 2 mus. First note of the diatonic scale of c major. 3 third hypothetical person or example. 4 third highest category etc. 5 algebra (usu. C) third known quantity. 6 (as a roman numeral) 100. 7 (also ©) copyright.
C2 symb. Carbon.
C3 abbr. (also c.) 1 celsius, centigrade. 2 coulomb(s), capacitance.
C. Abbr. 1 century. 2 cent(s).
C. Abbr. Circa.
Ca symb. Calcium.
Ca. Abbr. Circa.
Caa abbr. Civil aviation authority.
Cab n. 1 taxi. 2 driver's compartment in a lorry, train, or crane etc. [abbreviation of *cabriolet]
Cabal n. 1 secret intrigue. 2 political clique. [french from latin]
Cabaret n. Entertainment in a nightclub or restaurant. [french, = tavern]
Cabbage n. 1 vegetable with a round head and green or purple leaves. 2 = *vegetable 2. [french caboche head]
Cabbage white n. Butterfly whose caterpillars feed on cabbage leaves.
Cabby n. (also cabbie) (pl. -ies) colloq. Taxi-driver.
Caber n. Trimmed tree-trunk tossed as a sport in the scottish highlands. [gaelic]
Cabin n. 1 small shelter or house, esp. Of wood. 2 room or compartment in an aircraft or ship for passengers or crew. 3 driver's cab. [french from latin]
Cabin-boy n. Boy steward on a ship.
Cabin cruiser n. Large motor boat with accommodation.
Cabinet n. 1 a cupboard or case for storing or displaying things. B casing of a radio, television, etc. 2 (cabinet) committee of senior ministers in a government. [diminutive of *cabin]
Cabinet-maker n. Skilled joiner.
Cable —n. 1 encased group of insulated wires for transmitting electricity etc. 2 thick rope of wire or hemp. 3 cablegram. 4 (in full cable stitch) knitting stitch resembling twisted rope. —v. (-ling) transmit (a message) or inform (a person) by cablegram. [latin caplum halter, from arabic]
Cable-car n. Small cabin suspended on a looped cable, for carrying passengers up and down a mountain etc.
Cablegram n. Telegraph message sent by undersea cable.
Cable television n. Television transmission by cable to subscribers.
C!!!!!!!!!!!!
C !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! WE GOT TO THE C SECTION !!!!!!!!!!
#do you get it#do you get my joke#i waited for that joke#pls tell me you get it#i dont wanna explain#long post#dic anon#anon
0 notes