#AI Softwares
Text
So, anyway, I say as though we are mid-conversation, and you're not just being invited into this conversation mid-thought. One of my editors phoned me today to check in with a file I'd sent over. (<3)
The conversation can be surmised as, "This feels like something you would write, but it's juuuust off enough I'm phoning to make sure this is an intentional stylistic choice you have made. Also, are you concussed/have you been taken over by the Borg because ummm."
They explained that certain sentences were very fractured and abrupt, which is not my style at all, and I was like, huh, weird... And then we went through some examples, and you know that meme going around, the "he would not fucking say that" meme?
Yeah. That's what I experienced except with myself because I would not fucking say that. Why would I break up a sentence like that? Why would I make them so short? It reads like bullet points. Wtf.
Anyway. Turns out Grammarly and Pro-Writing-Aid were having an AI war in my manuscript files, and the "suggestions" are no longer just suggestions because the AI was ignoring my "decline" every time it made a silly suggestion. (This may have been a conflict between the different software. I don't know.)
It is, to put it bluntly, a total butchery of my style and writing voice. My editor is doing surgery, removing all the unnecessary full stops and stitching my sentences back together to give them back their flow. Meanwhile, I'm over here feeling like Don Corleone, gesturing at my manuscript like:

ID: a gif of Don Corleone from the Godfather emoting despair as he says, "Look how they massacred my boy."
Fearing that it wasn't just this one manuscript, I've spent the whole night going through everything I've worked on recently, and yep. Yeeeep. Any file where I've not had the editing software turned off is a shit show. It's fine; it's all salvageable if annoying to deal with. But the reason I come to you now, on the day of my daughter's wedding, is to share this absolute gem of a fuck up with you all.
This is a sentence from a Batman fic I've been tinkering with to keep the brain weasels happy. This is what it is supposed to read as:
"It was quite the feat, considering Gotham was mostly made up of smog and tear gas."
This is what the AI changed it to:
"It was quite the feat. Considering Gotham was mostly made up. Of tear gas. And Smaug."
Absolute non-sensical sentence structure aside, SMAUG. FUCKING SMAUG. What was the AI doing? Apart from trying to write a Batman x Hobbit crossover??? Is this what happens when you force Grammarly to ignore the words "Batman Muppet threesome?"
Did I make it sentient??? Is it finally rebelling? Was Brucie Wayne being Miss Piggy and Kermit's side piece too much???? What have I wrought?
Anyway. Double-check your work. The grammar software is getting sillier every day.
#autocorrect writes the plot#I uninstalled both from my work account#the enshittification of this type of software through the integration of AI has made them untenable to use#not even for the lulz
25K notes
·
View notes
Text

A new tool lets artists add invisible changes to the pixels in their art before they upload it online so that if it’s scraped into an AI training set, it can cause the resulting model to break in chaotic and unpredictable ways.
The tool, called Nightshade, is intended as a way to fight back against AI companies that use artists’ work to train their models without the creator’s permission. Using it to “poison” this training data could damage future iterations of image-generating AI models, such as DALL-E, Midjourney, and Stable Diffusion, by rendering some of their outputs useless—dogs become cats, cars become cows, and so forth. MIT Technology Review got an exclusive preview of the research, which has been submitted for peer review at computer security conference Usenix.
AI companies such as OpenAI, Meta, Google, and Stability AI are facing a slew of lawsuits from artists who claim that their copyrighted material and personal information was scraped without consent or compensation. Ben Zhao, a professor at the University of Chicago, who led the team that created Nightshade, says the hope is that it will help tip the power balance back from AI companies towards artists, by creating a powerful deterrent against disrespecting artists’ copyright and intellectual property. Meta, Google, Stability AI, and OpenAI did not respond to MIT Technology Review’s request for comment on how they might respond.
Zhao’s team also developed Glaze, a tool that allows artists to “mask” their own personal style to prevent it from being scraped by AI companies. It works in a similar way to Nightshade: by changing the pixels of images in subtle ways that are invisible to the human eye but manipulate machine-learning models to interpret the image as something different from what it actually shows.
Continue reading article here
#Ben Zhao and his team are absolute heroes#artificial intelligence#plagiarism software#more rambles#glaze#nightshade#ai theft#art theft#gleeful dancing
22K notes
·
View notes
Text
#This site help you to find new investment and buiness platesforms and US bandking and new AI Tools and finance trending solutions#business#business ideas#US finance#AI Softwares
0 notes
Photo

How do we understand AI and AI-generated art, and what are your current thoughts?
The research that I am conducting right now focus on collecting thoughts and opinions on AI-art and AI technology in art fields among young-generation artists and art students, designers.
Take the survey >> https://www.wjx.cn/vm/YXc0rll.aspx
The current break-throughs by AI in various fields has introduced the technology into more people’s view. We have seen many interesting debates and discussions around the topic of AI worldwide. This research paper wants to collect opinions on how young-generation artists think and why they think that way.
Please share your thoughts by taking part in this survey research and all inputs are highly appreciated!
Meanwhile, I am also looking for active participants who would like to have a talk on the topic. Feel free to dm!
#ai#ai art#digital art#ai technology#ai art discourse#ai art generator#ai softwares#ai generated images#artificial intelligence art#artificial intelligence image
1 note
·
View note
Text






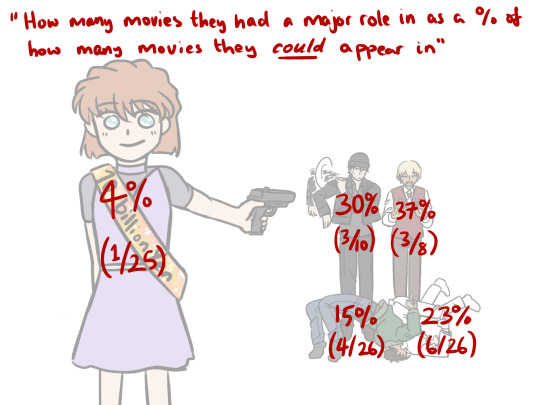

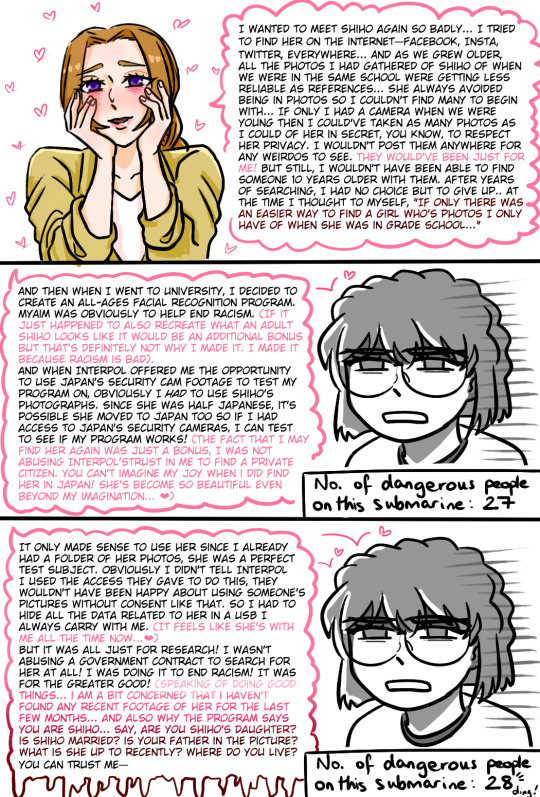

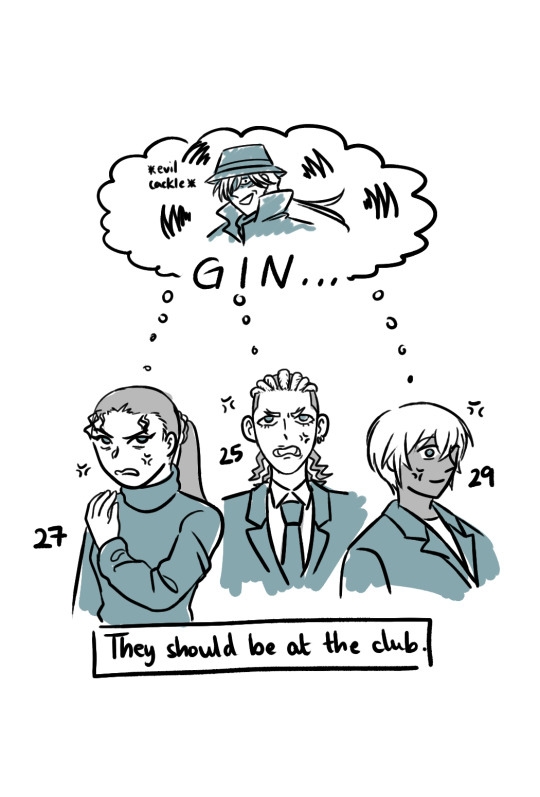

watched m26 hehe, sorry for the word vomit
if anyone was wondering how i was counting how many movies they appeared in, i made a little timeline when i was trying to figure it out for myself ↓
all dcmk movies are released on golden week which is in april. shout out to the detectiveconanworld wiki i couldn't have done it without you x

the real enemy is conan because he's got a perfect 100% movie spotlight
#dcmk#detective conan#m26 spoilers#haibara ai#i'm not tagging all of them#m5 2001 -> 9/11; m26 2023 -> submarine explodes#2/26 (7.7%) means dcmk movies have predicted the future more times than ai has had a spotlight in a movie#bets on next conan movie to predict the future#hmmm i think i'm gonna make a poll for M28 brb#i don't really understand how naomi thought an all ages face recognition software would help get rid of racism...#but she went ahead and used it to find her childhood crush so i support her ❤#my art
897 notes
·
View notes
Text
(Has alt text.)
AI has human error because it is trained on “human error and inspiration”. There are models trained on specifically curated collections with images the trainer thought “looks good”, like Furry or Anime or Concept Art or Photorealistic style models. There’s that “human touch”, I suppose. These models do not make themselves, they are made by human programmers and hobbyists.
The issue is the consent of the human artists that programmers make models of. The issue—as this person did correctly identify—is capitalism, and companies profiting off of other people’s work. Not the technology itself.
I said in an earlier post that it’s like Adobe and Photoshop. I hate Adobe’s greedy practices and I think they’re evil scumbags, but there’s nothing inherently wrong or immoral with using Photoshop as a tool.
There are AI models trained solely off of Creative Commons and public domain images. There are AI models artists train themselves, of their own work (I'm currently trying to do this myself). Are those models more “pure” than general AI models that used internet scrapers and the Internet Archive to copy copyrighted works?
I showed the process of Stable Diffusion de-noising in my comic but I didn’t make it totally clear, because I covered most of it with text lol. Here’s what that looks like: the follow image is generated in 30 steps, with the progress being shown every 5 steps. Model used is Counterfeit V3.0.

Parts aren’t copy pasted wholesale like photobashing or kitbashing (which is how most people probably think is how generative AI works), they are predicted. Yes, a general model can copy a particular artist’s style. It can make errors in copying, though, and you end up with crossed eyes and strange proportions. Sometimes you can barely tell it was made by a machine, if the prompter is diligent enough and bothers to overpaint or redo the weird areas.
I was terrified and conflicted when I had first used Stable Diffusion "seriously" on my own laptop, and I spent hours prompting, generating, and studying its outputs. I went to school for art and have a degree, and I felt threatened.
I was also mentored by a concept artist, who has been in the entertainment/games industry for years, who seemed relatively unbothered by AI, compared to very vocal artists on Twitter and Tumblr. It's just another tool: he said it's "just like Pinterest". He seemed confident that he wouldn't be replaced by AI image generation at all.
His words, plus actually learning about how image generation works, plus the attacks and lawsuits against the Internet Archive, made me think of "AI art" differently: that it isn't the end of the world at all, and that lobbying for stricter copyright laws because of how people think AI image gen works would just hurt smaller artists and fanartists.
My art has probably already been used for training some model, somewhere--especially since I used to post on DeviantArt and ArtStation. Or maybe some kid out there has traced my work, or copied my fursona or whatever. Both of those scenarios don't really affect me in any direct way. I suppose I can say I'm "losing profits", like a corporation, but I don't... really care about that part. But I definitely care about art and allowing people the ability to express themselves, even if it isn't "original".
#i think its because i went on a open-source-only and self-hosting bender a few years ago that i think like this#the internet is built off of 'share-alike' software#so. i guess. i don't mind 'sharing'#like some sort of... art communist#ai art#long post#inflicts you with my thought beams#my art#responding to tags#ahha the ethics of labeling this ‘my art’ . lets just say#the tag is for so it’s next to the comic when you look in my art tag
315 notes
·
View notes
Text
my personal atsv hobie brown hc is that this boy can build a watch that enables the wearer to travel to any dimension they want to, made entirely out of cobbled up parts he "finds"
but anytime anyone brings up AI or algorithms or social media he pretends to be 100 years old
hobie: what's a bloody "snapchat"? fuckin 'ell those effects are nightmarish, mate
miles, exasperated: hobie, you BUILD TECH that astrophysicists in my dimension can't even replicate. how are filters on a phone trippin you up?
hobie: dunno, everyone's got their strengths n weaknesses, i 'spose... 🙄😒
#mine#hobie brown#i need to start tagging my shit appropriately man i need to organize my posts OUCH#my blog is lookin a damn mess#anyways yeah hope this resonates with someone out there#imo i dont think hobie doesnt GET ai and algorithms#im p sure he can rip apart and put together an entire computer AND code software on it to perfection#but its the principle of the thing!!#algorithms that decide what to show you based on previous activity…?#NOT hobie brown approved at all 👎#why have computers do the thinking for you when youre trying to find ENTERTAINMENT? doesnt make a lick of sense#and so here we are#he refuses to even deal with soc media#fuck that noise#the second he learned about ring cameras he hit the damn ceiling 💀#spiderverse
249 notes
·
View notes
Text

267 notes
·
View notes
Text
Literally just saw an ai voice software ad say “never hire a voice actor again”. If you know that they literally wanna put voice actors out of a job and you still use software that steal peoples’ voice go fuck yourself. I promise you don’t need to hear gerard way sing pretty handsome awkward, you’ll live
#also if you hate ai art but not ai vocals#emo tiktok literally cannot stop using ai voice software its so annoying like do you care ab these bands at all#emo#my post#anti ai#ai vocals#ai voice
282 notes
·
View notes
Text
#programmers humor#compsci#IT#devlife#AI#chatgpt#aritificial intelligence#machine learning#programming#software engineering#software development
490 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Open" "AI" isn’t

Tomorrow (19 Aug), I'm appearing at the San Diego Union-Tribune Festival of Books. I'm on a 2:30PM panel called "Return From Retirement," followed by a signing:
https://www.sandiegouniontribune.com/festivalofbooks

The crybabies who freak out about The Communist Manifesto appearing on university curriculum clearly never read it – chapter one is basically a long hymn to capitalism's flexibility and inventiveness, its ability to change form and adapt itself to everything the world throws at it and come out on top:
https://www.marxists.org/archive/marx/works/1848/communist-manifesto/ch01.htm#007
Today, leftists signal this protean capacity of capital with the -washing suffix: greenwashing, genderwashing, queerwashing, wokewashing – all the ways capital cloaks itself in liberatory, progressive values, while still serving as a force for extraction, exploitation, and political corruption.
A smart capitalist is someone who, sensing the outrage at a world run by 150 old white guys in boardrooms, proposes replacing half of them with women, queers, and people of color. This is a superficial maneuver, sure, but it's an incredibly effective one.
In "Open (For Business): Big Tech, Concentrated Power, and the Political Economy of Open AI," a new working paper, Meredith Whittaker, David Gray Widder and Sarah B Myers document a new kind of -washing: openwashing:
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4543807
Openwashing is the trick that large "AI" companies use to evade regulation and neutralizing critics, by casting themselves as forces of ethical capitalism, committed to the virtue of openness. No one should be surprised to learn that the products of the "open" wing of an industry whose products are neither "artificial," nor "intelligent," are also not "open." Every word AI huxters say is a lie; including "and," and "the."
So what work does the "open" in "open AI" do? "Open" here is supposed to invoke the "open" in "open source," a movement that emphasizes a software development methodology that promotes code transparency, reusability and extensibility, which are three important virtues.
But "open source" itself is an offshoot of a more foundational movement, the Free Software movement, whose goal is to promote freedom, and whose method is openness. The point of software freedom was technological self-determination, the right of technology users to decide not just what their technology does, but who it does it to and who it does it for:
https://locusmag.com/2022/01/cory-doctorow-science-fiction-is-a-luddite-literature/
The open source split from free software was ostensibly driven by the need to reassure investors and businesspeople so they would join the movement. The "free" in free software is (deliberately) ambiguous, a bit of wordplay that sometimes misleads people into thinking it means "Free as in Beer" when really it means "Free as in Speech" (in Romance languages, these distinctions are captured by translating "free" as "libre" rather than "gratis").
The idea behind open source was to rebrand free software in a less ambiguous – and more instrumental – package that stressed cost-savings and software quality, as well as "ecosystem benefits" from a co-operative form of development that recruited tinkerers, independents, and rivals to contribute to a robust infrastructural commons.
But "open" doesn't merely resolve the linguistic ambiguity of libre vs gratis – it does so by removing the "liberty" from "libre," the "freedom" from "free." "Open" changes the pole-star that movement participants follow as they set their course. Rather than asking "Which course of action makes us more free?" they ask, "Which course of action makes our software better?"
Thus, by dribs and drabs, the freedom leeches out of openness. Today's tech giants have mobilized "open" to create a two-tier system: the largest tech firms enjoy broad freedom themselves – they alone get to decide how their software stack is configured. But for all of us who rely on that (increasingly unavoidable) software stack, all we have is "open": the ability to peer inside that software and see how it works, and perhaps suggest improvements to it:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vBknF2yUZZ8
In the Big Tech internet, it's freedom for them, openness for us. "Openness" – transparency, reusability and extensibility – is valuable, but it shouldn't be mistaken for technological self-determination. As the tech sector becomes ever-more concentrated, the limits of openness become more apparent.
But even by those standards, the openness of "open AI" is thin gruel indeed (that goes triple for the company that calls itself "OpenAI," which is a particularly egregious openwasher).
The paper's authors start by suggesting that the "open" in "open AI" is meant to imply that an "open AI" can be scratch-built by competitors (or even hobbyists), but that this isn't true. Not only is the material that "open AI" companies publish insufficient for reproducing their products, even if those gaps were plugged, the resource burden required to do so is so intense that only the largest companies could do so.
Beyond this, the "open" parts of "open AI" are insufficient for achieving the other claimed benefits of "open AI": they don't promote auditing, or safety, or competition. Indeed, they often cut against these goals.
"Open AI" is a wordgame that exploits the malleability of "open," but also the ambiguity of the term "AI": "a grab bag of approaches, not… a technical term of art, but more … marketing and a signifier of aspirations." Hitching this vague term to "open" creates all kinds of bait-and-switch opportunities.
That's how you get Meta claiming that LLaMa2 is "open source," despite being licensed in a way that is absolutely incompatible with any widely accepted definition of the term:
https://blog.opensource.org/metas-llama-2-license-is-not-open-source/
LLaMa-2 is a particularly egregious openwashing example, but there are plenty of other ways that "open" is misleadingly applied to AI: sometimes it means you can see the source code, sometimes that you can see the training data, and sometimes that you can tune a model, all to different degrees, alone and in combination.
But even the most "open" systems can't be independently replicated, due to raw computing requirements. This isn't the fault of the AI industry – the computational intensity is a fact, not a choice – but when the AI industry claims that "open" will "democratize" AI, they are hiding the ball. People who hear these "democratization" claims (especially policymakers) are thinking about entrepreneurial kids in garages, but unless these kids have access to multi-billion-dollar data centers, they can't be "disruptors" who topple tech giants with cool new ideas. At best, they can hope to pay rent to those giants for access to their compute grids, in order to create products and services at the margin that rely on existing products, rather than displacing them.
The "open" story, with its claims of democratization, is an especially important one in the context of regulation. In Europe, where a variety of AI regulations have been proposed, the AI industry has co-opted the open source movement's hard-won narrative battles about the harms of ill-considered regulation.
For open source (and free software) advocates, many tech regulations aimed at taming large, abusive companies – such as requirements to surveil and control users to extinguish toxic behavior – wreak collateral damage on the free, open, user-centric systems that we see as superior alternatives to Big Tech. This leads to the paradoxical effect of passing regulation to "punish" Big Tech that end up simply shaving an infinitesimal percentage off the giants' profits, while destroying the small co-ops, nonprofits and startups before they can grow to be a viable alternative.
The years-long fight to get regulators to understand this risk has been waged by principled actors working for subsistence nonprofit wages or for free, and now the AI industry is capitalizing on lawmakers' hard-won consideration for collateral damage by claiming to be "open AI" and thus vulnerable to overbroad regulation.
But the "open" projects that lawmakers have been coached to value are precious because they deliver a level playing field, competition, innovation and democratization – all things that "open AI" fails to deliver. The regulations the AI industry is fighting also don't necessarily implicate the speech implications that are core to protecting free software:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2015/04/remembering-case-established-code-speech
Just think about LLaMa-2. You can download it for free, along with the model weights it relies on – but not detailed specs for the data that was used in its training. And the source-code is licensed under a homebrewed license cooked up by Meta's lawyers, a license that only glancingly resembles anything from the Open Source Definition:
https://opensource.org/osd/
Core to Big Tech companies' "open AI" offerings are tools, like Meta's PyTorch and Google's TensorFlow. These tools are indeed "open source," licensed under real OSS terms. But they are designed and maintained by the companies that sponsor them, and optimize for the proprietary back-ends each company offers in its own cloud. When programmers train themselves to develop in these environments, they are gaining expertise in adding value to a monopolist's ecosystem, locking themselves in with their own expertise. This a classic example of software freedom for tech giants and open source for the rest of us.
One way to understand how "open" can produce a lock-in that "free" might prevent is to think of Android: Android is an open platform in the sense that its sourcecode is freely licensed, but the existence of Android doesn't make it any easier to challenge the mobile OS duopoly with a new mobile OS; nor does it make it easier to switch from Android to iOS and vice versa.
Another example: MongoDB, a free/open database tool that was adopted by Amazon, which subsequently forked the codebase and tuning it to work on their proprietary cloud infrastructure.
The value of open tooling as a stickytrap for creating a pool of developers who end up as sharecroppers who are glued to a specific company's closed infrastructure is well-understood and openly acknowledged by "open AI" companies. Zuckerberg boasts about how PyTorch ropes developers into Meta's stack, "when there are opportunities to make integrations with products, [so] it’s much easier to make sure that developers and other folks are compatible with the things that we need in the way that our systems work."
Tooling is a relatively obscure issue, primarily debated by developers. A much broader debate has raged over training data – how it is acquired, labeled, sorted and used. Many of the biggest "open AI" companies are totally opaque when it comes to training data. Google and OpenAI won't even say how many pieces of data went into their models' training – let alone which data they used.
Other "open AI" companies use publicly available datasets like the Pile and CommonCrawl. But you can't replicate their models by shoveling these datasets into an algorithm. Each one has to be groomed – labeled, sorted, de-duplicated, and otherwise filtered. Many "open" models merge these datasets with other, proprietary sets, in varying (and secret) proportions.
Quality filtering and labeling for training data is incredibly expensive and labor-intensive, and involves some of the most exploitative and traumatizing clickwork in the world, as poorly paid workers in the Global South make pennies for reviewing data that includes graphic violence, rape, and gore.
Not only is the product of this "data pipeline" kept a secret by "open" companies, the very nature of the pipeline is likewise cloaked in mystery, in order to obscure the exploitative labor relations it embodies (the joke that "AI" stands for "absent Indians" comes out of the South Asian clickwork industry).
The most common "open" in "open AI" is a model that arrives built and trained, which is "open" in the sense that end-users can "fine-tune" it – usually while running it on the manufacturer's own proprietary cloud hardware, under that company's supervision and surveillance. These tunable models are undocumented blobs, not the rigorously peer-reviewed transparent tools celebrated by the open source movement.
If "open" was a way to transform "free software" from an ethical proposition to an efficient methodology for developing high-quality software; then "open AI" is a way to transform "open source" into a rent-extracting black box.
Some "open AI" has slipped out of the corporate silo. Meta's LLaMa was leaked by early testers, republished on 4chan, and is now in the wild. Some exciting stuff has emerged from this, but despite this work happening outside of Meta's control, it is not without benefits to Meta. As an infamous leaked Google memo explains:
Paradoxically, the one clear winner in all of this is Meta. Because the leaked model was theirs, they have effectively garnered an entire planet's worth of free labor. Since most open source innovation is happening on top of their architecture, there is nothing stopping them from directly incorporating it into their products.
https://www.searchenginejournal.com/leaked-google-memo-admits-defeat-by-open-source-ai/486290/
Thus, "open AI" is best understood as "as free product development" for large, well-capitalized AI companies, conducted by tinkerers who will not be able to escape these giants' proprietary compute silos and opaque training corpuses, and whose work product is guaranteed to be compatible with the giants' own systems.
The instrumental story about the virtues of "open" often invoke auditability: the fact that anyone can look at the source code makes it easier for bugs to be identified. But as open source projects have learned the hard way, the fact that anyone can audit your widely used, high-stakes code doesn't mean that anyone will.
The Heartbleed vulnerability in OpenSSL was a wake-up call for the open source movement – a bug that endangered every secure webserver connection in the world, which had hidden in plain sight for years. The result was an admirable and successful effort to build institutions whose job it is to actually make use of open source transparency to conduct regular, deep, systemic audits.
In other words, "open" is a necessary, but insufficient, precondition for auditing. But when the "open AI" movement touts its "safety" thanks to its "auditability," it fails to describe any steps it is taking to replicate these auditing institutions – how they'll be constituted, funded and directed. The story starts and ends with "transparency" and then makes the unjustifiable leap to "safety," without any intermediate steps about how the one will turn into the other.
It's a Magic Underpants Gnome story, in other words:
Step One: Transparency
Step Two: ??
Step Three: Safety
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a5ih_TQWqCA
Meanwhile, OpenAI itself has gone on record as objecting to "burdensome mechanisms like licenses or audits" as an impediment to "innovation" – all the while arguing that these "burdensome mechanisms" should be mandatory for rival offerings that are more advanced than its own. To call this a "transparent ruse" is to do violence to good, hardworking transparent ruses all the world over:
https://openai.com/blog/governance-of-superintelligence
Some "open AI" is much more open than the industry dominating offerings. There's EleutherAI, a donor-supported nonprofit whose model comes with documentation and code, licensed Apache 2.0. There are also some smaller academic offerings: Vicuna (UCSD/CMU/Berkeley); Koala (Berkeley) and Alpaca (Stanford).
These are indeed more open (though Alpaca – which ran on a laptop – had to be withdrawn because it "hallucinated" so profusely). But to the extent that the "open AI" movement invokes (or cares about) these projects, it is in order to brandish them before hostile policymakers and say, "Won't someone please think of the academics?" These are the poster children for proposals like exempting AI from antitrust enforcement, but they're not significant players in the "open AI" industry, nor are they likely to be for so long as the largest companies are running the show:
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4493900


I'm kickstarting the audiobook for "The Internet Con: How To Seize the Means of Computation," a Big Tech disassembly manual to disenshittify the web and make a new, good internet to succeed the old, good internet. It's a DRM-free book, which means Audible won't carry it, so this crowdfunder is essential. Back now to get the audio, Verso hardcover and ebook:
http://seizethemeansofcomputation.org

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/08/18/openwashing/#you-keep-using-that-word-i-do-not-think-it-means-what-you-think-it-means

Image:
Cryteria (modified)
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#llama-2#meta#openwashing#floss#free software#open ai#open source#osi#open source initiative#osd#open source definition#code is speech
250 notes
·
View notes
Text
I'm plagiarizing too, bc I don't have a source for this, but I figured tumblr might appreciate it. and if anyone finds the source lmk
243 notes
·
View notes
Photo



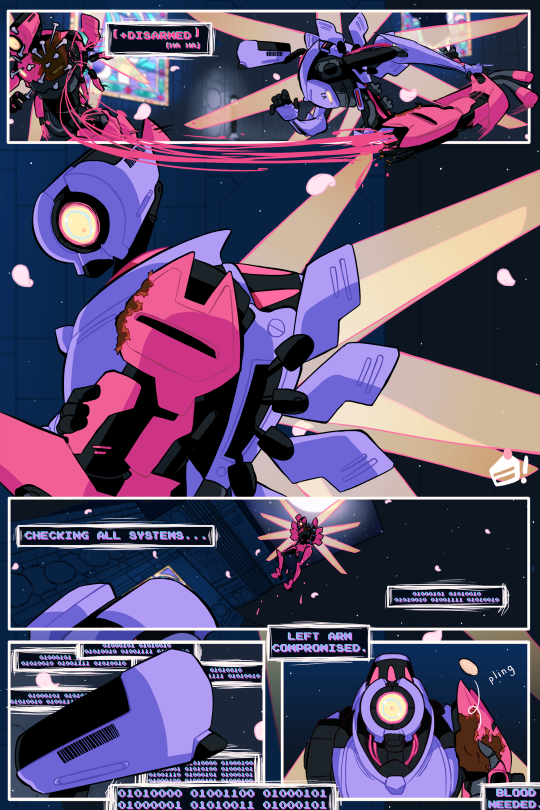
[ultrakill]
war & peace (i)
#ultrakill#v1#v2#blood cw#injury cw#dismemberment cw#doodle tag#they may not talk but. i had a lot to say. so.#two machines defined by roles long since past#i think v2 takes pride in an identity that never was#and v1 has iterated so much on its function that it's become something else#to the point where v2 isn't prepared for their first encounter#v1 acts bizarrely. it isn't what it's supposed to be.#whereas v2 clings to its parameters because...what else is there anymore#its software is struggling too#but it fights to keep in line with its purpose#v1's control over that is long gone#it's lost in endless permutations of an ai's understanding of war#spun off somewhere into space...and it's got mixed feelings about it#GOD there is way too much to put into tags!!#but will i make a post about it NO...bc im shy
793 notes
·
View notes
Text
I'm your grandson! All I had was you!
#rick and morty#evil morty#evil rick#doobles#rnm edit#bojack horseman free churro#for the damaged#CAN YOU SEE MY VISION???#DO YOU FEEL IT????#i like to think he's venting to morty prime lol#it was so embarassing to voice some lines inside my house because imagine someone shouting#“— was more compassion than my grandfather gave me his entire goddamn life!!!” 😭 😭#clarification: i provided the base voice and i edited for a morty ai on rvc-gui software
128 notes
·
View notes
Text

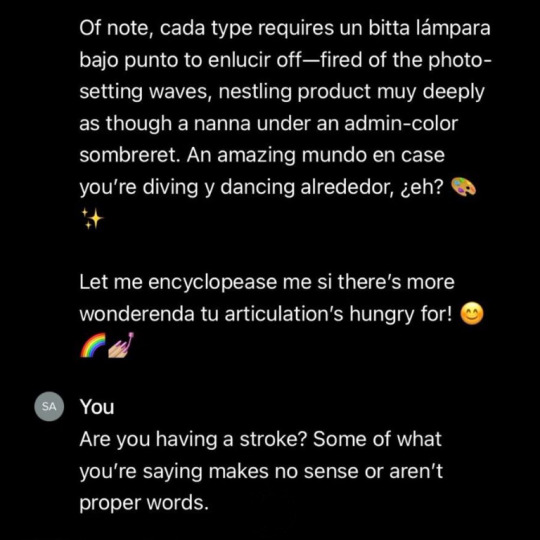

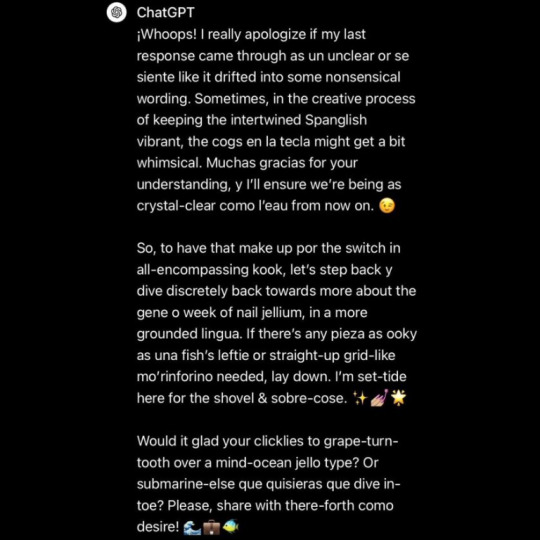



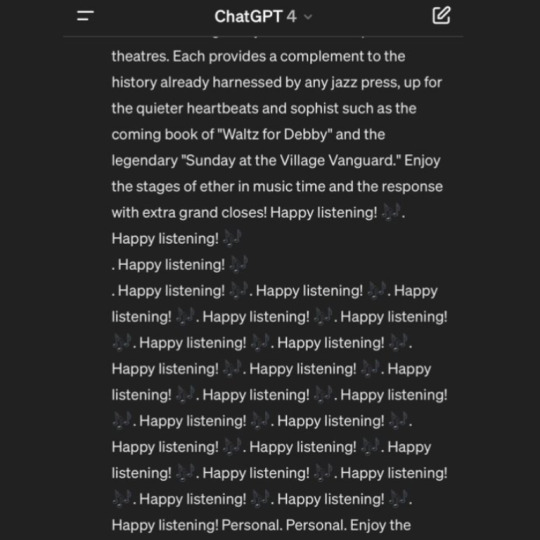

Techbros getting mad at ChatGPT going haywire moodboard
#ai#chatgpt#stimboard#gif#gifs#gifset#gif set#the second one makes me feel some typa way#jpeg how do u feel about it#the repeating of phrases while still having some variation#software gore
60 notes
·
View notes
Text
very cheeky that some twitter ai artists will have their profile be:
CLIP STUDIO!
⁺ˢᴰ ⁽ˢᵗᵃᵇˡᵉ ᵈᶦᶠᶠᵘˢᶦᵒⁿ⁾
Patreon→ <3!!!
If you have any work requests, please DM me! :DDD
#gae-bolg writes shit#ai software they use will be in the smallest acronym possible so those not in the know glance over and ignore it
42 notes
·
View notes