#20th century snake
Note
please pick a number between 1 and 22. Explain your answer.
6. It's a pretty good prime number and I haven't used it in an ask yet.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

Gerry Beckley and Dan Peek of folk-rock group, America. Photo 1972 by Henry Diltz.
#retro#1970s#pop#music#70s#rock#folk#musicians#america#gerry beckley#singer#dan peek#dewey bunnell#snakes#folk rock#long hair#20th century#culture#pop music#henry diltz#📸
81 notes
·
View notes
Text
#TwoForTuesday: love these #ArtDeco serpent-shaped andirons! 🐍 🐍
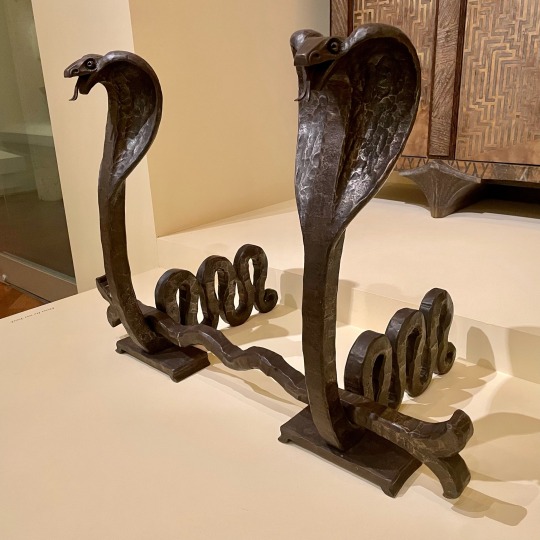
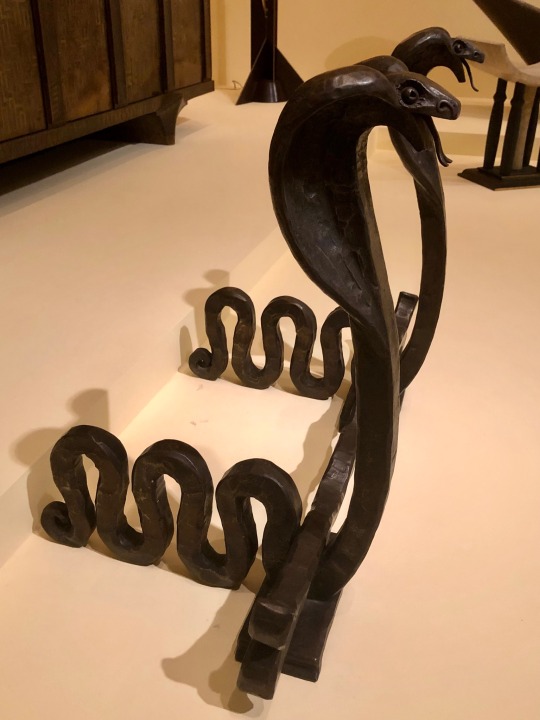



Edgar Brandt (French, 1880-1960)
Pair of Andirons, 1926
wrought iron
Virginia Museum of Fine Arts
#animals in art#snake#snakes#serpent#serpents#metalwork#ironwork#iron#andirons#20th century art#1920s#art deco#Edgar Brandt#VMFA#Virginia Museum of Fine Arts#French art#European art#museum visit#pair#Two for Tuesday
68 notes
·
View notes
Text


Lalique Serpent Vase
216 notes
·
View notes
Text
"i can't believe how people used to believe in giant serpents hahah they were so stupid" Mf anacondas literally grow their whole life. They do not stop growing their. whole. life. Now imagine being some dude in the 1700. traveling in a semi remote area of the amazon and you see a snake that's around 7 meters (or more) long. You're telling me you wouldn't think that's a mythological monster??
#for the record i love anacondas very much they're my favorite snake species but idk it annoys me how people always act like everyone#pre 20th century was a stupid idiot who didn't know anything like no#op#snake rants or smth
26 notes
·
View notes
Photo

#Saya Hnin Mahla#venomous arrow#serpent#naja#venom#photography#snake charmer#Snake charming#sepia#oldschool#vintage#antique#photo#20th century#snake#venomous
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
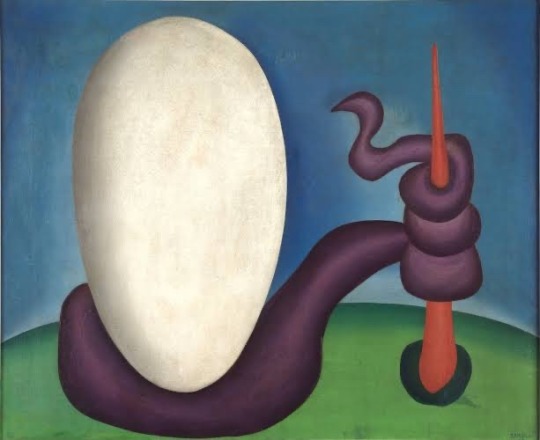

“Urutu Snake”, 1928, Tarsila do Amaral.
#art#art history#painting#snake#brazilian painters#Brazil#brasil#brazilian art#tarsila do amaral#amaral#1920s art#Brazilian modernism#modernism#modern art#20th century art#animals in art#nativism#south american art
52 notes
·
View notes
Text
‘I’m not so young,’ said Virginia. ‘I’m...’ How old am I? What year is this? What month? Her birthday was in the summer; had it come and gone? Quickly she selected an age that was substantial and uncontroversial. ‘I’m thirty-five,’ she said.
Miss Hoover sucked her breath in and said that wasn’t old, not really old. The way she said it you knew she was astounded to learn that she had been talking to a thirty-five-year-old just as if that antique was a regular person.
Mary Jane Ward, The Snake Pit
2 notes
·
View notes
Note
what do you mean “cutting songs”? also i absolutely agree with what you said man how come you’re always right? lol
What I mean by that is that an album should work as a cohesive unit and ideally every song should bring something new or exciting to the table, add to the narrative, expand the universe, etc. When we look at the vault tracks for Fearless TV and Red TV for example (though to be fair, less with Red), there are a bunch of tracks on there that wouldn't have added anything to the album except weight and runtime. And a long runtime makes a record less memorable imo – rarely am I going to take time out of my day to listen to an album that is 2+ hours long. And Taylor is a GREAT album artist, no doubt. I just dislike the narrative that has sprung up that Taylor releasing vault tracks etc. is a sign that she is freeee from the shakles of Big Machine where evil man Scott B told her to cut all of those good songs >:( like. Scott B fucking sucks but having an editor on you who really brings out your strengths and teaches you to sharpen your skill and vision is not bad per se. (I don't think their particular relationship was healthy in that regard, but that's not shocking information.) Obviously this is in part due to the streaming era, but we still have artists who create albums™ and I hope Taylor remains one of them.
#Also thank u <3#Personally i am also super overwhelmed with the amount of music at times but i get that way about new content#Listening to red tv took me ages#Idk let's all just look at dance fever or chloë and the new 20th century and see the vision in tracklisting and aesthetics#It's just pleasant!!!#And taylor is soooo good at this stuff#Ideally there is a way for her to be this concise again without finding it stifling#It's just interesting that both popcast n evolution of a snake (VERY different viewpoints hstgh but a fun mix)#Noted that they feel as if this outpour of content might harm her legacy because they feel like it is less polished
10 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Photography by Francesca Woodman
#francesca woodman#fine art#sad#sadnes#snakes#woman#photography#reality#deep#arte#photograph#sztuka#20th century#famous#darkness#ghostly#haunting#bnw#film camera
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
The truth about Medusa and her rape... Mythology breakdown time!
With the recent release of the Percy Jackson television series, Tumblr is bursting with mythological posts, and the apparition of Medusa the Gorgon has been the object of numerous talks throughout this website… Including more and more spreading of misinformation, and more debates about what is the “true” version of Medusa’s backstory.
Already let us make that clear: the idea that Medusa was actually “blessed” or “gifted” by Athena her petrifying gaze/snake-hair curse is to my knowledge not at all part of the Antique world. I still do not know exactly where this comes from, but I am aware of no Greek or Roman texts that talked about this – so it seems definitively a modern invention. After all, the figure of Medusa and her entire myth has been taken part, reinterpreted and modified by numerous modern women, feminist activist, feminist movements or artists engaged in the topic of women’s life and social conditions – most notably Medusa becoming the “symbol of raped women’ wrath and fury”. It is an interesting reading and a fascinating update of the ancient texts, and it is a worthy take on its own time and context – but today we are not talking about the posterity, reinvention and continuity of Medusa as a myth and a symbol. I want to clarify some points about the ACTUAL myth or legend of Medusa – the original tale, as told by the Greeks and then by the Romans.
Most specifically the question: Was Medusa raped?
Step 1: Yes, but no.
The backstory of Medusa you will find very often today, ranging from mythology manuals (vulgarization manuals of course) to Youtube videos, goes as such: Medusa was a priestess of Athena who got raped by Poseidon while in Athena’s temple, and as a result of this, Athena punished Medusa by turning her into the monstrous Gorgon.
Some will go even further claiming Athena’s “curse” wasn’t a punishment but a “gift” or blessing – and again, I don’t know where this comes from and nobody seems to be able to give me any reliable source for that, so… Let’s put this out of there.
Now this backstory – famous and popular enough to get into Riodan’s book series for example – is partially true. There are some elements here very wrong – and by wrong I do mean wrong.
The story of Medusa being raped and turned into a monster due to being raped does indeed exist, and it is the most famous and widespread of all the Medusa stories, the one people remembered for the longest time and wrote and illustrated the most about. Hence why Medusa became in the 20th century this very important cultural symbol tied to rape and the abuse of women and victim-blaming. HOWEVER – the origin of this story is Ovid’s Metamorphoses, from the first century CE or so. Ovid? A Roman poet writing for Roman people. “Metamorphoses”? One of the two fundamental works of Roman literature and one of the two main texts of Roman mythology, alongside Virgil’s Aeneid. This is a purely Roman story belonging to the Roman culture – and not the Greek one. The story of Medusa’s rape does not have Greek precedents to my knowledge, Ovid introduced the element of rape – which is no surprise given Ovid turned half of the romances of Greek mythology into rapes. Note that, on top of all this, Ovid wasn’t even writing for religious purposes, nor was his text an actual mythological effort – he wrote it with pure literary intentions at heart. It is just a piece of poetry and literature taking inspiration from the legends of the Greek world, not some sort of sacred text.
Second big point: The legend I summarized above? It isn’t even the story Ovid wrote, since there are a lot of elements that do not come from Ovid’s retelling of the story (book fourth of the Metamorphoses). For example Ovid never said Medusa was a priestess of Athena – all he said was that she was raped in the temple of Athena. I shouldn’t even be writing Athena since again, this is a Roman text: we are speaking of Minerva here, and of Neptune, not of Athena or Poseidon. Similarly, Minerva’s curse did not involve the petrifying gaze – rather all Ovid wrote about was that Minerva turned Medusa’s hair into snakes, to “punish” her because her hair were very beautiful, and it was what made her have many suitors (none of which she wanted to marry apparently), and it is also implied it is what made Neptune fall in love (or rather fall in lust) with her. I guess it is from this detail that the reading of “Athena’s curse was a gift” comes from – even though this story also clearly does victim-blaming of rape here.
But what is very fascinating is that… we are not definitively sure Neptune raped Medusa in Ovid’s retelling. For sure, the terms used by Ovid in his fourth book of Metamorphoses are clear: this was an action of violating, sexually assaulting, of soiling and corrupting, we are talking about rape. But Ovid refers several other times to Medusa in his other books, sometimes adding details the fourth-book stories does not have (the sixth book for examples evokes how Neptune turned into a bird to seduce Medusa, which is completely absent from the fourth book’s retelling of Medusa’ curse). And in all those other mentions, the terms to designate the relationship between Medusa and Neptune are more ambiguous, evoking seduction and romance rather than physical or sexual assault. (It does not help that Ovid has an habit of constantly confusing consensual and non-consensual sex in his poems, meaning that a rape in one book can turn into a romance in another, or reversal)
But the latter fact makes more sense when you recall that the rape element was invented and added by Ovid. Before, yes Poseidon and Medusa loved each other, but it was a pure romance, or at least a consensual one-night. Heck, if we go back to the oldest records of the love between Poseidon and Medusa, back in Hesiod’s Theogony, we have descriptions of the two of them laying together in a beautiful, flowery meadow – a stereotypical scene of pastoral romances – with no mention of any brutality or violence of any sort. As a result, it makes sense the original “romantic” story would still “leak” or cast a shadow over Ovid’s reinvented and slightly-confused tale.
Step 2: So… no rape?
Well, if we go by Greek texts, no, apparently Medusa was not raped in Greek mythology, and only became a rape victim through Ovid.
The Ancient Greek texts all record Poseidon and Medusa sleeping with each other and having children, but no mention of rape. And the whole “curse of Athena” thing is not present in the oldest records – no temple of Athena soiling, no angry Athena cursing a poor girl… “No curse?” you say “But then how did Medusa got turned into a Gorgon”? Answer: she did not. She was born like that.
As I said before, the oldest record of Medusa’s romance but also of her family comes from Hesiod’s Theogony (Hesiod being one of the two “founding authors” of Greek mythology, alongside Homer – Homer did wrote several times about Medusa, but only as a disembodied head and as a monster already dead, so we don’t have any information about her life). And what do we learn? That Medusa is part of a set of three sisters known as the Gorgons – because oh yes, Ovid did not mention Medusa’s sister now did he? How did Medusa’s sisters ALSO got snake-hair or petrifying-gaze if only Medusa was cursed for sleeping with Neptune? Ovid does not give us any answer because again, it is an “adaptational plot hole”, and the people that try to adapt Ovid’s story have to deal with the slight problem of Stheno and Euryale needing to share their sister’s curse despite seemingly not being involved in the whole Neptune business. Anyway, back to the Greek text.
So, you have those three Gorgon sisters, and Medusa is said to be mortal while her sisters are not. Why is it such a big deal? Because Medusa wasn’t originally some random human or priestess. Oh no! Who were the Gorgons’ parents? Phorcys and Keto/Ceto, aka two sea-gods. Not just two sea-gods – two sea-gods of the ancient, primordial generation of sea-gods, the one that predated Poseidon, and that were cousins to the Titans, the sea-gods born of Gaia mating with Pontos.
So the Gorgons were “divine” of nature – and this is why Medusa being a mortal was considered to be a MASSIVE problem and handicap for her, an abnormal thing for the daughter of two deities. But let’s dig a bit further… Who were Phorcys and Ceto? Long story short: in Greek mythology, they were considered to be sea-equivalents of Typhon and Gaia. They were the parents of many monsters and many sea-horrors: Keto/Ceto herself had her name attributed and equated with any very large creature (like whales) or any terrifying monster (like dragons) from the sea. The Gorgons themselves was a trio of monsters, but their sisters, that directly act as their double in the myth of Perseus? The Graiai – the monstrous trio of old women sharing one eye and one tooth. Hesiod also drops the fact that Ladon (the dragon that guarded the golden apples of the Hesperids), and Echidna (the snake-woman that mated with Typhon and became known as the “mother of monsters”) were also children of Phorcys and Ceto, while other authors will add other monster-related characters such as Scylla (of Charybdis and Scylla fame), the sirens, or Thoosa (the mother of Polyphemus the cyclop). Medusa herself is technically a “mother of monsters” since she birthed both Pegasus the flying horse and Chrysaor, a giant. So here is something very important to get: Medusa, and the Gorgons, were part of a family of monsters. Couple that with the absence of any mention of curses in these ancient texts, and everything is clear.
Originally Medusa was not a woman cursed to become a monster: she was born a monster, part of a group of monster siblings, birthed by monster-creating deities, and she belonged to the world of the “primordial abominations from the sea”, and the pre-Olympian threats, the remnants of the primordial chaos. It is no surprise that the Gorgons were said to live at the edge of the very known world, in the last patch of land before the end of the universe – in the most inhuman, primitive and liminal area possible. They were full-on monsters!
Now you might ask why Poseidon would sleep with a horrible monster, especially when you recall that the Greeks loved to depict the Gorgons as truly bizarre and grotesque. It wasn’t just snake-hair and petrifying gaze: they had boar tusks, and metallic claws, and bloated eyes, and a long tongue that constantly hanged down their bearded chin, and very large heads – some very old depictions even show her with a female centaur body! In fact, the ancient texts imply that it wasn’t so much the Gorgon’s gaze or eyes that had the power to turn people into stone – but that rather the Gorgon was just so hideous and so terrifying to look at people froze in terror – and then literally turned into stone out of fear and disgust. We are talking Lovecraftian level of eldritch horror here. So why would Poseidon, an Olympian god, sleep with one of these horrors? Well… If you know your Poseidon it wouldn’t surprise you too much because Poseidon had a thing for monsters. As a sort of “dark double” of Zeus, whereas Zeus fell in love with beautiful princesses and noble queens and birthed great gods and brave heroes, Poseidon was more about getting freaky with all sorts of unusual and bizarre goddesses, and giving birth to bandits and monsters. A good chunk of the villains of Greek mythology were born out of Poseidon’s loins: Polyphemus, Antaios, Orion, Charybdis, the Aloads… And even his most benevolent offspring has freaky stuff about it – Proteus the shapeshifter or Triton half-man half-fish… So yes, Poseidon sleeping with an abominable Gorgon is not so much out of character.
Step 3: The missing link
Now that we established what Medusa started out as, and what she ended up as… We need to evoke the evolution from point Hesiod to point Ovid, because while people summarized the Medusa debate as “Sea-born monster VS raped and punished woman”, there is a third element needed to understand this whole situation…
Yes Ovid did invent the rape. But he did not invent the idea that Medusa had been cursed by Athena.
The “gorgoneion” – the visual and artistic motif of the Gorgon’s head – was, as I said, a grotesque and monstrous face used to invoke fright into the enemies or to repel any vile influence or wicked spirit by the principle of “What’s the best way to repel bad stuff? Badder stuff”. Your Gorgon was your gargoyle, with all the hideous traits I described before – represented in front (unlike all the other side-portraits of gods and heroes), with the face being very large and flat, a big tongue out of a tusked-mouth, snake-hair, bulging crazy eyes, sometimes a beard or scales… Pure monster. But then… from the fifth century BCE to the second century BCE we see a slow evolution of the “gorgoneion” in art. Slowly the grotesque elements disappear, and the Gorgon’s face becomes… a regular, human face. Even more: it even becomes a pretty woman’s face! But with snakes instead of hair. As such, the idea that Medusa was a gorgeous woman who just had snakes and cursed-eyes DOES come from Ancient Greece – and existed well before Ovid wrote his rape story.
But what was the reason behind this change?
Well, we have to look at the Roman era again. Ovid’s tale of Medusa being cursed for her rape at the hands of Neptune had to rival with another record collected by a Greek author Apollodorus, or Pseudo-Apollodorus, in his Bibliotheca. In this collection of Greek myths, Apollodorus writes that indeed, Medusa was cursed by Athena to have her beautiful hair that seduced everybody be turned into snakes… But it wasn’t because of any rape or forbidden romance, no. It was just because Medusa was a very vain woman who liked to brag about her beauty and hair – and had the foolish idea of saying her hair looked better than Athena’s. (If you recall tales such as Arachne’s or the Judgement of Paris, you will know that despite Athena being wise and clever, one of her main flaws is her vanity).
“Wait a minute,” you are going to tell me, “The Bibliotheca was created in the second century CE! Well after Greece became part of the Roman Empire, and after Ovid’s Metamorphoses became a huge success! It isn’t a true Greek myth, it is just Ovid’s tale being projected here…” And people did agree for a time… Until it was discovered, in the scholias placed around the texts of Apollonios of Rhodes, that an author of the fifth century BCE named Pherecyde HAD recorded in his time a version of Medusa’s legend where she had been cursed into becoming an ugly monster as punishment for her vanity. We apparently do not have the original text of Pherecyde, but the many scholias referring to this lost piece are very clear about this. This means that the story that Apollodorus recorded isn’t a “novelty”, but rather the latest record of an older tradition going back to the fifth century BCE… THE SAME CENTURY THAT THE GORGONEION STARTED LOSING THEIR GROTESQUE, and that the face of Medusa started becoming more human in art.
[EDIT: I also forgot to add that this evolution of Medusa is also proved by strange literary elements, such as Pindar's mention in a poem of his (around 490 BCE) of "fair-cheeked Medusa". A description which seems strange given how Medusa used to be depicted as the epitome of ugliness... But that makes sense if the "cursed beauty" version of the myth had been going around at the time!]
And thus it is all connected and explained. Ovid did invent the rape yes – but he did not invent the idea of Athena cursing Medusa. It pre-existed as the most “recent” and dominating legend in Ancient Greece, having overshadowed by Ovid’s time the oldest Hesiodic records of Medusa being born a monster. So what Ovid did wasn’t completely create a new story out of nowhere, but twist the Greek traditions of Athena cursing Medusa and Medusa having a relationship with Poseidon, so that the two legends would form one and same story. And this explains in retrospect why Ovid focuses so much on describing Medusa’s beautiful hair, and why Ovid’s Minerva would think turning her hair into snake would be a “punishment fit for the crime”: these are leftovers of the Greek tale where Medusa was punished for her boasting and her vanity.
CONCLUSION
Here is the simplified chronology of how Medusa’s evolution went.
A) Primitive Greek myths, Hesiodic tradition: Born a monster out of a family of sea-monsters and monstrous immortals. Is a grotesque, gargoylesque, eldritch abomination. Athena has only an indirect conflict with her, due to being Perseus’ “fairy godmother”. Has a lovely romance with Poseidon.
B) Slow evolution throughout Classical Greece and further: Medusa becomes a beautiful, human-looking girl that was cursed to have snake for hair and petrifying eyes, instead of being a Lovecraftian horror people could not gaze upon. Her conflict with Athena becomes direct, as it is Athena that cursed her due to being offended by her vain boasting. Her punishment is for her vanity and arrogant comparison to the goddess.
C) Ovid comes in: Medusa’s romance with Poseidon becomes a rape, and she is now punished for having been raped inside Athena’s temple.
[As a final note, I want to insist upon the fact that the story of Medusa being raped is not less "worthy" than any other version of the myth. Due to its enormous popularity, how it shaped the figure of Medusa throughout the centuries, and how it still survives today and echoes current-day problems, to try to deny the valid place of this story in the world of myths and legends would be foolish. HOWEVER it is important to place back things in their context, to recognize that it is not the ONLY tale of Medusa, that it was NOT part of Greek mythology, but rather of Roman legends - and let us all always remember this time Poseidon slept with a Lovecraftian horror because my guy is kinky.]
EDIT:
For illustration, I will place here visuals showing how the Ancient art evolved alongside Medusa's story.
Before the 5th century BCE: Medusa is a full-on monster
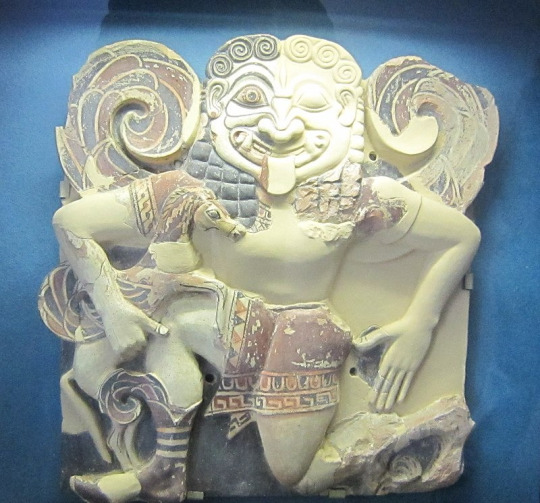






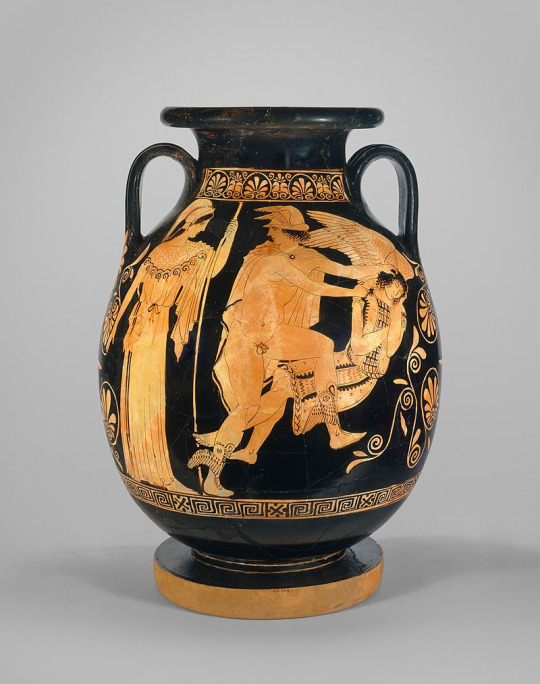
From the 5th century to the 2nd century BCE: A slow evolution as Medusa goes from a full-on monster to a human turned into a monster. As a result the two depictions of the grotesque and beautiful gorgoneion coexist.



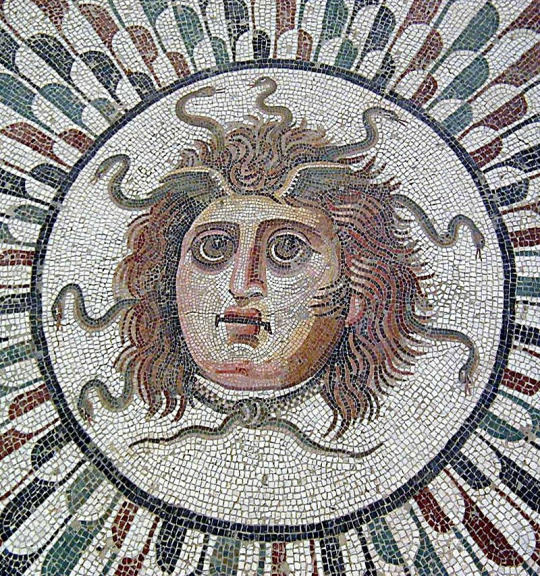
Post 2nd century BCE: Medusa is now a human with snake hair, and just that



#greek mythology#medusa#gorgon#athena#gorgons#poseidon#neptune#minerva#ovid#rape in mythology#greek monsters#roman mythology
4K notes
·
View notes
Text



For #WorldSerpentDay: Manasa, the Hindu snake goddess, trio of late 19th/early 20th c. Indian images:
1. Manasa, The Snake Goddess
c. 1890, Kalighat
watercolor, graphite, ink, and tin on paper
Cleveland Museum of Art
2. "Manasa, goddess presiding over snakes."
c.1895, Calcutta (Kolkata)
color lithograph/popular print
British Museum
3. Manasa, The Snake Goddess
c. 1920, West Bengal
by Jamini Roy (Indian, 1887–1972)
watercolor painting, gouache on paper
San Diego Museum of Art
#snake#snakes#serpent#serpents#snake goddess#serpent goddess#reptiles#19th century#20th century#1890s#1920s#Indian art#South Asian art#Hindu art#print#lithograph#painting#watercolor#works on paper#Cleveland Museum of Art#British Museum#San Diego Museum of Art#World Serpent Day#animals in art
20 notes
·
View notes
Note
What did Rocky think of the cornflakes?
It's not a Kellogg reference - not directly anyway. Kellogg is remembered because it was one of the few lasting things that emerged from an otherwise sprawling wellness fad.
There were mineral spring, hot spring, and medicinal spring resorts, spas, retreats, and hotels all over the US in the late 19th and early 20th century. Some were small and are all but forgotten to time. Some ended up with whole towns built up around them. Ultimately, the trend dried up as trends do, making way for the next thing. Its end may have been hastened somewhat by the government cracking down more forcefully on snake oil medicine starting in the 1900s, though.
No doubt some people gained some easily explained benefit from vacationing away from city air thick with coal dust to relax in a naturally occurring pool, but some facilities were also doing things like bottling and selling such waters without proper sanitization, and claiming it had vague yet miraculous curative properties.
Here are the ruins at Welch Spring - one such example in the Ozarks. It's an off-the-beaten-path place I went to check out while the pandemic was at its peak.
364 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Gladdest Thing Under the Sun
I honestly thought we were supposed to wait a couple of days after the zine’s release, but, heck, everyone else is doing it, so here we are: My contribution to @gensokyozine . I’ve wanted to do this story for a while, so I hope you enjoy!







Descriptive text for the visually impaired or for easy quotation:
PAGE 1
Title: "Shadowjack presents: The Gladdest Thing under the Sun"
Yuuka Kazami, a youkai woman, climbs the cracked stone steps to the ramshackle Hakurei Shrine. She carries a parasol. Up the wooded hill, through the pines, stand the shrine gate and two guardian komainu -- one of whom, Aunn, is alive and waving cheerfully, tail wagging. The plum and cherry trees atop the hill are in bloom. Dandelions sprout as Yuuka passes.
PAGE 2, PANEL 1
Title: "Yuuka Kazami, Flower Mistress of the Four Seasons"
Yuuka wears a summer outfit that evokes the mid-20th century: a vest over a short-sleeved blouse with a necktie, a knee-length pencil skirt, hose and heels, a handkerchief neatly folded in her vest pocket. She also wears glossy leather gauntlets and tight sleeve garters. Her hair is bobbed and curled in 1930s fashion. Her eyes are slitted, like a snake's.
She rests her head on her hand and gazes up at Reimu, rapt. A cat with black and white fur, spotted something like a yin-yang ball, lies nearby, watching her carefully.
PAGE 2, PANEL 2
Title: "Reimu Hakurei, Mysterious Shrine Maiden of Paradise"
Reimu, a human woman with a long ponytail, looks down at Yuuka, sweating slightly. She says, "Um... you know..."
PAGE 2, PANEL 3
Reimu wears her usual red-white shrine maiden robes and ribbons, much patched and threadbare. She is barefoot on the porch, holding a broom.
Reimu: "When you look at me like that, I get the feeling I'm about to be CUT and PRESSED."
Yuuka is shocked. "Oh, my! I would NEVER. A wild flower is best viewed in its natural habitat, always!"
PAGE 2, PANEL 4
Reimu, smiling: "I'm a wildflower?"
Yuuka, grinning: "One of the best!"
PAGE 3, PANEL 1
Reimu greets Yuuka at the entrance to her residence. Yuuka bows formally. She has brought a package, wrapped in cloth with a floral pattern.
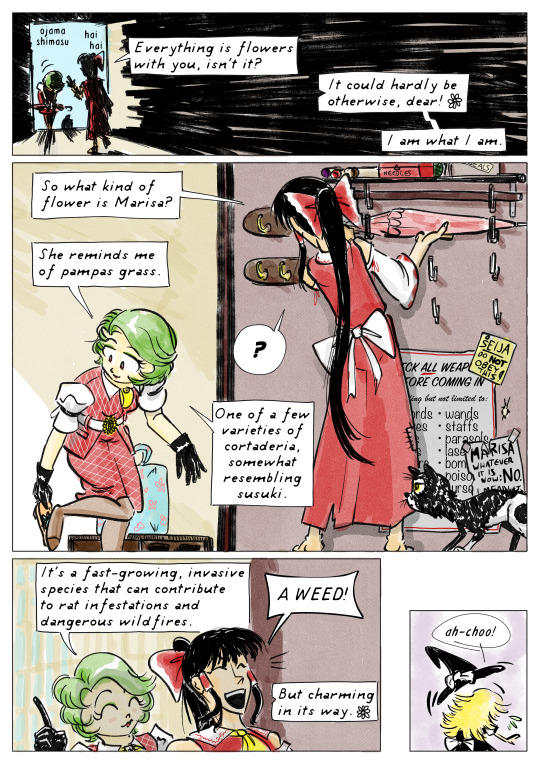
Yuuka: "Ojama shimasu."
Reimu: "Hai, hai."
Reimu: "Everything is flowers with you, isn't it?"
Yuuka: "It could hardly be otherwise, dear! I am what I am."
PAGE 3, PANEL 2
Yuuka takes off her shoes, while Reimu places the parasol on the weapons rack by the door. The top shelf holds scrolls, boxes labelled "needles" and "seals", and one Mk 2 hand grenade.
A large sign by the rack says in printed text, "Check ALL weapons before coming in! Including but not limited to: Swords, Axes, Bows, Spears, Guns, Wands, Staffs, Parasols, Lasers, Bombs, Poisons, Curses," and so on.
A handwritten post-it note has been tacked to it, saying, "SEIJA -- Do NOT obey this!"
Another, ripped and faded sign has been taped by the list, adding, "MARISA -- Whatever it is now: NO. I mean it."
There is a bullethole next to the sign.
A different yin-yang cat watches Yuuka.
Reimu says, "So what kind of flower is Marisa?"
Yuuka: "She reminds me of pampas grass."
Reimu: "?"
Yuuka: "One of a few varieties of cortaderia, somewhat resembling susuki."
PAGE 3, PANEL 3
The two women go inside where there's more shade.
Yuuka: "It's a fast-growing, invasive species that can contribute to rat infestations and dangerous wildfires."
Reimu, laughing: "A WEED!"
Yuuka: "But charming in its way."
PAGE 3, PANEL 4, OFFSET
Somewhere, Marisa sneezes.
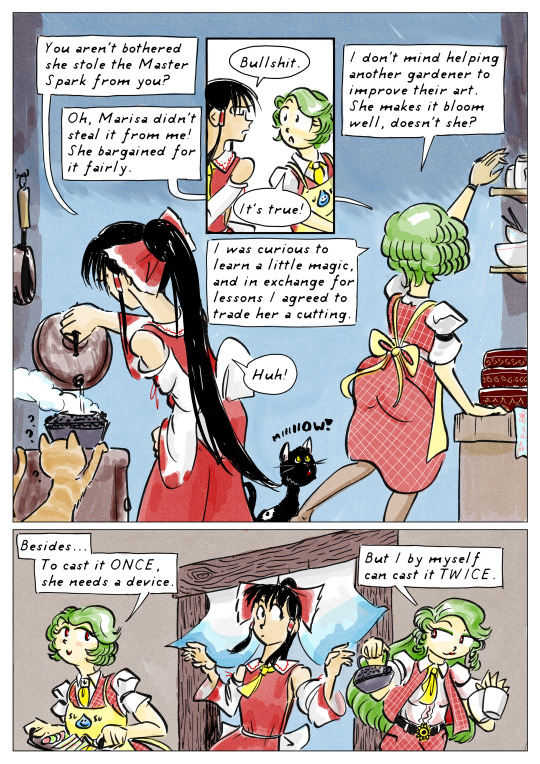
PAGE 4, PANEL 1
In Reimu's kitchen, the two together prepare afternoon tea, while two different cats beg at their feet. Reimu pours hot water from a large kettle into a cast-iron teapot. Yuuka takes down bowls and cups, and opens up the Japanese-style lunchboxes she brought.
Yuuka has put on an apron that parodies the "piyo piyo apron" worn by Kyoko in the manga "Maison Ikkoku", but instead of a drawing of a baby chick on the chest, it has a drawing of a Dragon Quest slime, saying "suu suu".
Reimu: "You aren't bothered she stole the Master Spark from you?"
Yuuka: "Oh, Marisa didn't steal it from me! She bargained for it fairly."
Reimu stops what she's doing to turn toward Yuuka. "Bullshit."
Yuuka: "It's true! I was curious to learn a little magic, and in exchange for lessons I agreed to trade her a cutting."
Reimu: "Huh!"
Yuuka: "I don't mind helping another gardener to improve their art. She makes it bloom well, doesn't she?"
PAGE 4, PANEL 2
Yuuka carries a tray of sandwiches and snacks out of the kitchen.
Yuuka: "Besides... to cast it ONCE, she needs a device."
A surprise second Yuuka, with long hair, and wearing trousers instead of a skirt, whisks the teapot and cups from Reimu's hands, leaving Reimu with nothing to do.
Yuuka, the second: "But I by myself can cast it TWICE."
PAGE 5, PANEL 1
Only one Yuuka again. Yuuka and Reimu kneel on the veranda to take their tea. One yin-yang cat nearby sprawls asleep in the sun, an orange tabby circles curiously, and a third cat sulks by Reimu.
Reimu: "Okay, then how about... Alice?"
Yuuka: "Ohhh... Alice is special. With her pride and ingenuity, she bears the seed of great potential for power."
PAGE 5, PANEL 2
Yuuka beams with enthusiasm. She says, "Why, if one could but prune away a few of her mortal failings -- such as 'restraint' or 'mercy' -- she could make a truly MARVELLOUS youkai!"
We can now observe that Yuuka's necktie is not knotted, but instead held by a silver woggle marked with a "lily of the valley" emblem.
PAGE 5, PANEL 3
Yuuka blushes happily. "She might even be stronger than I. Wouldn't that be an interesting day?" A heart floats in her words.
Reimu tries to hide her concern. She thinks, "Ganbatte, Alice-san..." But only says out loud, "...er, uh... and Yukari?"
PAGE 6, PANEL 1
Yuuka grins wolfishly. "Yukari and I have an arrangement: She doesn't meddle in my garden, and I don't BURN DOWN hers."
Reimu: "Isn't it weird that a youkai of FLOWERS is so good at fighting?"
Yuuka: "I'm surprised to hear that from a Japanese!"
Reimu: "You say that like you're not."
PAGE 6, PANEL 2
Yuuka: "I am known in many lands, by many names, wherever flowers grow."
Yuuka narrates the scene from the foreground, wearing a woman's kimono and lacquered okobo sandals. She carries now a Japanese-style paper parasol. Her hair is tied up in a bun with a cherry-blossom kanzashi, and she wears a sunflower hair ornament. She is surrounded by flowers: chrysanthemum, hollyhock, and birthwort, and above her spreads blooming sakura.
Yuuka: "Did not your own samurai describe themselves as cherry blossoms, and fight for emperor and shogun under the banners of the chrysanthemum and hollyhock?"
In the midground, two armored samurai clash. The lower-status one has fallen to the ground; the richer has a bloody slash across his left eye. He swings his sword and chops the grounded man's spear in two, but the other is undaunted.
In the background, an army of horse and foot mounts the top of the hill, banners billowing.
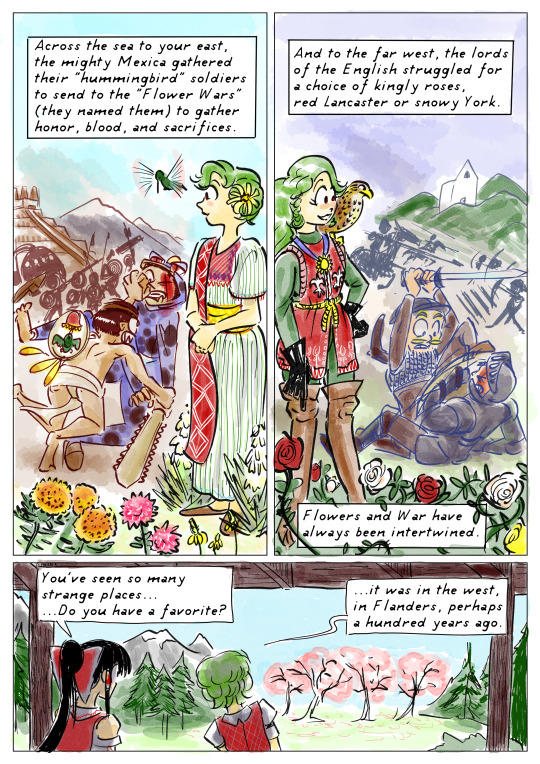
PAGE 7, PANEL 1
Now Yuuka narrates wearing a huipil dress with embroidered shawl, and simple leather slippers. Her hair is done in buns, with a Mexican sunflower by her ear. A hummingbird flies near her. Growing around her are Aztec marigold, dahlias, banana yucca, and Mexican hat flowers.
Yuuka: "Across the sea to your east, the mighty Mexica gathered their 'hummingbird' soldiers to send to the 'Flower Wars' (they named them) to gather honor, blood, and sacrifices."
In the midground, the fighters are now two Nahuatl, one poor, one rich with a slashed left eye. The poorer one wears only a loincloth, and has a shield slung over his shoulder. His shield is painted with a hummingbird design, and from it hang a few feathers. The richer soldier wears a full-body jaguar costume, and wields a macuahuitl war-club. The poor soldier leaps to his feet and tackles his enemy, disarming him.
In the background, an army of Aztecs battle below a stepped pyramid and high mountains.
PAGE 7, PANEL 2
Now Yuuka narrates wearing men's doublet and hose, embroidered with fleur-de-lis and tulips, along with knee-high riding boots and gauntlets. Around her neck is a sunflower pendant. On her shoulder perches a falcon. About her feet, and entangling the narration boxes, are red, white, and yellow roses.
Yuuka: "And to the far west, the lords of the English struggled for a choice of kingly roses, red Lancaster or snowy York."
In the midground, the fighters are now two Englishmen, again one poorer, the other richer with the eye injury. The poorer soldier has some mail pieces and a simple brimmed helmet; the richer has plate armor, a full helm, and a shield. The rich fighter is overthrown, his foe about to stab him through the visor with his own arming sword.
In the background, mounted knights charge a line of archers behind wooden stakes. A church or fort stands on hills in the far distance.
Yuuka: "Flowers and War have always been intertwined."
PAGE 7, PANEL 3
We return to Reimu's veranda and cherry trees.
Reimu: "You've seen so many strange places... Do you have a favorite?"
Yuuka: "...it was in the west, in Flanders, perhaps a hundred years ago."
PAGE 8, PANEL 1
Yuuka invisibly narrates: "Such a war, Reimu! The men burrowed like moles, or took to the air like kites."
Above barbed wire, two airplanes spit tracers at each other. It is World War One.
PAGE 8, PANEL 2
Yuuka: "They plowed the earth with cannon, night and day."
Shirtless German artillerymen fire their gun amid sandbags. Something explodes close by.
PAGE 8, PANEL 3
Yuuka: "They slew by shot and poison, fire and blade."
A gasmasked French soldier, armed with pistol and entrenching tool, cautiously moves down a trench. An unseen enemy waits around the corner with rifle and bayonet.
PAGE 8, PANEL 4
Yuuka: "And for no purpose that I could see, no treasure nor slave."
Barbed wire and ruined buildings.
PAGE 8, PANEL 5
Yuuka, narrating: "The destruction was so maniacal it seemed no tree, no blade of grass, would ever grow there again. I thought you humans had gone absolutely mad!"
Yuuka, wearing colorful hat, coat, and umbrella, stands on a windy no-man's land, surrounded by dull mud and broken pieces. Tracer fire crosses the sky, coming from a distant machine-gun nest. She notices, but does not bother to avoid, the few bullets that land near her.
Yuuka, narrating: "But it was I who did not understand your passion. When I learned your true intentions, I was deeply humbled."
PAGE 8, PANEL 6
Yuuka, narrating: "Did you know, Reimu? You can find graves in the wild by how the flowers grow. (Bone meal makes such good fertilizer.)"
The corpse of a soldier lies upon the ruined earth. But near his outstretched arm, a single bluebell, and a few patches of grass, have sprouted.
PAGE 8, PANEL 7
Now there are no bodies, but grass and wildflowers and bumblebees cover the ground. A shattered helmet has a flower growing through the holes.
Yuuka, narrating: "I tell you that after this great war, those fields FLUORISHED with color. Rainbows spilled on seas of green grass!"
PAGE 9
Yuuka, narrating: "And ever after, all through those lands, the people wore blood-red poppies, to remember and give thanks to their kindred who slept below, for this sight they had worked so hard to create."
Yuuka wears early-20th century men's hunting clothes: a sturdy jacket and breeches with knee-high boots and gloves. Her curled hair is in a loose pompadour. As ever, she has a parasol. The sun shines warmly. The hill Yuuka walks down is covered in grass and bright red poppy flowers, stretching on forever. The plants almost completely cover a few remaining pieces of military hardware: a broken machine-gun, a lost helmet, a twist of barbed wire. Yuuka smiles.
Yuuka, narrating: "Tens of thousands of men willingly buried themselves for nothing better than the GLORY of FLOWERS!"
PAGE 9, PANEL 2, INSET
We return to Reimu's veranda. Yuuka clutches a handkerchief, almost overcome with romantic tears.
Yuuka: "It was the most beautiful thing that I have ever seen!"
Reimu stares at her and says nothing.
PAGE 10, PANEL 1
Yuuka says, "Excuse me!", wipes her tears, and takes out her compact to redo her makeup.
Reimu thinks, "Yuuka is one of my oldest friends, but she really is a monster, isn't she? I don't even know how to BEGIN to explain the truth to her... or if I even should."
PAGE 10, PANEL 2
Title: "FLOWERS appearing in this story."
Many cut flowers are arranged on a wooden surface, with identifying captions. In no particular order, they are: primrose, fleur-de-lis (yellow iris), common sunflower, anemone, dandelion, Mexican sunflower, tulip, rose, cempoalxóchitl (Aztec marigold), dahlia, banana yucca, Mexican hat flower, pineapple sage, bee orchid, celandine, Flanders poppy, lily-of-the-valley, bluebell, daffodil, kiku (chrysanthemum), aoi (birthwort), hollyhock, ume (Japanese plum), and sakura (Japanese cherry).
PAGE 10, PANEL 3
In a simplified art style:
Reimu pats Alice on the shoulder and says, "Alice, we sure attract some weird ones, don't we?"
Alice wears her usual workdress and hairband, but also has sturdy explosive ordnance disposal goggles and gloves. She is inserting a stick of dynamite into the back of a Hatsune Miku doll. Other dolls and marionettes (and one teddy bear) fill the room, all with visible dynamite fuzes sticking out of their heads, and all with glowing eyes.
Alice says, "Don't disturb me when I'm setting the explosive charges! If they went off, they could hurt the dolls."
Reimu: "...This is why she likes you, you know."
Alice: "?"
END
237 notes
·
View notes
Text
A thing on Uran and Helena in Pluto

Okay a short little thing on Pluto. Uran and Helena are my absolute favourite characters in Pluto. Urasawa has always had amazing side characters, from Mr. Rosso in Monster to Lee Harvey Oswald and Jackie in Billy Bat to God in 20th Century Boys, but very few have tied off the emotional ends of the story like Uran and Helena.
Maybe I'm projecting here but much like myself I feel like Urasawa is absolutely obsessed with Frankenstein. And he recognizes the influence Frankenstein has on Dr. Umataro Tenma. Or at the very least, the similarities between the two. And so when he made the protagonist of one of his most popular works Monster, Dr Kenzo Tenma, he solidified that connection. Kenzo Tenma calls back to Victor Frankenstein needing to end his creation while also calling back to Japan's other famous Tenma, thus making the connection explicit. Another throughline between the three of them is that all three are father figures to their creations and have obligations to their children, though all three have varying levels of success with them.
I've only read what I like to call Urasawa's "Core Four", conspiracy minded thrillers that are essentially road trips featuring usually two main protagonists that we see the world through, Monster, 20th Century Boys, Pluto and Billy Bat. Though I still haven't caught up to Asadora and that could still possibly fit this mold, Urasawa's Core Four share a lot of themes and ideas. One of the most important being the responsibility for one's creations, whether it was Kenji Endo and the Book of Prophecy or Kevin Yamagata and Billy Bat or Dr. Kenzo Tenma and Johan, all of his protagonists could arguably be seen as someone with the need to take up the responsibility of their creations. So where do the protagonists of Pluto fit in there? That's where Uran and Helena come in.
But first, we should take a look at Pluto's themes. While I could be wrong, at a cursory glance, I feel like the general consensus towards it's themes is that it's about hatred. I don't really think that's what it is as I feel like Urasawa is more trying to show us what it is to be human and what it is to be alive. And in that, he has a hidden protagonist in Pluto. Someone who's influence snakes through the plot and isn't seen much, but without who the story's themes would remain incomplete. Pluto tackles what it is to be alive through many things, such as memory, sadness, grief, hatred, love and parenthood. But none of that works without the realization by Tenma of his own mistakes. And Uran and Helena bookend these revelations and are absolutley key to understanding that.

In my favourite chapter of the series, Chapter 37, Uran goes from person to person as she finds a way to deal with her grief and eventually comes across Tobio's grave, Tenma having left recently. It's an absolutely beautiful chapter that shows Uran's humanity and Urasawa's love for sharing these kind and soft moments. But it also sheds a light on Tenma as Uran realizes someone who was grieving has just left. Without saying much at all we realize that Tenma has finally realized his mistakes. In the process of grieving one son, he lost the other. While remembering Tobio, he let Atom go. His grief towards Tobio is clear in the following chapter, Chapter 38. All of the things he wanted Atom to be; Tobio come back to life, Tobio's ghost punishing him, Atom rejected. And Tenma could only see that rejection, and not what he had, another son.

Uran shows us very clearly what Pluto, the story, is. It's a chapter in their lives. And we've come into a story nearing the end for Tenma. And it's through the humanity of two absolutely amazing characters in their own right, Uran and Helena, that we are able to so fully understand Tenma. Despite being robots, these two characters are the most alive of everyone. They love fully and freely and are catalysts of change. Uran's vibrant and full of life in a way that really sticks out. And Helena has such depth that it's evident in every scene she's in. She's not pointed out to be made by any famous scientist so all the life she has is her own. These two represent the life of robot's more than any other characters in the series.
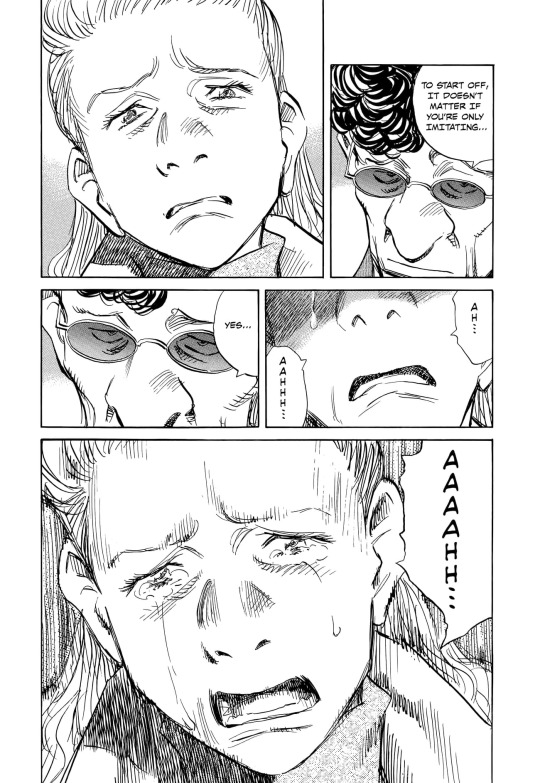


So it's that much more poignant when Helena finally breaks down after putting on such a strong front of everybody. Grief intersects and she brings out Tenma's sadness as well. They've both been putting up such strong fronts that it's heartbreaking to see them collapse. It completes Tenma's growth and strikes a heartbreaking contrast between the two. Tenma became the way he is through the loss of his son whereas Helena doesn't even get to remember her own loss. It makes you wonder if the grief for her and Geischt's child compounds her sorrow too.

Without these two and their grief, a large part of Pluto becomes inaccessible. Pluto is largely about death so when two characters come in who've never had a hand in the grim work of taking life, you see the world through a lens that's absolutely crucial in order to fully connect with all of the character's and their situations. Death and Grief has scarred the characters in Pluto. Time and time again they've chosen the worst path. They've chosen revenge and hatred. But Uran and Helena are different. Without them, the story is incomplete. They provide an alternative. They provide the path towards healing.
im sorry for this one:

#naoki urasawa's pluto#helena#uran#pluto#pluto anime#umataro tenma#astro boy#this was supposed to be short#also its largely unreasearched#i would need to read the original atom and read all of urasawa's other works and read up on the gulf war before tackling a proper piece#random thoughts I didn't put in:#something i love about Pluto is how each robot is a reflection of their creators in some way or another with Uran being Ochanamizu's love#the combination of jackie and lee harvey oswald will probably throw off so many people who don't know(totally not why I did it)#also God#honestly though no side characters feel insignificant in Pluto#Some more shared ideas between the Core Four are the burdens we carry and share and the importance of stories in our lives
142 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Statuette of a snake goddess
Early Aegean, Minoan Bronze Age, Late Minoan I Period or Modern about 1600–1500 B.C. or early 20th century
256 notes
·
View notes