#this is just how i view it as a modern reform jew
Note
if you feel like it (and if this question even ends up making sense lol), would you mind talking about how you feel about bruce being jewish? not like the idea of jewish bruce wayne, i mean the fact that in 2011 or so he was retconned kind of accidentally into being jewish. i ask bc i, as a jewish person, have a lot of mixed to negative feelings about the whole thing, and you seem not to. i really hope this doesn't come out as like judgy. i don't think you should feel negatively about it. i'm genuinely just interested in your thoughts and feelings about this. two jews, three opinions, lol
It's not judgy! As you said, two Jews, three opinions -- there's no right answer here.
As I mentioned in my Jewish Bruce post, the likely accidental ret-con of Bruce to likely being Jewish is a tricky subject. It's simultaneously a good moment for Jews who want to feel represented, and a bad one for those who think Bruce's story is not an adequate or appropriate vehicle to convey Judaism.
The reality is, Bruce isn't visibly Jewish now, nor is he practicing or displaying overt cultural, ethnic, or religious influences. He's Jewish by halacha, which is its own mess of significance for Jews.
Personally, I feel that Bruce's emergence as a Jew by halacha, and not by practiced religion or culture, is an important discussion to be had in our modern, interfaith, assimilating culture.
Barring the Orthodox communities, the number of young observant Jews is dropping. Jews are increasingly marrying into other faiths, assimilating, and raising their children outside of the faith. When Jews do stay in their communities, they tend to stay in more "liberal" ones such as Reconstructionist or Reform congregations. You can read more about this at the Pew site.
There are, and will continue to be, many people who find themselves cut off from Judaism and either halachically or ethnically Jewish in the next few years, with little to no connection to the religion, ethnicity, or cultural traditions.
So in this respect, Bruce being cut off from Judaism by nature of his family structure and abridged childhood is good to see, because it's representative of a new generation of Jewish children or interfaith families. Or it will be?
But. There are many Jews who do not identify with this at all -- who grew up in the community with strong ethnic, religious, and cultural ties, who see Bruce's (accidental?) ret-con to Judaism as rushed, dissatisfying, half-hearted, a million other words.
I don't want to assume what you or other Jews are thinking about this, but I can guess. It's not fun to see your religious identity thrown around somewhat flimsily, especially when there remains such a deep and consistent Jewish influence throughout the DC comics.
Why Bruce? Why not Hal? Why hint at it, or make him somewhat Jewish? Why not have a fully-Jewish character? Why not have a character who embraces Judaism as a belief system?
I think the mixed feelings over Bruce's ret-con highlight the growing divide within the Jewish community over who is, and isn't Jewish, and by which standards we judge those who are peripheral to the community.
Having worked with many converts and patrilineal Jews, I have deep sympathy for those cut off from the Jewish community, especially when it is by halachic rule. How can someone who was raised by a Jewish father, who is 50% Ashkenazi, who had a Bar Mitzvah and attends shul regularly, not be as Jewish as someone who was born to a Jewish mother and rarely, if ever, practiced the religion?
We make conversion to Judaism a tricky, difficult, and conditional process. Reform marriages and conversions are questioned by Orthodox rabbis and not considered valid by others. Some people are Jewish in one synagogue and not Jewish enough in another. It's so hard.
So yeah, in my other post linked above I think I called this a happy accident, which is how I'm trying to view it. It makes me happy to have a character to push Jewish headcanons and fic ideas into to, and to tease out the themes of community and what it means to truly be Jewish from Bruce's story. But I don't expect that to be everyone's else's experience at all.
I'd be curious to hear your, and anyone else's, thoughts on this. Again, two Jews, three opinions -- nobody is right here, and we all change our minds a LOT.
210 notes
·
View notes
Text
Shakespeare's Bohemian Rhapsodist
Joachim Gaunse was a Bohemian Jewish metallurgist whose innovative copper smelting technique was significant in England's victory over the 1588 Spanish Armada.
Gaunse (perhaps originally Gans) was also the first Bohemian (Czech) or Jew to visit the New World and becamethe putative model for 'Joabin' in Sir Francis Bacon's philosemitic novel, New Atlantis.

How could Shakespeare, surely eager to imitate the success of Christopher Marlowe's hatefest, The Jew of Malta, resist adding his own nuanced gloss on a subject that was so seriously important to the Elizabethans, that to be non-Christian - or not one of the right denomination - was to blaspheme; to be an enemy of both the State and of God and so face possible torture and public execution.
I reflect on this against the backdrop of a recent UK feminist production of The Merchant led by a Jewish actress who loathes the play, alongside ever-escalating global Jew hate and the cavernous rift in Israeli society caused by the fight for 'compassionate' democracy versus unyielding legalistic judicial reform.
Hey ho!
Our greatest modern writers need not make this up!
Just as the rigid Jewish nationalists trashed - no, devastated - an Arab village and were later seen dancing on the ruins with IDF personnel, I began reading Thomas Brackshaw's painstaking examination of how the concept of 'love' is treated in 11 of Shakespeare's best known plays.
For him, Shylock's Jewish heart is 'closed' while that of Christian Portia is opened most generously wide.
Back in the early 1970s, US-based Dr Brackshaw was probably working on his PhD thesis just as British scholar, A L Rowse first published his theory marking Emilia Bassano (Lanier) as 'the dark lady' of Shakespeare's sonnets.
My layperson's instinctive guess is that Shakespeare knew Gaunse as well as being Lanier's lover and that conversations with them both helped to seed the two pivotal, mirror-image speeches in the play (3.1.49–61 and 4.1.184-202) that make it soar sublimely higher than Marlowe's vicious grotesqueries.
So I ask Dr Brackshaw to consider Shakespeare's problematic black comedy from a Jewish as well as Christian perspective; to understand that 'mercy' is integral to Jewish tradition and that the Hebrew biblical concept of 'an eye for an eye' is an amalgam of several differrent passages that are not about vengeance but compensation.
By way of illustration, I suggest this is just one reason why the activities of the current Israeli government so deeply frighten vast swathes of its ordinary citizens. The argument is not really about the judiciary but that most of us worry about living in a puritanical, anachronistic theocracy of the type that has eternally used, abused and massacred us.
For example, some weeks ago a Knesset bill imposing the death penalty on terrorists who kill Israelis, was approved by a 55-9 majority in its preliminary reading.
Those casting their votes chose to forget the huge moral struggle the State of Israel underwent in its debate about whether to execute the Nazi, Adolf Eichmann.
When he was hanged in 1962, he became the only person ever to be executed in Israel on conviction by a civilian court. Secular law aside, this reflected the Talmudic view that a Sanhedrin (rabbinical supreme court) which effects an execution once in seven years – or even 70 years – should be branded a ‘destructive tribunal’.
I suggest that at the two points where the poetry in The Merchant is at its most rhapsodic, this wonderful drama about antisemitism itself becomes hateful as it propagates the tedious canards about pitiless Jewish revenge against saintly Christian mercy.
Although I must therefore disagree with Dr Brackshaw's stance, I thoroughly enjoyed reading this particular chapter of In the Theater of Love: An Analysis of Shakespeare's Major Plays and much appreciate that he endeavours to make Shakeseare's work 'accessible' to lay enthusiasts like me.
In the Theater of Love: An Analysis of Shakespeare's Major Plays is available from Amazon on Kindle and in paperback.
© Natalie Wood
25 March 2023
0 notes
Text
A “brief” reference guide to modern Jewish denominations / Jewish Writing Advice / Jewish Identity / Jewish Reference Guide [graphic at bottom]
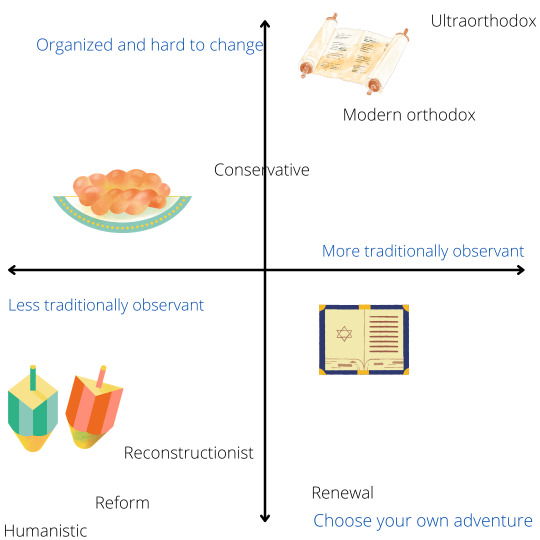
Writing a Jew or Jewish family? Aware that Judaism is not a monolith and want to honor that? Great! Need help with that? 100% cool - I’m here as your friendly (virtual) neighborhood Jewish professional to help. Just want to know more about Jewish denominations in comparison to one another? Also great! Fair warning - this is a long one. At least I included a graphic at the bottom?
Quick notes to acknowledge: As always, this is an American and Americanish perspective (and denominations as discussed here are MOSTLY relevant in the U.S. anyways). Additionally, the modern denominations as we think of them today really sprung from Ashkenazi communities in the 19th and 20th centuries. Most extant U.S. synagogues, day schools, and groups follow Ashkenazi customs and align with a denomination born of Ashkenazi tradition (aligning with the approximately 90% of Jewish-Americans who are Ashkenazi or Ashkenazi plus another community). Sephardi, Mizrachi, and other Jewish communities have their own traditions and jurisprudence. Most organized non-Ashkenazi communities in the U.S. identify as nondenominational but most closely compare in practice to orthodoxy, and many non-Ashkenazi Jews (especially outside of major population centers that may have other specific subgroup’s synagogues) are members of and very involved in Ashkenazi-originating movements, institutions, and synagogues.
For the purpose’s of today’s discussion, we’ll start in the 19th century, because Karaites vs Pharisees vs Sadducees is a (his)story for another time. This also isn’t a history of how these denominations came to be-with the exception of some ultraorthodox groups, which may have sprung from the shtel a little earlier, all the below movements popped out of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. I’m also going to list approximate percentage of the American Jewish population, and I’m going to (kinda) go in order from most to least strict/traditionally observant.
Ultraorthodox (aka Haredi): The strictest, more traditional and expansive observance of the Torah, Talmud, and minhagim (customs). About 1% of American Jews are ultraorthodox. Ultraorthodox is not a unified movement.
1a. Haredi, Satmar, and most other groups generally isolate themselves from the wider Jewish world and secular world.
1b. Chabad is also ultraorthodox, but specially seeks to interact with less observant Jews. I wouldn’t call it proselytizing, because they don’t seek to make gentiles Jewish, but they do try and find less observant Jews and bring them closer to Judaism, also establishes small synagogues around the country and world in isolated place.
1c. Ultraorthodox are the most visibly Jewish attired group, wearing Kippahs for all men and boys and tichels (headscarves) and/or wigs for married women. Very modest attire for all. In Ashkenazi Ultraorthodox communities, men also tend to only wear black and white, hats in addition to their kippah (for grown and married men), and wearing tzitzit (a garmet with four corners with strings attached worn under a shirt with the threads sticking out).
1d. Most likely to speak Yiddish or Hebrew as first language.
1e. No gender equality, very strict kosher, and intense community adherence to particular brand of Judaism.
1f. Communities generally led by a Rabbi and a Rebbetzin (Rabbi’s wife) as pair (rabbis are generally expected to be married).
1g. No female Rabbis, same-sex marriage, or intermarriage. Lots of children. Pretty much all boys have Bar Mitzahs, rarely do girls have Bat Mitzvahs.
1h. Services entirely in Hebrew (except maybe the sermon).
1i. Only count matrilineal Jews and converts-Jewish father and gentile mother doesn’t count for them.
1j. Very strict observance of prohibitions and commandments pertaining to Shabbat and holidays.
Modern orthodox: Orthodox, but with some adaptations to modern life. Roughly 9% of American Jews. Also some division within modern orthodoxy (with some congregations being more liberal than others, particularly in regards to women and LGBTQ+ folks), but there are a couple of major organizations that most modox rabbis and congregations affiliate with one another through larger denomination movements (i.e. the Orthodox Union and the Rabbinical Council of America).
2a. Modern orthodox Jews regularly interact with other Jews who are more liberal. They tend to live in more Jewish communities but no issues with interacting with outside world.
2b. Modest clothing and men wear kippot everywhere (when safe). Married women also usually cover their hair (with wigs or tichels). Men also typically wear tzitzit.
2b. Gender roles, but progress being made. Handful of female rabbis emerging in 2010s/2020s. Whether women count in a minyan depends on the specific congregation and many modern orthodox shuls will have separate women’s prayer groups. The prevalence of Bat Mitzvahs also varies wildly congregation to congregation.
2c. Like ultraorthodox, communities are typically led by a Rabbi and his wife the Rebbetzin. Some acceptance of homosexual individuals as members of the community, but no same-sex marriage (some alternate ceremonies emerging). Like one out gay male rabbi. No intermarriage.
2d. Very strict adherence to kosher, would likely not eat at someone less kosher’s home.
2e. Usually have on the higher end of a “normal” amount of children. Services entirely in Hebrew (except sermon).
2f. Only count matrilineal Jews and converts-Jewish father and gentile mother doesn’t count for them.
Less traditionally observant than this is often known as “liberal Judaism” - around 90% of American Jews.
2g. Very strict observance of prohibitions and commandments pertaining to Shabbat and holidays.
Conservative: Brands itself as middle of the road Jewish movement. about 18% of the American Jewish population. No connection to conservative politics, most Conservative with a C Jews are liberal or moderate politically. Often called “Masorti” outside the U.S and hypothetically a unified movement under several connected organizations (i.e. the Masorti Olami and the Jewish Theological Seminary).
3a. Gender equality. Female rabbis and LGBTQ rabbis definitely an acceptable thing, but not as common as with Reform or Reconstructionist.
3b. Formally sanctioned ceremony for same-sex couples to wed under Jewish law since 2012 and affirmation ceremonies since 2006.
3c. Modesty in synagogues but comparable to regular American attire otherwise.
3d. Generally comparable family size to other American families.
3e. Kosher, but not as strict as orthodoxy. Many Conservative Jews have kosher homes but are willing to be more lax when eating out. Synagogues are always kosher.
3f. Services mostly in Hebrew, sermons and some prayers definitely in local language.
3g. Intermarriage is frowned upon, but many otherwise Conservative Jews will be married by a less traditional rabbi or justice of the peace to non-Jewish partners. Although Conservative rabbis do not perform interfaith marriages, many interfaith couples are in Conservative synagogues. In the 90s/2000s it was way less friendly to interfaith couples/families (laughs in having a goyish dad) but that has improved in the past 3-5 years substantially.
3h. Observance of prohibitions and commandments pertaining to Shabbat and holidays is regulated but less strict than orthodoxy. Varies a bit by community. A good example to illustrate this is getting to synagogue on Shabbat:
By the book (not necessarily reflected by attendees): Orthodoxy says you have to walk there (no driving), Reform says it’s no issue to drive on Shabbat, and Conservative says you can drive but only to get to shul and back.
3i. As with orthodoxy, only matrilineal Jews count. Most interfaith families with non-Jewish moms (or moms who converted post-birth of the kid), particularly those who want to participate in Conservative communities will convert the child as a baby so they can have a normal Jewish upbringing (beyond an extra blessing/prayer in the Bnai Mitzvah process and social awkwardness that oft accompanies interfaith families in Jewish spaces).
3j. Most dress comparably to others in geographic area (synagogue notwithstanding, see my other post). Men on the higher end of observant might also wear kippahs all the time as well. Outside of explicitly Jewish contexts, similar lifestyles to surrounding populations. Around the same number of children as in gentile families.
Reform: Not at all traditionally observant. About 35% of American Jews. More or less a cohesive movement linked by organizations (i.e. Women of Reform Judaism and the Union for Reform Judaism).
4a. Reform Judaism is the largest group. It generally views Judaism through the lens of social justice, repairing the world, and cultural heritage as opposed to religious mandate.
4b. Very big on personal choice in what one observes, I like to call it “choose your own adventure” Judaism.
4c. Keeping kosher is uncommon. Some shuls aren’t even kosher.
4d. Reform services use the least Hebrew, although this is changing in some places.
4e. Reform’s standard of Jewishness is 1+ Jewish parent(s) and raised doing Jewish things, regardless of which parent is Jewish.
4f. Very feminist/egalitarian and welcoming to LGBTQ+ folks. Highest number of not-straight rabbis and female rabbis.
4g. Intermarriage very common and can be performed by Reform rabbis.
4h. Reform Judaism was way ahead of the curve in terms of LGBTQ+ rights and religion. The movement has had members advocating for homosexual rights (protection in housing, employment, civil marriage, and other nondiscrimination protections) since 1965 (finally passing formal resolutions in 1977), began proactively including/welcoming out gay rabbis in 1990, created same-gender marriage Jewish ceremonies in 1996/7, and has made resolutions explicitly including bi and trans people as well since 2004 (stuff earlier than that generally specified “gay and lesbian”). An additional resolution was passed in 2015 regarding trans and nonbinary inclusion, alongside guides to help congregations do so.
4i. See #3j - also applies here.
Orthodox, Conservative, and Reform, are the biggest and “standard” movements people will most typically list and identify with, most likely to appear in surveys and studies, are older than everything listed below. Modern Orthodox, Conservative, and Reform all started in the 19th century and some Ultraorthodox groups trace back further than that. I’ve outlined some practical differences, but the basic theoretical difference is that Orthodox considers traditional Jewish law (Halacha) binding and you can’t change it, Conservative believes it it’s binding but the community can change it, and Reform believes that it’s nonbinding.
Some smaller movements:
Reconstructionist - Newest even remotely well-known and organized movement, founded in the 1920s as an offshoot of the Conservative movement. I would describe it as “build your own adventure but Halacha matters (or at least some of it).” The first thing almost every recon Jew I’ve ever met has told me when describing reconstructionism is that they invented the bat mitzvah in 1922, which basically translates to “tradition matters but also egalitarianism.”
Maybe 2%-5% of American Jews today self-ID as Reconstructionist, but I would argue that a lot of nondenominal practitioners have philosophies fairly aligned with the recon ethos.
Jewish Renewal: very small and relatively disorganized movement started in the 1960s. Attempts to bring Jewish tradition and modern sensibilities, hippie Jews who care about Halacha. Big on mysticism and music, doing Jewish enthusiastically, and a tendency towards more traditional observance in conjunction with progressive politics. Kind of the laid-back cousin of reconstructionism, although neither sprung from the other.
(Cultural) Humanistic Judaism: “Non-theistic” Judaism for atheist Jews who still want a connection to their history, culture, and celebrations.
Nondenominational - Nondenominational and post-denominational Jews are the fast growing group. Variety of liberal/non-traditionally observant beliefs and practices, but most will still contextualize themselves around the denominational scale.
#writeblr#jewish writing advice#jewish writing help#writing jewish characters#writing jewish spaces#jumblr#jewblr#writing advice#ref#reference#jewish ref#jewish reference#jewish denominations#judiasm#another long one still not sorry#info dump
302 notes
·
View notes
Note
A couple weeks ago you mentioned in a post that most of what's known about Robespierre is propaganda, could you elaborate on that?
Of course Anon! I’m always glad to talk about anything pertaining to the Frev! I’m not sure how much you already know about the French revolution, but I know other people will read this so hold on, 'cause it’s about to get long and in-depth as hell!
Also: Just a reminder that I don’t have a degree in history or anything. I simply spend a majority of my free time looking up information cause I’m a nerd like that. And of course, my statement about Robespierre could be applied with different levels of accuracy to other historical figures at the time, including the monarchy. This is just how it applies to Maxime as requested. Any questions about any other aspects of the French Revolution are always welcome. I'll try to answer then as clearly, accurately, and respectfully as possible.
A majority of information commonly spread about Robespierre is that he was a vicious and cruel leader with no regard for anyone but himself. Supposedly, he was so obsessed with the ideas of perfection and ‘virtue’ that he lost any human emotion, rendering him cold, friendless, and willing to sacrifice anything or anyone to get his way. In fact, when I first was introduced to him and the French Revolution in school several years ago, I was under the impression that he personally was responsible for a majority of deaths that occurred during the revolution. That’s what caused me to first look into him. Morbid stuff has always interested me and I wanted to know all about the vicious relentless killer who had no regard for human life and wanted to purge France of anyone who lacked the necessary virtues of his twisted moral code.
As I began to research I realized the picture of Robespierre painted for me by the flawed American education system, the modern media, and a surprising amount of books summarizing the history of the world was incredibly skewed, usually in favor of the ‘poor monarchy’ who were ‘thrust into an impossible position and didn’t mean for anything to happen’.
In reality, Robespierre was, despite remaining a flawed individual like the rest of us, a quiet well dressed, polite man who was loyal to his friends, cared deeply about his family, wanted to reform the country in favor of the common people, and fought for what he believed in. Maxime had social anxiety and loved animals especially birds and dogs. Oftentimes he left his glasses places and couldn’t remember where he put them. He once wrote a poem about how much he loved tarts. Things made him angry, happy, and scared. The man who played such a crucial part in the revolution was still the same person as the young man who cried when his youngest sister Henriette died at age seventeen and the man who was praised as being a bright student at Louis-le-Grand. He advocated for women’s rights to an education, supported the rights of Jews in France (who were an unrepresented minority at the time), proposed laws in an attempt to decrease unnecessary violence (which he hated along with the war against Austria, the dechristianization of France, and the dangerous mob mentality). Maximilien Robespierre was an actual person who actually felt things like the rest of us. He was no heartless monster who preyed on innocent Frenchmen for no reason.
Now it’s time to point out the wrongs he committed. It can never be a fair judge of someone’s character, living or dead, without taking into account the bad things they have done. Robespierre did vote in favor of Louis XVI’s execution, mistakenly believing that France would benefit from the king’s death. After Capet’s execution violence spiraled out of control, resulting in a period of death known as The Reign of Terror. He also didn’t do as much as he should have to oust revolutionaries with dangerous tendencies and a penchant to condone mob violence. One of his biggest faults was his habit of compromising when he should have stood his ground and standing his ground when compromising would be the better option. His signature can be found on the arrest warrant sent out for the Dantonists, including his friend (to some degree) Georges Danton and childhood friend Camille Desmoulins, who eventually would go on to be executed.
Now the question is, how did a usually quiet, reserved individual become known as a bloodthirsty cult leader? The answer is, of course, Thermidorian Propaganda. For those of you that don’t know what that means, allow me to explain.
Thermidor was the name of the fifth month on the revolutionary calendar (which was implemented in 1793 and used in France through 1805 ) that spanned from July 19th to August 17th on the Gregorian Calendar. At the beginning of Thermidor Maximilien was to make a speech to the National Convention speaking about but refusing to then name of several members who were corrupt or had committed crimes against the revolution and defending his own part in trying to find them. (Actually, I believe he straight-up named three people, but I don’t remember their names so it’s not important.) Convention members who feared exposure by the speech conspired together to overthrow Robespierre, who was seen as the figurehead of the revolution, (similarly to how the president represents the United States as a whole) and save their reputations. Robespierre and those still loyal to him fled to the Hotel de Ville, were captured by the National Guard, and were sentenced to death via guillotine all within the span of a few days. Those who accused and condemned him have come to be known as Thermidorians and the event itself known as the Thermidorian Reaction.
In order to preserve their reputations, the Thermidorians began criminalizing Robespierre and using him as a scapegoat for crimes committed (and not committed at all) by different people during the revolution. As the common saying goes, “History is written by the winners.” Because they succeeded in their plot against the Robespierrists and frightened anyone who wished to stand up and support their own Robespierrist views, the Thermidorians were able to control the narrative and the light in which Robespierre is presented. As his rivals/enemies they wanted themselves to seem obviously correct and Robespierre to seem clearly in the wrong. Things were not so black and white, so they fudged the information a little to help their cause.
As a result our picture of Robespierre is very different from the actual man. I'd like to say that he did both helpful and problematic things over the course of his time in the spotlight. He was a human, simple as that. It isn't right to demonize him and completely butcher his true self the way the Thermidorians and many historians since have done, but in the same breath we also have to remember all the awful things he allowed and was a part of.
Sorry it got so long, but I hoped I cleared things up for you Anon. If you have more questions, please hit me up!
~Dara
42 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hey Bab, so quick question piggybacking off of your post about Jewish religion and culture, so then is it possible to be Jewish in a not religious way or vice versa? As in, can someone be one and not the other? Or do Jewish people both culturally and religiously claim Jewishness? I think I’m wording that weird but I’m intrigued haha. :))))
Hello my dear anon! Yes, it is absolutely possible to express your Jewishness in one way but not the other.
One of the things that has come about from modern times, is a pull away from religion in general. Many people, for whatever reason, simply don't agree with organized religion, or they don't believe in a higher power, or perhaps they have negative associations with religion from growing up. There's a multitude of reasons, and all of them are perfectly valid for someone to want to reject the religion. In fact, my own mother rejected Judaism the Religion, and at a pretty young age too.
But, culturally, she was raised by Jewish people, has Jewish blood, knows the food and the language and the music, and celebrates the holidays; because for her it's less about the spiritual or religious connotation, and more about family tradition and heritage. Kind of think about it the way that a lot of people celebrate Christmas. Sure some people view it as a highly religious holiday, but millions of people around the globe just like getting together with their families because it's what they've grown up doing.
Similarly, there are tons of people who practice Judaism the religion who don't come from that cultural background! People who convert to Judaism are just as Jewish as those who have been born to Jewish families. In fact, sometimes you'll find that people who have converted know even more about Judaism the Religion than ethnic Jews! This is because since they didn't grow up with it, they have to take it upon themselves to learn if they so choose, and a lot of folks want to learn. There are also people who are ethnically Jewish but maybe had no idea for a very long time, and are now as adults trying to reconnect with their heritage.
There is no one right way to be Jewish. Whether you're Orthodox, Reform, Convert, or frankly neither very religious nor very culturally practicing but have strong Jewish genes -- if you're a Jew, you're a Jew. What matters is that not what your background is, or how you express your Judaism, or how much you know about it. What matters is that you are, in whatever way that you are, and you're proud.
I hope that this answered your question my dear anon, and I'm sending you all my love!
7 notes
·
View notes
Note
heyy i saw your post about how americans and europeans have distinctive different views on the whole israel-palestine conflict can you elaborate? i'm just curious since i don't know too much about the subject so i didn't rlly notice any differences
Hey! Yes, of course! Please keep in mind, I’m a Christian German and by no means an expert on this topic. I’ve also never been to Israel or Palestine, just as the vast majority of Americans who reblog those takes. Although I’m not a practicing Christian, it means I was socialized in a society with inherent antisemitism and a people’s past of being colonizers (namely Namibia), although not to the extent of Great Britain or France for example, so I can’t say too much or anything on the topic of how Israel seems to be seen as colonizers in distinctive American takes on the conflict. What I will say in response to this argument is this: This argument reeks of antisemitism, but especially of antisemitism that’s different from German/nazi antisemitism and also from muslim antisemitism.
That’s the basics to my person, so you know what perspective I’m talking from.
Now to what I know/understand of the history of the region I’m talking about. Just the region, not countries. That region, including the Levant, has the strongest ties to what happened according to the writings of Judaism and Christianity and Islam. There also is one indigenous tribe on the soil of nowadays Ethopia who claim to be the oldest Jewish community in the world, but that’s a different topic.
Judaism is different from Christianity and Islam as in the fact that Judaism is also an ethno-religion. That’s one of the reasons why Jews long for their own state, their own country and land. Then comes the diaspora that started way before our time and goes back to ancient times.
Fast forward to modern times in the meaning of historical science (1800 to now). Great Britain colonized part of the Levant, where, at that time, Christian Palestinians lived. Jews were still in diaspora.
Now a smaller fast forward to what the Germans did. The specific German antisemitism that resulted in several pogroms of Jewish communities in the Middle Ages against the Ashkenazi Jews and the German antisemitism that got a big boost during the reformation with Martin Luther at the helm.
All that resulted in the genocide that the vast majority of people (not only Germans but other nationalities as well) call “Holocaust” which translates to “burn victim”. Jews call it “Shoa”, which translates to “Shame”.
That made it abudantly clear, even in the eyes of the world, that Jews needed their own state. That was in the mid to late 1940s. This times, just these five years, have several important things happening during that time:
British Colonies strived (and sometimes got) their indepency.
The UN were founded, as a response to what the Germans did and what the world got liberated from.
While there were six million Jews less than before, the diaspora is still very much happening.
People remember which parts of the world have the closest ties to the Jewish texts.
Jews now have an argument as to why they need their own state that’s so strong, there’s no stronger argument that also cannot be refuted, unless you’re araging antisemite.
(Yes, I know the last point sounds cynical. It is, but that doesn’t make it less true.)
All this culminates in Jews getting their state where it is today. Still, they get their state in a region where they’re surrounded by states who don’t recognize the right to existence of the state of Israel. So, Israel constantly feels threatened. If that’s always by everyone the case is another topic, but Israel as a state (not Jews, there’s a difference between Israelis and Jews) feels threatened. That’s also why the conflict is not entirely just about religion but also about land. And by that, existence.
That’s the basics of the situation. Now for the distinct German-Israeli situation.
Germany, because of its history, feels a special connection to Israel and especially Jewish Israelis which results in Germany (as a state) wants Israel to exist but at the same time recognizes the difference between Israel, the state, and Jews living there.
At the same time, Germany is not hostile to Palestine or their want for their own state. That’s why Germany favors a two-state-solution. What Germany is hostile to, however, is the Hamas. The Hamas rules over Palestine and is considered a terrorist organization. There also haven’t been elections held in 15 years in Palestine. Israel, at the moment (and for the last two years) has/had trouble to form a functioning government.
All of the above are the basics when Germans discuss the Israel Palestine Conflict.
And now for the actual answer:
In all the American takes, I almost never see the Hamas being mentioned. Not by name, not by “terrorist organization”, nothing. Never. They almost always only mention the civilian populace which ignores the part of Palestinians who gives the orders to attack Israel. At the same time, I almost always see the Israeli populace (no matter if they Christian, Jewish or Arabian Israelis) lumped in with the acting right wing government on Benjamin Netanjahu (acting, not legitimized), which in consequence makes every Israeli an Israeli who attacks Palestine.
Both aren’t true and are most likely furthering aversions against each other and a black and white thinking pattern.
In the German takes, the Hamas is mentioned. There’s a line drawn between the Hamas and the Palestinian populace. The Israeli government is mentioned with all its quarrels and why it feels it has to do what they do (same with the Hamas). The Israeli populace is mentioned as being different from their government.
All four parties (Hamas, Israeli government, Palestine populace, Israeli populace) are given space in news reports, etc to state their perspective.
During all this, Germany still wants a two state solution as the long term goal and the right to existence of Israel to remain and Israel to be safe.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Democratic Establishment is Freaking Out About Bernie. It should Calm Down.
The day after Bernie Sanders’s big win in Nevada, Joe Lockhart, Bill Clinton’s former press secretary, expressed the fear gripping the Democratic establishment: “I don't believe the country is prepared to support a Democratic socialist, and I agree with the theory that Sanders would lose in a matchup against Trump.”
Lockart, like the rest of the Democratic establishment, is viewing American politics through obsolete lenses of left versus right, with Bernie on the extreme left and Trump on the far right. “Moderates” like Bloomberg and Buttigieg supposedly occupy the center, appealing to a broader swath of the electorate.
This may have been the correct frame for politics decades ago when America still had a growing middle class, but it’s obsolete today. As wealth and power have moved to the top and the middle class has shrunk, more Americans feel politically dis-empowered and economically insecure. Today's main divide isn’t right versus left. It’s establishment versus anti-establishment.
Some background. In the fall of 2015 I visited Michigan, Wisconsin, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Kentucky, Missouri, and North Carolina, researching the changing nature of work. I spoke with many of the same people I had met twenty years before when I was secretary of labor, as well as some of their grown children. I asked them about their jobs and their views about the economy. I was most interested in their sense of the system as a whole and how they were faring in it.
What I heard surprised me. Twenty years before, most said they’d been working hard and were frustrated they weren’t doing better. Now they were angry – at their employers, the government, and Wall Street; angry that they hadn’t been able to save for their retirement, and that their children weren’t doing any better than they did. Several had lost jobs, savings, or homes in the Great Recession. By the time I spoke with them, most were employed but the jobs paid no more than they had two decades before.
I heard the term “rigged system” so often I began asking people what they meant by it. They spoke about the bailout of Wall Street, political payoffs, insider deals, CEO pay, and “crony capitalism.” These came from self-identified Republicans, Democrats, and Independents; white, black, and Latino; union households and non-union. Their only common characteristic was they were middle class and below.
With the 2016 primaries looming, I asked which candidates they found most attractive. At the time, party leaders favored Hillary Clinton or Jeb Bush. But the people I spoke with repeatedly mentioned Bernie Sanders and Donald Trump. They said Sanders or Trump would “shake things up,” “make the system work again,” “stop the corruption,” or “end the rigging.”
In the following year, Sanders -- a 74-year-old Jew from Vermont who described himself as a democratic socialist and wasn’t even a Democrat until the 2016 presidential primary -- came within a whisker of beating Hillary Clinton in the Iowa caucus, routed her in the New Hampshire primary, garnered over 47 percent of the caucus-goers in Nevada, and ended up with 46 percent of the pledged delegates from Democratic primaries and caucuses.
Trump, a 69-year-old ego-maniacal billionaire reality TV star who had never held elective office or had anything to do with the Republican Party, and lied compulsively about almost everything -- won the Republican primaries and then went on to beat Clinton, one of the most experienced and well-connected politicians in modern America (granted, he didn’t win the popular vote, and had some help from the Kremlin).
Something very big happened, and it wasn’t because of Sanders’s magnetism or Trump’s likeability. It was a rebellion against the establishment. Clinton and Bush had all the advantages –funders, political advisors, name recognition -- but neither could credibly convince voters they weren’t part of the system.
A direct line connected four decades of stagnant wages, the financial crisis of 2008, the bailout of Wall Street, the rise of the Tea Party and the “Occupy” movement, and the emergence of Sanders and Trump in 2016. The people I spoke with no longer felt they had a fair chance to make it. National polls told much the same story. According to the Pew Research Center, the percentage of Americans who felt most people could get ahead through hard work dropped by 13 points between 2000 and 2015. In 2006, 59 percent of Americans thought government corruption was widespread; by 2013, 79 percent did.
Trump galvanized millions of blue-collar voters living in places that never recovered from the tidal wave of factory closings. He promised to bring back jobs, revive manufacturing, and get tough on trade and immigration. “We can’t continue to allow China to rape our country, and that’s what they’re doing,” he roared. “In five, ten years from now, you’re going to have a workers’ party. A party of people that haven’t had a real wage increase in eighteen years, that are angry.” He blasted politicians and financiers who had betrayed Americans by “taking away from the people their means of making a living and supporting their families.”
Trump’s pose as an anti-establishment populist was one of the biggest cons in American political history. Since elected he’s given the denizens of C-suites and the Street everything they’ve wanted and hasn’t markedly improved the lives of his working-class supporters, even if his politically-incorrect, damn-the-torpedo’s politics continues to make them feel as if he’s taking on the system.
The frustrations today are larger than they were four years ago. Even though corporate profits and executive pay have soared, the typical worker’s pay has barely risen, jobs are less secure, and health care less affordable.
The best way for Democrats to defeat Trump’s fake anti-establishment populism is with the real thing, coupled with an agenda of systemic reform. This is what Bernie Sanders offers. For the same reason, he has the best chance of generating energy and enthusiasm to flip at least three senate seats to the Democratic Party (the minimum needed to recapture the Senate, using the vice president as tie-breaker).
He’ll need a coalition of young voters, people of color, and the working class. He seems on his way. So far in the primaries he leads among white voters, has a massive edge among Latinos, dominates with both women and men, and has done best among both college and non-college graduates. And he’s narrowing Biden’s edge with older voters and African Americans. [Add line about South Carolina from today's primary.]
The “socialism” moniker doesn't seem to have bruised him, although it hasn't been tested outside a Democratic primary or caucus. Perhaps voters won't care, just as they many don’t care about Trump’s chronic lies.
Worries about a McGovern-like blowout in 2020 appear far-fetched. In 1972 the American middle class was expanding, not contracting. Besides, every national and swing state poll now shows Sanders tied with or beating Trump. A Quinnipiac Poll last week shows Sanders beating Trump in Michigan and Pennsylvania. A CBS News/YouGov poll has Sanders beating Trump nationally. A Texas Lyceum poll has Sanders doing better against Trump in Texas than any Democrat, losing by just three points.
Instead of the Democratic establishment worrying that Sanders is unelectable, maybe it should worry that a so-called "moderate” Democrat might be nominated instead.
236 notes
·
View notes
Text
Doubting the Story of Exodus

By Teresa Watanabe
Los Angeles Times religion writer April 13, 2001
It’s one of the greatest stories ever told:
A baby is found in a basket adrift in the Egyptian Nile and is adopted into the pharaoh’s household. He grows up as Moses, rediscovers his roots and leads his enslaved Israelite brethren to freedom after God sends down 10 plagues against Egypt and parts the Red Sea to allow them to escape. They wander for 40 years in the wilderness and, under the leadership of Joshua, conquer the land of Canaan to enter their promised land.
For centuries, the biblical account of the Exodus has been revered as the founding story of the Jewish people, sacred scripture for three world religions and a universal symbol of freedom that has inspired liberation movements around the globe.
But did the Exodus ever actually occur?
On Passover last Sunday, Rabbi David Wolpe raised that provocative question before 2,200 faithful at Sinai Temple in Westwood. He minced no words.
“The truth is that virtually every modern archeologist who has investigated the story of the Exodus, with very few exceptions, agrees that the way the Bible describes the Exodus is not the way it happened, if it happened at all,” Wolpe told his congregants.
Wolpe’s startling sermon may have seemed blasphemy to some. In fact, however, the rabbi was merely telling his flock what scholars have known for more than a decade. Slowly and often outside wide public purview, archeologists are radically reshaping modern understanding of the Bible. It was time for his people to know about it, Wolpe decided.
After a century of excavations trying to prove the ancient accounts true, archeologists say there is no conclusive evidence that the Israelites were ever in Egypt, were ever enslaved, ever wandered in the Sinai wilderness for 40 years or ever conquered the land of Canaan under Joshua’s leadership. To the contrary, the prevailing view is that most of Joshua’s fabled military campaigns never occurred—archeologists have uncovered ash layers and other signs of destruction at the relevant time at only one of the many battlegrounds mentioned in the Bible.
Today, the prevailing theory is that Israel probably emerged peacefully out of Canaan—modern-day Lebanon, southern Syria, Jordan and the West Bank of Israel—whose people are portrayed in the Bible as wicked idolators. Under this theory, the Canaanites who took on a new identity as Israelites were perhaps joined or led by a small group of Semites from Egypt—explaining a possible source of the Exodus story, scholars say. As they expanded their settlement, they may have begun to clash with neighbors, perhaps providing the historical nuggets for the conflicts recorded in Joshua and Judges.
“Scholars have known these things for a long time, but we’ve broken the news very gently,” said William Dever, a professor of Near Eastern archeology and anthropology at the University of Arizona and one of America’s preeminent archeologists.
Dever’s view is emblematic of a fundamental shift in archeology. Three decades ago as a Christian seminary student, he wrote a paper defending the Exodus and got an A, but “no one would do that today,” he says. The old emphasis on trying to prove the Bible—often in excavations by amateur archeologists funded by religious groups—has given way to more objective professionals aiming to piece together the reality of ancient lifestyles.
But the modern archeological consensus over the Exodus is just beginning to reach the public. In 1999, an Israeli archeologist, Ze’ev Herzog of Tel Aviv University, set off a furor in Israel by writing in a popular magazine that stories of the patriarchs were myths and that neither the Exodus nor Joshua’s conquests ever occurred. In the hottest controversy today, Herzog also argued that the united monarchy of David and Solomon, described as grand and glorious in the Bible, was at best a small tribal kingdom.
In a new book this year, “The Bible Unearthed,” Israeli archeologist Israel Finklestein of Tel Aviv University and archeological journalist Neil Asher Silberman raised similar doubts and offered a new theory about the roots of the Exodus story. The authors argue that the story was written during the time of King Josia of Judah in the 7th century BC—600 years after the Exodus supposedly occurred in 1250 BC—as a political manifesto to unite Israelites against the rival Egyptian empire as both states sought to expand their territory.
Dever argued that the Exodus story was produced for theological reasons: to give an origin and history to a people and distinguish them from others by claiming a divine destiny.
Some scholars, of course, still maintain that the Exodus story is basically factual.
Bryant Wood, director of the Associates for Biblical Research in Maryland, argued that the evidence falls into place if the story is dated back to 1450 BC. He said that indications of destruction around that time at Hazor, Jericho and a site he is excavating that he believes is the biblical city of Ai support accounts of Joshua’s conquests.
He also cited the documented presence of “Asiatic” slaves in Egypt who could have been Israelites, and said they would not have left evidence of their wanderings because they were nomads with no material culture. But Wood said he can’t get his research published in serious archeological journals.
“There’s a definite anti-Bible bias,” Wood said.
The revisionist view, however, is not necessarily publicly popular.
Herzog, Finklestein and others have been attacked for everything from faulty logic to pro-Palestinian political agendas that undermine Israel’s land claims. Dever, a former Protestant minister who converted to Judaism 12 years ago, says he gets “hissed and booed” when he speaks about the lack of evidence for the Exodus, and regularly receives letters and calls offering prayers or telling him he’s headed for hell.
At Sinai Temple, Sunday’s sermon—and a follow-up discussion at Monday’s service—provoked tremendous, and varied, response. Many praised Wolpe for his courage and vision. “It was the best sermon possible, because it is preparing the young generation to understand all the truth about religion,” said Eddia Mirharooni, a Beverly Hills fashion designer.
A few said they were hurt—"I didn’t want to hear this,” one woman said—or even a bit angry. Others said the sermon did nothing to shake their faith that the Exodus story is true.
“Science can always be proven wrong,” said Kalanit Benji, a UCLA undergraduate in psychobiology.
Added Aman Massi, a 60-year-old Los Angeles businessman: “For sure it was true, 100%. If it were not true, how could we follow it for 3,300 years?”
But most congregants, along with secular Jews and several rabbis interviewed, said that whether the Exodus is historically true or not is almost beside the point. The power of the sweeping epic lies in its profound and timeless message about freedom, they say.
The story of liberation from bondage into a promised land has inspired the haunting spirituals of African American slaves, the emancipation and civil rights movements, Latin America’s liberation theology, peasant revolts in Germany, nationalist struggles in South Africa, the American Revolution, even Leninist politics, according to Michael Walzer in the book “Exodus and Revolution.”
Many of Wolpe’s congregants said the story of the Exodus has been personally true for them even if the details are not factual: when they fled the Nazis during World War II, for instance, or, more recently, the Islamic revolution in Iran. Daniel Navid Rastein, an Encino medical professional, said he has always regarded the story as a metaphor for a greater truth: “We all have our own Egypts—we are prisoners of something, either alcohol, drugs, cigarettes, overeating. We have to use [the story] as a way to free ourselves from difficulty and make ourselves a better person.”
Wolpe, Sinai Temple’s senior rabbi, said he decided to deliver the sermon to lead his congregation into a deeper understanding of their faith. On Sunday, he told his flock that questioning the Jewish people’s founding story could be justified for one reason alone: to honor the ancient rabbinical declaration that “You do not serve God if you do not seek truth.”
“I think faith ought not rest on splitting seas,” Wolpe said in an interview. “For a Jew, it should rest on the wonder of God’s world, the marvel of the human soul and the miracle of this small people’s survival through the millennia.”
Next year, the rabbi plans to teach a course on the Bible that he says will “pull no punches” in presenting the latest scholarship questioning the text’s historical basis.
But he and others say that Judaism has also traditionally been more open to nonliteral interpretations of the text than, say, some conservative Christian traditions.
“Among Reform, Conservative and Reconstructionist Jews, there is a much greater willingness to see the Torah as an extended metaphor in which truth comes through story and law,” said Rabbi Bradley Shavit Artson, dean of the Ziegler School of Rabbinic Studies at the University of Judaism in Los Angeles.
Among scholars, the case against the Exodus began crystallizing about 13 years ago. That’s when Finklestein, director of Tel Aviv University’s archeology institute, published the first English-language book detailing the results of intensive archeological surveys of what is believed to be the first Israelite settlements in the hilly regions of the West Bank.
The surveys, conducted during the 1970s and 1980s while Israel possessed what are now Palestinian territories, documented a lack of evidence for Joshua’s conquests in the 13th century BC and the indistinguishable nature of pottery, architecture, literary conventions and other cultural details between the Canaanites and the new settlers.
If there was no conquest, no evidence of a massive new settlement of an ethnically distinct people, scholars argue, then the case for a literal reading of Exodus all but collapses. The surveys’ final results were published three years ago.
The settlement research marked the turning point in archeological consensus on the issue, Dever said. It added to previous research that showed that Egypt’s voluminous ancient records contained not one mention of Israelites in the country, although one 1210 BC inscription did mention them in Canaan.
Kadesh Barnea in the east Sinai desert, where the Bible says the fleeing Israelites sojourned, was excavated twice in the 1950s and 1960s and produced no sign of settlement until three centuries after the Exodus was supposed to have occurred. The famous city of Jericho has been excavated several times and was found to have been abandoned during the 13th and 14th centuries BC.
Moreover, specialists in the Hebrew Bible say that the Exodus story is riddled with internal contradictions stemming from the fact that it was spliced together from two or three texts written at different times. One passage in Exodus, for instance, says that the bodies of the pharaoh’s charioteers were found on the shore, while the next verse says they sank to the bottom of the sea.
And some of the story’s features are mythic motifs found in other Near Eastern legends, said Ron Hendel, a professor of Hebrew Bible at UC Berkeley. Stories of babies found in baskets in the water by gods or royalty are common, he said, and half of the 10 plagues fall into a “formulaic genre of catastrophe” found in other Near Eastern texts.
Carol Meyers, a professor specializing in biblical studies and archeology at Duke University, said the ancients never intended their texts to be read literally. “People who try to find scientific explanations for the splitting of the Red Sea are missing the boat in understanding how ancient literature often mixed mythic ideas with historical recollections,” she said. “That wasn’t considered lying or deceit; it was a way to get ideas across.”
Virtually no scholar, for instance, accepts the biblical figure of 600,000 men fleeing Egypt, which would have meant there were a few million people, including women and children. The ancient desert at the time could not support so many nomads, scholars say, and the powerful Egyptian state kept tight security over the area, guarded by fortresses along the way.
Even Orthodox Jewish scholar Lawrence Schiffman said “you’d have to be a bit crazy” to accept that figure. He believes that the account in Joshua of a swift military campaign is less accurate than the Judges account of a gradual takeover of Canaan. But Schiffman, chairman of Hebrew and Judaic studies at New York University, still maintains that a significant number of Israelite slaves fled Egypt for Canaan.
“I’m not arguing that archeology proves the Exodus,” he said. “I’m arguing that archeology allows you, in ambiguity, to reach whatever conclusion you want to.”
Wood argued that the 600,000 figure was mistranslated and the real number amounted to a more plausible 20,000. He also said the early Israelite settlements and their similarity to Canaanite culture could be explained as the result of pastoralists with no material culture moving into a settled farming life and absorbing their neighbors’ pottery styles and other cultural forms.
The scholarly consensus seems to be that the story is a brilliant mix of myth, cultural memories and kernels of historical truth. Perhaps, muses Hendel, a small group of Semites who escaped from Egypt became the “intellectual vanguard of a new nation that called itself Israel,” stressing social justice and freedom.
Whatever the facts of the story, those core values have endured and inspired the world for more than three millenniums—and that, many say, is the point.
“What are the Egypts I need to free myself from? How does the story inspire me in some way to work for the freedom of all?” asked Rabbi Steven Carr Reuben of Kehillat Israel in Pacific Palisades. “These are the things that matter—not whether we built the pyramids.”
Teresa Watanabe
Teresa Watanabe covers education for the Los Angeles Times. Since joining the Times in 1989, she has covered immigration, ethnic communities, religion, Pacific Rim business and served as Tokyo correspondent and bureau chief. She also covered Asia, national affairs and state government for the San Jose Mercury News and wrote editorials for the Los Angeles Herald Examiner. A Seattle native, she graduated from USC in journalism and in East Asian languages and culture.
https://www.latimes.com/archives/la-xpm-2001-apr-13-mn-50481-story.html
_____________________________
Adam, Eve, Noah, Abraham, Isaac, Jacob, Moses and Joshua – there is no evidence any of them ever lived
The Divine Principle: Questions to consider about Old Testament figures
Unearthing the True Origins of the Bible
– interview with Dr. Andrew Henry
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
aaaaaaaaaaaaaa I wanna buy Judaica and I wanna work on my custom siddur project and I wanna move out so I can finally actually become as observant* as I’d like to be
*I’m not a huge fan of saying “observant” because like, different communities have different ideas of what that means and I don’t wanna imply that someone who’s Reform isn’t observant just because they have a different view on halacha, but also I really don’t know what other word I could use so. Personally my ideal level of observance would be like. Tradegal/Modern Orthodox-ish? just make it lgbt friendly
but I’m also kinda worried that becoming more observant is gonna be off-putting to people. like I may have been an oblivious idiot in high school but even then I knew I was seen as a weirdo for praying before meals
idk it’s weird how general American culture expects religion not to affect anything outside one’s house and place of worship – even Christianity! if you’re too Christian people are gonna Notice. Not necessarily in a bad way, mind you, but even here in the Bible Belt you don’t generally walk into a McDonald’s and see people saying grace unless maybe if it’s right after church services end.
Like, religion and culture aren’t separated into neat little boxes like that. Even if secular people think they’re not Christian, they definitely are gonna notice if someone is doing non-Christian things or visibly identify themselves with some other religion.
And even if people don’t mind me being observant, it’s still gonna affect my social life if I can’t do things on Saturdays or eat anywhere bc there’s no kosher restaurants in NC (that I know of) or have to run off in the middle of the afternoon for 15 minutes or so to daven mincha somewhere
like I try to keep it lowkey (tuck in tzitzit, wear a hat over my yarmulke, etc.), especially since religious hate crimes are far and away aimed at Jews, but I don’t wanna not be observant; I converted for a reason
also I know this is probably the dumbest thing to be worried about but like.........idk I know that since I converted I’m considered just as Jewish as someone born into it (at least, by everyone who accepts Conservative conversions) but I’m still kinda worried that my Jewish friends might resent me for essentially opting into antisemitism and/or knowing more about their religion than they do
(the latter of which is doubly silly because I don’t actually know how much they know about Judaism, and triply silly considering one of them is a Norse pagan and thus probably does not particularly care!)
bc like I KNOW my friends aren’t like that but also I’ve seen other converts and baalei teshuva say their friends got upset about them becoming “more” Jewish than them (which is nonsense; no one’s “more” Jewish than anyone else except like. people who literally are not Jews)
like I’m not Chabad, I ain’t gonna try to make people be Jewish in the same way that I am, and I sure as hell ain’t gonna try to convert anybody. On the contrary! I wanna hear EVERYTHING about other people’s religious and/or spiritual practices that they’re willing to share.
I love religions and I love being Jewish but actually being an observant Jew in a state (and country, tbh) with very few of those is uuuuuhhhhhhh daunting. I really wish there was an observant(ish?) community made up of mostly lgbt people that I could go live in/near
also that IS the one thing; I don’t wanna really live in a city area but since I don’t wanna drive on Shabbat I’d have to either resign myself to never going to services or deal with a very long walk. Or maybe stay the night at someone else’s place, but I’d feel bad doing that every single week
anyway on a mostly unrelated note, we gotta write papers for our HUM final and I wanna do mine on religious literacy in the USA
#idk this is just. what's the fucking word. stream of consciousness???#it's not exactly venting but it's not a super organized post#anyway I have homework to do#religious stuff
1 note
·
View note
Text
Gaza Conflict Stokes 'Identity Crisis' for Young American Jews
Dan Kleinman does not know quite how to feel.
As a child in the New York City borough of Brooklyn, he was taught to revere Israel as the protector of Jews everywhere, the “Jewish superman who would come out of the sky to save us” when things got bad, he said.
It was a refuge in his mind when white supremacists in Charlottesville, Virginia, chanted “Jews will not replace us,” or kids in college grabbed his shirt, mimicking a “South Park” episode to steal his “Jew gold.”
But his feelings have grown muddier as he has gotten older, especially now as he watches violence unfold in Israel and Gaza. His moral compass tells him to help the Palestinians, but he cannot shake an ingrained paranoia every time he hears someone make anti-Israel statements.
“It is an identity crisis,” Kleinman, 33, said. “Very small in comparison to what is happening in Gaza and the West Bank, but it is still something very strange and weird.”
As the violence escalates in the Middle East, turmoil of a different kind is growing across the Atlantic. Many young American Jews are confronting the region’s long-standing strife in a very different context, with very different pressures, from their parents’ and grandparents’ generations.
The Israel of their lifetime has been powerful, no longer appearing to some to be under constant existential threat. The violence comes after a year when mass protests across the United States have changed how many Americans see issues of racial and social justice. The pro-Palestinian position has become more common, with prominent progressive members of Congress offering impassioned speeches in defense of the Palestinians on the House floor. At the same time, reports of anti-Semitism are rising across the country.
Divides between some American Jews and Israel’s right-wing government have been growing for more than a decade, but under the Trump administration those fractures that many hoped would heal became a crevasse. Politics in Israel have also remained fraught, as Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu’s long-tenured government forged allegiances with Washington. For young people who came of age during the Trump years, political polarization over the issue only deepened.
Many Jews in America remain unreservedly supportive of Israel and its government. Still, the events of recent weeks have left some families struggling to navigate both the crisis abroad and the wide-ranging response from American Jews at home. What is at stake is not just geopolitical, but deeply personal. Fractures are intensifying along lines of age, observance and partisan affiliation.
In suburban Livingston, New Jersey, Meara Ashtivker, 38, has been afraid for her father-in-law in Israel, who has a disability and is not able to rush to the stairwell to shelter when he hears the air-raid sirens. She is also scared as she sees people in her progressive circles suddenly seem anti-Israel and anti-Jewish, she said.
Ashtivker, whose husband is Israeli, said she loved and supported Israel, even when she did not always agree with the government and its actions.
“It’s really hard being an American Jew right now,” she said. “It is exhausting and scary.”
Some young, liberal Jewish activists have found common cause with Black Lives Matter, which explicitly advocates for Palestinian liberation, concerning others who see that allegiance as anti-Semitic.
The recent turmoil is the first major outbreak of violence in Israel and Gaza for which Aviva Davis, who graduated this spring from Brandeis University, has been “socially conscious.”
“I’m on a search for the truth, but what’s the truth when everyone has a different way of looking at things?” Davis said.
Alyssa Rubin, 26, who volunteers in Boston with IfNotNow, a network of Jewish activists who want to end Jewish American support for Israeli occupation, has found protesting for the Palestinian cause to be its own form of religious observance.
She said she and her 89-year-old grandfather ultimately both want the same thing, Jewish safety. But “he is really entrenched in this narrative that the only way we can be safe is by having a country,” she said, while her generation has seen that “the inequality has become more exacerbated.”
In the protest movements last summer, “a whole new wave of people were really primed to see the connection and understand racism more explicitly,” she said, “understanding the ways racism plays out here, and then looking at Israel/Palestine and realizing it is the exact same system.”
But that comparison is exactly what worries many other American Jews, who say the history of white American slaveholders is not the correct frame for viewing the Israeli government or the global Jewish experience of oppression.
At Temple Concord, a Reform synagogue in Syracuse, New York, teenager after teenager started calling Rabbi Daniel Fellman last week, wondering how to process seeing Black Lives Matter activists they marched with last summer attack Israel as “an apartheid state.”
“The reaction today is different because of what has occurred with the past year, year and a half, here,” Fellman said. “As a Jewish community, we are looking at it through slightly different eyes.”
Nearby at Sha’arei Torah Orthodox Congregation of Syracuse, teenagers were reflecting on their visits to Israel and on their family in the region.
“They see it as Hamas being a terrorist organization that is shooting missiles onto civilian areas,” Rabbi Evan Shore said. “They can’t understand why the world seems to be supporting terrorism over Israel.”
In Colorado, a high school senior at Denver Jewish Day School said he was frustrated at the lack of nuance in the public conversation. When his social media apps filled with pro-Palestinian memes last week, slogans like “From the river to the sea” and “Zionism is a call for an apartheid state,” he deactivated his accounts.
“The conversation is so unproductive, and so aggressive, that it really stresses you out,” Jonas Rosenthal, 18, said. “I don’t think that using that message is helpful for convincing the Israelis to stop bombing Gaza.”
Compared with their elders, younger American Jews are overrepresented on the ends of the religious affiliation spectrum: a higher share are secular, and a higher share are Orthodox.
Ari Hart, 39, an Orthodox rabbi in Skokie, Illinois, has accepted the fact that his Zionism makes him unwelcome in some activist spaces where he would otherwise be comfortable. College students in his congregation are awakening to that same tension, he said. “You go to a college campus and want to get involved in anti-racism or social justice work, but if you support the state of Israel, you’re the problem,” he said.
Hart sees increasing skepticism in liberal Jewish circles over Israel’s right to exist. “This is a generation who are very moved and inspired by social justice causes and want to be on the right side of justice,” Hart said. “But they’re falling into overly simplistic narratives, and narratives driven by true enemies of the Jewish people.”
Overall, younger American Jews are less attached to Israel than older generations: About half of Jewish adults under 30 describe themselves as emotionally connected to Israel, compared with about two-thirds of Jews over age 64, according to a major survey published last week by the Pew Research Center.
And though the U.S. Jewish population is 92% white, with all other races combined accounting for 8%, among Jews ages 18 to 29 that rises to 15%.
In Los Angeles, Rachel Sumekh, 29, a first-generation Iranian American Jew, sees complicated layers in the story of her own Persian family. Her mother escaped Iran on the back of a camel, traveling by night until she got to Pakistan, where she was taken in as a refugee. She then found asylum in Israel. She believes Israel has a right to self-determination, but she also found it “horrifying” to hear an Israeli ambassador suggest other Arab countries should take in Palestinians.
“That is what happened to my people and created this intergenerational trauma of losing our homeland because of hatred,” she said.
The entire situation feels too volatile and dangerous for many people to even want to discuss, especially publicly.
Violence against Jews is increasingly close to home. Last year the third-highest number of anti-Semitic incidents in the United States were recorded since the Anti-Defamation League began cataloging them in 1979, according to a report released by the civil rights group last month. The ADL recorded more than 1,200 incidents of anti-Semitic harassment in 2020, a 10% increase from the previous year. In Los Angeles, the police are investigating a sprawling attack on sidewalk diners at a sushi restaurant Tuesday as an anti-Semitic hate crime.
Outside Cleveland, Jennifer Kaplan, 39, who grew up in a modern Orthodox family and who considers herself a centrist Democrat and a Zionist, remembered studying abroad at Hebrew University in 2002, and being in the cafeteria minutes before it was bombed. Now she wondered how the Trump era had affected her inclination to see the humanity in others, and she wished her young children were a bit older so she could talk with them about what is happening.
“I want them to understand that this is a really complicated situation, and they should question things,” she said. “I want them to understand that this isn’t just a, I don’t know, I guess, utopia of Jewish religion.”
Esther Katz, the performing arts director at the Jewish Community Center in Omaha, Nebraska, has spent significant time in Israel. She also attended Black Lives Matter protests in Omaha last summer and has signs supporting the movement in the windows of her home.
She has watched with a sense of betrayal as some of her allies in that movement have posted online about their apparently unequivocal support for the Palestinians, and compared Israel to Nazi Germany. “I’ve had some really tough conversations,” said Katz, a Conservative Jew. “They’re not seeing the facts, they’re just reading the propaganda.”
Her three children, who range in age from 7 to 13, are now wary of a country that is for Katz one of the most important places in the world. “They’re like, ‘I don’t understand why anyone would want to live in Israel, or even visit,’” she said. “That breaks my heart.”
This article originally appeared in The New York Times.
© 2021 The New York Times Company
source https://www.techno-90.com/2021/05/gaza-conflict-stokes-identity-crisis.html
2 notes
·
View notes
Note
abt ur Judaism post! what do u think abt how superman was created by jewish men and influenced by jewish figures (like Moses) and elements? is it cool, weird, good, lacking or anything? would u like it to be more apparent with how they write him?
Hey Anon!
Great question. I’ve had a few posts about this in the past, and for some reason it rubs some people the wrong way, which I don’t really get.
My opinion (just mine) on Superman’s Jewish Origins:
If you dig a little deeper, almost everything integral to Superman’s character (which I’ll share later) reflects Jewish concepts of justice, refugee status, persecution, and assimilation.
Personally, I think as long as folks remember that background, and respect it, Superman’s character can continue to evolve and change. The exception to this (for me) was Snyder’s Jesus-heavy motifs of Clark/Superman in BVS, which, as you mentioned, could have easily been subbed with Moses elements.
The story of Jewish persecution is, in many ways, completely separate from Jesus. It happened long before he was even around. But that can be tough to convey to audiences that don’t know the Jewish history behind Superman’s origins, and indeed see the white/Christian characterization of Clark as an “all American” hero and don’t think much beyond it.
So -- what about Superman is actually Jewish, or Jewish-inspired?
The answer is, surprisingly, a lot. I skimmed a few articles to refresh my memory on this, so here’s a few examples:
Kal-El’s origin on Krypton -- a failing planet about to explode -- and his hurried flight by parents desperately trying to save him from death, and staying behind themselves as he’s sent to earth, is a direct reference to the common Jewish story of flight at the beginning of the 20th century.
Superman’s creators were the children of Jewish immigrants. More specifically, the children of Jewish immigrants fleeing 1930′s Europe and its impending destruction. Sound familiar?
In the Holocaust, many Jewish families would have to make the terrible decision to smuggle their children out of ghettos or camps and into other countries, while they remained behind.
Clark’s characterization is influenced heavily by his lost connection to Krypton, his parents, and his powers. This longing is in conflict to the happy, simple life he leads in Kansas.
Jewish immigrants fleeing persecution, as well as their American children, often felt like they were living “in two worlds”. Tradition warred with assimilation, or the need to hide and stay safe, and Jewish Americans growing up in this period often didn’t know where they belonged.
Clark often faces villains or forces that make him choose between his Kryptonian heritage, and his life on Earth.
Often, this forces a comparison between Superman and Moses, as well -- an important Jewish figure who was also cast out by Jewish parents into gentile hands for his own safety, who grew up and discovered his Jewish community was at war with the adoptive life he had lived.
Kal-El, Jor-El, etc
In the Torah, or the scrolls which contain the original Old Testament, the Hebrew suffix “el” means “of God.” It denotes angels (Gabriel, Michael, Raphael, etc) as well as other biblical names.
Kal-El would mean “voice of God”
Jor-El would mean “God will uplift” or the “uplifting of God”
Superman as a modern “Golem”
Though not directly referenced, many have drawn connections between Clark’s ability to turn into Superman, a defender of the weak and purveyor of Justice, as an allusion to the Jewish concept of a Golem.
A Golem is a magical clay figure that can be brought to life by a Hebrew scroll placed into its mouth. Historically, it is said to protect the Jewish community, those battling antisemitism, and those who are powerless.
This connection is bolstered by one of superman’s creators losing his father to a shooting in New York as a child, and feeling powerless against such injustice.
So, why is an immigrant story of assimilation inherently Jewish?
Another great question. Isn’t the immigrant story of seeking refuge in an unfamiliar world universal, in many ways?
Yes, it definitely can be. But I would make the argument that Superman’s creators, the context of 1930′s Europe, and the Jewish concepts of justice (and naming) woven into Superman’s characterization indicate that this story is inherently about the Jewish experience.
As a final point, I would bring up the devastation that the Holocaust had on the Jewish global population. Just like Krypton, much of the historical culture, traditions, and treasures were destroyed. Jews are a minority in the world, and their numbers continue to dwindle every year. Clark is, in many ways, one of the last Kryptonians, if not the very last.
This story, even subtly woven into a comic series, resonates with me and many other Jews. It acknowledges the missing branches in our family trees, the forgotten traditions, and the pain of continuing those in a smaller and smaller community of fellow Jews every year.
#thank you anon!#I'm sorry i went on a bit of a rant#Superman#Clark Kent#Jewish Superman#Judaism#DC comics#I'm not an authority on this#just a kibitzer with an opinion#and too much time on my hands#asks#anon#please ask me questions!#they're not offensive#and I don't take offense if you disagree#this is just how i view it as a modern reform jew
278 notes
·
View notes
Note
The 40K fandom filling with alt-righters was predictable because GW won't stop rimming the Imperium at the expense of everyone else, original themes included, but how was Warhammer Fantasy going down the same way?
Its a lot more obvious with 40K because its basically been playing footsie with the Alt Right for decades now by openly embracing Neo Nazi symbolizing and imagery (its more complicated than that but i’m bitter). Warhammer fantasy doesn’t do that, it does draw on Germanic imagery but its more Holy Roman Empire than fascist/Imperial Germany. But it still has some narratives which appeal to fascists, even though the setting was 100% not designed to appeal to fascists (in fact a lot of the fluff is anti fascist). So its not deliberate but here are some default assumptions (I actually wrote a paper on this)

1) The lack of positive Emotions. Warhammer fantasy is a parody and is designed as a dark comedy, and lets admit that a lot of its fluff is very funny. But one of the problems with creating a setting where everything sucks and everybody is a bastard, is that it actually encourages the sort of nihilistic understanding of humanity which Neo Fascism (opposed to classic fascism) relies on so much. This is a world where diplomacy doesn’t work, kindness is foolish, and decency is unrewarded, all that matters is cruel war. And as a cynic myself, I can appreciate the joke they are going for, but the longer that joke goes on, the more it makes caring about humanity seem foolish. This also combines with the hatred of cute stuff (see also Doom). The Entire world view is very adolescent boy, which is about the emotional state of fascism.
2) For all of the games cynicism, it has a soft spot towards the glory of war. The world is shitty, incompetent, stupid, cruel, unjust and random, but Warhammer Fantasy tends to depict war as the only transcendental and glorious experience. This is most exemplified with the Chaos Warriors, who come off as rather noble despite being a faction whose entire existence is defined by war. Warhammer fantasy mocks many things but never war

3) It very much buys into the “Warrior Culture” myth (Seen also Conan), where some cultures are defined macho and violent opposed to softer and more civilized cultures. The Northern cultures near the Chaos wastes get this a lot. These cultures have a very “noble savage” way of writing, especially regarding the Viking/mongol based ones.

4) The background of the Empire of Man still buys into the conservative perspective of “Things were great in the past, but society steadily fell”. It actually takes this further because it attributes the fall to decadence, hedonism, and sexual immorality. I was just reading Historian and conservative shithead Niels Ferguston, who wrote
“the real threat is posed not by the rise of China, Islam or CO2 emissions, but by our own loss of faith in the civilization we inherited from our ancestors.” and that sort of view about what causes civilizations to fall fits into the Warhammer understanding of history. In fact if you go unto fascit forums, they often describe the Queer movement, especially trans activism, as Slaanesh worshipers

5) While Warhammer fantasy is not overtly sexist and I don’t think any of the writers have actual problems with women (though Games workshop is run by Satan) but the way female characters, especially female sexuality are depicted in the series is...telling. the Dark Elves and Slaanesh worshipers have a very “Sex, especially kinky sex is evil” feel. Now I don’t think the writers of Warhammer fantasy actually have a reactionary view towards sex and aren’t trying to make a fascist point, but I think that narrative supports the fascist narrative that decadence spiritually damages society. The genre is super male coded very strongly and tends to buy into macho notions of aethetic (which Warhammer 40k will take much further)

6) Because warhammer draws so much on real world societies, even by the standards of fantasy, its depiction of those societies is super telling. The Holy Roman Empire as presented in Warhammer is actually both less complicated and less international than its real world counterpart. Notably, the real holy Roman Empire actually controlled Spain and through it the New World, meaning it was by far the most ethnically diverse state in the world during the time of the Reformation. Because its drawing its influence from the Holy Roman Empire rather than more fantastical element (which I will grant gives setting a distinct Aesthetic which I mostly like) it contributes to the warped understanding of “Medievalism” which the Far Right takes advantage of. This is a problem with most fantasy and Warhamer is not alone here, but a lot of people’s default understanding of the Medieval/early modern Era is shaped more via fantasy than by an actual understanding of the era. Notable the intellectual, cultural, artistic...really any non military part of history. Which unfortunately is how a lot of people view the pre modern world, as just military history, which lends itself to conservatism.

7) Its Euro Centric as fuck. That is normal for most fantasy but because Warhammer is so balatant about its real life inspiration, the absence is notable. You have Fantasy France and Fantasy Holy Roman Empire, but you are missing the North African states, the Caliphate, and probalby most important of all, the Ottoman Empire, the greatest Rival to the Holy Roman Empire. The Holy Roman Empire and the Ottoman Empire had a century long series of wars/rivarlys/hatefucking relationship which is just absent. There is mention of a China based nation (Cathay really?) and some sort of Muslim power (Arabay) which the setting doesn’t care about and nobody ever visits. The new World exists, but the native Americans have been replaced by Dark Elves and Lizard People. You are even loss most of the real like ethnic diversity, their are new Jews and the Romani are confined to the Romania inspired vampire setting and basically exist as Bram Stoker people who dabble in dark magic. And the ogres (one of my favorite factions btw) have a very oriental visual design, which would be fine if there were actual asians in the setting. All of the non human races except the Chaos dwarves tend to look white or entirely alien which compounds this problem
8) The notion of cults. The Witch Hunters in Warhammer Fantasy play much the same role as the Inquisition who targeted Protestants, “Witches” (and in Spain at least) Muslims and Jews. Basically the inquisition was just an exercise in cruelty that just targeted entirely innocent people. In the Warhammer world, Daemon cults are real and the brutal methods of the inquisitions are largely justified, they kill a lot of innocents but they also destroy a lot of cults. This one is something I’m kinda mixed on, because the presence of evil cults dedicated the forces of hell is fun and it is a great plot for adventure, but it has the unintended side effect of making the notion of secret societies dedicated to profane rites seem less silly. Look at how Alt Rightists talk about the supposed leaders of the left, its language that is used to describe the cults in warhammer, I mean the Pizzagate conspiracy theory/Qanon conspiracy theory feel like people talking about Slaanesh and Tzeentch cults

9) Finally, the cynical nature of the setting, combined with its pro war narrative creates a world view where the world is corrupt, cruel, and unfair, the vast majority of people are ignorant morons and the nobles are decadent have weird sexual kinks. the only things holding the forces of hell at bay are the thuggish sadistic cruel soldiers who regularly indulge in torture and murder of civilians, and it is with these people you must trust. Its a brutal world where the only appropriate response is more brutality, which in addition to being ahistorical (the Early modern period was more than just war) but fits the fascist world view. The world is terrible and the only thing you can have faith in is a bunch of German war criminals with a fetish for eagles and skulls. Anybody trying to challenge that world view is either a Daemon Cultist or a naive idiot who is going to be taken over by a Daemon cultist.

(very Wagner)
Again, Warhammer Fantasy is not deliberate fascists, in fact there is a LOT in the material which rejects fascism but there is a lot of thoughtless assumptions that confirms their world view.
Also I never played/read Age of Sigmar so i don’t know if this carries over

#ask EvilElitest#Warhammer Fantasy#warhammer 40k#Holy Roman Empire#games workshop#Alt Right#Fascism#Conservatism#Daemon Cults#Pizzagate#Gamergate#Chaos Cults#Chaos Gods#nurgel#slaanesh#khorne#Tzeentch#Malice#Malal#empire of man
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
“Thirteen″ Tips for Writing About Synagogues / Jewish Writing Advice / Advice for Visiting Synagogues
So your story includes a Jew (or two) and you’ve a got a scene in a synagogue. Maybe there’s a bar mitzvah, maybe your gentile protagonist is visiting their partner’s synagogue. Maybe there’s a wedding or a community meeting being held there. For whatever reason, you want a scene in a shul. I’m here as your friendly (virtual) neighborhood Jewish professional to help you not sound like a gentile who thinks a synagogue is just a church with a Star of David instead of a cross.
Quick note: The are lots of synagogues around the world, with different specific cultural, local, and denominational practices. The Jewish community is made up of roughly 14 million people worldwide with all sorts of backgrounds, practices, life circumstances, and beliefs. I’m just one American Jew, but I’ve had exposure to Jewishness in many forms after living in 3.5 states (at several different population densities/layouts), attending Jewish day school and youth groups, doing Jewish college stuff, and landing a job at a Jewish non-profit. I’m speaking specifically in an American or Americanish context, though some of this will apply elsewhere as well. I’m also writing from the view of Before Times when gatherings and food and human contact was okay.
Bear in mind as well, in this discussion, the sliding scale of traditional observance to secular/liberal observance in modern denominations: Ultraorthodox (strict tradition), Modern Orthodox (Jewish law matters but we live in a modern world), Conservative (no relation to conservative politics, brands itself middle ground Judaism), Reconstructionist (start with Jewish law and then drop/add bits to choose your own adventure), and Reform (true build your own adventure, start at basically zero and incorporate only as you actively choose).
Synagogue = shul = temple. Mikvah (ritual bath) is its own thing and usually not attached to the shul. Jewish cemeteries are also typically nowhere near the shul, because dead bodies are considered impure.
A Bar/Bat/Bnai Mitzvah is the Jewish coming of age ceremony. Bar (“son”) for boys at 13+, Bat (“daughter”) at 12+, and Bnai (“children”) for multiples (i.e. twins/triplets/siblings) or non-binary kids (although the use of the phrase “Bnai Mitzvah” this way is pretty new). 12/13 is the minimum, 12-14 the norm but very Reform will sometimes allow 11 and anybody above 12/13 can have theirs. Probably a dedicated post for another time. Generally, however, the following will happen: the kid will lead some parts of services, read from and/or carry the Torah, and make a couple of speeches.
Attire: think Sunday Best (in this case Saturday), not come as you are. Even at very liberal reconstructionist/reform synagogues you wouldn’t show up in jeans and a t-shirt or work overalls. Unless they are seriously disconnected from their culture, your Jewish character is not coming to Saturday morning services in sneakers and jeans (their gentile guest, however, might come too casual and that’d be awkward).
1a. The more traditional the denomination, the more modest the attire. Outside of orthodoxy woman may wear pants, but dresses/skirts are more common. Tights for anything above knee common for Conservative/Reform/Recon, common for even below knee for orthodox shuls. Men will typically be wearing suits or close to it, except in very Reform spaces.
1b. Really, think business casual or nice dinner is the level of dressiness here for regular services. Some minor holidays or smaller events more casual is fine. Social events and classes casual is fine too.
1c. Even in reform synagogues, modesty is a thing. Get to the knee or close to it. No shoulders (this an obsession in many Jewish religious spaces for whatever reason), midriffs, or excessive cleavage (as I imagine to be the norm in most houses of worship).
Gendered clothing:
3a. Men and boys wear kippahs (alt kippot, yarmulkes) in synagogues, regardless of whether they’re Jewish or not out of respect to the space. Outside of Jewish spaces it’s saying “I’m a Jew” but inside of Jewish spaces it’s saying “I’m a Jew or a gentile dude who respects the Jewish space.” Outside of very Reform shuls, it’s a major faux pass to be a dude not wearing one.
3b. There are little buckets of loaner kippahs if you don’t bring your own and commemorative kippahs are given away at events (bar mitzvah, weddings). Your Jewish dude character not bringing or grabbing one is basically shouting “I’m new here.”
3c. Women are permitted to wear kippahs, but the adoption of a the traditionally masculine accessory will likely be interpreted by other Jews as LGBTQ+ presentation, intense feminism, and/or intense but nontraditional devoutness. Nobody will clutch their pearls (outside of ultraorthodoxy) but your character is sending a message.
3d. Tefillin are leather boxes and wrappings with prayers inside them that some Jewish men wrap around their arms (no under bar mitzvah or gentiles). Like with the kippah, a woman doing this is sending a message of feminism and/or nontraditional religious fervor.
3e. Additionally, prayer shawls, known as tallit, are encouraged/lightly expected of Jewish males (over 13) but not as much as Kippahs are. It is more common to have a personal set of tallit than tefillin. Blue and white is traditional, but they come in all sorts of fun colors and patterns now. Mine is purple and pink. It is much more common for women to have tallit and carries much fewer implications about their relationship to Judaism than wearing a kippah does.
3f. Married woman usually cover their hair in synagogues. Orthodox women will have wigs or full hair covers, but most Jewish woman will put a token scarf or doily on their head in the synagogue that doesn’t actually cover their hair. The shul will also have a doily loaner bucket.
Jewish services are long (like 3-4 hours on a Saturday morning), but most people don’t get there until about the 1-1.5 hour mark. Your disconnected Jewish character or their gentile partner might not know that though.
Although an active and traditional synagogue will have brief prayers three times every day, Torah services thrice a week, holiday programming, and weekly Friday night and Saturday morning services, the latter is the thing your Jewish character is most likely attending on the reg. A typical Saturday morning service will start with Shacharit (morning prayers) at 8:30-9, your genre savvy not-rabbi not-Bnai mitzvah kid Jewish character will get there around 9:30-10:15. 10:15-10:30 is the Torah service, which is followed by additional prayers. Depending on the day of the Jewish year (holidays, first day of new month, special shabbats), they’ll be done by 12:30 or 1 p.m. Usually.
After that is the oneg, a communal meal. Onegs start with wine and challah, and commence with a full meal. No waiting 4-8 hours to have a covered-dish supper after services. The oneg, outside of very, very, very Reform spaces will be kosher meat or kosher dairy.
To conduct certain prayers (including the mourner’s prayers and the Torah service) you need a Minyan, which at least 10 Jewish “adults” must be present, defined as post Bar/Bat/Bnai Mitzvah. In Conservative/Reform/Recon, men and women are counted equally. In Ultraorthodox women are not counted. In Modern Orthodox it depends on the congregation, and some congregations will hold women’s-only services as well with at least ten “adult” Jewish women present.
In Conservative and Orthodox shuls, very little English is used outside of speeches and sermons. Prayers are in Hebrew, which many Jews can read the script of but not understand. Transliterations are also a thing.
In Reform synagogues, there’s heavy reliance on the lingua franca (usually English in American congregations). Reconstructionist really varies, but is generally more Hebrew-based than Reform.
We’re a very inquisitive people. If your character is new to the synagogue, there will be lots of questions at the post-services oneg (meal, typically brunch/lunch). Are you new in town? Have you been here before? Where did you come from? Are you related to my friend from there? How was parking? Do you know my cousin? Are you single? What is your mother’s name? What do you think of the oneg - was there enough cream cheese? What summer camp did you go to? Can you read Hebrew? Have you joined?
A disconnected Jew or gentile might find it overwhelming, but many connected Jews who are used to it would be like “home sweet chaos” because it’s OUR chaos.
In Orthodox synagogues, men and women have separate seating sections. There may be a balcony or back section, or there may be a divider known as a mechitzah in the middle. Children under 12/13 are permitted on either side, but over 12/13 folks have to stay one section or the other. Yes, this is a problem/challenge for trans and nonbinary Jews.
Mechitzahs are not a thing outside of orthodoxy. Some older Conservative synagogues will have women’s sections, but no longer expect or enforce this arrangement.
Money. Is. Not. Handled. On. Shabbat. Or. Holidays. Especially. Not. In. The. Synagogue. Seriously, nothing says “goy writing Jews” more than a collection plate in shul. No money plate, no checks being passed around, even over calls for money (as opposed to just talking about all the great stuff they do and upcoming projects) are tacky and forbidden on Shabbat. Synagogues rely on donations and dues, and will solicit from members, but don’t outright request money on holidays and Shabbat.
Outside of Reform and very nontraditional Conservative spaces, no instruments on Shabbat or holidays. No clapping either. Same goes for phones, cameras, and other electronics outside of microphones (which aren’t permitted in Orthodox services either).
11a. In the now-times an increasing number of shuls have set up cameras ahead of time pre-programmed to record, so they don’t have to actively “make fire” which is “work” (this is the relevant commandment/mitzvah) on Shabbat, so services can be live-streamed.
11b. After someone has completed an honor (reading from the Torah, carrying the Torah, opening the ark, etc), the appropriate response is a handshake after and the words “Yasher Koach” (again, Before-Times).
Jewish services involve a lot of movement. Get up, sit down. Look behind you, look in front of you. Twist left, twist right. A disconnected Jew or gentile visitor would be best off just trying to follow along with what an exchange student we had once termed “Jewish choreography.”
Some prayers are standing prayers (if able), some are sitting prayers. It’s just how it is, although a handful of prayers have variations on who stands.
#jumlbr#jewblr#jewish#jewish writing help#jewish writing#jewish characters#writing jewish characters#jewish representation#writing advice#writeblr#writing jewish spaces#how to write synagogues#another long one sorry not sorry
228 notes
·
View notes
Photo










African not Black
Blackness Started in Slavery
We have to start this discussion in its most basic terms. Where do Black people originate from? Then if the answer is Africa, then what is the purpose of identifying with a color over our beautiful Motherland? We could end all discussions with just that simple sentence.
Black is a construction, which articulates a recent social-political reality of people of color (pigmented people). Black is not a racial family, an ethnic group or a super-ethnic group. Political blackness is thus not an identity but moreover a social-political consequence of a world which after colonialism and slavery existed in those color terms.
“white” depends for its stability on its negation, “black.” Neither exists without the other, and both come into being at the moment of imperial conquest– Fanon

The Invention of the White Race is a groundbreaking analysis of the birth of racism in America. When the first Africans arrived in Virginia in 1619, there were no “white” people, nor, according to colonial records, would there be for another sixty years. In his seminal two-volume work, Theodore W. Allen details the creation of the “white race” by the ruling class as a method of social control in response to labor unrest precipitated by Bacon’s Rebellion. By distinguishing European Americans from African Americans within the laboring class, white privileges enforced the myth of the white race through the years and has been central to maintaining ruling-class domination over the entire working class.

In our modern era old identities split apart and reform along more self-determined line to recover what was lost after the impact of conquest and domination. We see The Gypsies are now to be called “Roma,” and the reindeer-herding Lapps of Northern Scandinavia are the “Saami.” Similarly, some now claim the Iroquois Indians should be called the “Haudenosaunee” and the Cherokee the “Tsalagi”
Africans have gone from Negro (Spanish for Black) to Black (English for Negro) what has changed? Only the language. An identity is generally geographical and ties the people to their native environment or their core doctrine (Jews of Judaism, Muslims of Islam, Chinese of China).

Very few Africans are actually Black in color, so where is the foundation of a Black people or black people coming from? It is how Africans were seen relative to the European people. So relative to the pales skin of Europeans and White Arabs the most dominant thing about African was relative skin color. Hence the exonym Black in the eyes of the “other.” It was not the land, not the African hair, but the relative color of a diverse skin pigment – that is rarely black in color. For Indians it is their land, for Chinese it is their land, for Jews it is their faith and a notion of Israel. Yet Condolezza Rice feels the best thing that describes her in American is blackness. And to some extent she is right, because there is nothing in her cultural, ethical, aesthetic, outlook that resembles the continent her ancestors came from. She has replaced Africa with America, and finally Africaness with dreams of the White ideal.

African and black are not interchangeable just as Dark continent and Africa are not. Self-determination allows a people to re-examine definitions and sculpt them to their reality. Black, like Negro is facing linguistic extinction, especially in academic circles, due to its poor foundation in speaking about the oldest and most diverse people on the planet. Notice today only two races go by color labels; The race with the most oppression and the ones inflicting that oppression. “I am black and proud” is a song, nothing else. It is the rhetoric necessary at the time to lift an oppressed people who only knew of themselves through the eyes of their oppressor. It has run its course and has expired.
Some have argued that African people chose “black” as an acceptable identity. The evidence is in all the books African-Americans write where the word “black” (lowercase) is used without care. But self-determination has a condition – full knowledge of self. And this is why we see the new Nig*er identity which by the same mass consensus process seems to be a valid new identity. And just like “black” it is again almost exclusively the world view of a minority African population living in America.

In Mauritania, the Haratin account for as much as 40% of the Mauritanian population. They are sometimes referred to as “Black Moors“, in contrast to Beidane. The Haratin are Arabic-speakers, and generally claim a Berber or Arab origin, which is contrasted against other African peoples in southern Mauritania (such as the Wolof and Fula people who have populations in Mauritania). The Haratine, consider themselves part of the Moorish community. But where it becomes problematic is because they are “darker” in color, they are assumed to be slaves brought from “black Africa.” So powerful is the theory of “two” Africa’s that reality is twisted to accommodate its validity. Every study is looking at Africa through the lens of “Black and White”, “slave and master.” It is therefore never considered that these “black” populations, like the Kanuri, who migrated South from North Africa, are native to the region. In a struggle to sustain colonial linguistics all forms of pseudo -anthropology is imposed on the African reality posing itself as mainstream studies.

Ethiopia never had a history of “Black” identity
Brief History : During the displacement of the African Holocaust people were disconnected from culture, language and identity, they went from Fulani, Hausa, Igbo to a relative color, aptly describing their status in European society– Black. Now stuck with this name, and with no agency, no conscious of self outside of the chains of the Holocaust, being black became a source of reactionary pride. (especially in the 60’s). This happened also because the involuntary Diaspora had a deep self-hatred for their African connection, and would prefer to be a empty color than connected to their Motherland–that was the dept of the self hatred. And this produced reactionary love because they had to be something, and they could not be European, so in the psyche reaffirming a negative name was in some sense a statement of ownership–a statement of being. In reality it was a statement of displacement and self-hatred.
The word “Black” has no historical or cultural association, it was a name born when Africans were broken down in to transferable labor units and transported as chattel to the Americas. The re-labeling of the Mandika, Fulani, Igbo, Asante, into one bland color label- black, was part of the greater process of absolute removal of African identity; a color epithet that Europe believed to be the lowest color on Earth, thus reflecting the social designation of African people in European psyche. When Africans, out of their own agency refer to themselves they do so with internal paradigms and self-affirmation. No where in Africa did Africans see the obvious, the natural skin color they had, as the most distinctive characteristic in defining them:
Zulu – People of the sky
Khoi Khoi – King of men
Numunuu (Native Americans) – The people
Mediterranean — ” Our Sea”
Senegal – “Our land”
Navajo -“Diné” meaning “The People”
Han-in (Korean: 한인; Hanja: 韓人; literally “great people”)
Bantu – “human” {note}
In this history of Swahili the people called themselves “people” no color attached. Attaching color is only done to refer to “the other.” In Zulu Kingdom again we see no record of a self-reference to a “Black people” they called themselves “People of the Sky” until White people showed up and called them blacks. It is true the term Ethiopia in ancient times meant “burnt face” but the modern name Ethiopia is a name not a Greek word. And the critical thing is name verses descriptive terms. The same is true for Sudan.

ODD ETHNIC GROUP
Sesame Street use to play a game called Which one is the odd one out. Can you spot which of all of these so-called Ethnic names is the odd one out:
East Asian (a place)
Southeast Asian (a place)
South Asian (a place)
Black (a color)
Hispanic/Latino (a language group tied to a place)
Caucasian (a place)
Middle Eastern (a place)
Native American/First Nations (a place)
Pacific Islander (a place)
Arab (a place)
Linguistic evolution? COLORED – NEGRO – BLACK – AFRICAN-AMERICAN – NIG*ER

BLACK HISTORY
Black history is the history of enslavement; African history is the history of humanity. If there are no White people, could there be Black people? For over 100,000 years there were only native people of Africa on the planet, and since there were no “White” people there could not have been Black people, since everyone would have been “Black.” This is even more profound when you realize African people are the only truly native people of the place they inhabit—everyone else is at some point a settler.
Every ethnic group in this country has a reference to some land base, some historical cultural base. African-Americans have hit that level of cultural maturity… To be called African-American has cultural integrity– Jesse Jackson
And if all the “White people” vanished from the Earth, would the remaining “Black” people still be Black? So the older group must define itself relative to the European newcomers? Would it not make far more logical, historically, linguistically, and social to describe people by their land of origin. Negro = Negroid = Colored = Nigger = Black (all associated with color none are connected to a continent). Now compare this to Asiatic, Caucasoid, and Mongoloid (all are tied to land, all can be located on a map— but not so Negroid/Black). Black and White are therefore debunked as regressive incomplete terms for describing people.

For all of recorded history we see in every conflict a central theme — that of “land.” So critical as humans need land to grow crops on, to source water from (see Golan Heights), they need a place to build cities and a place to harvest mineral wealth from. So attaching your identity to land makes sense: Attaching your identity to an abstract color, does not. Black and African are not interchangeable in any logical sense. African people claim an African origin and Africa as their Motherland. There is nothing in “blackness” that logically implies any claim to anything of value, except into bondage. All it tells the world is relative to the dominant race class these group of people are “black.” And in Africa it is even worse, because language wise no majority defines themselves against a minority. i.e. Sudan (Northern Sudan) is still Sudan, but Southern Sudan has to insert “South” for clarity. Holocaust, on its own, is assigned to the Jews, who do not insert “Jews” before Holocaust, since they are the first to use the term in its modern context. How can the majority in South Africa need to identify themselves as “black” relative to a “white” when they are a overwhelming majority and hence “the norm”?
And what is even more revealing is that Dutch settlers in South Africa branded themselves as Afrikaners laying claim to the land they conquered. Signifying in that naming process they were the native European tribe of of Africa (per Zuma). And yet Natives in South Africa still refer to themselves, with glee, as blacks.
It is amazing in our modern era that an entire nation of people, who are free to think and free to reflect– the oldest nation on the planet, the parents to every other people are confined by a name that reflects only their supposed skin color — and nothing else. Being “black people” is still today indelible fixed in Western lexicon (both African American and White), despite all the evidence contradictory such color-based terminologies and the profound work of Malcolm X and especially Richard B. Moore to favor African over Black, which would give a humanist representation of marginalized people. And the perplexing thing is general contentment and seeming inability to see the obvious menace in the term. Only two groups remain on Earth adhering to color labels; the most exploited people in the history of humanity (Black people), and their apex oppressors (White people).
True freedom is not only the right to vote, but the right to self-define and the right to interrogate definitions imposed and formulate new ones, which favor the African in any given political climate

If linguistically we reject the term.Sub-Saharan Africa then therefore there is no Sub-Saharan history or people; as distinct from North Africa. We then only have Africanpeople and a history of Africa

We must realize these are still colonial classifications like Middle East which have nothing to do with historical Africa. We cannot discuss a history of Africa in these colonial boxes which only served to humiliate and take away from the continent. The terms create paradigms which limit, rather than expand, reality. If there are a black or Black people then where do “black” people come form? Since Asians come from Asia, Indians from India (all makes perfect logically sense).
So where do Black people come from? Blackia, Negroland or Blackistan, following the obvious naming convention. What is the capital city of the Black home world? Black City or Blackatropolis? So if Africans do not come from these fictitious places and we find that so-called Black people come from Africa (at some time in our recent history) then why not just call them Africans? At best the term is redundant. So what is the purpose of Blackness? Especially in a world where identity and land are exclusively interlinked for every other people: Jews of Israeli, Palestinians of Palestine, Indians of India, Zulu of Zululand, Masai of the Masai Mara
Twenty-two million African-Americans – that’s what we are – Africans who are in America– Malcolm X

Blackness, is largely a Western or American exonym, in which all so-called Black cultures around the world are forced to fit into. As Americanism expanded so to did this notion of blackness, which is attached to the civil rights struggle and today to the urban cultures of the inner cities. However, It cannot be transplanted into ancient history to describe a people such as Ancient Ethiopia who had no cultural similarities to the modern African-Americans communities. Neither can “Blackness” be put in history to say the Ancient Egyptians were not Black because they did not share characteristics with a group of Africans Europeans chose to label as the archetypal Black population (black skin, thick lips and kinky hair). To do so creates connections and disconnections where there are none. So “Black culture” or “Blackness” cannot be imposed anywhere beyond the modern era. But we can say Cultures of Africa, in which Egypt and Ethiopia were part of that African world. Being African doesn’t mean we all dance to the same music and worship the same tree. So outside of the suggestiveness of “black” and “negro” words are necessary in creating new paradigms or we will always get stuck hearing “Well the Egyptians were not Black” because of a language issue or some other technicality. Far less objections could be raised if we just stuck to “The Egyptians were Africans“. Especially if we claim African as oppose to let it float.
The political question of contributions of modern day African people must be addressed and in this respect Ancient Egypt, Ancient Ethiopia were African civilizations, the same way Greece was an Ancient European civilization (it was located in modern Europe). But this argument is a political because we live in a racialized world which discredits a people’s worth by notions of racial origin and assumes black skin is too inferior to construct civilization.
There is an academic debate that the Ancient Egyptians called themselves Black based upon KMT (Kemet) which in some circles is translated as “Black people.” Now at the end of the word KMT is an ideogram which can only mean physical place

The ideogram indicates the context in which the word applies. An ideogram for humans would always be used to represent a word that applied to people. However Kemet can only mean Black Land since the ideogram indicates it is describing a built or non-human environment. They called themselves “remetch en Kemet”, which means the “People of the Black Land.” Where rmt means simple without any adjectives “the people,” the same way the Numunuu means “the people.”(the authentic people) And likewise Zulu means people of heaven.
Ancient Egypt is commonly referred to as ‘km.t’ , with the theorized reference to the black Nile Delta earth. The determinative O49 is used to designate the term for ‘country, inhabited/cultivated land’, called the niw.t (a political designate). It is a circle with a cross which represents a street, ‘town intersection”(Gardiner 2005 (1957): 498)
But none of this discredits the founders of Kemet as being African people, just like the Fulani or the Amhara. “Black” in the North American context. The “social “construction of race in America does not rely on skin color. “African Americans,” as even Asante notes, ” constitute the most heterogeneous group in the United States biologically, but perhaps one of the most homogeneous socially.”

BLACK AND THE 60’s
Indians are from India , Chinese from China . There is no country called Blackia or Blackistan and a people must respectful be tied to geography as skin color is not the primary definitive identifier.. Hence, the ancestry-nationality model is more respectful and accurate: African-American, African-British, African-Arabian, African-Brazilian, and African-Caribbean. And if Black people has some validity as a political term it can not be limited in its application to people of African decent. Nostalgia is not an accurate place for African linguistic self-determination, and blackness is blatantly a cultural inheritance of oppressed people. The pattern of acceptance of a black identity globally walks hand in hand with European cultural oppression.
Black pride is reactionary pride, necessary then, Irrelevant now. As we blossom into a greater historical and cultural awareness of a Motherland a detachment with fictional attachments to slave names must be challenged, and we must end the romance with things that are a disservice to our identity today.
It is worth noting parts of African that are culturally intact such as in Ethiopia, Mali, Somalia, Nigeria and Niger have absolutely no fondness or linguistic presence of a “black identity.”
New York Times | The term African-American has crept steadily into the nation’s vocabulary since 1988, when the Rev. Jesse Jackson held a news conference to urge Americans to use it to refer to blacks. ”It puts us in our proper historical context,” Mr. Jackson said then, adding in a recent interview that he still favored the term. ”Every ethnic group in this country has a reference to some land base, some historical cultural base. African-Americans have hit that level of cultural maturity.” Since 1989, the number of blacks using the term has steadily increased, polls show. In a survey that year conducted by ABC and The Washington Post, 66 percent said they preferred the term black, 22 preferred African-American, 10 percent liked both terms and 2 percent had no opinion. In 2000, the Census Bureau for the first time allowed respondents to check a box that carried the heading African-American next to the term black. In 2003, a poll by the same news organizations found that 48 percent of blacks preferred the term African-American, 35 percent favored black and 17 percent liked both terms.

BLACK-AFRICA IS A RACIST TERM
Nobody on this planet puts a adjective on their identity, especially when they are a majority, except African people. Black Africa, Dark Continent, Heart of Darkness all articulate the colonial contempt for a continent and its people. But how does one arrive at the term “black Africans,” are there green Africans? Would you speak of “yellow Chinese,” or “brown Indians”? Even terms like “White Russian” are unused, despite Russia being a multi-ethnic nation. Because 80% white means the majority have no need for adding White to their Russian to qualify against a minority of “other” Russians. [3] Globally the term ” Red Indian” is rejected as deeply pejorative yet “black African” is still used even in South Africa which is used to define the majority of the population against the minority so-called white-Africans. Black African is as ridiculous as “rock stone”, rocks are stones so why double up two realities which are often the same?
There is an infinite an inexhaustible list of examples which show that no one with power wears and adjective on their identity, especially when equal or a majority. The peninsula of Korea is called Chosŏn Pando (조선반도; 朝鮮半島) in North Korea and Han Bando (한반도; 韓半島) in South Korea based on the respective names of the two countries. (wikipedia)They both use “Korea” as part of their official English names. In other words North Korea does not say they are North Korean, as far as they are concerned they are the KOREA. The South does not waste time defining itself as South Korea, again, as far as their national pride is concerned they are just Korea. Both countries have equal political and cultural agency. So how is it possible for a continent whose overwhelming demographic, political, cultural majority is African, need to refer to themselves as black + African? And with the split of N. Sudan and S. Sudan it would be shocking to see if N. Sudan adds the term “North” to its national rhetoric, to clarify itself from its new southern neighbor.
There is only one reason the term Black African exists and that is to deny nobility from African people. To explain away how Egypt could be nested in Africa but at the same time divorced from the majority of the African people. Therefore the argument “yes it is in Africa, but it is not Black African.” It is almost like saying Greece was a European civilization, but not a White European civilization.
If 95% of Africans are “Black” (capital B, if it must be used) then the minority should bear the adjective–not the majority. It is disrespectful to describe Africans with a label based solely on a color, especially when it does not accurately reflect the physical appearance of most Africans. This is made even more offensive when the etymological root of that label (black) is derived from the word Negro, and is used in place of the word African as a racial or cultural identity. In reality we must ask ourselves what is the difference between “Negro” and “Black” save historical association, the words mean the same thing, so we have moved from being Black in Spanish (negro) to Black in English (black). It is strange that despite all the genetic research and advance human anthropology we are still clinging to primitive 18th century post-Darwin model of race, which sole aim was/is to segregate and de-culturalize and enslave.
The concept of a “black Africa ” is a Eurocentric term based upon their ignorant primitive regressive deductions. It is true Arabs and Greeks referred to Africans as “black” but this was not a racial label, and moreover Africans themselves did not self-apply these external labels. Like the Phoenician who were called the “red people,” but no Phoenician would have referred to themselves in this way.

CHILDREN DIS-IDENTIFY WITH BLACK
In a recent survey conducted by the African Holocaust society it was noted that young African children (approx 4-5 years old, the age of race consciousness) when told they were members of the “black race” reacted with great confusion because they were also being taught the names of colors. Most of them objected to being called black and said they were not black but rather brown. A repeated survey found that when they were told they were African they did not object to the logic (they were African because their ancestors were from the continent called Africa). Blackness is illogical and only exist by force conditioning of children. This case study is profound because it shows how logic and identify form before social concepts are enforced.
WHITE AFRICANS
It would be very strange if a European, after 200 years in China or India, could be so powerful to alter the definition of Chinese just to be accommodated. Linguistic accommodation is only possible in Africa because of the prevailing injustice of a post-colonial dominance of European settlers. It is clear some European funded African politicians backed it, but where did it originate from? It is interesting to note Europeans (including white Arabs) constitute around 10 million people verses the 800 million plus Africans. Now this negligible minority by way of social influence has caused the majority to need to refer to themselves with the adjective of “black” to separate themselves from a serious minority group who want to be “white Africans.”Minorities of Europeans live in China, in India and in Arabia yet only in Africa has linguistic accommodation been given. Africans now must make room for those settlers who want to identify with the continent for capitalist reasons. Because once you identify with a continent then you have a legitimate claim to its resources. Thus the saying and the philosophy of Garvey “Africa for the Africans” becomes usurped. In South Africa the new trend of “Black Economic Empowerment” has seen the broadening, opening up of the borders of blackness so to speak. Indians are economically classified as ‘black’, and recently Chinese have been included in this definition. So again we see the relationship between linguistics and economic profit.In the scramble for linguistic real estate, why would these descendants of European colonialist who devastated and exploited the continent want to be called African? And in terms of self-determination who introduced these concepts?Despite claiming “African” in name they are very conscious of Whiteness when propagating the White dominant image on the broadcast mediums they control. Being White is clearly obvious when it comes to the dilemma of ownership which is still tipped in their favor. When all of these White South Africans rush home to Europe (when Africa gets a little sticky) do they encounter job discrimination experienced by fellow African South Africans or even 3rd and 4th generation African-British? They integrate seamlessly into the social environment created by White privilege. Seems like with the Indian “Africans”, African is a jacket worn to suit an economic or political opportunity.Race was not only defined in the 18th century, in Aksum and Kemet African peoples have always identified with degrees of racial inclusion and exclusion. The arrogance of Whiteness is to assume they are responsible for every single point of view that has ever existed on this planet. All the while South Africa remains White dominant and unchallenged by people who are the most vocal White Africans. Interestingly if you examine their lifestyle, you will find them to be the most racial conservative personalities. They date and marry women of their specific race, they socialize in White circles, they engage a distinctive non-African culture. And if they do have a few token “Black” friends they are often culturally compromised aberrations the continent can produce. The injustices of White dominance and the legacy of that dominance are smooth over by fictional fantasies of non-returning colonial tourist who still impose their reality as the norm for everyone else. Moreover, in dealing with these issues they always select broad base arguments and never deal with the core issue of African self-determination and agency.
Africa, unlike “black,” is a name, not a adjective. You can get on a plane and visit it, you can find it on a Sat Nav, it has boundaries, governments, you can grow crops on it, and build a house on it. But some say, Africa was a foreign name given to us, if this is true, it was given to us by our contemporaries not our conquerors. However, the word has Berber Tunisian origins meaning ” A sunny place” – Ifriqiya .Romans appropriated this word from which it is believed the modern word Africa came about the describe the entire continent. In addition, Africa is a unique name of a place and Africans are simply people who are native to that place. And over the course of history different names such as Habesha and Takruri were used to refer to African people of various regions, Ethiopia and West Africa respectively. Also the word Moor has been used across the centuries but as critics have established, the term “Moor” was used interchangeably with such other ambiguous terms such as “Ethiopian,” “Negro,” and even “Indian” to designate a figure from different parts or the whole of Africa (or beyond) who was either black or Muslim, neither, or both.
Massey, in 1881, stated that Africa is derived from the Egyptian af-rui-ka, meaning "to turn toward the opening of the Ka." The Ka is the energetic double of every person and the "opening of the Ka" refers to a womb or birthplace. Africa would be, for the Egyptians, "the birthplace.
Human skin color ranges in variety from the darkest brown to the lightest hues. An individual's skin pigmentation is the result of genetics, being the product of both of the individual's biological parents' genetic makeup, and exposure to sun. In evolution, skin pigmentation in human beings evolved by a process of natural selection primarily to regulate the amount of ultraviolet radiation penetrating the skin, controlling its biochemical effects https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_skin_color
“You can’t hate the roots of the tree without ending up hating the tree. You can’t hate your origin without ending up hating yourself. You can’t hate the land, your motherland, the place that you come from, and we can’t hate Africa without ending up hating ourselves - Malcolm X
While in Ghana, Dr. King Jr. told then U.S. Vice President, Richard Nixon, who was also in attendance at the event’s festivities: “I want you to come visit us down in Alabama where we are seeking the same kind of freedom the Gold Coast is celebrating”.Dr. King Jr. also returned from his trip deeply inspired about the Pan-African movement and penned a sermon called “Birth of a New Nation”. In it, he educated others, especially African Americans in the Civil Rights Movement, about Africa, then largely known as the “Dark Continent”. He highlighted various countries across the continent, including Egypt, Ethiopia, South Africa, Uganda, Nigeria, Liberia, Kenya, and Ghana and their plight. He used Ghana’s story to remind his brethren of the cost of freedom:“Ghana reminds us that freedom never comes on a silver platter. It’s never easy…Ghana reminds us of that. You better get ready to go to prison. When I looked out and saw the prime minister there with his prison cap on that night, that reminded me of that fact, that freedom never comes easy. It comes through hard labor and it comes through toil. It comes through hours of despair and disappointment.”2. In previously unreleased documents, it was discovered that Dr. King Jr. traveled to West Africa in 1960, this time, to attend the Inauguration of Nigeria’s Nnamdi Azikiwe in Lagos. He said the following about his trip to Nigeria:“I just returned from Africa a little more than a month ago and I had the opportunity to talk to most of the major leaders of the new independent countries of Africa and also leaders of countries that are moving toward independence. They are familiar with it and they are saying in no uncertain terms that racism and colonialism must go for they see the two are as based on the same principle, a sort of contempt for life, and a contempt for human personality.”
#african#alik shahadah#africanholocaust#black or african#black#black people#black pride#pride#egyptianart#egyptian mythology#kemet#africa#martin luther king#malcolm x#self pride#african pride#khepri#khepri neteru#musllim#habesha#ethiopian#trending topics#trending news
1K notes
·
View notes
Photo

Why George Orwell's Warning on 'Self-Censorship' Is More Relevant Than Ever
Just as George Orwell warned, governments don't have to be the censors for free speech and free expression to be fatally stifled.
By Brad Polumbo
Rule One: Speak your mind at your own peril. Rule Two: Never risk commissioning a story that goes against the narrative. Rule Three: Never believe an editor or publisher who urges you to go against the grain. Eventually, the publisher will cave to the mob, the editor will get fired or reassigned, and you’ll be hung out to dry.
The above is a quotation from George Orwell’s preface to Animal Farm, titled "The Freedom of the Press," where he discussed the chilling effect the Soviet Union’s influence had on global publishing and debate far beyond the reach of its official censorship laws.Wait, no it isn’t. The quote is actually an excerpt from the resignation letter of New York Times opinion editor and writer Bari Weiss, penned this week, where she blows the whistle on the hostility toward intellectual diversity that now reigns supreme at the country’s most prominent newspaper.A contrarian moderate but hardly right-wing in her politics, the journalist describes the outright harassment and cruelty she faced at the hands of her colleagues, to the point where she could no longer continue her work:
My own forays into Wrongthink have made me the subject of constant bullying by colleagues who disagree with my views. They have called me a Nazi and a racist; I have learned to brush off comments about how I’m ‘writing about the Jews again.’ Several colleagues perceived to be friendly with me were badgered by coworkers. My work and my character are openly demeaned on company-wide Slack channels where masthead editors regularly weigh in. There, some coworkers insist I need to be rooted out if this company is to be a truly ‘inclusive’ one, while others post ax emojis next to my name. Still other New York Times employees publicly smear me as a liar and a bigot on Twitter with no fear that harassing me will be met with appropriate action. They never are.
Weiss’s letter reminds us of the crucial warning Orwell made in his time: To preserve a free and open society, legal protections from government censorship, while crucial, are not nearly enough.
To see why, simply consider the fate that has met Weiss and so many others in recent memory who dared cross the modern thought police. Here are just a few of the countless examples of “cancel culture” in action:
— A museum curator in San Francisco resigned after facing a mob and petition for his removal simply because he stated that his museum would still collect art from white men.
— A Palestinian immigrant and business owner had his lease canceled and restaurant boycotted after activists dug up his daughter’s old offensive social media posts from when she was a teenager.
— A Hispanic construction worker was fired for making a supposedly “white supremacist” hand signal that for most people has always just meant “okay.”
— A soccer player was pushed off the Los Angeles Galaxy roster because his wife posted something racist on Instagram.
— The head opinion editor of the New York Times was fired and his colleague was demoted after they published an op-ed by a US senator arguing a widely held position and liberal colleagues claimed the words “put black lives in danger.’
— A random Boeing executive was recently mobbed and fired because he wrote an article 30 years ago arguing against having women serve in combat roles in the military.
— A data analyst tweeted out the findings of a research paper (by a black scholar) about the ineffectiveness of protests and was fired after colleagues claimed their safety was threatened.
— Led by progressives as prominent as New York Times columnist Paul Krugman, a woke mob tried to get a Chicago economist fired from his editorship of an economics journal for tweeting that embracing “Defund the Police” undercuts the Black Lives Matter movement’s chances of achieving real reform.
These are just a few examples of many. One important commonality to note is that none of these examples involve actual government censorship. Yet they still represent chilling crackdowns on free speech. As David French put it writing for The Dispatch, “Cruelty bullies employers into firing employees. Cruelty bullies employees into leaving even when they’re not fired. Cruelty raises the cost of speaking the truth as best you see it—until you find yourself choosing silence, mainly as a pain-avoidance mechanism.”
These recent observations echo what Orwell warned of decades ago:
Obviously it is not desirable that a government department should have any power of censorship... but the chief danger to freedom of thought and speech at this moment is not the direct interference of the [government] or any official body. If publishers and editors exert themselves to keep certain topics out of print, it is not because they are frightened of prosecution but because they are frightened of public opinion. In this country intellectual cowardice is the worst enemy a writer or journalist has to face, and that fact does not seem to me to have had the discussion it deserves.
Similarly, the British philosopher Bertrand Russell noted in a 1922 speech “It is clear that thought is not free if the professional of certain opinions makes it impossible to earn a living.”
Some might wonder why it’s really so important to protect speech and thought beyond the law. After all, if no one’s going to jail over it, how serious can the consequences really be?
While understandable as an impulse, this logic misses the point. Free and open speech is the only way a society can, through trial and error, get closer to the truth over time. It was abolitionist Frederick Douglas who described free speech as “the great moral renovator of society and government.” What he meant was that only the free flow of open speech can challenge existing orthodoxies and evolve society. From women’s suffrage to the civil rights movement, we never would have made so much progress on sexism and racism without the right to speak freely.
Silence enshrines the status quo. As John Stuart Mill put it:
If the opinion is right, they are deprived of the opportunity of exchanging error for truth: if wrong, they lose, what is almost as great a benefit, the clearer perception and livelier impression of truth, produced by its collision with error.
This great discovery process through free-flowing speech first and foremost requires a hands-off approach from the government, but it still cannot occur in a culture hostile to dissenting opinion and debate. When airing a differing view can get you mobbed or put your job in jeopardy, only society’s most powerful or those whose views align with the current orthodoxy will be able to speak openly without fear.
Orwell and Russell were right then, even if we’re only fully realizing it now. Self-censorship driven by culture, not government, erodes our collective discovery of truth all the same.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Time 4 Real Talk
The World has responded to the 'New Age' Lynching of George Floyd. The man lived a simple Life, but in Death, he was celebrated on a scale that matched James Brown's Homegoing; possibly a testament to his wealth of Spirit. His Death was horrible, but his Legacy is already bearing fruit. All four Officers involved in his death have been charged, & a National Spotlight has been trained on American Police Tactics.
It's very interesting to see how the 'Powers that Be' go about the business of shifting a narrative. Group Organizers have 'The Masses' calling for Police Reform, but they are missing the point. Police Officers aren't 'The Problem', they're only following protocol. Some Officers are more aggressive than others, but Society has allowed an acceptable range of violence when it comes to Black America. It's cool that Whitefolk (& some POC) have learned the phrase 'Systemic Racism', but that is just a byproduct. The phrase they should become acquainted w/, is White Supremacy.
The System of White Supremacy, is the true Dragon that needs to be slayed. News Flash: America is not a Democracy- It's a Capitalist Republic. A Republic built on the blood & bones of Black/ Indigenous (Copper Toned Aborigines) People that depends on their continued disenfranchisement. White Privilege, can be viewed as a method of wealth distribution & social autonomy. Modern day Law Enforcement Officers were assembled to uphold the racist principles (State & Federal Laws) that keep Blackfolk in that space between Human Being & untamed Animal.
White Privilege doesn't guarantee Whitefolk an escape from adversity. The wealthy White Class, classically called WASPs (White Anglo- Saxon Protestants), wanted poor Whites to take solace in the fact that no matter how bad Life gets for them, they will always be above Blackfolk. A lot of programming went into making this a reality, & Americans either have selective memory, or incredibly short memory spans... Now we are not so naive that we are blind to the fact that Law Enforcement Agencies exist to protect Corporate Interests, while The Military exists to expand Corporate Interests.
What we are saying, is that while the multiple Ethnic Groups that make up America compete w/ each other for a higher spot on the Food Chain, they All agree that Black America belongs on The Bottom. Nothing is absolute, so we know that we have always had allies; i'm just pointing out that each Federally Mandated attack on Black America, since the Hayes- Tilden Compromise (aka 'The Great Betrayal') of 1876 has been sanctioned by the (collective) silence of White America. They for the most part, stuck their heads in the sand, when it regarded the plight of Black America.
Schools featured books like "Uncle Tom's Cabin" & "Huckleberry Finn", Theaters ran 'Minstrel Shows' for nearly 100Yrs- even the modern day clown can be traced to Minstrel (Black faced) performers that mocked emancipated Slaves that traveled the rails in tattered clothes (i.e. Hobos). All of these images allowed the typical American to have little to no compassion for Us before The Civil Rights Movement. Television Cameras were as instrumental in that 'Revolt', as Phone Cameras are in this current one. Back then, Southern Whites were the mean villains in The Story, just as Police Officers are today. Northerners gasped in astonishment @ the atrocities being done in plain sight.
Then a funny thing happened- attention to Black Oppression shifted to Northern Cities. The Black Codes were here as well. We were Redlined into industrial areas, far away from the white picket fences. Blackfolk took to the Streets, & Northern Whites weren't so supportive anymore. Blue Collar Workers felt that Black migration North was jeopardizing their job security. 1968 brought 'The Great Exodus'- White Democrats in Northern States, particularly in the current Rust Belt States fled en mass to the Republican Party.
Ronald Reagan read the tea leaves as well then, as Donald Trump does now, & acted on White America's 'collective vibe' of That's enough for Black America... [*Note: Joe Biden embodied this sentiment literally up to the point when he joined the Obama Ticket in 2008]. Reagan, like Trump, pushed a Conservative Agenda that starved the Middle Class & rewarded Corporate Elites. Donald Trump became a rock star during this time. Reagan blamed the Recession he caused on Black Welfare Cheats & 'Bleeding Heart Liberals'; Trump blames Barack Obama's policies. Joe Biden was a prominent player in Reagan Era Legislation. By his own admission, he had a hand in every Anti- Crime Law on the books since 1976. Each Law played a role in systematically destroying Black Families; together, they decimated a generation of Black Men.
The Conservative Agenda for Black America was pretty clear- 'No Soup for you!' They never hid their intent. Liberals on the other hand, preached a brand of Coalition Politics that required Black Votes, but advanced a non- Black 'Minority' Agenda. The focus was on: White Women, White LGBTQ..., People of Color, & Black Women- in that order. Black Men were targeted by the Liberal Party's 'Tough On Crime' Legislation. Mandatory Minimum Sentencing kept Black Men out of Society, & Felony Convictions ensured they would have a hard time getting back in. Middle Class Black Communities were hit as hard as White Communities, but White Families were able to weather the hardship as a Family Unit; Black Women were forced to assume the roles of Mother & Father, in the face of rising drug & gang activity .
Its pretty awesome to see so many people of different ethnicities & social backgrounds coming together to protest Racism in general, & Anti- Black Racism specifically. Black America has been oppressed by White Supremacy for 400Yrs & counting; We need more than justice, We need to be indemnified- made whole. It's a total insult for the American Gov't to tell Us 'No' to Reparations, after watching European Jews, & Japanese receive payment for far less than we endured. An even bigger insult, is this notion that ALL 'Afrikan Americans', & Native Americans should get a share of what is specifically owed to Us. American Descendants of (Chattal) Slavery (ADOS) are a specific group w/ a specific need. No one else shares Our experience in America.
This plays into the White Supremacist view that whatever we give to Black America, we can give to Everyone else. This is how Affirmative Action Programs for Black Americans became Diversity Initiatives for 'Minorities'. It's no surprise that the Immigration Act was passed the same Year that the Civil Rights Law went into effect. White Supremacy thrives on the misfortune of Black People. America has used immigration as a weapon for over 150Yrs to slow any progress in the Black/ ADOS Community. They have not been able to kill Us off, so they are perpetually watering down Our overall percentage of the population.
Immigrants are offered Grants & Services that are denied to Black America/ ADOS. Immigrant Enclaves in Cities & Suburbia are thriving, while Black Communities are starved of resources, leaving them vulnerable to 'gentrification'- modern day Homesteading. These same Immigrants set up Stores in Black Communities, where they are welcomed, but Blackfolk are critiqued when we enter these Immigrant Communities- much like the way we are, when we enter White areas.
The Black- Brown Alliance sounds heart warming, but honestly, most use this 'Alliance' to profit off Black Effort & Dollars. A lot of these people identified as 'White' on past Census rolls. 50Yrs ago, Black Men were the focus of that attention; today, it's Black Women. Divide & Conquer is a tried & true weapon of White Supremacy. Black America flounders because of the inner conflict instigated by this method over the Centuries. I'm aware that every group had to endure this assault, but Black America is the one target that Everyone else seems to agree on exploiting. There's no hiding from this.
While i'm happy to see multicultural crowds globally protesting anti- Black racism, I can't help but wonder how far will support go? If We judge by past acts, not far enough. Resources are necessary, & Society has a limit to how much it's willing to spend on Black Problems, before extending those same resources to Everyone else. Politicians talk about Equality, but never about Equity. To be honest, Black America only needs to be left alone. Our Story is one of perpetual 'Arrested Development'. Black Codes, Klan violence, Jim Crow, Redlining, Imminent Domain, & Benign Neglect created the current State of Black America. So called 'Empowerment or Opportunity Zones' are disingenuous @ best... I'm not sure what Society will do, but one thing is certain- as Black America goes, so will the Black Diaspora.
#ADOS
#B1
8 notes
·
View notes