#theatre history
Text
You can’t be too good at your job: FALSE.
Richard Mansfield’s 1880s onstage portrayal of Dr. Jekyll’s transformation into Mr. Hyde was so good that people accused him of being Jack the Ripper and even wrote letters to the London police encouraging his arrest.

#why is this so funny#imagine if Zefron got accused of being a serial killer bc of his Ted Bundy portrayal#you’re getting a little too accurate there my guy#jekyll and hyde#dr jekyll and mr hyde#Richard Mansfield#plays#books#novels#jack the ripper#literature#classic literature#classics#robert louis stevenson#history#theatre#theatre history#history facts#fun facts#acting
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
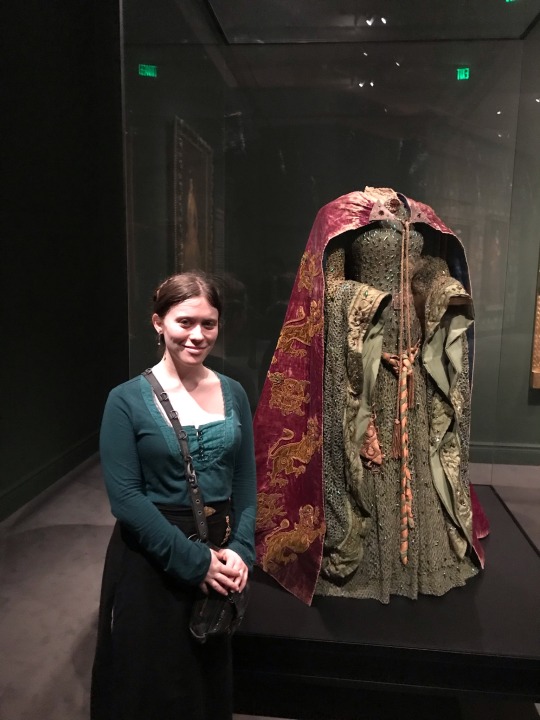

OHMYGOD OHMYGOD OHMYGOD
#fashion history#theatre history#ellen terry#yes I asked a complete stranger to take this#lady Macbeth dress#beetle wings#gpoy#my face
207 notes
·
View notes
Text


Jeanna de Waal as Mrs Lovett in Sweeney Todd on Broadway
Jeanna is the Lovett and Beggar Woman Standby! 📷: @Lizovich on Instagram
#Jeannadewaal#sweeney todd#mrs lovett#stephen sondheim#sondheim#standby#understudy#broadway#musical theatre#theatre kid#annaleigh ashford#josh groban#Ruthie Ann Miles#into the woods#a little night music#sunday in the park with george#theatre history#theatre
70 notes
·
View notes
Text
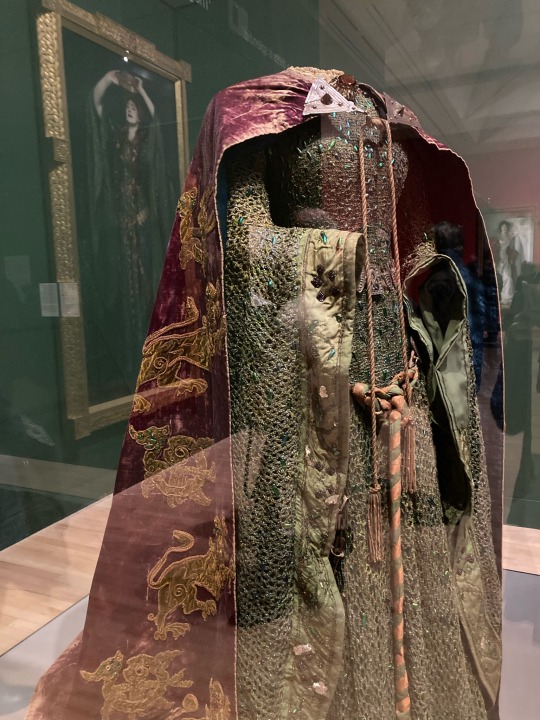
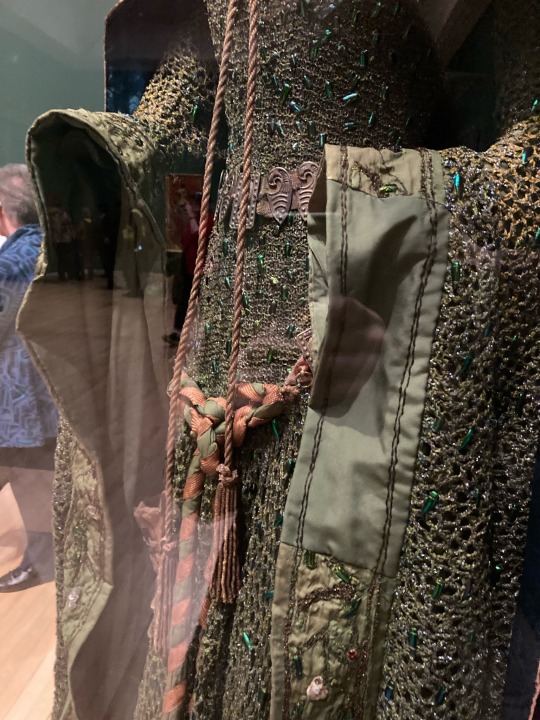





Went to the Sargent and Fashion exhibition last week and wasn’t prepared for this. Excuse the shoddy quality, I was too excited
#costuming#costume design#shakespeare#costume#1890s#1890s fashion#victorian#victorian fashion#aestheticism#pre raphaelite#lady macbeth#ellen terry#art history#fashion history#theatre history#john singer sargent#tate britain
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
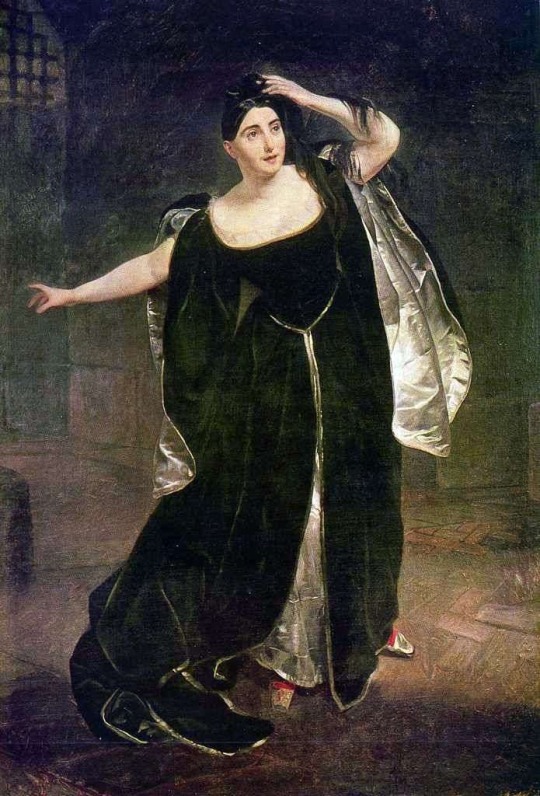

Giuditta Pasta in the role of Anne Boleyn by Karl Brullov (1830)
#this role was specifically written for her🥰#anne boleyn#queen anne boleyn#anna bolina#anna bolena#opera#portrait#romantisism#19th century art#19th century#tudor history#the tudors#english history#henry viii#tudor era#gaetano donizetti#theatre#theatre history#history#art#tudor dynasty#art history#giuditta pasta#italian#italian opera
71 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Your Favorite Godspell Song Says About You:
Prepare Ye: Is it crack? Is it weed? What drugs do you take, or are you just high on life?
God Save the People: I, too, am healing from religious trauma
Day By Day: Hello, LGBT community
Learn Your Lessons Well: You’re a stage production purist who hates the movie. I politely disagree, but you’re valid
Bless The Lord: You go up and dance if there’s live music around. Keep at it!
All for the Best: You’re an old time theatre kid who craves the smell of dance rosin
All Good Gifts: Ya damn hippie! (tbf so am I)
Light of the World: You live for chaos and have probably committed a crime. You also take the “let’s have some wine” line a bit too seriously
Turn Back, O Man: Okay, material gworl. I see you
Alas for You: You enjoy callout posts and internet drama
By My Side: You’re definitely sentimental about the little things and you slept with all your stuffed animals as a kid because you felt bad that they’d be lonely
We Beseech Thee: Yeehaw, pardner! Giddy up, I do declare 🤠
Beautiful City: You enjoy Jesus x Judas unironically
On The Willows: Ugly sobbing during a movie is perfectly okay and I want you to know that
Finale: You’re either here for the sick guitar licks or you’re a sadistic bastard who thinks the crucifixion is funny
#broadway#musical theater#rock musical#cult musical#godspell#godspell 1973#jesus x judas#rock opera#stephen schwartz#old Broadway#schmicago#carnegie mellon#theatre history#theatre kid
113 notes
·
View notes
Text
“New Women” and Stoker’s Theatre Job
Given Bram’s “New Woman” rant at the end of Mina’s 10 August diary entry, now seems like a good time to discuss two of the great actresses of the Fin de Siècle stage!
First of all, we have Ellen Terry -- onstage partner to (you guessed it) our pal Henry Irving, and probably most widely recognizable in this John Singer Sargent painting of her as Lady Macbeth.

While the beetle-wing green dress deserved to be immortalized in all its stately glory, the tone of the portrait is actually very different from that of Terry’s Lady M -- she never crowned herself onstage, and the character was played with a much more “fragile” brand of late-Victorian femininity. Despite a scandalous private life (including two children born out of wedlock, gasp!) Terry’s public persona was aligned with a series of “virtuous” Shakespeare heroines (Ophelia, Cordelia, Desdemona, Portia, Beatrice, Imogen).
In 1878, when Henry Irving became manager of the Lyceum theatre (where Bram Stoker soon became business manager), he convinced Ellen Terry to join the company as his leading lady. Both actors were separated from their spouses (Terry from her second husband) at this point, so their partnership publicly mirrored that of earlier husband-wife leading pairs. At least officially, Irving dictated the company’s artistic choices, the casting, and Terry’s (record breaking) salary, and onstage, Lady M may have been evil, but she was also Macbeth’s perfectly loyal wife.

Ellen Terry’s Imogen (see the colorized edit of a publicity photograph above), opposite Henry Irving’s villainous Iachimo in 1896 is regarded by some as a key inspiration for Lucy Westenra (interesting article/abstract here and book chapter/summary here, apologies for the paywalls). Given that Iachimo creeps on Imogen while she’s asleep and then uses this encounter to threaten her life / accuse her of promiscuity, there are certainly some parallels to be had if you go looking for them.
Interestingly enough, however, when Stoker produced a staged reading of Dracula at the Lyceum in 1897 (in order to claim copyright over any future stage adaptation), Ellen Terry’s daughter, Edith Craig, played Mina. And Edith was very definitely a card-carrying, suffrage-supporting, queer and polyamorous New Woman. Fun fact: in the post-Lyceum phase of her career, Ellen Terry was actually a pretty active suffrage campaigner / fundraiser too. (And I suspect, if we were to carry Mina and Lucy forward to their hypothetical Dracula-free, untouched by Bram Stoker’s authorial misogyny futures, both of our heroines eventually would be too).

While we’re on the subject of the scandalous New Woman, however, the other late Victorian actress I cannot go without mentioning is the French sensation Sarah Bernhardt (who by the time Dracula was published had a substantial performance history in England and the US as well). A rough contemporary of Ellen Terry, Bernhardt, by contrast, cultivated her own reputation for the scandalous. Bernhardt quite intentionally broke gendered boundaries left right and center.

Visually, Bernhardt is perhaps most strongly associated with the art nouveau posters she commissioned (from artist Alphonse Mucha) for her theatre company in Paris - examples of 1899′s Hamlet and La Tosca are above. While there are also plenty of photographs of her as Hamlet (although far from the first woman to play the role, Bernhardt’s performance is one of the most famous) and in other promotional images, the photo I’d rather draw your attention to is this one:
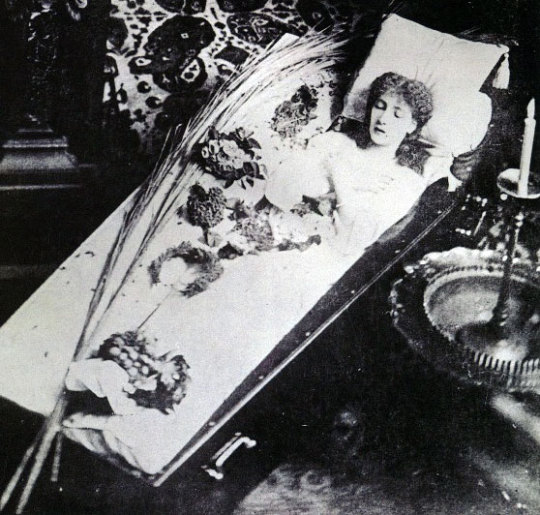
Yes, that is a young Sarah Bernhardt lying asleep in a coffin -- a coffin which she is said to have traveled with and claimed to sleep in regularly. Quite the publicity stunt (and pre-Dracula too)! Other features of her eccentric public persona included traveling with a menagerie of wild animals -- including an alligator, at least one variety of big cat, and a number of lizards and/or chameleons.
Bernhardt was also a sculptor, and her Self-Portrait as a Chimera (circa 1880, below) notably features bat-like wings, instead of more traditionally feathered, bird-like ones.
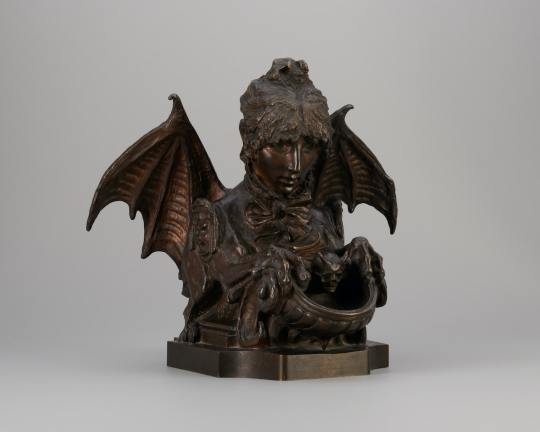

Which is to say, I think we’ve found another vampire!
#ellen terry#sarah bernhardt#Bram Stoker#our good friend henry irving#fin de siècle#the new woman (gasp!)#dracula daily#theatre history#shakespearean / stage manager reading dracula#cymbeline#hamlet#lady macbeth
585 notes
·
View notes
Text






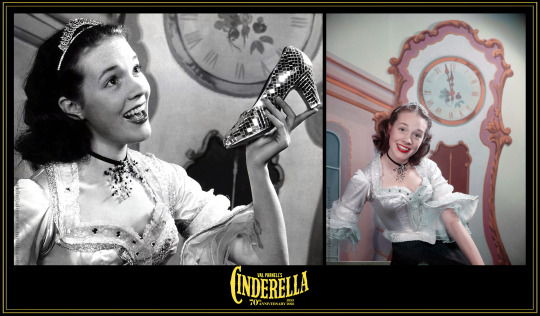






70th anniversary of Cinderella
London Palladium, 122 performances
(24 December 1953 - 6 March 1954)
This month marks the 70th anniversary of a milestone in the early career of Julie Andrews: the opening of Val Parnell's lavish Christmas pantomime, Cinderella, at the London Palladium on 24 December 1953.
Cinderella would be Julie’s fifth and final UK pantomime, following earlier runs in Humpty Dumpty (1948), Red Riding Hood (1950) Aladdin (1951), and Jack and the Beanstalk (1952). It was the biggest theatrical production Julie had yet undertaken and it would prove a turning point in the young star's career.
'No Pigtails for Julie'
By 1953, Julie was turning 18 and fast outgrowing the "infant prodigy" label of her early career. Efforts had been made for some time to update Julie's star image with a more mature look and an expanded musical repertoire. Much was made in the press about the new "[g]rown up now (or almost) Julie Andrews" (Bendle 1953: 2). "The tiny pigtailed schoolgirl who at age 13 sang in a Royal Command Performance," remarked one newspaper commentator, "is now a long-limbed attractive young lady who is wearing her first strapless dresses" (Pearce 1954: 6).
As an archetypal tale of girl-to-woman metamorphosis, Cinderella was an ideal vehicle with which to advance these transformative ambitions. It not only gave Julie titular 'principal girl' status, but called on her to assume a role of emotional nuance and adult sophistication.
Even Julie's mother, Barbara, is reported to have exclaimed:
“Julie, this is the perfect part for you at the perfect age. It couldn’t have come at a better time in your career" (Andrews 2008: 156-57).
Val Parnell presents...
Underscoring the significance of Cinderella was the fact it was a Val Parnell production. Dubbed 'Britain's Mr. Show Business', Parnell was a hugely influential impresario who dominated the British entertainment scene for many decades. He had started in provincial variety management before progressively rising up the ranks to assume control of the prestigious Moss Empires theatre chain (Bullar & Evans 1950: 219). Later, Parnell would go on to play a significant role in the expansion of the British television industry as General Manager of ATV, the first commercial television network in the United Kingdom (Sendall 1982: 250).
Renowned for his astute promotion of new talent, Parnell had been instrumental in launching Julie's career when he cast her in her first professional show at just 12 years of age: the now legendary Starlight Roof at the London Hippodrome in 1947/48 (Alldridge 1954: 1). Cinderella would bring the two together again for the first time in six years. To hear Parnell tell the story, it was a reunion long in the making.
"From the moment [I] first heard her sing," he declared, I "made a mental note that one day [I] was going to present Julie Andrews as Cinderella." As he explained:
"So many child performers are inclined to be precocious...But Julie was not. She had that appealing simplicity which she still retains. It struck me at the time that she had all the qualities of an ideal Cinderella -- youth. freshness, charm" (Lanchbery 1954: 1).
At the London Palladium
Of all the theatres managed by Parnell, none was more celebrated than the London Palladium, a 2200 seat theatre noted for its opulent architecture and state-of-the-art stage facilities (Woodward 2009). Parnell's adept leadership propelled the Palladium to international acclaim as the most famous variety theatre in the world and a top drawcard for international stars. "To appear at the Palladium is the goal to which every artist strives," noted a 1957 newspaper commentary, "to appear at the Palladium is to have achieved star status!" (Hoddinott 1957: 4).
The Palladium was also an important venue for Christmas pantomimes. Under Parnell, the Palladium "became the home of spectacular pantomime" with audiences eagerly anticipating each year's offering (Baker 2014: 219). Parnell applied the same triumphant formula to the humble British panto that he used in his variety revues: a blend of star power, spectacle, and money.
Writing in 1952, Ian Beven chronicled Parnell's studied approach to his annual pantomime at the Palladium:
"Each year...Parnell has tried to produce something bigger and better than the year before...He starts in midsummer, with a bare stage. By the third week in December, he has spent about £25,000 on scenery, costumes, musical arrangements, script, and rehearsals...Running costs of the show are high, as Parnell is prodigal with talent and fills his stage with people, and there are only about 140 performances on which to make a profit; but there is no disguising the fact that pantomime in this manner is a highly remunerative proposition, for there is rarely an empty seat throughout the run" (Seven 1952: 223).
Val Parnell's Magnificent 'Cinderella'
Cinderella would be Parnell's sixth pantomime at the Palladium. It would also be the only fully-staged panto in the West End for the 1953 Christmas season. In a sign of the rapidly changing post-war theatre scene, most of the other major London houses were tied up with long-running musicals and plays, largely imported from America. In addition, arena-style ice spectaculars were increasingly in vogue with a slew of new-fangled pantos "on ice" scheduled for suburban venues, leading some wags to quip that Parnell should call his show "Cinderella on Wood" ('Old fashioned Val' 1953: 6).
While many lamented it as a sign of "the decline and fall of the honoured institution" of the traditional panto, the absence of competition gave Parnell a distinct commercial advantage ('At the Pantomime', 1954: 4). When pre-sales for Cinderella opened in the autumn of 1953, the booking office was inundated and the show would become the theatre's most successful pantomime to date (Alldridge 1954: 4).
It also spoke to Parnell's innate sense of theatrical traditionalism. Though he was certainly not averse to innovation and was quick to adopt state-of-the-art technologies, Parnell was a producer of the old school. He believed in sticking to the tried-and-true and giving audiences what they expected. "Audiences haven't changed at all," he opined, "Certainly not the Palladium audiences. It's the same as it ever was. People go the the theatre to enjoy themselves...My job is to give it to them in bigger and better shows" (Hoddinott, 1957: 4)
True to this crowd-pleasing philosophy, Parnell determined to make Cinderella his most spectacular panto yet. Planning for the show started early in 1953. "I always start pantomime with a bare stage," he declared, "Everything must be new" (Fagence 1958: 4). Heading the production team were two influential figures who were something of righthand men to Parnell: Charles Henry and Charles Reading.
Henry was Chief of Production at the Moss Empire chain for over thirty years. During his tenure, he would produce over 200 revues and pantomimes, as well as fourteen Royal Command Performances (Born & Frame 1960: 4; 'Charles Henry' 1959: 1). Known as a canny talent-spotter with an encyclopaedic memory -- Bud Flanagan famously called him "a blinking card index of comedy" -- Henry was fondly remembered by Parnell at his passing in 1968 as "one of the theatre's greatest backroom boys" and "my closest associate" (Evening Standard Reporter 1968: 17).
Reading was an equally trusted majordomo for Parnell. A true theatre polymath, Reading trained as an actor before expanding into production, direction, writing, and design. It was the latter talent that brought Reading initial fame with a series of innovative opera and ballet designs for Sadler's Wells and the Old Vic. He subsequently moved into designing more commercial fare in the West End and, in 1947, was contracted by Parnell as resident designer and production assistant at the Palladium (Barker 199: 20; Vallance 199: 36).
Together Parnell, Henry, and Reading set about staging Cinderella as an unparalleled spectacular. Set and costume design alone was budgeted at over £20,000, which equates to almost £700,000 in today's money (Webster 2013). Reading designed an intricate series of progressively spectacular sets, including a palatial Ballroom, a Cave of Crystal Lustres, and a Palace of Porcelain for the grand finale (V&A 2015).
Famed stage couturier, Robert St John-Roper, designed a complementary suite of costumes including a dazzling ballgown and bejewelled wedding dress for Julie. In her 2008 memoir, Julie recalled the breathtaking splendour of it all:
"Everything about that 1953/1954 production of Cinderella had a certain elegance...The production values on the show were terrific; there were revolving stages, and real white ponies pulling the spectacularly gilded coach...In the grand finale wedding sequence, my crinoline was so huge that I had to arrive backstage dressed in my bodice, sleeves, and petticoat, and walk into the crinoline skirt, which was braced on a stand because it was so bejewelled and cumbersome. The company, Prince Charming, and I were brought up from below stage on a hydraulic elevator, to be revealed in a sparkling white set and costumes for the final tableau" (Andrews 2008: 155-57).
Spectacle, Humour, and Charm
Careful attention was equally paid to the other production elements of Cinderella to ensure a well-wrought work of quality theatrical entertainment. To write the script, Parnell commissioned a trio of talented young writers who were only then beginning to make a name for themselves but who would go on to become giants of British comedy: Eric Sykes, Spike Milligan, and Mike Bishop. Their original treatment hewed closely to the core elements of the well-known fairy story but embroidered with innovations and, true to panto style, comic flourishes.
In the Sykes et al script, the story opens with Baron Pastry of Stoneybroke Hall lamenting that he has fallen on hard times (Stoneybroke...get it?!). He lives with his beloved daughter, Cinderella, and their faithful but hopeless retainer, Buttons who carries an unrequited flame for Cinderella. The Baron announces he has just married a wealthy widow in the vain hope of restoring his fortune. She comes to the Hall with her two unloved and unlovable daughters -- the Ugly Stepsisters, of course -- and they set about making Cinderella's life a misery. The requisite Royal Ball, benevolent Fairy Godmother, and Glass Slipper hunt all ensue before the inevitable happily-ever-after ending (Sykes et al. 1953).
Woven around these well-worn plot points were a series of comic interludes designed to accomodate the pantomime conventions of audience participation and novelty acts. These ran the gamut from a demonic door and a bomb-toting spaceman ("it's behind you") to jive singing footmen and a giant electric washing machine that tumbled a hapless Baron Pastry along with an assortment of oversized clothes (Sykes et al. 1953).
Song and Dance
No pantomime would be complete without music and dance and Cinderella served both in abundance. Overseeing the musical side of things were another pair of Palladium panto stalwarts: Phil Park and Bobby Howell.
Park had been a star cinema organist during the picture palace era but, following the war, he turned his attention to composing and arranging. It was in this capacity that Park worked frequently for Parnell on his Palladium pantos which he "tailored to the stars appearing in the shows but always preserved the time-honoured tradition" ('Obituary: Phil Park' 1978: 6).
Bobby (aka Bobbie) Howell was a prominent band leader of the inter-war years, touring the cinema and dance circuits. After the Second World War, he became a musical director in the West End, working on a string of successful shows such as Strike a New Note, The Lisbon Story, and Piccadilly Hayride. He also worked as musical director and conductor on many of Parnell's pantomimes, including Cinderella ('Bobby Howell' 1962: 3).
In crafting the musical score for Cinderella, Park and Howell followed typical pantomime form of mixing existing well-known tunes with bespoke compositions. Many of the latter were written by Park including a humorous duet between Cinderella and Buttons (played by Max Bygraves). In this duet, Cinderella fantasises about a romantic future with the Prince, while Buttons humorously interjects with sardonic quips:
Cinders: There's a lady -- and she curtseys,
Who she is, I cannot guess.
She might be me, except that she
Has such a pretty dress.
And there's her handsome partner,
Who is he, do you suppose?
Buttons: All I see's a turkey,
With a whopping parson's nose!
Cinders: Now I see him very clearly,
With a smile upon his face;
I'm certain he's a Prince,
Because he bows with royal grace.
See now he takes her hand,
And lifts it gently to his lips!
Buttons: He looks like George Dawson,
With a plate of fish and chips!
In addition to the duets, Julie had two showcase solos in Cinderella: "Chasing Shadows", a 1935 torch song by Silver and Davis, and "Is it Any Wonder," a lilting pop ballad by Bob Hayes and Roy Rodde which had been a recent chart hit for Joni James.
Interestingly, both solos were modern pop standards and, thus, a marked departure from the light classical repertoire that had been Julie's stock-in-trade. She did get to do some limited coloratura trilling in the extended Transformation Scene at the climax of Act 1 where Strauss waltzes formed the musical accompaniment, but the strong emphasis on popular tunes was indicative of the strategic shift in Julie's image mentioned earlier.
A number of reviewers remarked that Julie didn't seem to do as much singing in Cinderella as they were expecting. She did, however, compensate with quite a bit of dancing -- more dancing in fact than she'd ever done in a professional context.
Not only was there the mandatory waltz with the Prince, but Julie had a solo dance early in Act 1. She was also a key part of the pre-intermission ballet sequence. Choreography for Cinderella was provided by Pauline Grant with whom Julie had worked so happily the previous year in Jack and the Beanstalk. Pre-show publicity photos showcased Julie's dance rehearsals with Grant, underscoring her now mature lithe figure and womanly style.
A Who’s Who of Cinderella
Alongside Julie, the cast of Cinderella was a roster of star names and variety notables:
Max Bygraves as Buttons: Born in 1922 in London, Bygraves was a versatile entertainer known for his Cockney persona, humorous storytelling, and sentimental singing. His endearing catchphrases and relaxed chummy style made him a beloved figure in British entertainment. Growing up in a modest family, he showed early signs of showmanship, encouraged by his prizefighter father. Bygraves left school at 14 and served in the RAF during WWII, where he began entertaining troops. His career took off post-war with various stage and radio appearances, including Educating Archie where he first performed alongside Julie. He made several films in the 1950s and his recordings, often nostalgic or comedic, were hugely popular. He continued performing internationally for many years, eventually settling in Australia. Recognised for his contribution to entertainment, he was awarded an OBE in 1982. He passed away in 2012 (Leigh 2012: 37).
Richard Hearne as Baron Pastry: Born in Norwich in 1909, Hearne came from a family with deep roots in music hall and circus arts, and he started performing on stage as a child. Hearne's career in variety and revue culminated in the creation of the beloved Mr. Pastry, a bowler-hatted, walrus-moustached character that brought him success in West End shows, pantomime, and TV, both in the UK and internationally. His role in Cinderella was effectively an adaptation of Mr Pastry complete with his signature comic dance, "The Lancers". A dedicated philanthropist, Hearne was a very active supporter of handicapped children and was honoured with an OBE in 1970 for his charity work. He passed away in 1979 ('Obituary: Richard Hearne', 1979: 27).
Adele Dixon as Prince Charming: Born in South London in 1908, Adele Dixon was a versatile performer known for her roles in London and Broadway musicals, Palladium pantomimes, and Shakespearean plays. After training at the Italia Conti Academy and the Royal Academy of Dramatic Art, she joined the Old Vic company. There, she shone in roles like Juliet and Ophelia. Dixon's transition to musical comedy in the 1930s made her a celebrated figure in the West End, admired for her red-gold hair, expressive brown eyes, and clear soprano voice. Her noteworthy performances included leading roles in Lucky Break, Anything Goes, and Over She Goes. Additionally, she appeared in the film Calling the Tune and became the first female performer on BBC Television in 1936. Dixon continued her success in post-war years with major hits like The Fleet's Lit Up and All Clear. She was also highly acclaimed as a Principal Boy in pantomimes, performing in these trouser roles 14 times throughout her career. Her portrayal of Prince Charming in the 1953 production of Cinderella marked her last appearance on the West End stage. While she continued to perform in provincial roles, health issues forced her into early retirement in the late 1950s. Dixon passed away in 1992 (Thornton, 1992: 29).
Joan Mann as Dandini: Welsh-born Mann trained as a dancer and started touring the variety circuit in her teens where she appeared on bills with stars including Max Miller and Tommy Trinder. A tall attractive brunette with a pleasant voice and shapely dancer’s legs, Mann was a perfect pantomime boy. She played opposite Julie in Jack and the Beanstalk (1952) and also toured with her as part of the musical revue, ‘Cap and Belles’ in 1953 (Andrews 2008: 146). Though she wasn't Principal Boy in Cinderella, Mann played the other leading pants role of Dandini, the Prince's Squire. Mann’s greatest fame came later as part of the celebrated Fols-de-Rols variety troupe with whom she performed for almost two decades. She also starred opposite Dame Anna Neagle in the hit West End musical, Charlie Girl in the late-1960s. Mann died in 2007 aged 87 (P.N., 2007: 53).
Jon Pertwee as Buttercup: Born in 1919, Pertwee was a versatile actor who left a significant mark in television, radio, theatre, and film. Educated at Sherborne, he belonged to a family of distinguished artists and made his acting debut in 1939 in Brighton. His notable wartime service on the HMS Hood led to a fruitful collaboration with Eric Barker in comedy writing and radio. Pertwee became a household name with his long-running role in the BBC radio series, The Navy Lark. He gained even greater international fame on television as the third Doctor Who from 1970 to 1975, and as Worzel Gummidge. Pertwee's career spanned over 100 films, including two Carry On movies, and numerous stage productions. In Cinderella, Pertwee took on the comic drag role of Buttercup, one of the Ugly Sisters. Pertwee passed away in 1996, leaving a legacy as a unique and memorable actor (Newley, 1996: 38).
Tony Sympson as Dandelion: Born in East London in 1907, Tony Sympson had a dynamic career in music and theatre. Initially trained as a choral scholar at St Clement Danes Church Strand, he made his stage debut as a specialty dancer in Dear Love. A mainstay character actor in West End theatre, he appeared in plays, musicals, revues, pantomimes, and operas. Sympson also featured in television ads where he earned a reputation for well-conceived characterisations. A pantomime regular, Sympson played the second of the Ugly Sisters, Dandelion, in Cinderella, a role he would repeat in subsequent productions. Sympson died in 1983 at the age of seventy-six (Marriott, 1983: 7).
Cyril Wells as Baroness Pastry: Born in Belfast in 1907, Wells' entry into acting was fortuitous. Initially a bank clerk, his passion for dancing led him to become a rehearsal partner for actress Jessie Matthews. This collaboration resulted in Wells being cast as her dance partner in the 1936 film It's Love Again, his only appearance on screen but a stepping stone into show business. He then featured in West End musical comedies like Order to View (1938), Here's Looking at Them (1939), and The Charcoal-Burner's Son (1939). Post-war, Wells shifted to comic roles in theatre and variety, notably in pantomime. In Cinderella, he played the Dame role of the blue-wigged Baroness. Wells passed away in 1958 in Southport, Lancashire ('Obituary: Cyril Wells', 1958: 9).
Ted and George Durante as the Broker's Men: One of several novelty acts to appear in Cinderella, the Durantes were a popular acrobat comic duo who found popularity on the post-war variety circuit. Contrary to their billing as brothers, the duo actually comprised two unrelated individuals, Ted Aston and George Mooney. They met in 1946 while performing as part of an acrobatic troupe and decided to branch out as partners, adopting the Durante surname at random. Their act ran for nine years till the late-1950s when Ted married and formed a new double act with his wife, becoming 'Ted and Hilda Durante'. This husband-and-wife team continued for many decades, becaming regulars on TV variety shows in the sixties and seventies (Wilmut, 1985: 182).
Elaine Garreau as the Godmother: Anglo-French actor Garreau, born in 1903, had an extensive and diverse career in British theatre, film, and television. She trained as a dancer, starting on the London stage at age 11 with a company of child artists. At 16, she was principal dancer at the Théâtre des Ambassadeurs in Paris and, at 20, understudy to the legendary Mistinguett. Returning to the UK, Garreau transitioned to acting and performed for many years in various London and provincial troupes across drama, comedy and musicals. Throughout the 40s and 50s, Garreau appeared frequently in pantomimes. In Cinderella, she took on the role of the magical Fairy Godmother. A few years later in 1958, Garreau would play again opposite Julie as part of the original London production of My Fair Lady, in the role of Lady Boxington. Garreau would remain with the show for over 10 years in both the Drury Lane and touring productions, racking up over 3,000 performances which was a world record. In her later career, Garreau increasingly appeared as a character actor in film and television. Garreau died in 2000 at the grand age of 97.
Silvia Ashmole as the Fairy Queen: Born in 1926, Ashmole enjoyed an idyllic childhood, travelling through Europe with her affluent parents and attending Cheltenham Ladies College. A trip with her mother to the ballet in London inspired Ashmole to take dancing lessons and, at age 16, she enrolled in the Cone-Ripman School of Dance, where she quickly excelled. Soon thereafter she secured a place in the coveted Royal Ballet (Sadler's Wells) and toured with them for several years. During a season at Glyndebourne, she met and eventually married the renowned Anglo-German opera director Peter Ebert. Ashmole continued her career as a dancer, often performing in operas at Glyndebourne and Edinburgh. She also worked frequently with choreographer Pauline Grant who contracted her to appear as the Fairy Queen in Cinderella (Wigglesworth 2018).
The Casavecchia Troupe as the Clowns: Billed as the "World's Greatest Comedy Tumblers," the Casavecchia Troupe was a team of acrobats who had worked individually in circus and variety before combining their talents. They toured widely in the UK variety circuit during the late-40s and early-50s. In Cinderella, they appeared as part of the Harlequinade sequence where their slapstick routine offered well-received comic relief.
William Barrett and Edna Busse as Harlequin and Columbine: Barrett and Busse were a pair of classically trained ballet dancers who danced the classic roles of Harlequin and Columbine in the Act 1 Harlequinade. Barrett was born in 1919 in Staffordshire and joined the Sadler's Wells Ballet company in the late-40s, touring with them to the US ('From Farm' 1954: 11). In the 60s and 70s, he performed in theatre and TV as a resident member of the Black and White Minstrel Show. He later retrained as a drama teacher and passed in 1995 (Jevons 1995: 29). Edna Busse was born in Melbourne in 1918. A protégé of Edouard Borovansky, she later honed her skills in London with Mathilde Kschessinska. Returning to Australia, she continued to perform, before transitioning into a revered ballet teacher. She passed in 2019, aged 100 (Yeo 2019).
The Aida Foster Babes: One of many companies of dancing juveniles popular in the era, the Aida Foster Babes were students of the Aida Foster Academy in Golders Green, London. Established in 1929, the Academy trained several generations of young hopefuls till ists closure in 1970, including several famous alumni such as Jean Simmons and Barbara Windsor ('End' 1970: 43). For Cinderella, Foster provided a group of 12 ‘babes’ who performed in several of the show’s lavish dance sequences.
Critical and Popular Reception
Cinderella was very well received by audiences and critics alike. The following excerpts give a sense of the uniformly glowing notices earned by the show, with particular mention of Julie:
Daily News: "Mr. Val Parnell has really done us proud. There can hardly be two more endearing comics than Max Bygraves and Richard Hearne. Julie Andrews, less operatic than I would have expected, is just the girl for Cinders, and she dances gracefully...a most spiffing pantomime" (E.F. 1953: 4).
The Tatler: "Cinderella has taste, beauty and elegance...But if there is more spectacle than of other good things who will complain, since the result...is so giddily splendiferous. The lighting and the costumes and the scenery could not better done...The principals are worthy of their splendiferous surroundings. Miss Adele Dixon has the right princely strut and Miss Julie Andrews, though she is less vocal than she was expected to be, makes Cinderella a young lady of character and charm" (Cookman 1954: 10).
Daily Mail: "Star names may shine all over the programme -- Max Bygraves and Richard Hearne here; Adele Dixon and Julie Andrews there -- but spectacle is the real star of Val Parnell's typically sumptuous pantomime. Instead of scuffling through the usual sleight-of-stagehand transformation scene Cinderella escapes from the kitchen by way of magic force, fairy spinning wheel, and luminous flying ballet to the cave of crystal lustres: a silvery-white vision as glittering as a wedding cake brush to life" (Wilson 1953: 4).
The Guardian: "Pantomime, though represented only by a single Cinderella in Central London, still flourishes...Cinders (Julie Andrews) croons before the dying kitchen fire...Max Bygraves and Richard Hearne use routine 'biz' to good effect...But what is really remarkable and characteristic of Pantomime 1953 is the standard of the ballet: the scene before Cinders goes off in her glittering coach is as smart, fast, extravagant and excitingly danced as a finale at the Moscow Opera" (F.B. 1953: 3).
The Observer: "The new Palladium Cinderella is magnificent to the eve and its Transformation Scene has fine taste as well as sumptuosity...Julie Andrews is a most attractive Cinderella but not so vocal as I expected" (Brown 1953: 6).
Daily Telegraph: "Cinderella...is up to the best Palladium standard. Elaborate spectacle and attractive dancing combine to delight one's eye. Adele Dixon is an admirable Prince Charming -- she has always been able to fill a big stage with her personality -- and Julie Andrews, kept oddly short of chances to sing, makes Cinderella a young lady of character and charm" (Darlington 1953: 7).
The People: "This is a grand and glamorous show with Julie Andrews as Cinderella. But it would have been grander still had they let her sing more. Adele Dixon constantly charms as the Prince. Max Bygraves and Richard Hearne provide a crescendo of laughs" (Shepherd 1953: 5).
The Times: "It is a hard fact for traditionalists to swallow that there is only one pantomime on the grand scale in the West End...yet if the dismayed traditionalists go the Palladium..., they will soon be cheered up....Here, it seems to say with complete confidence, is one of the few things in a changing world that have remained constant...The humour...is received with every sign of enjoyment and the romantic side of the show is from the first in good trim...Miss Adele Dixon and Miss Julie Andrews belong to the order of unobtrusively pleasant principles. They are an appealing pair, and they have in Mr. Max Bygraves an affable Buttons" ('The Palladium' 1953: 8).
The Stage: "Mr. Parnell has thrown everything into a demonstration of faith, assembling a director's dream of a cast and applying it to all the skill, experience and efficiency that have set the Palladium high in the world of entertainment. He lavishes talent and creative art, he employs every device of lighting, mechanical contrivance and novel effect that the theatre possesses, underlines it all with a defiant and traditional Harlequinade, and the result is the pantomime of pantomimes...Julie Andrews's fragile charm graces Cinderella's rags and raiments alike, and Adele Dixon's slim figure and are of intelligent humour are a delight" ('Christmas Shows' 1953: 5).
The Sketch: "It is the happiest panto-subject, and this is as happy a version as I remember. Richard Hearne in the bowels of a washing-machine, Adele Dixon and Julie Andrews to end rightly as Prince and Princess, Max Bygraves to chant 'Bighead!' -- here they all are, and Val Parnell has never had a spectacle more satisfying than the magical creation of coach and gown." (Trewin 1954: 18).
A Real-Life Cinderella
In many ways, Cinderella signalled something of a pinnacle for Julie's early British career. She was now a young woman in a starring role on the West End stage and, in professional terms, could scarcely go much further. Julie herself writes that "I felt that with Cinderella, my career had peaked" and whatever future she may have would be a continued cycle of "radio, vaudeville and pantomime" (Andrews 2008: 157).
But the theatre gods had other plans and a real-life Fairy Godmother materialised to change the course of Julie's life forever. Midway through the run of Cinderella, Julie was paid a backstage visit by Vida Hope, the producer of the smash hit London musical, The Boy Friend. There were plans to take the show to New York with a new company, but the producers were struggling to cast the lead role of Polly Browne. At the suggestion of Hattie Jacques, Julie's former co-star in Educating Archie, Hope went to see Julie in Cinderella and offered her the role.
It is part of theatrical lore that Julie was initially reluctant to accept the offer, but she was eventually persuaded to seize the opportunity (Andrews 2008: 157-58). Five months after the close of Cinderella, Julie flew off to New York and the rest, as they say, is history...
References:
Alldridge, John (1954). 'Oh, for another Gracie! says Mr Show Business.' Manchester Evening News. 12 October 1954: 1.
Andrews, Julie (2008). Home: A memoir of my early years. London: Weidenfeld and Nicolson.
'At the Pantomime.' (1953). Belfast Telegraph. 30 December: 4.
Baker, Richard Anthony (2005). British Music Hall : An Illustrated History. Stroud: Sutton.
Barker, Dennis. (1999). 'Obituary: Charles Reaaing.' The Guardian. 19 May: 20.
Bendle, Alan (1953). 'Keeping a Straight Bat on a Sticky Wicket.' Manchester Evening News. 15 August: 2.
Bevan, Ian (1952). Top of the Bill: The Story of the London Palladium. London: Frederick Muller Ltd.
'Bobby Howell.' (1962) The Stage and Television Today. 8 February: 3.
Brown, Ivor (1953). "At the Theatre: Not on Ice." The Observer. 27 December: 6.
Bullar, Guy R. & Evans, Len (1950). The Performer: Who's Who in Variety. London: The Performer Ltd.
Cameron, Don (1958). 'The Val Parnell Story Parts 1-4'. The :
Chanticleer (1953). 'People: Old Fashioned Val.' Daily Herald. 3 November: 6.
'Charles Henry Resigning.' (1959). The Stage. 2 April: 1.
'Christmas Shows: The Palladium "Cinderella'".' (1953). The Stage. 31 December: 5.
Cookman, Anthony (1954). 'At the Theatre: Cinderella (London Palladium).' The Tatler and Bystander. 6 January: 10.
Cottrell, John (1968). Julie Andrews: The Story of a Star. London: Arthur Barker.
Darlington, W.A. (1953). "Christmas Shows: Modern Twist to Cinderella, Elaborate Show at Palladium." Daily Telegraph. 28 December: 7.
Double, Oliver (2012). Britain Had Talent: A History of Variety Theatre. London: Palgrave MacMillan.
E.F. (1953). 'A Most Spiffing Pantomime." Daily News. 28 December: 4.
Even Standard Reporter. (1968). 'Ex-Palladium Showman Dies.' Evening Standard. 28 February: 17.
Fagence, Maurice (1958). 'Curtain Up on Mr. Palladium'. Daily Herald. 17 February: 4.
F.B. (1953). "From a Nose in Egypt to Abandon in the Outer Suburbs." The Guardian. 28 December: 3.
Frame, Colin & Boorn, Bill. (1960). 'Palladium Nights.' The Birmingham Evening Mail. 9 November: 6.
Hoddinott, Derek (1957). 'Val Parnell Speaks". The Stage. 29 August: 4.
Lanchbery, Edward (1954). 'Teen-age Cinderella task to the CN: Julie Andrews' dream comes true.' Children's Newspaper. 16 January: 1.
Leigh, Spencer (2012). 'Obituary: Max Bygraves.' The Independent. 3 September: 37
Marriott, R.B. (1983). 'Obituary: Tony Sympson'. The Stage and Television Today. 21 April: 7.
Newley, Patrick. (1996). 'Obituary: Jon Pertwee'. The Stage. 23 May: 38.
'Obituary: Cyril Wells' (1958). The Stage. 17 April: 9.
'Obituary: Phil Park' (1978). The Stage and Television Today. 23 November: 6.
'Obituary: Richard Hearne' (1979). The Stage and Television Today. 30 August: 27.
Pearce, Emery (1954). “No Pigtails for Julie.” Daily Herald. 11 January: 6.
P.N. (2007). ‘Obituary: Joan Mann’. The Stage. 6 December: 53.
Ray, Ted (1956). 'Palladium Nights.' The Liverpool Echo. 27 October: 3.
Sean, Neil (2014). Live from the London Palladium: The World's Most Famous Theatre in the Words of the Stars Who Have Played There. London: Amberley Publishing.
Shepherd, Ross (1953). "London Holiday Shows." The People. 28 December: 5.
Sykes, Eric; Milligan, Spike; Bishop, Michael; and, Park, Phil. (1953). Val Parnell's Cinderella: For production at the London Palladium Xmas 1953. Moss Empires Ltd. [Manuscript held in the Lord Chamberlain's Plays Collection, British Library].
"The Palladium: Cinderella." (1953). The Times. 28 December: 8.
Thornton, Michael. (1992). 'Obituary: Adele Dixon.' The Stage. 4 June: 29.
Trewin, C.W (1954). "At the Theatre: Cinderella (Palladium)." The Sketch. 13 January: 18.
V&A (2015). 'Charles Reading.' V&A Theatre and Performance Collection. https://collections.vam.ac.uk.
Vallance, Tom. (1999). 'Obituary: Charles Reading.' The Independent. 17 June: 36.
'Variety Stage: Palladium Plans' (1953). The Stage. 17 September: 3.
Webster, Ian (2013). 'U.K. Inflation Calculator.' In2013dollars.com. https://www.in2013dollars.com/UK-inflation.
Wilmut, Roger (1985). Kindly leave the stage! : the story of variety, 1919-1960. London: Methuen.
Wilson, Cecil (1953). "Spectacle gets the star role." Daily Mail. 28 December: 4.
Woodward, Chris (2009). The London Palladium: The Story of the Theatre and its Stars. Huddersfield: Northern Heritage Pub.
©2023, Brett Farmer. All rights reserved.
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
In light of a local park yanking permission for a production of Romeo & Juliet because the production design emphasizes queer themes (rainbow costumes, 2 afab actors in the title roles), how about some theatre history?
I mean, yes, everyone knows about how the Elizabethan stage would have had two men kissing in the original production. But today, let’s talk about the Cushman Sisters!

In the mid-19th century, the Cushman sisters, Susanna & Charlotte, had a sensational run portraying Romeo & Juliet. Rather than causing a scandal, Charlotte was praised for elevating the “soppy” Romeo. The siblings had a critically & commercially successful run of the play in London, and Charlotte would go on to play over 30 “masculine” roles across her career. (I use ‘her,’ because that is the pronoun Ms. Cushman used in life. She played both masculine and femine roles, though often styled herself in a mixture of masculine & feminine elements in dress)

Advertisement for the Cushman sisters

Charlotte Cushman as Romeo
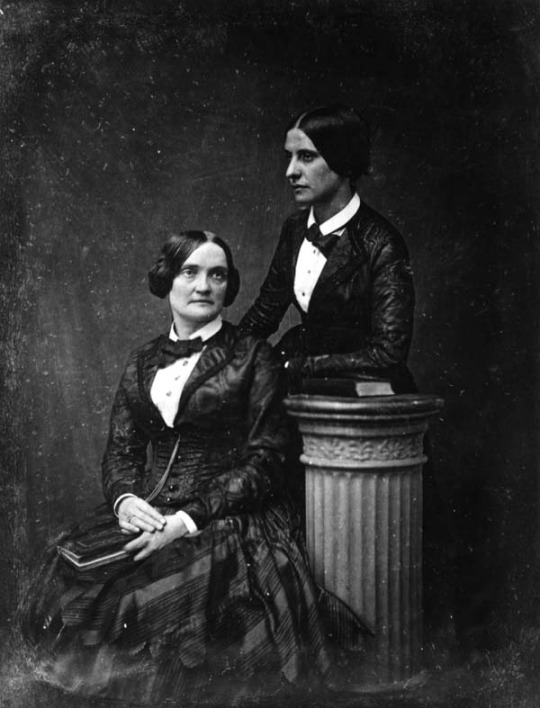

Charlotte Cushman and Matilda Hays, one of several women who was an “intimate associate” and, rather openly for the time, a known romantic partner. Cushman also was known to have had a relationship with the actress Rosalie Sully, sculptor Harriet Hosmer, and several other women.
There are, of course, Staffordshires of the sisters.

33 notes
·
View notes
Text
Let's Talk Costuming: The Globe Costume Collection
Alright my loves this is a very slight tangent to my usual Good Omens direct analysis but I promise it's vaguely related! Inspired by a comment from @theonevoice on my analysis of the costumes used in the Shakespearean scene, which were borrowed direct from The Globe's costume collection, I went on a self-indulgent research journey into Shakespearean costume design history.

So the question that started it all was whether Crowley's outfit in this scene could potentially have been worn or designed for a "classic" Hamlet in its past life. With theatrical costume collections, these items are worn again and again by actors for different shows and even lent out, depending on the shop, to other productions. It's one of my favorite things about live theatre. This means that all of the gorgeous costumes worn for this scene have been worn at least once, likely many times, for other shows.
I was largely on the lookout for anything black that David might have worn here, with little luck on specific pieces, but I'm here to share what I've found that was similar and/or interesting!
[gorgeous postcard with lots of cool costumes, leaving it as a link so y'all can see it in full glory]

[Olivia and Malvolio, Twelfth Night, The Globe, 2013]
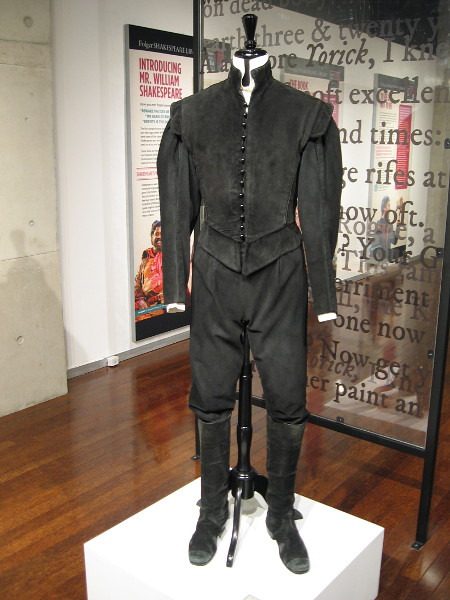

[Hamlet, Hamlet, San Diego Central Library exhibit borrowed from Old Globe Theatre, production 2007]

[Hamlet set sketch, Cyril Walter, 20th century]

[costume workshop, image from Royal Shakespeare Company]

[Hamlet, The Globe, 2022]
At my most optimistic, I was hoping to strike gold and perhaps find evidence of the use of these glorious costumes from the past, but either way I had a blast tracking down Shakespearean costumes for y'all's enjoyment.
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
hey i have a redbubble shop if anyone is looking for bad theatre history joke stickers including an "it's friday afternoon there goes antigone to be buried alive" one and a "shout to greek tragedies for getting me through a bad time by making it worse" one and other such nonsense
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
instagram
Do you ever “randomly” get a song stuck in your head? I put randomly in quotes because I’m sure the reason will reveal itself sooner or later. This week, it’s Duke Ellington’s “Creole Love Call” featuring Adelaide Hall.
“I was standing in the wings behind the piano when Duke first played it (“Creole Love Call”). I started humming along with the band. He stopped the number and came over to me and said, “That’s just what I was looking for. Can you do it again?” I said, “I can’t, because I don’t know what I was doing.” He begged me to try. Anyway, I did, and sang this counter melody, and he was delighted and said “Addie, you’re going to record this with the band.” A couple of days later I did.” - Adelaide Hall
📷 - Wikimedia Commons (circa early 1920s)
📖 - The Independent (Nov. 8, 1993)
#music history#theatre history#broadway history#adelaide hall#duke ellington#black history#black herstory#1920s america#1930s america#creole love call#harlem history#harlem renaissance#Instagram
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

i can’t believe this man drove a mercedes with a METHOD license plate
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Sad, Sad Tale of Hanswurst.
Alright, so I've got a BFA in Acting degree and am not using for a whole lot of anything right now so... gather around children, and let's learn you some *Theatre History*.
So, in general, by the late 16th and early 17th century, theatre was doing pretty well in Europe, and Comedy Especially. Everyone was enjoying their own form of semi-satirical farce utilizing stock characters; whether it be Commedia Dell'arte in Italy, or Comedy of Humours and Comedy of Manners in England. Germany (Or, the general region which would become Germany if you rather) however, had a slightly different take on Comedy. While they did use stock characters, most of their biggest original hits were formed around a central recurring character: Hanswurst (Aka "Johnny Sausage" or, as I prefer, "Weiner John"). A name derived from a popular insult at the time.
Hanswurst was basically your typical buffoon: Bumbling into and out-of danger and trouble without really paying much attention to it. And people LOOOOOOVED it. Whether he was played by flesh and blood actors or portrayed by a Puppet, Children and Parents alike could not get enough of the little guy.
This, *would* be a problem to some, however.
You see by the mid 1700's, some folks in German theatrical circles started to feel a bit constrained by the clownish, half-improvised stylings Hanswurst symbolized. Theatre elsewhere was rapidly growing and evolving, but some German Actors, Writers, and Philosophers felt like their theatre was stagnating.
Scholar and Philosopher Johann Christoph Gottsched and Actress Friederike Caroline Neuber agreed that Hanswurst was the root cause of their problem. And so, they conspired to KILL the Puppet.
"But, how do we get rid of Hanswurst?"
"The heart, Johann! We need to go for the heart!"
And so, their dark plot was put into motion. The pair, and fellow conspirators, held a public execution of Hanswurst. They burned a Hanswurst puppet on-stage in an effort to 'Banish' him, once and for all. The public and the audience did not take kindly to this.
Whether or not it was immediately successful, the execution of Hanswurst did mark the end of an era, as it were. Though German Comedy wouldn't really take off the way Comedy in other European countries did, Germany would leave a mark in the form of musical theatre (for better and for worse, one cannot talk about German theatre without bringing up Wagner). The "Hanswurst Debate" will always be a story that will always stick with me, both because of the absurdity of it, and because it serves as a reminder that no matter the year or the country; theatre kids will always solve problems like theatre kids.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Stephen Sondheim’s “Here We Are” Final Song Lyrics (UNOFFICIAL Video)
This is the last song in the show and the only song in Act 2. I have personally dubbed it: “(What’s Wrong With) Superficial”
Of the very few songs in this show, two really stood out to me as being so obviously Sondheim.
The other one (Denis O’Hare’s song in the Restaurant) embodies Sondheim’s lyrical prowess where this one’s melody is what stands out to me.
Rachel Bay Jones is so special in this show. (The entire cast is!)
I’ll admit, I am not a huge DEH fan so my exposure to her work is somewhat limited (Adored her in a Christmas Story: the Musical)
Her voice in this recording kind of reminds me of the incredible Victoria Clark, I’m not sure why.
About the show:
Inspired by two Luis Buñuel films, The Discreet Charm of the Bourgeoisie and The Exterminating Angel, Here We Are has music and lyrics by Sondheim and a book by David Ives.
The cast features Francois Battiste, Tracie Bennett, Bobby Cannavale, Micaela Diamond, Amber Gray, Jin Ha, Rachel Bay Jones, Denis O'Hare, Steven Pasquale, David Hyde Pierce, and Jeremy Shamos. The understudies are Bradley Dean, Adam Harrington, Bligh Voth, Adante Carter, Mehry Eslaminia, and Lindsay Nicole Chambers.
“Here We Are” is Playing at the Shed from October 22, 2023-January 21, 2024
Please go see this show!!
Disclaimer: I do not own this music.
This video is for educational purposes only!
#Sondheim#stephen sondheim#here we are#musical theatre#slime tutorial#rachel bay jones#denis o'hare#david hyde pierce#musicals#theatre history#off broadway#theatre kid#theatre#sweeney todd#into the woods#a little night music#micaela diamond#company musical#sunday in the park with george#lyrics
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
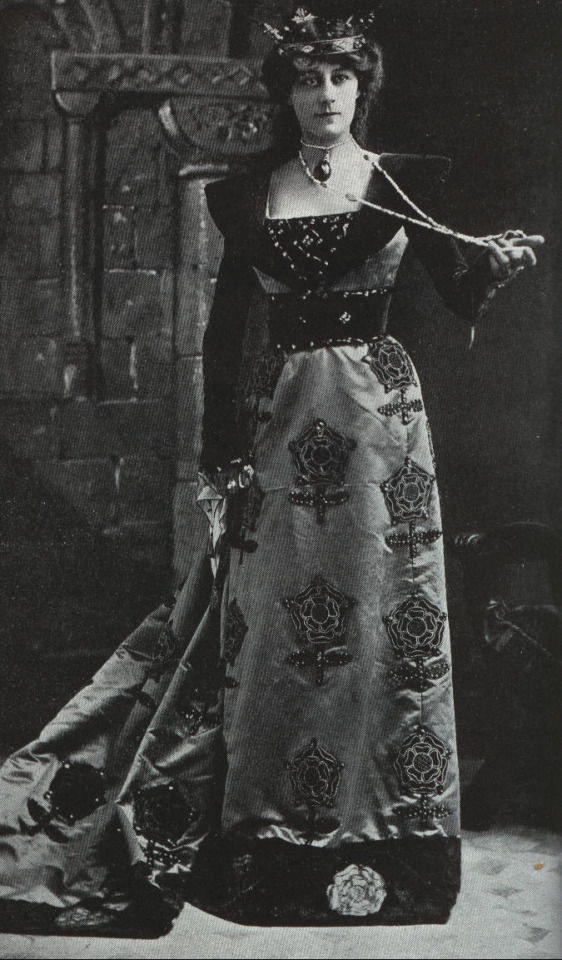


Violet Vanbrugh as Queen Catherine of Aragon in Shakespeare’s Henry VIII (1910)
#she’s got little Tudor roses on her dress 🥺#catherine of aragon#katherine of aragon#catalina de aragon#shakespeare’s henry viii#william shakespeare#shakespeare#henry viii#the tudors#tudor history#english history#tudor era#violet vanburgh#1910#1910s#20th century#early 20th century#edwardian#theatre#theatre history#idk what i’m doing anymore#i’m so tired#I’m literally fighting to stay awake#and I have no reason to be awake#ugh#old shit#vintage#tudor rose
377 notes
·
View notes