#structural and functional claim
Note
do you ever think about how even though chell is the only living being in aperature, the robotic facility is somehow more alive than her. all chell has done is the rigorous testing originally designed by the scientists for robots they deemed unfeeling and unthinking, but now that they are gone we can see turrets that were built for destruction composing beautiful symphonies based on a love they were never thought to originally have, p-body and atlas have moments of interaction that show how much they can care about each other in their limited capacity for communication, and even glados slowly comes around on caring about chell. free from those who would do them harm, aperture has outgrown its original limitations and become something greater than it was ever designed to be
I THINK ABOUT IT ALL THE FUCKING TIME ARE YOU KIDDING ME. the idea of chell as a contrast to apertures humanity is SO INTERESTING TO ME because the facility is just positively teeming with life and humanity-- glados and wheatley joke, they have emotions like relief and happiness, anger, jealousy, insecurity-- they lash out when angry and cower and beg for mercy when terrified and, when really and truly confronted with what theyve done, they feel remorse. the turrets beg for their lives and forgive and the personality cores display charisma and arrogance and enthusiasm and for the 400 billionth time everything SINGS to you and chell exemplifies little to none of that. when shes hurt or terrified or remorseful she doesnt show it, she just trucks right on because she has a single goal in mind and by god is she going to execute it. and the idea of the human character being the cold, calculating, goal oriented one who doesnt show fear doesnt show remorse while all the robots are the ones loving and losing and realizing their own personhood makes me so jdflsjksjdfgdfgdkjfgksjdfioesruto435609568039485234i3t][er[;]23[4p][234;r23[4]5p45;6][7456. like. while the facility forces the devices to grow beyond their capabilities and intended functions it forces chell to grow beyond her humanity into this fearless, tenacious specimen that knows what it wants and isnt going to let mortality stop her. i think im goign to throw up
#aperture outgrowing its limitations also makes me nuts because those limitations are very much still there#glados has full control over the facility and yet has to answer to it when it claims shes too corrupted to continue functioning#wheatley is in constant fear of repercussion when theres no one around anymore to even doll out those consequences#personality cores long for things that their structure will never allow them to accomplish (aside from. space core i guess. lmao)#(ALTHOUGH SPACE CORE HAS A LOT OF LINES WHERE HE SUGGESTS HES GETTING BORED OF WHAT HE WAS MADE#TO DO. WHICH WAS ENJOY SPACE. SO ONCE AGAIN THERES ANOTHER INSTANCE OF APERTURE DEVICES#GROWING BEYOND THEIR INTENDED CAPABILITIES)#like! they are the facility and yet they are still trapped by it nonetheless. the scientists might be dead but theyre still#a looming presense because they were always supposed to be a looming presense in the minds of the machines they created. fuck.#also i dont think chell is literally inemotional i think shes actually a strangely forgiving person considering. everything#otherwise why save glados from the bird why reach out for wheatley in the end. yk#im normal. about this 16 year old game series.
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Transmasculine people who claim to be adversely affected by sexism are bioessentialists cloaked in progressive language, discrimination on the basis of ""biological sex"" isn't real!"
Oh right, sorry. I forgot that sexism in medical research means that endometriosis, ME/CFS, migraines, post-concussive syndrome, Raynaud's phenomenon, and so many other conditions are only understudied in women. Of course endometriosis For Men™, ME/CFS For Men™, migraines For Men™, post-concussive syndrome For Men™, Raynaud's phenomenon For Men™, etc., are all well-funded fields of research and totally understood. Medical research cares only about the gender of an individual patient, not the association of a condition with people of a certain gender. Patriarchal devaluation of women's health, women's illnesses being treated as fundamentally hysteric, and (peri)cissexist reductions of any individual to the reproductive system(s) they were born with clearly only affect people whose gender is woman, nobody else.
Wilfully ignorant motherfuckers.
#HOW can you rightfully argue that sexism is systemic#and ALSO claim that it only affects people according to their self-identified rather than socially-assigned gender.#i do not know how to explain to you that structural oppression has both personal and impersonal modalities#my own post wow#sorry for the heavy sarcasm this is just so fucking deeply frustrating#anyone who is sufficiently proximal to woman-ness gets caught up in this is it truly not difficult to understand#was my [conditions] being brushed aside medical sexism when i ID'ed as a girl but now that i ID as nonbinary the same dismissal is not#the same dismissal is not related to the fact that doctors still see me as basically-a-woman#a personal in a ''female body''#with Women's Health problems#obviously this is still fucking sexism!#and also obviously trans women experience a shitton of medical sexism!#they are not immune to ME/CFS or migraines or whatever just bc doctors see them as ''male bodied''!!!#they are gonna face the same ''i think this is all in your head'' sexist hysteric-woman bullshit!#but like. claiming that transmascs who arent women cant possibly face sexism just means you will not look at how sexism actually functions#fuck. cis men with migraines are still fucked by the sexist lack of research into a condition that so disproportionally disables women#this is not new. nothing I'm saying is new.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Similar to how the Minecraft cave spider is slightly smaller than the average spider model, I think glow squids should have a smaller model than the normal squid
#Which makes sense too since a lot of bioluminescent squids are smaller than your traditional/more common squid#and I just think it would be a fun little detail#like the squid having a smaller size would change absolutely none of its mechanics it’s purely aesthetic#like there are so many non-functional that were originally in Minecraft#that I find it funny when Mojang tries to claim they couldn’t add something because it wasn’t practical or realistic#cough cough fireflies cough like dude you made ocelots completely obsolete when making cats a different animal#my beef with Mojang is simple: they haven’t been updating the game they have been revamping and re-branding it#nether update? no fuck no! they added a lot of new Contant but they did not improve upon any pre-existing elements#but what about the zombie Pigman weren’t they updated? no they were replaced by something inspired by them#with a zombie version to calm the crowd.#because if they’re their own species now with their own spawning structures then who the fuck do the nether fortress is belong to!?#The nether update added a lot of things that were inspired off of pre-existing things in the nether but none of them are direct improvements#for example the nether wart forest would you are unable to get nether wart from#The new soul sand valley is interesting but I wish your soul Sand actually looked like it had souls in it like the classic stuff#and I think the new sand could be improved upon if you made it look like there were hands of the souls#because I always thought you walked slowly on soul Sand because the souls were trying to drag you down with them✨#it’s funny how much Minecraft is treated like a Game for all ages because when you really look at it I think it’s actually quite dark#but take what I say with a pinch of salt because I’m just rambling and this post was originally about squids#glow squid#minecraft glow squid#bioluminescent squid#bioluminescent#Minecraft#squid#Minecraft squid#bioluminescence#caves and cliffs#minecraft nether
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
there are a LOT of things you can speculate about regarding what twsa was actually like as a novel but what's most interesting to me is that you can make the argument that twsa was an "unpolished" version of what orv is. it's a version of a similar novel that likely dealt with a lot of similar themes but was seemingly bogged down by poor structure, pacing, expository handling, and focus. (all of which are things that orv is shockingly excellent at.)
and of course, han sooyoung's novel, sssss-grade infinite regressor, is the "polished" version of the idea. it's well-written, probably well-plotted, and was successful enough to make han sooyoung rich and famous. we don't know what sssss-grade infinite regressor is like as a novel either, but we sort of get the impression that it's not very emotionally rich even if it is good on a technical level. han sooyoung herself doesn't seem intensely attached to it despite being proud of her work, and kim dokja of course doesn't hold it in high regard. (though of course he's a gigantic unreliable narrator and also a hater.)
what's interesting is that despite orv very strongly emphasizing the ways these works are flawed from the outset, orv itself functions as an argument in these works' favor. both twsa and infinite regressor are stand-ins for the "mass-produced" genre of webnovels. they are popular fiction, relying on a very familiar pool of tropes and clichés in order to deliver on a relatively predictable story to appeal to a wide audience. it's not a coincidence that they are so similar - both literally and in a meta sense, they are drawing on the same exact story-building and genre material. twsa is just the unsuccessful version, and infinite regressor is the successful one.
orv is what I would consider the most "impressive" version of the genre. it's well-structured, thrillingly plotted, interestingly written, has fascinating ideas and characters, and is even "literary" - that is, it has deeply considered themes and is often drawing from the realm of literary, postmodern fiction in order to express its ideas. a less sincere story would disavow itself from its pop-fiction origins and claim to be the best version of its genre. nothing else could be like it, so the worst versions of its genre wouldn't be worth considering.
but orv, while technically functioning as an argument that the genre can be "good" simply because it's a great novel that is deeply rooted in its genre, goes much further. it argues in-text that any sort of story, even those that are bad on a technical level or those that were somewhat cynically produced for a mass audience, are worth finding value in, simply because stories have meaning to their readers. the most uncritical reproduction of a genre's conventions can still mean something to someone who likes it. twsa, if it existed in our reality, would still probably be considered a very bad novel, but it wouldn't need to be polished up and turned into infinite regressor or orv in order to have value. orv itself is telling you that you should find value in twsa as it is, and by extension, every badly-done work of fiction that twsa could be a stand-in for!
#narrates#orv#all of this is Fascinating for in-universe texts to have as relationships to the actual text btw#scratching at the walls like I KNOW ITS THE POINT THAT WE CANT READ THEM... BUT I WANNA READ TWSA AND INFINITE REGRESSOR...
731 notes
·
View notes
Text


Propaganda
Yvonne De Carlo (Frontier Gal, The Ten Commandments, Casbah)— Although most famous for playing Lily Munster in The Munsters, Yvonne De Carlo had a successful movie career throughout the 1940s and 1950s, appearing in such films as “The Ten Commandments”, “Sea Devils” and two Munster movies later in life.
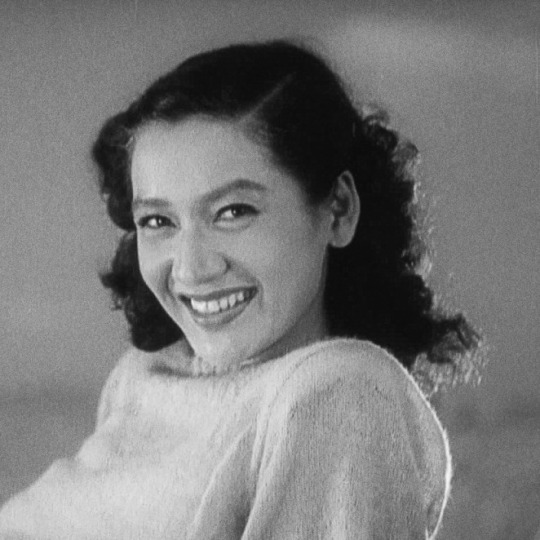
Setsuko Hara (Tokyo Story, Late Spring, The Idiot)— "'The only time I saw Susan Sontag cry,' a writer once told me, his voice hushed, 'was at a screening of a Setsuko film.' What Setsuko had wasn’t glamour—she was just too sensible for that—it was glow, one that ebbed away and left you concerned, involved. You got the sense that this glow, like that of dawn, couldn’t be bought. But her smiles were human and held minute-long acts, ones with important intermissions. When she looked away, she absented herself; you felt that she’d dimmed a fire and clapped a lid on something about to spill. Over the last decade, whenever anyone brought up her lips—'Setsuko’s eternal smile,' critics said, that day we learned that she’d died—I thought instead of the thing she made us feel when she let it fall." - Moeko Fujii
This is round 2 of the tournament. All other polls in this bracket can be found here. Please reblog with further support of your beloved hot sexy vintage woman.
[additional propaganda submitted under the cut]
Yvonne de Carlo:

The woman who brought Burt Lancaster to his knees.


Setsuko Hara:

One of the best Japanese actresses of all time; a symbol of the golden era of Japanese cinema of the 1950s After seeing a Setsuko Hara film, the novelist Shūsaku Endō wrote: "We would sigh or let out a great breath from the depths of our hearts, for what we felt was precisely this: Can it be possible that there is such a woman in this world?"

One of the greatest Japanese actresses of all time!! Best known for acting in many of Yasujiro Ozu's films of the 40s and 50s. Also she has a stunning smile and beautiful charm!
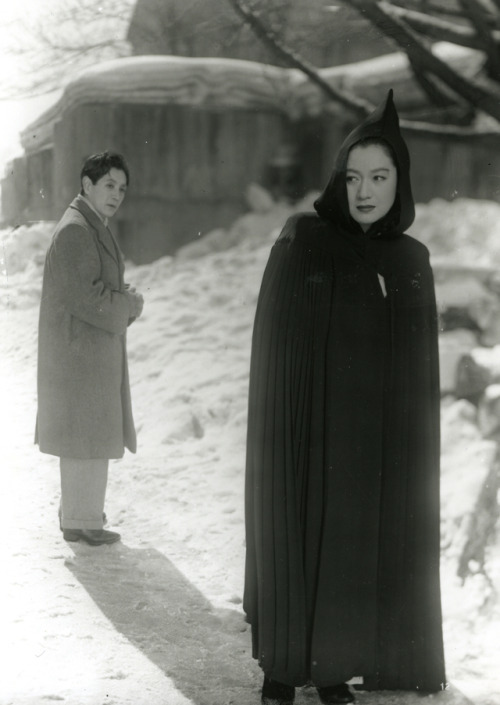



Linked gifset
Linked gifset 2
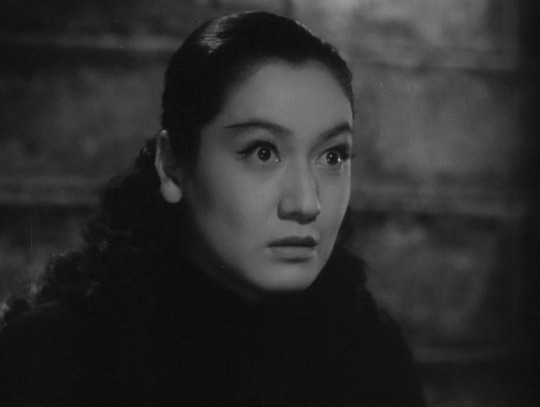



She's considered by some to be the greatest Japanese actress of all time! In Kurosawa's The Idiot she haunts the screen, and TOTALLY steals the show from Mifune every time she appears.

"No other actor has ever mastered the art of the smile to the same extent as Setsuko Hara (1920–2015), a celebrated star and highly regarded idol who was one of the outstanding actors of 40s and 50s Japanese cinema. Her radiant smile floods whole scenes and at times cautiously undermines the expectations made of her in coy, ironic fashion. Yet her smile's impressive range also encompasses its darker shades: Hara's delicate, dignified, melancholy smile with which she responds to disappointments, papers over the emotions churning under the surface, and flanks life's sobering realizations. Her smiles don't just function as a condensed version of her ever-precise, expressive, yet understated acting ability, they also allow the very essence of the films they appear in to shine through for a brief moment, often studies of the everyday, post-war dramas which revolve around the break-up of family structures or the failure of marriages. Her performances tread a fine line between social expectation and personal desire in post-war Japan, as Hara attempts to lay claim to the autonomy of the female characters she plays – frequently with a smile." [link]

Leading lady of classic Japanese cinema with a million dollar smile
Maybe the most iconic Japanese actress ever? She rose to fame making films with Yasujiro Ozu, becoming one of the most well-known and beloved actresses in Japan, working from the 30s through the 60s in over 100 hundred. She is still considered one of the greatest Japanese actresses ever, and in my opinion, just one of the greatest actresses of all time. And she was HOT! Satoshi Kon's film Millennium Actress was largely based on her life and her career.

366 notes
·
View notes
Text
I will add my voice to the chorus that chronological feed is at this point one of Tumblr's biggest selling points, because chronological is a default form of ownership. I can edit my feed to match exactly my expectations by following & unfollowing who I want, because chronology as a concept is completely scrutable to me. Algorithms are fine as everything is an algorithm; its the lack of comprehensibility and agency most platforms inflict on you that makes them so hostile to users who actively curate what they engage with.
I in fact think Tumblr would benefit from more feed options! I would absolutely enable deviations from the chronology based on the people I follow and the moods I am in - but they again would need to be under my control.
The discoverability problem is real, and I do in fact think that there should be better ways. I don't object to the "you may also like" in the corner for example. In reality Tumblr's search functions are the place to do this; they aren't as bad as many claim but they aren't great, they are exactly the choice-focused place to surface new blogs. Make that tool better and I will find others like me and give them a shot.
But. Another thing that makes tumblr great is the fact that it is 'community' based over 'content' based. I follow the people I follow, and they follow me, because we interacted with each other over time. It is a facsimile of actual socializing; you make a few comments on a post, you build up the courage for a reblog or two, you are discoursing, you tag them on a meme, now you are mutuals. Content creators are not community members - that is a hierarchical relationship, the 'lead' and the 'fan', and is defined by parasocial and weak connections. Tumblr can be more than one thing ofc, I follow some art blogs who never talk to their followers, that is a content-follow. But in the main I don't think most people want their community-based feed structure to be disrupted by attempts to content-itize it.
This is again one of Tumblr's strengths - every other site (besides partially Facebook) has pivoted to content-style models over community-style models due to inherent winner-take-all dynamics and greater monetization applications. But Tumblr cannot chase YouTube, it is going to lose, YouTube already exists. I don't see much of anything in that post that recognizes that, and that is imo a huge mistake.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
a point about the IA situation that I cannot make on twitter without death threats
Like many authors, I have complicated feelings about the IA lawsuit. IA has a whole raft of incredibly invaluable services, that's not in dispute. The current eBook licensing structure is also clearly not sustainable. Neither was IA's National Emergency Library, which was unrestricted lending of unlicensed digital copies. There are some thoughtful posts about how their argument to authors, "you'll be paid in exposure," is not especially compelling.
But I'm not here to discuss that; I'm here to talk about the licensing. TL;DR I don't want my work being fed into an AI or put on the blockchain, and to enforce that, you need a license.
So, here's the thing. IA's argument for the NEL boils down to "if we possess a physical copy of the book we should be able to do what we want" and that's frankly unserious. (Compare: Crypto Bros who thought spending $3 million on a single copy of a Dune artbook meant they owned the copyright.) Their claim is that by scanning a physical copy of the book and compiling the scans into a digital edition, that is sufficiently transformative to be considered fair use.
What that gives them is something that functions almost identically to an eBook, without the limitations (or financial obligations) of an eBook license. And I'm sure some of you are thinking, "so what, you lose six cents, get over yourself," but this isn't actually about the money. It's about what they can do with the scans.
A license grants them the right to use the work in specific, limited ways. It also bars them from using it in ways that aren't prescribed.
For example, what if IA decides to expand their current blockchain projects and commit their scanned book collections to the blockchain "for preservation"? Or what if IA decides to let AI scrapers train on the scanned text? One of their archivists sees AI art as a "toy" and "fears [AI art] will be scorned by the industry's gatekeeping types."
Bluntly, an unlicensed, unrestricted collection seems to be what they're gunning for. (Wonky but informative thread from a lawyer with a focus on IP; this cuts to the pertinent part, but the whole thing's good reading.) The Authors Guild is in no way unbiased here, but in the fifth paragraph of this press release, they claim that they offered to help IA work out a licensing agreement back in 2017, and got stonewalled. (They also repeat this claim on Twitter here.)
At the end of the day, I don't want the IA to fold; I don't think anyone does. As a matter of fact, I'd be open to offering them an extremely cheap license for Controlled Digital Lending. (And revamping eBook library licensing while we're at it.) I think there's a lot of opportunity for everyone to win there. But IA needs to recognize that licenses exist for a reason, not just as a cash grab, and authors have the right to say how their work is used, just like any artist.
#good god I'm not putting tags on this#can you imagine#though maybe I'm just twitchy from my time in the twitter trenches#twenches? twinches? they both sound like felonies?
1K notes
·
View notes
Note
I read your review of Poor Things and I was wondering if you had any thoughts on the section in Alexandria? It was horrifically executed on many levels but narratively, that part of the film is about Bella learning about class structure. She rebels against the cruelty of society through charity then by working as a prostitute, during which time she has cruelty inflicted upon her instead. Finally, she realizes that God’s creation of her was ultimately cruel, and then she runs away with her ex-husband-father only to realize that her prior self-mother was fundamentally characterized by cruelty, especially to her “lessers.” She then decides once again that she does not want to be cruel, but then she achieves this by taking God’s place as the doctor-patriarch and ruling his household with a new pet goat. The entire film is also about Bella learning about feminism: the arbitrary oppression of women is not only nonsensical, it’s bad! But then the ending has her reproduce almost all those power structures and cruelty she claims to reject, and has the unfortunate consequence of positioning her as ultimately equally cruel/callous as God, the guy she meets on the boat who shows her all the starving people, and her former self-mother, etc. I was wondering if you had any thoughts on why this is or like, what the director’s message was beyond self-contradiction and taking cheap shots at starving people?
so i would quibble a bit with the idea that bella's experience in the maison-close is exclusively or even primarily portraying sex-for-pay as a site of cruelty. i think it's more depicting paid sex as work, and work as unpleasant and repressive, and that's why the maison is the site where bella gets involved in socialist politics—if moral philosophy is the arena by which she responds to the injustice of the poverty in alexandria, then labour politics plays the analogous role where the maison is concerned. her problems there aren't inherently with the idea of being paid for sex, but with specific elements of the work arrangement (eg, she suggests that the women should choose their clients, rather than vice versa). ofc she has some customers who are cruel or thoughtless or rude, but i didn't read the film as suggesting that was universal to sex work, and the effect of the position is more to demystify sex, for bella, than to convert it into being purely a site of trauma or misery. now i don't think this film offers a particularly blistering or deep analysis of sex work or socialism or wage labour, dgmw, but i do think the function of the maison is different narratively to that of the alexandria section.
anyway to answer your actual question: yeah so this is really my central gripe with the film. lanthimos (slash his screenwriter tony mcnamara) spends much of the film gesturing toward bella's growing awareness of several hierarchical structures that other characters take for granted: the uneven nature of the parent/child relationship (god took her body and created her without asking); class stratification (alexandria); the 'civilisation' of individuals and societies via education and bio-alteration (bella's talk about 'improving' herself; her 'progression' from essentially a pleasure-seeking child to an educated and 'articulate' adult). these three dimensions often overlap (eg, the conflation of 'childishness' with lack of education with inability to behave in 'high society'), though, most overtly, it's in that third one that we can see how these notions of improvement and biological melioration speak to discourses about the 'progress' and 'regress' of whole societies and peoples, and voluntarist ideas about how human alteration of biology (namely, our own) might produce people, and therefore societies, that are better or worse on some metric: beauty, fitness, intelligence, morality, longevity, &c. this is why i keep saying that like.... this film is about eugenics djkdjsk.
the issue with the alexandria section to me is, first, it's like 2 minutes (processed in the hollywood yellow filter) where the abject poverty of other people is a life lesson for bella. we're not asking any questions like, how is that poverty produced, and might it have anything to do with the ship bella is on or the fantastical lisbon she left or the comparative wealth of paris and london...? secondly, everything that the film thinks it's doing for the entire runtime by having bella grapple with learning about cruelty, and misery, and the kinds of received social truths that lanthimos is able to problematise through her eyes because she's literally tabula rasa—all of that is just so negated by having an ending in which she bio-engineers her shitty ex-husband, played as a triumphant moment. i don't even inherently have an issue with the actual plot point; certainly she has motive, and narratively it could have worked if it were framed as what it is: bella ascending to the powerful position in the oppressive system that created her, and using her status to enact cruelty against someone who 'deserves' it—ie, leveraging her class and race within the existing social forms rather than continuing to question or challenge them. if that ending were played as a tragedy, or a bleak satire, it would at least be making A Point. but it's not even, because it's just framed as deserved comeuppance for this guy we were introduced to in the 11th hour as a scumbag, so it's psychologically beneficial for bella actually to do the sci-fi surgery to him that literally reduces him to what's framed as a lower life form. unserious
#the favourite and the lobster also have some troubling body and disability politics and i think this is a throughline with lanthimos#but this one is particularly egregious to me given the ending lol#poor things
209 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ω PJO DEMIGOD HEADCANONS: 🦉 ATHENA: Goddess of Wisdom & Reason, of Strategy & Warfare, Crafts & Arts 🧠
author's note: I had a sudden idea about writing some headcanons Camp Halfblood demigods being claimed and what it's like for each respective god and cabin, followed by a small blurb afterwards. Thank you for reading and please like and reblog! The order is not in order of the cabin numbers. [PJO DEMIGOD HEADCANONS MASTERLIST]
When you get claimed, it's after a moment of brilliance. You could be giving someone an insightful observation, successfully mediating two opposing forces, creating your own invention, or when you successfully performed a maneuver. You’ve shown your intellect and Athena claims you at that moment.
The Athena cabin cheers for you and welcomes you in.
You look in awe at the architectural structure of your cabin. You can tell the foundation and the base of the cabin was structured like the rest of the other cabins, but over the years, it was elevated.
You’re shown where you’ll be sleeping but as you set up, you immediately clock in how everything is placed. All the bunks are pushed to the side, row by row and then there are desks lining along the same way with dual tables, and there are the rows of books and a workshop further in the back. You see inventions being made, architectural models, and more.
Among the children of Athena, you slowly figure out which intellectual you lean more towards: Educated (developing theories and plans), Productive (philosophy, literary criticism, sociology, law, medicine, etc), or an Artistic (literature, music, painting, sculpture, etc). Whichever you are or of those you find yourself in, you’re in good company.
If you want to bounce off ideas of someone, there’s no shortage of siblings to have a sound board of.
Whatever craft you find yourself in, you’re immediately put into consultation and you find yourself either being asked to get an input on or seeking input from others.
Fortunately and unfortunately, since demigods aren’t allowed to use the internet, your cabin is the next best option for Google.
Spider repellents everywhere. There’s not a single dust bunny in sight, not even in the corners or behind the unseen books. Aside from the piling books, scrolls, and tools (and the few coffee cups), the Athena cabin is the cleanest cabin after the Apollo cabin.
When there was a spider somehow, you witness everyone scream and grab several torches before incinerating the arachnid into nothingness.
That or an overly complicated set up of a machine to destroy that one spider. Then you find out that there’s a lot of contraptions that they’ve built for one, very specific, function.
You just had pulled off an emergency strategy maneuver during the Capture the Flag. It was a close call with the new camper but you couldn’t mistake them for not being a child of Ares. They were a monster on the field and you had to make sure at least get some upper hand.
You managed to take out half of the other team’s numbers, using the layout of the forest and its terrain to your advantage, and your eyes noticing the body language of your opponent.
You still lost because the new camper, who has the undeniable glow of Ares on them, demolished through your forces, but it wasn’t half-bad since the casualty was the same on both sides.
“You’re fast on your feet. A bit foolish, but it was a nice maneuver.”
You jumped at the voice and turned to it, seeing a blonde girl with gray eyes. You knew her, Annabeth Chase, daughter of Athena.
“Oh, uh, yeah” you said lamely, dusting yourself off as an attempt to keep your hands from shaking. “I figured at that point, we could at least make it fair or we just lose really badly.”
Annabeth nodded, as she smiled. “I guess, there’s plenty of time to hone your intelligence with us.”
“Wait what?”
Annabeth gestured up your head and you looked to see the glowing image of an owl over your head. You made a “oh” and looked owl-eyed at your new sister as she held out her hand.
“Welcome to the Athena cabin, I’m Annabeth Chase. Cabin Leader and your new half-sibling.”
#pjo fanfic#pjo imagine#annabeth chase#percy jackson and the olympians imagines#pjo#pjo imagines#pjo x reader#pjo reader insert#annabeth pjo imagines#annabeth chase imagines#annabeth chase imagine#child of athena#children of athena#athena#pjo x you#demigod h/cs#demigod reader#demigod headcanons#demigod imagines#athena cabin#cabin 6#percy jackson and the olympians imagine#percy jackon and the olympians
168 notes
·
View notes
Text
my suffering is profound and legitimate, yours is frivolous nonsense
Just reading a blogger I like but I had to laugh because she was talking about how beauty practices are bad for women's mental health, and she left a note saying "unlike gender affirming care! gender affirming care improves people's mental health and it's nothing at all like cosmetic practices."
TIL, when an older woman gets botox to remove her wrinkles and avoid facing the inevitability of decline and death, her problem is spiritual/structural and she needs to Do The Work to deprogram her ageism, unlike people with dysphoria, who of course have legitimate claims to cosmetic alteration.
And it is cosmetic - no part of the body that is altered by HRT or SRS or any of the feminization/masculinization surgeries is failing to function or functioning poorly. The problem is with the brain, which perceives the body parts as foreign or undesirable. We may sympathize with someone struggling with such a condition, but that does not change that the body parts being altered were already healthy and the alterations are cosmetic, and the relief being brought about is mental.
But plenty of trans people openly admit that separating body dysmorphia and gender dysphoria is a losing game. Contrapoints's video on "Beauty" (transcript) has the observation that she feels least dysphoric when she is meeting feminine beauty norms:
But I also think that trans people often talk like gender dysphoria is this intrinsic, personal experience that's always 100% valid and never has anything at all to do with the external pressure of beauty standards. But in fact, gender dysphoria is not sealed away in a vacuum away from the influence of societal ideals and norms.
[...] When I try to psychoanalyze myself, I find that my desires to look female, to look feminine, and to look beautiful are not exactly the same, but they're woven together so tightly that it's kind of difficult to untangle them. And the opposite is also true, that for me feeling mannish or dysphoric usually goes along with feeling ugly. I don't have a lot of days where I walk out the house thinking "well, I'm giving femme queen realness, but apart from that I look like absolute shit".
Max Robinson's book "Detransition," from an FTM perspective, points out how the prospective trans man views his suffering as unique from and distinct from women's, even as the surgeries they seek are not especially different:
The stereotypical cosmetic surgery patient is seeking to become closer to being perfectly feminine - she wants to be beautiful. Transitional cosmetic surgery, on the other hand, is widely understood to mark the patient as ex-female and therefore unfemale; this is part of the meaning FTMs seek to create through surgery. FTM desire for cosmetic surgery is positioned as something totally different than the stereotype of a woman who 'merely' seeks beauty at her frivolous leisure. FTMs are deemed to have a rare affliction that needs urgent, life-saving treatment. Conversely, there is nothing more common than for a woman to become obsessed with her socially-deemed 'unsatisfactory' looks and desperately seek to change them, believing that such a change is the only thing that can restore her quality of life.
This comparison will feel like an insult to the FTM. It will feel that way because we believe other women's suffering doesn't matter, and recognize how much ours does. Women's suffering is ordinary but ours is extraordinary. For us to matter, we must be differentiated from the silly little woman who wants to be pretty so badly she'll pay thousands of dollars (now billable to credit cards and loan programs designed to pay for elective surgeries!) to risk her life and health. These women don't need to be fixed; we do. FTMs know that we don't deserve a woman's fate but have not yet realized that no woman does.
I have more to write on the topic of the relationship between gender identity and beauty culture, but I'll end this one here. It makes sense that somebody who is identified with the opposite sex would also be affected by the standards of beauty expected of that sex. (Non-binary identification is more complicated and requires separate treatment.)
185 notes
·
View notes
Text
Asking for breeders to health test is not too much work. (Ensures dog is free of genetic health issues as much as possible)
Asking for breeders to breed temperamentally stable dogs is not too much work. (Ensures puppies will also be temperamentally stable as much as possible).
Asking for breeders to breed structurally healthy dogs is not too much work. (Ensures dog can function as a dog).
Asking for proof of correct temperament from an outside source like an evaluator, working/sporting test, or real world application such as actual work is not too much work (ensures dog can do what breeder claims they can do as much as possible).
These are like bottom of the barrel expectations for a “responsible” dog breeder. Asking for less is ridiculous. We are responsible for ensuring future dogs are healthy and stable and lowering such expectations below this point is like asking a bar on the floor if it can possibly go lower.
#dogblr#dog breeding#while I think asking for some types of titles is silly I don’t think it is unreasonable at ALL to ask for unbiased (as possible) proof#the dog can: hunt or pull or work or be a companion or show in a show ring
881 notes
·
View notes
Text
some rambling thoughts on shivers (red bolding mine throughout):
so shivers says this to harry after he has a dance-induced seizure in the church, right:
YOU - But who am *I*? Why are you talking to me?
SHIVERS - YOU ARE AN OFFICER OF THE CITIZENS MILITIA. *AGENTES IN REBUS*, WHEN YOU WEAR YOUR COAT, YOU WEAR MY SOUL.
SHIVERS - YOU MOVE THROUGH MY STREETS FREELY IN MOTOR CARRIAGES AND ON FOOT. YOU HAVE ACCESS TO THE HIDDEN PLACES. YOU ALSO CIRCULATE AMONG THOSE WHO ARE HIDDEN.
here's wikipedia on "agentes in rebus":
"The agentes in rebus were the late Roman imperial and Byzantine courier service and general agents of the central government from the 4th to the 7th centuries."
"Being outside the control of the provincial governors, some agentes ... were appointed as inspectors ... for which they gained a reputation as a secret police force. As their routine assignments brought them into contact with matters of great concern to the court, and as they reported back to the court on everything they saw or heard on their varied missions, the agentes can be seen to have had an intelligence function ... This role, as well as their extraordinary power, made them feared: the 4th-century philosopher Libanius accused them of gross misconduct, terrorizing and extorting the provincials, "sheep-dogs who had joined the wolf pack". Nevertheless, the vast majority operated quite openly, and the claims of the agentes operating as a modern-day secret police are certainly exaggerated."
hey shivers. why are you invoking the RCM as your secret police, via a term not just associated with collection of information, but with corruption and manipulation of power.
and, if you fuck up the dance check and call kim a slur, she says:
"SHIVERS - BY THE WAY, APOLOGIZE TO YOUR PARTNER AT ONCE. UNITY AMONG THE RANKS IS PARAMOUNT."
which sticks out to me, because earlier we have this encyclopedia check with noid:
NOID - "A life is true if it's free from fear and internal division among oneself. And others -- mankind has seeds of greatness in it. A germinal will come, a return to trueness. It will be hard core."
YOU - "How would you go about *returning* to this true life?"
NOID - "Beats and bright lights to shatter falsehoods. Nerve impulses for the collective body. We are very much alike in basic structure. A hard enough beat would awaken everyone to a truer calling -- in unity!"
ENCYCLOPEDIA - Rejection of the right-left axis, emphasis on *unity*, appreciation of some primordial mode of being -- what does that remind you of?
YOU - "Sort of like fascism then?"
now, i don't think either noid or shivers are outright fascist :p but i do think the purpose of this encyclopedia line is to highlight how those criteria are flawed and damaging, how they are red flags, whatever the intention.
some comparisons:
1. return to trueness. le retour. the return of... what? in both cases, truly quite vague except for the idea of some dramatic upheaval of the current order, the idea of "returning" to some idealized past state or event.
2. nerve impulses. shivers. "appeal to nature" type fallacy, appeal to a baser instinct... invocation of physical reactions as metaphor for political reactionism, perhaps?
3. unity. on the surface, shivers telling harry to make things right with kim is touching, certainly. but specifically "unity among the ranks" is an interesting framing 🤨 as though the crucial thing is that their forces are not divided for what's to come, regardless of kim's feelings, regardless of harry's potential racism.
likewise, noid's call for unity addresses... nothing at all. simply that everyone would be awoken from their petty, false divisions into unity. neither this nor his criticisms of left vs. right acknowledge that the division is not equal, that one side in most social power conflicts is invested in stripping the rights of the other... because that is simply not on the radar when the priority is unity above all else. in its way, unity is authoritarian where it does not abide difference or dissent in the interest of the of the stasis/power of the institution.
this is all to say. hey. let's talk about the inherent nationalist nature of la revacholiere, my problematic wife ♥️
#de tag#disco elysium#i feel like i could make this more coherent / essay-like but i just cant be bothered#im certain there's other shivers lines like this that had me like <__< girl........#racism ment /
157 notes
·
View notes
Text
Music Theory Notes (for science bitches) 1: chords & such
This is one of these series where I use my blog as a kind of study blog type thing. If you're knowledgeable about music theory, it will be very basic. But that's kind of the problem, I've really struggled to absorb those basics!
When I was a teenager I learned to play violin and played in orchestras. I could read music, and play decently enough, but I didn't really understand music. I just read what was on the page, and played the scales I had to play for exams.
Lately I've been trying to learn music again. This time my instruments are zhonghu, voice, and DAWs. At some point I might get my violin back too. But really, I'm a total beginner again, and this time I want to do it properly.
For a long time when I tried to learn about music I would get overwhelmed with terminology and jargon and conventions. I might watch videos on composition and they'd be interesting but a lot of it would just fly over my head, I'd just have to nod along because I had no idea what all the different types of chord and such were. I tried to learn from sites like musictheory.net, but I found it hard to figure out the logical structure to fit it all into.
I feel like I'm finally making a bit of headway, so it's time to take some notes. The idea here is not just to answer the what, but also to give some sense of why, a motivation. So in a sense this is a first attempt at writing the introduction to music theory I wish I'd had. This is going to assume you know a little bit about physics, but basically nothing about music.
What is music? From first principles.
This is impossible to answer in full generality, especially since as certain people would be quick to remind me, there's a whole corner of avant-garde composers who will cook up counterexamples to whatever claim you make. So let's narrow our focus: I'm talking about the 'most common' type of music in the society I inhabit, which is called 'tonal music'. (However some observations may be relevant to other types of music such as noise or purely rhythmic music.)
Music is generally an art form involving arranging sound waves in time into patterns (in the sense that illustration is about creating patterns on a 2D surface with light, animation is arranging illustrations in time, etc.).
Physically, sound is a pressure wave propagating through a medium, primarily air. As sound waves propagate, they will reflect off surfaces and go into superposition, and depending on the materials around, certain frequencies might be attenuated or amplified. So the way sound waves propagate in a space is very complicated!
But in general we've found we can pretty decently approximate the experience of listening to something using one or two 'audio tracks', which are played back at just one or two points. So for the sake of making headway, we will make an approximation: rather than worry about the entire sound field, we're going to talk about a one-dimensional function of time, namely the pressure at the idealised audio source. This is what gets displayed inside an audio editor. For example, here's me playing the zhonghu, recorded on a mic, as seen inside Audacity.

A wrinkle that is not relevant for this discussion: The idealised 'pressure wave' is a continuous real function of the reals (time to pressure). By contrast, computer audio is quantised in both the pressure level and time, and this is used to reconstruct a continuous pressure wave by convolution at playback time. (Just like a pixel is not a little square, an audio sample is not a constant pressure!) But I'm going to talk about real numbers until quantisation becomes relevant.
When the human eye receives light, the cone cells in the eye respond to the frequencies of EM radiation, creating just three different neural signals, but with incredibly high sensitivity to direction. By contrast, when the human ear receives sound, it is directed into an organ called the cochlea which is kind of like a cone rolled up into a spiral...

Inside this organ, the sound wave moves around the spiral, which has a fascinatingly complex structure that means different frequencies of wave will excite tiny hairs at different points along the tube. In effect, the cochlea performs a short-time Fourier transform of the incoming sound wave. Information about the direction of the incoming wave is given by the way it reflects off the shape of the ear, the difference between ears, and the movement of our head.
So! In contrast to light, where the brain receives a huge amount of information about directions of incoming light but only limited information of the frequency spectrum, with sound we receive a huge amount of information about the frequency spectrum but only quite limited information about its direction.
Music thus generally involves creating patterns with vibration frequencies in the sound wave. More than this, it's also generally about creating repeating patterns on a longer timescale, which is known as rhythm. This has something to do with the way neurons respond to signals but that's something I'm not well-versed in, and in any case it is heavily culturally mediated.
All right, so, this is the medium we have to play with. When we analyse an audio signal that represents music, we chop it up into small windows, and use a Fourier transform to find out the 'frequencies that are present in the signal'.
Most musical instruments are designed to make sounds that are combinations of certain frequencies at integer ratios. For example here is a plot of the [discrete] Fourier transform of a note played on the zhonghu:

The intensity of the signal is written in decibels, so it's actually a logarithmic scale despite looking linear. The frequency of the wave is written in Hertz, and plotted logarithmically as well. A pure sine wave would look like a thin vertical line; a slightly wider spike means it's a combination of a bunch of sine waves of very close frequencies.
The signal consists of one strong peak at 397Hz and nearby frequencies, and a series of peaks at (roughly) integer multiples of this frequency. In this case the second and third peaks are measured at 786Hz, and 1176Hz. Exact integer ratios would give us 794Hz and 1191Hz, but because the first peak is quite wide we'd expect there to be some error.
Some terminology: The first peak is called the fundamental, and the remaining peaks are known as overtones. The frequency of the fundamental is what defines this signal as a particular musical note, and the intensities of the overtone and widths of the peaks define the quality of the note - the thing that makes a flute and a violin playing the same fundamental frequency sound different when we listen to them. If you played two different notes at the same time, you'd get the spectrums of both notes added together - each note has its own fundamental and overtones.
OK, so far that's just basic audio analysis, nothing is specific to music. To go further we need to start imposing some kind of logical structure on the sound, defining relationships between the different notes.
The twelve-tone music system
There are many ways to do this, but in the West, one specific system has evolved as a kind of 'common language' that the vast majority of music is written in. As a language, it gives names to the notes, and defines a space of emotional connotations. We unconsciously learn this language as we go through the process of socialisation, just as we learn to interpret pictures, watch films, etc.
The system I'm about to outline is known as 12-tone equal temperament or "12TET". It was first cooked up in the 16th century almost simultaneously in China and Europe, but it truly became the standard tuning in the West around the 18th century, distilled from a hodgepodge of musical systems in use previously. In the 20th century, classical composers became rather bored of it and started experimenting with other systems of tonality. Nevertheless, it's the system used for the vast majority of popular music, film and game soundtracks, etc.
Other systems exist, just as complex. Western music tends to create scales of seven notes in an octave, but there are variants that use other amounts, like 6. And for example classical Indian music uses its own variant of a seven-note scale; there are also nuances within Western music such as 'just intonation' which we'll discuss in a bit; really, everything in music is really fucking complicated!
I'll be primarily discussing 12TET because 1. it's hard enough to understand just one system and this one is the most accessible; 2. this has a very nice mathematical structure which tickles my autismbrain. However, along the way we'll visit some variants, such as 'Pythagorean intervals'.
The goal is to try and not just say 'this is what the notation means' but explain why we might construct music this way. Since a lot of musical stuff is kept around for historical reasons, that will require some detours into history.
Octaves
So, what's the big idea here? Well, let's start with the idea of an octave. If you have two notes, let's call then M and N, and the frequency of N is twice the frequency of M... well, to the human ear, they sound very very closely related. In fact N is the first overtone of M - if you play M on almost any instrument, you're also hearing N.
Harmony, which we'll talk about in a minute, is the idea that two notes sound especially pleasant together - but this goes even further. So in many many music systems around the world, these two notes with frequency ratio of 2 are actually identified - they are in some sense 'the same note', and they're given the same name. This also means that further powers of 2, of e.g. 4, 8, 16, and so on, are also 'the same note'. We call the relationship between M and N an octave - we say if two notes are 'an octave apart', one has twice the frequency of the other.
For example, a note whose fundamental frequency is 261.626Hz is known as 'C' in the convention of 'concert pitch'. This implies an infinite series of other Cs, but since the human ear has a limited range of frequencies, in practice you have Cs from 8.176Hz up through 16744.036. These are given a series of numbers by convention, so 261.626Hz is called C4, often 'middle C'. 523.251Hz is C5, 1046.502Hz is C6, and so on. However, a lot of the time it doesn't matter which C you're talking about, so you just say 'C'.
But the identification of "C" with 261.626Hz * 2^N is just a convention (known as 'concert pitch'). Nothing is stopping you tuning to any other frequency: to build up the rest of the structure you just need some note to start with, and the rest unfolds using ratios.
Harmony and intervals
Music is less about individual notes, and more about the relationship between notes - either notes played at the same time, or in succession.
Between any two notes we have something called an interval determined by the ratio of their fundamental frequencies. We've already seen one interval: the octave, which has ratio 2.
The next interval to bring up is the 'fifth'. There are a few different variants of this idea, but generally speaking if two notes have a ratio of 1.5, they sound really really nice together. Why is this called a 'fifth'? Historical reasons, there is no way to shake this terminology, we're stuck with it. Just bear with me here, it will become semi-clear in a minute.
In the same vein, other ratios of small integers tend to sound 'harmonious'. They're satisfying to hear together. Ratios of larger integers, by contrast, feel unsatisfying. But this creates an idea of 'tension' and 'resolution'. If you play two notes together that don't harmonise as nicely, you create a feeling of expectation and tension; when you you play some notes that harmonise really well, that 'resolves' the tension and creates a sense of relief.
Building a scale - just intonation
The exact 3:2 integer ratio used in two tuning systems called 'Pythagorean tuning' and 'just intonation'. Using these kinds of integer ratios, you can unfold out a whole series of other notes, and that's how the Europeans generally did things before 12TET came along. For example, in 'just intonation', you might start with some frequency, and then procede in the ratios 9/8, 5/4, 4/3, 3/2, 5/3, 15/8, and at last 2 (the octave). These would be given a series of letters, creating a 'scale'.
What is a scale? A scale is something like the 'colour palette' for a piece of music. It's a set of notes you use. You might use notes from outside the scale but only very occasionally. Different scales are associated with different feelings - for example, the 'major scale' generally feels happy and triumphant, while a 'minor scale' tends to feel sad and forlorn. We'll talk a lot more about scales soon.
In the European musical tradition, a 'scale' consists of seven notes in each octave, so the notes are named by the first seven notes of the alphabet, i.e. A B C D E F G. A scale has a 'base note', and then you'd unfold the other frequencies using the ratios. An instrument such as a piano would be tuned to play a particular scale. The ratios above are one definition of a 'major scale', and starting with C as the base note, the resulting set of notes is called 'C Major'.
All these nice small-number ratios tend to sound really good together. But it becomes rather tricky if you want to play multiple scales on the same instrument. For example, say your piano is tuned in just intonation to C Major. This means, assuming you have a starting frequency we'll call C, you have the following notes available in a given octave:

C, D=(9/8)C, E=(5/4)C, F=(4/3)C, G=(3/2)C [the fifth!], A=(5/3)C, B=(15/8)C, and 2C [the start of the next octave].
Note: the interval we named the 'fifth' is the fifth note in this scale. It's actually the fifth note in the various minor scales too.
But now suppose you want to play with some different notes - let's say a scale we'll call 'A major', which has the same frequency ratios starting on the note we previously called A. Does our piano have the right keys to play this scale?
Well, the next note up from A would be (9/8)A, which would be (9/8)(5/3)C=(15/8)C - that's our B key, so far so good. Then (5/4)A=(5/4)(5/3)C=(25/12)C and... uh oh! We don't have a (25/12)C key, we have 2C, so if we start at A and go up two keys, we have a note that is slightly lower frequency than the one we're looking for.
What this means is that, depending on your tuning, you could only approximate the pretty integer ratios for any scale besides C major. (25/12) is pretty close to 2, so that might not seem so bad, but sometimes we'd land right in between two notes. We can approximate these notes by adding some more 'in between' piano keys. How should we work out what 'extra' keys to include? Well, there were multiple conventions, but we'll see there is some logic to it...
[You might ask, why are you spending so long on this historical system that is now considered obsolete? Well, intervals and their harmonious qualities are still really important in modern music, and it makes most sense to introduce them with the idea of 'small-integer ratios'.]
The semitone
We've seen if we build the 'major scale' using a bunch of 'nice' ratios, we have trouble playing other scales. The gap above may look rather haphazard and arbitrary, but hold on, we're working in exponential space here - shouldn't we be using a logarithmic scale? If I switch to a logarithmic x-axis, we suddenly get a rather appealing pattern...

All the gaps between successive notes are about the same size, except for the gap between E and F, and B and C, which are about half that size. If you try to work that out exactly, you run into the problems we saw above, where C to D is 9/8 or 1.125, but D to E is 10/9 or 1.11111... Even so, you can imagine how people who were playing around with sounds might notice, damn, these are nice even steps we have here. Though you might also notice places where, in this scheme, it's not completely even - for example G to A (ratio 10/9) is noticeably smaller than A to B (ratio 9/8).
We've obliquely approached the idea of dividing the octave up into 12 steps, where each step is about the size of the gap between E and F or B and C. We call each of these steps a 'semitone'. Two semitones make a 'whole tone'. We might fill in all the missing semitones in our scale here using whole-number ratios, which gives you the black keys on the piano. There are multiple schemes for doing this, and the ratios tend to get a bit uglier. In the system we've outlined so far, a 'semitone' is not a fixed ratio, even though it's always somewhere around 1.06.
The set of 12 semitones is called the 'chromatic scale'. It is something like the 'colour space' for Western music. When you compose a piece, you select some subset of the 12 semitones as your 'palette' - the 'scale of' a piece of music.
But we still have a problem here, which is the unevenness of the gaps we discussed above. This could be considered a feature, not a bug, since each scale would have its own 'character' - it's defined by a slightly different set of ratios. But it does add a lot of complication when moving between scales.
So let's say we take all this irregularity as a bug, and try to fix it. The solution is 'equal temperament', which is the idea that the semitone should always be the exact same ratio, allowing the instrument to play any scale you please without difficulty.
Posed like this, it's easy to work out what that ratio should be: if you want 12 equal steps to be an octave, each step must be the 12th root of 2. Which is an irrational number that is about 1.05946...
At this point you say, wait, Bryn, didn't you just start this all off by saying that the human ear likes to hear nice simple integer ratios of frequencies? And now you're telling me that we should actually use an irrational number, which can't be represented by any integer ratio? What gives? But it turns out the human ear isn't quite that picky. If you have a ratio of 7 semitones, or a ratio of 2^(7/12)=1.4983..., that's close enough to 1.5 to feel almost as good. And this brings a lot of huge advantages: you can easily move ('transpose') between different scales of the same type, and trust that all the relevant ratios will be the same.
Equal temperament was the eventual standard, but there was a gradual process of approaching it called stuff like 'well-tempered' or 'good temperament'. One of the major steps along the way was Bach's collection 'the well-tempered klavier', showing how a keyboard instrument with a suitable tuning could play music in every single established scale. Here's one of those pieces:
youtube
Although we're using these irrational numbers, inside the scale are certain intervals that are considered to have certain meanings - some that are 'consonant' and some that are 'dissonant'. We've already mentioned the 'fifth', which is the 'most consonant' ratio. The fifth consists of 7 semitones and it's roughly a 1.5 ratio in equal temperament. Its close cousin is the 'fourth', which consists of 5 semitones. Because it's so nice, the fifth is kind of 'neutral' - it's just there but it doesn't mean a lot on its own.
For the other important intervals we've got to introduce different types of scale.
The scale zoo
So, up above we introduced the 'major' scale. In semitones, the major scale is intervals of 2, 2, 1, 2, 2, 2, 1. This is also called a 'mode', specifically the 'Ionian mode'. There are seven different 'modes', representing different permutations of these intervals, which all have funky Greek names.
The major scale generally connotes "upbeat, happy, triumphant". There are 12 different major scales, taking the 12 different notes of the chromatic scale as the starting point for each one.
Next is the minor scale, which tends to feel more sad or mysterious. Actually there are a few different minor scales. The 'natural minor' goes 2, 1, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2. You might notice this is a cyclic permutation of the major scale! So in fact a natural minor scale is the same set of notes as a major scale. What makes it different?
Well, remember when we talked about tension and resolution? It's about how the notes are organised. Our starting note is the 'root' note of the scale, usually established early on in the piece of music - quite often the very first note of the piece. The way you move around that root note determines whether the piece 'feels' major or minor. So every major scale has a companion natural minor scale, and vice versa. The set of notes in a piece is enough to narrow it down to one minor and one major, but you have to look closer to figure out which one is most relevant.
The 'harmonic minor' is almost the same, but it raises the second-last note (the 7th) a semitone. So its semitone intervals are 2, 1, 2, 2, 1, 3, 1.
The 'melodic minor' raises both the 6th and 7th by one semitone, (edit: but usually only on the way up). So its semitone intervals are 2, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1. (edit: When you come back down you tend to use the natural minor.)
If you talk about a 'minor scale' unqualified, you mean the natural minor. It's also the 'Aeolian mode' in that system of funky Greek names I mentioned earlier.
So that leads to a set of 24 scales, a major and minor scale for every semitone. These are the most common scale types that almost all Western tonal music is written in.
But we ain't done. Because remember I said there were all those other "modes"? These are actually just cyclic permutations of the major scale. There's a really nerdy Youtube channel called '8-bit music theory' that has a bunch of videos analysing them in the context of videogame music which I'm going to watch at some point now I finally have enough background to understand wtf he's talking about.
youtube
And of top of that you have all sorts of other variants that come from shifting a note up or down a semitone.
The cast of intervals
OK, so we've established the idea of scales. Now let's talk intervals. As you might guess from the 'fifth', the intervals are named after their position in the scale.
Let me repeat the two most common scale modes, in terms of number of semitones relative to the root note:
position: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8
major: 0, 2, 4, 5, 7, 9, 11, 12
minor: 0, 2, 3, 5, 7, 8, 10, 12
So you can see the fourth and fifth are the same in both. But there's a difference in three places: the third, the sixth, and the seventh. In each case, the minor is down a semitone from the major.
The interval names are... not quite as simple as 'place in the scale', but that's mostly how it works. e.g. the 'major third' is four semitones and the 'minor third' is three.
The fourth and fifth, which are dual to each other (meaning going up a fifth takes you to the same note as going down a fourth, and vice versa) are called 'perfect'. The note right in between them, an interval of 6 semitones, is called the 'tritone'.
(You can also refer to these intervals as 'augmented' or 'diminished' versions of adjacent intervals. Just in case there wasn't enough terminology in the air. See the table for the names of every interval.)
So, with these names, what's the significance of each one? The thirds, sixths and sevenths are important, because they tell us whether we're in minor or major land when we're building chords. (More on that soon.)
The fifth and the octave are super consonant, as we've said. But the notes that are close to them, like the seventh, the second and even more so the tritone, are quite dissonant - they're near to a nice thing and ironically that leads to awkward ratios which feel uncomfy to our ears. So generally speaking, you use them to build tension and anticipation and set up for a resolution later. (Or don't, and deliberately leave them hanging.)
Of course all of these positions in the scale also have funky Latin names that describe their function.
There's a lot more complicated nuances that make the meaning of a particular interval very contextual, and I certainly couldn't claim to really understand in much depth, but that's basically what I understand about intervals so far.
Our goofy-ass musical notation system
So if semitones are the building block of everything, naturally the musical notation system we use in the modern 12TET era spaces everything out neatly in terms of semitones, right?
Right...?

Lmao no. Actually sheet music is written so that each row of the stave (or staff, the five lines you write notes on) represents a note of the C major scale. All the notes that aren't on the C major scale are represented with special symbols, namely ♯ (read 'sharp') which means 'go up a semitone', and ♭ (read 'flat') which means 'go down a semitone'. That means the same note can be notated in two different ways: A♯ and B♭ are the same note.
The above image shows the chromatic scale, notated in two different ways. Every step is exactly one semitone.
Since a given scale might end up using one of these 'in between' notes that has to be marked sharp or flat, and you don't want to do that for every single time that note appears. Luckily, it turns out that each major/minor scale pair ends up defining a unique set of notes to be adjusted up or down a semitone, called the 'key signature'. So you can write the key signature at the beginning of the piece, and it lasts until you change key signature. For example, the key of 'A♭ major' ends up having four sharps:
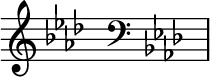
There is a formula you can use to work out the set of sharps or flats to write for a given key. (That's about the point I checked out on musictheory.net.)
There is some advantage to this system, which is that it very clearly tells you when the composer intends to shift into a different scale, and it saves space since with the usual scales there are no wasted lines. But it's also annoyingly arbitrary. You just have to remember that B to C is only a semitone, and the same for E to F.
What are those weird squiggly symbols? Those are 'clefs'. Each one assigns notes to specific lines. The first one 𝄞 is the 'treble clef', the second one 𝄢 is the 'bass clef'. Well, actually these are the 'G-clef' and the 'F-clef', and where they go on the stave determines note assignment, but thankfully this has been standardised and you will only ever see them in one place. The treble clef declares the lines to be E G B D F and the bass clef G B D F A.
There is also a rarer 'C-clef' which looks like 𝄡. This is usually used as the 'Alto clef' which means F A C E G.
This notation system seems needlessly convoluted, but we're rather stuck with it, because most of the music has been written in it already. It's not uncommon for people to come up with alternative notations, though, such as 'tabs' for a stringed instrument which indicate which position should be played on each string. Nowadays on computers, a lot of DAWs will instead use a 'piano roll' presentation which is organised by semitone.
And then there's chords.
Chords! And arpeggios!
A chord is when you play 3 or more notes at the same time.
Simple enough right? But if you wanna talk about it, you gotta have a way to give them names. And that's where things get fucking nuts.
But the basic chord type is a 'triad', consisting of three notes, separated by certain intervals. There are two standard types, which you basically assemble by taking every other note of a scale. In terms of semitones, these are:
Major triad: 0 - 4 - 7
Minor triad: 0 - 3 - 7
Then there's a bunch of variations, for example:
Augmented: 0 - 4 - 8
Diminished: 0 - 3 - 6
Suspended: 0 - 2 - 7 (sus2) or 0 - 5 - 7 (sus4)
Dominant seventh: 0 - 4 - 7 - 10
Power: 0 - 7
There is a notation scheme for chords in pop, jazz, rock, etc., which starts with a root note and then adds a bunch of superscripts to tell you about any special features of a chord. So 'C' means the C Major triad (namely C,E,G) and 'Cm' or 'c' means the C Minor triad (namely C,E♭,G).
In musical composition, you usually tend to surround the melody (single voice) with a 'chord progression' that both harmonises and creates a sense of 'movement' from one chord to another. Some instruments like guitar and piano are really good at playing chords. On instruments that can't play chords, they can still play 'arpeggios', which is what happens if you take a chord and unroll it into a sequence of notes. Or you play in an ensemble and harmonise with the other players to create a chord together. Awww.
Given a scale, you can construct a series of seven triad chords, starting from each note of the scale. These are generally given scale-specific Roman numerals corresponding to the position in the scale, and they're used to analyse the progression of chords in a song. I pretty much learned about this today while writing this post, so I can't tell you much more than that.
Right now, that's about as far as I've gotten with chords. On a violin, you can play just two strings at the same time after all - I never had much need to learn about them so it remains a huge hole in my understanding of music. I can't recognise chords by ear at all. So I gotta learn more about them.
As much as I wrote this for my own benefit... if you found this post interesting, let me know. I might write more if people find this style of presentation appealing. ^^'
239 notes
·
View notes
Text
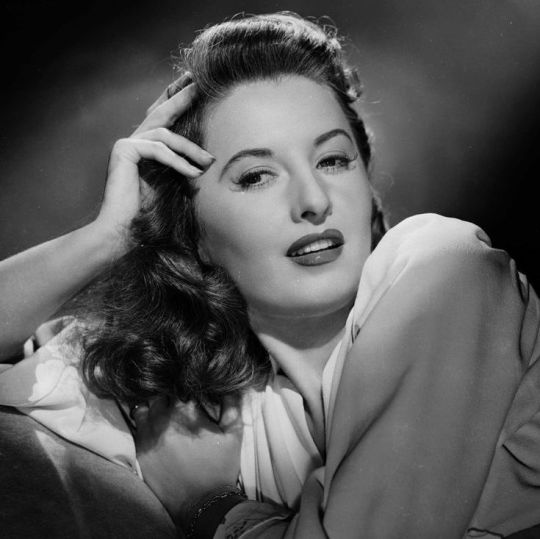
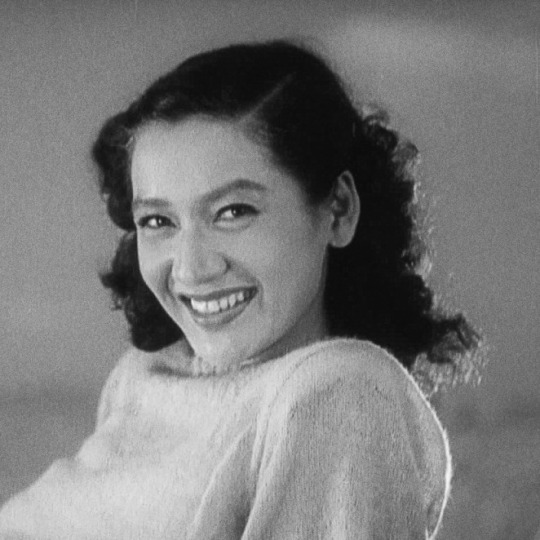


Propaganda
Barbara Stanwyck (Ball of Fire, The Lady Eve, Double Indemnity)—I hope someone else has submitted better propaganda than I because I don't want my girl's prospects to rest on me just yelling PLEASE VOTE FOR MY TERRIBLE HOT GIRLFRIEND. She is a delight in everything! She is often a sexy jerk! (It's most of the plot of Baby Face!) Even when she plays a "good girl" (as an example, Christmas in Connecticut, which more people should see) she's still kind of a jerk and I love her for it! She won't take men's shit and she sure wouldn't take mine!
Setsuko Hara (Tokyo Story, Late Spring, The Idiot)— "'The only time I saw Susan Sontag cry,' a writer once told me, his voice hushed, 'was at a screening of a Setsuko film.' What Setsuko had wasn’t glamour—she was just too sensible for that—it was glow, one that ebbed away and left you concerned, involved. You got the sense that this glow, like that of dawn, couldn’t be bought. But her smiles were human and held minute-long acts, ones with important intermissions. When she looked away, she absented herself; you felt that she’d dimmed a fire and clapped a lid on something about to spill. Over the last decade, whenever anyone brought up her lips—'Setsuko’s eternal smile,' critics said, that day we learned that she’d died—I thought instead of the thing she made us feel when she let it fall." - Moeko Fujii
This is round 4 of the tournament. All other polls in this bracket can be found here. Please reblog with further support of your beloved hot sexy vintage woman.
[additional propaganda submitted under the cut.]
Setsuko Hara:

One of the best Japanese actresses of all time; a symbol of the golden era of Japanese cinema of the 1950s After seeing a Setsuko Hara film, the novelist Shūsaku Endō wrote: "We would sigh or let out a great breath from the depths of our hearts, for what we felt was precisely this: Can it be possible that there is such a woman in this world?"



One of the greatest Japanese actresses of all time!! Best known for acting in many of Yasujiro Ozu's films of the 40s and 50s. Also she has a stunning smile and beautiful charm!
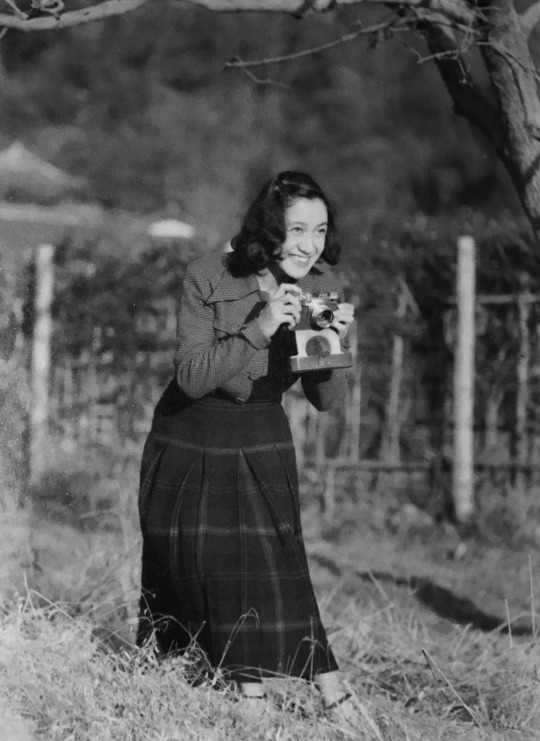
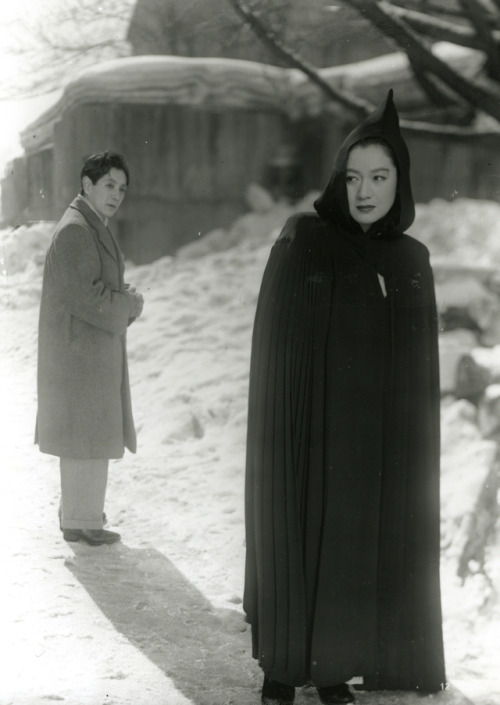


Linked gifset
Linked gifset 2
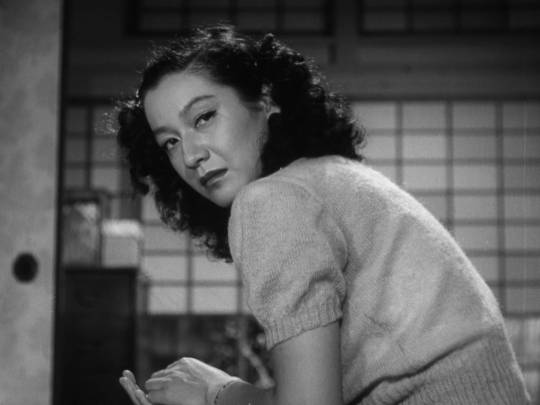


She's considered by some to be the greatest Japanese actress of all time! In Kurosawa's The Idiot she haunts the screen, and TOTALLY steals the show from Mifune every time she appears.
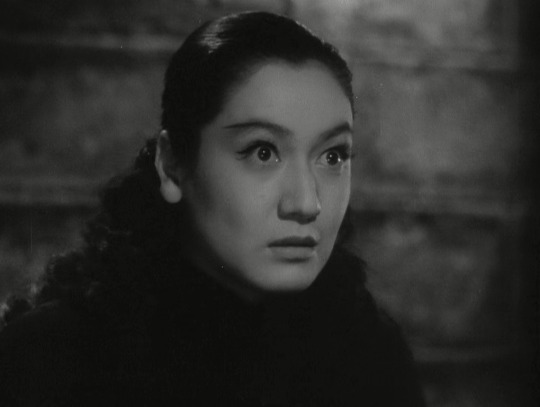

She's considered by some to be the greatest Japanese actress of all time! In Kurosawa's The Idiot she haunts the screen, and TOTALLY steals the show from Mifune every time she appears.

"No other actor has ever mastered the art of the smile to the same extent as Setsuko Hara (1920–2015), a celebrated star and highly regarded idol who was one of the outstanding actors of 40s and 50s Japanese cinema. Her radiant smile floods whole scenes and at times cautiously undermines the expectations made of her in coy, ironic fashion. Yet her smile's impressive range also encompasses its darker shades: Hara's delicate, dignified, melancholy smile with which she responds to disappointments, papers over the emotions churning under the surface, and flanks life's sobering realizations. Her smiles don't just function as a condensed version of her ever-precise, expressive, yet understated acting ability, they also allow the very essence of the films they appear in to shine through for a brief moment, often studies of the everyday, post-war dramas which revolve around the break-up of family structures or the failure of marriages. Her performances tread a fine line between social expectation and personal desire in post-war Japan, as Hara attempts to lay claim to the autonomy of the female characters she plays – frequently with a smile." [link]
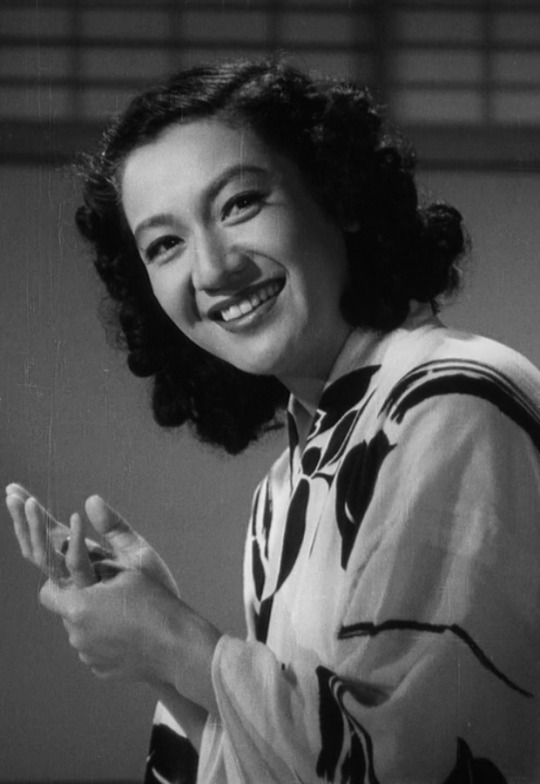

Leading lady of classic Japanese cinema with a million dollar smile
Maybe the most iconic Japanese actress ever? She rose to fame making films with Yasujiro Ozu, becoming one of the most well-known and beloved actresses in Japan, working from the 30s through the 60s in over 100 hundred. She is still considered one of the greatest Japanese actresses ever, and in my opinion, just one of the greatest actresses of all time. And she was HOT! Satoshi Kon's film Millennium Actress was largely based on her life and her career.

Barbara Stanwyck:
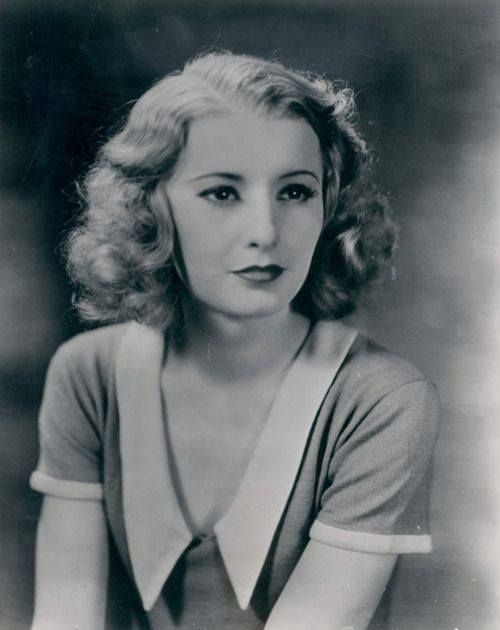

"THE leading lady of the golden age of hollywood. One of the only actresses to work independent of a studio, making short-term contracts that enabled her to make movies wherever she wanted. She had so much range, and could act in basically any genre. She's been rumored to be a lesbian literally since she was active in Hollywood; most notable is the rumor that she had a long time on-and-off relationship with famously bi Joan Crawford, her "best friend" for decades (They lived right next door to one another). She also lived with Helen Ferguson, her "live-in publicist" for many years. She was the quintessential femme fatale in Double Indemnity, and really pushed sexual boundaries in her pre-code films like Baby Face, and the famous screwball The Lady Eve, where she plays basically a downlow domme. Allegedly, when a journalist asked her if she was a lesbian, she straight up threw him out of her house. She even played a lesbian in Walk on the Wild Side"
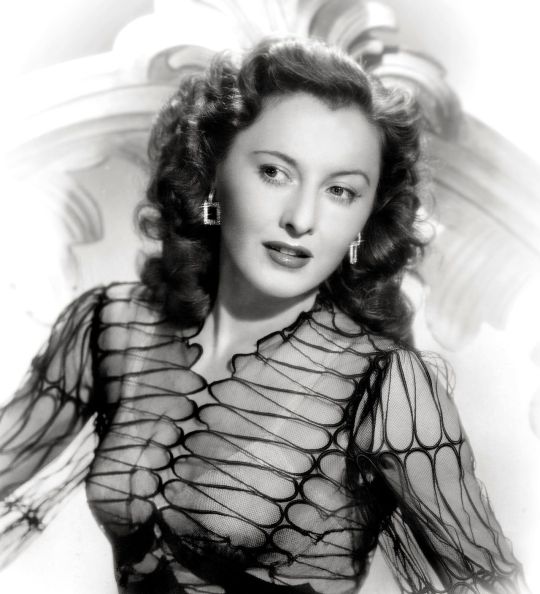

"THE queen of screwball comedies. I adore her, I'd kill for her, I will cry if she's not gonna win this poll."
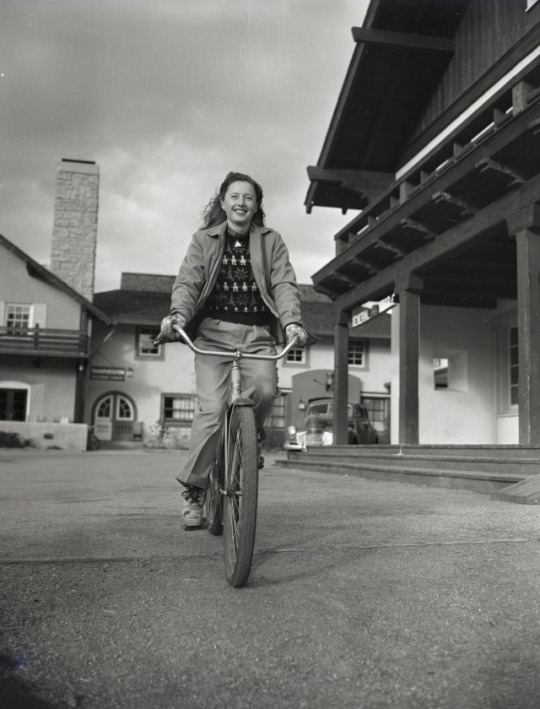

"listen ok she had awful politics she was a mccarthyist right wing wacko BUT she's so incredibly hot that i've deluded myself into believing i could fix her. if you see her onscreen she carries herself in a way that's just so effortlessly sexy AND she has just a stunning face. imo she was at her hottest in the 1940s but even as early as the late 1920s she had a rly captivating screen presence and just a beautiful face, and then post-1950 she was just irresistibly milfy so really she was just always incredibly hot. she was also an incredibly talented actress who was equally stellar in melodrama, film noir, and unhinged screwball comedy. the blonde wig they made her wear in double indemnity is notoriously silly looking but she still looks sexy in it so that's gotta count for something. i've watched so many terrible movies just for a chance at seeing her that i think her estate should be paying me damages."
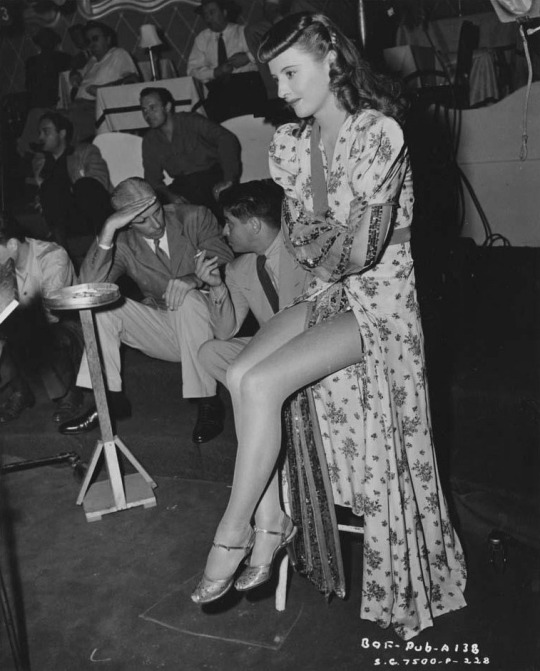
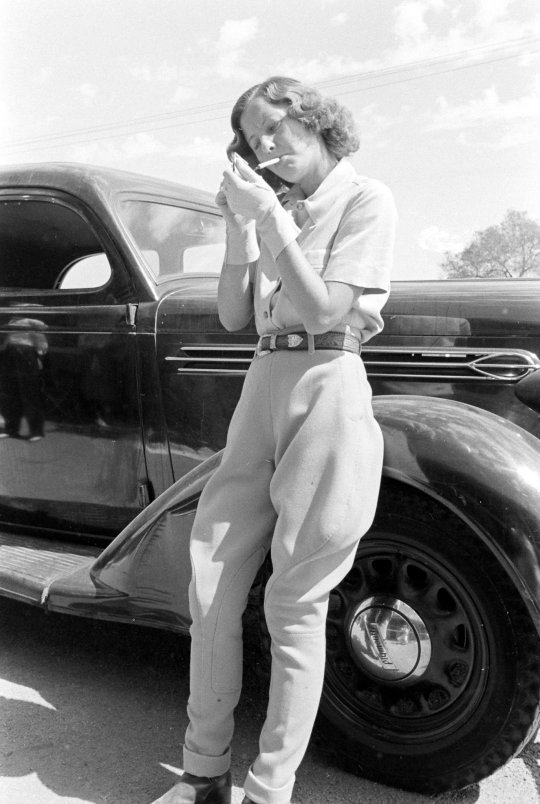



"Not often thought of for her sultriness, Barbara Stanwyck was incredible in that she could actually choose to be hot if the role called for it, and then have a glow-down to look ordinary for another role. She wasn't the most beautiful or effervescent, but damn did she have rizz. Watch her with Gary Cooper in Ball of Fire teaching him about "yum-yum" or with Henry Fonda in The Lady Eve whispering huskily into his ear."
youtube
"She is always the smartest woman in the room. Watching her play Henry Fonda like a befuddled fiddle in The Lady Eve was a highlight of my life. Femme fatale in Double Indemnity, comedy queen in Ball of Fire. She can do anything."
"She was part of my gay awakening"
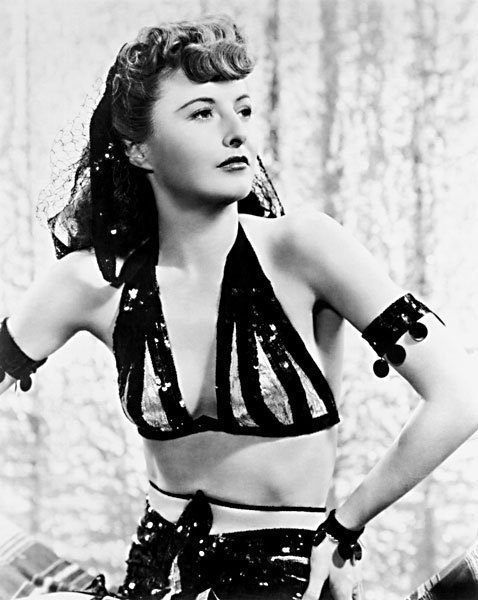



"SHE'S A PRE-CODE QUEEN. She did everything, drama, comedy. The most beautiful woman in the world to watch weep. Beg for to step on you with those legs. Fun Babs story: Ginger Rogers was offered the role in Ball of Fire but said, “Oh, I would never play that part, she’s too common.” So they called Barbara Stanwyck and they said “We offered this to Ginger Rogers but she’s turned it down, would you be interested?” And she read the script and she said; “You bet! I LOVE playing common broads. [link]"
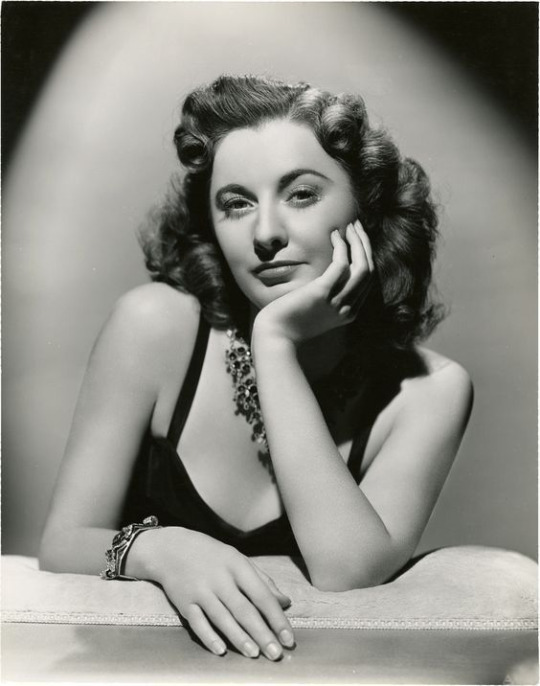

299 notes
·
View notes
Text
Gonna make this a quick one since I just don’t have the spoons for a really big effort post:
Pre-CCP 20th Century China Did Not Have Feudal or Slave-like Land Tenancy Systems
Obviously what counts as ��slave-like” is going to be subjective, but I think it's common, for *ahem* reasons, for people to believe that in the 1930’s Chinese agriculture was dominated by massive-scale, absentee landlords who held the large majority of peasant workers in a virtual chokehold and dictated all terms of labor.
That is not how Chinese land ownership & agricultural systems worked. I am going to pull from Chinese Agriculture in the 1930s: Investigations into John Lossing Buck’s Rediscovered ‘Land Utilization in China’ Microdata, which is some of the best ground-level data you can get on how land use functioned, in practice, in China during the "Nanjing Decade" before WW2 ruins all data collection. It looks at a series of north-central provinces, which gives you the money table of this:
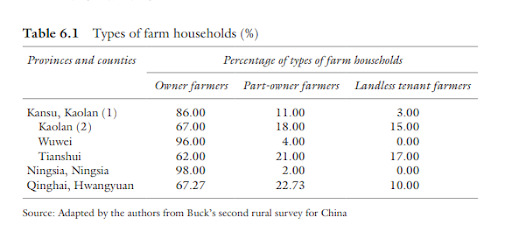
On average, 4/5ths of Chinese peasants owned land, and primarily farmed land that they owned. Tenancy was, by huge margins, the minority practice. I really don’t need to say more than this, but I'm going to because there is a deeper point I want to make. And it's fair to say that while this is representative of Northern China, Southern China did have higher tenancy rates - not crazy higher, but higher.
So let's look at those part-owner farmers; sounds bad right? Like they own part of their land, but it's not enough? Well, sometimes, but sometimes not:
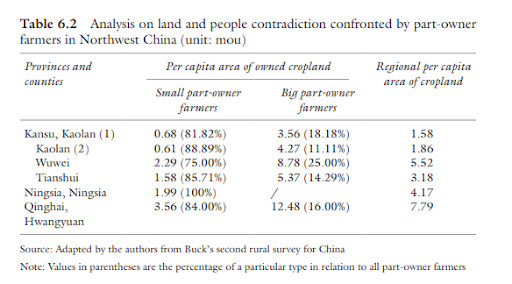
A huge class (about ~1/3rd) of those part-owners were farming too much land, not too little; they were enterprising households renting land to expand their businesses. They would often engage in diversified production, like cash crops on the rented land and staple crops on their owned land. Many of them would actually leave some of their owned land fallow, because it wasn’t worth the time to farm!
Meanwhile the small part-owners and the landless tenant farmers would rent out land to earn a living…sometimes. Because that wasn’t the only way to make a living - trades existed. From our data, if you are a small part-owner, you got a substantial chunk of your income from non-farm labor; if you owned no land you got the majority of your income from non-farm labor:
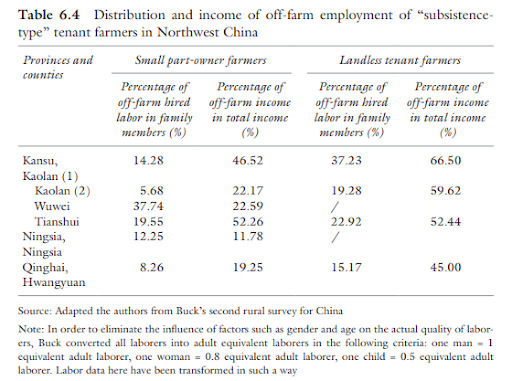
(Notice how that includes child labor by default, welcome to pre-modernism!)
So the amount of people actually doing full-tenancy agriculture for a living is…pretty small, less than 10% for sure. But what did it look like for those who do? The tenancy rates can be pretty steep - 50/50 splits were very common. But that is deceiving actually; this would be called “share rent”, but other systems, such as cash rents, bulk crop rents, long-term leases with combined payment structures, etc, also existed and were plentiful - and most of those had lower rent rates. However, share rent did two things; one, it hedged against risk; in the case of a crop failure you weren't out anything as the tenant, a form of insurance. And two, it implied reciprocal obligations - the land owner was providing the seed, normally the tools as well, and other inputs like fertilizer.
Whether someone chose one type of tenancy agreement or the other was based on balancing their own labor availability, other wage opportunities, the type of crop being grown, and so on. From the data we have, negotiations were common around these types of agreements; a lot of land that was share rent one year would be cash rent another, because the tenants and market conditions shifted to encourage one or the other form.
I’m doing a little trick here, by throwing all these things at you. Remember the point at the top? “Was this system like slavery?” What defines slavery? To me, its a lack of options - that is the bedrock of a slave system. Labor that you are compelled by law to do, with no claim on the output of that work. And as I hit you with eight tiers of land ownership and tenancy agreements and multi-source household incomes, as you see that the median person renting out land to a tenant farmer was himself a farmer as a profession and by no means some noble in the city, what I hope becomes apparent is that the Chinese agricultural system was a fully liquid market based on choice and expected returns. By no means am I saying that it was a nice way to live; it was an awful way to live. But nowhere in this system was state coercion the bedrock of the labor system. China’s agricultural system was in fact one of the most free, commercial, and contract-based systems on the planet in the pre-modern era, that was a big source of why China as a society was so wealthy. It was a massive, moving market of opportunities for wages, loans, land ownership, tenancy agreements, haggled contracts, everyone trying in their own way to make the living that they could.
It's a system that left many poor, and to be clear injustices, robberies, corruption, oh for sure were legion. Particularly during the Warlord Era mass armies might just sweep in and confiscate all your hard currency and fresh crops. But, even ignoring that the whole ‘poverty’ thing is 90% tech level and there was no amount of redistribution that was going to improve that very much, what is more important is that the pre-modern world was *not* equally bad in all places. The American South was also pretty poor, but richer than China in the 19th century. And being a slave in the American South was WAY worse than being a peasant in China during times of peace - because Confederate society built systems to remove choice, to short-circuit the ebb and flow of the open system to enshrine their elite ‘permanently’ at the top. If you lived in feudal Russia it was a good deal worse, with huge amounts of your yearly labor compelled by the state onto estates held by those who owned them unimpeachably by virtue of their birthright (though you were a good deal richer just due to basic agriculture productivity & population density, bit of a tradeoff there).
If you simply throw around the word “slavery” to describe every pre-modern agricultural system because it was poor and shitty, that back-doors a massive amount of apologia for past social systems that were actively worse than the benchmarks of the time. Which is something the CCP did; their diagnosis of China’s problem for the rural poor of needing massive land redistribution was wrong! It was just wrong, it was not the issue they were having. It was not why rural China was often poor and miserable. It could help, sure, I myself would support some compensated land redistribution in the post-war era as a welfare idea for a fiscally-strapped state. But that was gonna do 1% of the heavy lifting here in making the rural poor's lives better. And I don’t think we should continue to the job of spreading the CCP's propaganda for them.
There ya go @chiefaccelerator, who alas I was not permitted to compel via state force into writing this for me, you Qing Dynasty lazy peasant.
258 notes
·
View notes
Note
There's this weird thing going on Reddit right now where people are claiming that legally, Rhaenyra children are not bastards. And I was wondering if you agree or disagree. I think that people are just making up their own canon lore at this point.
Hi anon,
I think what gets kind of muddled in this discussion is what "legally" means in the context. Generally speaking, children born within wedlock are considered legitimate until proven otherwise. Now in the medieval world, it's not like you were issued a birth certificate that you could whip out and say see, it says right here who the father is! There were no DNA tests, it was all a matter of word, and by and large a woman's virtue was her word, and it was what kept her and her children protected within the framework of medieval marriage. But the reason why bastardy matters in this context is also important. It's not like Rhaenyra is trying to collect child support here, nor is she a common merchant's wife whose husband has decided just to roll with it. She's the heir to the throne and the parentage of her children is a matter of inheritance and dynastic succession, so it's not a situation where a legal loophole is particularly helpful as a gotcha. There is not at this point in history a comprehensive codified law that clearly defines what these terms mean and defines the rights and obligations of parents and children legitimate and illegitimate, mostly you have combinations of precedent, tradition, oath, and a healthy dose of might makes right.
(I saw another reply to this question in which the responded basically goes, "free yourself from the shackles of this construct! Marriage isn't real it's an oppressive institution and the idea of bastardy is made up, so let it go," and while it's true that marriage, legitimacy, etc. are all social constructs and not absolute states of being, they started off as having a functional purpose within a certain social framework. And this is a basic problem a lot of people have with George's world, it's not that we have to have the views of a 12th century French peasant, or that everything has to be historically accurate, but George chose the medieval world as a setting for a reason, and it's not just an aesthetic one. Characters in even a quasi-historical setting have to act within the constraints of that setting. We have to understand that people don't know what they don't know. The medieval world doesn't have any framework for the introduction of feminist ideals. Westeros hasn't even had a Christine de Pizan yet. You couldn't walk up to a medieval peasant woman and say "marriage is a tool of patriarchal oppression and bastardy is a social construct," they'd look at you like you had two heads. And so we have to acknowledge that you can't simply start dismantling existing social structures if the framework doesn't exist to replace them with something better that offers more protections for a broader group of people, and at this point it definitely doesn't. Making an exception for one very privileged woman does not mean progress for all women, instead it often means destabilization of the flawed system that does exist, and even more violence against those less powerful in order to enforce the exceptional status).
So from a medieval point of view, marriage was pretty much a non-negotiable for a woman. And women weren't simply getting married because they were pressured into it by their families or because their fathers were opportunistic assholes, they got married because unmarried women had no legal status or standing. In most places they could not sign contracts or own land. A woman could join the church or get married (or become a prostitute, but it's not like sex workers had freedoms or protections either). Divorce wasn't a thing, and annulment was hard to get and usually available only as a tool for men to set aside their wives. So, for all intents and purposes, once you were married, that was generally it, you were stuck for life (the upside is that widows did get a lot more freedom, so marrying an older guy and waiting it out was not a bad option sometimes, all things considered). But what marriage did provide was assurance that you and your children would be protected and provided for. Marriage was a practical agreement, involving dowries, inheritances, and alliances sealed in blood. And this is one of the reasons why bastards could not inherit. Inheritance for once's children was one of the few perks of a marriage for a woman (this is, incidentally, why Alicent is so pressed about her children being effectively disinherited. There is NO reason for her, as an eligible maiden of good standing, to marry a man who will not provide for her sons, king or not). And of course, a man's bastards are obvious and are disqualified from inheriting (setting aside legitimization because it is not nearly the easy out that people think it is). You can't really pass them off as legitimate because your wife clearly knows which children she gave birth to, whereas a man might be told he is the father of a child when that child's father is in fact someone else.
In a dynastic marriage, all of this becomes even more important. Marriages were made as alliances and to strengthen the ties between kingdoms or houses. A child seals the marriage agreement by binding two bloodlines and creating kinship bonds that will last beyond the current generation. Those kinship bonds can ensure peace between kingdoms at war, trade agreements, and military aid. Passing a bastard off as trueborn breaks that agreement; it violates the very principle by which the agreement was made. And in this context, it doesn't actually matter if the father claims the children as his, because in a dynastic marriage inheritance is not just a personal matter, it's a matter of the state. The truth matters to a great many people, more than just the immediate family. A lie doesn't become the truth simply because the liar isn't caught, and there's no statute of limitations or court ruling that will ever put the matter to rest for good. Passing off a bastard as trueborn destabilizes the succession and breaks the dynastic bonds that the marriage was meant to establish. When the bastard heir in question attempts to take the throne, it won't be a smooth transition.
So what does it mean that Laenor and Corlys agree to pass Rhaenyra's children off as trueborn? It means that their bastardy cannot be proven at the moment insofar as the legal father, Rhaenyra's husband, is playing along and covering for Rhaenyra, and Viserys is backing them up by giving this his "legal" stamp of approval. But again, our view that it's no one else's business but Laenor and Rhaenyra's and that Viserys "legalized" their status is very modern. Jaehaeyrs and Alysanne were not considered married in the eyes of the Westerosi until they'd had a bedding ceremony, that is, the consummation of their marriage was witnessed. Royal marriages and the children that come from them are a public matter because the succession affects everyone in the realm. Laenor, Corlys, and Viserys can protect those children in the short term, but Laenor and Corlys and Viserys won't live forever, and they could withdraw their support for those children and renounce them as bastards at any time. Harwin could admit to fathering them, Rhaenyra and Harwin could get caught in the act, or someone else close to them might confess. Sure right now the black faction are all one big happy family, but 20 years down the line when bastard Jace takes the throne over trueborn Aegon III? There are multiple people in the family who could confess to knowledge of the bastardy, including Aegon III himself. The bastardy is too obvious and there are too many legitimate heirs of both house Targaryen and house Velaryon getting pushed aside in favor of bastard born children for it to be an issue that simply disappears because Rhaenyra and Laenor say so.
So "legal bastardy" is a pretty meaningless concept when it comes to royal succession because it's not a matter that's going to be settled by some neutral third party in a court of law. What matters in the long run is not whether or not Laenor claimed the kids, what matters is whether or not the situation is questionable enough that people with the power to challenge it might challenge it. And we see even within the actual narrative of the Dance that this is indeed the case. There is already a situation brewing with the other branches of the Velaryon family who are rightfully pretty pissed to see their ancestral seat pass to someone with no blood ties to the family (and as an aside, people will say Vaemond was self-serving, and of course he was, but that doesn't make him wrong, and maybe Baela or Rhaena should have inherited instead, but neither they nor their father were pressing their claims because they were backing up the bastard claimants, so was Vaemond supposed to do that for them?). And yes the king and Rhaenyra can cry treason and they can kill Vaemond and cut out tongues, but using force to silence people for telling the objective truth is by definition tyranny, and that's exactly the sort of situation that would get the nobility nervous. Because if Rhaenyra has to silence people already and she's not even queen yet, what will Jace have to do when he takes the throne? That's the real problem, not the "legal" status of Jace and his brothers, but the practical ramifications of hiding the truth.
122 notes
·
View notes