#national family health survey
Text
Mental Health Crisis in Kashmir: A Call for Urgent Action
“The heightened mental health crisis, compounded by human rights abuses and psychological stress from perpetual violence and loss in Kashmir.”
Mehr un Nisa*
The Vienna Declaration and Programme of Action highlight the inextricable link between human rights and health and emphasise the fundamental right to the highest attainable standard of health for all. When applied to the disturbed region of…

View On WordPress
#41 psychiastrists serving 12.5 million#47 percent population suffers from trauma#A call for urgent action#Article 370#Fundamental right of health#Human Rights and Health#Kashmir conflict#Kashmir Institutte of International Relations#Kashmiris#Kashmiris with depression#KIIR#Mental Health Crisis in Kashmir#Mental health problems#National Family Health Survey#Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder#Premature Ovarian Failure#PTSD#Revocation of Article 370#Shortage of psychiatrists#Standard of health for all#Stigmatisation#Stress and Anxiety levels#Struggle for peace and justice#Toll on Mental health#Vulnerable population
0 notes
Text
Chota News is a first of its kind unique mobile media company in the country. We produce & distribute “Made for Mobile Content” to Indian local language audience. Like TV media & Print media, we are building a technology based mobile media company with short news and other rich content in Indian local languages
1 note
·
View note
Text
#women issues in india#womenissues#social issues#marriage#national family health survey nfhs#nfhs#nfhs data#nfhs report#news
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
National Family Health Survey Flags Obesity Among Women in South India; TN Records Highest Increase
National Family Health Survey Flags Obesity Among Women in South India; TN Records Highest Increase
तेलंगाना, आंध्र प्रदेश, कर्नाटक, केरल और तमिलनाडु के दक्षिणी राज्यों में महिलाओं के मोटापे की स्थिति पर एक सांख्यिकीय बुलेटिन से पता चला है कि महिलाएं देश-स्तर पर पुरुषों की तुलना में अधिक वजन या मोटापे से ग्रस्त हैं (24% पर महिलाएं, 22.9% पर पुरुष) ), साथ ही आंध्र प्रदेश, केरल और तमिलनाडु में भी।
हालांकि कर्नाटक और तेलंगाना में घटना मामूली रूप से कम है, लेकिन सभी दक्षिणी राज्यों में पुरुषों और…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
The more women are paid, the less eager they are to marry. A 1982 study of three thousand singles found that women earning high incomes are almost twice as likely to want to remain unwed as women earning low incomes. "What is going to happen to marriage and childbearing in a society where women really have equality?" Princeton demographer Charles Westoff wondered in the Wall Street Journal in 1986. "The more economically independent women are, the less attractive marriage becomes."
Men in the '80s, on the other hand, were a little more anxious to marry than the press accounts let on. Single men far outnumbered women in dating services, matchmaking clubs, and the personals columns, all of which enjoyed explosive growth in the decade. In the mid-80s, video dating services were complaining of a three-to-one male-to-female sex ratio in their membership rolls. In fact, it had become common practice for dating services to admit single women at heavily reduced rates, even free memberships, in hopes of remedying the imbalance.
Personal ads were similarly lopsided. In an analysis of 1,200 ads in 1988, sociologist Theresa Montini found that most were placed by thirty-five-year-old heterosexual men and the vast majority "wanted a long-term relationship." Dating service directors reported that the majority of men they counseled were seeking spouses, not dates. When Great Expectations, the nation's largest dating service, surveyed its members in 1988, it found that 93 percent of the men wanted, within one year, to have either "a commitment with one person" or marriage. Only 7 percent of the men said they were seeking "lots of dates with different people." Asked to describe "what concerns you the day after you had sex with a new partner," only 9 percent of the men checked "Was I good?" while 42 percent said they were wondering whether it could lead to a "committed relationship."
These men had good cause to pursue nuptials; if there's one pattern that psychological studies have established, it's that the institution of marriage has an overwhelmingly salutary effect on men's mental health. "Being married," the prominent government demographer Paul Glick once estimated, "is about twice as advantageous to men as to women in terms of continued survival." Or, as family sociologist Jessie Bernard wrote in 1972:
“There are few findings more consistent, less equivocal, [and] more convincing, than the sometimes spectacular and always impressive superiority on almost every index—demographic, psychological, or social—of married over never-married men. Despite all the jokes about marriage in which men indulge, all the complaints they lodge against it, it is one of the greatest boons of their sex.”
Bernard's observation still applies. As Ronald C. Kessler, who tracks changes in men's mental health at the University of Michigan's Institute for Social Research, says: "All this business about how hard it is to be a single woman doesn't make much sense when you look at what's really going on. It's single men who have the worst of it. When men marry, their mental health massively increases."
The mental health data, chronicled in dozens of studies that have looked at marital differences in the last forty years, are consistent and overwhelming: The suicide rate of single men is twice as high as that of married men. Single men suffer from nearly twice as many severe neurotic symptoms and are far more susceptible to nervous breakdowns, depression, even nightmares. And despite the all-American image of the carefree single cowboy, in reality bachelors are far more likely to be morose, passive, and phobic than married men.
When contrasted with single women, unwed men fared no better in mental health studies. Single men suffer from twice as many mental health impairments as single women; they are more depressed, more passive, more likely to experience nervous breakdowns and all the designated symptoms of psychological distress—from fainting to insomnia. In one study, one third of the single men scored high for severe neurotic symptoms; only 4 percent of the single women did.
-Susan Faludi, Backlash: the Undeclared War Against American Women
430 notes
·
View notes
Text
christian universalism strikes again
(Reposted from Twitter)

So a rabbi I know came back from LA pretty jazzed about a Jewish addiction treatment facility there called Beit T'shuvah and so we talked about their approach and that got me curious about non-AA approaches to dealing with addiction which, my friends, was fascinating.
I’ll admit that almost everything I know about AA is more or less from The West Wing. I'm fortunate in that no one in my immediate family has dealt with substance abuse issues, and as far as I know, none of my close friends are alcoholics. My knowledge is pop culture knowledge.
But hearing about Beit T’shuvah was very interesting to me because:
I'd heard that a lot of people who aren't Christian have a hard time with AA because it's so Christian.
The difference in philosophy was subtle at first glance but actually paralleled a lot of the differences between Judaism and Christianity if you dug into it.
Anyway, I got curious about whether success rates were different for Christians vs. non-Christians and started googling. I didn't find much in the way of the data I was looking for, but I did find something a lot more disturbing, which is that the whole 12-step thing is not science-based. At all. For example:
The National Center on Addiction and Substance Abuse compared the current current state of addiction treatment to medicine in the early 1900s, when there weren't a lot of standards for who could practice medicine. In order to be a substance abuse counselor in many states, you don't need much more than a GED or high school diploma.
A 2006 survey found "no experimental studies unequivocally demonstrated the effectiveness of AA or TSF approaches for reducing alcohol dependence or problems."
And I want to make clear here that I'm not saying AA is bad--clearly it's helped people. The problem is that it's touted as a universal approach, which is a problem when it's not based on any sort of actual science.
AA claims that its success rates for people who "really try" are 75%. (And boy does that mirror gaslighting diet language.) But the most precise study out there that's NOT coming from AA (https://amazon.com/dp/B00FIMWI1O) put actual success rates at 5-8%. One of the major textbooks on treating addiction ranks it at 38th out of 48 on its list of effective treatments.
So just like most fad diets, it fails for almost everyone who tries it, and then blames the individual for its failure.
A glaring issue is that the 12 steps don't really acknowledge--or provide any guidance or structure for dealing with--other mental/emotional health issues. That’s a giant problem when people with substance abuse issues have higher than average rates of those issues. (Take a moment to consider how the victim-blaming approach of “if you didn’t succeed, it’s because you didn’t try hard enough” is going to intersect with someone’s major depression.)
Now, if 12-step programs were just one available treatment approach out of many, this wouldn’t be that big of an issue.
But 12% of AA members are there because of court orders. Our legal system is requiring people to undergo treatment that is:
Christian-based
Not scientifically supported
A failure for the vast majority of people
I mean, here's a pretty comprehensive breakdown that talks about the lack of scientific support for it, alternative treatments (like those in Finland, and naltrexone), and the fundamentalist origins of AA.
The founder was a member of the Oxford Group, an evangelical organization that taught that all human problems stemmed from fear and selfishness, and could be solved by turning your life over to divine providence, basically. Sound familiar? He based AA on those principles, and given that the only alternative was "drying out" in a sanatorium, and that AA members would show up at bedsides there and invite inpatients to meetings, it must have looked really enlightened to people. In 2022, it bears a queasy resemblance to evangelizing to people in prison, literally a captive audience.
To be fair--to their credit--they were some of the first people out there saying alcoholism was a disease, and not a moral failing. But they didn’t treat it like a disease when it came to testing treatment options:
Mann also collaborated with a physiologist named E. M. Jellinek. Mann was eager to bolster the scientific claims behind AA, and Jellinek wanted to make a name for himself in the growing field of alcohol research. In 1946, Jellinek published the results of a survey mailed to 1,600 AA members. Only 158 were returned. Jellinek and Mann jettisoned 45 that had been improperly completed and another 15 filled out by women, whose responses were so unlike the men’s that they risked complicating the results. From this small sample—98 men—Jellinek drew sweeping conclusions about the “phases of alcoholism,” which included an unavoidable succession of binges that led to blackouts, “indefinable fears,” and hitting bottom. Though the paper was filled with caveats about its lack of scientific rigor, it became AA gospel.
And then Senator Harold Hughes, who was an AA member, got Congress to establish the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, which promoted AA's beliefs, and sometimes suppressed research that conflicted with them:
In 1976, for instance, the Rand Corporation released a study of more than 2,000 men who had been patients at 44 different NIAAA-funded treatment centers. The report noted that 18 months after treatment, 22 percent of the men were drinking moderately. The authors concluded that it was possible for some alcohol-dependent men to return to controlled drinking. Researchers at the National Council on Alcoholism charged that the news would lead alcoholics to falsely believe they could drink safely. The NIAAA, which had funded the research, repudiated it. Rand repeated the study, this time looking over a four-year period. The results were similar.
The standard 28-day rehab stay, prescribed and insured:
Marvin D. Seppala, the chief medical officer at the Hazelden Betty Ford Foundation in Minnesota, one of the oldest inpatient rehab facilities in the country, described for me how 28 days became the norm: “In 1949, the founders found that it took about a week to get detoxed, another week to come around so [the patients] knew what they were up to, and after a couple of weeks they were doing well, and stable. That’s how it turned out to be 28 days. There’s no magic in it.”
The last sentence here (bolded for emphasis) is especially chilling.
That may be heartening, but it’s not science. As the rehab industry began expanding in the 1970s, its profit motives dovetailed nicely with AA’s view that counseling could be delivered by people who had themselves struggled with addiction, rather than by highly trained (and highly paid) doctors and mental-health professionals. No other area of medicine or counseling makes such allowances.
There is no mandatory national certification exam for addiction counselors. The 2012 Columbia University report on addiction medicine found that only six states required alcohol- and substance-abuse counselors to have at least a bachelor’s degree and that only one state, Vermont, required a master’s degree. Fourteen states had no license requirements whatsoever—not even a GED or an introductory training course was necessary—and yet counselors are often called on by the judicial system and medical boards to give expert opinions on their clients’ prospects for recovery.
And, again, the idea that this is the One True And Only Way to deal with alcohol abuse leads to medical professionals ignoring research and treatment options that could be helping people. They are, in essence, taking all this completely on faith.
There has been some progress: the Hazelden center began prescribing naltrexone and acamprosate to patients in 2003. But this makes Hazelden a pioneer among rehab centers. “Everyone has a bias,” Marvin Seppala, the chief medical officer, told me. “I honestly thought AA was the only way anyone could ever get sober, but I learned that I was wrong.”
Stephanie O’Malley, a clinical researcher in psychiatry at Yale who has studied the use of naltrexone and other drugs for alcohol-use disorder for more than two decades, says naltrexone’s limited use is “baffling.”
“There was never any campaign for this medication that said, ‘Ask your doctor,’ ” she says. “There was never any attempt to reach consumers.” Few doctors accepted that it was possible to treat alcohol-use disorder with a pill. And now that naltrexone is available in an inexpensive generic form, pharmaceutical companies have little incentive to promote it.
I'm not saying that AA is bad. I'm saying its hegemony is bad. It clearly is effective for some people--a minority of people. But it's not for the majority of people, and that's a problem when it's being prescribed by courts (and doctors) as if it's a one-size-fits-all approach.
It’s not an accident that a Christian approach to treating addiction presents itself as the One True Way For All Humankind, insists that courts and doctors privilege it, demands that people take its effectiveness on faith, and blames anyone for whom it doesn’t work for not believing/trying hard enough.
Hegemony is a problem.
(Photo credit: Pixabay)
#christian hegemony#addiction#christian supremacy#aa#maybe courts should be recommending treatment with a better than 8% success rate and actual science behind them just saying
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
I thought y'all should read this
I have a free trial to News+ so I copy-pasted it for you here. I don't think Jonathan Haidt would object to more people having this info.
Tumblr wouldn't let me post it until i removed all the links to Haidt's sources. You'll have to take my word that everything is sourced.
End the Phone-Based Childhood Now
The environment in which kids grow up today is hostile to human development.
By Jonathan Haidt
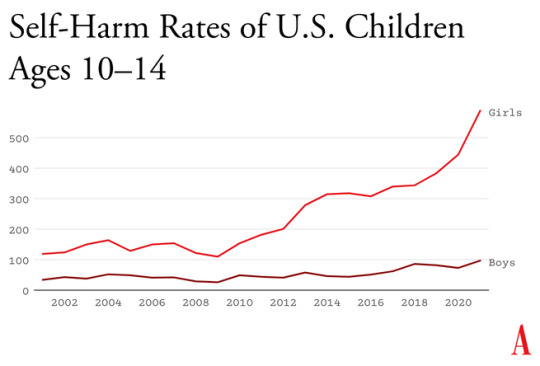
Something went suddenly and horribly wrong for adolescents in the early 2010s. By now you’ve likely seen the statistics: Rates of depression and anxiety in the United States—fairly stable in the 2000s—rose by more than 50 percent in many studies from 2010 to 2019. The suicide rate rose 48 percent for adolescents ages 10 to 19. For girls ages 10 to 14, it rose 131 percent.
The problem was not limited to the U.S.: Similar patterns emerged around the same time in Canada, the U.K., Australia, New Zealand, the Nordic countries, and beyond. By a variety of measures and in a variety of countries, the members of Generation Z (born in and after 1996) are suffering from anxiety, depression, self-harm, and related disorders at levels higher than any other generation for which we have data.
The decline in mental health is just one of many signs that something went awry. Loneliness and friendlessness among American teens began to surge around 2012. Academic achievement went down, too. According to “The Nation’s Report Card,” scores in reading and math began to decline for U.S. students after 2012, reversing decades of slow but generally steady increase. PISA, the major international measure of educational trends, shows that declines in math, reading, and science happened globally, also beginning in the early 2010s.
As the oldest members of Gen Z reach their late 20s, their troubles are carrying over into adulthood. Young adults are dating less, having less sex, and showing less interest in ever having children than prior generations. They are more likelyto live with their parents. They were less likely to get jobs as teens, and managers say they are harder to work with. Many of these trends began with earlier generations, but most of them accelerated with Gen Z.
Surveys show that members of Gen Z are shyer and more risk averse than previous generations, too, and risk aversion may make them less ambitious. In an interview last May, OpenAI co-founder Sam Altman and Stripe co-founder Patrick Collison noted that, for the first time since the 1970s, none of Silicon Valley’s preeminent entrepreneurs are under 30. “Something has really gone wrong,” Altman said. In a famously young industry, he was baffled by the sudden absence of great founders in their 20s.
Generations are not monolithic, of course. Many young people are flourishing. Taken as a whole, however, Gen Z is in poor mental health and is lagging behind previous generations on many important metrics. And if a generation is doing poorly––if it is more anxious and depressed and is starting families, careers, and important companies at a substantially lower rate than previous generations––then the sociological and economic consequences will be profound for the entire society.
What happened in the early 2010s that altered adolescent development and worsened mental health? Theories abound, but the fact that similar trends are found in many countries worldwide means that events and trends that are specific to the United States cannot be the main story.
I think the answer can be stated simply, although the underlying psychology is complex: Those were the years when adolescents in rich countries traded in their flip phones for smartphones and moved much more of their social lives online—particularly onto social-media platforms designed for virality and addiction. Once young people began carrying the entire internet in their pockets, available to them day and night, it altered their daily experiences and developmental pathways across the board. Friendship, dating, sexuality, exercise, sleep, academics, politics, family dynamics, identity—all were affected. Life changed rapidly for younger children, too, as they began to get access to their parents’ smartphones and, later, got their own iPads, laptops, and even smartphones during elementary school.
As a social psychologist who has long studied social and moral development, I have been involved in debates about the effects of digital technology for years. Typically, the scientific questions have been framed somewhat narrowly, to make them easier to address with data. For example, do adolescents who consume more social media have higher levels of depression? Does using a smartphone just before bedtime interfere with sleep? The answer to these questions is usually found to be yes, although the size of the relationship is often statistically small, which has led some researchers to conclude that these new technologies are not responsible for the gigantic increases in mental illness that began in the early 2010s.
But before we can evaluate the evidence on any one potential avenue of harm, we need to step back and ask a broader question: What is childhood––including adolescence––and how did it change when smartphones moved to the center of it? If we take a more holistic view of what childhood is and what young children, tweens, and teens need to do to mature into competent adults, the picture becomes much clearer. Smartphone-based life, it turns out, alters or interferes with a great number of developmental processes.
The intrusion of smartphones and social media are not the only changes that have deformed childhood. There’s an important backstory, beginning as long ago as the 1980s, when we started systematically depriving children and adolescents of freedom, unsupervised play, responsibility, and opportunities for risk taking, all of which promote competence, maturity, and mental health. But the change in childhood accelerated in the early 2010s, when an already independence-deprived generation was lured into a new virtual universe that seemed safe to parents but in fact is more dangerous, in many respects, than the physical world.
My claim is that the new phone-based childhood that took shape roughly 12 years ago is making young people sick and blocking their progress to flourishing in adulthood. We need a dramatic cultural correction, and we need it now.
1. The Decline of Play and Independence
Human brains are extraordinarily large compared with those of other primates, and human childhoods are extraordinarily long, too, to give those large brains time to wire up within a particular culture. A child’s brain is already 90 percent of its adult size by about age 6. The next 10 or 15 years are about learning norms and mastering skills—physical, analytical, creative, and social. As children and adolescents seek out experiences and practice a wide variety of behaviors, the synapses and neurons that are used frequently are retained while those that are used less often disappear. Neurons that fire together wire together, as brain researchers say.
Brain development is sometimes said to be “experience-expectant,” because specific parts of the brain show increased plasticity during periods of life when an animal’s brain can “expect” to have certain kinds of experiences. You can see this with baby geese, who will imprint on whatever mother-sized object moves in their vicinity just after they hatch. You can see it with human children, who are able to learn languages quickly and take on the local accent, but only through early puberty; after that, it’s hard to learn a language and sound like a native speaker. There is also some evidence of a sensitive period for cultural learning more generally. Japanese children who spent a few years in California in the 1970s came to feel “American” in their identity and ways of interacting only if they attended American schools for a few years between ages 9 and 15. If they left before age 9, there was no lasting impact. If they didn’t arrive until they were 15, it was too late; they didn’t come to feel American.
Human childhood is an extended cultural apprenticeship with different tasks at different ages all the way through puberty. Once we see it this way, we can identify factors that promote or impede the right kinds of learning at each age. For children of all ages, one of the most powerful drivers of learning is the strong motivation to play. Play is the work of childhood, and all young mammals have the same job: to wire up their brains by playing vigorously and often, practicing the moves and skills they’ll need as adults. Kittens will play-pounce on anything that looks like a mouse tail. Human children will play games such as tag and sharks and minnows, which let them practice both their predator skills and their escaping-from-predator skills. Adolescents will play sports with greater intensity, and will incorporate playfulness into their social interactions—flirting, teasing, and developing inside jokes that bond friends together. Hundreds of studies on young rats, monkeys, and humans show that young mammals want to play, need to play, and end up socially, cognitively, and emotionally impaired when they are deprived of play.
One crucial aspect of play is physical risk taking. Children and adolescents must take risks and fail—often—in environments in which failure is not very costly. This is how they extend their abilities, overcome their fears, learn to estimate risk, and learn to cooperate in order to take on larger challenges later. The ever-present possibility of getting hurt while running around, exploring, play-fighting, or getting into a real conflict with another group adds an element of thrill, and thrilling play appears to be the most effective kind for overcoming childhood anxieties and building social, emotional, and physical competence. The desire for risk and thrill increases in the teen years, when failure might carry more serious consequences. Children of all ages need to choose the risk they are ready for at a given moment. Young people who are deprived of opportunities for risk taking and independent exploration will, on average, develop into more anxious and risk-averse adults.
Human childhood and adolescence evolved outdoors, in a physical world full of dangers and opportunities. Its central activities––play, exploration, and intense socializing––were largely unsupervised by adults, allowing children to make their own choices, resolve their own conflicts, and take care of one another. Shared adventures and shared adversity bound young people together into strong friendship clusters within which they mastered the social dynamics of small groups, which prepared them to master bigger challenges and larger groups later on.
And then we changed childhood.
The changes started slowly in the late 1970s and ’80s, before the arrival of the internet, as many parents in the U.S. grew fearful that their children would be harmed or abducted if left unsupervised. Such crimes have always been extremely rare, but they loomed larger in parents’ minds thanks in part to rising levels of street crime combined with the arrival of cable TV, which enabled round-the-clock coverage of missing-children cases. A general decline in social capital––the degree to which people knew and trusted their neighbors and institutions––exacerbated parental fears. Meanwhile, rising competition for college admissions encouraged more intensive forms of parenting. In the 1990s, American parents began pulling their children indoors or insisting that afternoons be spent in adult-run enrichment activities. Free play, independent exploration, and teen-hangout time declined.
In recent decades, seeing unchaperoned children outdoors has become so novel that when one is spotted in the wild, some adults feel it is their duty to call the police. In 2015, the Pew Research Center found that parents, on average, believed that children should be at least 10 years old to play unsupervised in front of their house, and that kids should be 14 before being allowed to go unsupervised to a public park. Most of these same parents had enjoyed joyous and unsupervised outdoor play by the age of 7 or 8.
2. The Virtual World Arrives in Two Waves
The internet, which now dominates the lives of young people, arrived in two waves of linked technologies. The first one did little harm to Millennials. The second one swallowed Gen Z whole.
The first wave came ashore in the 1990s with the arrival of dial-up internet access, which made personal computers good for something beyond word processing and basic games. By 2003, 55 percent of American households had a computer with (slow) internet access. Rates of adolescent depression, loneliness, and other measures of poor mental health did not rise in this first wave. If anything, they went down a bit. Millennial teens (born 1981 through 1995), who were the first to go through puberty with access to the internet, were psychologically healthier and happier, on average, than their older siblings or parents in Generation X (born 1965 through 1980).
The second wave began to rise in the 2000s, though its full force didn’t hit until the early 2010s. It began rather innocently with the introduction of social-media platforms that helped people connect with their friends. Posting and sharing content became much easier with sites such as Friendster (launched in 2003), Myspace (2003), and Facebook (2004).
Teens embraced social media soon after it came out, but the time they could spend on these sites was limited in those early years because the sites could only be accessed from a computer, often the family computer in the living room. Young people couldn’t access social media (and the rest of the internet) from the school bus, during class time, or while hanging out with friends outdoors. Many teens in the early-to-mid-2000s had cellphones, but these were basic phones (many of them flip phones) that had no internet access. Typing on them was difficult––they had only number keys. Basic phones were tools that helped Millennials meet up with one another in person or talk with each other one-on-one. I have seen no evidence to suggest that basic cellphones harmed the mental health of Millennials.
It was not until the introduction of the iPhone (2007), the App Store (2008), and high-speed internet (which reached 50 percent of American homes in 2007)—and the corresponding pivot to mobile made by many providers of social media, video games, and porn—that it became possible for adolescents to spend nearly every waking moment online. The extraordinary synergy among these innovations was what powered the second technological wave. In 2011, only 23 percent of teens had a smartphone. By 2015, that number had risen to 73 percent, and a quarter of teens said they were online “almost constantly.” Their younger siblings in elementary school didn’t usually have their own smartphones, but after its release in 2010, the iPad quickly became a staple of young children’s daily lives. It was in this brief period, from 2010 to 2015, that childhood in America (and many other countries) was rewired into a form that was more sedentary, solitary, virtual, and incompatible with healthy human development.
3. Techno-optimism and the Birth of the Phone-Based Childhood
The phone-based childhood created by that second wave—including not just smartphones themselves, but all manner of internet-connected devices, such as tablets, laptops, video-game consoles, and smartwatches—arrived near the end of a period of enormous optimism about digital technology. The internet came into our lives in the mid-1990s, soon after the fall of the Soviet Union. By the end of that decade, it was widely thought that the web would be an ally of democracy and a slayer of tyrants. When people are connected to each other, and to all the information in the world, how could any dictator keep them down?
In the 2000s, Silicon Valley and its world-changing inventions were a source of pride and excitement in America. Smart and ambitious young people around the world wanted to move to the West Coast to be part of the digital revolution. Tech-company founders such as Steve Jobs and Sergey Brin were lauded as gods, or at least as modern Prometheans, bringing humans godlike powers. The Arab Spring bloomed in 2011 with the help of decentralized social platforms, including Twitter and Facebook. When pundits and entrepreneurs talked about the power of social media to transform society, it didn’t sound like a dark prophecy.
You have to put yourself back in this heady time to understand why adults acquiesced so readily to the rapid transformation of childhood. Many parents had concerns, even then, about what their children were doing online, especially because of the internet’s ability to put children in contact with strangers. But there was also a lot of excitement about the upsides of this new digital world. If computers and the internet were the vanguards of progress, and if young people––widely referred to as “digital natives”––were going to live their lives entwined with these technologies, then why not give them a head start? I remember how exciting it was to see my 2-year-old son master the touch-and-swipe interface of my first iPhone in 2008. I thought I could see his neurons being woven together faster as a result of the stimulation it brought to his brain, compared to the passivity of watching television or the slowness of building a block tower. I thought I could see his future job prospects improving.
Touchscreen devices were also a godsend for harried parents. Many of us discovered that we could have peace at a restaurant, on a long car trip, or at home while making dinner or replying to emails if we just gave our children what they most wanted: our smartphones and tablets. We saw that everyone else was doing it and figured it must be okay.
It was the same for older children, desperate to join their friends on social-media platforms, where the minimum age to open an account was set by law to 13, even though no research had been done to establish the safety of these products for minors. Because the platforms did nothing (and still do nothing) to verify the stated age of new-account applicants, any 10-year-old could open multiple accounts without parental permission or knowledge, and many did. Facebook and later Instagram became places where many sixth and seventh graders were hanging out and socializing. If parents did find out about these accounts, it was too late. Nobody wanted their child to be isolated and alone, so parents rarely forced their children to shut down their accounts.
We had no idea what we were doing.
4. The High Cost of a Phone-Based Childhood
In Walden, his 1854 reflection on simple living, Henry David Thoreau wrote, “The cost of a thing is the amount of … life which is required to be exchanged for it, immediately or in the long run.” It’s an elegant formulation of what economists would later call the opportunity cost of any choice—all of the things you can no longer do with your money and time once you’ve committed them to something else. So it’s important that we grasp just how much of a young person’s day is now taken up by their devices.
The numbers are hard to believe. The most recent Gallup data show that American teens spend about five hours a day just on social-media platforms (including watching videos on TikTok and YouTube). Add in all the other phone- and screen-based activities, and the number rises to somewhere between seven and nine hours a day, on average. The numbers are even higher in single-parent and low-income families, and among Black, Hispanic, and Native American families.
In Thoreau’s terms, how much of life is exchanged for all this screen time? Arguably, most of it. Everything else in an adolescent’s day must get squeezed down or eliminated entirely to make room for the vast amount of content that is consumed, and for the hundreds of “friends,” “followers,” and other network connections that must be serviced with texts, posts, comments, likes, snaps, and direct messages. I recently surveyed my students at NYU, and most of them reported that the very first thing they do when they open their eyes in the morning is check their texts, direct messages, and social-media feeds. It’s also the last thing they do before they close their eyes at night. And it’s a lot of what they do in between.
The amount of time that adolescents spend sleeping declined in the early 2010s, and many studies tie sleep loss directly to the use of devices around bedtime, particularly when they’re used to scroll through social media. Exercise declined, too, which is unfortunate because exercise, like sleep, improves both mental and physical health. Book reading has been declining for decades, pushed aside by digital alternatives, but the decline, like so much else, sped up in the early 2010s. With passive entertainment always available, adolescent minds likely wander less than they used to; contemplation and imagination might be placed on the list of things winnowed down or crowded out.
But perhaps the most devastating cost of the new phone-based childhood was the collapse of time spent interacting with other people face-to-face. A study of how Americans spend their time found that, before 2010, young people (ages 15 to 24) reported spending far more time with their friends (about two hours a day, on average, not counting time together at school) than did older people (who spent just 30 to 60 minutes with friends). Time with friends began decreasing for young people in the 2000s, but the drop accelerated in the 2010s, while it barely changed for older people. By 2019, young people’s time with friends had dropped to just 67 minutes a day. It turns out that Gen Z had been socially distancing for many years and had mostly completed the project by the time COVID-19 struck.
You might question the importance of this decline. After all, isn’t much of this online time spent interacting with friends through texting, social media, and multiplayer video games? Isn’t that just as good?
Some of it surely is, and virtual interactions offer unique benefits too, especially for young people who are geographically or socially isolated. But in general, the virtual world lacks many of the features that make human interactions in the real world nutritious, as we might say, for physical, social, and emotional development. In particular, real-world relationships and social interactions are characterized by four features—typical for hundreds of thousands of years—that online interactions either distort or erase.
First, real-world interactions are embodied, meaning that we use our hands and facial expressions to communicate, and we learn to respond to the body language of others. Virtual interactions, in contrast, mostly rely on language alone. No matter how many emojis are offered as compensation, the elimination of communication channels for which we have eons of evolutionary programming is likely to produce adults who are less comfortable and less skilled at interacting in person.
Second, real-world interactions are synchronous; they happen at the same time. As a result, we learn subtle cues about timing and conversational turn taking. Synchronous interactions make us feel closer to the other person because that’s what getting “in sync” does. Texts, posts, and many other virtual interactions lack synchrony. There is less real laughter, more room for misinterpretation, and more stress after a comment that gets no immediate response.
Third, real-world interactions primarily involve one‐to‐one communication, or sometimes one-to-several. But many virtual communications are broadcast to a potentially huge audience. Online, each person can engage in dozens of asynchronous interactions in parallel, which interferes with the depth achieved in all of them. The sender’s motivations are different, too: With a large audience, one’s reputation is always on the line; an error or poor performance can damage social standing with large numbers of peers. These communications thus tend to be more performative and anxiety-inducing than one-to-one conversations.
Finally, real-world interactions usually take place within communities that have a high bar for entry and exit, so people are strongly motivated to invest in relationships and repair rifts when they happen. But in many virtual networks, people can easily block others or quit when they are displeased. Relationships within such networks are usually more disposable.
These unsatisfying and anxiety-producing features of life online should be recognizable to most adults. Online interactions can bring out antisocial behavior that people would never display in their offline communities. But if life online takes a toll on adults, just imagine what it does to adolescents in the early years of puberty, when their “experience expectant” brains are rewiring based on feedback from their social interactions.
Kids going through puberty online are likely to experience far more social comparison, self-consciousness, public shaming, and chronic anxiety than adolescents in previous generations, which could potentially set developing brains into a habitual state of defensiveness. The brain contains systems that are specialized for approach (when opportunities beckon) and withdrawal (when threats appear or seem likely). People can be in what we might call “discover mode” or “defend mode” at any moment, but generally not both. The two systems together form a mechanism for quickly adapting to changing conditions, like a thermostat that can activate either a heating system or a cooling system as the temperature fluctuates. Some people’s internal thermostats are generally set to discover mode, and they flip into defend mode only when clear threats arise. These people tend to see the world as full of opportunities. They are happier and less anxious. Other people’s internal thermostats are generally set to defend mode, and they flip into discover mode only when they feel unusually safe. They tend to see the world as full of threats and are more prone to anxiety and depressive disorders.
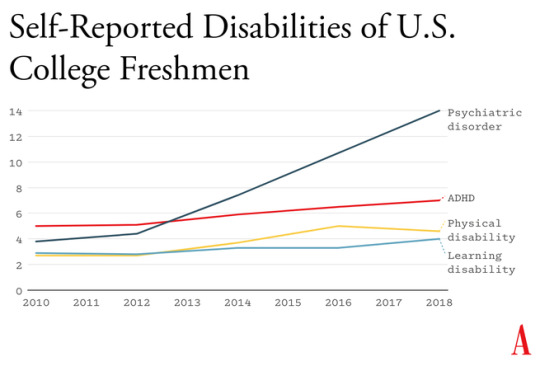
A simple way to understand the differences between Gen Z and previous generations is that people born in and after 1996 have internal thermostats that were shifted toward defend mode. This is why life on college campuses changed so suddenly when Gen Z arrived, beginning around 2014. Students began requesting “safe spaces” and trigger warnings. They were highly sensitive to “microaggressions” and sometimes claimed that words were “violence.” These trends mystified those of us in older generations at the time, but in hindsight, it all makes sense. Gen Z students found words, ideas, and ambiguous social encounters more threatening than had previous generations of students because we had fundamentally altered their psychological development.
5. So Many Harms
The debate around adolescents’ use of smartphones and social media typically revolves around mental health, and understandably so. But the harms that have resulted from transforming childhood so suddenly and heedlessly go far beyondmental health. I’ve touched on some of them—social awkwardness, reduced self-confidence, and a more sedentary childhood. Here are three additional harms.
Fragmented Attention, Disrupted Learning
Staying on task while sitting at a computer is hard enough for an adult with a fully developed prefrontal cortex. It is far more difficult for adolescents in front of their laptop trying to do homework. They are probably less intrinsically motivated to stay on task. They’re certainly less able, given their undeveloped prefrontal cortex, and hence it’s easy for any company with an app to lure them away with an offer of social validation or entertainment. Their phones are pinging constantly—one study found that the typical adolescent now gets 237 notifications a day, roughly 15 every waking hour. Sustained attention is essential for doing almost anything big, creative, or valuable, yet young people find their attention chopped up into little bits by notifications offering the possibility of high-pleasure, low-effort digital experiences.
It even happens in the classroom. Studies confirm that when students have access to their phones during class time, they use them, especially for texting and checking social media, and their grades and learning suffer. This might explain why benchmark test scores began to decline in the U.S. and around the world in the early 2010s—well before the pandemic hit.
Addiction and Social Withdrawal
The neural basis of behavioral addiction to social media or video games is not exactly the same as chemical addiction to cocaine or opioids. Nonetheless, they all involve abnormally heavy and sustained activation of dopamine neurons and reward pathways. Over time, the brain adapts to these high levels of dopamine; when the child is not engaged in digital activity, their brain doesn’t have enough dopamine, and the child experiences withdrawal symptoms. These generally include anxiety, insomnia, and intense irritability. Kids with these kinds of behavioral addictions often become surly and aggressive, and withdraw from their families into their bedrooms and devices.
Social-media and gaming platforms were designed to hook users. How successful are they? How many kids suffer from digital addictions?
The main addiction risks for boys seem to be video games and porn. “Internet gaming disorder,” which was added to the main diagnosis manual of psychiatry in 2013 as a condition for further study, describes “significant impairment or distress” in several aspects of life, along with many hallmarks of addiction, including an inability to reduce usage despite attempts to do so. Estimates for the prevalence of IGD range from 7 to 15 percent among adolescent boys and young men. As for porn, a nationally representative survey of American adults published in 2019 found that 7 percent of American men agreed or strongly agreed with the statement “I am addicted to pornography”—and the rates were higher for the youngest men.
Girls have much lower rates of addiction to video games and porn, but they use social media more intensely than boys do. A study of teens in 29 nations found that between 5 and 15 percent of adolescents engage in what is called “problematic social media use,” which includes symptoms such as preoccupation, withdrawal symptoms, neglect of other areas of life, and lying to parents and friends about time spent on social media. That study did not break down results by gender, but many others have found that rates of “problematic use” are higher for girls.
I don’t want to overstate the risks: Most teens do not become addicted to their phones and video games. But across multiple studies and across genders, rates of problematic use come out in the ballpark of 5 to 15 percent. Is there any other consumer product that parents would let their children use relatively freely if they knew that something like one in 10 kids would end up with a pattern of habitual and compulsive use that disrupted various domains of life and looked a lot like an addiction?
The Decay of Wisdom and the Loss of Meaning
During that crucial sensitive period for cultural learning, from roughly ages 9 through 15, we should be especially thoughtful about who is socializing our children for adulthood. Instead, that’s when most kids get their first smartphone and sign themselves up (with or without parental permission) to consume rivers of content from random strangers. Much of that content is produced by other adolescents, in blocks of a few minutes or a few seconds.
This rerouting of enculturating content has created a generation that is largely cut off from older generations and, to some extent, from the accumulated wisdom of humankind, including knowledge about how to live a flourishing life. Adolescents spend less time steeped in their local or national culture. They are coming of age in a confusing, placeless, ahistorical maelstrom of 30-second stories curated by algorithms designed to mesmerize them. Without solid knowledge of the past and the filtering of good ideas from bad––a process that plays out over many generations––young people will be more prone to believe whatever terrible ideas become popular around them, which might explain why videos showing young people reacting positively to Osama bin Laden’s thoughts about America were trending on TikTok last fall.
All this is made worse by the fact that so much of digital public life is an unending supply of micro dramas about somebody somewhere in our country of 340 million people who did something that can fuel an outrage cycle, only to be pushed aside by the next. It doesn’t add up to anything and leaves behind only a distorted sense of human nature and affairs.
When our public life becomes fragmented, ephemeral, and incomprehensible, it is a recipe for anomie, or normlessness. The great French sociologist Émile Durkheim showed long ago that a society that fails to bind its people together with some shared sense of sacredness and common respect for rules and norms is not a society of great individual freedom; it is, rather, a place where disoriented individuals have difficulty setting goals and exerting themselves to achieve them. Durkheim argued that anomie was a major driver of suicide rates in European countries. Modern scholars continue to draw on his work to understand suicide rates today.
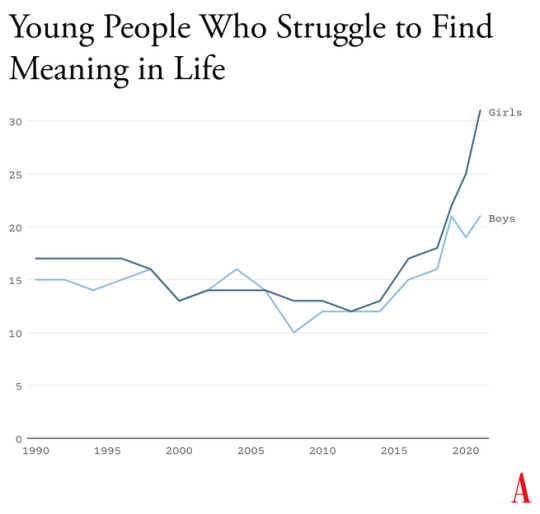
Durkheim’s observations are crucial for understanding what happened in the early 2010s. A long-running survey of American teens found that, from 1990 to 2010, high-school seniors became slightly less likely to agree with statements such as “Life often feels meaningless.” But as soon as they adopted a phone-based life and many began to live in the whirlpool of social media, where no stability can be found, every measure of despair increased. From 2010 to 2019, the number who agreed that their lives felt “meaningless” increased by about 70 percent, to more than one in five.
6. Young People Don’t Like Their Phone-Based Lives
How can I be confident that the epidemic of adolescent mental illness was kicked off by the arrival of the phone-based childhood? Skeptics point to other events as possible culprits, including the 2008 global financial crisis, global warming, the 2012 Sandy Hook school shooting and the subsequent active-shooter drills, rising academic pressures, and the opioid epidemic. But while these events might have been contributing factors in some countries, none can explain both the timing and international scope of the disaster.
An additional source of evidence comes from Gen Z itself. With all the talk of regulating social media, raising age limits, and getting phones out of schools, you might expect to find many members of Gen Z writing and speaking out in opposition. I’ve looked for such arguments and found hardly any. In contrast, many young adults tell stories of devastation.
Freya India, a 24-year-old British essayist who writes about girls, explains how social-media sites carry girls off to unhealthy places: “It seems like your child is simply watching some makeup tutorials, following some mental health influencers, or experimenting with their identity. But let me tell you: they are on a conveyor belt to someplace bad. Whatever insecurity or vulnerability they are struggling with, they will be pushed further and further into it.” She continues:
Gen Z were the guinea pigs in this uncontrolled global social experiment. We were the first to have our vulnerabilities and insecurities fed into a machine that magnified and refracted them back at us, all the time, before we had any sense of who we were. We didn’t just grow up with algorithms. They raised us. They rearranged our faces. Shaped our identities. Convinced us we were sick.
Rikki Schlott, a 23-year-old American journalist and co-author of The Canceling of the American Mind, writes,
"The day-to-day life of a typical teen or tween today would be unrecognizable to someone who came of age before the smartphone arrived. Zoomers are spending an average of 9 hours daily in this screen-time doom loop—desperate to forget the gaping holes they’re bleeding out of, even if just for … 9 hours a day. Uncomfortable silence could be time to ponder why they’re so miserable in the first place. Drowning it out with algorithmic white noise is far easier."
A 27-year-old man who spent his adolescent years addicted (his word) to video games and pornography sent me this reflection on what that did to him:
I missed out on a lot of stuff in life—a lot of socialization. I feel the effects now: meeting new people, talking to people. I feel that my interactions are not as smooth and fluid as I want. My knowledge of the world (geography, politics, etc.) is lacking. I didn’t spend time having conversations or learning about sports. I often feel like a hollow operating system.
Or consider what Facebook found in a research project involving focus groups of young people, revealed in 2021 by the whistleblower Frances Haugen: “Teens blame Instagram for increases in the rates of anxiety and depression among teens,” an internal document said. “This reaction was unprompted and consistent across all groups.”
7. Collective-Action Problems
Social-media companies such as Meta, TikTok, and Snap are often compared to tobacco companies, but that’s not really fair to the tobacco industry. It’s true that companies in both industries marketed harmful products to children and tweaked their products for maximum customer retention (that is, addiction), but there’s a big difference: Teens could and did choose, in large numbers, not to smoke. Even at the peak of teen cigarette use, in 1997, nearly two-thirds of high-school students did not smoke.
Social media, in contrast, applies a lot more pressure on nonusers, at a much younger age and in a more insidious way. Once a few students in any middle school lie about their age and open accounts at age 11 or 12, they start posting photos and comments about themselves and other students. Drama ensues. The pressure on everyone else to join becomes intense. Even a girl who knows, consciously, that Instagram can foster beauty obsession, anxiety, and eating disorders might sooner take those risks than accept the seeming certainty of being out of the loop, clueless, and excluded. And indeed, if she resists while most of her classmates do not, she might, in fact, be marginalized, which puts her at risk for anxiety and depression, though via a different pathway than the one taken by those who use social media heavily. In this way, social media accomplishes a remarkable feat: It even harms adolescents who do not use it.
A recent study led by the University of Chicago economist Leonardo Bursztyn captured the dynamics of the social-media trap precisely. The researchers recruited more than 1,000 college students and asked them how much they’d need to be paid to deactivate their accounts on either Instagram or TikTok for four weeks. That’s a standard economist’s question to try to compute the net value of a product to society. On average, students said they’d need to be paid roughly $50 ($59 for TikTok, $47 for Instagram) to deactivate whichever platform they were asked about. Then the experimenters told the students that they were going to try to get most of the others in their school to deactivate that same platform, offering to pay them to do so as well, and asked, Now how much would you have to be paid to deactivate, if most others did so? The answer, on average, was less than zero. In each case, most students were willing to pay to have that happen.
Social media is all about network effects. Most students are only on it because everyone else is too. Most of them would prefer that nobody be on these platforms. Later in the study, students were asked directly, “Would you prefer to live in a world without Instagram [or TikTok]?” A majority of students said yes––58 percent for each app.
This is the textbook definition of what social scientists call a collective-action problem. It’s what happens when a group would be better off if everyone in the group took a particular action, but each actor is deterred from acting, because unless the others do the same, the personal cost outweighs the benefit. Fishermen considering limiting their catch to avoid wiping out the local fish population are caught in this same kind of trap. If no one else does it too, they just lose profit.
Cigarettes trapped individual smokers with a biological addiction. Social media has trapped an entire generation in a collective-action problem. Early app developers deliberately and knowingly exploited the psychological weaknesses and insecurities of young people to pressure them to consume a product that, upon reflection, many wish they could use less, or not at all.
8. Four Norms to Break Four Traps
Young people and their parents are stuck in at least four collective-action traps. Each is hard to escape for an individual family, but escape becomes much easier if families, schools, and communities coordinate and act together. Here are four norms that would roll back the phone-based childhood. I believe that any community that adopts all four will see substantial improvements in youth mental health within two years.
No smartphones before high school
The trap here is that each child thinks they need a smartphone because “everyone else” has one, and many parents give in because they don’t want their child to feel excluded. But if no one else had a smartphone—or even if, say, only half of the child’s sixth-grade class had one—parents would feel more comfortable providing a basic flip phone (or no phone at all). Delaying round-the-clock internet access until ninth grade (around age 14) as a national or community norm would help to protect adolescents during the very vulnerable first few years of puberty. According to a 2022 British study, these are the years when social-media use is most correlated with poor mental health. Family policies about tablets, laptops, and video-game consoles should be aligned with smartphone restrictions to prevent overuse of other screen activities.
No social media before 16
The trap here, as with smartphones, is that each adolescent feels a strong need to open accounts on TikTok, Instagram, Snapchat, and other platforms primarily because that’s where most of their peers are posting and gossiping. But if the majority of adolescents were not on these accounts until they were 16, families and adolescents could more easily resist the pressure to sign up. The delay would not mean that kids younger than 16 could never watch videos on TikTok or YouTube—only that they could not open accounts, give away their data, post their own content, and let algorithms get to know them and their preferences.
Phone‐free schools
Most schools claim that they ban phones, but this usually just means that students aren’t supposed to take their phone out of their pocket during class. Research shows that most students do use their phones during class time. They also use them during lunchtime, free periods, and breaks between classes––times when students could and should be interacting with their classmates face-to-face. The only way to get students’ minds off their phones during the school day is to require all students to put their phones (and other devices that can send or receive texts) into a phone locker or locked pouch at the start of the day. Schools that have gone phone-free always seem to report that it has improved the culture, making students more attentive in class and more interactive with one another. Published studies back them up.
More independence, free play, and responsibility in the real world
Many parents are afraid to give their children the level of independence and responsibility they themselves enjoyed when they were young, even though rates of homicide, drunk driving, and other physical threats to children are way down in recent decades. Part of the fear comes from the fact that parents look at each other to determine what is normal and therefore safe, and they see few examples of families acting as if a 9-year-old can be trusted to walk to a store without a chaperone. But if many parents started sending their children out to play or run errands, then the norms of what is safe and accepted would change quickly. So would ideas about what constitutes “good parenting.” And if more parents trusted their children with more responsibility––for example, by asking their kids to do more to help out, or to care for others––then the pervasive sense of uselessness now found in surveys of high-school students might begin to dissipate.
It would be a mistake to overlook this fourth norm. If parents don’t replace screen time with real-world experiences involving friends and independent activity, then banning devices will feel like deprivation, not the opening up of a world of opportunities.
The main reason why the phone-based childhood is so harmful is because it pushes aside everything else. Smartphones are experience blockers. Our ultimate goal should not be to remove screens entirely, nor should it be to return childhood to exactly the way it was in 1960. Rather, it should be to create a version of childhood and adolescence that keeps young people anchored in the real world while flourishing in the digital age.
9. What Are We Waiting For?
An essential function of government is to solve collective-action problems. Congress could solve or help solve the ones I’ve highlighted—for instance, by raising the age of “internet adulthood” to 16 and requiring tech companies to keep underage children off their sites.
In recent decades, however, Congress has not been good at addressing public concerns when the solutions would displease a powerful and deep-pocketed industry. Governors and state legislators have been much more effective, and their successes might let us evaluate how well various reforms work. But the bottom line is that to change norms, we’re going to need to do most of the work ourselves, in neighborhood groups, schools, and other communities.
There are now hundreds of organizations––most of them started by mothers who saw what smartphones had done to their children––that are working to roll back the phone-based childhood or promote a more independent, real-world childhood. (I have assembled a list of many of them.) One that I co-founded, at LetGrow.org, suggests a variety of simple programs for parents or schools, such as play club (schools keep the playground open at least one day a week before or after school, and kids sign up for phone-free, mixed-age, unstructured play as a regular weekly activity) and the Let Grow Experience (a series of homework assignments in which students––with their parents’ consent––choose something to do on their own that they’ve never done before, such as walk the dog, climb a tree, walk to a store, or cook dinner).
Parents are fed up with what childhood has become. Many are tired of having daily arguments about technologies that were designed to grab hold of their children’s attention and not let go. But the phone-based childhood is not inevitable.
The four norms I have proposed cost almost nothing to implement, they cause no clear harm to anyone, and while they could be supported by new legislation, they can be instilled even without it. We can begin implementing all of them right away, this year, especially in communities with good cooperation between schools and parents. A single memo from a principal asking parents to delay smartphones and social media, in support of the school’s effort to improve mental health by going phone free, would catalyze collective action and reset the community’s norms.
We didn’t know what we were doing in the early 2010s. Now we do. It’s time to end the phone-based childhood.
This article is adapted from Jonathan Haidt’s forthcoming book, The Anxious Generation: How the Great Rewiring of Childhood Is Causing an Epidemic of Mental Illness.
178 notes
·
View notes
Text
Greedflation, but for prisoners

I'm touring my new, nationally bestselling novel The Bezzle! Catch me TOMORROW (Apr 21) in TORINO, then Marin County (Apr 27), Winnipeg (May 2), Calgary (May 3), Vancouver (May 4), and beyond!

Today in "Capitalists Hate Capitalism" news: The Appeal has published the first-ever survey of national prison commissary prices, revealing just how badly the prison profiteer system gouges American's all-time, world-record-beating prison population:
https://theappeal.org/locked-in-priced-out-how-much-prison-commissary-prices/
Like every aspect of the prison contracting system, prison commissaries – the stores where prisoners are able to buy food, sundries, toiletries and other items – are dominated by private equity funds that have bought out all the smaller players. Private equity deals always involve gigantic amounts of debt (typically, the first thing PE companies do after acquiring a company is to borrow heavily against it and then pay themselves a hefty dividend).
The need to service this debt drives PE companies to cut quality, squeeze suppliers, and raise prices. That's why PE loves to buy up the kinds of businesses you must spend your money at: dialysis clinics, long-term care facilities, funeral homes, and prison services.
Prisoners, after all, are a literal captive market. Unlike capitalist ventures, which involve the risk that a customer will take their business elsewhere, prison commissary providers have the most airtight of monopolies over prisoners' shopping.
Not that prisoners have a lot of money to spend. The 13th Amendment specifically allows for the enslavement of convicted criminals, and so even though many prisoners are subject to forced labor, they aren't necessarily paid for it:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/02/captive-customers/#guillotine-watch
Six states ban paying prisoners anything. North Carolina caps prisoners' pay at one dollar per day. Nationally, prisoners earn $0.52/hour, while producing $11b/year in goods and services:
https://www.dollarsandsense.org/archives/2024/0324bowman.html
So there's a double cruelty to prison commissary price-gouging. Prisoners earn far less than any other kind of worker, and they pay vastly inflated prices for the necessities of life. There's also a triple cruelty: prisoners' families – deprived of an incarcerated breadwinner's earnings – are called upon to make up the difference for jacked up commissary prices out of their own strained finances.
So what does prison profiteering look like, in dollars and sense? Here's the first-of-its-kind database tracking the costs of food, hygiene items and religious items in 46 states:
https://theappeal.org/commissary-database/
Prisoners rely heavily on commissaries for food. Prisons serve spoiled, inedible food, and often there isn't enough to go around – prisoners who rely on the food provided by their institutions literally starve. This is worst in prisons where private equity funds have taken over the cafeteria, which is inevitable accompanied by swingeing cuts to food quality and portions:
https://theappeal.org/prison-food-virginia-fluvanna-correctional-center/
So you have one private equity fund starving prisoners, and another that's gouging them on food. Or sometimes it's the same company. Keefe Group, owned by HIG Capital, provides commissaries to prisons whose cafeterias are managed by other HIG Capital portfolio companies like Trinity Services Group. HIG also owns the prison health-care company Wellpath – so if they give you food poisoning, they get paid twice.
Wellpath delivers "grossly inadequate healthcare":
https://theappeal.org/massachusetts-prisons-wellpath-dentures-teeth/
And Trinity serves "meager portions of inedible food":
https://theappeal.org/clayton-county-jail-sheriff-election/
When prison commissaries gouge on food, no part of the inventory is spared, even the cheapest items. In Florida, a packet of ramen costs $1.06, 300% more inside the prison than it does at the Target down the street:
https://www.documentcloud.org/documents/24444312-fl_doc_combined_commissary_lists#document/p6/a2444049
America's prisoners aren't just hungry, they're also hot. The climate emergency is sending temperatures in America's largely un-air-conditioned prisons soaring to dangerous levels. Commissaries capitalize on this, too: an 8" fan costs $40 in Delaware's Sussex Correctional Institution. In Georgia, that fan goes for $32 (but prisoners are not paid for their labor in Georgia pens). And in scorching Texas, the commissary raised the price of water by 50% last summer:
https://www.tpr.org/criminal-justice/2023-07-20/texas-charges-prisoners-50-more-for-water-for-as-heat-wave-continues
Toiletries are also sold at prices that would make an airport gift-shop blush. Need denture adhesive? That's $12.28 in an Idaho pen, triple the retail price. 15% of America's prisoners are over 55. The Keefe Group – sister company to the "grossly inadequate" healthcare company Wellpath – operates that commissary. In Oregon, the commissary charges a 200% markup on hearing-aid batteries. Vermont charges a 500% markup on reading glasses. Imagine spending decades in prison: toothless, blind, and deaf.
Then there's the religious items. Bibles and Christmas cards are surprisingly reasonable, but a Qaran will run you $26 in Vermont, where a Bible is a mere $4.55. Kufi caps – which cost $3 or less in the free world – go for $12 in Indiana prisons. A Virginia prisoner needs to work for 8 hours to earn enough to buy a commissary Ramadan card (you can buy a Christmas card after three hours' labor).
Prison price-gougers are finally facing a comeuppance. California's new BASIC Act caps prison commissary markups at 35% (California commissaries used to charge 63-200% markups):
https://theappeal.org/price-gouging-in-california-prisons-newsom-signature/
Last year, Nevada banned any markup on hygiene items:
https://www.leg.state.nv.us/App/NELIS/REL/82nd2023/Bill/10425/Overview
And prison tech monopolist Securus has been driven to the brink of bankruptcy, thanks to the activism of Worth Rises and its coalition partners:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/08/money-talks/
When someone tells you who they are, believe them the first time. Prisons show us how businesses would treat us if they could get away with it.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/20/captive-market/#locked-in
#pluralistic#carceral state#price gouging#greedflation#prisons#the bezzle#captive markets#capitalists hate capitalism#monopolies#the appeal#keefe group#hig capital#guillotine watch#wellpath#trinity services group#sussex correctional institute#cooked alive#air conditioning#climate change#idaho#oregon#freedom of religion#vermont#florida#kentucky#georgia#arkansas#wyoming#missouri#ramen
168 notes
·
View notes
Text
The leader of the Choctaw Nation is joining an outpouring of support for the family of a 16-year-old student whose death is being investigated in Oklahoma.
Nex Benedict passed away on February 8, following a physical altercation at a high school the day prior. Chief Gary Batton confirmed that the young student’s mother is enrolled with the Choctaw Nation.
“The loss of a child is always difficult for a community and a family to accept,” Batton said in a statement on Wednesday.
“Although Nex does not appear to be affiliated with our tribe, their mother, Sue Benedict, is a registered member,” Batton continued. “Nex’s death weighs heavily on the hearts of the Choctaw people. We pray Nex’s family and their loved ones will find comfort,” Batton concluded.
Nex’s death has directed widespread attention to Oklahoma, where Republican officials have increasingly adopted policies hindering the rights and freedoms of Two Spirit and LGBTQ+ people. Sue Benedict has embraced her child’s gender identity and has vowed to donate funds to other youth experiencing some of the same struggles.
Two Spirit and LGBTQ+ advocates incorrectly identified Nex as being a citizen of the Cherokee Nation, whose reservation borders that of the Choctaw Nation. Cherokee Chief Hoskin Jr. expressed support for the Benedict family on Tuesday.
“As Chief, the health and welfare of all children within the Cherokee Nation Reservation is of concern,” Hoskin said in a statement.
Nex attended Owasso High School in Owasso, located on the Cherokee Reservation. Local authorities are investigating the death and have said they will forward the results of the investigation to prosecutors in Tulsa County for potential action.
Hoskin has offered the support of the Cherokee Nation Marshal Service as the investigation continues. The Owasso Police Department indicated in a statement on Tuesday that interviews would be taking place “over the course of the next two weeks.”
Oklahoma Gov. Kevin Stitt (R), a Republican who happens to be a citizen of the Cherokee Nation, has not spoken publicly about the death. He has repeatedly derided efforts to address diversity, equity and inclusion as discriminatory.
But a senior official with President Joe Biden, a Democrat, has weighed in. White House Press Secretary Karine Jean-Pierre offered a message of support from the administration in a post on social media.
“Every young person deserves to feel safe and supported at school,” Jean-Pierre wrote on her official government account. “Our hearts are with Nex Benedict’s family, their friends, and their entire school community in the wake of this horrific tragedy.”
“For many LGBTQI+ students across the country, this may feel personal and deeply painful,” Jean-Pierre continued. “There is always someone you can talk to if you’re going through a hard time. Dial 988 and press 3 to reach a counselor dedicated to serving LGBTQI+ young people.
According to the 2023 LGBTQ+ Youth Report, a project of Human Rights Campaign and the University of Connecticut, more than half of transgender and gender-expansive youth feel unsafe at school. In particular, nearly a third said they feel unsafe in school restrooms.
“All students, including trans and gender-expansive students like Nex, have the right to feel safe and protected while attending school,” Tori Cooper, the campaign director of Community Engagement for the Transgender Justice Initiative at the Human Rights Campaign, said in a statement on Wednesday. “That Nex was only 16 years old compounds this tragic injustice and they should have lived to see a fulfilling and authentic life.”
The 2023 study was based on a survey of nearly 3,000 LGBTQ+ youth ages 13-18 nationwide, according to the organization. Some 0.6 percent of respondents identified themselves as American Indian or Alaska Native.
According to Owasso Public Schools, a “physical altercation” took place in a bathroom at the high school on February 7. The Owasso police responded to a local hospital on the same day of the incident.
Police then said they were informed that a “juvenile” was taken back to a hospital on February 8, the same day as Nex’s passing.
#op#links#trans#non-binary#choctaw#nex benedict#oklahoma#transphobia#hate crime#murder#child death#transphobic violence#uspol#news#bad news
122 notes
·
View notes
Text
From the article:
Results from the largest survey of transgender people in the United States were released Wednesday, revealing key insights into their lives and experiences at a time when trans rights haveincreasingly come under attack.
The 2022 US Transgender Survey Early Insights report, conducted by the National Center for Transgender Equality, polled an “unprecedented” 92,329 binary and nonbinary transgender people ages 16 and older living in the US, its territories or military bases, according to the report.
Respondents were surveyed on issues including their family life, health care, employment, education, housing and public accommodation. While many transgender people surveyed who have transitioned said they were satisfied with their lives, the report also noted transgender people continue to face disparities and discrimination across the country.
95 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Mandatory Nudity Study
Congratulations! We are delighted to inform you that you have been accepted into our Masters of Psychology program. Classes begin August 26, 2024, and you are expected to attend all of your courses in person.
As part of your graduate coursework, you have been selected to participate in a research project that will pay for your tuition, student fees, on-campus housing, meal card, and provide an additional twenty-thousand dollar stipend per semester.
If you decide to opt into our program, participation in this research project is mandatory.
Your assigned research project: The impact of Mandatory Nudity on Mental Health.
Overview: For the entirety of a graduate program (three years), one male student will be required to surrender every fiber of clothing he owns to the Psychology Department. This student will then complete coursework, assist classmates with their research, and teach a Psychology 101 Course each semester, sans all clothing. The nude student will conduct weekly mental-health check-ins and attend weekly group and individual therapy sessions to monitor the mental health impact of his mandatory nudity.
Directions for the Nude Subject:
Arrive fully clothed on the first day of courses. We recommend you where your favorite clothes. This will be the last time you will be allowed to wear clothing until after your graduation ceremony. Pack up the rest of your clothing. All of your clothing. Even a forgotten sock will result in rejection from this study (see "Consequences of an Incomplete Study below).
Bring your packed clothing to the campus-wide graduate student orientation. At some point during the orientation, you will be invited on stage in front of all of your peers. Once on stage, you will be invited to hand off all of your packed clothes. Then you will be handed your nudity pass, which you must carry with you everywhere. Your nudity pass can be given to any business or law enforcement officer to allow you to live a normal life while having your clothing restricted. Once you have your nudity pass, you will be asked to surrender the last pieces of your clothing: the shirt, pants, shoes, socks, undergarments, etc. off your back).
You are expected to live on campus and eat at least 90% of your meals throughout your graduate studies in the campus cafeteria. There will be no exceptions to these rules.
Your clothing will not be returned to you until after graduation (in three years time). You are not permitted to buy any clothing until after graduation. This means that you will spend your summers and holiday breaks nude as well. If you choose to return home to your family during holidays and summers, please report to your professor to receive a Traveling Nude Pass which is accepted at all national airports, but may not be accepted by local law enforcement, so travel with caution. If you are arrested for public indecency, it is up to you to ensure that you do not wear any prison assigned clothing. Again: If we discover that you have reserved any clothing or worn a single scrap of clothing (this includes baseball caps, glasses (if you need glasses, we will provide you contact lenses), socks, jewelry, or even towels wrapped around your waist), you will be rejected from the study.
Carry on a normal life. You should work to get involved in student clubs, make friends, attend all of your classes, etc. while remaining fully nude.
You are allowed thirty minutes a day where you can use your hands to cover your genitals. It is up to you to monitor this time, but if we discover that you have spent a second more than your allotted thirty minutes covering yourself with your hands, you will be ejected from the survey.
Attend all mandated therapies. You are assigned to group therapy twice a week, and individual therapy once a week to monitor your mental health throughout this research.
After you walk the stage at graduation, your clothing will be returned to you. Note: If you find that your experience with mandatory nudity has had a positive impact on your mental health, you have the option to retain your Nude Pass for the rest of your life, and the Psychology Department is prepared to redistribute all of your clothing during the graduation ceremony.
Rules of the Study:
You are not allowed to purchase, ask for, or wear any scrap of clothing for the entirety of your graduate program (from orientation to the end of your graduation ceremony. This study defines clothing as anything other than your own hands used to cover even a millimeter of your naked skin (i.e. backpacks, watches, etc.).
You are allowed exactly thirty minutes of time per day to use your hands to cover your genitals.
You must carry your nude pass with you at all times.
You must surrender every article of clothing that you own at the start of your study.
Consequences of an Incomplete Study:
If you are unable to complete this study for any reason, or if you are caught violating any of the rules of the study, your clothing will be retained by the Psychology Department. You will be required to repay the Psychology Department your semesterly stipend of $20,000. Additionally, you will be required to repay your tuition, student fees, housing costs, and meal card. For the sake of fully informed consent, we do not expect you to be able to repay these debts, we simply intend for you to be at the mercy of others' kindness in order to ever wear clothing again.
In order to accept your position in this study and in this program, please send our department your acceptance along with a single pair of your underwear to help mentally prepare yourself for the eventual surrender of every single stitch of your clothing.
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
The practice of men and women sharing hospital rooms violates human rights and should be prohibited, a group of academics argues.
In a paper just published in the Journal of Medical Ethics, the researchers outline how mixed-gender hospital rooms go against the fundamental human rights of personal security and dignity.
Lead author Dr Cindy Towns, of the University of Otago, Wellington, says placing male and female patients in the same room “compromises the safety of female patients and threatens the dignity of all patients”.
“Risk of rights violations and subsequent harm is exacerbated by the high rates of physical, cognitive, and sensory impairment experienced by people in hospital wards.
“New Zealand needs to immediately adopt specific national policies prohibiting mixed-gender hospital rooms and mandating public reporting of breaches,” she says.
Despite being prohibited in the United Kingdom for more than a decade, the practice is common and increasing in New Zealand.
Previous research by the group showed mixed rooms were common in a major New Zealand public hospital – in the more than 160,000 admissions analysed, 48 per cent were affected by mixed-gender rooms. The prevalence also increased over the eight-year period studied, and disproportionately affected vulnerable older adults.
Health system reviews, patient surveys and media reports in Australia and the UK have highlighted increased distress and fear of assault among women in mixed-gender rooms.
“Being forced into a room with men when unwell and vulnerable – often separated by only a curtain – may be traumatising to many women, even if the perception of threat or danger isn’t realised. It’s not surprising that the practice has been a frequent topic of complaint in feedback from patients, their families and the staff who care for them.
“Mixed-gender rooms breach the psychological safety of these patients, but this is avoidable by changing bed management practices,” Towns says.
The researchers argue that hospitals need to be designed with single-occupancy rooms as the standard of care.
“The majority of patients prefer having their own room. It allows for visitor access without disturbing other patients, improves infection control and enhances the disclosure of private health information.
“It would also enable more respectful care for gender-diverse patients who may not identify with a male or female gender binary.”
Because redesigning or rebuilding hospitals would take time, even if support and financing were obtained, the researchers argue the best approach to respect patient rights and reduce harm is single-gender rooms.
“Male and female patients express a preference for single-gender rooms. For female patients, this preference is associated with fear of violence while for male patients it is expressed as general concern and discomfort.
“Respecting these preferences is essential to maintain patient dignity during their hospital stay.”
82 notes
·
View notes
Text
A lot of rhetoric in support of anti-trans legislation to restrict gender-affirming care talks about regret and detransitioning.
Some proportion of people experience regret for any medical procedure, from chemotherapy to orthopedic surgery. Nonetheless, we don’t see a plethora of opinion pieces about the awful risks of hip replacements. It’s inevitable that some percentage of people who transition will regret it; the real question is whether the medical care is beneficial on the whole—not whether the occasional person later regrets a medical choice they made when younger.
In 2021, it was found that 13.1% of transgender people participating in the U.S. Transgender Survey reported detransitioning at some point in their lives.
The authors of this study are careful to note “these experiences did not necessarily reflect regret regarding past gender affirmation.” Family and societal pressure are the driving forces that lead many people to detransition – not because people wake up and decide they're not actually trans. All those who took part in the survey still identified as trans, thus it's presumed that the detransitioning was temporary.
Transitioning and detransitioning is complex. You can stop taking hormones and still be trans. You can regret taking steps that alienate you from your family, even as you wish your family would accept you living how you want to live. You can even regret some aspects of a treatment (any kind of medical treatment) while being grateful for the knowledge you gained by trying it out.
Detransitioning doesn't equal regret. Regret doesn’t always mean that people wish they hadn’t transitioned, it just means that there are some parts of the story that they long to change.
What’s clear from this evidence is that the vast majority of people do not experience regret, however defined, after transitioning genders. The rate of regret is still better than other treatments which don’t require national debates over their use, which really begs the question of why the health decisions of this group gets so much attention, and why so many people weigh in even though they have no medical or psychological training and aren't directly involved the treatment of transgender people.
————————————————————
The study included a sample of the responses of the reasons by those who detransitioned at some point in their life. I think they are insightful.
External factors
Caregiving reasons
“I was caring for my 80+ year old mother who had severe dementia, and it was just too confusing for her.”
Difficult to blend in as identified gender
“I don't pass, even after FFS [facial feminization surgery] etc.”
Financial reasons
“Unable to afford HRT [hormone replacement therapy]”
Lack of support
“Lack of trans community at the time”
“Back in 1997, virtually no one had heard of queergender people. I couldn't find a support system, and I couldn't figure out how to tell people what I was.”
Legal reasons
“Social services legal pressure regarding child custody”
“Forced to by going to federal prison for two years”
“Family court order—part of custody award”
Medical reasons
“Blood clotting from estrogen”
“Pain in binding large chest”
Fertility reasons
“We decided to have kids so [I] went back to testosterone long enough to bank sperm so we can do IVF [in vitro fertilization].”
Pressure from a medical health professional
“Parents took me to a region with hostile doctors.”
“Medical supervisor at federal facility removed regional-approved treatment because I didn't fit his idea of ‘a gay man so gay [he] wants to be a woman so it's easier to sleep with men’ after I had identified as lesbian to him.”
Pressure from a mental health professional
“Mental health professional told me I am not transgender and thought I was just crazy.”
“In those days you couldn't be diagnosed trans if you were also gay or lesbian.”
Pressure from a parent
“Moved home after college. Had to conform for parents.”
“I was facing being pulled out of school by my family.”
Pressure from the community or societal stigma
“With the high level of transphobia that exist[s], life gets very lonely.”
“I live in a very conservative place and was afraid for my safety.”
Pressure from my employer
“There are times when my current job requires me to present [as] female.”
I had trouble getting a job
“I flip flopped genders because of needed employment.”
Military-related reasons
“Military forced me to detransition while in service.”
Pressure from friends or roommates
“Staying with people I knew would harass me”
Pressure from unspecified or nonparent family members
“Visiting conservative extended family for the holidays”
“I temporarily detransition during visits with my in laws.”
Pressure from religion or a religious counselor
“Religious pressure (Mormon)”
“Pressure from religion”
Pressure from school
“School staff harassed and abused me daily for my gender expression.”
“Exclusion by Peers in School, No Mechanism for Getting Preferred Name on School Rosters”
Pressure from a spouse or partner
“I began to really clearly identify as transgender … but I realized it was pushing my marriage apart. At the time, I decided to try living as my assigned gender and set these feelings aside, but they kept cropping back up.”
Wanting to find a spouse or partner
“My partner of 4 years and I split up and I felt that I would always be alone as a trans person.”
“Difficult to find lovers, dates”
Sexual or physical assault
“Traumatized by corrective rape so recloseted”
“I have become frightened of the police since being sexually molested by an officer.”
Sports-related reasons
“Playing competitive sports”
Travel or relocation
“North Dakota is not a friendly place for anyone outside the gender binary. When I go back home, I butch up.”
“I was studying abroad in a country hostile to LGBTQ* people (Russia).”
Unable to access gender-affirming hormones
“Living in rural area, couldn't get hormones”
“I lost access to HRT and stopped passing.”
Internal factors
Psychological reasons
“Wasn't emotionally ready, I was scared of my identity.”
“Transition had to be put on hold due to mental health issues.”
“suicide attempt”
Uncertainty or doubt around gender
“Unsure of my exact gender identity”
“Thought I might have been wrong/confused”
Fluctuations in identity or desire
“My gender feels complicated and changing all the time.”
“I enjoy having the ability to go back and forth between genders.”
Note: internal factors can be the result of external factors (e.g., self-doubt regarding one's gender identity in response to being persistently misgendered or rejected).
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ryan Adamczeski at The Advocate:
Forced outing has devastating consequences for LGBTQ+ people, and queer youth are at an even greater risk.
One-third of LGBTQ+ minors who were outed without their consent were more likely to experience depression, as well as face less support from their families, according to a new study from the University of Connecticut. Two-thirds said that the event caused significant stress.
Outing is the act of revealing a person's sexual orientation or gender identity without their consent. The UConn study analyzed responses from 9,200 queer youth ages 13 to 17 in the Human Rights Campaign's 2017 LGBTQ National Teen Survey which showed a correlation between outing and stress.
The data also showed that LGBTQ+ youth experience stress from outing differently, as transgender, nonbinary, and asexual respondents reported higher stress levels than cisgender gay, lesbian and bisexual participants. In all cases, respondents reported lower stress when they also reported have parents or guardians who are educated on sexuality and gender identity.
More than 550 anti-LGBTQ+ bills were introduced across the U.S. in 2023, and 80 were passed into law. In 2024, 487 anti-LGBTQ+ bills have been introduced and 20 have passed into law, according to the American Civil Liberties Union. There are currently five states that mandate schools report transgender children to their parents if they request to go by a different name or pronouns. Another six “promote” forced outing, according to the Movement Advancement Project.
A new study from UCONN that came out reveals that anti-LGBTQ+ forced outing policies lead to higher rates of depression and familial rejection among LGBTQ+ youths.
#LGBTQ+#Studies#Forced Outing#LGBT Youth#University of Connecticut#Transgender Youth#Movement Advancement Project
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pretty in pink: Kazuki K & subversion (an homage)
Note: For Kazukiweek 2023: Acceptance
Pink is fresh. It is a happy color. It is positive. It is a sign of good health. That says a lot about Kazuki Kurusu. He has a bubbly personality, his optimism is brimming, especially after the seventh episode. It sure helps that Rei and Miri have become his ethos, have accepted to welcome the changes after five years of losing Yuzu. Usually, he wears his emotions on his sleeve. (But I think that’s only a front.) I love him. Right to the 11th episode, he has totally embraced the new life he’s been leading with Rei and Miri. The fact that he wanted it all along but was apprehensive because of his traumatic experiences made him cautious of the way he dealt with Rei and Miri. Rei’s determination on the second balcony scene was the catalyst because he knew how much K wanted it.

That fond looks K gives toward his family.

In the West, we are past that era where men cannot subvert pink’s gendered stereotype. You see men wear pink dress shirts, pink suits and other piece of clothing and they look spectacularly good. It is still a test of bravery for some though. Small boys still despise this color perceiving it as a girly stuff. New mothers try to veer their daughters away from this color by consciously not purchasing and introducing pink-coloured merchandise to their daughters’ color palette only to be disappointed because of peer pressure in the kindergartens. You know Elsa and Anna and the beautiful ladies of Disney and their association with pink? Too common, too banal.
However, “in contemporary Japanese culture, says (Barbara) Nemitz, pink is perceived as a masculine and mournful color that represents ‘young warriors who fall in battle while in the full bloom of life.’” Slain young samurai. All right. (Thanks to PA Works, it didn’t come to that though.)

It is also the color of sakura, cherry blossoms, which are the Japanese’s favourite flower. They do picnics just enjoying and gazing at the beauty of cherry blossoms (and later, peach blossoms). The Hanami. Some Japanese migrants adapted this ritual/event to their host countries and it is a sight to behold.

Different shades/nuances of pink worn by K and the moms
Pink has long been associated with homosexuality. The pink triangle. The lgbtq movement reclaimed the former badge of shame used by the Nazis incorporating it into the pride flag later. Though almost 70 per cent of the Japanese society supports it, it still is a huge problem to come out.
While there are no legal implications, coming out remains taboo for many in Japan for fear of being ostracized. A survey of young LGBTQ people published last year found high levels of mental anguish, including suicidal thoughts. More than 90% said they couldn’t talk about their sexuality with their guardians. Very few people in national politics or the corporate world are openly gay, although homosexual themes and LGBTQ celebrities are a staple of television and other forms of entertainment.
“Buddy Daddies” is not marketed as BL, but the show makers can write whatever about their characters. Sometimes implying them without direct confirmation. It depends how the viewers interpret it.

But K also symbolizes subversion. K’s characterization nonetheless goes against of what is perceived to be the norm in the Japanese society. He is both a nurturer and a protector, though Rei certainly will take over this “protector/saviour” task without any question. From the looks of it, he’d do anything for K and Miri.

Rei always in front to gauge the danger
An odd man out, K does the household chores while he can carry an adult man without any problem. We have seen him does it more than twice already. He’s loud and conspicuous. In Japan, you must never stand out. (<< - Shogo’s videos are highly recommended to watch btw!) He (and Rei) (go) goes against the rules. They blur the gender stereotyping in all aspects of life.
The crew presented the scenarios as if they were a matter of fact, normal, without making fun or light of it. No further commentary. One can say that it is subversive in a sense they want the audience to become aware of their thoughts on adoption, new family dynamics, the bureaucratic hurdles of enrolling your children and better access to daycare centres/schools to the ever-present mothers who have to give up their jobs and dedicate their lives to their kids, etc.
(It was unfortunate that they didn’t follow it up with Misaki Unasaka.)
Why do I get this feeling that one way or another “Buddy Daddies” had been the show makers’ thinly veiled social commentary on their society?
Anyway, I will miss his winking. Either way, I can still rewatch it.
Many happy returns, K!




#buddy daddies#buddy daddies anime#kazuki kurusu#buddy daddies wall of text#rei suwa#miri unasaka#kazurei#i could write an essay about K#and his love for the color pink#he’s not afraid of his masculinity#episode 9: no sweet without sweat#i salute all men who wear pink#and they look good on them tbh#apologies I overuse the word subversion#a birthday homage to K#happy birthday k#kazukiweek2023
86 notes
·
View notes
Text

Democrat Rep. Barbara Lee (D-CA), who is running for late Sen. Diane Feinstein’s U.S. Senate seat, is calling for a $50 minimum wage, defending her position during a debate Monday night.
The moderator asked Lee to defend her call for a $50-an-hour minimum wage during the event, noting that it is “seven times the current national minimum wage of $7.25 an hour.”
When asked how that would be economically sustainable for small businesses, Lee immediately said that she owned and ran a small business for over a decade, creating “hundreds of jobs, benefits, retirement benefits, [and] also health care benefits.”
“I know what worker productivity means, and that means that you have to make sure that your employees are taken care of and have a living wage in the Bay Area,” Lee said. “I believe it was the United Way [that] came out with a report that — very recently — [said] $127,000 for a family of four is just barely enough to get by,” she said, pointing to another survey that identified $104,000 as not being enough for one person, essentially classifying them as low income “because of the affordability crisis.”
She added:
And so, just do the math. Just do the math. Of course, we have national minimum wages that we need to raise to a living wage — you’re talking about $20, $25 — fine, but I have got to be focused on what California needs and what the affordability factor is when we calculate this wage.
Lee ultimately failed to answer the question.SUBSCRIBE
By subscribing, you agree to our terms of use & privacy policy. You will receive email marketing messages from Breitbart News Network to the email you provide. You may unsubscribe at any time.
Fox 40 notes that “a wage of $50 an hour would total $104,000 over the course of a year.”
WATCH:
Her call generated mockery from critics, including Sen. Ted Cruz (R-TX), who asked, “Who not $500 per hour?”
“Okay, why not $100 then? $1,000? Why not just make the minimum wage a billion dollars an hour? Then we’d all be richer than Elon Musk!” Turning Point USA founder Charlie Kirk remarked.
“Economic illiteracy like Rep. Lee’s has been around for centuries. Every country that adopts it becomes a dystopian nightmare,” he added as others piled on:
Lee’s call comes as inflation comes roaring back with no immediate signs of relief, as detailed in Breitbart Business Digest.
RELATED — CNN’s Sidner: Hotter-Than-Expected Inflation Report “Another Sign” Economy “Getting Better”
19 notes
·
View notes