#compress mov file
Text
Streamlining Video Production: Top Tips for Using MOV Compressors Effectively

In today's fast-paced digital landscape, video content has become a dominant force across various platforms and industries. Whether you're a professional videographer, content creator, or business owner, optimizing video production workflows is essential for staying competitive and meeting audience demands. One key aspect of streamlining video production is effectively utilizing MOV compressors. These tools play a crucial role in reducing file sizes without sacrificing video quality, making it easier to store, share, and distribute content. In this guide, we'll explore top tips for using MOV compressors effectively to streamline your video production process.
Understanding the Role of MOV Compressors:
Before delving into tips for using MOV compressors, it's important to understand their role in video production. MOV compressors, also known as video encoders or transcoders, are software applications designed to compress video files encoded in the MOV format. The MOV format, commonly associated with Apple devices and software, offers high-quality video but often results in large file sizes. MOV compressors help mitigate this issue by reducing file sizes while preserving as much video quality as possible.
Tips for Using MOV Compressors Effectively:
1. Choose the Right Compression Settings:
When using a MOV compressor, selecting the appropriate compression settings is paramount. Balancing compression ratio with video quality is crucial for achieving optimal results. Experiment with different settings such as bitrate, resolution, and codec options to find the right balance for your specific needs. Higher compression ratios result in smaller file sizes but may lead to loss of detail and clarity, so it's essential to strike a balance that meets your quality standards.
2. Prioritize Video Quality:
While reducing file sizes is important for efficient storage and distribution, it should not come at the expense of video quality. Aim to preserve as much detail and clarity as possible during the compression process. Opt for compression algorithms that offer efficient file size reduction while minimizing artifacts and degradation. Conduct thorough testing to ensure that compressed videos meet your quality standards before distribution.
3. Batch Process Multiple Videos:
To maximize efficiency, consider batch processing multiple videos using your MOV compressor. Most compressors support batch encoding, allowing you to queue up multiple files for compression simultaneously. This saves time and effort, especially when dealing with large volumes of video content. Prioritize organization and categorization to streamline the batch processing workflow and ensure consistent compression settings across multiple videos.
4. Utilize Presets and Profiles:
Many MOV compressors offer preset profiles tailored for specific use cases or platforms. Take advantage of these presets to simplify the compression process and ensure compatibility with target devices or platforms. Whether you're optimizing videos for web streaming, mobile devices, or social media, preset profiles can help expedite the compression workflow while maintaining optimal quality and compatibility.
5. Monitor Compression Progress and Results:
During the compression process, closely monitor progress and results to ensure that videos are compressed accurately and efficiently. Pay attention to any errors or warnings generated by the compressor and address them promptly to prevent issues with output quality. Conduct thorough quality checks on compressed videos to verify that they meet your standards for clarity, color accuracy, and overall presentation.
6. Optimize Compression for Streaming:
If you intend to stream compressed videos online, optimize compression settings for streaming delivery. Consider factors such as bitrate, resolution, and encoding techniques optimized for streaming platforms. By tailoring compression settings to the requirements of streaming services, you can ensure smooth playback and efficient delivery of video content to your audience.
7. Maintain Backup Copies of Original Files:
Before compressing any video files, always create backup copies of the original uncompressed files. This serves as a safety net in case of unexpected issues during the compression process or the need to revisit and re-compress videos with different settings. Store backup copies securely to prevent data loss and ensure access to pristine source files for future editing or archival purposes.
Conclusion:
Effectively using MOV compressors is essential for streamlining video production workflows and optimizing content for storage, sharing, and distribution. By following these top tips, you can leverage MOV compressors to reduce file sizes without sacrificing video quality, maximize efficiency through batch processing, utilize presets and profiles for streamlined compression, and monitor compression progress and results to ensure optimal outcomes. Incorporate these strategies into your video production workflow to enhance efficiency, maintain quality standards, and deliver compelling video content to your audience across various platforms and channels.
1 note
·
View note
Note
Hi! Your gifs are so generous!. Can I ask what programs you use to make them, and also what type of file you think is better to make gifs?
Have a lovely day!
hi! i use kmplayer for screencapping and photoshop for making the gifs. i always use either 1080p or 4k footage, but i honestly usually prefer 1080p because 4k can be annoying to color. regarding file formats, i'd recommend using .mkv or .mov which are less compressed than .mp4 -> better quality (but file size is what matters the most of course) :)
i hope you're having a great day too!
3 notes
·
View notes
Video
you get stuck in the void at the end
HORRIBLE GUIDE ON HOW TO MAKE SP WITH IPAD PRO SCREEN RECORDING
notes for myself so i dont have to punish myself going thru this again
YOU NEED: iPad pro, separate mac computer, air drop enabled, adobe premiere pro, adobe media encoder
1 screen record on your ipad. it gonna be like 3 hours of footage that suck up space for a fucking short drawing session.
2 airdrop files to computer after editing all clips together in iMovie (CUT AS MUCH AS POSSIBLE TO REDUCE FILE SIZE! SAVE AS 1280x720)
3 go to after effects and drag the movie in it. change comp size to 1280 if iMovie forces you to save bigger
3.5 MAKE TIME CHANGE! speed up your VID file FIRST! you make like a time stretch i think. change 30fps to 3fps i dont remember what the guy said
4 separate your audio (if you were listening to sm on your iPad, i listen to music) in effects and add in ur speedpaint audio you will need to go to youtube wav converter . org i think it was called? that one has no porn bots n crap and then put the mp3s in the editing composition and move the audio how its supposed to be
5 omfg ummm if the last song is too long look up a vid on how to trim audio i was too fucking tired
6 OPEN adobe media encoder
7 EXPORT to adobe media encoder reader
8go to your best friend media encoder and drag your aep project and drop it in there if exporting doesnt work. it willl hold ur hand and say ok hon what do you want do you want a quicktime or a h.247 click h/246 whatever it means mp4 i need to sleep
9click and wait a reasonable 10 minutes to compress 3 hours of sped up footage
10 drop and drag your same aep to create a QUICKTIME export just incase the mp4/mov is too big
10.5 i held a grunge against after effects so it turns out you can trim the end of your clips in media encoder so i trimmed the long end of the song off there!
11 omh it works i dragged it on tumblr and youtube and it worked df. IT HAS TO BE MP4! THE MOV FILES ARE TOO BIG!
12 wait a day for your videos to be posted and then DELETE and PERMANENT TRASH all the files you used! you dont need it anymore it will free up space
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Demystifying Digital Images and Video: Formats, Tools, Copyright, and More.
Introduction
In today's digital age, images and videos have become an integral part of our daily lives. From personal photographs shared on social media to professional content uploaded on platforms like YouTube and Twitch, understanding the intricacies of image and video file formats, codecs, and manipulation tools is essential. This blog post aims to provide a comprehensive overview of these digital elements, focusing on the definitions of common file types, export settings for popular broadcasting platforms, image manipulation tools, and the critical aspects of image copyright.
Definitions of Commonly Used Image and Web Video Formats, Wrappers, and Codecs
Image Formats:
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group): JPEG is the most widely used image format for photographs and digital images. It uses lossy compression, which reduces file size while maintaining reasonable image quality.
PNG (Portable Network Graphics): PNG is preferred for images with transparent backgrounds or crisp, high-quality graphics. Unlike JPEG, it uses lossless compression.
GIF (Graphics Interchange Format): GIFs are a popular choice for short, looping animations and simple graphics. They use lossless compression and support transparency.
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format): TIFF is a versatile format commonly used in professional photography and graphic design. It supports lossless compression and maintains high image quality.
BMP (Bitmap): BMP is a Windows-native format known for its lack of compression. It results in large file sizes but retains image quality.
Video Formats and Codecs:
MP4 (MPEG-4): MP4 is a widely supported video format that uses the H.264 codec. It offers a balance between quality and file size, making it ideal for streaming and sharing on the web.
AVI (Audio Video Interleave): AVI is an older format that supports various codecs. It is not as efficient as MP4 in terms of compression and is used less frequently nowadays.
MOV (QuickTime Movie): MOV is a format developed by Apple and is popular among Mac users. It can use various codecs, such as H.264 and ProRes, for high-quality video.
MKV (Matroska): MKV is an open-source container format that can contain videos with a variety of codecs, making it highly customizable.
Export Settings for Popular Broadcast Platforms
When it comes to sharing images and videos on popular broadcasting platforms like YouTube, Twitch, and Facebook, selecting the right export settings is crucial for optimal quality and compatibility.
YouTube: For video content on YouTube, the recommended format is MP4 with H.264 video codec and AAC audio codec. The ideal resolution is 1080p (1920x1080) or 4K (3840x2160) for higher quality. These settings balance quality and compatibility across devices.
Twitch: Twitch also prefers the MP4 format with H.264 video and AAC audio codecs. A resolution of 720p (1280x720) or 1080p is recommended, depending on the viewer's internet speed and quality preferences.
Facebook: Facebook accepts a wide range of video formats, including MP4 and MOV. However, MP4 with H.264 video and AAC audio codecs is a reliable choice. The resolution should be adapted to the target audience and device capabilities.
Commonly Used Image Manipulation Tools and Techniques
Image manipulation tools are essential for enhancing and editing images. Here are some commonly used tools and techniques, along with their purposes:
Adobe Photoshop: Photoshop is a versatile image editing software that can be used for tasks like retouching, color correction, and compositing.
Adobe Lightroom: Lightroom is perfect for photo organization and enhancement, with features like exposure adjustment, color grading, and batch processing.
GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation Program): GIMP is a free alternative to Photoshop, offering similar features for image editing and manipulation.
Canva: Canva is a user-friendly online tool for creating graphics and social media content. It simplifies design tasks for non-designers.
Cropping and Resizing: These techniques are fundamental for adjusting image dimensions and removing unwanted parts of an image.
Image Copyright Essentials
Artists and content creators must be aware of copyright laws to protect their intellectual property. Key copyright essentials include:
Ownership: Creators automatically own the copyright to their work upon creation, but registration provides additional legal protection.
Fair Use: Fair use allows limited use of copyrighted material without permission for purposes like criticism, commentary, news reporting, and education.
Licensing: Creators can license their work under specific terms, such as Creative Commons licenses, allowing others to use their work while respecting their rights.
Public Domain: Works in the public domain are not protected by copyright and can be used freely.
DMCA Takedowns: The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) enables copyright owners to request the removal of infringing content from online platforms.
Attribution: When using copyrighted material, proper attribution is often required to credit the creator.
Conclusion
Understanding digital image and video formats, codecs, export settings, image manipulation tools, and copyright essentials is essential for content creators, whether amateur or professional. By adhering to best practices and legal guidelines, creators can ensure their work is of high quality, reaches the right audience, and is protected from unauthorized use. Whether you're a budding photographer, a vlogger, or a graphic designer, the knowledge presented in this blog post can serve as a valuable resource to navigate the digital content landscape successfully.
References
Reference list
Arts Law Centre of Australia 2010, Copyright - Arts Law Centre of Australia, Arts Law Centre of Australia.
Attorney-General's Department 2022, Copyright basics, Attorney-General’s Department.
Image Manipulation: The What, How, and Why 2021, Clipping Path Campus.
Image Processing: Techniques, Types, & Applications [2022] n.d., www.v7labs.com.
Video File Formats, Codecs, and Containers Explained | TechSmith 2018, Welcome to the TechSmith Blog.
By: Juan Gutierrez.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Simplified Video Compressor: Free Compression for Your Video Content
In today's digital landscape, managing multimedia content effectively is crucial. With the proliferation of high-definition videos, storage and sharing can become cumbersome due to large file sizes. Simplified steps in as an essential tool, offering free video compression capabilities that empower users to manage their video content efficiently without sacrificing quality.
What is Simplified?
Simplified is a robust, user-friendly video compression tool designed to help users reduce the size of their video files effortlessly. Its intuitive interface and advanced compression algorithms ensure that users of all skill levels can easily navigate and utilize the software. Simplified’s mission is to democratize free video compressor, making it accessible to everyone from casual users to professional content creators.
Key Features of Simplified
User-Friendly Interface
Simplified's design prioritizes ease of use. Its clean, straightforward interface guides users through the compression process with clear instructions, making it accessible even to those with minimal technical knowledge. The simplicity of the interface means that users can focus on what matters most: their video content.
High-Quality Compression
One of the standout features of Simplified is its ability to compress videos without significant loss of quality. Utilizing state-of-the-art compression algorithms, Simplified ensures that your videos retain their original clarity and detail, even after substantial size reduction. This makes it ideal for both professional use and personal projects where maintaining video quality is crucial.
Multiple Format Support
Simplified supports a wide range of video formats, including MP4, AVI, MOV, and more. This versatility allows users to compress videos from various sources without worrying about compatibility issues. Whether you're working with footage from a professional camera or a smartphone, Simplified has you covered.
Rapid Processing
Time is often a critical factor when dealing with video files, especially large ones. Simplified is designed to process video compression quickly, saving you valuable time. This fast processing capability is particularly beneficial for users who need to compress multiple videos in a short period, such as content creators and marketers.
Accessibility: Online and Offline
Simplified offers both an online platform and a downloadable version. The online platform is perfect for quick, on-the-go compression needs and is accessible from any device with an internet connection. For more frequent use, the downloadable version provides additional convenience and functionality, ensuring that you can compress videos without relying on constant internet access.
Benefits of Using Simplified
Optimized Storage
By reducing the size of your video files, Simplified helps you free up valuable storage space on your devices. This is particularly advantageous for users with limited storage capacity, such as those using smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
Enhanced Shareability
Smaller video files are easier to share via email, social media, or cloud services. Simplified ensures that your videos can be shared quickly and effortlessly, bypassing file size limitations and reducing upload times. This feature is especially useful for social media influencers, marketers, and anyone who regularly shares video content online.
Quality Preservation
With Simplified, you don't have to worry about losing video quality during compression. The advanced algorithms used by the tool ensure that your videos maintain their visual and audio integrity, making them suitable for professional presentations, marketing materials, and personal keepsakes.
Cost-Effective Solution
As a free tool, Simplified provides an economical solution for video compression needs. Users do not have to invest in expensive software or subscription services, making it an ideal choice for students, freelancers, small businesses, and anyone looking to manage their video content on a budget.
Conclusion
Simplified empowers users with the ability to compress video files efficiently and effectively. Its user-friendly interface, high-quality compression, support for multiple formats, fast processing speeds, and dual access options make it an invaluable tool for anyone dealing with video content. Whether you're a professional content creator or someone who enjoys sharing videos with friends and family, Simplified offers a reliable, free, and easy-to-use solution for all your video compression needs. Experience the benefits of Simplified today and take control of your video content with confidence and ease.
Read More - https://simplified.com/video-compressor
Address - USA,California
1 note
·
View note
Text
Convert Your MP4 Files to AVI Online at No Cost

In the expansive universe of digital media, formats play a pivotal role in determining compatibility, quality, and accessibility. Among the myriad formats that have shaped the landscape of multimedia, MP4 to AVI stand as stalwarts, each with its own unique characteristics and contributions. The transition from MP4 to AVI represents a significant chapter in the ongoing narrative of technological evolution, marked by advancements in compression, encoding, and versatility. MP4, short for MPEG-4 Part 14, emerged as a revolutionary format in the late 1990s, designed to accommodate a wide range of multimedia content including audio, video, and subtitles. Its adoption was swift, owing to its efficient compression algorithms and widespread support across devices and platforms. MP4's versatility made it the preferred choice for streaming services, digital cameras, and portable media players, enabling users to enjoy high-quality content on the go. However, as technology progressed and demands for higher resolutions and enhanced features intensified, MP4 began to encounter limitations. One of the primary challenges was its inability to maintain optimal quality at higher compression levels, leading to compromises in visual fidelity. Additionally, the emergence of new encoding standards and evolving user preferences necessitated the development of more robust formats capable of meeting modern requirements. Enter AVI, or Audio Video Interleave, a format that traces its origins back to the early days of digital video. Initially introduced by Microsoft in the early 1990s, AVI gained prominence for its simplicity and compatibility with Windows-based systems. Despite its age, AVI remained relevant due to its uncompressed or minimally compressed nature, preserving the original quality of audio and video streams without significant loss. The transition from MP4 to AVI marked a paradigm shift in the realm of digital media, driven by the need for higher fidelity and greater flexibility. While MP4 excelled in compression and portability, AVI offered unparalleled quality and fidelity, making it the preferred choice for professional applications such as video editing and post-production. Moreover, AVI's support for diverse codecs and codecs enabled users to tailor their multimedia experience to their specific requirements, whether it be archival preservation or cinematic masterpiece. Nevertheless, the journey from MP4 to AVI was not without its challenges. Compatibility issues, file size constraints, and encoding complexities posed obstacles for users navigating the transition. Additionally, the proliferation of alternative formats such as MKV and MOV further diversified the digital landscape, offering compelling alternatives to both MP4 and AVI. In the contemporary era, the coexistence of MP4 and AVI reflects the nuanced needs and preferences of users across different domains. While MP4 continues to dominate the realm of online streaming and portable media, AVI maintains its stronghold in professional environments and archival preservation. Moreover, advancements in compression technologies and multimedia standards have blurred the lines between these formats, offering hybrid solutions that combine the best of both worlds. In conclusion, the evolution from MP4 to AVI embodies the dynamic nature of digital media, characterized by innovation, adaptation, and diversity. Each format represents a distinct chapter in the ongoing saga of technological progress, shaped by the evolving needs and aspirations of users worldwide. As we embark on the next phase of multimedia evolution, the legacy of MP4 and AVI serves as a testament to the enduring power of innovation in shaping the future of digital entertainment.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Understanding Video Formats and Codecs
In the realm of digital video editing, understanding video formats and codecs is paramount to achieving optimal results. Each format and codec comes with its own specifications and considerations, influencing factors such as file size, quality, and compatibility. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the intricacies of video formats and codecs, shedding light on their importance in the video editing process.

Exploring Video Formats
Overview of Video Formats
Video formats refer to the structure in which video data is encoded and stored. Common video formats include MP4, AVI, MOV, and WMV, each with its unique characteristics and applications.
Understanding Popular Video Formats
MP4 (MPEG-4): Widely used for online streaming and sharing due to its efficient compression and high-quality output.
AVI (Audio Video Interleave): A legacy format known for its compatibility with various media players, although it tends to produce larger file sizes.
MOV (QuickTime Movie): Developed by Apple, MOV files are commonly used in Mac environments and offer excellent support for multimedia content.
WMV (Windows Media Video): Primarily associated with Windows platforms, WMV files provide efficient compression and are suitable for web streaming.
Deciphering Video Codecs
What Are Video Codecs?
Algorithms called video codecs are used to both compress and decompress video data. They play a crucial role in balancing file size and video quality, allowing for efficient storage and transmission of digital video content.
Commonly Used Video Codecs
H.264 (Advanced Video Coding): One of the most widely used codecs for online video streaming and playback, known for its high compression efficiency and widespread compatibility.
HEVC stands for High-Efficiency Video Coding, and it's also H.265, HEVC offers improved compression efficiency over H.264, making it ideal for 4K and high-definition video content.
VP9: Developed by Google, VP9 is an open-source codec designed to deliver high-quality video streaming with reduced bandwidth requirements, commonly used in web browsers and streaming platforms.
Choosing the Right Format and Codec
Considerations for Video Editing
When selecting a video format and codec for your editing projects, consider factors such as the intended use of the video, platform compatibility, and storage limitations. opt for formats and codecs that strike a balance between quality and file size, ensuring optimal performance throughout the editing process.
Benefits of Enrolling in a Video Editing Course in Dehradun - DSOM
At DSOM (Design School of Online Marketing) Video editing course in Dehradun, we offer specialized video editing courses designed to equip aspiring editors with the knowledge and skills needed to navigate the complexities of digital video editing. Our comprehensive curriculum covers topics such as video formats, codecs, editing techniques, and industry best practices, providing students with a solid foundation for success in the field of video editing.
Conclusion
Understanding video formats and codecs is essential for achieving professional results in digital video editing. By familiarizing yourself with the characteristics and applications of different formats and codecs, you can make informed decisions throughout the editing process, ensuring the highest quality output for your projects.
0 notes
Text
Format Freedom: Mastering Video Conversion Techniques"
Introduction:
In the dynamic landscape of digital content creation, the pursuit of format freedom has become a crucial endeavor. This guide, titled "Format Freedom: Mastering Video Conversion Techniques," is an exploration of the art and science behind video conversion. Join us on a journey to master the techniques that liberate your videos from format constraints, providing the freedom to be experienced seamlessly across various platforms and devices.
1. Decoding the Language of Video Formats:
Understanding the nuances of video formats is the first step toward achieving format freedom. From the ubiquitous MP4 to the specialized realms of AVI, MKV, and MOV, each format speaks its own language. This section serves as a primer, decoding the language of video formats and laying the foundation for mastering the art of video conversion.
2. Motivations for Seeking Format Freedom:
a. Universal Accessibility:
The primary motivation behind mastering video conversion lies in achieving universal accessibility. In a world saturated with diverse devices, format freedom ensures that your content is not bound by the limitations of a single format, allowing it to reach audiences on any screen.
b. Tailoring for Streaming Platforms:
As streaming platforms continue to evolve, mastering video conversion is about tailoring content for various platforms. It's not just about changing formats; it's about optimizing for each platform's unique requirements, ensuring a seamless streaming experience for your audience.
c. Efficient Storage without Compromise:
Achieving format freedom involves efficient storage without compromising quality. Video conversion allows for the compression of files into more efficient formats, striking a delicate balance between preserving visual integrity and minimizing digital footprint.
3. Palette of Video Conversion Tools:
a. Online Converters:
For those seeking user-friendly solutions, online converters are an accessible entry point into video conversion. This guide explores popular online tools, providing insights into their features and offering guidance on leveraging them effectively to achieve format freedom.
b. Software Solutions:
Venturing into more advanced terrain, software solutions open up a realm of possibilities for mastering video conversion. This section explores comprehensive video conversion programs, highlighting their features, customization options, and the efficiency they bring to the process.
c. Command Line Empowerment:
For users comfortable with a more technical approach, mastering video conversion involves delving into command-line tools such as FFmpeg. Unveiling the power of command-line empowerment, this section provides insights into a hands-on approach, giving users greater control over the conversion process.
4. Crafting Seamless Conversion Workflows:
a. Batch Processing Brilliance:
Efficiency is key in mastering video conversion. The guide shares tips on orchestrating batch processing brilliance, allowing users to transform multiple videos simultaneously and streamline their workflows with precision.
b. Quality vs. Compression Mastery:
In the delicate balance between quality and compression, mastering video conversion is about achieving the perfect blend. This section provides insights into striking the right balance, ensuring that your videos maintain their visual brilliance while being optimized for various applications and devices.
5. Navigating Challenges and Preserving Quality:
a. Preserving Visual Integrity:
A central tenet of mastering video conversion is the preservation of visual integrity. The guide addresses challenges related to quality loss, offering techniques and settings to mitigate risks and empower users to maintain the essence of their content during conversion.
b. Ensuring Compatibility Across Screens:
Just as an artist adapts their work for different canvases, mastering video conversion ensures compatibility across diverse devices and platforms. This section explores common compatibility challenges, offering insights to ensure that your content is appreciated seamlessly on every screen.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Content with Format Freedom:
"Format Freedom: Mastering Video Conversion Techniques" is not just a guide; it's a roadmap to empower your content with the freedom to transcend format boundaries. As you embark on this journey, mastering the techniques within video conversion becomes a skill that liberates your videos, allowing them to shine brilliantly across screens and platforms. By embracing the art and science of video conversion, you not only achieve format freedom but also elevate your digital content to new heights, ensuring it resonates seamlessly with your audience's diverse preferences and devices.
0 notes
Text
Converting Brilliance: Unlocking Video Potential
Introduction:
In the dynamic realm of digital content, where creativity and innovation converge, the process of converting video formats emerges as a transformative gateway—unlocking the true potential of visual brilliance. This guide, titled "Converting Brilliance: Unlocking Video Potential," embarks on a journey to explore the motivations, methods, and the untapped potential residing within the art of video conversion.
1. The Genesis of Video Formats:
To truly understand the power of converting brilliance, it's essential to trace the genesis of video formats. From the foundational MP4 to the specialized realms of AVI, MKV, and MOV, each format contributes a unique note to the symphony of digital content. This section serves as a prelude, introducing the language of video formats that sets the stage for unlocking their potential.
2. Motivations Driving Video Alchemy:
a. Universal Accessibility:
The core motivation behind video conversion lies in achieving universal accessibility. In a world where devices vary widely, video alchemy becomes the key to ensuring that brilliance is not confined to a specific format, making content universally accessible across diverse screens.
b. Adaptive Streaming Enhancement:
The rise of streaming platforms demands adaptability. Video conversion goes beyond mere format changes; it adapts content for various streaming platforms, enhancing the viewer experience by catering to the unique requirements of each channel.
c. Storage Efficiency without Sacrificing Brilliance:
Optimizing storage without compromising brilliance is an art. Video alchemy achieves this by compressing files into efficient formats, retaining the visual essence while minimizing the digital footprint. This section delves into the delicate balance between file size and preserving brilliance.
3. The Palette of Video Conversion Tools:
a. Online Converters:
For those seeking simplicity, online converters provide an accessible entry point into video conversion. The guide explores popular online tools, shedding light on their features and guiding users on leveraging these platforms effectively to unlock the brilliance within their videos.
b. Software Solutions:
Venturing into more advanced terrain, software solutions amplify the possibilities of video conversion. This section explores comprehensive video conversion programs, highlighting their capabilities, customization options, and the efficiency they bring to the art of unlocking brilliance.
c. Command Line Mastery:
For those inclined towards a more technical approach, the guide introduces the power of command-line tools such as FFmpeg. Unveiling the potential of command line mastery, this section provides insights into a hands-on approach to video conversion, granting users greater control over the process.
4. Crafting Seamless Conversion Workflows:
a. Batch Processing Brilliance:
Efficiency is the hallmark of converting brilliance. The guide shares insights into orchestrating batch processing brilliance, empowering users to transform multiple videos simultaneously, streamlining workflows with artistic finesse.
b. Quality vs. Compression Symphony:
In the delicate symphony between quality and compression, the guide provides insights into striking the right balance. It's an art of finding the perfect harmony, ensuring that the brilliance of the video is maintained while optimizing it for various applications and devices.
5. Navigating Artistic Challenges:
a. Preserving Artistic Integrity:
Preserving artistic integrity is a priority in the world of converting brilliance. The guide addresses the challenge of quality loss, providing techniques and settings to mitigate risks and empower users to maintain the essence of their artistic vision during the conversion process.
b. Ensuring Compatibility on Every Canvas:
Just as an artist adapts their work for different canvases, video conversion ensures compatibility across diverse devices and platforms. This section explores common compatibility challenges, offering insights to ensure that the brilliance of the video is appreciated on every screen.
Conclusion: Elevating Video Conversion to Art:
"Converting Brilliance: Unlocking Video Potential" transcends the technicalities of video conversion; it's an exploration of video alchemy as an art form. As users embark on this transformative journey, understanding the motivations, methods, and potential within the process becomes essential. This guide serves as a compass, guiding users to not just convert videos but to unlock the brilliance within, ensuring that their visual creations shine brightly across the diverse canvas of the digital landscape. By embracing the art of video conversion, users can elevate their digital experiences, transforming videos into masterpieces that resonate seamlessly across screens and platforms.
Introduction:
In the dynamic realm of digital content, where creativity and innovation converge, the process of converting video formats emerges as a transformative gateway—unlocking the true potential of visual brilliance. This guide, titled "Converting Brilliance: Unlocking Video Potential," embarks on a journey to explore the motivations, methods, and the untapped potential residing within the art of video conversion.
1. The Genesis of Video Formats:
To truly understand the power of converting brilliance, it's essential to trace the genesis of video formats. From the foundational MP4 to the specialized realms of AVI, MKV, and MOV, each format contributes a unique note to the symphony of digital content. This section serves as a prelude, introducing the language of video formats that sets the stage for unlocking their potential.
2. Motivations Driving Video Alchemy:
a. Universal Accessibility:
The core motivation behind video conversion lies in achieving universal accessibility. In a world where devices vary widely, video alchemy becomes the key to ensuring that brilliance is not confined to a specific format, making content universally accessible across diverse screens.
b. Adaptive Streaming Enhancement:
The rise of streaming platforms demands adaptability. Video conversion goes beyond mere format changes; it adapts content for various streaming platforms, enhancing the viewer experience by catering to the unique requirements of each channel.
c. Storage Efficiency without Sacrificing Brilliance:
Optimizing storage without compromising brilliance is an art. Video alchemy achieves this by compressing files into efficient formats, retaining the visual essence while minimizing the digital footprint. This section delves into the delicate balance between file size and preserving brilliance.
3. The Palette of Video Conversion Tools:
a. Online Converters:
For those seeking simplicity, online converters provide an accessible entry point into video conversion. The guide explores popular online tools, shedding light on their features and guiding users on leveraging these platforms effectively to unlock the brilliance within their videos.
b. Software Solutions:
Venturing into more advanced terrain, software solutions amplify the possibilities of video conversion. This section explores comprehensive video conversion programs, highlighting their capabilities, customization options, and the efficiency they bring to the art of unlocking brilliance.
c. Command Line Mastery:
For those inclined towards a more technical approach, the guide introduces the power of command-line tools such as FFmpeg. Unveiling the potential of command line mastery, this section provides insights into a hands-on approach to video conversion, granting users greater control over the process.
4. Crafting Seamless Conversion Workflows:
a. Batch Processing Brilliance:
Efficiency is the hallmark of converting brilliance. The guide shares insights into orchestrating batch processing brilliance, empowering users to transform multiple videos simultaneously, streamlining workflows with artistic finesse.
b. Quality vs. Compression Symphony:
In the delicate symphony between quality and compression, the guide provides insights into striking the right balance. It's an art of finding the perfect harmony, ensuring that the brilliance of the video is maintained while optimizing it for various applications and devices.
5. Navigating Artistic Challenges:
a. Preserving Artistic Integrity:
Preserving artistic integrity is a priority in the world of converting brilliance. The guide addresses the challenge of quality loss, providing techniques and settings to mitigate risks and empower users to maintain the essence of their artistic vision during the conversion process.
b. Ensuring Compatibility on Every Canvas:
Just as an artist adapts their work for different canvases, video conversion ensures compatibility across diverse devices and platforms. This section explores common compatibility challenges, offering insights to ensure that the brilliance of the video is appreciated on every screen.
Conclusion: Elevating Video Conversion to Art:
"Converting Brilliance: Unlocking Video Potential" transcends the technicalities of video conversion; it's an exploration of video alchemy as an art form. As users embark on this transformative journey, understanding the motivations, methods, and potential within the process becomes essential. This guide serves as a compass, guiding users to not just convert videos but to unlock the brilliance within, ensuring that their visual creations shine brightly across the diverse canvas of the digital landscape. By embracing the art of video conversion, users can elevate their digital experiences, transforming videos into masterpieces that resonate seamlessly across screens and platforms.
0 notes
Text
Digital Image Overview
Image design is all about establishing an engaging atmosphere that advances the plot in films and television. A movie's professionally created visual design elements add to the immersion and bind everything together for the audience. But , a lot of us still might have no idea about what makes an image, commonly used image/video formats, wrappers, and codec. So, today i’ll be talking about all those things on my blog including a lot of other information which you should know if you are a Film Student.
Let's start with the basics.
What is Image and Video? What are they made up of?
When hearing the term Image everyone comes with the common sentence : a visual representation of something. And to say it in a simple way that’s what it is.
A person's public perception can also be considered while defining an image. For example, a rock star trying to improve his image would dress like a professor and pick up chess. But that’s not the ‘Image' I am talking about right now.
In simple sentences, Image is a still visual representation of either subject or object while Video is an electronic representation of moving visual image in the form of encoded digital data.
Now what are they actually made up of in the context of the digital world? Are they just the pictures?
Pixels is the right response. A picture is made up of pixels. The smallest addressable unit on a screen is a pixel, and the number of pixels an image uses determines its quality.
Understanding Image/Video Format, Codec and Container/Wrapper
There are a lot of Image/Video Formats, Codecs and Wrappers that are being used nowadays but today i’ll be talking about most commonly used image & web video formats, wrapper and codecs.
The Codec word itself is a blend of the words coder and decoder, as well as compression and decompression.It refers to what encodes and compressees, then decodes and decompresses the data that makes up your image/video.Data is compressed for storing and sharing via codecs. The data is then decoded and uncompressed for viewing and modification. H.264 or AVC is the most widely used codec for video compression. Audio file formats or file extensions are the container or wrapper for those codecs i.e. these codecs are housed or wrapped in audio file formats or file extensions.(https://www.adobe.com/au/creativecloud/video/discover/best-video-format.html#:~:text=Video%20file%20format%20and%20codec%20basics.&text=Codecs%20encode%20data%20to%20compress,or%20wrappers%20for%20these%20codecs. )
The varieties of video file formats are numerous. To assist you better understand when to utilize each, we've compiled information on some of the most popular.
1. MP4
The most typical and widely used video format is MP4. It can store audio, video, subtitles, text, and still images and is the most widely compatible. For use on Facebook, Instagram, Youtube, and Twitter, it is the ideal choice.
2. MOV
The MOV file format was created expressly by Apple for use with Quicktime Player and is relatively similar to the MP4 format. The greatest video format for Apple devices is this one.
3. AVI
Microsoft's response to the MOV video file format was the AVI format. It is one of the earliest video file formats still in use, having been created in 1995. Because of the big file size, it is less suitable for streaming and sharing but is perfect for short videos and television.
4. WMV
WMV files, which are AVI's replacement, may be played on both Windows and Apple devices as long as Windows Media Player is installed. One of the few video file types that can compress data more efficiently than MP4 is WMW.
5. WEBM
Google created WEBM, another open source video file format, for HTML5. There is no need for Flash Player or any other plugins because it plays right in the browser.
(https://www.techsmith.com/blog/video-file-formats/ )
Image file format that are mostly used in web are listed below:
APNG
Animated Portable Network Graphics(.apng)
Good choice for lossless animation sequences (GIF is less performant). AVIF and WebP have better performance but less broad browser support.
Supported: Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Opera, Safari.
AVIF
AV1 Image File Format (.avif)
Good choice for both images and animated images due to high performance and royalty free image format. It offers much better compression than PNG or JPEG with support for higher color depths, animated frames, transparency, etc. Note that when using AVIF, you should include fallbacks to formats with better browser support (i.e. using the <picture> element).
Supported: Chrome, Firefox (still images only: animated images not implemented), Opera, Safari.
GIF
Graphics Interchange Format(.gif)
Good choice for simple images and animations. Prefer PNG for lossless and indexed still images, and consider WebP, AVIF or APNG for animation sequences.
Supported: Chrome, Edge, Firefox, IE, Opera, Safari.
JPEG
Joint Photographic Expert Group image(.jpg, .jpeg, .jfif, .pjpeg, .pjp)
Good choice for lossy compression of still images (currently the most popular). Prefer PNG when more precise reproduction of the image is required, or WebP/AVIF if both better reproduction and higher compression are required.
Support: Chrome, Edge, Firefox, IE, Opera, Safari.
PNG
Portable Network Graphics (.png)
PNG is preferred over JPEG for more precise reproduction of source images, or when transparency is needed. WebP/AVIF provide even better compression and reproduction, but browser support is more limited.
Support: Chrome, Edge, Firefox, IE, Opera, Safari.
SVG
Scalable Vector Graphics(.svg)
Vector image format; ideal for user interface elements, icons, diagrams, etc., that must be drawn accurately at different sizes.
Support: Chrome, Edge, Firefox, IE, Opera, Safari.
WebP
Web Picture format(.webp)
Excellent choice for both images and animated images. WebP offers much better compression than PNG or JPEG with support for higher color depths, animated frames, transparency etc. AVIF offers slightly better compression, but is not quite as well-supported in browsers and does not support progressive rendering.
Support: Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Opera, Safari
(https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/Media/Formats/Image_types#common_image_file_types )
Export setting used for popular platforms like Youtube, Facebook, Twitch e.t.c.
While many video formats can be used effectively with these platforms, it’s important to consider details like time required to upload, process and play the video – this is tightly tied to the file size associated with the video. To maximize effectiveness, and for optimal results:
Youtube:
It itself recommends the MP4 video file format with AAC-LC audio Codec and H.264 video Codec.The optimal resolution is 1080p (1920x1080), or for better quality, 4K (3840x2160). These options strike a compromise between device compatibility and quality.
Facebook:
MP4 and MOV are the most highly recommended, with MP4 coming out on top once again due to its smaller file size and fewer losses during compression. The target audience and device capabilities should be considered while choosing the resolution.
Twitch video format:
MP4, MOV, AVI, and FLV files. AAC audio. Depending on the viewer's internet bandwidth and desired level of quality, a resolution of 720p (1280x720) or 1080p is advised.
Commonly used image manipulation tools and techniques:
Tools for image modification are necessary for altering and improving images. Here are some often employed methods and instruments along with what they are utilized for:
Adobe Photoshop - Photoshop is a flexible image editing programme that is useful for operations like retouching, color correction, and compositing.
Lightroom - With capabilities like exposure correction, color grading, and batch processing, Adobe Lightroom is ideal for organizing and enhancing photos.
GIMP - GIMP(GNU Image Manipulation Programme) is a free alternative to Photoshop that provides tools for editing and manipulating images that are similar to those of Photoshop.
Canva-An easy-to-use internet application for designing graphics and social media material. For non-designers, it makes design jobs simpler.
Image Copyright Essential and Important Legal Information that artists need to know regarding intellectual property:
Copyright is intellectual property law. Copyright and moral rights, and are legal tools that practitioners can use to protect their work from unauthorized use, to protect their reputation or brand, and generate income.
Copyright regulations must be understood by artists and content producers in order to safeguard their creative property. Important copyright requirements include:
Ownership: When a work is created, its creators immediately acquire the copyright to it. However, registration offers further legal protection.
Fair Use: Fair use permits the limited, unrestricted use of copyrighted content for functions including criticism, commentary, news reporting, and teaching without seeking prior authorisation.
Creative Commons licenses, for example, allow creators to grant certain conditions under which their work may be used while still upholding their rights.
Attribution: When using copyrighted material, proper attribution is often required to credit the creator.
Public Domain: Public domain works are free to use and are not covered by copyright.
DMCA Takedowns: Under the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA), content that violates copyrights can be removed from online platforms upon request.
For content makers, whether amateur or professional, understanding digital image and video formats, codecs, export settings, image modification tools, and copyright essentials is crucial. Creators may make sure their work is of a high standard, gets seen by the correct audience, and is shielded from unauthorized usage by following legal requirements and best practices. Whether you're an aspiring photographer, YouTuber, or graphic designer, the information provided in this blog article might be a useful tool for navigating the world of digital material.
References :
Arts Law Centre of Australia 2010, Copyright - Arts Law Centre of Australia, Arts Law Centre of Australia.
Attorney-General's Department 2022, Copyright basics, Attorney-General’s Department.
Image Manipulation: The What, How, and Why 2021, Clipping Path Campus.
Image Processing: Techniques, Types, & Applications [2022] n.d., www.v7labs.com.
How to choose the right video format | Adobe Australia. Available at: https://www.adobe.com/au/creativecloud/video/discover/best-video-format.html (Accessed: 10 October 2023).
Owen, A. (2023) Understanding video file formats, codecs and containers, The TechSmith Blog. Available at: https://www.techsmith.com/blog/video-file-formats/ (Accessed: 13 October 2023).
MozDevNet (no date) Image file type and format guide - web media technologies: MDN, Web media technologies | MDN. Available at: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/Media/Formats/Image_types#common_image_file_types (Accessed: 08 October 2023).
0 notes
Text
Title: Navigating the World of Digital Imagery: Formats, Editing, and Copyright
Introduction:
In our increasingly digital world, the significance of images and videos cannot be underestimated. From personal social media posts to professional content creation, having a profound understanding of digital image and video files is essential. This blog post aims to provide a comprehensive exploration of digital image and video formats, codecs, and common practices for image manipulation. Additionally, we will delve into the core principles of image copyright and the legal framework surrounding intellectual property. Let's embark on this enlightening journey into the realm of digital media.
Exploring Commonly Used Image and Video Formats, Wrappers, and Codecs:
Image Formats:
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group): The preferred choice for photographs and images with intricate color schemes, employing lossy compression.
PNG (Portable Network Graphics): Excelling in images with transparency and sharp edges, it utilizes lossless compression.
GIF (Graphics Interchange Format): Mainly used for uncomplicated animations and images with limited colors.
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format): Suited for professional graphics and printing due to its support for lossless compression and high quality.
BMP (Bitmap): A straightforward format widely embraced for basic images but resulting in large file sizes.
Video Formats:
MP4 (MPEG-4 Part 14): A versatile video format that strikes a balance between quality and file size, widely compatible across various devices and platforms.
AVI (Audio Video Interleave): An older format that persists due to its compatibility with legacy systems.
MOV (QuickTime): Developed by Apple, it is predominantly employed in Mac-related applications.
MKV (Matroska): Acknowledged for its high-quality video and audio capabilities, often the choice for high-definition video.
WebM: An open-source format renowned for its video quality and compact file size, popular in web videos.
Codecs:
H.264 (Advanced Video Coding): Widely used for video compression, offering a fine equilibrium between quality and file size.
H.265 (High-Efficiency Video Coding): A contemporary codec boasting enhanced compression efficiency, albeit potentially demanding more processing power.
VP9: An open-source video codec developed by Google, frequently employed for web streaming.
AAC (Advanced Audio Coding): A popular audio codec known for its high-quality audio compression.
MP3 (MPEG Audio Layer III): Famed for audio compression, although it provides slightly lower quality compared to AAC.
Optimal Export Settings for Popular Broadcast Platforms:
When preparing digital content for broadcast on platforms such as YouTube, Twitch, and Facebook, comprehending the finest export settings is imperative for ensuring top-notch quality and compatibility. Noteworthy settings include resolution, frame rate, and bit rate:
YouTube: For YouTube, the recommendation is to export videos in the MP4 format with the H.264 codec. A standard setting is 1080p resolution at 30fps with a bit rate of approximately 10 Mbps. These settings strike a harmonious balance between quality and seamless streaming.
Twitch: Twitch also favors the MP4 format with the H.264 codec. Popular settings comprise a 720p resolution at 30fps with a bit rate ranging from 3 to 6 Mbps, ensuring a delightful viewing experience for live streams.
Facebook: On Facebook, the go-to format is MP4 with the H.264 codec. A prevalent choice is a 720p resolution at 30fps with a bit rate between 2 to 4 Mbps, catering to a diverse range of devices and internet speeds.
Common Image Manipulation Tools and Techniques:
Image manipulation constitutes an integral aspect of crafting visually striking content. The following are conventional tools and techniques:
Adobe Photoshop: Revered for its versatility, Photoshop facilitates in-depth image editing, encompassing everything from retouching to crafting intricate designs.
Adobe Lightroom: Ideal for enhancing and color-correcting photos, particularly favored by photographers.
GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation Program): A free and open-source alternative to Photoshop, offering an extensive array of image editing capabilities.
Cropping and Resizing: Fundamental yet imperative techniques for framing and resizing images.
Filters and Effects: Platforms like Instagram and Snapchat present various filters for swift enhancements.
Layering: The art of amalgamating multiple images or elements to generate composite images or graphics.
Image Copyright Essentials:
Respecting intellectual property is a pivotal component of digital media. When employing images or videos produced by others, a comprehension of copyright essentials is indispensable:
Public Domain: Works in the public domain lack copyright protection and are available for unrestricted use.
Creative Commons: Certain creators permit specified uses of their work under predefined conditions through Creative Commons licenses.
Fair Use: In particular cases, limited use of copyrighted material may be permissible for purposes such as criticism, commentary, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, and research.
Attribution: Always attribute the creator when utilizing their work.
Permission: When in doubt, seek permission from the copyright holder before employing their work.
In conclusion, the digital landscape of images and videos is multifaceted, and a comprehensive understanding of formats, codecs, and manipulation tools is essential for content creators. Simultaneously, honoring copyright laws and intellectual property rights is vital for ethical content creation. By adhering to best practices, one can confidently navigate the digital realm, creating, sharing, and appreciating visual content responsibly.
References:
Smith, J. (2022). "The Ultimate Guide to Video File Formats." Videomaker.
Adobe. (n.d.). "Supported file formats in Lightroom Classic." Adobe Help Center.
"MP4 Export Settings for YouTube in Premiere Pro CC." (2017). Vimeo Blog.
"Common Video Frame Rates." (n.d.). Vimeo Help Center.
"Fair Use." (n.d.). U.S. Copyright Office.
0 notes
Text
Select the product type you are selling
E-book
E-book
Upload the file your buyers will download after purchase
0 / 1
Upload
Got more than one file? Upload a compressed folder instead. Maximum file size: 600 MB
Popular file types
Compressed Files
Compressed Files
.zip
Documents
Documents
.pdf, .doc, .docx, .ppt, .pptx, .pps, .ppsx, .odt, .xls, .xlsx, .psd
Images
Images
.jpg, .jpeg, .png, .gif, .ico
Photo Filters
Photo Filters
.dng, .xmp
Other:
Audio
Audio
.mp3, .m4a, .ogg, .wav
Video
Video
.mp4, .m4v, .mov, .wmv, .avi, .mpg, .ogv, .3gp, .3g2
0 notes
Text
TOOL TUTORIAL 3
FFmpeg | Script 2
GIF GENERATION AND OPTIMIZATION
Tool type: Command Line tool
Operating systems: Mac, Windows, and Linux
Difficulty: Moderate to Advanced
Input: Video files (any video file format).
Installation
I recommend you install via Homebrew if you're on Mac or Linux by pasting this into your terminal (if/once Homebrew is installed):
brew install ffmpeg
Windows users or other users who don't want Homebrew can follow directions on the FFMPEG website.
Converting one video file to GIF
In your system shell (Powershell on Windows, Terminal on Mac) change directories to the location containing your MP4 file (or whatever video file type you have—just replace .mp4 in the script with .mkv or whatever extension you have). Use this command:
cd FilePathToYourMP4
fmpeg -y -i input.mp4 -filter_complex "fps=18,smartblur=ls=-0.25,scale=540:-1:flags=lanczos,split[s0][s1];[s0]palettegen=max_colors=256[p];[s1][p]paletteuse=dither=bayer:bayer_scale=2" output.gif
Explaining and altering the script
The script does the following to your the clip you want to turn into a GIF, input.mp4:
Generate a gif with 18 frames per second (fps=18 controls frames per second. Change the number to changes the FPS).
Sharpen each frame (smartblur=ls=-0.25 controls sharpening. Negative values between -1 and 0 sharpen the image).
Scale every frame in the gif down to a 500 pixels using the lanczos technique. (scale=540 controls scale. Change 540 to different numbers to scale up and down)
Generate dither called bayer to overlay on your gif as a filter (split[s0][s1];[s0]palettegen=max_colors=256[p];[s1][p]paletteuse=dither=bayer:bayer_scale=2) Change 256 to a lower number to reduce the maximum number of colors for further compression. Increase bayer scale from 2 to 3 for a finer dither, or lower to 1 for a bigger dither.
Generates and saves the resulting gif under the name output.gif.
NOTE: Video files inputs don't have to be .mp4. You can use .mkv, .mov, or any other video type.
Converting a folder of video files to GIF
Place all of your video clips into a folder called gifset1. Put an empty subfolder inside the gifset1 folder called gifs. Go to your system shell and copy and paste the following indented text:
Mac and Linux users:
cd ~/Desktop/gifset1
for i in .mp4; do ffmpeg -y -i "$i" -filter_complex "fps=18,smartblur=ls=-0.25,scale=540:-1:flags=lanczos,split[s0][s1];[s0]palettegen=max_colors=256[p];[s1][p]paletteuse=dither=bayer:bayer_scale=2" gifs/${i%.}.gif; done
Windows users:
cd ~\Desktop\gifset1
for i in .mp4; do ffmpeg -y -i "$i" -filter_complex "fps=18,smartblur=ls=-0.25,scale=540:-1:flags=lanczos,split[s0][s1];[s0]palettegen=max_colors=256[p];[s1][p]paletteuse=dither=bayer:bayer_scale=2" gifs\${i%.}.gif; done
Once the process is finished running (your shell prompt will reappear allowing you to type in commands again) if you go to to the gifs subfolder in your gifset1 folder, you will find an optimized gif of every video file has been rendered.
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to Use a Computer, Part 3: Common Filetypes in Windows
In this section, we’ll talk about files and what software tends to open it.
Text and Word Processing
DOC & DOCX: Microsoft Word documents. Word can open DOCX, OpenOffice and LibreOffice can open DOC.
ODT: OpenDocument Text. OpenOffice and LibreOffice use this filetype natively. Word will (begrudgingly) open it, but it will complain about the file being corrupt (the only thing corrupt around here is Microsoft).
RTF: Rich Text Format document. WordPad, Word, OpenOffice, and LibreOffice can open it.
TXT: Text file. Notepad and Wordpad can open it.
Audio
MP3: MPEG Layer-3 file. Every audio player can open it.
WAV: Microsoft PCM sample. Every audio player and audio editor can open it.
AIFF: Apple PCM sample. Every audio player and most audio editors can open it.
MID: Sequenced MIDI file. Windows Media Player can open this, but you might need the MIDI mapper driver on Win 8-11.
FLAC: Free lossless audio compression. Sort of obscure still, but VLC media and most audio editors can open it.
Video
MP4: MPEG Layer-4 file. Every video player can open it.
MKV: Matroska Video Container file. VLC media player can open it.
MPEG: Ye olde thyme videoe filee. MPEG is still supported in Windows Media Player (for some reason).
AVI: Audiovisual Interleave. Every video player can open it.
MOV: Apple iMovie file. Most video players can open it. WMP used to have a problem with MOV, but that got ironed out in Windows 7, I think.
Images
JPG: JPEG file. Every image viewer, editor, web browser, and desktop publishing application can open this.
PNG: Portable Network Graphic file. All the same software that can open JPG can also open PNG.
GIF: You’re on Tumblr. You know what a GIF is. Windows Image Viewer on Windows 7 for some reason can’t open GIFs, relegating them to Internet Explorer.
ICO: Icon file. Most of Windows’ stock icons are packed away in DLLs, but you can edit standalone ICO files and create new ones in GIMP and Photoshop.
File compression and archives
ZIP: WinZip compressed folder. Windows can open these natively.
7Z: 7-Zip file. 7-Zip and, I think WinRAR, can open these. Only 7-Zip can save files in 7Z format.
RAR: WinRAR compressed folder. WinRAR and 7-Zip can open these, only WinRAR can save files in RAR format.
Miscellaneous and Windows system formats
EXE: Binary executable. These are the actual software programs that you run to do stuff with, like GZDoom, Mozilla Firefox, Snes9x, WordPad, and all that.
MSI: Windows installer file. Usually, installers are in EXE format, but a scattering of developers, particularly Microsoft, Mozilla, and Google use MSI. If you need to install something from MSI, just treat it like an EXE and click on it.
DLL: Dynamic link library. Software file directories are lousy with DLLs, but there’s not really any need to mess with them.
CFG: Configuration file. Human-readable configuration settings that can be opened in Notepad and reset manually. Usually, there won’t be any need to do that, though.
There are loads more esoteric filetypes in Windows, but these have been the kinds you’ll encounter the most as a casual computer user. Tune in next time as we discuss Mozilla Firefox.
0 notes
Text
Compress Video Size Compressor v5.0.9 (Pro) APK Free Download 2023
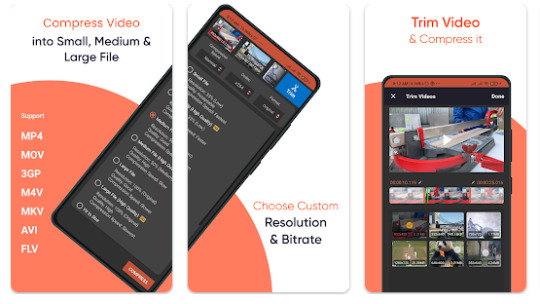
Compress Video Size Compressor v5.0.9 (Pro) APK: Are you tired of large video files taking up too much storage space on your device?
Do you need to compress your videos to make them easier to share or upload?
If so, you might be interested in the Compress Video Size Compressor v5.0.9 (Pro) APK.
We will provide you with everything you need to know about this app, including its features, benefits, and how to download it.
Introduction to Compress Video Size Compressor
Compress Video Size Compressor is an app designed to help you compress the size of your videos without losing quality. It supports a wide range of video formats, including MP4, 3GP, AVI, FLV, and more. The app is available for both Android and iOS devices.
Features of Compress Video Size Compressor
The app offers a range of features that make it a popular choice among users. Some of the key features include:
- Video Compression: Compress Video Size Compressor allows you to reduce the size of your videos without losing quality. This can be helpful when you need to share or upload videos that are too large.
- Batch Compression: You can compress multiple videos at once, saving you time and effort.
- Video Conversion: The app also allows you to convert your videos to different formats, making them compatible with different devices and platforms.
- Customizable Settings: Compress Video Size Compressor offers a range of customizable settings, such as video resolution, bitrate, and frame rate, allowing you to fine-tune your videos to your liking.
- Simple and User-Friendly Interface: The app is easy to use, with a simple and intuitive interface that even beginners can navigate.
Benefits of Compress Video Size Compressor
Using Compress Video Size Compressor offers several benefits, including:
- Reduced File Size: Compressing your videos can significantly reduce their file size, making them easier to store, share, and upload.
- Increased Compatibility: Converting your videos to different formats can make them compatible with different devices and platforms, allowing you to share them with a wider audience.
- Improved Video Quality: Compressing your videos using Compress Video Size Compressor does not result in a loss of quality, ensuring that your videos look as good as ever.
How to Download Compress Video Size Compressor
To download Compress Video Size Compressor, follow these simple steps:
- Click on the download button to start the download.
- Once the download is complete, install the app on your device.
- Open the app and start compressing your videos!

Overview & Features of Compress videotape Size Compressor v5.0.9( Pro)
Before you download Compress videotape Size Compressor v5.0.9( Pro) APK, You can read a brief overview and features list below.
Overview VidCompact is a free videotape motor audio motor videotape compressor and trimmer for android. It supports nearly all videotape and audio formats HD videotape HTML5 videotape WMV MKV FLV AVI MP4 MOV. We also give videotape editing features likemerge
Compress-Video-Size-Compressor-v5.0.9-Pro-APK-Free-Download-1-OceanofAPK.com,. png
Supported videotape Formats
Choose from predefined multiple contraction biographies with different quality and size settings.
Compress the videotape to a manually inputted size.
Shows a exercise of a small duration for the chosen contraction settings before the contraction process starts. Helps druggies to understand the quality of the contraction beforehand.
line multiple vids to compress them in batch mode.
Choose between X264 and X265( HEVC) codecs for contraction. HEVC codec provides much further contraction than the X264 codec. But X264 is important faster than X265 in terms of contraction speed.
Choose Compression process speed. Advanced the speed larger the compressed videotape size.
Choose a custom resolution.
Compresses a videotape by dwindling the resolution videotape bitrate. In this option, the stoner can see the estimated compressed videotape size before compressing. This does n’t save the original quality.
Compare compressed and original vids by playing them contemporaneously on the same screen.
cancel compressed or original lines after contraction from the app.
Reduces videotape size shrinks videotape to save and clears the device’s storehouse space.
High- quality videotape contraction and Low- quality videotape contraction.
Convert videotape to MP4 MKV AVI 3GP FLV MTS M4V MOV formats.( PRO Feature)
Convert videotape from MP4 MKV AVI 3GP FLV MTS MPEG MPG WMV M4V MOV VOB formats.
Play Compressed and Converted videotape.
Share compressed converted and size- reduced vids.
Video Compressor – Compact Video operations can compress and convert nearly any format of videotape. It provides druggies with dereliction compress/ preset biographies. druggies can choose asked contraction quality contraction speed videotape resolution bitrate etc.
Also, this compressor and motor let the stoner input the asked compressed videotape size and it compresses the videotape to that size. Also, you can compress vids in batch mode by queuing multiple vids.
This videotape Compressor can compress an uncompressed videotape without losing quality using X264 and X265( HEVC) codecs. It can also compress a compressed videotape by dwindling the quality which is Resolution Bitrate.
This videotape compressor gives the stoner a transparent and flexible way to choose the contraction position by customizing the resolution and bitrate of the videotape.
It shows the estimated size of the compressed videotape before the contraction begins. This helps you decide how important space you want to save with what quality of the contraction. It supports numerous videotape formats.
This is the stylish videotape compressor and motor app in the request which provides every possible setting for compressing your videotape.
Mod Info
◉ Pro/ Paid Features uncorked
◉ Promo Apps Removed
◉ AOSP Compatible/ No Google
◉ CPUs arm64- v8a, armeabi- v7a
◉ Full Multi Languages
◉ All remedy Info Removed
◉ Original hand Changed
Modded by Mixroot
What is New
Fixed some major bugs and crashes.
This app has credit announcements
Read the full article
#bestvideocompressorapk#compressvideosizecompressormodapk#videocompressorandvideocutterapk#videocompressorapkforpc#videocompressorcompactapkdownload#videocompressorfastcompressvideoandphotoapkdownload#videocompressoronlinefree#videocompressorproapk
0 notes
Text
Common Mistakes to Avoid with YouTube Video Sizes - Technology Org
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/common-mistakes-to-avoid-with-youtube-video-sizes-technology-org/
Common Mistakes to Avoid with YouTube Video Sizes - Technology Org
In the ever-expanding realm of online video content, YouTube reigns supreme as a platform where creators can showcase their talents, share knowledge, or simply entertain a global audience. However, behind the scenes of captivating content creation lies a technical aspect that is often underestimated but can significantly impact a video’s success – the aspect of YouTube video size, specifically its width and height.
Understanding YouTube Video Size
Before delving into the common mistakes to avoid, it’s essential to grasp what YouTube video size entails. Video size refers to several key elements, including resolution, aspect ratio, and format. All these factors collectively determine how your video appears on YouTube, impacting its visual quality, compatibility, and overall viewer experience.
Resolution: Resolution defines the number of pixels in each dimension, typically denoted as width x height (e.g., 1920×1080 for 1080p). It plays a critical role in determining the video’s sharpness and clarity. YouTube supports a variety of resolutions, from standard definition to high definition and even 4K for the crispest visuals.
Aspect Ratio: Aspect ratio represents the proportional relationship between the YouTube video size width and height. Common aspect ratios for YouTube include 16:9 and 4:3. The choice of aspect ratio influences how your video is displayed on various devices, affecting the viewing experience.
Format: YouTube supports various video formats, such as MP4, AVI, MOV, and WMV. Selecting the right format ensures compatibility across a wide range of devices and playback systems.
Now that we’ve clarified the components of YouTube video size let’s explore the common mistakes that creators often make, and how to avoid them.
1. Neglecting Resolution Considerations
One of the most prevalent mistakes is not paying enough attention to the resolution when preparing videos for YouTube. Using the wrong resolution can result in videos that appear pixelated, blurry, or stretched, detracting from the overall viewing experience, says https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image_resolution . Creators often mistakenly upload content with low resolutions, such as 360p, thinking it will save on file size, but this compromises visual quality.
Avoidance Strategy: Always aim for higher resolutions, such as 720p (1280×720) or 1080p (1920×1080), especially if your content relies on visuals. Higher resolutions provide greater clarity and are better suited for today’s high-definition displays.
2. Ignoring Aspect Ratio Guidelines
Mismatched aspect ratios can lead to awkward black bars or distorted images. It’s crucial to adhere to YouTube’s recommended aspect ratios to ensure your video displays correctly across various devices. The standard aspect ratio for YouTube is 16:9, which works well on most screens.
Avoidance Strategy: Before shooting or editing your video, consider the intended aspect ratio. If you’re using footage with a different aspect ratio, make sure to adjust it properly during editing to avoid unwanted black bars or stretching.
3. Overlooking Video Format Compatibility
Using an unsupported video format can lead to technical issues, preventing your video from playing correctly on YouTube. Neglecting this aspect may result in viewers encountering playback errors, and it can significantly hinder the reach of your content.
Avoidance Strategy: Always export your videos in formats recommended by YouTube, such as MP4. Check YouTube’s official guidelines for a comprehensive list of supported formats to ensure your videos are compatible.
4. Skipping Bitrate Optimization
Bitrate refers to the amount of data processed per unit of time in a video. Insufficient bitrate can lead to compression artifacts, reducing video quality. Conversely, excessively high bitrates can result in larger file sizes, potentially causing buffering issues for viewers with slower internet connections.
Avoidance Strategy: Follow YouTube’s recommended bitrate settings based on your chosen resolution to maintain a balance between quality and accessibility. This ensures viewers can enjoy your content without interruptions.
5. Neglecting Mobile Viewers
With an increasing number of viewers accessing YouTube on mobile devices, it’s essential to consider their experience. Failing to optimize video size for mobile can result in content that doesn’t display correctly or is challenging to watch on smaller screens.
Avoidance Strategy: Test your videos on various mobile devices to ensure they are displayed correctly. Use responsive aspect ratios and ensure that text and important visuals are visible even on smaller screens.
6. Disregarding Thumbnails and Titles
While not directly related to video size, thumbnails and titles play a crucial role in attracting viewers. Ignoring their significance can limit the discoverability of your content, regardless of its quality.
Avoidance Strategy: Create compelling thumbnails and titles that accurately represent your video’s content. Eye-catching thumbnails and descriptive titles can significantly boost click-through rates and engagement.
7. Ignoring Analytics Data
YouTube provides valuable analytics data that can help you understand how viewers interact with your videos. Failing to leverage this data means missing out on opportunities to improve your content and tailor it to your audience’s preferences.
Avoidance Strategy: Regularly review your video analytics to gain insights into audience behavior, watch time, and engagement metrics. Use this information to refine your content strategy and create videos that resonate with your viewers.
In Conclusion: Mastering YouTube Video Size
YouTube video size, encompassing resolution, aspect ratio, format, and other technical considerations, is a critical aspect of content creation on the platform. Avoiding common mistakes related to video size is essential to ensure that your content looks its best, reaches a wider audience, and provides an enjoyable viewing experience. By paying attention to these details and following best practices, creators can maximize the impact of their videos on YouTube and create content that stands out in the crowded online video landscape.
#4K#Accessibility#Analytics#Behavior#comprehensive#compression#content creation#creators#data#details#devices#display#displays#Editing#eye#Global#guidelines#how#how to#images#insights#Internet#issues#it#Landscape#list#Mastering#Mobile#mobile devices#One
0 notes