#cloth brands in pakistan
Text
Oaklynn Kidswear: Revolutionizing Kidswear in Pakistan’s Fashion Industry

The place of Oaklynn kidswear in Pakistan’s clothing industry is unmatched. Oaklynn has, with time become a recognized house of quality, style, and innovation in the current market. Therefore, it means that for all parents and fashion-conscious kids and shoppers looking to purchase the best quality of children clothes, Oaklynn remains the face of quality and style.
#kidswear#Oaklynn Kidswear#kidswear clothing#Oaklynn clothing#Kidswear Oaklynn#clothing brand of Pakistan
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
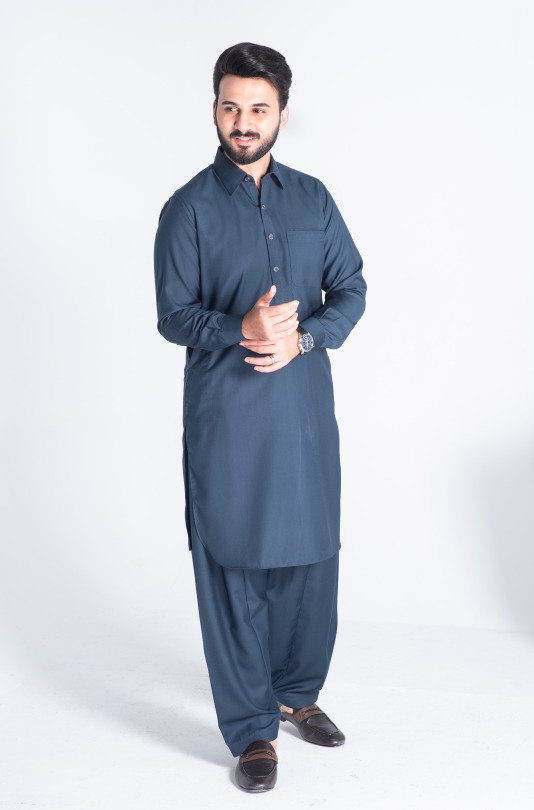
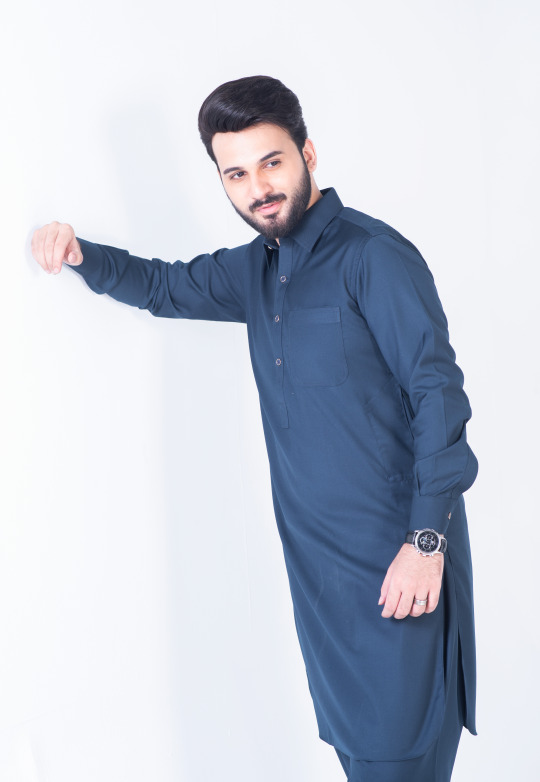
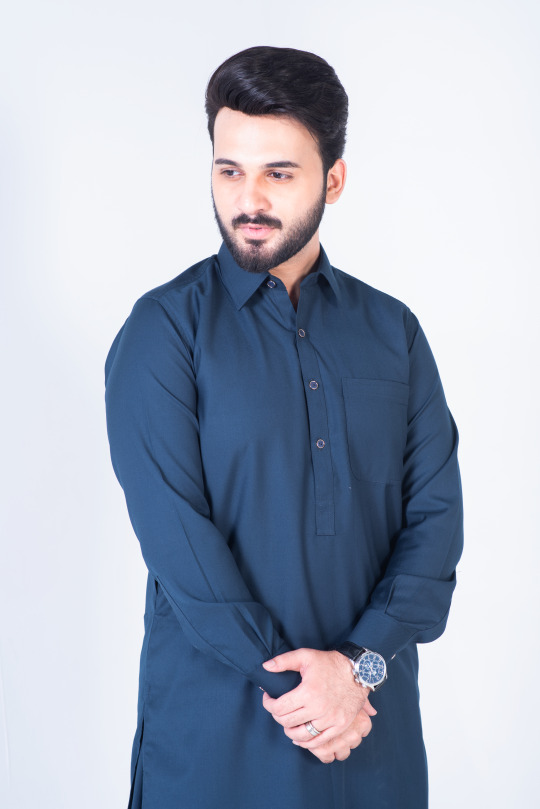
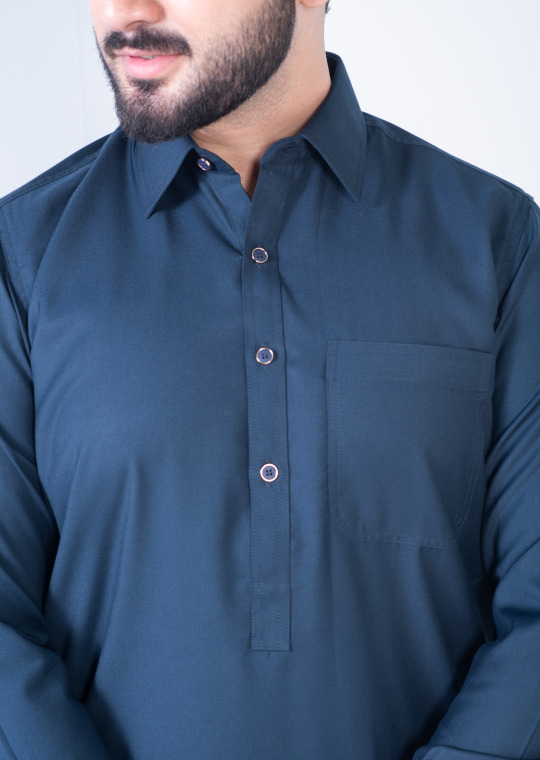
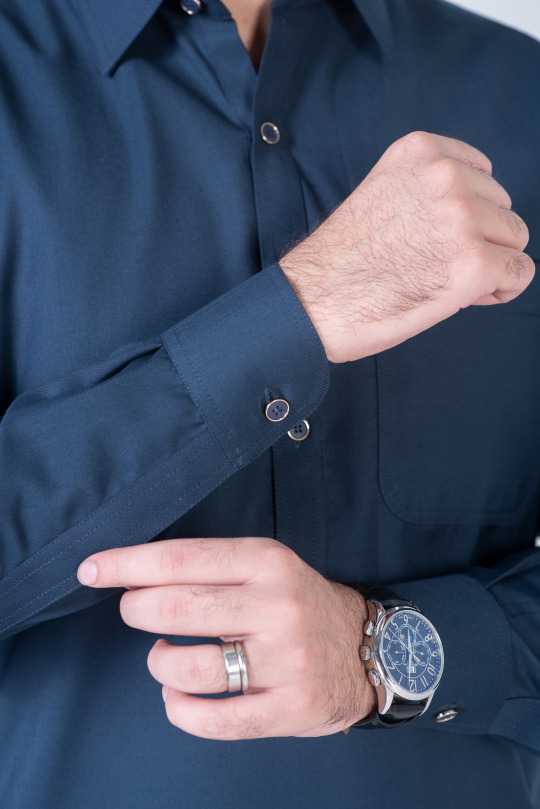





Steel Blue tropical shalwar kameez cut and sew with straight point collar and premium double stitching. Metal buttons create a sleek silhouette, while the one front pocket and two side pockets add utility.
Minimal rivet details of the visible placket and round cuff. With its high-quality fabric and construction, you can wear it all day long and feel confident and comfortable.
#Dandy#dandy designs#shalwar kameez for men#best clothing brand in Pakistan#shalwar kameez#top male clothing brands in Pakistan#top 20 clothing brands in Pakistan#mens shalwar kameez design#top clothing brands in Pakistan#shalwar kameez with waistcoat#shalwar kameez design gents#Pakistani mens shalwar kameez#shalwar kameez color#man kameez design#Pakistan top brands#men's clothing online#online shopping for men#best online clothing brands in Pakistan#best online clothing stores in Pakistan#best online clothing shopping website in Pakistan#men shalwar kameez sale#mens stitched shalwar kameez#steel blue shalwar kameez#steel blue shalwar kameez for men#steel blue shalwar kameez by dandy#buy steel blue shalwar kameez online#blue shalwar kameez for men
1 note
·
View note
Text
#available

0 notes
Text
#KooKoo Kids#Kids Clothing Brand in Pakistan#Kidswear Clothing Brand in Pakistan#Kidswear Collection
0 notes
Text
The Real Cost of the Fashion Industry

Atacama Desert, in Alto Hospicio, Iquique, Chile. (source)
The textile industry is destroying the world. The industry is wasting massive amounts of energy and materials, and polluting the air, the ground and the water supplies. It overwhelmingly exploits it's labour and extracts wealth from colonized countries, especially in Asia. I assume we all broadly understand this, but I think it's useful to have it all laid out in front of you to see the big picture, the core issues causing this destruction and find ways how to effectively move forward.
The concerning trend behind this ever-increasing devastation are shortening of trend cycles, lowering clothing prices and massive amount of wasted products. Still in year 2000 it was common for fashion brands to have two collections per year, while now e.g. Zara produces 24 collections and H&M produces 12-16 collections per year. Clothing prices have fallen (at leas in EU) 30% from 1996 to 2018 when adjusted to inflation, which has contributed to the 40% increase in clothing consumption per person between 1996 and 2012 (in EU). (source) As the revenue made by the clothing industry keep rising - from 2017 to 2021 they doubled (source) - falling prices can only be achieved with increasing worker exploitation and decreasing quality. I think the 36% degrees times clothing are used in average during the last 15 years (source) is a clear indication on the continuing drop in quality of clothing. Clothing production doubled between 2000 and 2015, while 30% of the clothes produced per year are never sold and are often burned instead (source), presumably to prevent the returns from falling due to oversupply.
These all factors are driving people to overconsume. While people in EU keep buying more clothes, they haven't used up to 50% of the clothes in their wardrobe for over a year (source). This overconsumption is only made much worse by the new type of hyper fast fashion companies like SHEIN and Temu, which are using addictive psychological tactics developed by social media companies (source 1, source 2). They are cranking up all those concerning trends I mentioned above.
Under the cut I will go through the statistics of the most significant effects of the industry on environment and people. I will warn you it will be bleak. This is not just a fast fashion problem, basically the whole industry is engaging in destructive practices leading to this damage. Clothing is one of those things that would be actually relatively easy to make without massive environmental and human cost, so while that makes the current state of the industry even more heinous, it also means there's hope and it's possible to fix things. In the end, I will be giving some suggestions for actions we could be doing right now to unfuck this mess.
Carbon emissions
The textile industry is responsible for roughly 10% of the global CO2 emissions, more than aviation and shipping industry combined. This is due to the massive supply chains and energy intensive production methods of fabrics. Most of it can be contributed to the fashion sector since around 60% of all the textile production is clothing. Polyester, a synthetic fiber made from oil which accounts for more than half of the fibers used in the textile industry, produces double the amount of carbon emissions than cotton, accounting for very large proportions of all the emissions by the industry. (source 1, source 2)
Worker exploitation
Majority of the textiles are produced in Asia. Some of the worst working conditions are in Bangladesh, one of the most important garment producers, and Pakistan. Here's an excerpt from EU Parliament's briefing document from 2014 after the catastrophic Rana Plaza disaster:
The customers of garment producers are most often global brands looking for low prices and tight production timeframes. They also make changes to product design, product volume, and production timeframes, and place last-minute orders without accepting increased costs or adjustments to delivery dates. The stresses of such policies usually fall on factory workers.
The wage exploitation is bleak. According to the 2015 documentary The True Cost less than 2% of all garment factory workers earned a living wage (source). Hourly wages are so low and the daily quotas so high, garment workers are often forced through conditions or threats and demand to work extra hours, which regularly leads to 10-12 hour work days (source) and at worst 16 hour workdays (source), often without days off. Sometimes factories won't compensate for extra hours, breaching regulations (source).
Long working hours, repetitive work, lack of breaks and high pressure leads to increased risks of injuries and accidents. Small and even major injuries are extremely common in the industry. A study in three factories in India found that 70% of the workers suffered from musculosceletal symptoms (source). Another qualitative study of female garment workers and factory doctors in Dhaka found that long hours led to eye strain, headaches, fatigue and weight loss in addition to muscular and back pains. According to the doctors interviewed, weight loss was common because the workers work such long hours without breaks, they didn't have enough time to eat properly. (source) Another study in 8 factories in India found that minor injuries were extremely common and caused by unergonomic work stations, poor organization in the work place and lack of safety gear, guidelines and training (source). Safety precautions too are often overlooked to cut corners, which periodically leads to factory accidents, like in 2023 lack of fire exists and fire extinguishers, and goods stacked beyond capacity led to a factory fire in Pakistan which injured dozens of workers (source) or like in 2022 dangerous factory site led to one dead worker and 9 injured workers (source).
Rana Plaza collapse in 2013 is the worst industrial accident in recent history. The factory building did not have proper permits and the factory owner blatantly ignored signs of danger (other businesses abandoned the building a day before the collapse), which led to deaths of 1 134 workers and injuries to 2 500 workers. The factory had or were at the time working for orders of at least Prada, Versace, Primark, Walmart, Zara, H&M, C&A, Mango, Benetton, the Children's Place, El Corte Inglés, Joe Fresh, Carrefour, Auchan, KiK, Loblaw, Bonmarche and Matalan. None of the brands were held legally accountable for the unsafe working conditions which they profited off of. Only 9 of the brands attended a meeting to agree on compensation for the victim's families. Walmart, Carrefour, Auchan, Mango and KiK refused to sight the agreement, it was only signed by Primark, Loblaw, Bonmarche and El Corte Ingles. The compension these companies provided was laughable though. Primemark demanded DNA evidence that they are relatives of one of the victims from these struggling families who had lost their often sole breadwinner for a meager sum of 200 USD (which doesn't even count for two months of living wage in Bangladesh (source)). This obviously proved to be extremely difficult for most families even though US government agreed to donate DNA kits. This is often said to be a turning point in working conditions in the industry, at least in Bangladesh, but while there's more oversight now, as we have seen, there's clearly still massive issues. (source 1, source 2)
One last major concern of working conditions in the industry I will mention is the Xinjiang raw cotton production, which is likely produced mainly with forced labour from Uighur concentration camps, aka slave labour of a suspected genocide. 90% of China's raw cotton production comes from Xinjiang (source). China is the second largest cotton producer in the world, after India, accounting 20% of the yearly global cotton production (source).
Pollution
Synthetic dyes, which synthetic fibers require, are the main cause of water pollution caused by the textile industry, which is estimated to account for 20% of global clean water pollution (source). This water pollution by the textile industry is suspected of causing a lot of health issues like digestive issues in the short term, and allergies, dermatitis, skin inflammation, tumors and human mutations in the long term. Toxins also effect fish and aquatic bacteria. Azo dyes, one of the major pollutants, can cause detrimental effects to aquatic ecosystems by decreasing photosynthetic activity of algae. Synthetic dyes and heavy metals also cause large amounts of soil pollution. Large amounts of heavy metals in soil, which occurs around factories that don't take proper environmental procautions, can cause anaemia, kidney failure, and cortical edoem in humans. That also causes changes in soil texture, decrease in soil microbial diversity and plant health, and changes in genetic structure of organisms growing in the soil. Textile factory waste water has been used for irrigation in Turkey, where other sources of water have been lacking, causing significant damage to the soil. (source)
Rayon produced through viscose process causes significant carbon disulphide and hydrogen sulphide pollution to the environment. CS2 causes cardiovascular, psychiatric, neuropsychological, endocrinal and reproductive disorders. Abortion rates among workers and their partners exposed to CS2 are reported to be significantly higher than in control groups. Many times higher amounts of sick days are reported for workers in spinning rooms of viscose fiber factories. China and India are largest producers of CS2 pollution, accounting respectively 65.74% and 11,11% of the global pollution, since they are also the major viscose producers. Emission of CS2 has increased significantly in India from 26.8 Gg in 2001 to 78.32 Gg in 2020. (source)
Waste
The textile industry is estimated to produce around 92 million tons of textile waste per year. As said before around 30% of the production is never sold and with shortening lifespans used the amount of used clothing that goes to waster is only increasing. This waste is large burned or thrown into landfills in poor countries. (source) H&M was accused in 2017 by investigative journalists of burning up to 12 tonnes of clothes per year themselves, including usable clothing, which they denied claiming they donated clothing they couldn't sell to charity instead (source). Most of the clothing donated to charity though is burned or dumbed to landfills (source).
Most of the waste clothing from rich countries like European countries, US, Australia and Canada are shipped to Chile (source) or African countries, mostly Ghana, but also Burkina Faso and Côte d'Ivoire (source). There's major second-hand fashion industries in these places, but most of the charity clothing is dumbed to landfills, because they are in such bad condition or the quality is too poor. Burning and filling landfills with synthetic fabrics with synthetic dyes causes major air, water and soil pollution. The second-hand clothing industry also suppresses any local clothing production as donated clothing is inherently more competitive than anything else, making these places economically reliant on dumbed clothing, which is destroying their environment and health, and prevents them from creating a more sustainable economy that would befit them more locally. This is not an accident, but required part of the clothing industry. Overproduction let's these companies tap on every new trend quickly, while not letting clothing the prices in rich countries drop so low it would hurt their profits. Production is cheaper than missing a trend.
Micro- and nanoplastics
There is massive amounts of micro- and nanoplastics in all of our environment. It's in our food, drinking water, even sea salt (source). Washing synthetic textiles accounts for roughly 35% of all microplastics released to the environment. It's estimated that it has caused 14 million tonnes of microplastics to accumulate into the bottom of the ocean. (source)
Microplastics build up into the intestines of animals (including humans), and have shown to probably cause cause DNA damage and altered organism behavior in aquatic fauna. Microplastics also contain a lot of the usual pollutants from textile industry like synthetic dyes and heavy metals, which absorb in higher quantities to tissues of animals through microplastics in the intestines. Studies have shown that the adverse effect are higher the longer the microplastics stay in the organism. The effects cause major risks to aquatic biodiversity. (source) The health effects of microplastics to humans are not well known, but studies have shown that they could have adverse effects on digestive, respiratory, endocrine, reproductive and immune systems. (source)
Microplastics degrade in the environment even further to nanoplastics. Nanoplastic being even smaller are found to enter blood circulation, get inside cells and cross the blood-brain barrier. In fishes they have been found to cause neurological damage. Nanoplastics are also in the air, and humans frequently breath them in. Study in office buildings found higher concentration of nanoplastics in indoor air than outdoor air. Inside the nanoplastics are likely caused mostly by synthetic household textiles, and outdoors mostly by car tires. (source) An association between nanoplastics and mitochondrial damage in human respiratory cells was found in a recent study. (source)
Micro and nano plastics are also extremely hard to remove from the environment, making it even more important that we reduce the amount of microplastics we produce as fast as possible.
What can we do?
This is a question that deserves it's own essays and articles written about it, but I will leave you with some action points. Reading about these very bleak realities can easily lead to overwhelming apathy, but we need to channel these horrors into actions. Whatever you do, do not fall into apathy. We don't have the luxury for that, we need to act. These are industry wide problems, that simply cannot be fixed by consumerism. Do not trust any clothing companies, even those who market themselves as ethical and responsible, always assume they are lying. Most of them are, even the so called "good ones". We need legislation. We cannot allow the industry to regulate itself, they will always take the easy way out and lie to their graves. I will for sure write more in dept about what we can do, but for now here's some actions to take, both political and individual ones.
Political actions
Let's start with political actions, since they will be the much more important ones. While we are trying to dismantle capitalism and neocolonialism (the roots of these issues), here's some things that we could do right now. These will be policies that we should be doing everywhere in the world, but especially rich countries, where most of the clothing consumption is taking place. Vote, speak to others, write to your representative, write opinion pieces to your local papers, engage with democracy.
Higher requirements of transparency. Right now product transparency in clothing is laughably low. In EU only the material make up and the origin country of the final product are required to be disclosed. Everything else is up to the company. Mandatory transparency is the only way we can force any positive changes in the production. The minimum of transparency should be: origin countries of the fibers and textiles in the product itself; mandatory reports of the lifecycle emissions; mandatory reports of whole chain of production. Right now the clothing companies make their chain of production intentionally complex, so they have plausible deniability when inevitably they are caught violating environmental or worker protection laws (source). They intentionally don't want to be able to track down their production chain. Forcing them to do so anyway would make it very expensive for them to keep up this unnecessarily complex production chain. These laws are most effective when put in place in large economies like EU or US.
Restrictions on the use of synthetic fibers. Honestly I think they should be banned entirely, since the amount of microplastics in our environment is already extremely distressing and the other environmental effects of synthetic fibers are also massive, but I know there are functions for which they are not easily replaced (though I think they can be replaces in those too, but that's a subject of another post), so we should start with restrictions. I'm not sure how they should be specifically made, I'm not a law expert, but they shouldn't be used in everyday textiles, where there are very easy and obvious other options.
Banning viscose. There are much better options for viscose method that don't cause massive health issues and environmental destruction where ever it's made, like Lyocell. There is absolutely no reason why viscose should be allowed to be sold anywhere.
Governmental support for local production by local businesses. Most of the issues could be much more easily solved and monitored if most clothing were not produced by massive global conglomerations, but rather by local businesses that produce locally. All clothing are made by hand, so centralizing production doesn't even give it advantage in effectiveness (only more profits for the few). Producing locally would make it much more easier to enforce regulations and it would reduce production chains, making production more effective, leaving more profits into the hands of the workers and reducing emissions from transportation. When the production is done by local businesses, the profits would stay in the producing country and they could be taxed and utilized to help the local communities. This would be helpful to do in both exploited and exploiter countries. When done in rich countries who exploit poorer ones, it would reduce the demand for exploitation. In poor countries this is not as easily done, since poor means they don't have money to give around, but maybe this could be a good cause to put some reparations from colonizers and global corporations, which they should pay.
Preventing strategic accounting between subsidiaries and parent companies. Corporate law is obviously not my area of expertise, but I know that allowing corporations to move around the accounting of profits and losses between subsidiaries and parent companies in roughly 1980s, was a major factor in creating this modern global capitalist system, where corporations can very easily manipulate their accounting to utilize tax heavens and avoid taxes where they actually operate, which is how they are upholding this terrible system and extracting the profits from the production countries. How specifically this would be done I can't tell because again I know shit about corporate law, so experts of that field should plan the specifics. Overall this would help deal with a lot of other problems than just the fashion industry. Again for it to be effective a large economic area like EU or US should do this.
Holding companies accountable for their whole chain of production. These companies should be dragged to court and made to answer for the crimes they are profiting of off. We should put fear back into them. This is possible. Victims of child slavery are already doing this for chocolate companies. If it's already not how law works everywhere, the laws should be changed so that the companies are responsible even if they didn't know, because it's their responsibility to find out and make sure they know. They should have been held accountable for the Rana Plaza disaster. Maybe they still could be. Sue the mother fuckers. They should be afraid of us.
Individual actions
I will stress that the previous section is much more important and that there's no need to feel guilty for individual actions. This is not the fault of the average consumer. Still we do need to change our relationship to fashion and consumption. While it's not our fault, one of the ways this system is perpetuated, is by the consumerist propaganda by fashion industry. And it is easier to change our own habits than to change the industry, even if our own habits have little impact. So these are quite easy things we all could do as we are trying to do bigger change to gain some sense of control and keep us from falling to apathy.
Consume less. Better consumption will not save us, since consumption itself is the problem. We consume too much clothing. Don't make impulse purchases. Consider carefully weather you actually need something or if you really really want it. Even only buying second-hand still fuels the industry, so while it's better than buying new, it's still better to not buy.
Take proper care of your clothing. Learn how to properly wash your clothing. There's a lot of internet resources for that. Never wash your wool textiles in washing machine, even if the textile's official instructions allow it. Instead air them regularly, rinse them in cool water if they still smell after airing and wash stains with water or small amount of (wool) detergent. Never use fabric softener! It damages the fabrics, prevents them from properly getting clean and is environmentally damaging. Instead use laundry vinegar for making textiles softer or removing bad smells. (You can easily make laundry vinegar yourself too from white vinegar and water (and essential oils, if you want to add a scent to it) which is much cheaper.) Learn how to take care of your leather products. Most leather can be kept in very good condition for a very long time by occasional waxing with beeswax.
Use the services of dressmakers and shoemakers. Take your broken clothing or clothing which doesn't fit anymore to your local dressmaker and ask them if they can do something about it. Take your broken and worn leather products to your local shoemaker too. Usually it doesn't cost much to get something fixed or refitted and these expert usually have ways to fix things you couldn't even think of. So even if the situation with your clothing or accessory seems desperate, still show it to the dressmaker or shoemaker.
If it's extremely cheap, don't buy it. Remember that every clothing is handmade. Only a small fraction of the cost of the clothing will be paying the wages of the person who made it with their hands. If a shirt costs 5 euros (c. 5,39 USD), it's sewer was only payed mere cents for sewing it. I'm not a quick sewer and it takes me roughly 1-2 hours to cut, prepare and sew a simple shirt, so I'm guessing it would take around half an hour to do all that for a factory worker on a crunch, at the very least 15 minutes. So the hourly pay would still be ridiculously low. However, as I said before, the fact that the workers in clothing factories get criminally low pay is not the fault of the consumer, so if you need a clothing item, and you don't have money to buy anything else than something very cheep, don't feel guilty. And anyway expensive clothing in no way necessarily means reasonable pay or ethical working conditions, cheep clothing just guarantee them.
Learn to recognize higher quality. In addition to exploitation, low price also means low quality, but again high price doesn't guarantee high quality. High quality allows you to buy less, so even if it's not as cheep as low quality, if you can afford it, when you need it, it will be cheaper in long run, and allows you to consume less. Check the materials. Natural fibers are your friends. Do not buy plastic, if it's possible to avoid. Avoid household textiles from synthetic fibers. Avoid textiles with small amounts of spandex to give it stretch, it will shorten the lifespan of the clothing significantly as the spandex quickly wears down and the clothing looses it's shape. Also avoid clothing with rubber bands. They also loose their elasticity very quickly. In some types of clothing (sport wear, underwear) these are basically impossible to avoid, but in many other cases it's entirely possible.
Buy from artisans and local producers, if you can. As said better consumption won't fix this, but supporting artisans and your local producers could help keep them afloat, which in small ways helps create an alternative to the exploitative global corporations. With artisans especially you know the money goes to the one who did the labour and buying locally means less middlemen to take their cut. More generally buy rather from businesses that are located to the same country where the production is, even if it's not local to you. A local business doesn't necessarily produce locally.
Develop your own taste. If you care about fashion and style, it's easy to fall victim to the fashion industry's marketing and trend cycles. That's why I think it's important to develop your personal sense of style and preferences. Pay attention at what type of clothes are comfortable to you. Go through your wardrobe and track for a while which clothing you use most and which least. Understanding your own preferences helps you avoid impulse buying.
Consider learning basics of sewing. Not everyone has the time or interest for this, but if you in anyway might have a bit of both, I suggest learning some very simple and basic mending and reattaching a button.
Further reading on this blog: How to see through the greenwashing propaganda of the fashion industry - Case study 1: Shein
Bibliography
Academic sources
An overview of the contribution of the textiles sector to climate change, 2022, L. F. Walter et al., Frontiers in Environmental Science
How common are aches and pains among garment factory workers? A work-related musculoskeletal disorder assessment study in three factories of south 24 Parganas district, West Bengal, 2021, Arkaprovo Pal et al., J Family Med Prim Care
Sewing shirts with injured fingers and tears: exploring the experience of female garment workers health problems in Bangladesh, 2019, Akhter, S., Rutherford, S. & Chu, C., BMC Int Health Hum Rights
Occupation Related Accidents in Selected Garment Industries in Bangalore City, 2006, Calvin, Sam & Joseph, Bobby, Indian Journal of Community Medicine
A Review on Textile and Clothing Industry Impacts on The Environment, 2022, Nur Farzanah Binti Norarmi et al., International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences
Carbon disulphide and hydrogen sulphide emissions from viscose fibre manufacturing industry: A case study in India, 2022, Deepanjan Majumdar et al., Atmospheric Environment: X
Microplastics Pollution: A Brief Review of Its Source and Abundance in Different Aquatic Ecosystems, 2023, Asifa Ashrafy et al., Journal of Hazardous Materials Advances
Health Effects of Microplastic Exposures: Current Issues and Perspectives in South Korea, 2023, Yongjin Lee et al., Yonsei Medical Journal
Nanoplastics and Human Health: Hazard Identification and Biointerface, 2022, Hanpeng Lai, Xing Liu, and Man Qu, Nanomaterials
Other sources
The impact of textile production and waste on the environment (infographics), 2020, EU
Chile’s desert dumping ground for fast fashion leftovers, 2021, AlJazeera
Fashion - Worldwide, 2022 (updated 2024), Statista
Fashion Industry Waste Statistics & Facts 2023, James Evans, Sustainable Ninja (magazine)
Everything You Need to Know About Waste in the Fashion Industry, 2024, Solene Rauturier, Good on You (magazine)
Textiles and the environment, 2022, Nikolina Šajn, European Parliamentary Research Service
Help! I'm addicted to secondhand shopping apps, 2023, Alice Crossley, Cosmopolitan
Addictive, absurdly cheap and controversial: the rise of China’s Temu app, 2023, Helen Davidson, Guardian
Workers' conditions in the textile and clothing sector: just an Asian affair? - Issues at stake after the Rana Plaza tragedy, 2014, Enrico D'Ambrogio, European Parliamentary Research Service
State of The Industry: Lowest Wages to Living Wages, The Lowest Wage Challenge (Industry affiliated campaign)
Fast Fashion Getting Faster: A Look at the Unethical Labor Practices Sustaining a Growing Industry, 2021, Emma Ross, International Law and Policy Brief (George Washington University Law School)
Dozens injured in Pakistan garment factory collapse and fire, 2023, Hannah Abdulla, Just Style (news media)
India: Multiple factory accidents raise concerns over health & safety in the garment industry, campaigners call for freedom of association in factories to ‘stave off’ accidents, 2022, Jasmin Malik Chua, Business & Human Rights Resource Center
Minimum Wage Level for Garment Workers in the World, 2020, Sheng Lu, FASH455 Global Apparel & Textile Trade and Sourcing (University of Delaware)
Rana Plaza collapse, Wikipedia
Buyers’ compensation for Rana Plaza victims far from reality, 2013, Ibrahim Hossain Ovi, Dhaka Tribune (news media)
World cotton production statistics, updated 2024, The World Counts
Dead white man’s clothes, 2021, Linton Besser, ABC News
#fashion#fashion industry#sustainability#sustainable fashion#sustainable clothing#environment#climate change#i will be continuing the series of how to see through fashion industry propaganda at some point#i just felt compelled to write this because i feel like people so often miss the forest for the trees in this conversation
455 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Waterproof Mattress Cover by FABRICO plus https://fabricoplus.com/product-category/home/waterproofmatresscover/ #mattresscover #waterproofing #bestquality #branding #fabricoplus #bestchoice #bestoption #rightchoice #onlineshopping #onlinestore #woldwideshipping #trustedseller #pakistan #pakistaniwedding #clothing #fabric #outfitgoals #metoday #stylegoals #fashionpost #stylediaries #microinfluencer #blogger #streetstyle #aesthetic #styleaddict #styleinspo #styleinspiration #fashion #todaysoutfit https://www.instagram.com/p/Ce4qnU5N9No/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
#mattresscover#waterproofing#bestquality#branding#fabricoplus#bestchoice#bestoption#rightchoice#onlineshopping#onlinestore#woldwideshipping#trustedseller#pakistan#pakistaniwedding#clothing#fabric#outfitgoals#metoday#stylegoals#fashionpost#stylediaries#microinfluencer#blogger#streetstyle#aesthetic#styleaddict#styleinspo#styleinspiration#fashion#todaysoutfit
0 notes
Text
Nasir Mansoor has spent 40 years fighting for Pakistan’s workers. Whether demanding compensation on behalf of the hundreds of people who died in a devastating 2012 factory fire in Karachi or demonstrating against Pakistani suppliers to global fashion brands violating minimum wage rules, he’s battled many of the country’s widespread labor injustices.
Yet so far, little has improved, said Mansoor, who heads Pakistan’s National Trade Union Federation in Karachi. Despite spending most of his time dealing with issues in the country’s garment sector, labor laws are still routinely flouted inside factories. Not even European Union trade schemes such as the Generalized Scheme of Preferences—which benefits developing countries such as Pakistan but requires them to comply with international conventions on labor rights—have helped curb violations in an industry notorious for them. Regulations and trade protocols look good on paper, but they rarely trickle down to the factory level. “Nobody cares,” Mansoor said. “Not the government who makes commitments, not the brands, and not the suppliers. The workers are suffering.”
But change might finally be on the horizon after Germany’s new Supply Chain Act came into force last year. As Europe’s largest economy and importer of clothing, Germany now requires certain companies to put risk-management systems in place to prevent, minimize, and eliminate human rights violations for workers across their entire global value chains. Signed into law by German Chancellor Olaf Scholz in January 2023, the law covers issues such as forced labor, union-busting, and inadequate wages, for the first time giving legal power to protections that were previously based on voluntary commitments. Companies that violate the rules face fines of up to 8 million euros ($8.7 million).
For decades, Western companies based in countries with highly paid workers and strong labor protections have sourced from low-income countries where such laws don’t exist or are weakly enforced. While this business model cuts costs, it’s made it incredibly difficult for workers to seek justice when problems arise. Given the garment sector’s long history of poor labor conditions—whose victims are a predominantly female workforce—rights groups say the industry will feel some of the highest impacts of new due diligence laws such as Germany’s.
Until now, promises made by fashion brands to safeguard workers stitching clothes in factories around the world have been largely voluntary and poorly monitored. If the promises failed or fell short and that information became public, the main fallout was reputational damage. As governments come to realize that a purely voluntary regimen produces limited results, there is now a growing global movement to ensure that companies are legally required to protect the people working at all stages of their supply chains.
The German law is just the latest example of these new due diligence rules—and it’s the one with the highest impact, given the size of the country’s market. A number of other Western countries have also adopted similar legislation in recent years, including France and Norway. A landmark European Union law that would mandate all member states to implement similar regulation is in the final stages of being greenlighted.
Although the United States has legislation to prevent forced labor in its global supply chains, such as the 2021 Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act, there are no federal laws that protect workers in other countries from abuses that fall short of forced labor. That said, a proposed New York state bill, the Fashion Act, would legally require most major U.S. and international brands to identify, prevent, and remediate human rights violations in their supply chain if passed, with noncompliance subject to fines. Since major fashion brands could hardly avoid selling their products in New York, the law would effectively put the United States on a similar legal level as Germany and France.
Abuses in textile manufacturing have been well documented. Horror stories about brutal violence or building collapses make the news when there’s a major incident, but every day, members of a predominantly female workforce live on low wages, work long hours, and endure irregular contracts. Trade unions, when they are allowed, are often unable to protect workers. A decade ago, the European Parliament described the conditions of garment workers in Asia as “slave labour.”
As of January, Germany’s new law applies to any company with at least 1,000 employees in the country, which covers many of the world’s best-known fast fashion retailers, such as Zara and Primark. Since last January, German authorities say they have received 71 complaints or notices of violations and conducted 650 of their own assessments, including evaluating companies’ risk management.
In Pakistan, the very existence of the German law was enough to spark action. Last year, Mansoor and other union representatives reached out to fashion brands that sourced some of their clothing in Pakistan to raise concerns about severe labor violations in garment factories. Just four months later, he and his colleagues found themselves in face-to-face meetings with several of those brands—a first in his 40-year career. “This is a big achievement,” he said. “Otherwise, [the brands] never sit with us. Even when the workers died in the factory fire, the brand never sat with us.”
Nearly 12 years on from the 2012 fire, which killed more than 250 people, violations are still rife for Pakistan’s 4.4 million garment sector workers, who produce for many of the major global brands. Several of these violations were highlighted in research conducted by FEMNET, a German women’s rights nonprofit, and the European Center for Constitutional and Human Rights (ECCHR), a Berlin-based nongovernmental organization, into how companies covered by the Supply Chain Act were implementing their due diligence obligations in Pakistan. With the help of Mansoor and Zehra Khan, the general secretary of the Home-Based Women Workers Federation, interviews with more than 350 garment workers revealed the severity of long-known issues.
Nearly all workers interviewed were paid less than a living wage, which was 67,200 Pakistan rupees (roughly $243) per month in 2022, according to the Asia Floor Wage Alliance. Nearly 30 percent were even paid below the legal minimum wage of 25,000 Pakistani rupees per month (roughly $90) for unskilled workers. Almost 100 percent had not been given a written employment contract, while more than three-quarters were either not registered with the social security system—a legal requirement—or didn’t know if they were.
When Mansoor, Khan, and some of the organizations raised the violations with seven global fashion brands implicated, they were pleasantly surprised. One German retailer reacted swiftly, asking its supplier where the violations had occurred to sign a 14-point memorandum of understanding to address the issues. (We’re unable to name the companies involved because negotiations are ongoing.) The factory complied, agreeing to respect minimum wages and provide contract letters, training on labor laws, and—for the first time—worker bonuses.
In February, the factory registered an additional 400 workers with the social security system (up from roughly 100) and will continue to enroll more, according to Khan. “That is a huge number for us,” she said.
It’s had a knock-on effect, too. Four of the German brand’s other Pakistani suppliers are also willing to sign the memorandum, Khan noted, which could impact another 2,000 workers or so. “The law is opening up space for [the unions] to negotiate, to be heard, and to be taken seriously,” said Miriam Saage-Maass, the legal director at ECCHR.
After decades of issues being swept under the carpet, it’s a positive step, Mansoor said. But he’s cautious. Of the six remaining global fashion brands contacted, three are in discussions with the union, while three didn’t respond. Implementation is key, he said, particularly because there has already been pushback from some Pakistani factory owners.
Last month, EU member states finally approved a due diligence directive after long delays, during which the original draft was watered down. As it moves to the next stage—a vote in the European Parliament—before taking effect, critics argue that the rules are now too diluted and cover too few companies to be truly effective.
Still, the fact that the EU is acting at all has been described as an important moment, and unionists such as Mansoor and Khan wait thousands of miles away with bated breath for the final outcome. Solidarity from Europe is important, Khan said, and could change the lives of Pakistan’s workers. “The eyes and the ears of the people are looking to [the brands],” Mansoor said. “And they are being made accountable for their mistakes.”
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
reminder:
“In Pakistan, the pandemic has driven workers from their machines and to the factory gates, manifesting their outrage at unpaid wages. Their employers – many of whom are suppliers to international brands – responded with mass layoffs and gun fire.”
instagram
During the #COVID19 crisis large clothing brands are demanding discounts up to 30% from their suppliers.
instagram
https://www.fastcompany.com/90531703/i-dont-really-have-a-choice-la-garment-workers-are-risking-their-lives-to-sew-masks
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
Grocery List
Remember to get raw meat—the kind that resembles the palms of your hands before they turn into angry fists; also, get tomatoes, you’ll know it’s good when it’s as red as your face like when you’re about to burst out of frustration; bite your own tongue, nobody believes a girl your age, instead, pick up some cow tongue for tonight’s curry; leave your heart to rest at home, people become greedy and grabby over things that aren’t theirs; grab milk, skip the skim, you’re not here to impress anyone; get this brand of chai masala, the one that impresses a man, but not enough to make him stay; skip the clothing store; find a salwar kameez cut from the same cloth as you and me, it’s cheaper that way; make sure you grab a newspaper on your way back; don’t stay out too late, it gets dangerous; have you heard about the mother who intentionally broke her daughter’s leg to save her? no amma, and please don’t do that to me, I promise I'll come home to you every night, just like I always do, I have nowhere else to go; only buy this particular brand of sugar, it’s sweet enough to satisfy a man’s desires yet respectful enough to safeguard a woman’s integrity; your split ends need attention; get bhringaraja oil, almond oil, and alma oil—specifically Dabur Vatika, not Parachute, that’s what you’ll need to grow hair long enough to keep you warm on cold nights, when there’s nobody to hold you; no need for jasmine perfumes; bottle your sadness into a scent, like the salty oceans out front; pick up some basmati rice; it’s just around the corner from the mishti store—what, you don’t know where it is? no, ma, there’s nothing there, the mishti store hasn’t been around for years; there was one, at least when I was younger; it must have been Pakistan that razed it to the ground; flames would seep from ruptured points and exit wounds on the streets as I made my way home from school; did you know they would sell rasgulla and rajbhog for a couple hundred taka? just like the amount your parents sold you off? Was it love then?; Mamoni, if it’s love that you’re looking for, you won’t find it for sale anywhere, true love only exists in poetry and books; can’t I buy books and read it out loud enough times until it becomes real enough for me to hold it in my hands?; mark off the food mold at the top of the list; it seems like it’s already shaped you into the woman you needed to become; don’t flash anger on me; anger is what a man exhibits when feeling insecure; are you any less than a man? no, amma, but sometimes I feel lesser than the lizards that crawl out inbetween the cracks of our walls at night; it’s not cruel; our ammas make us do this too, turning us into constant wars in our minds with no clear sight of the goal and out of reach; don’t look too deeply into the man with kajal under his eyes, dressed in a black kurti, even if he greets you with his hands down; he’s not the type to pen dramatic shayaris for you during arguments; he’s fluent only in Hindi, can’t even read Sanskrit, while you effortlessly weave poetry in Bengali, Hindi, Arabic, and hold onto the little Urdu you know, only because I raised you that way; he won’t opt for rickshaws or autos when you can easily walk the 8-minute distance to the grocery store; he’ll buy you the saris; he’ll buy you the jhumkas; he’ll even buy you the mendhi but won’t learn how to apply it for you; he won’t treat you to pani puri from the street vendor outside or let you coax the older bhai to add more chili powder to the mysterious liquid that’ll most definitely give you food poisoning; he won’t center your bindi for you; won’t allow you to adjust the collar of his kurti; doesn’t even consider offering you the last samosa; he’s a man raised among girls who were taught that their thoughts speak louder than words, and sometimes, not to speak at all; he won’t let you experience the freedom you have with me; don’t even entertain the idea of leaving me; oh, and one last thing, don’t forget to wear that dupatta; you always forget; sometimes, I think you do it deliberately to upset me
#excerpt from a book i'll never write#spilled ink#thoughts#writers on tumblr#poetry#writers creed#anger#desi tumblr#desi aesthetic#desi core
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

SHIVAANI TARA DARLING
শিবানি তারা ডার্লিং ইতালির উপকূলে অবস্থিত ফ্যাশন ব্র্যান্ড এবং বুটিক শিভানীর স্রষ্টা। 27 বছর বয়সে, শিবানি আধুনিক দিনের ইতালীয়দের ট্রেন্ডিং লাউঞ্জ এবং বিলাসবহুল পোশাকে ব্যাপক প্রভাব ফেলেছে। প্রতিটি ডিজাইনের ফ্যাব্রিক এবং লেসের মধ্যে বোনা একটি অসাধারণ স্তরের কারুকার্য এবং দক্ষতার অফার করার সময় তার ডিজাইনগুলি জনসাধারণের কাছে সাশ্রয়ী মূল্যের থেকে যায়। তিনি, তার ব্র্যান্ডের পিছনে খ্যাতি থাকা সত্ত্বেও, বেনামী থাকা বেছে নেন।
Shivaani Tara Darling is the creator of the fashion brand and boutique located off the coast of Italy. At 27 years old, Shivaani has made a massive impact on the trending lounge and luxury wear of modern day Italians. Her designs remain affordable to the public while offering a remarkable level of craftsmanship and skill woven into the fabric and lace of each and every design. She, despite the fame behind her brand, chooses to remain anonymous.
not even gonna pretend to know if that even makes sense bc i also dont know bengali ☠☠
FUN FACTS ABOUT VAANI!!
VIRGO!!
introverted ash but had to learn to get over it when she was a kid because she was basically a spokesperson for her family to 'connect' with the youth for political reasons
knows how to speak begali, urdu, english (better than seth even lmao), italian, and spanish.
can shoot a gun but only because she asked for lessons as a teen. before that her parents made her do archery
RICH FAMILY!! this girl was given almost anything she could think of as long as it was 'ladylike' or wtvs. in exchange she had to do literally everything htey wanted hre to which is why she knows so many languages
oldest grandchild and has a 4 year age gap with the next sibling so yikes for her shes stuck with making sure she's the perfect sister
was her grandpa's fave grandkid which is why when she was essentially disowned she was like, literally depressed bc he owuld've had to agree to it
has always liked to draw to the point where she would doodle on all her tests up until her parents told her she couldn't or else they would just take away all her art stuff
learned how to sew from her grandma and loved to make her own clothes. her mom didn't like that though because she thought that that was something poor people did
very veryyy smart and understanding. she would've been a great politician if she wanted. strong bond with her community n everything
super protective over june because if she somehow dies then she has literally no one besides seth. yeah she has friends but definitely not enough for it to be any easier.
whenever she forgets a word in italian she gets super upset with herself bc she feels dumb in front of the people she's speaking to 😭
her middle name is her grandmas name so she tries to avoid having to write it down as much as possible bc it hurtsss
collects pens for fun and has a notebook where she writes down her rating
makes most of junes clothes
obsessed with lego. she tells herself that she buys them for june but really she plays with them more than the kid
has been invited to a ton of weddings but never goes bc a) she wants to say anonymous and b) she hates crowds of people
june's a massive extrovert though so she has to suck it up when she has friends over
was almost kidnapped likeeee twice?? when she lived in pakistan and once in italy (did not end well for the kidnapper though soz seth does not play ☠)
#shivaani.*#resident evil oc#resident evil ocs#ts4#the sims 4#the sims#sims#sims 4#oc#ocs#render#renders#sims render#sims renders#sims 4 renders#sims 4 render#blender render#blender
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Emergence of Premium Kidswear

Premium kidswear isn't just about looking good; it's about providing our children with clothing that supports their active lifestyles while ensuring comfort and durability. High-end kidswear clothing often features superior fabrics, meticulous craftsmanship, and innovative designs that cater to the unique needs of children.
1 note
·
View note
Text
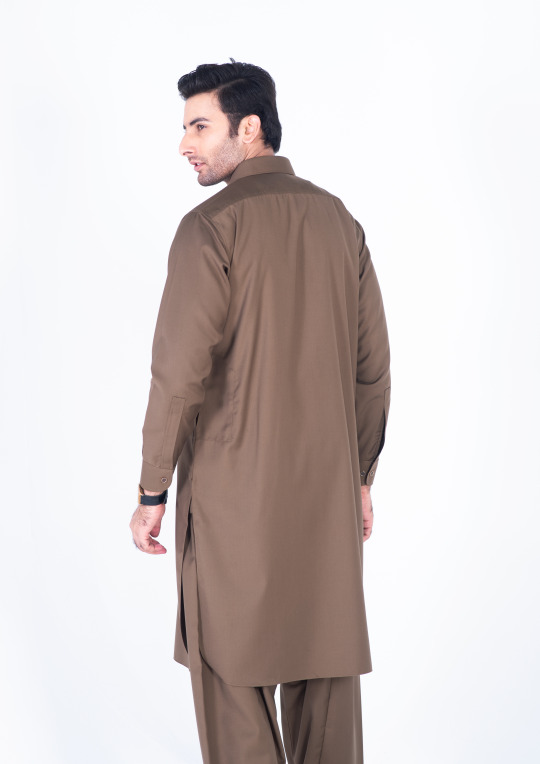
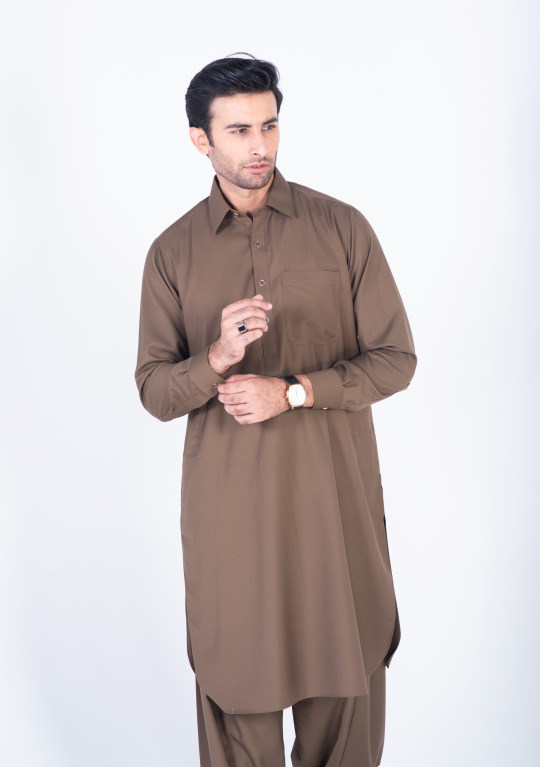
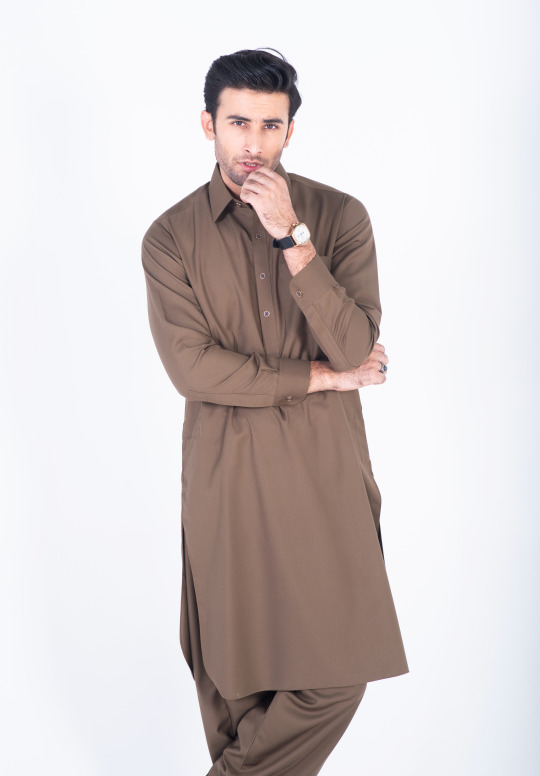
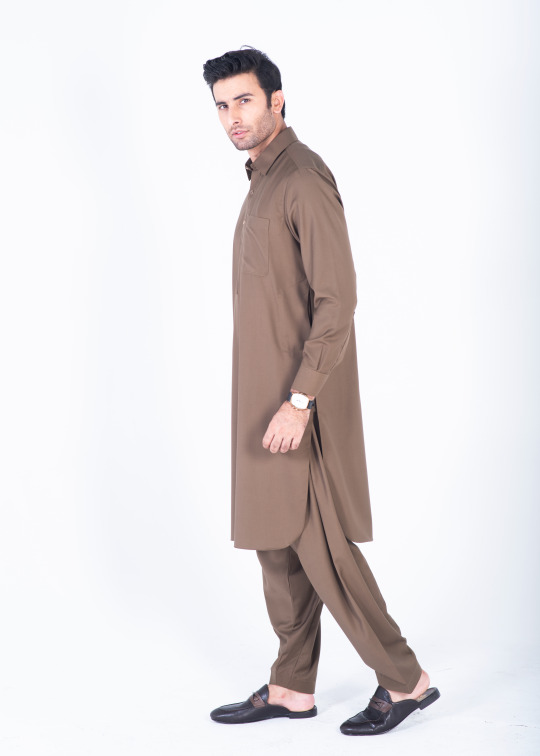
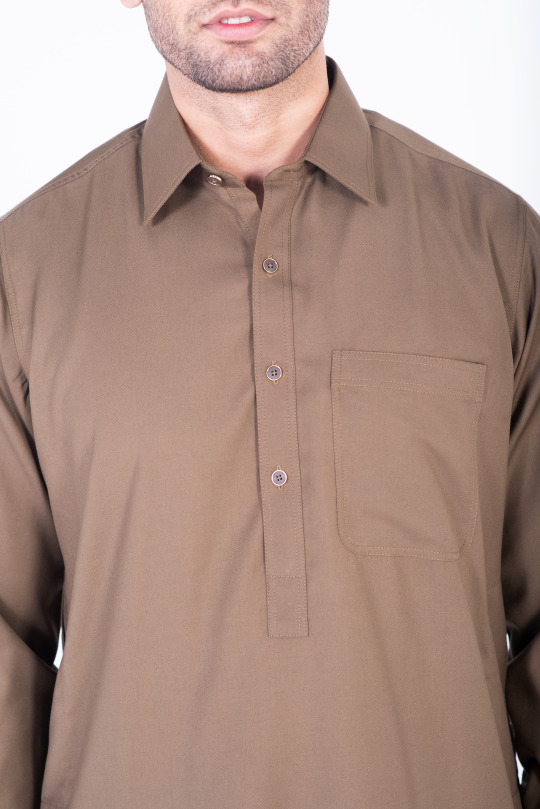





Chestnut brown shalwar kameez double stitched in pure cotton with rounded cuff and straight point collar. This shalwar kameez has a tropical fabric and its classic design of one front pocket and two side pockets, and metal buttons add more touch to its look.
Get the season’s chestnut brown kameez shalwar with our luxury superfine fabric of visible placket. This outfit is best for any occasion as it is the perfect combination of style and comfort.
#Dandy#dandy designs#shalwar kameez for men#best clothing brand in Pakistan#shalwar kameez#top male clothing brands in Pakistan#top 20 clothing brands in Pakistan#mens shalwar kameez design#top clothing brands in Pakistan#shalwar kameez with waistcoat#shalwar kameez design gents#Pakistani mens shalwar kameez#shalwar kameez color#man kameez design#Pakistan top brands#men's clothing online#online shopping for men#best online clothing brands in Pakistan#best online clothing stores in Pakistan#best online clothing shopping website in Pakistan#men shalwar kameez sale#mens stitched shalwar kameez#Chestnut Brown Shalwar Kameez#Chestnut Brown Shalwar Kameez for men
0 notes
Text
Mahira Khan Biography, Age, Height, Husband, Son, Wedding, Net Worth & More
Mahira Khan is a famous Pakistani actress and Former VJ. She has many television shows, movies, web series, modeling shoots, advertisements, etc. Mahira is known as Pakistan’s sexiest woman.

Mahira’s father was born in Delhi, British India. After the partition, he migrated to Pakistan with his family.
Mahira started her acting career at the age of 27 years older.
In 2013, Mahira won her 1st Television award “Satellite Best TV Actress” for best acting in the Humsafar drama serial.
In 2023, Mahira launched her own clothes brand “M By Mahira”.
Read More About Mahira Khan
#mahira khan#mahira khan chhattisgarh#mahira khan age#mahira khan husband#mahira khan hot#mahira khan movies and tv shows#mahira khan son#mahira khan raees#mahira khan drama list#mahira khan parliament#mahira khan instagram#mahira khan net worth#mahira khan pakistani actress#mahira khan movies#pakistani actress mahira khan#mahira khan height#mahira khan sexy#mahira khan and ranbir#mahira khan son age#mahira khan serial#mahira khan humsafar#mahira khan chhattisgarh biography#fawad khan and mahira khan#mahira khan husband name#mahira khan serials#mahira khan and husband#who is mahira khan#mahira khan and shahrukh khan#mahira khan chhattisgarh instagram#mahira khan biography
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sarojini Nagar Market | Delhi Sarojini Nagar Market
Named after the renowned Indian freedom fighter and poet, Sarojini Naidu, Sarojini Nagar Market stands as a vibrant centerpiece in Delhi’s bustling shopping landscape. This market, a treasure trove for bargain hunters, seamlessly blends history with the eclectic energy of one of Delhi’s most popular shopping destinations.

History and Evolution of Sarojini Nagar
The #SarojiniNagar Market, a name that resonates with the spirit of Delhi’s vibrant shopping culture, owes its identity to the esteemed freedom fighter, Sarojini Naidu. Nestled in South West Delhi, this market is encircled by prominent neighborhoods, including Safdarjung Enclave and Chanakyapuri, the latter being a diplomatic hub with embassies like those of the United States and Russia. Originally christened as ‘Vinay Nagar’, the market underwent a significant transformation, both in name and function, to honor Sarojini Naidu in the 1970s.
Initial Purpose and Evolution:
Originally Built: For the Sarojini Nagar Government Colony residents, catering to their daily needs.
Transformation: From ‘Vinay Nagar’ to ‘Sarojini Nagar’, reflecting its evolution from a local market to a bustling shopping destination.
Diverse Offerings: Known for its export surplus garments, stylish outfits, and fabrics at unbeatable prices.
Market Structure:
Divisions: Comprising Central Market, Babu Market, and Sabzi Market.
Shop Count: Central Market houses 200 shops, while Babu Market boasts 110.
Specialties: Export surplus items including stylish clothes, fake designer bags, and fashionable jewelry.
The market’s inception in the 1950s and its establishment in 1965 marked the beginning of a journey tailored to accommodate the needs of refugees from Pakistan post-Partition. Over the decades, Sarojini Nagar Market has transformed into a pivotal shopping destination, attracting a diverse crowd with its low prices and a wide range of products, thanks to the sale of export surplus from global brands like Zara or H&M. This evolution underscores the market’s role in offering affordable retail options, making it an essential visit for both locals and tourists.
Know More
1 note
·
View note
Text
KooKoo Kids Kidswear Clothing Brand in Pakistan
KooKoo Kids is the best kidswear clothing brand in Pakistan that offers online clothes for girls and boys from 1 to 12 years old. Grab now with up to 60% off. Visit our website https://thekookookids.com
#KooKoo Kids#Kids Clothing Brand in Pakistan#Kidswear Clothing Brand in Pakistan#Kidswear Collection
1 note
·
View note