#Public-Policy --- THAT
Text
A general tip for students who are sending those dreaded Religious Absence Emails to your professors: Rather than asking permission to take the day(s) off, politely let them know that you will be taking the day(s) off.
In other words, consider not saying this:
"May I miss class on [date] so I can observe [holiday]?"
It's not that there's anything wrong with the above, per se. But because it's phrased as a request, it risks coming across as optional — a favor you hope to be granted. Problem is, favors are not owed, and so unfortunately asking permission opens the door for the professor to respond "Thanks for asking. No, you may not. :)"
Instead, try something along the lines of:
"I will need to miss class on [date] because I will be observing [holiday]. I wanted to let you know of this conflict now, and to ask your assistance in making arrangements for making up whatever material I may miss as a result of this absence."
This is pretty formal language (naturally, you can and should tweak it to sound more like your voice). But the important piece is that, while still being respectful, it shifts the focus of the discussion so that the question becomes not "Is it okay for me to observe my religion?", but rather, "How can we best accommodate my observance?"
Because the first question should not be up for debate: freedom of religion is a right, not a favor. And the second question is the subject you need to discuss.
(Ideally, do this after you've looked up your school's policy on religious absences, so you know what you're working within and that religious discrimination is illegal. Just in case your professor forgot.)
#this strategy got me through all of college#and some professors were a lot more supportive than others but no one ever told me no#because i didn't give them the chance#jumblr#judaism#religious absences#relevant to other minority religions as well#as well as non-religious accommodations#and non-school settings#dandelion says#jewish dandelion#note: the policy/legality details will vary depending on where you live and go to school#when i talk about religious discrimination laws this is based on public universities in the us
17K notes
·
View notes
Text

Source

Source
#end homelessness#homelessness#housing#housing crisis#news#current events#politics#us politics#government#public policy#progressive#the left#capitalism
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
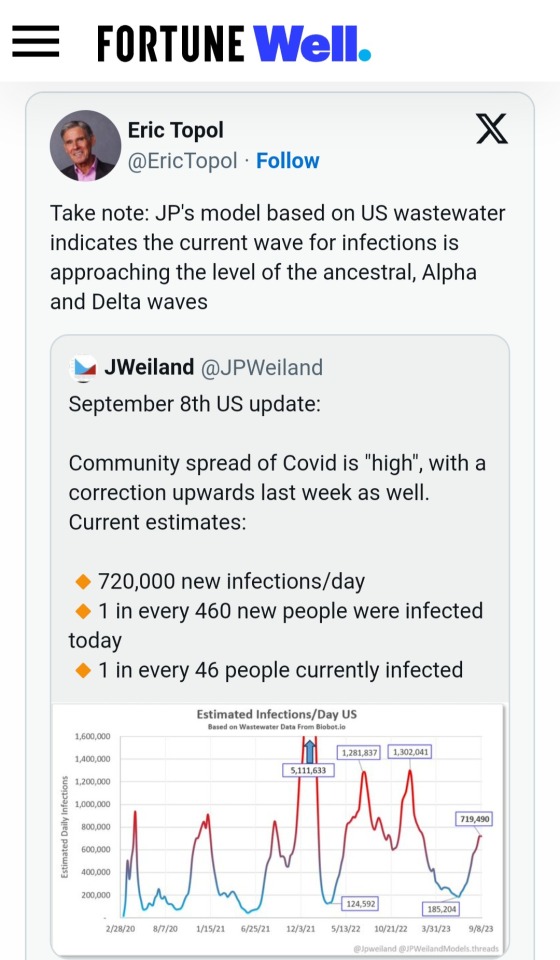
"The pandemic is over"
795 notes
·
View notes
Note
how do you feel about gen ed requirements in college majors?
Oooh, that's a good question, because I feel genuinely conflicted about it.
Cards on the table, I should say that I picked my undergraduate university precisely because it had a broad core curriculum of literature, philosophy, art, music, and science (and because it didn't require math) for all majors.
As a freshman, I had very wide-ranging interests and wasn't sure what I wanted to do for my major when I started, even though I started taking as many history electives as possible starting in my second semester. But even though I didn't need much time to "find myself," I still feel that the "well-rounded" education I received was good for my intellectual development, my ability to participate in society, and so forth.
And then there's the fact that my grad school career was entirely dependent on history classes being used as gatekeeping requirements for poli sci, communications, and sociology majors, which generated a steady demand for TA labor. So I do recognize that gen ed requirements are absolutely essential to the economics of many disciplines, and universities would have to rethink how they fund departments if they got rid of gen ed requirements altogether.
That being said, I do recognize that these kinds of requirements can also be really bad for students who are quite different from myself. As generations of students forced to take Physics for Poets or English for Engineers can testify, it can be legitimately frustrating for people who have a strength and an interest in an area that they want to develop that they can't specialize and instead have their academic success depend in part on their weakest subjects. Moreover, given the rise of tuition prices and student debt, every additional class a student has to take is more of a burden on their shoulders.
This is where I see a symptoms/cause long-term/short-term thing going on. Because of increasing competition, credentialism and credential inflation, and the increasing uncertainty about whether rising educational costs will be requited with secure employment at a professional income, I totally understand those people who want to make the college experience shorter and more specialized as a way to save money.
At the same time, if we ask ourselves why we provide education as a society (as opposed to making employers pay the bill for the training of their workforce), I go the other way. In order for modern democracy to function effectively, we need the population to have a baseline of quantitative reasoning so that they can tell when someone is lying with statistics, to be able to close-read texts so that they can tell when someone is lying with rhetoric, and to be sufficiently media-literate to spot propaganda and misinformation.
That being said, if we are going to say to young people that they have to acquire all these skills, the quid-pro-quo is that we have to provide education as a de-commodified public good, and guarantee a job to everyone, so that the economic incentives pushing us towards shorter, more specialized higher education no longer exist.
416 notes
·
View notes
Text
Normalize updating laws and regulations that are no longer fit for purpose.
Normalize working with powerful enemies to find a solution where everybody wins.
Normalize mutual compromise.
Normalize collaboration over opposition.
Normalize civil discourse on divisive issues.
Normalize good faith and the principle of charity.
Normalize discussion of specific social, political, and economic issues.
Normalize advocacy for specific and implementable policy reforms to to tackle said issues.
Normalize imperfect solutions.
Normalize civic engagement.
Normalize public sector action.
Normalize incremental success.
Normalize improving society instead of destroying and rebuilding it from the ground up.
NORMALIZE PROGRESS!!!
#solarpunk#hopepunk#politics#political discourse#public policy#civic engagement#civic duty#georgism#transit#urban planning#accessibility#disability justice#disabled#healthy politics#policymakers#social justice#societal improvement#retain hope#societal progress#climate change#climate action#advocacy#trains#political activist#political action#activism#hanlon's razor#good regulations work#good faith arguments#good faith
225 notes
·
View notes
Text
In defense of bureaucratic competence

Sure, sometimes it really does make sense to do your own research. There's times when you really do need to take personal responsibility for the way things are going. But there's limits. We live in a highly technical world, in which hundreds of esoteric, potentially lethal factors impinge on your life every day.
You can't "do your own research" to figure out whether all that stuff is safe and sound. Sure, you might be able to figure out whether a contractor's assurances about a new steel joist for your ceiling are credible, but after you do that, are you also going to independently audit the software in your car's antilock brakes?
How about the nutritional claims on your food and the sanitary conditions in the industrial kitchen it came out of? If those turn out to be inadequate, are you going to be able to validate the medical advice you get in the ER when you show up at 3AM with cholera? While you're trying to figure out the #HIPAAWaiver they stuck in your hand on the way in?
40 years ago, Ronald Reagan declared war on "the administrative state," and "government bureaucrats" have been the favored bogeyman of the American right ever since. Even if Steve Bannon hasn't managed to get you to froth about the "Deep State," there's a good chance that you've griped about red tape from time to time.
Not without reason, mind you. The fact that the government can make good rules doesn't mean it will. When we redid our kitchen this year, the city inspector added a bunch of arbitrary electrical outlets to the contractor's plans in places where neither we, nor any future owner, will every need them.
But the answer to bad regulation isn't no regulation. During the same kitchen reno, our contractor discovered that at some earlier time, someone had installed our kitchen windows without the accompanying vapor-barriers. In the decades since, the entire structure of our kitchen walls had rotted out. Not only was the entire front of our house one good earthquake away from collapsing – there were two half rotted verticals supporting the whole thing – but replacing the rotted walls added more than $10k to the project.
In other words, the problem isn't too much regulation, it's the wrong regulation. I want our city inspectors to make sure that contractors install vapor barriers, but to not demand superfluous electrical outlets.
Which raises the question: where do regulations come from? How do we get them right?
Regulation is, first and foremost, a truth-seeking exercise. There will never be one obvious answer to any sufficiently technical question. "Should this window have a vapor barrier?" is actually a complex question, needing to account for different window designs, different kinds of barriers, etc.
To make a regulation, regulators ask experts to weigh in. At the federal level, expert agencies like the DoT or the FCC or HHS will hold a "Notice of Inquiry," which is a way to say, "Hey, should we do something about this? If so, what should we do?"
Anyone can weigh in on these: independent technical experts, academics, large companies, lobbyists, industry associations, members of the public, hobbyist groups, and swivel-eyed loons. This produces a record from which the regulator crafts a draft regulation, which is published in something called a "Notice of Proposed Rulemaking."
The NPRM process looks a lot like the NOI process: the regulator publishes the rule, the public weighs in for a couple of rounds of comments, and the regulator then makes the rule (this is the federal process; state regulation and local ordinances vary, but they follow a similar template of collecting info, making a proposal, collecting feedback and finalizing the proposal).
These truth-seeking exercises need good input. Even very competent regulators won't know everything, and even the strongest theoretical foundation needs some evidence from the field. It's one thing to say, "Here's how your antilock braking software should work," but you also need to hear from mechanics who service cars, manufacturers, infosec specialists and drivers.
These people will disagree with each other, for good reasons and for bad ones. Some will be sincere but wrong. Some will want to make sure that their products or services are required – or that their competitors' products and services are prohibited.
It's the regulator's job to sort through these claims. But they don't have to go it alone: in an ideal world, the wrong people will be corrected by other parties in the docket, who will back up their claims with evidence.
So when the FCC proposes a Net Neutrality rule, the monopoly telcos and cable operators will pile in and insist that this is technically impossible, that there is no way to operate a functional ISP if the network management can't discriminate against traffic that is less profitable to the carrier. Now, this unity of perspective might reflect a bedrock truth ("Net Neutrality can't work") or a monopolists' convenient lie ("Net Neutrality is less profitable for us").
In a competitive market, there'd be lots of counterclaims with evidence from rivals: "Of course Net Neutrality is feasible, and here are our server logs to prove it!" But in a monopolized markets, those counterclaims come from micro-scale ISPs, or academics, or activists, or subscribers. These counterclaims are easy to dismiss ("what do you know about supporting 100 million users?"). That's doubly true when the regulator is motivated to give the monopolists what they want – either because they are hoping for a job in the industry after they quit government service, or because they came out of industry and plan to go back to it.
To make things worse, when an industry is heavily concentrated, it's easy for members of the ruling cartel – and their backers in government – to claim that the only people who truly understand the industry are its top insiders. Seen in that light, putting an industry veteran in charge of the industry's regulator isn't corrupt – it's sensible.
All of this leads to regulatory capture – when a regulator starts defending an industry from the public interest, instead of defending the public from the industry. The term "regulatory capture" has a checkered history. It comes out of a bizarre, far-right Chicago School ideology called "Public Choice Theory," whose goal is to eliminate regulation, not fix it.
In Public Choice Theory, the biggest companies in an industry have the strongest interest in capturing the regulator, and they will work harder – and have more resources – than anyone else, be they members of the public, workers, or smaller rivals. This inevitably leads to capture, where the state becomes an arm of the dominant companies, wielded by them to prevent competition:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/06/05/regulatory-capture/
This is regulatory nihilism. It supposes that the only reason you weren't killed by your dinner, or your antilock brakes, or your collapsing roof, is that you just got lucky – and not because we have actual, good, sound regulations that use evidence to protect us from the endless lethal risks we face. These nihilists suppose that making good regulation is either a myth – like ancient Egyptian sorcery – or a lost art – like the secret to embalming Pharaohs.
But it's clearly possible to make good regulations – especially if you don't allow companies to form monopolies or cartels. What's more, failing to make public regulations isn't the same as getting rid of regulation. In the absence of public regulation, we get private regulation, run by companies themselves.
Think of Amazon. For decades, the DoJ and FTC sat idly by while Amazon assembled and fortified its monopoly. Today, Amazon is the de facto e-commerce regulator. The company charges its independent sellers 45-51% in junk fees to sell on the platform, including $31b/year in "advertising" to determine who gets top billing in your searches. Vendors raise their Amazon prices in order to stay profitable in the face of these massive fees, and if they don't raise their prices at every other store and site, Amazon downranks them to oblivion, putting them out of business.
This is the crux of the FTC's case against Amazon: that they are picking winners and setting prices across the entire economy, including at every other retailer:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/25/greedflation/#commissar-bezos
The same is true for Google/Facebook, who decide which news and views you encounter; for Apple/Google, who decide which apps you can use, and so on. The choice is never "government regulation" or "no regulation" – it's always "government regulation" or "corporate regulation." You either live by rules made in public by democratically accountable bureaucrats, or rules made in private by shareholder-accountable executives.
You just can't solve this by "voting with your wallet." Think about the problem of robocalls. Nobody likes these spam calls, and worse, they're a vector for all kinds of fraud. Robocalls are mostly a problem with federation. The phone system is a network-of-networks, and your carrier is interconnected with carriers all over the world, sometimes through intermediaries that make it hard to know which network a call originates on.
Some of these carriers are spam-friendly. They make money by selling access to spammers and scammers. Others don't like spam, but they have lax or inadequate security measures to prevent robocalls. Others will simply be targets of opportunity: so large and well-resourced that they are irresistible to bad actors, who continuously probe their defenses and exploit overlooked flaws, which are quickly patched.
To stem the robocall tide, your phone company will have to block calls from bad actors, put sloppy or lazy carriers on notice to shape up or face blocks, and also tell the difference between good companies and bad ones.
There's no way you can figure this out on your own. How can you know whether your carrier is doing a good job at this? And even if your carrier wants to do this, only the largest, most powerful companies can manage it. Rogue carriers won't give a damn if some tiny micro-phone-company threatens them with a block if they don't shape up.
This is something that a large, powerful government agency is best suited to addressing. And thankfully, we have such an agency. Two years ago, the FCC demanded that phone companies submit plans for "robocall mitigation." Now, it's taking action:
https://arstechnica.com/tech-policy/2023/10/telcos-filed-blank-robocall-plans-with-fcc-and-got-away-with-it-for-2-years/
Specifically, the FCC has identified carriers – in the US and abroad – with deficient plans. Some of these plans are very deficient. National Cloud Communications of Texas sent the FCC a Windows Printer Test Page. Evernex (Pakistan) sent the FCC its "taxpayer profile inquiry" from a Pakistani state website. Viettel (Vietnam) sent in a slide presentation entitled "Making Smart Cities Vision a Reality." Canada's Humbolt VoIP sent an "indiscernible object." DomainerSuite submitted a blank sheet of paper scrawled with the word "NOTHING."
The FCC has now notified these carriers – and others with less egregious but still deficient submissions – that they have 14 days to fix this or they'll be cut off from the US telephone network.
This is a problem you don't fix with your wallet, but with your ballot. Effective, public-interest-motivated FCC regulators are a political choice. Trump appointed the cartoonishly evil Ajit Pai to run the FCC, and he oversaw a program of neglect and malice. Pai – a former Verizon lawyer – dismantled Net Neutrality after receiving millions of obviously fraudulent comments from stolen identities, lying about it, and then obstructing the NY Attorney General's investigation into the matter:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/08/31/and-drown-it/#starve-the-beast
The Biden administration has a much better FCC – though not as good as it could be, thanks to Biden hanging Gigi Sohn out to dry in the face of a homophobic smear campaign that ultimately led one of the best qualified nominees for FCC commissioner to walk away from the process:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/12/15/useful-idiotsuseful-idiots/#unrequited-love
Notwithstanding the tragic loss of Sohn's leadership in this vital agency, Biden's FCC – and its action on robocalls – illustrates the value of elections won with ballots, not wallets.
Self-regulation without state regulation inevitably devolves into farce. We're a quarter of a century into the commercial internet and the US still doesn't have a modern federal privacy law. The closest we've come is a disclosure rule, where companies can make up any policy they want, provided they describe it to you.
It doesn't take a genius to figure out how to cheat on this regulation. It's so simple, even a Meta lawyer can figure it out – which is why the Meta Quest VR headset has a privacy policy isn't merely awful, but long.
It will take you five hours to read the whole document and discover how badly you're being screwed. Go ahead, "do your own research":
https://foundation.mozilla.org/en/privacynotincluded/articles/annual-creep-o-meter/
The answer to bad regulation is good regulation, and the answer to incompetent regulators is competent ones. As Michael Lewis's Fifth Risk (published after Trump filled the administrative agencies with bootlickers, sociopaths and crooks) documented, these jobs demand competence:
https://memex.craphound.com/2018/11/27/the-fifth-risk-michael-lewis-explains-how-the-deep-state-is-just-nerds-versus-grifters/
For example, Lewis describes how a Washington State nuclear waste facility created as part of the Manhattan Project endangers the Columbia River, the source of 8 million Americans' drinking water. The nuclear waste cleanup is projected to take 100 years and cost 100 billion dollars. With stakes that high, we need competent bureaucrats overseeing the job.
The hacky conservative jokes comparing every government agency to the DMV are not descriptive so much as prescriptive. By slashing funding, imposing miserable working conditions, and demonizing the people who show up for work anyway, neoliberals have chased away many good people, and hamstrung those who stayed.
One of the most inspiring parts of the Biden administration is the large number of extremely competent, extremely principled agency personnel he appointed, and the speed and competence they've brought to their roles, to the great benefit of the American public:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/10/18/administrative-competence/#i-know-stuff
But leaders can only do so much – they also need staff. 40 years of attacks on US state capacity has left the administrative state in tatters, stretched paper-thin. In an excellent article, Noah Smith describes how a starveling American bureaucracy costs the American public a fortune:
https://www.noahpinion.blog/p/america-needs-a-bigger-better-bureaucracy
Even stripped of people and expertise, the US government still needs to get stuff done, so it outsources to nonprofits and consultancies. These are the source of much of the expense and delay in public projects. Take NYC's Second Avenue subway, a notoriously overbudget and late subway extension – "the most expensive mile of subway ever built." Consultants amounted to 20% of its costs, double what France or Italy would have spent. The MTA used to employ 1,600 project managers. Now it has 124 of them, overseeing $20b worth of projects. They hand that money to consultants, and even if they have the expertise to oversee the consultants' spending, they are stretched too thin to do a good job of it:
https://slate.com/business/2023/02/subway-costs-us-europe-public-transit-funds.html
When a public agency lacks competence, it ends up costing the public more. States with highly expert Departments of Transport order better projects, which need fewer changes, which adds up to massive costs savings and superior roads:
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4522676
Other gaps in US regulation are plugged by nonprofits and citizen groups. Environmental rules like NEPA rely on the public to identify and object to environmental risks in public projects, from solar plants to new apartment complexes. NEPA and its state equivalents empower private actors to sue developers to block projects, even if they satisfy all environmental regulations, leading to years of expensive delay.
The answer to this isn't to dismantle environmental regulations – it's to create a robust expert bureaucracy that can enforce them instead of relying on NIMBYs. This is called "ministerial approval" – when skilled government workers oversee environmental compliance. Predictably, NIMBYs hate ministerial approval.
Which is not to say that there aren't problems with trusting public enforcers to ensure that big companies are following the law. Regulatory capture is real, and the more concentrated an industry is, the greater the risk of capture. We are living in a moment of shocking market concentration, thanks to 40 years of under-regulation:
https://www.openmarketsinstitute.org/learn/monopoly-by-the-numbers
Remember that five-hour privacy policy for a Meta VR headset? One answer to these eye-glazing garbage novellas presented as "privacy policies" is to simply ban certain privacy-invading activities. That way, you can skip the policy, knowing that clicking "I agree" won't expose you to undue risk.
This is the approach that Bennett Cyphers and I argue for in our EFF white-paper, "Privacy Without Monopoly":
https://www.eff.org/wp/interoperability-and-privacy
After all, even the companies that claim to be good for privacy aren't actually very good for privacy. Apple blocked Facebook from spying on iPhone owners, then sneakily turned on their own mass surveillance system, and lied about it:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/11/14/luxury-surveillance/#liar-liar
But as the European experiment with the GDPR has shown, public administrators can't be trusted to have the final word on privacy, because of regulatory capture. Big Tech companies like Google, Apple and Facebook pretend to be headquartered in corporate crime havens like Ireland and Luxembourg, where the regulators decline to enforce the law:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/05/15/finnegans-snooze/#dirty-old-town
It's only because of the GPDR has a private right of action – the right of individuals to sue to enforce their rights – that we're finally seeing the beginning of the end of commercial surveillance in Europe:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2022/07/americans-deserve-more-current-american-data-privacy-protection-act
It's true that NIMBYs can abuse private rights of action, bringing bad faith cases to slow or halt good projects. But just as the answer to bad regulations is good ones, so too is the answer to bad private rights of action good ones. SLAPP laws have shown us how to balance vexatious litigation with the public interest:
https://www.rcfp.org/resources/anti-slapp-laws/
We must get over our reflexive cynicism towards public administration. In my book The Internet Con, I lay out a set of public policy proposals for dismantling Big Tech and putting users back in charge of their digital lives:
https://www.versobooks.com/products/3035-the-internet-con
The most common objection I've heard since publishing the book is, "Sure, Big Tech has enshittified everything great about the internet, but how can we trust the government to fix it?"
We've been conditioned to think that lawmakers are too old, too calcified and too corrupt, to grasp the technical nuances required to regulate the internet. But just because Congress isn't made up of computer scientists, it doesn't mean that they can't pass good laws relating to computers. Congress isn't full of microbiologists, but we still manage to have safe drinking water (most of the time).
You can't just "do the research" or "vote with your wallet" to fix the internet. Bad laws – like the DMCA, which bans most kinds of reverse engineering – can land you in prison just for reconfiguring your own devices to serve you, rather than the shareholders of the companies that made them. You can't fix that yourself – you need a responsive, good, expert, capable government to fix it.
We can have that kind of government. It'll take some doing, because these questions are intrinsically hard to get right even without monopolies trying to capture their regulators. Even a president as flawed as Biden can be pushed into nominating good administrative personnel and taking decisive, progressive action:
https://doctorow.medium.com/joe-biden-is-headed-to-a-uaw-picket-line-in-detroit-f80bd0b372ab?sk=f3abdfd3f26d2f615ad9d2f1839bcc07
Biden may not be doing enough to suit your taste. I'm certainly furious with aspects of his presidency. The point isn't to lionize Biden – it's to point out that even very flawed leaders can be pushed into producing benefit for the American people. Think of how much more we can get if we don't give up on politics but instead demand even better leaders.
My next novel is The Lost Cause, coming out on November 14. It's about a generation of people who've grown up under good government – a historically unprecedented presidency that has passed the laws and made the policies we'll need to save our species and planet from the climate emergency:
https://us.macmillan.com/books/9781250865939/the-lost-cause
The action opens after the pendulum has swung back, with a new far-right presidency and an insurgency led by white nationalist militias and their offshore backers – seagoing anarcho-capitalist billionaires.
In the book, these forces figure out how to turn good regulations against the people they were meant to help. They file hundreds of simultaneous environmental challenges to refugee housing projects across the country, blocking the infill building that is providing homes for the people whose homes have been burned up in wildfires, washed away in floods, or rendered uninhabitable by drought.
I don't want to spoil the book here, but it shows how the protagonists pursue a multipronged defense, mixing direct action, civil disobedience, mass protest, court challenges and political pressure to fight back. What they don't do is give up on state capacity. When the state is corrupted by wreckers, they claw back control, rather than giving up on the idea of a competent and benevolent public system.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/10/23/getting-stuff-done/#praxis
#pluralistic#nerd harder#private right of action#privacy#robocalls#fcc#administrative competence#noah smith#spam#regulatory capture#public choice theory#nimbyism#the lost cause#the internet con#evidence based policy#small government#transit#praxis#antitrust#trustbusting#monopoly
379 notes
·
View notes
Video
What if it wasn’t
these are policy choices.
598 notes
·
View notes
Text
There are three main models of disability that are in common use. The moral model, the medical model, and the social model.
You may not have heard of the moral model before, but if you are disabled, you have felt the impact of it. The moral model is disability as a failure of character. It sources the problem of disability in the character of the disabled person. It's the people who insist that if you just tried harder, were better, had a better attitude, that you would no longer be disabled. It is a model that is used by ableists in order to conceptualize of disability as a failing of the individual. An extreme example of this mindset are the Christian Scientists, who believe that all illnesses and disabilities should be healed by the grace of their god and that if you are not healed, something is wrong with you. It is the the most cruel of the models, and the least successful at assisting disabled people.
The medical model is the model used by the medical establishment and by those who put their stock in medical authority. It sources the problem of disability in the body. It measures disability against a theoretical average person, and seeks to make disabled people match that average person more closely. This model works very well for disabled people with disabilities that can be measured, have a potential treatment plan, and want their disability gone. It does not work very well for people who do not match all three criteria. If they match the first and second but not the third, then strict adherents of the medical model often fall back on the moral model, stating that they are stupid, lazy, or selfish for not being interested in being cured. This also often happens if treatment fails to improve the condition of the disabled person.
The social model is a newer model, largely designed by disability activists and scholars and often defined in opposition to the medical model. It sources the problem of disability in the interaction between the disabled person and their physical and social environment. It argues that the solution of disability is to change the environment so that impairments are no longer an issue. This model works very well for disabled people who consider their disability not to be an issue when fully accommodated. It does not work well for people who consider their disability an inherent impairment and/or desire a cure. Strict adherents of the social model often fall back on the moral model when considering these people, stating that they are short-sighted or that they worship the medical model. These are the people who state things such as that depression would not exist in a world without capitalism.
When a disabled person fails to behave as expected by the model a person has of disability, the moral model is almost always the fallback position, because many people cannot conceive of why someone would disagree with them other than a lack of good character. This is a problem, because the moral model proposes no solution but to ignore or abuse the disabled person until they behave as expected.
Another notable interaction is that adherents of the medical model can often be persuaded to support the more traditional parts of the social model, such as providing large text resources to people with impaired vision, so long as there is empirical research backing it. However, they rarely support more radical arguments that challenge how we define disability and how society should be structured or restructured.
All three models have major failure points. The moral model fails every disabled person it is applied to. The medical and social models both fail different disabled people when adhered to strictly. The best approach at the moment seems to be hybridizing the social and medical models, so that they cover each other's weak points and fit the needs of the widest spectrum of disabled people. The main barrier to this is that they are often defined in opposition to each other.
#I personally adhere to a hybridized model of the medical and social models that I informally call the independence model#If an individual is disabled or not is their personal call#as is what they do about it.#it does need to be acknowledged who is considered disabled by our society and how that will affect someone#even if they do not consider themselves disabled#Medical care and accommodations should be available to whoever wants it#but should never be forced or pressed on anyone#Public spaces and events should be accessible to as wide a variety of people as possible#The main failure point of the independence model is that it does not call for a single clear solution#and basing a model around personal choice makes it difficult to make policy proposals
144 notes
·
View notes
Text

and each one of these is public policy entered in the records
#politics#racism#black history month#antiblackness#us politics#black history#public policy#social justice#social issues#ion know y they turned off reblogs for this post but its a banger
58 notes
·
View notes
Text
I will say, I've seen some folks saying that the legal precedent for "raw" AI art being automatically in the public domain, due to that case with the monkey selfie showing that art not made by a human is auto-PD, would be the "death" of AI art
But speaking with the people who actually care about the art side of AI art, most of us see it as not only a good compromise, but even as a win-win for everyone except the megacorps.
Cause, a lot of us into the ethical side of AI art still aren't much fond of copyright, because most of us are pinko leftist-types. And, it maeks sense from a principle of reciprocity that an artform that draws from the commons (Which is what AI art actually is rather than "stealing," but that's for its own post) should in turn contribute to that commons too.
And if that so happens to let AI artists continue practicing their craft while still preventing megacorps from laying off traditional artists (because megacorps want stuff they can own outright), well, that's three birds with one stone...
#art#ai art#copyright#policy#compromise#ai artists are not your enemies#at least the ones who aren't dicks about it#public domain
524 notes
·
View notes
Text
My New Article at WIRED
Tweet
So, you may have heard about the whole zoom “AI” Terms of Service clause public relations debacle, going on this past week, in which Zoom decided that it wasn’t going to let users opt out of them feeding our faces and conversations into their LLMs. In 10.1, Zoom defines “Customer Content” as whatever data users provide or generate (“Customer Input”) and whatever else Zoom generates from our uses of Zoom. Then 10.4 says what they’ll use “Customer Content” for, including “…machine learning, artificial intelligence.”
And then on cue they dropped an “oh god oh fuck oh shit we fucked up” blog where they pinky promised not to do the thing they left actually-legally-binding ToS language saying they could do.
Like, Section 10.4 of the ToS now contains the line “Notwithstanding the above, Zoom will not use audio, video or chat Customer Content to train our artificial intelligence models without your consent,” but it again it still seems a) that the “customer” in question is the Enterprise not the User, and 2) that “consent” means “clicking yes and using Zoom.” So it’s Still Not Good.
Well anyway, I wrote about all of this for WIRED, including what zoom might need to do to gain back customer and user trust, and what other tech creators and corporations need to understand about where people are, right now.
And frankly the fact that I have a byline in WIRED is kind of blowing my mind, in and of itself, but anyway…
Also, today, Zoom backtracked Hard. And while i appreciate that, it really feels like decided to Zoom take their ball and go home rather than offer meaningful consent and user control options. That’s… not exactly better, and doesn’t tell me what if anything they’ve learned from the experience. If you want to see what I think they should’ve done, then, well… Check the article.
Until Next Time.
Tweet
Read the rest of My New Article at WIRED at A Future Worth Thinking About
#ai#artificial intelligence#ethics#generative pre-trained transformer#gpt#large language models#philosophy of technology#public policy#science technology and society#technological ethics#technology#zoom#privacy
123 notes
·
View notes
Text
"It’s not just the larger American audience that misinterprets the meaning of Juneteenth. Across the diaspora the message gets distorted, reflected in how most Juneteenth event flyers often have the colors of the Pan-African movement instead of Juneteenth’s actual colors. The official Juneteenth colors are red, white, and blue. The presence of the patriotic colors symbolizes the American flag, serving as a poignant reminder that slaves and their descendants were, and continue to be, an integral part of the United States."
- Shelby Stewart in "As Juneteenth Becomes Co-Opted, Don't Forget Its Texas Roots" for Okayplayer
#juneteenth#texas#black history#american history#public policy#federal holiday#black culture#american culture#history#journalism#politics#usa#music journalism
156 notes
·
View notes
Note
Which federal laws and policies would you get rid of or modify in order to help the American labor movement.
I was looking through the labor law tag on my blog and your ask reminded me I haven't actually written a comprehensive post about this on Tumblr. (Indeed, you'd have to go back to my old, old policy blog from 2009...it's been a while.)
One silver lining of the Sisyphean struggle to restore American labor law that's been going on since the 1970s is that the labor movement and their allies in Congress, academia, think tanks, and progressive media have been thinking through this very issue of "what reforms would make a real difference" for a long time. I'm not going to say it's a solved question, but the research literature is pretty robust.

For the purposes of this post, I'm going to focus on the three most recent reform packages: the Employee Free Choice Act that was the main vehicle during the Obama years, Bernie Sanders' Workplace Democracy Act (which was introduced repeatedly between 1992 and 2018), and the Richard L. Trumka Protecting the Right to Organize Act (PRO Act) that is the current proposal of the Democratic legislative caucuses. There's going to be quite a bit of overlap between these proposals, because it's very much an iterative process where allies in the same movement are trading ideas with one another and trying to stay abreast of new developments, but I'll try to tease out some of the similarities and differences.
EFCA
While EFCA contained a number of provisions that sought to close various loopholes in U.S labor law, the three main provisions largely target the flaws that have made it extremely difficult to win a union through the National Labor Relations Act process devised in 1935 that has turned into a Saw-style gauntlet thanks to the professionalization of union-busting and the Federalist Society's strategy of death-by-a-thousand-cuts:
"Card check." Probably the most common pattern of union-busting in the workplace today is a war of attrition by management waged by an industry of specialized law firms. Generally what happens is that the union files for election with a super-majority of ~70% workers having signed union cards, then management delays the vote as long as possible to give their hired "union-avoidance" firm to systematically intimidate, surveil, propagandize, and divide workers, up to and including illegally firing pro-union workers pour encouragez les autres. Over several months, what happens is that the initial 70% of pro-union support starts to erode as workers decide it's just too dangerous to stick their necks out, until the vote happens and the union loses either by a squeaker or a landslide.
Card check short-circuits this process by just saying that if the union files with a majority of cards, you skip the election and the union is recognized. And for all the pearl-clutching by the right, this is actually how labor law works in many democratic countries, because the idea of a fair election that lets management participate is an oxymoron.
Arbitrated first contract. In the event that enough workers keep the faith and actually vote for a union, management's next move is to draw out collective bargaining for a year or more. After a year, the original vote is no longer considered binding and employers can push for a "decertification" vote, which they usually win because workers either give up hope or change jobs. So this provision says that if the two sides can't reach an agreement on a first contract within 120 days, a Federal arbitrator will just impose one, so that at least for two years there will be a union contract no matter what management wants.
Strengthening enforcement. As I said above, one of the problems with existing labor law is that there are basically no penalties for management knowingly breaking the law; companies literally just budget in a line-item and do it anyway. This provision would allow unions to file an injunction against employers for unfair labor practices or ULPs (at present, injunctions are only required for violations done by unions), and would add triple back pay for illegal firings and fines of $20,000 for each ULP. This would make union-busting much more expensive, because companies routinely rack up hundreds and hundreds of them during a campaign.
Workplace Democracy Act
Sanders' proposal includes the main proposals from EFCA, and adds a bunch of additional reforms, like mis-classifying workers as independent contractors, banning captive audience meetings, making "joint employers" liable for labor law violations by franchisees, legalizing secondary boycotts, and requiring employers to report to the NLRB on all anti-union expenditures during a campaign and barring anyone convicted of an unfair labor practice from being hired for anti-union campaigns and making "union-avoidance" consultants liable for fines for ULPs (which would kill the "union-avoidance" industry, because they commit ULPs for a living).
PRO Act
The PRO Act is very much an updating of the previous efforts we've talked about. It bans captive audience meetings, allows for secondary strikes and boycotts, massively increases fines and allows for compensatory damages, ends mis-classification, speeds up the election process, etc.
It also contains a couple new and ambitious proposals:
it allows unions to sue management in court instead of having to complain to the NLRB, which opens management up to a very expensive legal proceeding and discovery.
it bans "right-to-work" as established by the Taft-Hartley Act.
it requires that any worker who's fired for pro-union activity be immediately reinstated while their unfair labor practice process or civil lawsuit is going through the process. This would be enormous just on its own, because it changes the entire veto structure of illegal firing. As it stands, employers fire people and maybe maybe have to pay some back wages in a couple years when the worker has found another job and is unlikely to come back. This would reverse the balance of power, such that the worker is immediately back and other workers can see that they can speak up without getting fired, which makes illegal firings a giant waste of time and money for management.
In terms of stuff that's not on this list that I would add, I would say that an enormous difference could be made by simply making it illegal for management to lock-out their workers or hire scabs. You do that, and unions can win almost every strike.
75 notes
·
View notes
Text
Today the EPA finalized rules that fully ban the use of asbestos in the US. This is a massive step forward for the safety of American workers and American consumers. Asbestos is linked to more than 40,000 deaths every year, not just from lung and laryngeal cancer and mesothelioma, but also from ovarian cancer.
This is yet another instance where who resides in the White House matters. This was a part of the Biden policy regarding preventing, treating and curing cancers brought to fruition.
Donald Trump is a big supporter of asbestos and asbestos products, and wanted to increase its use in the US despite its risks and harms being well-known for a half century. If re-elected Trump will undoubtedly do his best to undo today’s rule, and he and the far right caucus of congressional Republicans would like to eliminate the EPA altogether.
(It is probably just a giant coincidence that the majority of asbestos in the world is produced in Russia by oligarch-owned companies. Probably.)
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
Officers working for Gov. Greg Abbott’s border security initiative have been ordered to push small children and nursing babies back into the Rio Grande, and have been told not to give water to asylum seekers even in extreme heat, according to an email from a Department of Public Safety trooper who described the actions as “inhumane.”
The July 3 account, reviewed by Hearst Newspapers, discloses several previously unreported incidents the trooper witnessed in Eagle Pass, where the state of Texas has strung miles of razor wire and deployed a wall of buoys in the Rio Grande.
According to the email, a pregnant woman having a miscarriage was found late last month caught in the wire, doubled over in pain. A four-year-old girl passed out from heat exhaustion after she tried to go through it and was pushed back by Texas National Guard soldiers. A teenager broke his leg trying to navigate the water around the wire and had to be carried by his father.
The email, which the trooper sent to a superior, suggests that Texas has set “traps” of razor wire-wrapped barrels in parts of the river with high water and low visibility. And it says the wire has increased the risk of drownings by forcing migrants into deeper stretches of the river.
The trooper called for a series of rigorous policy changes to improve safety for migrants, including removing the barrels and revoking the directive on withholding water.
“Due to the extreme heat, the order to not give people water needs to be immediately reversed as well,” the trooper wrote, later adding: “I believe we have stepped over a line into the inhumane.”
Department of Public Safety spokesman Travis Considine did not comment on all the contents of the trooper’s email, but said there is no policy against giving water to migrants.
Considine also provided an email from DPS Director Steven McCraw on Saturday calling for an audit to determine if more can be done to minimize the risk to migrants. McCraw wrote troopers should warn migrants not to cross the wire, redirect them to ports of entry and to closely watch for anyone who needs medical attention.
In another email, McCraw acknowledged that there has been an increase in injuries from the wire, including seven incidents reported by Border Patrol where migrants needed “elevated medical attention” from July 4 to July 13. Those were in addition to the incidents detailed by the trooper.
“The purpose of the wire is to deter smuggling between the ports of entry and not to injure migrants,” McCraw wrote. “The smugglers care not if the migrants are injured, but we do, and we must take all necessary measures to mitigate the risk to them including injuries from trying to cross over the concertina wire, drownings and dehydration.”
The incidents detailed in the email come as Abbott has stepped up efforts in recent weeks to physically bar migrants from entering the country through his Operation Lone Star initiative, escalating tensions between state and federal officials and drawing increased scrutiny from humanitarian groups who say the state is endangering asylum seekers. The most aggressive initiatives have been targeted at Eagle Pass.
The state has also now deployed a wall of floating buoys in the Rio Grande, which triggered complaints over the weekend from Mexico.
Federal Border Patrol officials have issued internal warnings that the razor wire is preventing their agents from reaching at-risk migrants and increasing the risk of drownings in the Rio Grande, Hearst Newspapers reported last week.
The DPS trooper expressed similar concerns, writing that the placement of the wire along the river “forces people to cross in other areas that are deeper and not as safe for people carrying kids and bags.”
The trooper’s email sheds new light on a series of previously reported drownings in the river during a one-week stretch earlier this month, including a mother and at least one of her two children, who federal Border Patrol agents spotted struggling to cross the Rio Grande on July 1.
According to the email, a DPS boat found the mother and one of the children, who went under the water for a minute.
They were pulled from the river and given medical care before being transferred to EMS, but were later declared deceased at the hospital. The second child was never found, the email said.
The Governor has said he is taking necessary steps to secure the border and accused federal officials of refusing to do so.
“Texas is deploying every tool and strategy to deter and repel illegal crossings between ports of entry as President Biden’s dangerous open border policies entice migrants from over 150 countries to risk their lives entering the country illegally," said Andrew Mahaleris, Abbott’s press secretary. "President Biden has unleashed a chaos on the border that’s unsustainable, and we have a constitutional duty to respond to this unprecedented crisis.”
The DPS trooper’s email details four incidents in just one day in which migrants were caught in the wire or injured trying to get around it.
On June 30, troopers found a group of people along the wire, including a 4-year-old girl who tried to cross the wire and was pressed back by Texas Guard soldiers “due to the orders given to them,” the email says. The DPS trooper wrote that the temperature was “well over 100 degrees” and the girl passed out from exhaustion.
“We provided treatment to the unresponsive patient and transferred care to EMS,” the trooper wrote. A spokesperson for the Texas National Guard did not respond to a request for comment.
In another instance, troopers found a 19-year-old woman “in obvious pain” stuck in the wire. She was cut free and given a medical assessment, which determined she was pregnant and having a miscarriage. She was then transferred to EMS.
The trooper also treated a man with a “significant laceration” in his left leg, who said he had cut it while trying to free his child who was “stuck on a trap in the water,” describing a barrel with razor wire “all over it.” And the trooper treated a 15-year-old boy who broke his right leg walking in the river because the razor wire was “laid out in a manner that it forced him into the river where it is unsafe to travel.”
In another instance, on June 25, troopers came across a group of 120 people camped out along a fence set up along the river. The group included several small children and babies who were nursing, the trooper wrote. The entire group was exhausted, hungry and tired, the trooper wrote. The shift officer in command ordered the troopers to “push the people back into the water to go to Mexico,” the email says.
The trooper wrote that the troopers decided it was not the right thing to do “with the very real potential of exhausted people drowning.” They called command again and expressed their concerns and were given the order to “tell them to go to Mexico and get into our vehicle and leave,” the trooper wrote. After they left, other troopers worked with Border Patrol to provide care to the migrants, the email said.
The trooper did not respond to a request for comment Monday. His email was shared by a confidential source with knowledge of border operations. It was unclear whether the trooper received a response from the sergeant he’d messaged.
Considine acknowledged that DPS was aware of the email and provided the additional agency emails in response. Those emails detail seven other incidents reported by federal border agents in which migrants were injured on the wires, including a child who was taken to the hospital on Thursday with cuts on his left arm, a mother and child who were taken to the hospital on Wednesday with “minor lacerations” on their “lower extremities,” and another migrant taken to San Antonio on July 4 to receive treatment for “several lacerations” that required staples.
Victor Escalon, a DPS director who oversees South Texas, wrote in an email Friday to other agency officials that troopers “may need to open the wire to aid individuals in medical distress, maintain the peace, and/or to make an arrest for criminal trespass, criminal mischief, acts of violence, or other State crimes.”
“Our DPS medical unit is assigned to this operation to address medical concerns for everyone involved,” Escalon wrote. “As we enforce State law, we may need to aid those in medical distress and provide water as necessary.”
#us politics#news#houston chronicle#2023#immigration policy#immigration and customs enforcement#immigration reform#immigrants#texas#us border patrol#texas national guard#texas department of public safety#gov. greg abbott#Hearst Newspapers#eagle pass#rio grande#mexico#us mexico border#Travis Considine#Steven McCraw#Operation Lone Star#Andrew Mahaleris
114 notes
·
View notes
Text
Yes, Public Policies can make a different.
Top 3 Points:
The numbers of suicides are at their lowest during winter (December, January, February). It is not clear why, but they tend to peak in spring and early summer. “If you are depressed, your brain and body react differently to the increase in exposure to sunlight. It may make you suffer more from insomnia, for example. You become more restless, anxious, so the level of anxiety increases and it may worsen your depression."
Drinking culture is strongly correlated with suicidal rates. “Our suicide rate has gone down at the same rate that our drinking has gone down. So it’s strongly related. And now when, especially the youth, [people] don’t drink that much any more, of course they don’t have that many suicides.”
The suicide rate fell 51% from 1990 to 2022. In 2022 Finland recorded 1,512 deaths by suicide, according to the THL, in what was then a population of just under 5 million. By contrast, in 2022 Finland had 740 suicides, in a population of 5.6 million – more in line with (though slightly higher than) the EU average.

30 notes
·
View notes