#NOVA | PBS
Text
Atomic Secrets: The Scientists Who Built The Atom Bomb 💣
Science and the military converged under a cloak of secrecy at Los Alamos National Laboratory. As part of the Manhattan Project, Los Alamos — both its very existence and the work that went on there — was hidden from Americans during World War II.
Many of the thousands of scientists on the project were not officially aware of what they were working on. Though they were not permitted to talk to anyone about their work, including each other, by 1945 some had figured out that they were in fact building an atomic bomb.
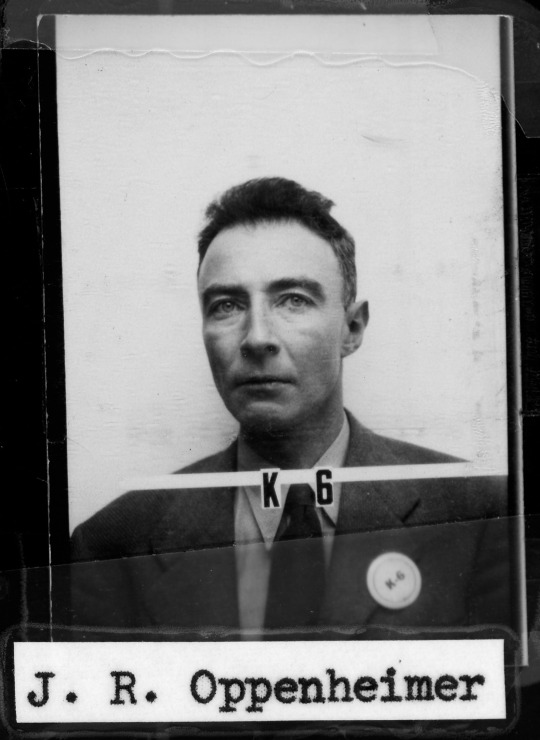

In 1943 J. Robert Oppenheimer was named the director of the Bomb Project at Los Alamos, a self-contained area protected -- and completely controlled -- by the U.S. Army. Special driver's licenses had no names on them, just ID numbers. Credit: Courtesy of the Los Alamos National Laboratory Archives

Robert Oppenheimer's wife Kitty was not above scrutiny. All who were affiliated with the project -- and their spouses -- were thoroughly screened and had a security file with the FBI. Credit: Courtesy of the F.B.I.
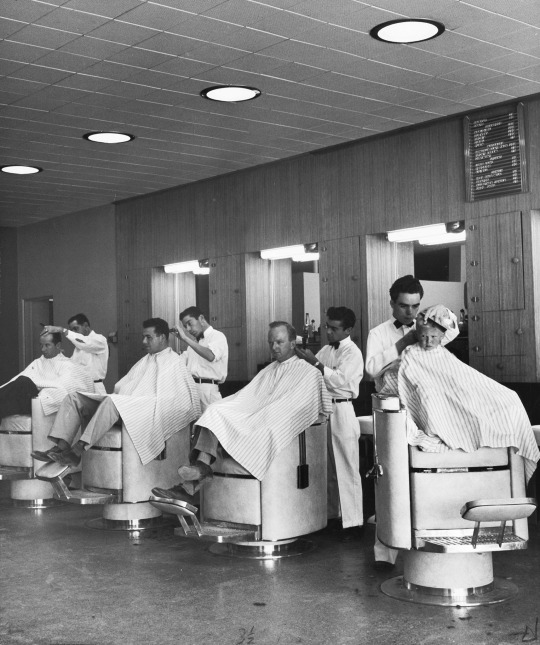

Less than a year after Oppenheimer proposed using the remote desert site for the laboratory, Los Alamos was already home to a thousand scientists, engineers, support staff… and their families. By the end of the war the population was over 6,000, and the compound included amenities like this barber shop. Credit: Time Life/Getty Images

Atomic Bomb Project employees having lunch at Los Alamos. Though food was often in scant supply, residents made the best of life in their isolated community by putting on plays and organizing Saturday night square dances. Some singles’ parties in the dormitories reportedly served a brew of lab alcohol and grapefruit juice, cooled with dry ice out of a 32-gallon GI can. Credit: Copyright Bettmann/CORBIS
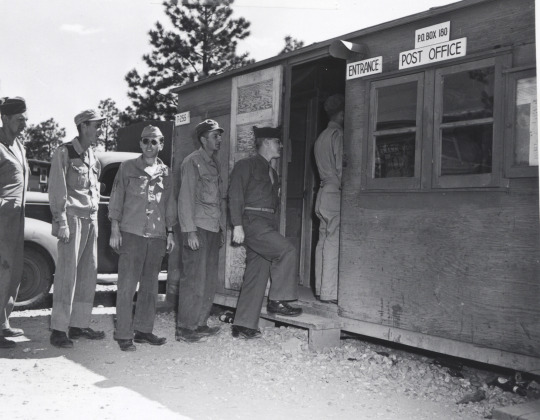

Completely self-contained, the Los Alamos facility did not officially exist in its early years except as a post office box. Scientists’ families were mostly kept in the dark about the nature of the project, learning the truth only after the bomb was dropped on Hiroshima. Credit: Courtesy of the Los Alamos National Laboratory Archives

Credited with inventing the cyclotron, University of California-Berkeley physicist Ernest Lawrence (squatting, center) looks on as Robert Oppenheimer points out something on the 184” particle accelerator. Harvard University supplied the cyclotron that was used to develop the atomic bomb. Credit: Copyright CORBIS
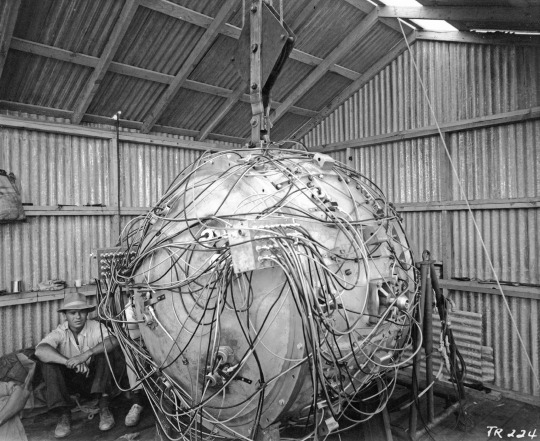

The Trinity bomb was the first atomic bomb ever tested. It was detonated in the Jornada del Muerto (Dead Man’s Walk) Desert, near Alamogordo, New Mexico, on July 16, 1945. The test was a resounding success. The United States would drop similar bombs on Japan just three weeks later. Credit: Courtesy of the Los Alamos National Laboratory Archives

Oppenheimer and General Leslie Groves inspect the melted remnants of the 100-foot steel tower that held the Trinity bomb. Ensuring that the testing of a bomb with unknown strength would remain completely secret, the government chose a location that was so remote they had to import their water from over 150 miles away. Credit: Copyright CORBIS

Oppenheimer and General Leslie Groves stand in front of a map of Japan, just five days before the bombing of Hiroshima. Credit: Copyright CORBIS

Though there was no evidence that Oppenheimer had betrayed his country in any way, several officials called his loyalty into question in the Cold War environment of 1954. After being subjected to months of hearings, “the most famous physicist in the world” eventually lost his government security clearance. Credit: Reprinted courtesy of TIME Magazine
#Atomic Secrets#Scientists#Atomic Bomb#American 🇺🇸 Experience#NOVA | PBS#Los Alamos National Laboratory#Manhattan Project#World War II#J. Robert Oppenheimer#Katherine Oppenheimer#New Mexico#Hiroshima | Nagasaki#University of California-Berkeley#Harvard University#Jornada del Muerto (Dead Man’s Walk) Desert 🐪#Alamogordo New Mexico#General Leslie Groves#Japan 🇯🇵#TIME Magazine
21 notes
·
View notes
Text




If you're in the US and a something of a science geek, I can highly recommend the recent Nova episodes that aired last week on PBS that covered the dig in North Dakota that provided the first fossil remains of animals that died on the day of the Chicxulub impact 66 million years ago. I knew about the heat pulse that killed the dinosaurs around the globe. But I didn't know anything about the massive tremors sent through the Earth that caused localized tidal waves thousands of miles away from the impact site.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
oh also FYI there's a lot of PBS documentaries on youtube for free uploaded by pbs themselves. nova, american experience, frontline--it's there!
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
This was aired back in 2020. In time of posting this it’s 2024. This is a very fascinating documentary about the climate of the planet in the past, and what it might look like in the future. I highly suggest everyone watch this.
Paleontologist Kirk Johnson explores the dynamic history—and future—of ice at the poles. (Aired February 5, 2020)
Official Website: https://to.pbs.org/3EUn0KC | #novapbs
In this two-hour special, renowned paleontologist Kirk Johnson takes us on an epic adventure through time at the polar extremes of our planet. Following a trail of strange fossils found in all the wrong places—beech trees in Antarctica, hippo-like mammals in the Arctic—Johnson uncovers the bizarre history of the poles, from miles-high ice sheets to warm polar forests teeming with life. What caused such dramatic changes at the ends of the Earth? And what can the past reveal about our planet’s climate today—and in the future?
Chapters
00:00:00 Introduction
00:05:49 Hunting for Fossils on Islands near the North and South Poles
00:22:52 Fossil of New Dinosaur Species Found in Patagonia
00:29:04 Was Death Valley Always the Hottest Place on the Planet?
00:37:32 How Have Carbon Dioxide Levels Changed on Earth Over Time?
00:49:18 How Do Ice Sheets Form in Antarctica
00:56:47 How Did Life Persist Through the Ice Age?
01:11:29 Impacts of Rising Temperatures on Ice Cycles of the Planet
01:31:30 What Was the Warm World Like Before the Ice Age
01:43:04 This Cave Has Been Frozen for 100,000 Years
01:50:30 Conclusion
© 2020 WGBH Educational Foundation
All rights reserved
This program was produced by GBH, which is solely responsible for its content.
This program is made possible by viewers like you. Support your local PBS station here: https://pbs.org/donate/
Enjoy full episodes of your favorite PBS shows anytime, anywhere with the free PBS App: https://to.pbs.org/2QbtzhR
Stay up to date on the latest science discoveries, full episodes, articles, videos, and more by signing up for NOVA's newsletter here: https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/newslet...
FOLLOW US:
NOVA
YouTube:  / novaonline
Facebook:  / novapbs
Twitter:  / novapbs
Instagram:  / novapbs
TikTok:  / novapbs
PBS
Facebook:  / pbs
Twitter:  / pbs
Instagram:  / pbs
YouTube:  / pbs
TikTok:  / pbs
Shop: https://shop.pbs.org/
#paleontology #paleontologist #antarctica #antarctic #northpole #southpole #iceage #arctic #dinosaur #dinosaurs #deathvalley #deathvalleynationalpark
Where is the north pole, north pole temperature, ellesmere island, is antarctica the south pole, new dinosaur discovered, new dinosaur documentary, patagonia chile, what is the carbon cycle, death valley weather, death valley temperatures, snowball earth, ice sheet, drake passage
#NOVA PBS Official#solarpunk#Polar Extremes#Ice Worlds#NOVA#climate change#climate collapse#climate crisis#global warming#global heating#Kirk Johnson#Antarctica#Arctic#fossils#ice caps#glacier#north pole#south pole#alaska#canada#ellesmere island#death valley#Youtube
3 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
When Whales Could Walk | Full Documentary | NOVA | PBS
new ep just dropped 🐳🐋
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
On March 3, 1974, the long running science program "Nova" premiered on Public Television. ("The Making of a Natural History Film", Nova, TV, event)

#nerds yearbook#tv#real life event#science#march#1974#nova#documentary#pbs#making of a natural history film
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
I feel miserable and am probably sick, which means I don't have the attention span or coordination to play video games, but at least that means I can curl up and watch NOVA documentaries
#i binged all of the History of the Earth channel#and noticed NOVA and PBS documentaries in the recommended videos#i remember binging NOVA & Nat Geo on netflix in high school#time to go back to that#but with youtube lmao#isa babble
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Scientists say it's "almost certain" that debris from the Chicxulub asteroid that led to the mass extinction of the dinosaurs can be found on the moon.

#facts#interesting facts#dinosaurs#pbs#ancient history#chicxulub#space#moon#moon facts#dinosaur facts#mass extinction#dinosaur extinction#paleontology#earth history#science#science facts#space facts#pbs nova#dinosaur apocalypse#david attenborough
76 notes
·
View notes
Text

Don’t forget to vote for us as Best Podcast in this year’s Best of Halifax Awards (if you haven’t already)! If you’ve already voted, thank you!
Go to vote.thecoast.ca, and go to the Arts & Culture section to find us. You will have to register with a Canadian postal code.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Today, Earth is enveloped by a thin veil of gas, a narrow band of atmosphere that protects a world covered in lush green vegetation, deep blue oceans, and abundant life. But 4.5 billion years ago, Earth was a very different place: a hellscape of molten lava and barren rock, under relentless bombardment from meteors, and with no atmosphere whatsoever. So how did our familiar blue sky come to be? Breathtakingly realistic animations and a chorus of science experts reveal how the primordial inferno first gave rise to an orange-hued cauldron of toxic gasses that would be deadly to us today. Witness how the first drops of rain splashed down on the searing planet, setting the stage for the evolution of life. And discover how life itself helped create the air we all breathe today.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mapping Gilded Age New York
The Gilded Age was a study in contrasts. Immigrants arrived in New York City with little to nothing in their pockets, while just uptown some of the richest men and women in America built mansions that resembled European palaces. As more and more people carved out their homes on the island at the end of the 19th century, different ideas about what New York was and who belonged there emerged. American Experience spoke to Jack Tchen, Associate Professor at NYU’s Gallatin School of Individualized Study, about the way race and class tensions played out against the vibrant, dynamic landscape of New York City in the Gilded Age
— By Jack Tchen | American Experience | Published: February 2018 | November 04, 2023

J. W. Williams, Root & Tinker/Library of Congress
1. The Spine
Leading up to and during the Gilded Age, New York City begins to define itself along its spine, the middle of the city, rather than by its shoreline. The wealthy are gravitating away from the shoreline, which is seen as rougher and more dangerous. If you have money, you’re afraid that the workers in your counting house or your factory are going be jealous. You want to find other people who have money. And Fifth Avenue becomes the place where you find them. From Bowling Green to Washington Square Park, from Washington Square Park to Madison Park, and from Madison Park up to Central Park and 57th Street — this becomes what wealthy white Anglo-American Protestants feel is their New York. They feel that the greatest wealth of the city and of the nation is being generated and being expressed along this spine. The global branding of Fifth Avenue really emerges at a moment in which the Fifth Avenue merchants come together and say, “We have to protect Fifth Avenue. Fifth Avenue is ours and to maintain our identity, we have to keep out all the new immigrants who are trying to make money, who are setting up garment factories.” They begin to re-territorialize what had been a neighborhood of small producers, and to claim a kind of ascendancy and superiority.

Charles Pollock/Library of Congress
2. Metropolitan Opera House - Broadway and 39th Street
The building of the Metropolitan Opera House in 1883 is a great example of how cultural capital actually works. Did the people who went to the Met love opera? Probably not. In some ways, this was an emulation of European culture, especially Italian culture — but in Italy, opera was actually a mass activity that people from all stations of life loved. In the new world, it was transformed into this rarified art that supposedly only elites could understand. It was stilted in terms of performance, especially in comparison to the more popular forms of theater. And it was in a foreign language.
But the building was important. The box seats were important. Who was sponsoring the performances was important. So in a sense, supporting the opera became the perfect vehicle for elites to outdo each other.

Ernest Marx/Library of Congress
3. Vanderbilt House — 1 West 57th Street in New York City
Alva Vanderbilt was the driving force behind the “Petite Chateau” Vanderbilt mansion, which was completed in 1883. It was built of limestone, in contrast to neighboring brownstones, in the style of a French Renaissance palace. Her housewarming party was one for the ages. Twelve-hundred guests attended. Their costumes were sheer excess and outré; one woman, Miss Kate Strong (nicknamed “Puss”), wore a taxidermied cat head and seven cat’s tails decorating her skirt. By today’s dollars, the party was said to cost $6 million—one quarter of which went to the finest champagne.
What’s really important here is to acknowledge the role of women in the wealth-building process itself. Because it’s not just wealth building in terms of actual dollars — it’s also wealth building in terms of status. And women are the ones who know how to build that kind of social and cultural capital that gives their families the standing and prestige that other families of wealth will begin to recognize and accept.
In some ways, the women who are leading these families and creating these parties are like the ad men on Madison Avenue. They’re branding the family. They’re making the public — other elites especially — appreciative of why they belong and why they should be recognized widely. So when Alva Vanderbilt builds her mansion, she’s being very creative, very thoughtful, and very tenacious in trying to establish that profile of the Vanderbilt family.

Petite Chateau, Library of Congress
4. Seventh Regiment Armory - 640 Park Ave., Bet. East 66th & East 67th
The street grid of New York City means that people of great wealth are cheek-to-jowl next to people living in extreme poverty. That sense of injustice and the divide between the wealthy and the poor is palpable.
The Gilded Age was a fractious time, and amidst growing wealth and opulence, a sense of desperation and resentment emerged. I think the wealthy felt some anxiety at the thought that at some point that tension would erupt.
So they built armories to defend against riots and protests. The armories housed volunteer regiments — the precursor of the National Guard. The Seventh Regiment, also known as the “Silk Stocking” or “Blue-Bloods” regiment, was a who’s who of the Gilded Age elite. It was first headquartered on the Lower East Side — but it moved uptown as the wealth of the city did. The armory now on Park Avenue opened its doors in 1880.

The New York Public Library
5. Harbor
New York Harbor was deep enough that it didn’t freeze over, so it could actually operate year-round. Lots of raw products — grains, sugars from the Caribbean — can all be exchanged in this deep-water port and then processed and sent by way of the Erie Canal into the heartland, and also traded across the Atlantic. So New York becomes kind of a central economic exchange hub, feeding and processing so much of what is being consumed by the growing middle classes of North America, and Europe.
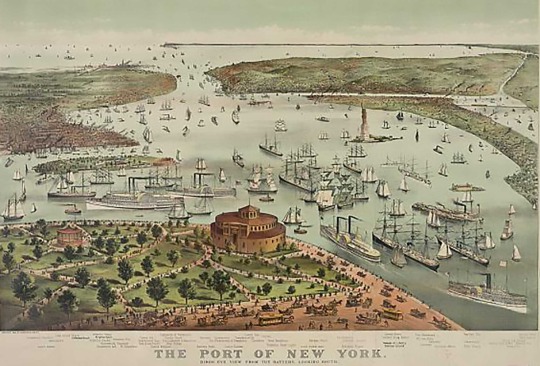
Currier & Ives/Library of Congress
6. Orchard Street
As the wealthy Protestant elite move uptown, away from the waterfront, the lower east side becomes a neighborhood of immigrants. Jewish and Italian immigration really starts in great numbers in the latter part of the 19th century. Millions of people are coming to New York. They’re dazzled by visions of streets of gold.
The older tenements on the lower east side become jam-packed. The whole notion of a middle class apartment with one person in a room — that didn’t exist. A single apartment could house multiple extended family members; a family might even rent out a room to make ends meet. The idea of how you used space was different. The streets were really an extension of where you lived.
Take the market on Orchard Street. It was really an American reproduction of the small market towns that many Jews had left in eastern Europe. If you look at old photos, you can just imagine the sounds and smells. Jews, Italians, and Chinese are living side by side. And out of that, a port culture begins to emerge. People are bringing the cultures that they left. Lots of languages are being spoken, and lots of new dishes and new fashions are being created. It’s all part of this new, intermingled culture. And that intermingling, I think, is what’s distinctive to New York City — as opposed to the culture of the uptown elites, who are really emulating their fantasy of the european aristocracy.
The uptown elites, by the way, are really scared of this new, intermingled port culture. They have a certain notion of Protestant destiny in terms of who this country properly belongs to. They’re concerned with who’s creating value — monetary, but also the cultural value of the nation. Meanwhile, these non-Protestants of suspect racial origin keep coming into the city. So there’s a growing guardedness of who should count, who belongs there.

Bain News Service/Library of Congress
7. Bowery
While the elites are walking up and down Broadway, checking each other out in a way that prefigures the shopping mall or the arcade, immigrants and members of the white working class hang out on the Bowery. It’s where people go for dime museums, tattoo parlors, bars; all that kind of popular culture that we tend to think of now as connected to Coney Island originates on the Bowery.
These new immigrant and working class audiences are constantly looking for new and exciting forms of expression. They’re willing to pay maybe five cents to see what’s happening on the stage, what’s happening in music, and in bars. Essentially, what happens is street culture gets brought into the commercial culture, the indoor culture in which people are willing to pay for entertainment.

Library of Congress
#The Gilded Age | Article#American Experience#NOVA | PBS#New York | Gilded Age#Jack Tchen | Associate Professor | NYU’s Gallatin School of Individualized Study
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Keep your cats inside
#keep your cats inside#pbs#nova#ocean invaders#cats might be the single most invasive species to exist
3 notes
·
View notes
Link
might have to come back to this! particularly interested in learning the arctic sinkholes and the ice age footprints
2 notes
·
View notes
Link
Ending HIV in America Premieres Wednesday, September 21, 2022 at 9pm ET/8C on PBS #janetwalker #hautelifestylecom #theentertainmentzonecom #hiv #aids #pbs
#janet walker#haute-lifestyle.com#the-entertainment-zone.com#pbs#hiv#aids crisis#aidsawareness#aids treatment#nova
2 notes
·
View notes