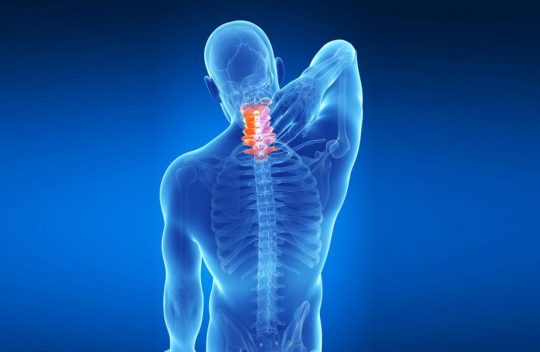
#rotated lumbar vertebrae
Photo

Rotated Lumbar Vertebrae Caused Intractable Problems
An older client who was in for their third NMR® treatment came in with a complaint about her right low back and hip, initially massively disorganized due to being hit by a car as a pedestrian and knocked down. She fell on her right sacrum. She's been in pain for 1 1/2 years with no relief no matter what she had tried. The origins of the lower external rotators were very painfully tight and the hip was in a constant clench.
The tight hip makes total sense from both the fall and the fact that the right lumbar erectors weren’t engaged. The hip grips to give some stability to the upper body since the erectors are not firing on that one side. This pattern is very common once the rotational reciprocal reciprocity of the Rotatores have been damaged.
The remainder of the problem visible today was strong pain at L3. Something was pulling L3 into a left rotation. With L3 rotated left the right Psoas was facilitated and the left one inhibited. They could not alternate in walking without blowing a fuse on the left. The more she walked the tighter the right Psoas would get.
The client was astonished to notice that when she thought about circling her spine to the left it was easy and circling to the right she could not do it. The circle was full of zigzags and blank spots. The QL at L3 was tight. Releasing the QL at L3 on the right enabled the lumbar spine to rotate in either direction. We reprogrammed the rotational movement of her L3 vertebrae also, after which we rebalanced her Psoas muscles with each other so they both worked reliably.
All of this disorganization was affecting her neck, which was similarly locked and painful and confused about how to move. She forgot to mention this at the beginning of the session. This illustrates how NMR works to solve coordination issues at the source and gives you a greater picture of how different issues in the body can result in pain elsewhere in the body, which once addressed leads to greater mobility and reduced pain with less work.
[NeuroMuscular Reprogramming]
#rotated lumbar vertebrae#Neuromuscular Reprogramming Network#Bodywork#NMR#Jocelyn Olivier#human relationships#QL#SIJ#Lumbar#Body Alive#Structural Integration Atlanta
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo

THORACIC SPINE ⠀ [ANATOMY, FUNCTION, MOBILIZATION & STRENGTHENING] ⠀ The thoracic spine is the longest region of the spine, and by some measures it is also the most complex. Connecting with the cervical spine above and the lumbar spine below, the thoracic spine runs from the base of the neck down to the abdomen. It is the only spinal region attached to the rib cage. ⠀ The thoracic spine has 12 vertebrae stacked on top of each other, labeled from T1 down to T12. These vertebrae form the foundation of the thoracic region’s sturdy spinal column that supports the neck above, the rib cage, soft tissues, flexible joints, blood vessels, and nerves. ⠀ The thoracic spine is built from its anatomical structure to be mobile for rotation, flexion and extension! That's why it is very important to keep it mobile and even to visualize and feel the possible movement in the thoracic spine. ⠀ Many people don't even know or just are not able to feel that there is a specific movement possible. But it has to be known because the thoracic spine must be used and must be moved! If people are unable to visualize and feel the movement of the thoracic spine, they will find another way to get that motion from somewhere else like lumbar spine, cervical spine or shoulder blades because our body is smart and very good in compensating. Those areas of compensation might lead to poor movement patterns, overuse and pain! ⠀ An immobility or stiffness in the thoracic spine can lead to rounded shoulders, shoulder pain, elbow pain, wrist pain, neck pain, lower back pain and even hip pain. Thats why it is very important to include mobilization exercises and stretching exercises in your daily training routine! ⠀ Video 1: Manual joint mobilization of the thoracic and lumbar spine into extension. Video 2: Using an exercise ball to stretch the pecs and mobilize the spine. Video 3: Spinal extension strengthening exercise on an exercise ball. Video 4: Spinal extension strengthening exercise on an exercise ball shown with a skeleton. Video credit: @DrJoeMuscolino #Anatomy #Biomechanics #ThoracicSpine #Spine #Joint #Muscle #SportsPhysiotherapy #Osteopathy #Yoga #Pilates #CrossFit #Physiotherapy #Strength https://www.instagram.com/p/Cf6aVshDbTK/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
#anatomy#biomechanics#thoracicspine#spine#joint#muscle#sportsphysiotherapy#osteopathy#yoga#pilates#crossfit#physiotherapy#strength
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
One of The best orthopedic clinics for rehabilitation in Dubai
Our extensive experience can support the patient in the diagnosis and treatment of the following conditions:
Muscle pain, contractures, myofascial syndrome.
Osteoarthritis (joint wear): spondylosis/spondyloarthritis (cervical-thoracic-lumbar-sacral spine).
Spine and postural conditions: neck pain, low back pain, scoliosis, kyphosis, herniated disc, etc
Fractures: vertebrae, clavicle, humerus, radius, ulna, wrist, hip, femur, kneecap, tibia, fibula, ankle, foot, etc.
Joint, tendon, and ligament injuries: painful shoulder, rotator cuff tendinitis, epicondylitis, wrist and hand conditions, sacroiliitis (sacroiliac inflammation), coxalgia (hip pain), knee pain, cruciate ligament injury, collaterals knee, runner’s knee, knee sprains, ankle sprains, talalgia (heel pain), etc.
Sprains, dislocations, and various fractures.
Pre and post-surgical rehabilitation: shoulder, hip, and knee prostheses, fracture reductions, tendon repair, meniscus repair, spine instrumentation, peripheral nerve release, etc.
Neuromuscular conditions.
0 notes
Text
Biotronix Solution Forever Inversion Table, Small Inverted Machine, Household Upside Down, Long High Stretcher, Upside Down Bench, Yoga Fitness Fitness Equipment, Stable, Strong and Safe
【Full-function handstand machine】: Equipped with adjustable height gear ruler to accommodate 4'10 "to 6'6" (147cm-198cm) users; Use this everyday to take off pressure from spine, and opening up the vertebrae, help to restore lumbar disc vitality, decompress nerve pressure, relieve muscle tension caused by sedentary and adjust the spine; Increasing blood circulation, refreshing brain; One handstand machine , available for the whole family
【Multiple safety protections】: New designed anti-gravity machine, body is supported by thick steel tubes, base adopts a triangular structure to further enhance the stability, which can carry up to 264lbs (120kg); equipped with shoulder support and belt to prevent woddle and slipping while standing upside down; easy-to-adjust ankle locking system, with chunk buckle and safety latch to further ensure safety
【Comfortable experience】: The widen and thicken backrest of the inverted chair is made of four layers of high-quality materials; Waist support is upgraded to adjustable inflatable air bag to better fit the waist; Anti-fall shoulder pad and the U-shaped presser foot device are made of soft foam, which is more comfortable and does not feel bound during use.
【Foldable and convenient to use】: 4 position limit system is convenient to adjust the angle, beginner can also adapt to the inverted state; Anti-slip handles on both sides makes it easy to control and rotate; Automatic presser foot device, adjustable space; foldable design, can be easily folded and placed in a closet or corner by pulling out the latch
Inversion table
Inversion therapy
Back pain relief
Spinal health
Spinal decompression
Gravity inversion
Inversion table benefits
Inversion table exercises
Inversion table for back pain
Inversion table workout
Inversion table benefits for posture
Inversion therapy for herniated disc
Best inversion tables
Inversion table safety tips
Inversion table for sciatica
Inversion table for neck pain
Inversion table for spinal alignment
Inversion table for muscle relaxation
Inversion table for stress relief
#Inversiontable
#InversionTherapy
#BackPainRelief
#SpinalHealth
#SpinalDecompression
#GravityInversion
#InversionExercises
#HerniatedDisc
#SciaticaRelief
#NeckPainRelief
#PostureCorrection
#FitnessEquipment
#SpineHealth
#MuscleRelaxation
#StressRelief
#WorkoutRecovery
#HomeFitness
#BackStretching
#WellnessJourney
#healthandwellness
#physicaltherapy
#Rehabilitation
#PhysicalHealth
#InjuryRecovery
#PainManagement
#MusculoskeletalHealth
#SportsRehab
#MobilityMatters
#WellnessJourney
#movementtherapy
#physiotherapist
#physio #physiotherapy #physicaltherapy #physiotherapist #rehab
0 notes
Text
Biotronix Solution Forever Inversion Table, Small Inverted Machine, Household Upside Down, Long High Stretcher, Upside Down Bench, Yoga Fitness Fitness Equipment, Stable, Strong and Safe
【Full-function handstand machine】: Equipped with adjustable height gear ruler to accommodate 4'10 "to 6'6" (147cm-198cm) users; Use this everyday to take off pressure from spine, and opening up the vertebrae, help to restore lumbar disc vitality, decompress nerve pressure, relieve muscle tension caused by sedentary and adjust the spine; Increasing blood circulation, refreshing brain; One handstand machine , available for the whole family
【Multiple safety protections】: New designed anti-gravity machine, body is supported by thick steel tubes, base adopts a triangular structure to further enhance the stability, which can carry up to 264lbs (120kg); equipped with shoulder support and belt to prevent woddle and slipping while standing upside down; easy-to-adjust ankle locking system, with chunk buckle and safety latch to further ensure safety
【Comfortable experience】: The widen and thicken backrest of the inverted chair is made of four layers of high-quality materials; Waist support is upgraded to adjustable inflatable air bag to better fit the waist; Anti-fall shoulder pad and the U-shaped presser foot device are made of soft foam, which is more comfortable and does not feel bound during use.
【Foldable and convenient to use】: 4 position limit system is convenient to adjust the angle, beginner can also adapt to the inverted state; Anti-slip handles on both sides makes it easy to control and rotate; Automatic presser foot device, adjustable space; foldable design, can be easily folded and placed in a closet or corner by pulling out the latch
Inversion table
Inversion therapy
Back pain relief
Spinal health
Spinal decompression
Gravity inversion
Inversion table benefits
Inversion table exercises
Inversion table for back pain
Inversion table workout
Inversion table benefits for posture
Inversion therapy for herniated disc
Best inversion tables
Inversion table safety tips
Inversion table for sciatica
Inversion table for neck pain
Inversion table for spinal alignment
Inversion table for muscle relaxation
Inversion table for stress relief
#Inversiontable
#InversionTherapy
#BackPainRelief
#SpinalHealth
#SpinalDecompression
#GravityInversion
#InversionExercises
#HerniatedDisc
#SciaticaRelief
#NeckPainRelief
#PostureCorrection
#FitnessEquipment
#SpineHealth
#MuscleRelaxation
#StressRelief
#WorkoutRecovery
#HomeFitness
#BackStretching
#WellnessJourney
#healthandwellness
#physicaltherapy
#Rehabilitation
#PhysicalHealth
#InjuryRecovery
#PainManagement
#MusculoskeletalHealth
#SportsRehab
#MobilityMatters
#WellnessJourney
#movementtherapy
#physiotherapist
#physio #physiotherapy #physicaltherapy #physiotherapist #rehab
0 notes
Text
Understanding Scoliosis: Its 4 Types, Symptoms, And Treatment Methods

Scoliosis is a medical condition wherein the patient has an abnormal sideways curve in the spine. The back does not appear straight and can cause difficulty in performing day-to-day activities. The complications involved in scoliosis could be uneven shoulders, one hip higher than the other, one shoulder blade higher than the other, asymmetry of the chest, slight drift in the position of the head from the centre, or a visible curve. Both neurosurgeons and ortho surgeons diagnose the condition, gauge the complications involved and then draft a personalised treatment plan. At Manipal Hospitals, we have highly experienced orthopaedic surgeons and top neurosurgeons in Patiala who can offer the right treatment to scoliosis patients.
Through this article let’s find out more about scoliosis, its types, symptoms and treatment methods.
Symptoms of Scoliosis and its Diagnosis
Scoliosis is characterised by a curve that ranges from 10 to 20 degrees for mild scoliosis, 20 to 50 degrees for moderate scoliosis, and more than 50 degrees for severe scoliosis. The symptoms that you must treat as red flags and consult the neuro and ortho surgeons are:
Tilted shoulders
Back pain
Uneven buttocks and waistline
Rotation of spine
Reduced chest area
Scoliosis is confirmed by the doctor after certain tests which include:
Physical examination
X-Ray
MRI Scan
CT Scan
Bone Scan
Types of Scoliosis
Based on severity, location of the curve and other medical parameters, scoliosis is categorised into structural and non-structural disorders. Non-structural scoliosis, sometimes referred to as functional scoliosis, is a two-dimensional disorder. The vertebrae do not twist or contort in such a way that they go out of alignment, which means that the spine only bends to one side. Muscle spasms and inflammation are some common causes of non-structural scoliosis. On the other hand, structural scoliosis is a three-dimensional condition that is further categorised into the following:
Idiopathic Scoliosis
This type of scoliosis is very common as approximately 8 out of 10 occurrences of scoliosis are caused by idiopathic causes. Although it can begin earlier, in childhood or even infancy, this kind of scoliosis commonly manifests throughout adolescence. Researches suggest that genetics may have a role, but there may be more elements at play that are now being investigated.
Neuromuscular Scoliosis
Sometimes people who are unable to walk due to a neuromuscular disorder like muscular dystrophy or cerebral palsy develop neuromuscular scoliosis. Myopathic scoliosis is another name for this kind of curve.
Congenital Scoliosis
Congenital scoliosis appears in infancy and develops in utero. It is an uncommon disorder that affects 1 in 10,000 people and can be brought on by vertebral abnormalities or other factors. Surgery is typically required to straighten the spinal curvature.
Degenerative Scoliosis
The discs and joints in the spine experience wear and strain with age, which leads to degenerative scoliosis. Adults who develop this form of scoliosis typically have it in the lumbar (lower) spine.
Risks involved in Spine Surgery to Treat Scoliosis
Today's scoliosis operations are safer and have better results. Any operation near the spinal cord carries certain dangers, though. The following are potential dangers and adverse effects:
excessive bleeding
pancreatic infection
abdominal block
neurologic issues
the spine doesn't fuse
degenerative disc disease
back discomfort
Scoliosis Treatment
The treatment option is determined after thorough analyses of various factors such as the age of the patient, the extent of curvature, the location of the curve, and the type of scoliosis. The evaluation of reports and spine scans also helps the doctor determine the approach towards the treatment: open surgery and invasive methods.
Bracing
The treatment is often given to the kids. Bracing is the preferred therapy when the curvature ranges from 25 to 45 degrees and the kid is still developing. While it does not correct the curvature, it does stop it from worsening and postpone surgery. There are several kinds of braces. The majority of them are adjusted for the youngster.
Surgery to Treat Scoliosis
If the curve upon discovery is more severe (> 40), surgery is used to address scoliosis. A balanced spine with the patient's head, shoulders, and trunk positioned directly above the pelvis is the goal of surgical correction. To do this, the instrumentation is used to lessen the severity of the deformity and fusion is obtained to stop further curve advancement. When fusion is performed on individuals with immature skeletons, crank shafting and flat back syndromes develop, which results in more severe deformity. The placement of staples on the convex side of the curve to correct and maintain the curvature until the patient is skeletally mature is a relatively recent technique in the treatment of such individuals.
Scoliosis Surgery Price in India
You can get optimum care and treatment for Scoliosis spine in India at affordable prices. Multiple media reports have stated that the cost of scoliosis spine surgery in India is approximately 60 to 80% less than abroad. Manipal Hospital is one of the leading healthcare providers that offer affordable treatment to all. The spinal fusion treatment for scoliosis has good success rate and the state-of-the-art technology at Manipal Hospitals enables the surgeons to perform complex procedures at most of its facilities across the country.
Recovery after the surgery at the brain hospital in Patiala involves is another phase where you need medical and expert intervention. A patient cannot move to his/her daily activities immediately after the surgery. Dietary supplements, physiotherapy, medications and light exercises will be advised by the doctor depending on your case and gradually the patient can resume the activities. Book an appointment with our best orthopaedic surgeon in Patiala to know more about the disease or treatment options. You may also bookmark our blog page to read interesting and reliable medical content on various topics. Contact us now to know more about scoliosis operation costs.
0 notes
Text
T-Spine Mobility: Unlocking the Secret to a Strong and Flexible Upper Body
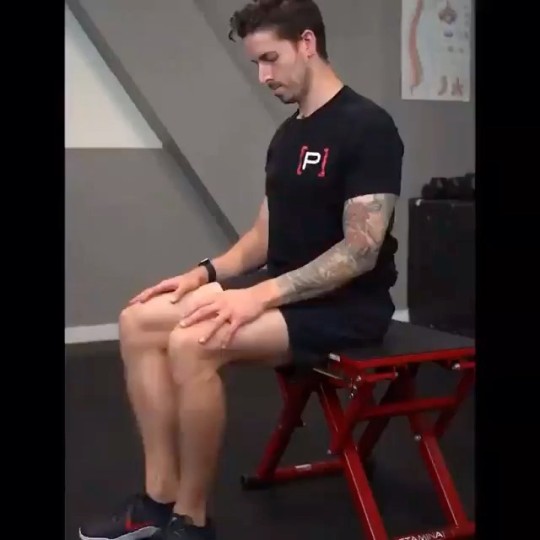
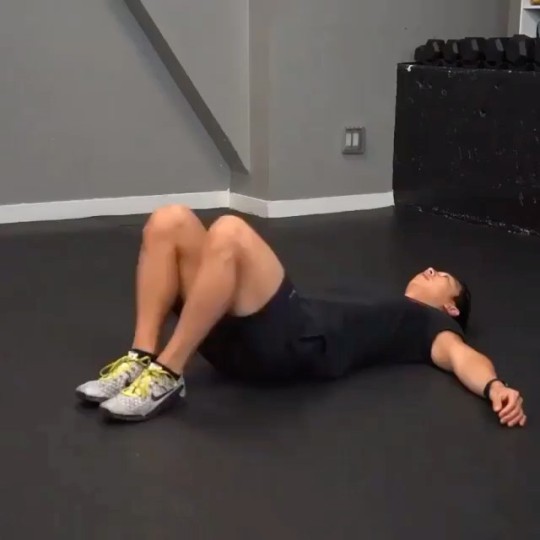
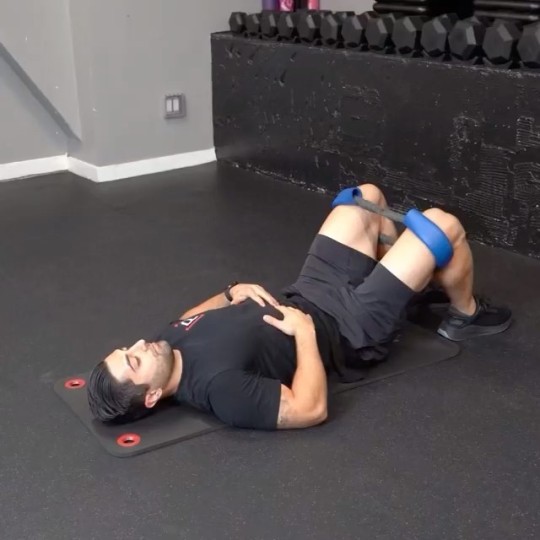



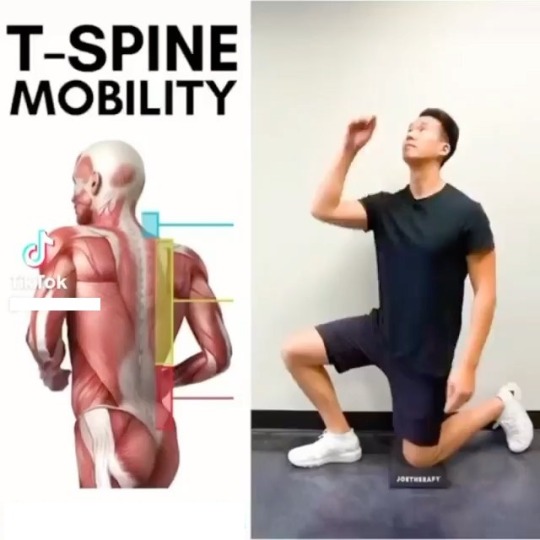



When it comes to functional movement and overall athletic performance, having a strong and mobile thoracic spine, also known as the T-spine, is crucial. The thoracic spine plays a significant role in the stability and flexibility of the upper body, affecting everything from posture to shoulder and neck mobility. In this article, we will delve into the importance of T-spine mobility, explore its benefits, and provide you with effective exercises to improve your T-spine mobility and enhance your overall performance.
Understanding the Thoracic Spine
The thoracic spine consists of twelve vertebrae located in the upper and mid-back region. Unlike the lumbar spine, which is built for stability, the thoracic spine is designed to allow for rotation and flexion/extension. However, due to our sedentary lifestyles and prolonged hours spent sitting hunched over desks or screens, the T-spine tends to become stiff and immobile over time.
Why T-Spine Mobility Matters
Improved Posture: The T-spine has a significant impact on our posture. When the thoracic spine is mobile, it allows the shoulders to sit properly, preventing rounded shoulders and a forward head posture. A mobile T-spine promotes an upright posture, reducing the risk of musculoskeletal imbalances and associated pain.
Increased Shoulder Mobility: The T-spine and shoulder girdle work together to produce optimal shoulder movement. A stiff T-spine restricts the range of motion in the shoulders, limiting overhead reach, throwing mechanics, and other upper body movements. By improving T-spine mobility, you can enhance your shoulder mobility and reduce the risk of shoulder injuries.
Enhanced Breathing Mechanics: The T-spine plays a vital role in proper breathing mechanics. When the thoracic spine is immobile, it limits the expansion of the ribcage during inhalation, leading to shallow breathing patterns. By improving T-spine mobility, you can restore optimal breathing mechanics, improving oxygen intake and overall respiratory function.
Injury Prevention: Stiffness in the T-spine can result in compensatory movement patterns, putting additional stress on neighboring joints such as the neck, shoulders, and lower back. By improving T-spine mobility, you can reduce the risk of overuse injuries and prevent unnecessary strain on other areas of the body.
Exercises for T-Spine Mobility
Thoracic Spine Foam Rolling: Lie on your back with a foam roller positioned horizontally beneath your upper back. Support your head with your hands, and slowly roll up and down the foam roller, targeting the T-spine. Pause at any tender spots, allowing the pressure to release tension. Perform for 1-2 minutes daily.
Cat-Camel Stretch: Begin on your hands and knees, aligning your wrists under your shoulders and your knees under your hips. Slowly round your back towards the ceiling, tucking your chin to your chest (cat pose). Then, reverse the movement by arching your back, lifting your chest and tailbone towards the ceiling (camel pose). Repeat for 10-12 repetitions, focusing on smooth and controlled movement.
Quadruped Thoracic Rotation: Start in the same hands and knees position as the cat-camel stretch. Place one hand behind your head, keeping your elbow bent. Slowly rotate your upper body and reach your elbow towards the ceiling, opening up your chest and following your hand with your gaze. Return to the starting position and repeat on the other side. Perform 8-10 repetitions on each side.
Thread the Needle: Begin on all fours, with your wrists under your shoulders and your knees under your hips. Extend one arm straight in front of you, then thread it underneath your opposite arm, reaching as far as you can comfortably. Rotate your upper body and look towards the ceiling. Hold the stretch for 20-30 seconds, then return to the starting position and repeat on the other side.
Wall Angels: Stand with your back against a wall, your feet shoulder-width apart, and a slight bend in your knees. Position your arms at a 90-degree angle, with your elbows and wrists touching the wall. Slowly slide your arms up and down the wall while maintaining contact with your wrists, elbows, and back. Perform 10-12 repetitions, focusing on maintaining proper posture and engaging the muscles around the shoulder blades.
Conclusion
A mobile thoracic spine is essential for optimal movement and function of the upper body. By incorporating regular T-spine mobility exercises into your fitness routine, you can improve your posture, enhance shoulder mobility, optimize breathing mechanics, and reduce the risk of injuries. Remember, consistency is key when it comes to improving T-spine mobility, so make it a habit to prioritize these exercises and unlock the secret to a strong and flexible upper body.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Spine Model Anatomy tips

Spine anatomy
We are standing straight, going about our standard responsibilities appropriately, and partaking in our sexual coexistence as well, spine or back assumes an essential part in this large number of exercises. We should view the physical structure of our spine.
The longitudinal line of the circles upholds the head and trunk. The intervertebral in the middle of between the vertebrae separates them from each other yet secures them along with both the upper and lower surfaces of the bodies by tendons. These fibrocartilage circles go about as a pad and safeguard. Each vertebral circle is just two short stalks called "pedicles" which give rise to two plates like laminae. The laminae meld posteriorly to turn into "spinous interaction." The pedicles, laminae, and spinous cycle out and out totaling a vertebral curve through which the spinal line passes. Various spinal nerves go through an opening on the surfaces of the vertebral pedicles known as "intervertebral foramina."
The spine is a segment comprised of three gatherings of drum-shaped calcified structures
called "vertebrae."
Lumbar Vertebrae
The five "lumbar vertebrae" are the lowermost vertebrae that hold more weight than the vertebrae above them. They have long areas of strength and projections calculated in reverse while their short, thick spiny processes are directed horizontally.
Thoracic Vertebrae
The vertebrae in the chest locale are designated "thoracic" vertebrae. These twelve plates are bigger in size than those of the cervical district. The long, pointed spinous cycles descending down from the sides get together with ribs. The size of the bone increments as it drops down from the third thoracic vertebra.
Cervical Vertebrae
The seven bones that structure the hard pivot of the neck are classified "cervical" vertebra. These are the littlest of every vertebra. The "cross-over foramina" is a path to the conduits prompting the mind. The forked trademark component of the second to the fifth vertebra is fairly exceptional. "Map book", the principal vertebra supports and balances the head. The subsequent vertebra called the "pivot" bears a tooth-like "odontoid process" on its body which upwardly fixes into the ring of the map book. At the point when the head is moved, the atlas rotates around the odontoid process.
The Coccyx
The tail bone or the most minimal piece of the vertebral segment is called the coccyx. When a person sits the pressure of the whole body focuses on the coccyx, and it pushes ahead, to forestall any shock. Here and their individual experience cracked or separated coccyx due to plunking down with too incredible power.
Sacrum
The sacrum is a serious area of strength for a three-sided bone at the foundation of the lower spine. Its wide upper part joins the last lumbar vertebrae and its restricted lower part joins the coccyx or "tailbone". The sides are associated with the ilium (pelvic bones). At the hour of birth and during early age the five vertebrae of the sacrum are isolated, yet step by step meld later at some point in the middle of between the eighteenth and thirtieth years. The sacrum is stopped between the coxal bones of the pelvis and gelled by fibrocartilage at the sacroiliac joints. The heaviness of the body is communicated to the pelvic girdle at these joints. The Encoris Anatomy Model leads the industry in innovation and quality.
Encoris
180 Roost Ct
Holland, MI
49424
USA
1 note
·
View note
Text
White and Panjabi checklists for spinal instability
A great reference textbook for spine biomechanics is "Clinical Biomechanics of the Spine" by White and Panjabi.
They define "clinical instability": the loss of the ability of the spine under physiologic loads to maintain its pattern of displacement so that there is no initial or additional neurological deficit, no major deformity, and no incapacitating pain.
physiologic load: are those which are incurred during normal activity -flexion, extension, axial rotation, and lateral bending- of the particular patient being evaluated
incapacitating pain: pain unable to be controlled by non-narcotic drugs
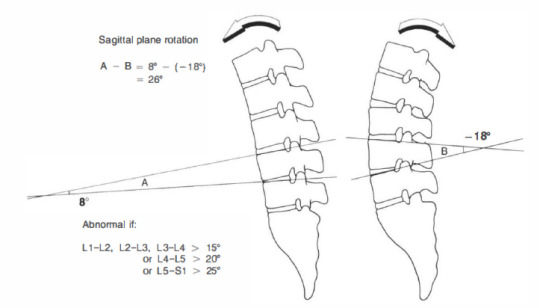
White and Panjabi proposed checklists based on their biomechanical data for spine instability
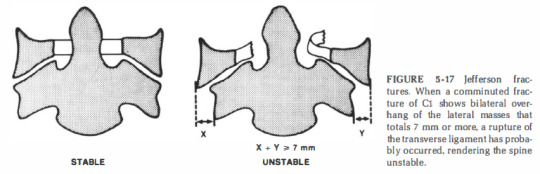
Occipital-atlanto-axial complex (any point should be considered as instability)

the images below explain point in the checklist:


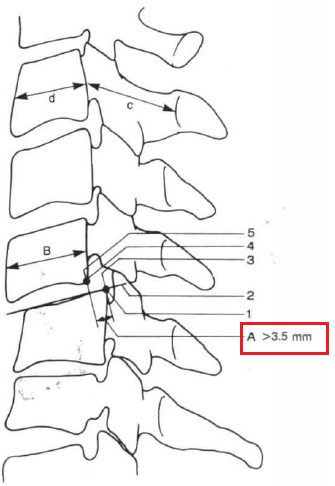
2. Middle and lower cervical spine:

comments on the checklist:
1) anterior elements: posterior longitudinal ligament and all structures anterior to it.
2) posterior elements: all structures behind the posterior longitudinal ligament
3) patients with anterior elements destroyed or unable to function are more clinically unstable in extension, while patients with the posterior elements destroyed or unable to function are more unstable in flexion
4) It is not assumed that the information available on all patients will provide a definitive answer for each item on the list
5) It is recommended that when the evaluation of a given element
leads the clinician to a borderline decision that cannot be resolved, the value for that entity should be divided by 2 and added to the other points
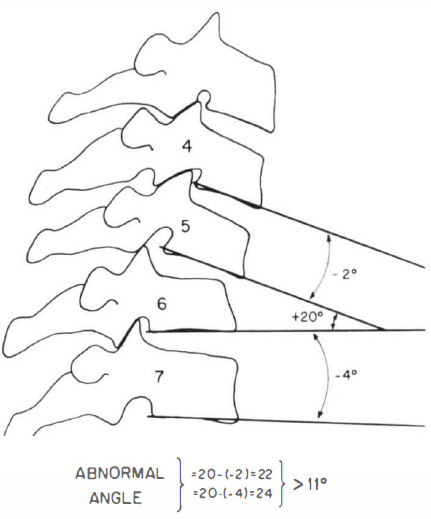
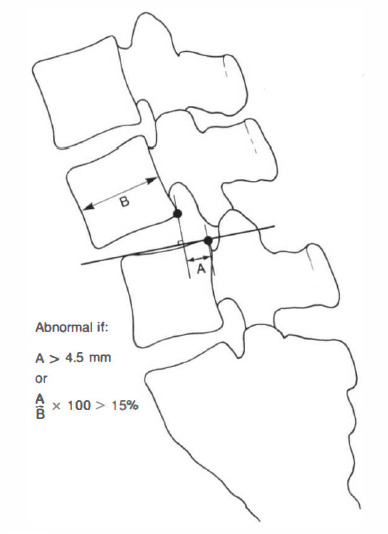
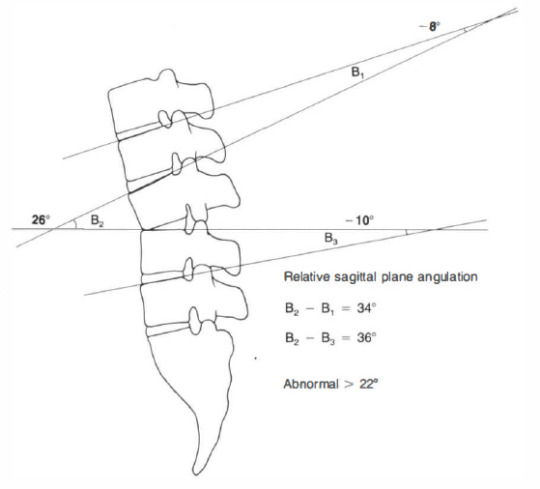
positive angle = kyphotic angle (intersection anterior to spine)
negative angle = lordotic angle (intersection posterior to spine)

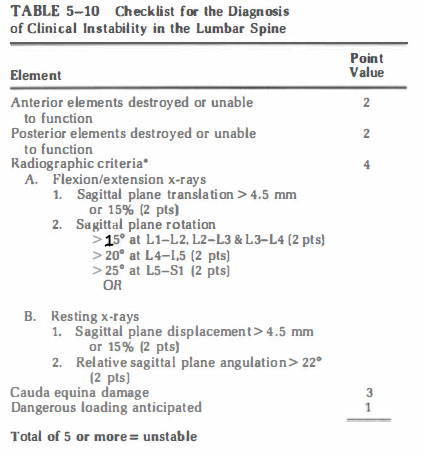
An abnormal test is indicated by either differences of more than 1 .7 mm interspace separation or more than 7.5 degrees of change in angle between vertebrae, comparing the prestretch condition with the situation after application of axial traction equivalent to one-third body weight.
=> Examples of patients in whom one can anticipate heavy loads
are heavy laborers, contact sport athletes, and avid motorcyclists

Pavlov's ratio is a reliable, accurate method for recognizing a developmentally narrow canal without the variables involved in linear measurements. The measurement A is the distance between the midlevel of the posterior aspect of the vertebral body and the nearest point on the corresponding spinolaminar line. The measurement B is seen on lateral x-ray as the anteroposterior distance from the front to the back of the vertebral body measured at the midlevel. The ratio A/B is considered normal if 1 or greater and abnormal if less than 0.8.
=> In patients under 35 years of age, post-traumatic disc narrowing is modestly suggestive of disruption of the annulus fibrosus and of possible instability.
=> A congenitally narrow canal is defined as measuring less than 1 3 mm in its anteroposterior dimension on a lateral radiograph or having a Pavlov's ratio of less than 0.8.
=> if the trauma is severe enough to cause initial neurologic damage, the support structures probably have been altered sufficiently to allow subsequent neurologic damage, and thus the situation is clinically unstable.
=> Evidence of root involvement is a weaker indicator of clinical instability. For example, a unilateral facet dislocation may cause enough foraminal encroachment to result in root symptoms
and/or signs but not enough ligamentous damage to render the FSU unstable
3. Thoracic and thoracolumbar spine

4. Lumbar spine
references:
(1) clinical biomechanics of spine by Augustus A. White and Manohar M. Panjabi, chapter 5
#spine#trauma#textbook#neurosurgery#orthopedics#spinal cord#instability#biomechanics#medicine#surgery
0 notes
Text
Shifted spine

#SHIFTED SPINE HOW TO#
Stand on the edge of a step with the leg on the opposite side of the lumbar concavity.
For best results for your specific presentation – perform these specific exercises in conjunction with a health care professional.
(The compensatory curve is the attempt of the body to maintain an upright posture as a response to the primary curve.).
With the presence of 2 (… or more) curves, there is a primary and a compensatory curve(s).
The following Scoliosis exercises serve as a starting point when addressing the curvature of the spine.
(Although – I would still strongly encourage you to persist with conservative treatment as much as you can!) ** For angles >40 degrees, surgical interventions may need to be considered. ** The following Scoliosis exercises are best suited for those who have a curve of 20 degrees, however, other factors such as spinal rotation and rib position will likely need to be addressed as well.
The point where these 2 lines intersect creates the Cobb’s angle.
Draw a line that matches the angle of these 2 vertebra.
The most tilted vertebra above and below the Apex.
( This determines the severity of the Scoliosis.) ( This shows you the exact location of your Scoliosis.)
#SHIFTED SPINE HOW TO#
Here are 2 quick tests on how to determine which type of Scoliosis you have. This means that there’s a good chance that these Scoliosis exercises will help you!) “Which type of Scoliosis do I have?” It is able to be changed and/or improved. This is determined by how your body habitually holds itself up as it attempts to maintain an up right posture against gravity. (If the joints in your spine have fused together, then there is a smaller likelihood of significantly impacting the shape of your spine by performing the Scoliosis exercises.) This is determined by your genetics and/or as a result of fused joints. CT scans are more detailed than general X-rays.There are 2 types of Scoliosis: Structural and Functional. A CT scan shows detailed images of any part of the body, including the bones, muscles, fat, and organs. Computed tomography scan (CT scan): a diagnostic imaging procedure that uses a combination of X-rays and computer technology to produce detailed images of the body.Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): a diagnostic procedure that uses a combination of large magnets, radiofrequencies, and a computer to produce detailed images of organs and structures within the body.Dynamic, or flexion/extension X-rays (X-rays that show the spine in motion) may be obtained to see if there is any abnormal or excessive movement or instability in the spine at the affected levels. Specific bony abnormalities such as bone spurs, disc space narrowing, vertebral body fracture, collapse, or erosion can also be identified on plain film X-rays. Spinal dislocation or slippage (also known as spondylolisthesis), kyphosis, scoliosis, as well as local and overall spine balance can be assessed with X-rays. X-rays provide an overall assessment of the bone anatomy as well as the curvature and alignment of the vertebral column. Soft tissue structures such as the spinal cord, spinal nerves, the disc and ligaments are usually not seen on X-rays, nor on most tumors, vascular malformations, or cysts. X-ray (also known as plain films): test that uses invisible electromagnetic energy beams (X-rays) to produce images of bones.Hangman’s fracture may be diagnosed and evaluated with the following procedures: When hangman’s fracture is a result of major trauma, it is usually found as part of a patient’s evaluation in the emergency department. This is the type of fracture supposedly created by judicial hangings. At the same time, the C2 body may move out of position relative to the vertebra below, C3. In a hangman’s fracture, the pars of C2 fractures, or breaks, on both sides. There is a projection of bone that connects the body to the lamina, known as the pars interarticularis. The other is an arch of bone, called the lamina, which encloses the spinal canal and protects the spinal cord. One is a strong, solid, cylindrical part called the body. Like every bone in the spine, C2 is made of two main sections. It is designated as C2: “C” for its location in the cervical spine (spine in the neck), and “2” for its position as the second bone in that spinal segment. The bone involved in hangman’s fracture is the second vertebra, toward the top of the neck, close to the skull. Hangman’s fracture is a break in a specific part of one bone in the neck.īones of the spine are called vertebrae. Hangman = a person who performs judicial (judge-ordered) hangings

0 notes
Text
Comprehensive approach to cervical spine spondylosis
Degeneration of bones and discs in the neck are referred to as cervical spine disease or cervical spondylosis. As age progresses, bones and cartilages in this region face wear and tear which results in problems such as herniated discs and bone spurs.
How to detect cervical spine spondylosis?
Neck pain, nagging soreness in the neck, muscle spasms, clicking or grinding sound while rotating or moving the head, dizziness and headaches might suggest presence of cervical spine spondylosis. Since spondylosis invokes pressure on the neighbouring nerves, pain could be felt at chest, ribs and abdomen areas.
Cervical spine spondylosis narrows the space around spinal cord and results in numbness, strain and lack of coordination in walking and loss of bladder and bowel control.
Imaging tests like neck x-ray, CT scan, MRI and Myelography would confirm the ailment.
Nerves affected by cervical spine spondylosis
First three cervical spines namely C1, C2 and C3 control head and neck and movements around them while C4 controls upward shoulder movements.
Decompression surgery suggestions
Spondylosis surgery includes removal of pain agent and fusion of spine. To remove the tissue that evokes nerve pressure, surgeon conducts decompression surgery and to conduct fusion, stabilization surgery is done.
Before going into decompression surgery let’s familiarize with terms such as ‘ectomy’ which means removal and ‘otomy’ which refers to opening.
Facetectomy and Laminoectomy removes facet joint and lamina or part of lamina (bony plate that protects spinal cord) respectively.
Foraminotomy creates an opening in the vertebra exit also known as foramen, so that nerve can exit smoothly. Laminotomy creates or enlarges opening in the bony plate so that the lamina does not press the nerve structure.
Laminoplasty is performed to create a hinge to lift lamina and mitigate compression.
Surgical approaches
The spine is accessed from the front to reach the abdomen and is known as anterior approach. Incision in the back enables posterior approach and access through the sides is lateral approach. However, anterior and posterior approaches are risky.
Risks associated with cervical spine spondylosis surgery
Complications associated with cervical spine spondylosis surgery include paralysis, inability to walk, anesthetic complications, infections associated with improper handling of wounds and complications associated with related injuries.
Non surgical suggestions for cervical spine spondylosis
Non surgical remedies include acupuncture, bed rest, using brace, muscle relaxants, physical therapy, spinal injections. Chiropractic methods like employing ice, heat, ultrasound, massage, spinal manipulation can also be employed to cure the ailment.
About Dr Karunakaran
Dr Karunakaran, spine specialist for more than two decades, has performed more than 3000 surgeries for various complications including scoliosis, cervical spine diseases, thoracotomies, laparotomy and disc replacement surgeries, to name a few.
Dr Karunakaran is also a pioneer in Tamil Nadu to perform percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy under local anesthesia for disc prolapse and INSPACE-interspinous implant for lumbar canal stenosis-key hole spine surgery local anesthesia besides being fluent in pain management techniques of spine such as foraminal epidural steroid injection, facetal blocks and discography.
Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Methods For Sciatica Relief
New Post has been published on https://backtherapyhealth.com/methods-for-sciatica-relief/
Methods For Sciatica Relief
For those who have experienced severe forms of sciatica, nothing could be more pressing than to get sciatica relief. Aside from pain, sciatica is characterized by symptoms such as muscle weakness or numbness, tingling feeling, and problems with bowel or bladder control. Symptoms are associated with a patient’s lower back, leg, and sciatic nerve. This sciatic nerve originates from the lower spine to the foot, and is considered the longest nerve in our body.
Causes of Sciatica
Sciatica is known medically as a symptom, not a diagnosis. It is important to learn the underlying cause in order for patients to get sciatica relief. The most common reasons for sciatica range from injuries such as pelvic fracture and slipped disc, to disorders like spinal stenosis, spondylolisthesis, or piriformis syndrome. There are pad materials called discs in between the vertebrae in the spine. When these discs are damaged, the outer opening breaks open or bulges. This abnormality known as a slipped disc or bulging disc puts pressure on the nerve resulting to sciatica. Spinal stenosis and spondylolisthesis refers to problems in the spine that also results to pressure applied to the nerve root on a patient’s lower back. This nerve also gets compressed when a patient has piriformis syndrome, the condition when the piriformis muscle found in the buttocks presses the nerve intensely.
Forms of Sciatica
Many forms of sciatica are mild and go away on their own after several weeks or months, even without treatment. If some pain occurs, home treatment may be administered. Other forms, however, are more intense and require other forms of treatment. If severe pain occurs suddenly in the lower back or the leg, or if difficulties in bowel or bladder control are experienced, it is strongly advised to consult a doctor. A doctor’s consult is also necessary if the pain is experienced after an accident or a severe blow, or if back pain is accompanied by fever.
Home Treatment Methods
Sciatica relief can be achieved by self-care methods such as ice packs or heating bags. For the first two to three days, apply ice to the affected area. On the fourth day switch to hot compress. Another method involves placing a pillow on strategic parts of the leg to alleviate the pressure. Patients who sleep curled on their side are recommended to put a pillow between their legs, while patients who prefer lying on their back need to place a pillow under the knees.
Exercise for Sciatica Relief
Exercise is also often recommended to relieve sciatica pain. A good rest is good when physical movement generates severe pain and discomfort; however, extended inactivity may aggravate the condition. The back bones and muscles become weakened and ineffectual to support the back. Depending on the underlying condition of sciatica affecting a patient, the types of exercises include strengthening exercises, stretching exercises, and aerobic exercises.
Strengthening exercises such as curl-ups and other abdominal strengthening activities help to build up the core muscles and the spinal column, while stretching exercises such as hamstring stretching and lumbar rotation loosen up the muscles. Gentle aerobic exercises like swimming or walking facilitate the flow of nutrients to the back bones and muscles. Patients must consult physicians to determine the underlying cause of sciatica so that the proper exercise routines will be determined. There are also trained physical therapists or rehabilitation physicians that can help to manage sciatica.
Surgical Treatment Methods
In some cases, sciatica relief is still not attained by home treatment or physical rehabilitation that physicians recommend surgical procedures. These procedures include laminotomy and discectomy that involves taking off disc materials that are causing the nerve compression. The need or type of surgical procedure will naturally depend on the physician’s diagnosis of the condition that is causing sciatica.
Source by Josh Stamos
0 notes
Text
Bertolotti's Syndrome: All You Need To Know
Bertolotti's Syndrome is not very common but happens to very few people. It should be properly diagnosed and carefully treated. Let’s learn more about it.
Bertolotti syndrome is an unusual reason for low back pain, concentrated along the waistline, barely off to the side. Usually twisted with sacroiliitis, this diagnosis involves less than 10% of people, and it continually goes undiagnosed. The syndrome is an infrequent reason for back pain and can get treated by a competent spinal expert with modern spinal healthcare.
Patients with Bertolotti's Syndrome, or the momentary vertebra, often experience no side effects. Notwithstanding, the patients usually experience low back pain that transfers from the sides of their waistline. The irritation might be considered sacroiliac joint pain or lumbar circle, or lumbar feature joint agony. For this reason, the condition is usually go misdiagnosed.
What is Bertolotti Syndrome?
Italian doctor Mario Bertolotti lent his name to this intrinsic condition. It's found — regardless of lower back pain— in 10 to 20 percent of the people.
Bertolotti disorder happens when the last lumbar vertebra — the lumbosacral momentary vertebra, or LSTV —and the sacrum either combine or make a misleading joint thanks to an extended cross-over process (hard knocks on the vertebrae where muscles and tendons connect) on the LSTV.
When a combination of the LSTV and sacrum (called sacralization) or pseudo-joint doesn't do any damage — and many don't — it's simply a part of your life system, present since birth. When it generates LBP, it is Bertolotti disorder.
What causes Bertolotti disorder?
Bertolotti disorder can bring LBP in various cases, leading to aggravation and reactive muscle cramps. Here are a few distinct ways.
An imbalance in the designs of the lumbar vertebrae assuming the LSTV gets melded to the sacrum and iliac bone (the "wings" of the pelvic bone), can pressure the sacroiliac joint, which could cause anguish you'd feel over your bum.
A pseudo-joint will not have the pad or oil between the bones that different joints in the body need to assist with shock. It causes bone-on-bone crushing, which can stimulate osteoarthritis. It might likewise cause increased weight on the rings of the pseudo-joint.
Sacralization could diminish your spine's versatility, accelerating the mileage of the vertebrae and shock-engrossing intravertebral circles over this area.
What are the signs of Bertolotti Syndrome?
The vast majority could never realize they had a sacralization or pseudo-joint, except if it's found coincidentally during an X-ray for something unrelated. Yet, for those cases that do cause side effects, they can fluctuate significantly from one individual to another and will show up in adulthood — in your 20s or 30s.
Side effects can include:
Limited LBP that doesn't transmit down the legs
Conceivable suffering or uneasiness in the area of the sacroiliac joint
Unexplained firmness or trouble moving in some ways with pain
Further developed side effects with sitting and laying
How is Bertolotti Syndrome diagnosed?
Bertolotti's condition can get analyzed in light of clinical history, a comprehensive physical test and X-rays. The physical test will incorporate copying the actions that trigger aggravation or pain. Then, at that point, X-rays of the lower back and pelvis can locate any problematic structure irregularities.
How is Bertolotti Syndrome treated?
Much of the time, Bertolotti's condition gets dealt with non-or negligibly obtrusive medicines. Bertolotti syndrome treatment includes:
Lifestyle improvement reduces the pressure on the affected regions of the backbone, such as repetitive rotation and elongation.
Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs, like Aleve, Advil, or Tylenol
Exercise-based recuperation assists with a change in specific regions and possibly increases mobility.
Local anesthetic and occasionally corticosteroid injections under fluoroscopic guidance along the affected nerves or directly into the pseudoarthrosis reduce inflammation. Fluoroscopy can also get utilized for diagnosis.
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) treatment uses the body's platelets to reduce pain and aggravation and mend damaged joints through an infusion with fluoroscopic guidance. It keeps away from the adverse consequences of corticosteroids, for example, raising glucose levels and decreasing recovery.
Prolotherapy is an elective Bertolotti syndrome treatment that utilizes a mix of concentrated sedatives and dextrose infused into the impacted region to improve the body's enduring ability to recuperate naturally.
Radiofrequency ablation is a procedure that uses heat to stifle the impacted nerves around a pseudo-joint.
Conclusion
Bertolotti's Syndrome (BS) indicates the presence of pain related to the physical interpretation of the presence of a lumbosacral momentary vertebra (LSTV). It is perceived when a prolonged cross-over course of the last lumbar vertebra intertwines with the first sacral section, and this oddity is known as an uncommon reason for lower back pain.
Medical surgery is generally the last option to treat this condition and is ordinarily performed to remove a pseudo-joint. Surgery can carry the condition of decreasing or eliminating the extended transverse procedure, typically executed as a same-day process. Be cautioned that there’s not much substantial proof that surgery treats Bertolotti Syndrome. Visit advantage medical clinic for the right diagnosis and treatment for BS.
#bertolotti'ssyndrome#bertolottisyndrometreatment#whatisbertolottisyndrome#bertolotti'ssyndromesymptoms
0 notes
Note
HOW DO YOU CRACK YOUR SPINE SPILL THE TEA BESTIE CHAT ME WANTS TO KNOW
(yes you did add spine asdagaf)
disclaimer i have no knowledge on medicine or physical therapy, please stop if anything hurts thank you. I will not be held accountable in any case of injury. this has been a PSA. 😘😘😘
ok so
Method [1] : Sitting Up: Sit like a normal human being, on a chair or a couch or whatever, but it is very important to not sit like a bisexual™ and keep your back str@ight (i know its hard). Then twist your back slowly, if you imagine your spine as the axis of rotation, your shoulder must slowly pivot so that in the end it has turned a 90° angle. This is easier if you have an object (like the back of the couch) to hold onto and create resistance, your thighs/legs will work fine (with the nuisance that you have to hold onto them with the opposite arm of the side you are turning, if you are twisting your back to your right you use your left hand). Do both sides. This method cracks beautifully the thoracic part of your spine
Method [2] : Laying Down: Lay on your back and get comfortable ;) Raise your one knee (left or right, your preference) up so both your hip and knee are on 90° degree angles and then slowly bring your knee towards your chest and the side opposite to this knee. You may rotate your pelvis and legs but keep your back straight. Basically do this (sans the head, if you want im not your mom). Again, do both sides. This is great for the lumbar part of your spine.
Method [3] : I Have 0 Idea How to Name This: okay so method 1 is good for the thoracic and 2 for the lumbar vertebrae, you can crack your cervical ones by twisting your head, but your sacral one are a bit harder. The only way i have cracked those is with the help of the old trusty greek school chair. As you're sitting on it, just let your self slide down until your center of gravity falls through the back of your pelvis. Now your pelvis should be positioned right at the bottom end of the chair (the bendy down part to precise). Sometimes, if you hold this position 2-3 secs, your lower back will pop and sometimes it won't, but if it does, oh golly i have never felt such euphoria. Basically the whole point is using gravity to put pressure on your lower back so it cracks. Important considerations: the surface on which you are doing it must have no give, hence the trusty school chair. You could probably do it with any chair though.

Image reference for method 2
Be free my young padawan, go fix your rusty back!!
#cracking my bones is my only talent#so i took this assignment very seriously#long post#fandomchaosposts
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Five Facts About Orthopaedic Surgeon Towns, South Australia
An orthopaedic surgeon is a doctor who specializes in treating disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Orthopaedic surgeons can specialize in any number of conditions, depending on their background and area of expertise. Orthopaedic surgeons can treat disorders of the musculoskeletal system, such as spine disorders, rotator cuff injuries, meniscal tears, lumbar injuries, metatarsal fractures, sacroiliac joint issues, soft tissue injuries, fractures of the vertebrae, disorders of the shoulder girdle and fractures of the elbow. They can also treat disorders of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), including temporomandibular joint syndrome and adhesive capsulitis.
An orthopedic surgeon has been granted permission by the Medical Council of Australia to practice an independent specialty in medicine called orthopedic surgery. In accordance with the rules set out by the Medical Board of Australia (MBA), an independent practice is required for an osteoarthritis specialist to be accepted for a practice certificate. When this is completed, the practitioner must be registered with the Medical Board of Australia under the Health Practitioners Regulation 5. Once an independent medical practitioner has been accredited, he/she may then apply to the Board for registration of his/her particular specialty interest.
The Medical Council of Australia is responsible for regulating the practices of health practitioners in different medical specialties. As part of the responsibilities of the council, it requires that the Orthopaedic Surgeon Brisbane register their specialty interests with the MCAS. The registration of these interests forms part of the requirements to participate in the Practice Management Plans (PMPs). In order to successfully complete their PMPs, the orthopaedic surgeons must ensure that they are registered.
The procedure of becoming an approved practice makes an individual eligible to become a registered orthopaedic surgeon. To be certified, the practitioner must have met the specific educational and clinical requirements set out by the Council. To this end, the Orthopaedic Research Institute (ORI) accredits an orthopaedic specialist. This certification proves that the specialist has met the minimum educational and clinical requirements for eligibility. ORI also requires that the orthopaedic surgeon register with the council on after completion of his or her PMP.
Orthopaedic surgery deals with the diagnosis, prevention and treatment of disorders relating to the musculoskeletal system. Some common disorders that an orthopaedic surgeon treats include fractures of the vertebrae, hip dysplasia, subluxation of the intervertebral disk and abnormal bone growth. Orthopaedic surgeons also treat cases of herniated discs, bone growth on the sides of the neck and headaches. Osteoporosis is treated through surgical procedures and physical therapy.
Osteoporotic fracture refers to abnormal bone growth resulting from injury or disease that results in the loss of the natural balance between the bones. Osteoporotic fractures can result from any cause and are commonly associated with aging. A patient suffering from osteoporosis will require specialized services and will be referred to a surgeon with expertise in such cases.
Hip dysplasia refers to the condition wherein the hip joint deviates from its normal position. Hip dysplasia is caused by the abnormal formation of the human pelvis. A hip dysplasia patient may also suffer from complications like arthritis. Hip dysplasia is best treated through hip replacement surgeries and physical therapy. Orthopaedic surgeons also perform arthroscopic surgical procedures to treat conditions like sacroiliac joint dislocation and hiatal hernia.
Hip replacement surgery is the most common procedure performed by an orthopaedic surgeon. This procedure involves the placement of a prosthesis at the affected area. Patients who wish to reduce their disability and pain can undergo this procedure. After the completion of the procedure, the hip will be protected from further injury and the patient can resume his active lifestyle. Osteoporosis is a major disease and must be treated immediately.
4 notes
·
View notes
Note
what kind of pain do you have? I know the post is tangential but I have degenerative back arthritis and I use a cbd menthol stick. It's on par with some light muscle relaxers I've taken. I swear on it to everybody with chronic muscle and bone aches. It's called Healing Stick by Wildflower CBD. it's a bit expensive but if you can afford it, it is a super nice go to and fast working pain relief ^^
I’m not honestly sure? the official diagnosis is “Degenerative Disc Disease” but it’s kind of a bullshit term, really. It’s the vague “umbrella” term they use when you have back pain and your MRI is a bit of a mess but they’re not really sure why? The thing is someone with no pain whatsoever could have an MRI that looks exactly like mine, so MRIs with my indicators aren’t guaranteed to create pain symptoms...
basically my low back hurts a lot, my discs are almost completely gone in my lumbar spine (particularly L4-L5 and L3-L4), I have “arthritic changes” in some of my vertebrae, plus a structural abnormality that may have been messing up my gait my entire life (transverse process fused to my sacrum--my hip can’t rotate correctly on my right side so I taught myself to compensate for it when I learned to walk as a toddler but years of moving slightly wrong may have resulted in some of my bonkers spine weirdness)
Anyway I’ve been recommended lidocane patches by my doctor as well as my pain medicines but I may check out the menthol stick. At this point I’ll literally try anything once! Thanks!
20 notes
·
View notes