#roger wakefield
Text
Outlander Parallels: 1.5 x 7.6
“How many of you know what Waulking Songs are?”
(edit made by me using CapCut)
#I’m so proud of this idea and edit!#🤍💜🧡#outlander edit#outlander#parallels#my edit#claire fraser#claire randall#claire beauchamp#roger mackenzie#roger Wakefield#outlander parallels#video edit#1.5#7.6#mine#made by me#claire#roger#quotes#outlander season 7#outlander season 1#scotland
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
Land Con 5. 29-30 April.












#Outlander#alexander vlahos#AlexanderVlahos#AllanChristie#Allan Christie#richard rankin#RichardRankin#roger mackenzie#RogerMacKenzie#roger wakefield#rogerWakefield#RogerWakefieldMacKenzie#Roger Wakefield MacKenzie#sophie skelton#SophieSkelton#brianna fraser#BrainnaFraser#brianna randall#BriannaRandall#BriannaRandallFraser#BriannaRandallFraserMacKenzie#duncan lacroix#DuncanLacroix#murtagh fraser#MurtaghFraser#murtagh fitzgibbons fraser#MurtaghFitzgibbonsFraser#StevenCree#steven cree#ian murray
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
Still my favourite aesthetic.
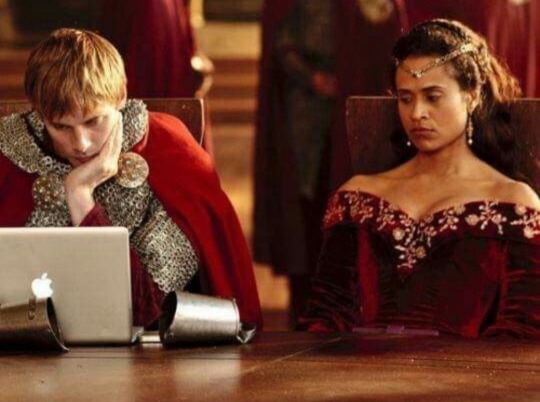
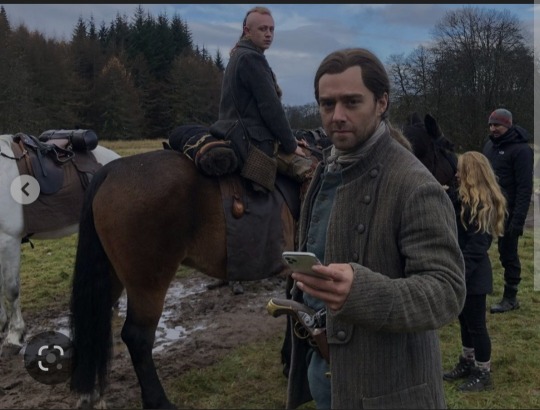
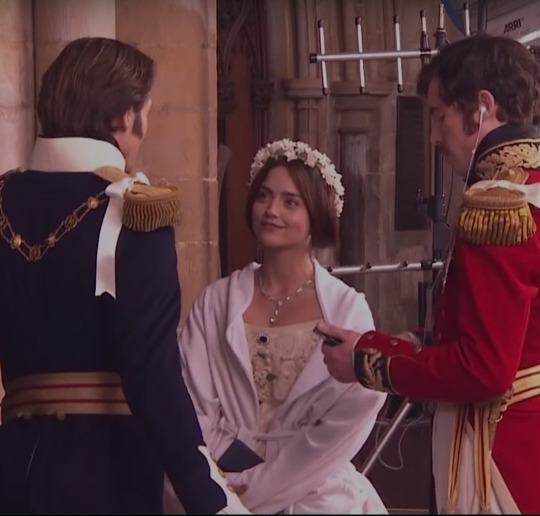






#merlin#bradley james#angel coulby#anthony head#arthur pendragon#gwenevere#uther pendragon#outlander#catriona balfe#sam heughan#richard rankin#john bell#claire randall#claire beauchamp#claire fraser#jamie fraser#roger wakefield#young ian#victoria#david oakes#tom hughes#jenna coleman#queen victoria#prince albert#marie antoniette 2006#kristen dunst#jason schwartzman#marie annette#louis xvi#period drama
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
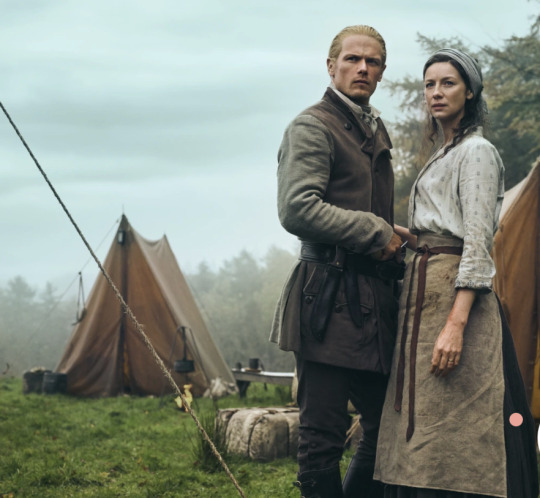

1st episode Review: Just a beautiful cinematography, amazing visuals, and sitting-at-the-edge-of-my-couch mood. There is parts that you think and feel you are in the east coast instead of Scottish set. The Writers did a wonderful job adapting this part of the book. The characters were more defined this time then from last season. The Director decided to emphasized the depth of Jamie’s eyes (amazing acting by Sam). Catriona ‘s acting always on point. I am really looking forward to next episode!!!
#outlander#sam heughan#outlander series#love outlander series#sam heughan fan#team jamie#jamie & claire fraser#jamie fraser#heughligans#cait and sam#roger wakefield#brianna fraser#the Mackenzie’s#ian murray
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

WIP Big Bang 2023 Round Starting April 1st!
What is the WIP Big Bang? Good question! This is a Big Bang with one goal in mind: to clean out your fanfic drafts folder. These are stories that were unfinished for whatever reason, that authors returned to and completed, and the art that goes with them!
Please read our FAQ/check out our schedule for more details.
#signal boost#fandom event#outlander#claire fraser#jamie fraser#frank randall#jonathan wolverton randall#dougal mackenzie#angus mhor#murtagh fitzgibbons fraser#rupert mackenzie#geillis duncan#jenny fraser murray#edward gowan#clarence marylebone#roger wakefield#brianna randall#john grey
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
I LOOOOOOOOOOOOOVED THIS SCENE <3
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Doing an outlander re-watch and I've just gotten to the part where Roger slut-shames Brianna. It makes me hate him every time.
Him expecting her to be a sweet catholic virgin girl for him when they get married!? But it's okay that he's slept with other girls right? Because he didn't love those girls. So they didn't matter.
It would have been fine if he'd said he wanted to wait for them to be married before sex but to make it about her virginity is gross. 🤮🤮🤮 And his excuse is that he's old fashioned or something... Like na you're just a misogynistic loser...
#outlander starz#outlander#Outlander s4e3#brianna randall#brianna fraser#roger wakefield#roger mackenzie
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Outlander: Roger Wakefield [ISFJ 2w1]
Outlander: Roger Wakefield [ISFJ 2w1]
Function Order: Si-Fe-Ti-Ne
Roger comes into Brianna’s circle because he’s a Scottish historian; the past, in all its incarnations, is important to him, and he engages his students in thinking about the past and the future, even what their ‘final words’ will be. Though he goes through the stones in pursuit of her, and prepares carefully for the journey, ultimately his ambition is to take them…

View On WordPress
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
I don't like show!Roger anymore than book!Roger. At least that's consistent.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Roger baby you're the sweetest omg
0 notes
Text

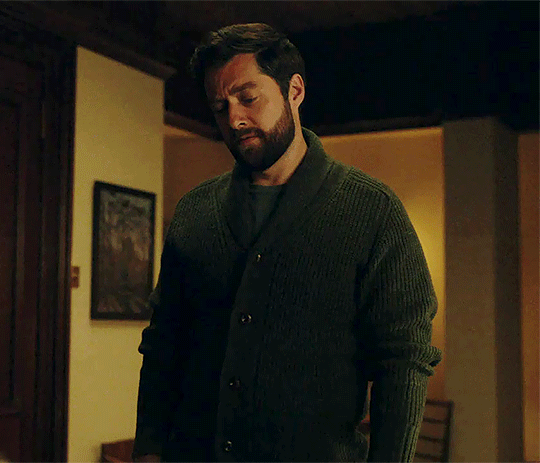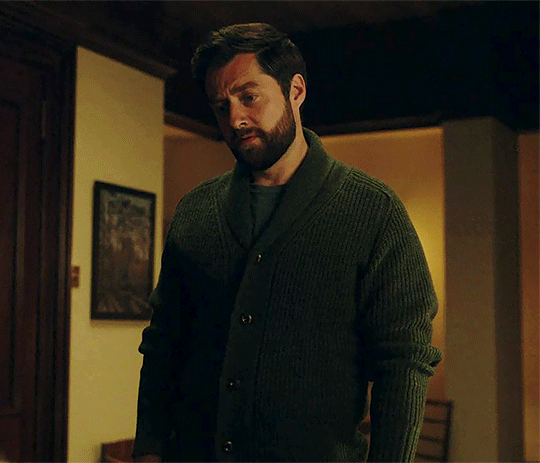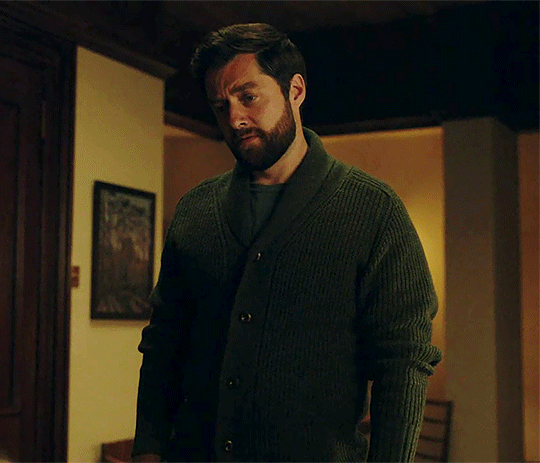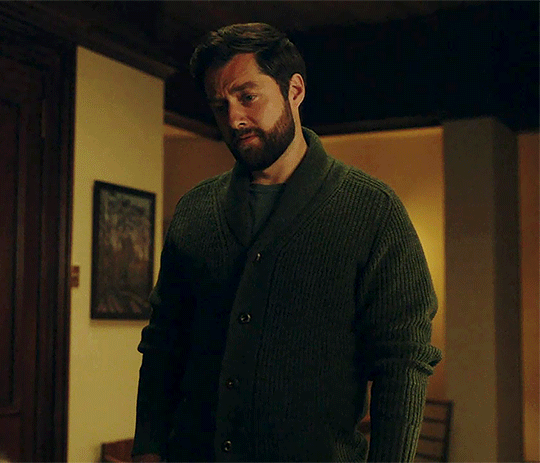







Outlander 7x05
#outlanderedit#outlander#outlander spoilers#outlander 7x05#roger mackenzie#brianna mackenzie#roger and bree#roger mac#roger mackenzie wakefield#brianna fraser#roger x bree#themackenziesarehere#my gifs#mod post
123 notes
·
View notes
Text
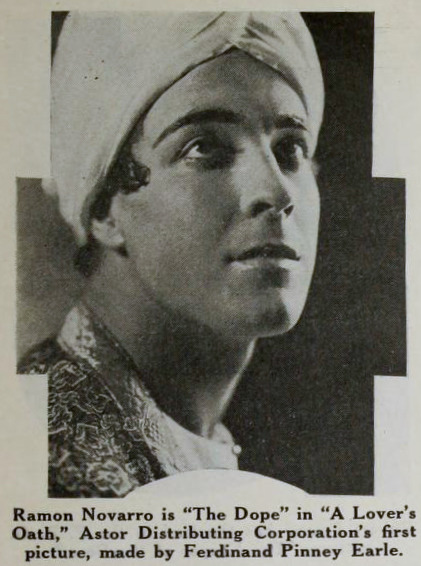
(Mostly) Lost, but Not Forgotten: Omar Khayyam (1923) / A Lover’s Oath (1925)
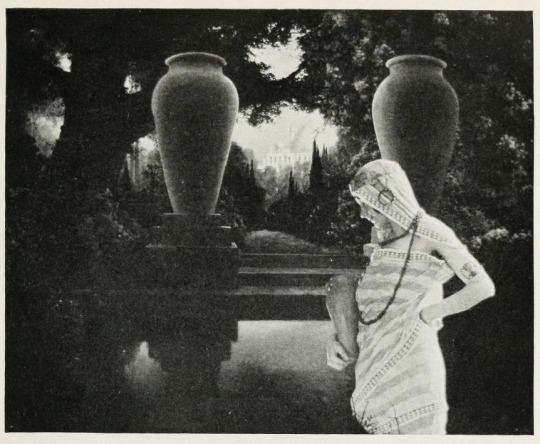












Alternate Titles: The Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam, The Rubaiyat, Omar Khayyam, Omar
Direction: Ferdinand Pinney Earle; assisted by Walter Mayo
Scenario: Ferdinand P. Earle
Titles: Marion Ainslee, Ferdinand P. Earle (Omar), Louis Weadock (A Lover’s Oath)
Inspired by: The Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam, as edited & translated by Edward FitzGerald
Production Manager: Winthrop Kelly
Camera: Georges Benoit
Still Photography: Edward S. Curtis
Special Photographic Effects: Ferdinand P. Earle, Gordon Bishop Pollock
Composer: Charles Wakefield Cadman
Editors: Arthur D. Ripley (The Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam version), Ethel Davey & Ferdinand P. Earle (Omar / Omar Khayyam, the Director’s cut of 1922), Milton Sills (A Lover’s Oath)
Scenic Artists: Frank E. Berier, Xavier Muchado, Anthony Vecchio, Paul Detlefsen, Flora Smith, Jean Little Cyr, Robert Sterner, Ralph Willis
Character Designer: Louis Hels
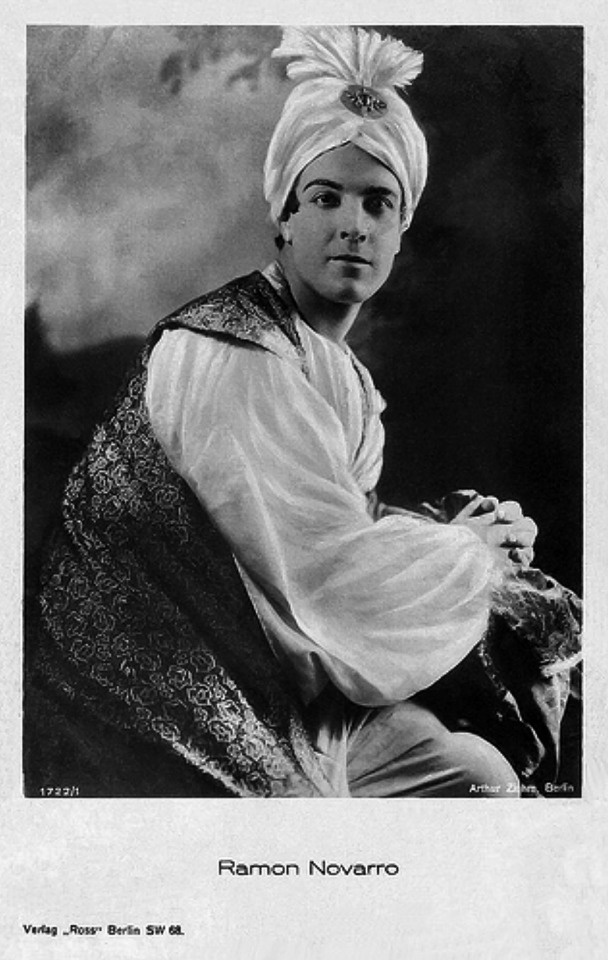
Choreography: Ramon Novarro (credited as Ramon Samaniegos)
Technical Advisors: Prince Raphael Emmanuel, Reverend Allan Moore, Captain Dudley S. Corlette, & Captain Montlock or Mortlock
Studio: Ferdinand P. Earle Productions / The Rubaiyat, Inc. (Production) & Eastern Film Corporation (Distribution, Omar), Astor Distribution Corporation [States Rights market] (Distribution, A Lover’s Oath)
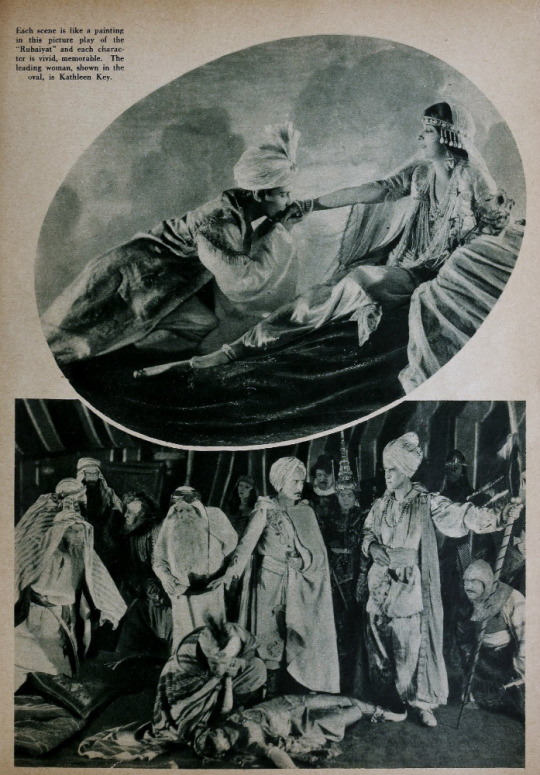
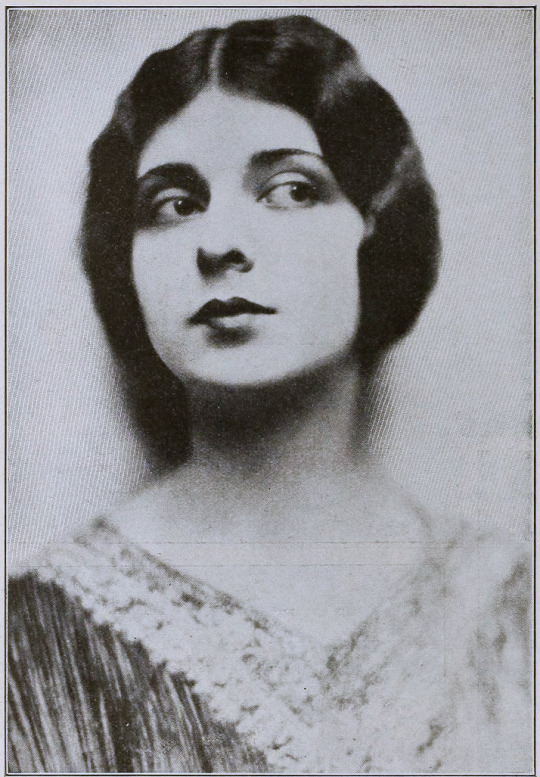
Performers: Frederick Warde, Edwin Stevens, Hedwiga Reicher, Mariska Aldrich, Paul Weigel, Robert Anderson, Arthur Carewe, Jesse Weldon, Snitz Edwards, Warren Rogers, Ramon Novarro (originally credited as Ramon Samaniegos), Big Jim Marcus, Kathleen Key, Charles A. Post, Phillippe de Lacy, Ferdinand Pinney Earle
Premiere(s): Omar cut: April 1922 The Ambassador Theatre, New York, NY (Preview Screening), 12 October 1923, Loew’s New York, New York, NY (Preview Screening), 2 February 1923, Hoyt’s Theatre, Sydney, Australia (Initial Release)
Status: Presumed lost, save for one 30 second fragment preserved by the Academy Film Archive, and a 2.5 minute fragment preserved by a private collector (Old Films & Stuff)
Length: Omar Khayyam: 8 reels , 76 minutes; A Lover’s Oath: 6 reels, 5,845 feet (though once listed with a runtime of 76 minutes, which doesn’t line up with the stated length of this cut)
Synopsis (synthesized from magazine summaries of the plot):
Omar Khayyam:
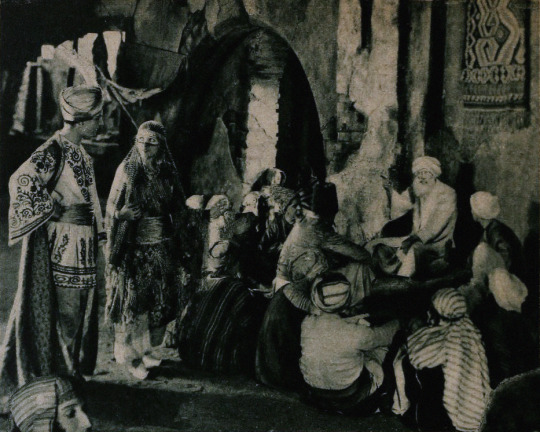
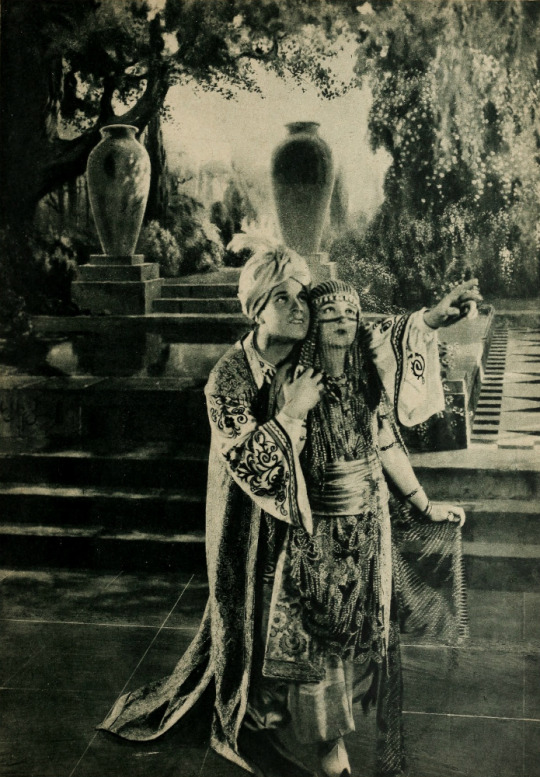
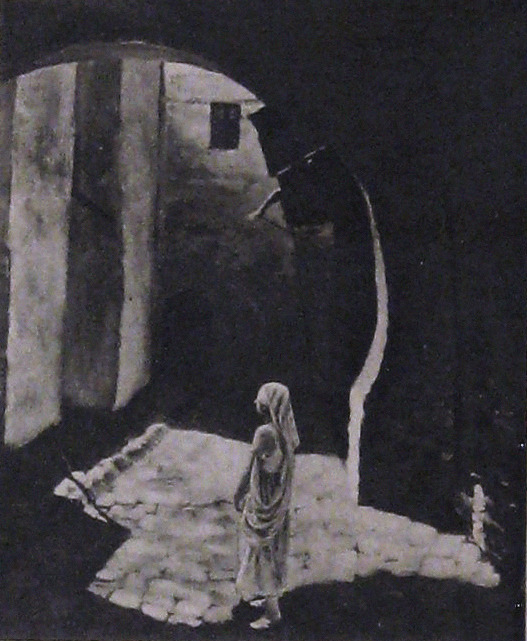
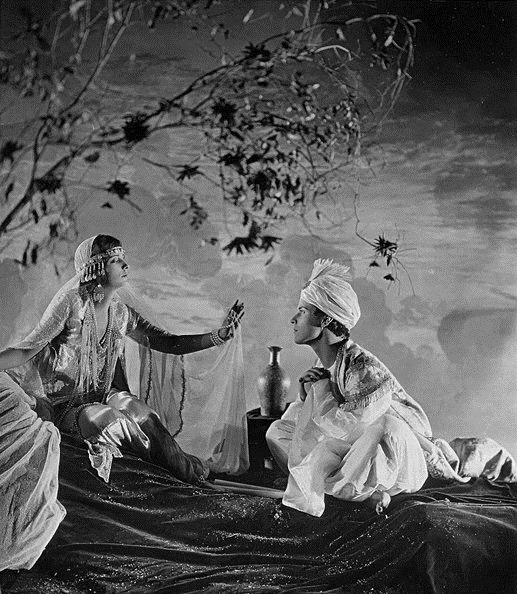
Set in 12th century Persia, the story begins with a preface in the youth of Omar Khayyam (Warde). Omar and his friends, Nizam (Weigel) and Hassan (Stevens), make a pact that whichever one of them becomes a success in life first will help out the others. In adulthood, Nizam has become a potentate and has given Omar a position so that he may continue his studies in mathematics and astronomy. Hassan, however, has grown into quite the villain. When he is expelled from the kingdom, he plots to kidnap Shireen (Key), the sheik’s daughter. Shireen is in love with Ali (Novarro). In the end it’s Hassan’s wife (Reicher) who slays the villain then kills herself.
A Lover’s Oath:
The daughter of a sheik, Shireen (Key), is in love with Ali (Novarro), the son of the ruler of a neighboring kingdom. Hassan covets Shireen and plots to kidnap her. Hassan is foiled by his wife. [The Sills’ edit places Ali and Shireen as protagonists, but there was little to no re-shooting done (absolutely none with Key or Novarro). So, most critics note how odd it is that all Ali does in the film is pitch woo, and does not save Shireen himself. This obviously wouldn’t have been an issue in the earlier cut, where Ali is a supporting character, often not even named in summaries and news items. Additional note: Post’s credit changes from “Vizier” to “Commander of the Faithful”]
Additional sequence(s) featured in the film (but I’m not sure where they fit in the continuity):
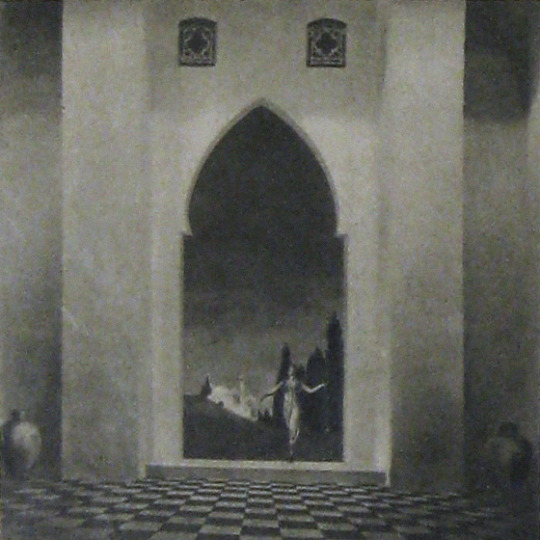
Celestial sequences featuring stars and planets moving through the cosmos
Angels spinning in a cyclone up to the heavens
A Potters’ shop sequence (relevant to a specific section of the poems)
Harem dance sequence choreographed by Novarro
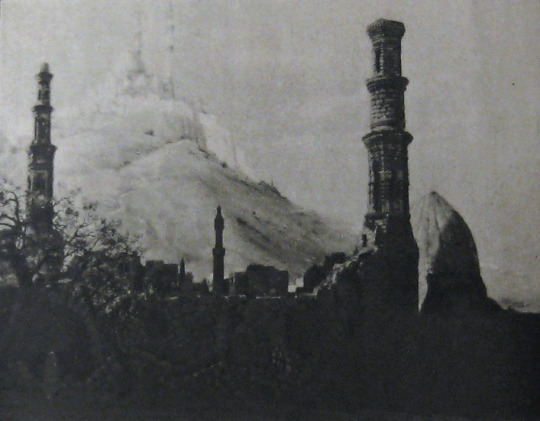
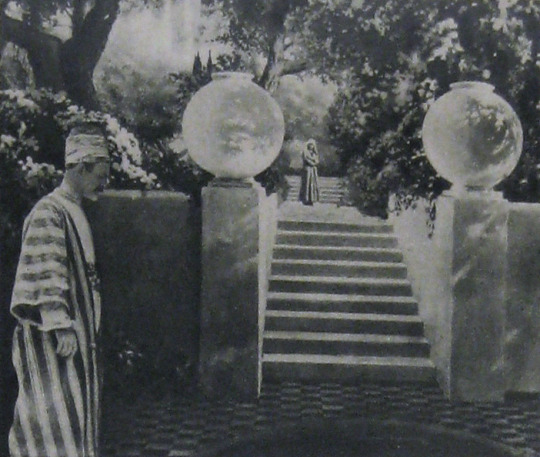
Locations: palace gardens, street and marketplace scenes, ancient ruins
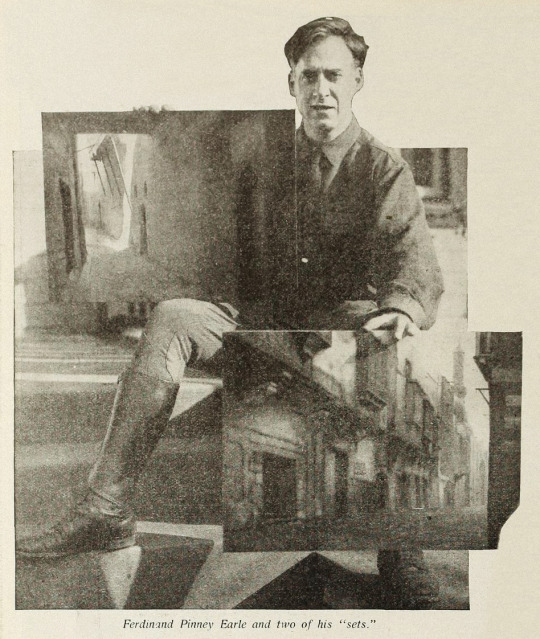
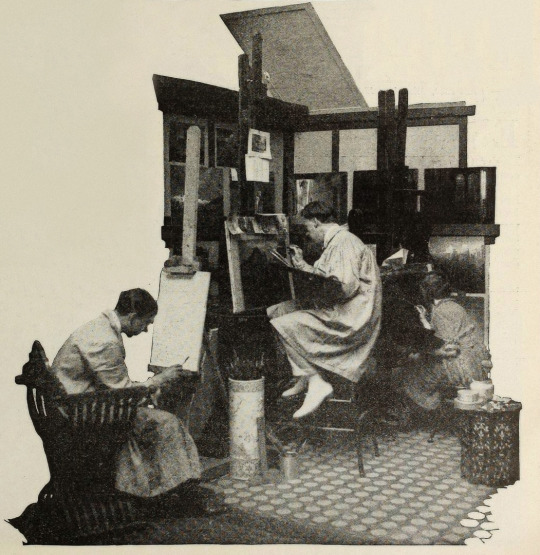
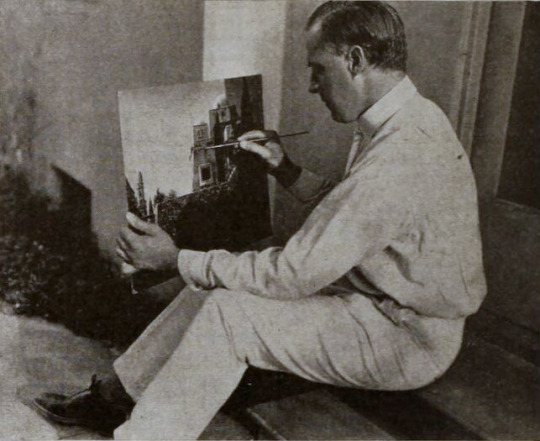





Points of Interest:
“The screen has been described as the last word in realism, but why confine it there? It can also be the last word in imaginative expression.”
Ferdinand P. Earle as quoted in Exhibitors Trade Review, 4 March 1922
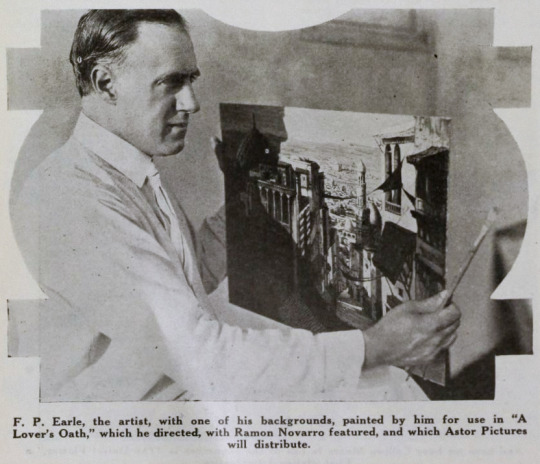
The Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam was a massive best seller. Ferdinand Pinney Earle was a classically trained artist who studied under William-Adolphe Bougueraeu and James McNeill Whistler in his youth. He also had years of experience creating art backgrounds, matte paintings, and art titles for films. Charles Wakefield Cadman was an accomplished composer of songs, operas, and operettas. Georges Benoit and Gordon Pollock were experienced photographic technicians. Edward S. Curtis was a widely renowned still photographer. Ramon Novarro was a name nobody knew yet—but they would soon enough.
When Earle chose The Rubaiyat as the source material for his directorial debut and collected such skilled collaborators, it seemed likely that the resulting film would be a landmark in the art of American cinema. Quite a few people who saw Earle’s Rubaiyat truly thought it would be:
William E. Wing writing for Camera, 9 September 1922, wrote:
“Mr. Earle…came from the world of brush and canvass, to spread his art upon the greater screen. He created a new Rubaiyat with such spiritual colors, that they swayed.”
…
“It has been my fortune to see some of the most wonderful sets that this Old Earth possesses, but I may truly say that none seized me more suddenly, or broke with greater, sudden inspiration upon the view and the brain, than some of Ferdinand Earle’s backgrounds, in his Rubaiyat.
“His vision and inspired art seem to promise something bigger and better for the future screen.”
As quoted in an ad in Film Year Book, 1923:
“Ferdinand Earle has set a new standard of production to live up to.”
Rex Ingram
“Fifty years ahead of the time.”
Marshall Neilan
The film was also listed among Fritz Lang’s Siegfried, Chaplin’s Gold Rush, Fairbanks’ Don Q, Lon Chaney’s Phantom of the Opera and The Unholy Three, and Erich Von Stroheim’s Merry Widow by the National Board of Review as an exceptional film of 1925.
So why don’t we all know about this film? (Spoiler: it’s not just because it’s lost!)
The short answer is that multiple dubious legal challenges arose that prevented Omar’s general release in the US. The long answer follows BELOW THE JUMP!
Earle began the project in earnest in 1919. Committing The Rubaiyat to film was an ambitious undertaking for a first-time director and Earle was striking out at a time when the American film industry was developing an inferiority complex about the level of artistry in their creative output. Earle was one of a number of artists in the film colony who were going independent of the emergent studio system for greater protections of their creative freedoms.
In their adaptation of The Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam, Earle and Co. hoped to develop new and perfect existing techniques for incorporating live-action performers with paintings and expand the idea of what could be accomplished with photographic effects in filmmaking. The Rubaiyat was an inspired choice. It’s not a narrative, but a collection of poetry. This gave Earle the opportunity to intersperse fantastical, poetic sequences throughout a story set in the lifetime of Omar Khayyam, the credited writer of the poems. In addition to the fantastic, Earle’s team would recreate 12th century Persia for the screen.
Earle was convinced that if his methods were perfected, it wouldn’t matter when or where a scene was set, it would not just be possible but practical to put on film. For The Rubaiyat, the majority of shooting was done against black velvet and various matte photography and multiple exposure techniques were employed to bring a setting 800+ years in the past and 1000s of miles removed to life before a camera in a cottage in Los Angeles.
Note: If you’d like to learn a bit more about how these effects were executed at the time, see the first installment of How’d They Do That.
Unfortunately, the few surviving minutes don’t feature much of this special photography, but what does survive looks exquisite:

see all gifs here
Earle, knowing that traditional stills could not be taken while filming, brought in Edward S. Curtis. Curtis developed techniques in still photography to replicate the look of the photographic effects used for the film. So, even though the film hasn’t survived, we have some pretty great looking representations of some of the 1000s of missing feet of the film.

Nearly a year before Curtis joined the crew, Earle began collaboration with composer Charles Wakefield Cadman. In another bold creative move, Cadman and Earle worked closely before principal photography began so that the score could inform the construction and rhythm of the film and vice versa.
By the end of 1921 the film was complete. After roughly 9 months and the creation of over 500 paintings, The Rubaiyat was almost ready to meet its public. However, the investors in The Rubaiyat, Inc., the corporation formed by Earle to produce the film, objected to the ample reference to wine drinking (a comical objection if you’ve read the poems) and wanted the roles of the young lovers (played by as yet unknown Ramon Novarro and Kathleen Key) to be expanded. The dispute with Earle became so heated that the financiers absconded with the bulk of the film to New York. Earle filed suit against them in December to prevent them from screening their butchered and incomplete cut. Cadman supported Earle by withholding the use of his score for the film.
Later, Eastern Film Corp. brokered a settlement between the two parties, where Earle would get final cut of the film and Eastern would handle its release. Earle and Eastern agreed to change the title from The Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam to simply Omar. Omar had its first official preview in New York City. It was tentatively announced that the film would have a wide release in the autumn.
However, before that autumn, director Norman Dawn launched a dubious patent-infringement suit against Earle and others. Dawn claimed that he owned the sole right to use multiple exposures, glass painting for single exposure, and other techniques that involved combining live action with paintings. All the cited techniques had been widespread in the film industry for a decade already and eventually and expectedly Dawn lost the suit. Despite Earle’s victory, the suit effectively put the kibosh on Omar’s release in the US.
Earle moved on to other projects that didn’t come to fruition, like a Theda Bara film and a frankly amazing sounding collaboration with Cadman to craft a silent-film opera of Faust. Omar did finally get a release, albeit only in Australia. Australian news outlets praised the film as highly as those few lucky attendees of the American preview screenings did. The narrative was described as not especially original, but that it was good enough in view of the film’s artistry and its imaginative “visual phenomena” and the precision of its technical achievement.
One reviewer for The Register, Adelaide, SA, wrote:
“It seems almost an impossibility to make a connected story out of the short verse of the Persian of old, yet the producer of this classic of the screen… has succeeded in providing an entertainment that would scarcely have been considered possible. From first to last the story grips with its very dramatic intensity.”
While Omar’s American release was still in limbo, “Ramon Samaniegos” made a huge impression in Rex Ingram’s Prisoner of Zenda (1922, extant) and Scaramouche (1923, extant) and took on a new name: Ramon Novarro. Excitement was mounting for Novarro’s next big role as the lead in the epic Ben-Hur (1925, extant) and the Omar project was re-vivified.

A new company, Astor Distribution Corp., was formed and purchased the distribution rights to Omar. Astor hired actor (note, not an editor) Milton Sills to re-cut the film to make Novarro and Key more prominent. The company also re-wrote the intertitles, reduced the films runtime by more than ten minutes, and renamed the film A Lover’s Oath. Earle had moved on by this point, vowing to never direct again. In fact, Earle was indirectly working with Novarro and Key again at the time, as an art director on Ben-Hur!
Despite Omar’s seemingly auspicious start in 1920, it was only released in the US on the states rights market as a cash-in on the success of one of its actors in a re-cut form five years later.
That said, A Lover’s Oath still received some good reviews from those who did manage to see it. Most of the negative criticism went to the story, intertitles, and Sills’ editing.
What kind of legacy could/should Omar have had? I’m obviously limited in my speculation by the fact that the film is lost, but there are a few key facts about the film’s production, release, and timing to consider.
The production budget was stated to be $174,735. That is equivalent to $3,246,994.83 in 2024 dollars. That is a lot of money, but since the production was years long and Omar was a period film set in a remote locale and features fantastical special effects sequences, it’s a modest budget. For contemporary perspective, Robin Hood (1922, extant) cost just under a million dollars to produce and Thief of Bagdad (1924, extant) cost over a million. For a film similarly steeped in spectacle to have nearly 1/10th of the budget is really very noteworthy. And, perhaps if the film had ever had a proper release in the US—in Earle’s intended form (that is to say, not the Sills cut)—Omar may have made as big of a splash as other epics.
It’s worth noting here however that there are a number of instances in contemporary trade and fan magazines where journalists off-handedly make this filmmaking experiment about undermining union workers. Essentially implying that that value of Earle’s method would be to continue production when unionized workers were striking. I’m sure that that would absolutely be a primary thought for studio heads, but it certainly wasn’t Earle’s motivation. Often when Earle talks about the method, he focuses on being able to film things that were previously impossible or impracticable to film. Driving down filming costs from Earle’s perspective was more about highlighting the artistry of his own specialty in lieu of other, more demanding and time-consuming approaches, like location shooting.
This divide between artists and studio decision makers is still at issue in the American film and television industry. Studio heads with billion dollar salaries constantly try to subvert unions of skilled professionals by pursuing (as yet) non-unionized labor. The technical developments of the past century have made Earle’s approach easier to implement. However, just because you don’t have to do quite as much math, or time an actor’s movements to a metronome, does not mean that filming a combination of painted/animated and live-action elements does not involve skilled labor.
VFX artists and animators are underappreciated and underpaid. In every new movie or TV show you watch there’s scads of VFX work done even in films/shows that have mundane, realistic settings. So, if you love a film or TV show, take the effort to appreciate the work of the humans who made it, even if their work was so good you didn’t notice it was done. And, if you’ve somehow read this far, and are so out of the loop about modern filmmaking, Disney’s “live-action” remakes are animated films, but they’ve just finagled ways to circumvent unions and low-key delegitimize the skilled labor of VFX artists and animators in the eyes of the viewing public. Don’t fall for it.
VFX workers in North America have a union under IATSE, but it’s still developing as a union and Marvel & Disney workers only voted to unionize in the autumn of 2023. The Animation Guild (TAG), also under the IATSE umbrella, has a longer history, but it’s been growing rapidly in the past year. A strike might be upcoming this year for TAG, so keep an eye out and remember to support striking workers and don’t cross picket lines, be they physical or digital!
Speaking of artistry over cost-cutting, I began this post with a mention that in the early 1920s, the American film industry was developing an inferiority complex in regard to its own artistry. This was in comparison to the European industries, Germany’s being the largest at the time. It’s frustrating to look back at this period and see acceptance of the opinion that American filmmakers weren’t bringing art to film. While yes, the emergent studio system was highly capitalistic and commercial, that does not mean the American industry was devoid of home-grown artists.
United Artists was formed in 1919 by Douglas Fairbanks, Charlie Chaplin, Mary Pickford, and D.W. Griffith precisely because studios were holding them back from investing in their art—within the same year that Earle began his Omar project. While salaries and unforgiving production schedules were also paramount concerns in the filmmakers going independent, a primary impetus was that production/distribution heads exhibited too much control over what the artists were trying to create.
Fairbanks was quickly expanding his repertoire in a more classical and fantastic direction. Cecil B. DeMille made his first in a long and very successful string of ancient epics. And the foreign-born children of the American film industry, Charlie Chaplin, Rex Ingram, and Nazimova, were poppin’ off! Chaplin was redefining comedic filmmaking. Ingram was redefining epics. Nazimova independently produced what is often regarded as America’s first art film, Salome (1923, extant), a film designed by Natacha Rambova, who was *gasp* American. Earle and his brother, William, had ambitious artistic visions of what could be done in the American industry and they also had to self-produce to get their work done.
Meanwhile, studio heads, instead of investing in the artists they already had contracts with, tried to poach talent from Europe with mixed success (in this period, see: Ernst Lubitsch, F.W. Murnau, Benjamin Christensen, Mauritz Stiller, Victor Sjöström, and so on). I’m in no way saying it was the wrong call to sign these artists, but all of these filmmakers, even if they found success in America, had stories of being hired to inject the style and artistry that they developed in Europe into American cinema, and then had their plans shot down or cut down to a shadow of their creative vision. Even Stiller, who tragically died before he had the opportunity to establish himself in the US, faced this on his first American film, The Temptress (1926, extant), on which he was replaced. Essentially, the studio heads’ actions were all hot air and spite for the filmmakers who’d gone independent.





Finally I would like to highlight Ferdinand Earle’s statement to the industry, which he penned for from Camera in 14 January 1922, when his financial backers kidnapped his film to re-edit it on their terms:
MAGNA CHARTA
Until screen authors and producers obtain a charter specifying and guaranteeing their privileges and rights, the great slaughter of unprotected motion picture dramas will go merrily on.
Some of us who are half artists and half fighters and who are ready to expend ninety per cent of our energy in order to win the freedom to devote the remaining ten per cent to creative work on the screen, manage to bring to birth a piteous, half-starved art progeny.
The creative artist today labors without the stimulus of a public eager for his product, labors without the artistic momentum that fires the artist’s imagination and spurs his efforts as in any great art era.
Nowadays the taint of commercialism infects the seven arts, and the art pioneer meets with constant petty worries and handicaps.
Only once in a blue moon, in this matter-of-fact, dollar-wise age can the believer in better pictures hope to participate in a truely [sic] artistic treat.
In the seven years I have devoted to the screen, I have witnessed many splendid photodramas ruined by intruding upstarts and stubborn imbeciles. And I determined not to launch the production of my Opus No. 1 until I had adequately protected myself against all the usual evils of the way, especially as I was to make an entirely new type of picture.
In order that my film verison [sic] of the Rubaiyat of Omar Khayyam might be produced under ideal conditions and safeguarded from intolerable interferences and outside worries, I entered into a contract with the Rubaiyat, Inc., that made me not only president of the corporation and on the board of directors, but which set forth that I was to be author, production manager, director, cutter and film editor as well as art director, and that no charge could be made against the production without my written consent, and that my word was to be final on all matters of production. The late George Loane Tucker helped my attorney word the contract, which read like a splendid document.
Alas, I am now told that only by keeping title to a production until it is declared by yourself to be completed is it safe for a scenario writer, an actor or a director, who is supposedly making his own productions, to contract with a corporation; otherwise he is merely the servant of that corporation, subject at any moment to discharge, with the dubious redress of a suit for damages that can with difficulty be estimated and proven.
Can there be any hope of better pictures as long as contracts and copyrights are no protection against financial brigands and bullies?
We have scarcely emerged from barbarism, for contracts, solemnly drawn up between human beings, in which the purposes are set forth in the King’s plainest English, serve only as hurdles over which justice-mocking financiers and their nimble attorneys travel with impunity, riding rough shod over the author or artist who cannot support a legal army to defend his rights. The phrase is passed about that no contract is invioliable [sic]—and yet we think we have reached a state of civilization!
The suit begun by my attorneys in the federal courts to prevent the present hashed and incomplete version of my story from being released and exhibited, may be of interest to screen writers. For the whole struggle revolves not in the slightest degree around the sanctity of the contract, but centers around the federal copyright of my story which I never transferred in writing otherwise, and which is being brazenly ignored.
Imagine my production without pictorial titles: and imagine “The Rubaiyat” with a spoken title as follows, “That bird is getting to talk too much!”—beside some of the immortal quatrains of Fitzgerald!
One weapon, fortunately, remains for the militant art creator, when all is gone save his dignity and his sense of humor; and that is the rapier blade of ridicule, that can send lumbering to his retreat the most brutal and elephant-hided lord of finance.
How edifying—the tableau of the man of millions playing legal pranks upon men such as Charles Wakefield Cadman, Edward S. Curtis and myself and others who were associated in the bloody venture of picturizing the Rubaiyat! It has been gratifying to find the press of the whole country ready to champion the artist’s cause.
When the artist forges his plowshare into a sword, so to speak, he does not always put up a mean fight.
What publisher would dare to rewrite a sonnet of John Keats or alter one chord of a Chopin ballade?
Creative art of a high order will become possible on the screen only when the rights of established, independent screen producers, such as Rex Ingram and Maurice Tourneur, are no longer interferred with and their work no longer mutilated or changed or added to by vandal hands. And art dramas, conceived and executed by masters of screen craft, cannot be turned out like sausages made by factory hands. A flavor of individuality and distinction of style cannot be preserved in machine-made melodramas—a drama that is passed from hand to hand and concocted by patchworkers and tinkerers.
A thousand times no! For it will always be cousin to the sausage, and be like all other—sausages.
The scenes of a master’s drama may have a subtle pictorial continuity and a power of suggestion quite like a melody that is lost when just one note is changed. And the public is the only test of what is eternally true or false. What right have two or three people to deprive millions of art lovers of enjoying an artist’s creation as it emerged from his workshop?
“The Rubaiyat” was my first picture and produced in spite of continual and infernal interferences. It has taught me several sad lessons, which I have endeavored in the above paragraphs to pass on to some of my fellow sufferers. It is the hope that I am fighting, to a certain extent, their battle that has given me the courage to continue, and that has prompted me to write this article. May such hubbubs eventually teach or inforce a decent regard for the rights of authors and directors and tend to make the existence of screen artisans more secure and soothing to the nerves.
FERDINAND EARLE.
---
☕Appreciate my work? Buy me a coffee! ☕
Transcribed Sources & Annotations over on the WMM Blog!
See the Timeline for Ferdinand P. Earle's Rubaiyat Adaptation
#1920s#1923#1925#omar khayyam#ferdinand pinney earle#ramon novarro#independent film#american film#silent cinema#silent era#silent film#classic cinema#classic movies#classic film#film history#history#Charles Wakefield Cadman#cinematography#The Rubaiyat#cinema#film#lost film
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
Easter Eggs and Spoilers for 7x03 below the cut!

The Big House
The big house burns - and we learn that Arch Bug had been hiding a secret right beneath Jamie and Claire’s nose. But what I found especially interesting about this storyline (and even more so when I first read the books), was the discovery that their obituary was written in error, and why.
Claire and Jamie remark that it is not January at the time that the house burns down, and it’s clearly not even Fall in the show (in the books the house burns on December 21st). Claire also makes a comment about how newspapers never get anything correct, which is comical considering Jamie’s previous profession as a printer.
In the epilogue of A Breath of Snow and Ashes, we discover that the news of their deaths was reported by a reader of the local paper in Wilmington, and was used to fill a page beneath General Washington’s address to the troops. Spoiler territory, but it was actually Tom Christie who heard of the big house fire and wanted to put a formal obituary in the paper to honor Claire and Jamie. We see that Tom is very much still alive in the preview for this week’s episode, so that will cover the rest of that storyline.
But back to the book epilogue. The printer admits that he was told the news of their deaths in December, but printed the date as January because he had set the page in a specific font which had been missing the November and December slugs, and would have had to type it out in separate letters (which he did not feel was worth it, since after all, they are dead).
1980’s
Back in the future, we are in Inverness with Fiona and her husband and daughters. We briefly see Jemmy and Fiona’s kids playing in the yard, with Mandy in the bassinet and implied to be recovering from her heart surgery. The year is 1980 but it’s implied they have been there for a little while now - I know a lot of people were confused as to why there was such a time jump. Claire and Jamie are in 1776, and while Claire always says she went back 200 years, we will soon learn once Roger begins writing his book on time travel that it’s not exact every time.
There, Fiona gives Bree and Roger a mystery box which had been delivered to Reverend Wakefield’s former address and kept by the bank for over 200 years. In the books, Claire and Jamie deliver this chest to a bank in Edinburgh once they arrive back in Scotland so that one day in the future it would be delivered to Jemmy. So to ensure that no one else would ever open the box at that time, they gave strict instructions that it not be opened by anyone other than the name on the top, and used Jemmy’s full name (presumably so that no other Scot with a similar name could claim it as theirs). We see them writing those letters in this episode to Brianna and Roger, updating them as to what has happened and their journey to Scotland.
In the books, the end of A Breath of Snow and Ashes is Bree reading the letter and line “we are alive”, then the book ends. I like that we don’t have that cliffhanger here and can see this storyline unfold right away as it is one of my favorites from the books. In this moment we were able to get excerpts from a few more letters which are taken directly from An Echo in the Bone, and can see how Jamie and Claire had both taken turns writing to the McKenzie’s.
In the books, the box includes letters, two books, and Sawnee, Jamie’s toy snake from his brother. In the show, they included a musket ball which we saw them making out of the stolen French gold in the episode. Another difference is that in the books, the letter is written on December 31st, ten days after the fire. In the show, it’s written in April.
Bree and William
In Echo in the Bone, the opening scene takes place with Bree and Roger still in Wilmington, and standing with William watching Stephen Bonnet tied up in the harbor (obviously this has been rearranged in the show, since the Bonnet storyline wrapped up in Season 5). It is on the shore that she meets William, and William meets Mandy and Jemmy as well. Then we cut to Lallybroch in September of 1980, where Bree and Roger are continuing to read the first letter from Claire. Having been so immersed in the show, it’s easy to forget how many storylines they have moved around from the books.
Like the books, Roger points out that Bree’s matches are in fact the thing that caused the fire of the Big House while reading Claire’s letter. He points out that in trying to prevent their deaths they had succeeded, and changed the future. This is reminiscent of Claire and Jamie’s journey to France and how their attempts to prevent an event were likely the very thing that caused it.
Ian and William
Back at the Big House, Claire, Jamie and Ian are going through the rubble in search of anything they can recover. Amongst the items are a few of Claire’s books, Jamie’s old tartan, and a piece of the french gold. Young Ian is also able to recover the portrait of William that Lord John had given Jamie.
In the books, Ian had been suspicious of William’s parentage the first time he met him as a child back on the Ridge when he and Lord John had visited. He had recognized his stubborn nature as one that mirrored Jamie’s and his mother’s, but never made mention of it to Jamie. In the show they took this opportunity to have Jamie and Ian share that really lovely moment. You can tell what a relief it has been to Jamie each and every time someone else learns of this secret he has been harboring. And Ian has such a huge role in Jamie’s life as his only true remaining family to be with him now. I really think John Bell is the perfect Young Ian.
French Gold
Arch Bug and Jamie have their inevitable confrontation where he admits that he had been taking it back from Hector Cameron bit by bit each time he was sent to River Run. For backstory and a refresher, Jocasta Cameron (Jamie’s aunt) was married to a man named Hector Cameron, who we briefly saw in a flashback during season 4. Hector, his brother in law Dougal (Jamie’s Uncle), and a third man (who we now know was Arch Bug’s Laird, Malcolm Grant) had the gold and intended to use it to support the Jacobite cause and aid Charles Stuart’s rebellion.
When Hector Cameron and Jocasta fled Scotland after the rising, they took their share of the Jacobite gold with them and used it to fund River Run. It was during that journey that Hector accidentally killed he and Jocasta’s daughter, Morna. Arch felt that the gold was misused and Hector was a traitor to Scotland and the cause. He felt it was his duty to take it back, and in doing so he stole from Jamie’s family. Jamie terminates Arch’s employment at the Ridge and releases him of his oath to him.
In the books this moment is substantial because the Bugs are less of background characters and we have seen how much they mean to the Frasers. The show isn’t able to capture that properly, and even more so with Mrs Bug. It isn’t until An Echo in the Bone where Mrs. Bug returns to the Big House in search of the remaining gold where she is mistaken for Arch and is killed by Ian. She was a grandmother figure to Ian whom he deeply loved and appreciated so this was heartbreaking in the books. I suspect in episode 4 we will see Ian and Rachel meet and perhaps by the end of this first half of season 7 we will have Arch return. In the books he goes after Rachel a few times, as Ian is in love with her. William is the one who saves her a few times, and I’m looking forward to him and Ian interacting with one another for the rest of this season.
Return to Scotland
Back on the Ridge, time has passed (as made evident by Claire’s hair). Jamie and Claire discuss where they might set out to build another house, and they share a conversation about where they would like their body’s buried should either of them be killed which is direct from the books. Jamie tells Claire that he wishes to first return to Scotland, as he had promised Ian and Jenny that he would return young Ian to them. With the war looming, it is now or never. They agree that they should go and begin making plans to travel back across the ocean to Lallybroch.
In the books he does not admit that to Claire right away but instead says his reason for returning is to fetch his printing press. The Ridge is no longer a safe place for them while there is so much unrest regarding Malva and now Mrs Bug. Claire thinks they can go live with Fergus and Marsali in New Bern, and it is then Jamie tells her he wishes to bring Ian home and have him avoid the war.
That night, while in bed, Claire can hear Jamie praying. In the books, he leaves their room and goes to a small pool or water near their cabin to pray, and Claire finds him there only to pick up on him praying to God to let him be enough. I enjoyed how this scene was shot in the show better, to be honest. And rolls perfectly into the following morning when Jamie tells Claire of his most recent dream.
The frequency of Jamie’s dreams of the future seem to be increasing, and this time he tells Claire that he saw the McKenzie’s. They were walking up to a house, and looked happy. He is able to tell Claire the name of the woman speaking to them both, Fiona, which Claire knows she had not shared with Jamie before. He also tells Claire that Jemmy was trying to talk to him through a box he’d never seen before, and she tells him it is a telephone.
To hide what was left of the French Gold, Jamie uses some of it for musket balls and the remainder he puts into a chest. He and Claire then return to a cave that we find out he used to come to with Jemmy. Inside the cave, Jamie shows Claire the remains of a Spanish man who died there. This is later important in Jamie’s cryptic letter to Roger and Bree which reveals Jemmy holds the key to finding it. The storyline with Jemmy in the future gets very interesting, and I feel like the cliffhanger for the end of this first half of the season might be his kidnapping.
A New Knife
Back on the Ridge, Jamie and Claire share a scene straight from the books where he gives her a new knife for their journey. There are lots of direct quotes from the books, minus a few dirty comments from Jamie. The two blood the blade and call back to the iconic line from their wedding, “Blood of my Blood” with a reworked version of their theme song.
I loved this parallel to their wedding, where Claire was not given a choice to share her blood and partake in this act. Now, we see her blood her own blade willingly and choose Jamie once again. The theme of Echo and the Bone is definitely heavy on Jamie’s self worth and Claire choosing him over and over again. Their strength as a couple will be needed more than ever this season, so I like that they are reinforcing that with these scenes.
Lallybroch
At the end of the episode, Bree and Roger drive up to Lallybroch. Ironically they were filming at when I was in Scotland last year and my tour was cancelled because they ended up extending filming due to rain. While there, Bree explains to Roger how much he would have loved the house in its hay day. They cut to a shot of Bree sitting on the steps looking through the gate like Claire had back in season 3 imagining Jamie there. Worried they are trespassing when another car arrives, they learn that the property is actually up for sale. When we see them in the future again in the books they had already purchased it, so I liked getting to see this scene in the show. The house is so central to their storyline and feels like a strong return to seasons 1 and 2. When Jamie and Claire go back to Scotland this season the two couples will be at Lallybroch simultaneously across time and I think that will be incredible to watch.
Wilmington again
Claire and Jamie travel to Wilmington (doesn’t it feel like they just left and were only home on the ridge for a long weekend) and along the way Claire spots Adso. She knows she cannot take him with her and sadly leaves him in the woods to live out his life at the ridge. She has a moment where the reality of their home being gone again hits her all at once and they have a really touching scene where she sees the stake that Jamie first put down in season 4 when they arrived at Fraser's Ridge.
She asks Jamie if they will make it back there one day, and he admits he never thought he’d see Scotland again but the Ridge is where they are bound, so they will. This ties back to his conversation with Bree where she tells him that the freedom gained in this war is worth fighting for, so Jamie knows he must take part. To wrap a nice bow around the episode, Claire says to him that he will always be enough for her, and it was the sweetest moment as the two ride off towards their next adventure in Wilmington as they prepare to travel to Scotland.
A good episode, pacing is still quite quick, but I’m enjoying this season a lot.
#outlander#outlanderedit#jamie x claire#jamie fraser#claire fraser#sam heughan#claire x jamie#jammf#caitriona balfe#james alexander malcolm mackenzie fraser#outlander spoilers#outlander review#outlander 7x03#outlander season 2
75 notes
·
View notes
Text
character list
the title is self explanatory. this is a list of the characters i'll write for. it'll probably change over time, and if you see a character you'd like but don't see them on the list, just ask cause i might've forgotten about them
Hamilton
Eliza Schuyler
Angelica Schuyler
Peggy Schuyler
Maria Reynolds
Alexander Hamilton
John Laurens
Philip Hamilton
Lafayette
Hercules Mulligan
James Madison
Thomas Jefferson
Aaron Burr
Umbrella Academy
Viktor Hargreeves
Diego Hargreeves
Klaus Hargreeves
Allison Hargreeves
Luther Hargreeves
Five Hargreeves
Ben Hargreeves (Umbrella or Sparrow)
Sloane Hargreeves
Jayme Hargreeves
Stranger Things
Will Byers (non female readers only)
Mike Wheeler
Lucas Sinclair
Dustin Henderson
Eleven Hopper
Max Mayfield
Robin Buckley (non male readers only)
Nancy Wheeler
Jonathan Byers
Steve Harrington
Eddie Munson
21 Chump Street
Justin Laboy
The Goldfinch
Boris Pavlikovsky
Theodore Decker
Marvel
Peter Parker (any actor)
Steve Rogers
Bucky Barnes
Sam Wilson
Makkari
Sersi
Sprite (platonic only)
Steven Grant
Marc Spector
Layla El-Faouly
America Chavez (non male readers only)
Kate Bishop
Yelena Belova (platonic only)
Shuri
Namor
Riri Williams
X-Men
Mystique
Kitty Pryde
Peter Maximoff
Rogue
In The Heights (movie version)
Usnavi de la Vega
Vanessa
Nina Rosario
Benny
Sonny de la Vega
Heathers
Veronica Sawyer
JD (Jason Dean)
Heather Chandler
Heather McNamara
Heather Duke
John Doe
John Doe
Ride The Cyclone
Noel Gruber (male or nb readers only)
Ocean O'Connel Rosenburg
Mischa Bachinski
Constance Blackwood
Ricky Potts
Hatchetfieldverse
Paul Matthews
Emma Perkins
Ted Spankoffski
Bill Woodard
Ruth Fleming
Pete Spankoffski
Richie Lipschitz
Max Jagerman
Grace Chasity
Lex Foster
Ethan Green
Hannah Foster (platonic only)
Heartstopper
Charlie Spring (non female readers only)
Nick Nelson
Tara Jones (non male readers only)
Darcy Olsson (non male readers readers only)
Elle Argent
Tao Xu (non male readers only(headcanoning him as bi or pan is disrespectful and transphobic))
Tori Spring
Imogen Heaney
Isaac Henderson (platonic only)
Do Revenge
Eleanor Levetan (non male readers only)
Drea Torres
Deadpool
Wade Wilson/Deadpool
Wednesday
Wednesday Addams
Enid Sinclair
Bianca Barclay
Xavier Thorpe
Ajax Petropolus
Eugene Otinger
(young) Morticia Addams
(young) Gomez Addams
Beetlejuice
Lydia Deetz
Tomorrow When The War Began
Ellie Linton
Lee Takkam
Fiona Maxwell
Homer Yannos
Spider-Man: Into the Spider-Verse/Across the Spider-Verse
Miles Morales
Gwen Stacy
Pavitr Prabhakar
Hobie Brown
Margo Kess
Miles G Morales (earth 42)
Miguel O’Hara
Maze Runner
Thomas
Newt (non female readers only)
The Broken Hearts Gallery
Lucy Gulliver
Nadine (non male readers only)
Nick Danielson
Treasure Planet
Jim Hawkins
Enola Holmes
Enola Holmes
Lord Tewkesbury
Turning Red
Mei Mei
Miriam
Abby
Priya
Raising Dion
Nicole Warren
Tevin Wakefield
Dion Warren (platonic only)
Julie and the Phantoms
Julie Molina
Luke Patterson
Reggie Peters
Alex Mercer (non female readers only)
Flynn
Carrie
Abbott Elementary
Janine Teagues
Jacob Hill (non female readers only)
Gregory Eddie
Brooklyn Nine-Nine
Jake Peralta
Amy Santiago
Rosa Diaz
Love Victor
Victor Salazar (non female readers only)
Benji (non female readers only)
Felix Weston
Pilar Salazar
Lake Meriwether
Lucy
Mia Brooks
Andrew
In Treatment
Eladio
Laila
Spree
Kurt Kunkle
Once Upon a Time
Emma Swan
Regina Mills
Killian Jones
Mary Margaret Blanchard
David Nolan
Henry Mills
Mulan (non male readers only)
Graham
Neal Cassidy
Peter Pan
Jefferson
Dash and Lily
Dash
Lily
Boomer
Juno
Juno MacGuff
Paulie Bleeker
Summer Days Summer Nights
Debbie Espinoza
Frankie Espinoza
Scream (1 through 6)
Sidney Prescott
Billy Loomis
Mickey Altieri
Roman Bridger
Jill Roberts
Charlie Walker
Sam Carpenter
Tara Carpenter
Amber Freeman
Chad Meeks-Martin
Mindy Meeks-Martin
Quinn Bailey
Venom
Eddie Brock
Honest Thief
Ramon Hall
Beth Hall
Wild Child
Poppy Moore
Kate
Drippy
Freddie Kingsley
Monsters and Men
Manny Ortega
Marisol Ortega
Ghostbusters: Afterlife
Trevor Spengler
Phoebe Spengler (platonic only)
Error 143
Micah Yujin
Community
Abed Nadir
Troy Barnes
Annie Edison
Jeff Winger
Britta Perry
The Obession
Logan
Delilah
The New Girl
Lia Setiawan
Stacey Hoffman
Mythic Quest
Poppy Li
Brad Bakshi
Adventure Time
Finn
Princess Bubblegum
Marceline
Marshall Lee
Prince Bubblegum
Flame Princess
School Spirits
Madison
Simon
Charley (non female readers only)
Wally
Rhonda
Dungeons and Dragons: Honour Among Thieves
Simon Aumar
Disventure Camp
Aiden (non fem readers only)
James (non fem readers only)
Grease: Rise of the Pink Ladies
Jane Facciano
Olivia Valdovinos
Nancy Nakagawa
Cynthia Zdunowski
Richie Valdovinos
Ted Lasso
Ted Lasso
Roy Kent
Jamie Tartt
Keeley Jones
Sam Obisanya
Transformers: Rise of the Beasts
Noah Diaz
Elena Wallace
Mirage
Helluva Boss
Blitzø
Stolas (non female readers only)
Loona
Millie
Moxxie
Octavia
Verosika Mayday
Fizzarolli
Asmodeus
Hazbin Hotel
Charlie Morningstar
Vaggie (non male readers only)
Angel Dust (non female readers only)
Husk
Alastor (platonic only)
Vox
Lucifer
Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles (rise + mutant mayhem + tmnt 2007 + tmnt 2012)
Donnie
Mikey
Raph
Leo
April
The After Party
Yasper Lennov
Space Force
Tony Scarapiducci
Renfield
Teddy Lobo
Robert Montague Renfield
Undercovers
Bill Hoyt
Amazing Digital Circus
Jax
Parks and Recreation
Leslie Knope
Ben Wyatt
April Ludgate
Andy Dwyer
Jean-Ralphio Saperstein
Randy Cunningham: 9th Grade Ninja
Randy Cunningham (18+ people DNI unless requesting platonic stories)
The Earliest Show
Josh Bath
House of Lies
Clyde Oberholt
Mean Girls (movie + musical + movie musical)
Cady Heron
Regina George
Gretchen Wieners
Karen Smith/Shetty
Janis Ian/Sarkisian/Imi'ike (non male readers only)
Damian Hubbard (non female readers only)
Warm Bodies
R
Peep World
Nathan Meyerwitz
Your Boyfriend
Peter Dunbar
#froggywritesstuff#tgwdlm x reader#John doe x reader#Heartstopper x reader#do revenge x reader#Deadpool x reader#Wednesday x reader#tomorrow when the war began x reader#treasure Planet X reader#Enola Holmes x reader#love Victor x reader#in treatment x reader#kurt kunkle x reader#once upon a time x reader#dash and Lily x reader#summer days summer nights x reader#venom x reader#honest theif x reader#Ghostbusters Afterlife x reader#Micah Yujin x reader#the obsession x reader#Simon Aumar x reader#rottmnt x reader#ben schwartz x reader#teddy lobo x reader#mean girls#Warm bodies#adventure time#mythic quest#your boyfriend
111 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sunday sounds: the prisoner's song
Before leaving these trenches for almost three days - courtesy of a very important work meeting on Monday, for which I have to fly home-home -, I am grateful for Roger and Brianna going to that Celtic Festival, back in 1969.
It should keep us covered for a while:
youtube
'And for the last, an old favorite that you’ll know. This song is said to have been sent by a Jacobite prisoner, on his way to London to be hanged, to his wife in the Highlands …”
She spread her hands out flat on top of the pictures, as though to keep anyone from seeing them. An icy shock went through her. Wedding pictures. Snapshots of their wedding day. Of course; they’d been married in Scotland. The Reverend Wakefield wouldn’t have done the ceremony, not being a Catholic priest, but he was one of her father’s oldest friends; the reception must have been held at the manse.
Yes. Peeking through her fingers, she could make out familiar bits of the old house in the background. Then, reluctantly sliding her hand aside, she looked again at her mother’s young face.
Eighteen. Claire had married Frank Randall at eighteen—perhaps that explained it. How could anyone know their mind so young?
“By yon bonnie banks, and by yon bonnie braes,
Where the sun shines bright on Loch Lomond,
Where me and my true love were ever wont to gae …”
But Claire had been sure—or she’d thought so. The broad clear brow and delicate mouth admitted of no doubt; the big, luminous eyes were fixed on her new husband with no sign of reservation or misgiving. And yet—
“But me and my true love will never meet again
On the bonnie, bonnie banks of Loch Lomond.”
Oblivious of the toes she stepped on, Brianna blundered out of the row and fled, before anyone should see the tears.'
(Diana Gabaldon - Drums of Autumn)
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
Viaplay has found its Inspector Rebus and author Sir Ian Rankin is keeping it in the name.
Outlander star Richard Rankin – no relation to the source material’s scribe – will play the lead in the Nordic streamer’s debut UK original Rebus. He follows in the footsteps of fellow Scottish actors John Hannah and Ken Stott, who led the ITV version 20 years ago.
Viaplay’s reboot, which is planned as a returning series and will soon unveil more cast, follows 40-year-old Inspector John Rebus at a psychological crossroads following an altercation with an infamous Edinburgh gangster. At odds with a job increasingly driven by technocrats, involved in a toxic affair he knows he needs to end, and all but supplanted in his daughter’s life by his ex-wife’s wealthy new husband, Rebus begins to wonder if he still has a role to play – either as a family man or a police officer.
Viaplay has found its Inspector Rebus and author Sir Ian Rankin is keeping it in the name.
Outlander star Richard Rankin – no relation to the source material’s scribe – will play the lead in the Nordic streamer’s debut UK original Rebus. He follows in the footsteps of fellow Scottish actors John Hannah and Ken Stott, who led the ITV version 20 years ago.
Viaplay’s reboot, which is planned as a returning series and will soon unveil more cast, follows 40-year-old Inspector John Rebus at a psychological crossroads following an altercation with an infamous Edinburgh gangster. At odds with a job increasingly driven by technocrats, involved in a toxic affair he knows he needs to end, and all but supplanted in his daughter’s life by his ex-wife’s wealthy new husband, Rebus begins to wonder if he still has a role to play – either as a family man or a police officer.
RELATED STORY
Former Film & TV Charity Boss Alex Pumfrey To Head Up Partnerships For ITV
Richard Rankin, who plays Roger Wakefield in Starz drama Outlander and whose past credits include The Last Kingdom and Trust Me, said he “feels very lucky to be given the honour of bringing such an iconic Scottish character back to TV screens.”
Ian Rankin backed Richard Rankin to “bring the character to life,” adding: “He’s the perfect fit for the role, and not just because we coincidentally share the same surname.”
71 scribe Gregory Burke is penning the adaptation from Magpie Murders outfit Eleventh Hour Films. The project is a big UK bet for Viaplay, having launched in the territory just four months ago.
Viaplay Chief Content Officer Filippa Wallestam said it is a “privilege to have such a famous character spearheading Viaplay’s original storytelling in the UK.”
Rankin wrote 24 Rebus novels between 1987 and 2002. The TV series ran from 2000 to 2007 on ITV and saw first Hannah then Stott portray the main character.
55 notes
·
View notes