#plants (species)
Text

As if "swallowed by the earth" is a way to describe someone who's gone missing without a trace, particularly in the woods, but in Ditovo it may be more than just a saying. At least if you believe the many legends and folktales about giant plumsaina, or as they're more commonly known "earth belly". The plant does exist but usually it is only big enough to catch small vertebrates, which it does when prey step onto its camouflaged trap door and fall into the pit of the plant filled with digestive liquid and downward pointing spikes preventing escape. The roots of the plant are for storing nutrients and other substances, as well as firmly anchoring the plant in the ground when prey is thrashing about inside it. In order to reproduce the earth belly sprouts a red flower above the surface, a red flag that may perhaps save the life of one who recognizes it.
#original species#worldbuilding#world building#plant design#fantasy species#fantasy plant#flora#cursed papaya looking spud
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
That's so cool! And they found a few of them, and they're now growing seedlings in greenhouses for eventual replanting!
Quercus tardifolia is a relic species leftover from when the climate was much cooler and wetter in the past, and can only really live in a few high-elevation spots in Texas. It's definitely still at risk of extinction due to increasing heat and drought caused by climate change, but the discovery means this species still has a chance.
#oak#oak trees#Quercus#Quercus tardifolia#Lazarus species#endangered species#extinction#trees#plants#botany#nature#climate change#global warming
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
In the Willamette Valley of Oregon, the long study of a butterfly once thought extinct has led to a chain reaction of conservation in a long-cultivated region.
The conservation work, along with helping other species, has been so successful that the Fender’s blue butterfly is slated to be downlisted from Endangered to Threatened on the Endangered Species List—only the second time an insect has made such a recovery.
[Note: "the second time" is as of the article publication in November 2022.]
To live out its nectar-drinking existence in the upland prairie ecosystem in northwest Oregon, Fender’s blue relies on the help of other species, including humans, but also ants, and a particular species of lupine.
After Fender’s blue was rediscovered in the 1980s, 50 years after being declared extinct, scientists realized that the net had to be cast wide to ensure its continued survival; work which is now restoring these upland ecosystems to their pre-colonial state, welcoming indigenous knowledge back onto the land, and spreading the Kincaid lupine around the Willamette Valley.
First collected in 1929 [more like "first formally documented by Western scientists"], Fender’s blue disappeared for decades. By the time it was rediscovered only 3,400 or so were estimated to exist, while much of the Willamette Valley that was its home had been turned over to farming on the lowland prairie, and grazing on the slopes and buttes.

Pictured: Female and male Fender’s blue butterflies.
Now its numbers have quadrupled, largely due to a recovery plan enacted by the Fish and Wildlife Service that targeted the revival at scale of Kincaid’s lupine, a perennial flower of equal rarity. Grown en-masse by inmates of correctional facility programs that teach green-thumb skills for when they rejoin society, these finicky flowers have also exploded in numbers.
[Note: Okay, I looked it up, and this is NOT a new kind of shitty greenwashing prison labor. This is in partnership with the Sustainability in Prisons Project, which honestly sounds like pretty good/genuine organization/program to me. These programs specifically offer incarcerated people college credits and professional training/certifications, and many of the courses are written and/or taught by incarcerated individuals, in addition to the substantial mental health benefits (see x, x, x) associated with contact with nature.]
The lupines needed the kind of upland prairie that’s now hard to find in the valley where they once flourished because of the native Kalapuya people’s regular cultural burning of the meadows.
While it sounds counterintuitive to burn a meadow to increase numbers of flowers and butterflies, grasses and forbs [a.k.a. herbs] become too dense in the absence of such disturbances, while their fine soil building eventually creates ideal terrain for woody shrubs, trees, and thus the end of the grassland altogether.
Fender’s blue caterpillars produce a little bit of nectar, which nearby ants eat. This has led over evolutionary time to a co-dependent relationship, where the ants actively protect the caterpillars. High grasses and woody shrubs however prevent the ants from finding the caterpillars, who are then preyed on by other insects.
Now the Confederated Tribes of Grand Ronde are being welcomed back onto these prairie landscapes to apply their [traditional burning practices], after the FWS discovered that actively managing the grasslands by removing invasive species and keeping the grass short allowed the lupines to flourish.
By restoring the lupines with sweat and fire, the butterflies have returned. There are now more than 10,000 found on the buttes of the Willamette Valley."
-via Good News Network, November 28, 2022
#butterflies#butterfly#endangered species#conservation#ecosystem restoration#ecosystem#ecology#environment#older news but still v relevant!#fire#fire ecology#indigenous#traditional knowledge#indigenous knowledge#lupine#wild flowers#plants#botany#lepidoptera#lepidopterology#entomology#insects#good news#hope
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
I think it's so adorable that early humans took wild gourds - a tiny fruit that hollows out as it dries, making it float - and decided to make something out of it

they thought the tiny fruit was so good that they bred it for thousands of years, making it larger to form into bowls and cups, and different shapes to become bottles and spoons
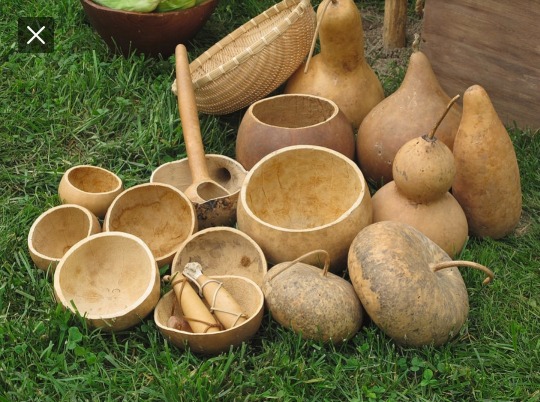


and musical instruments
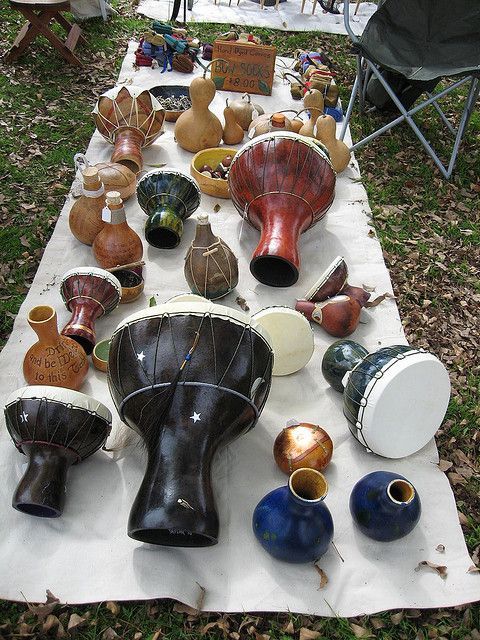
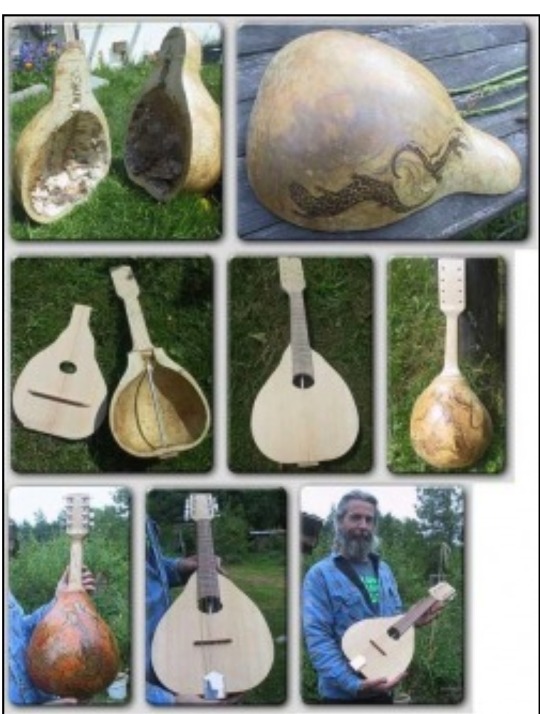



And then, people took the hollow gourds they farmed, and they turned them into houses for birds. We adapted them into the perfect houses for birds, and now there are specific breeds of birdhouse gourd just for making into birdhouses
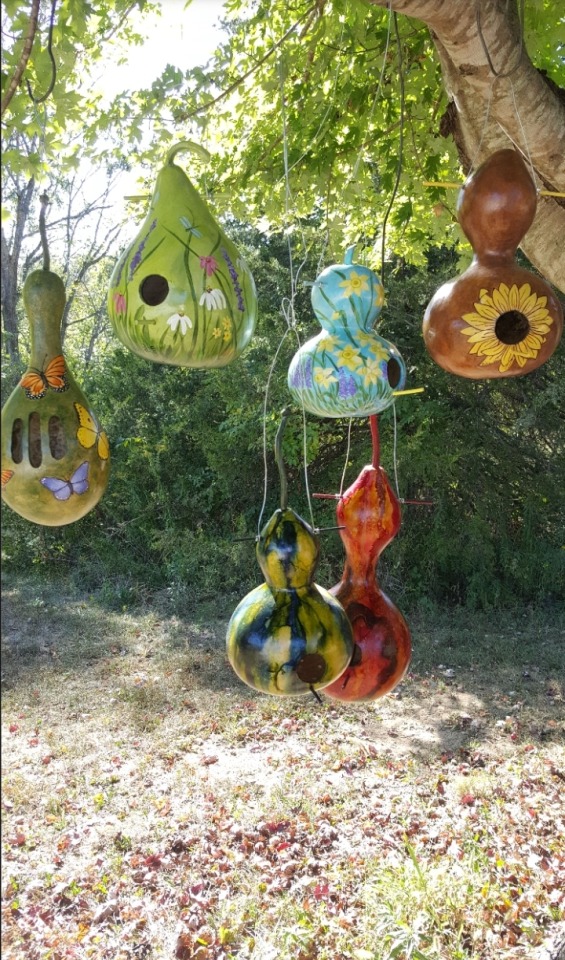
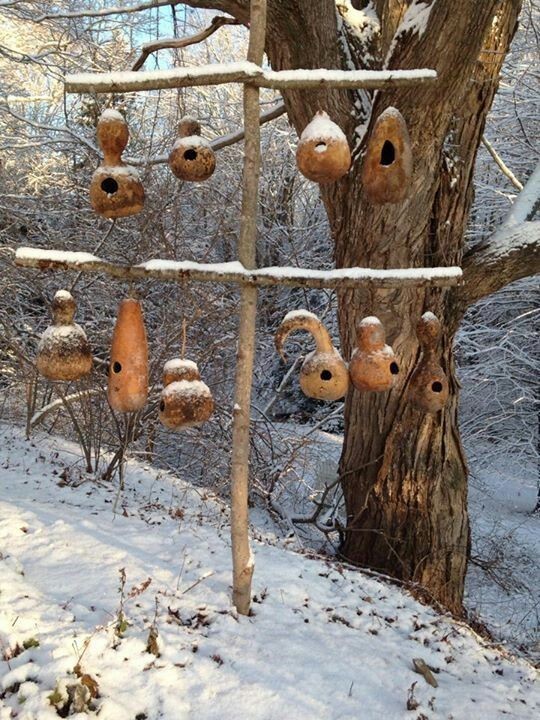


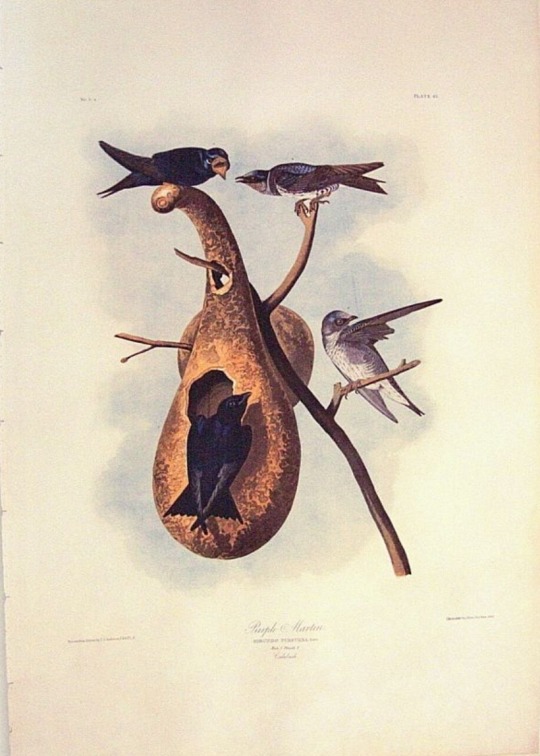
And humans dedicated gardening space and time and thousands of years of breeding to make the gourds so absolutely perfect for birds, that there is a species of bird that lives almost exclusively in them

#yes I KNOW i posted about this the other day but *crying* i just love plant domestication and the history of agriculture#and humanity's positive affect on the ecosystems we live in#mine#image IDs in alt text#hmm. I'm gonna tag this#permaculture#just to pspsps @ that community to look at how cool gourds are please everyone grow birdhouse gourds and give cavity nesters places to live#i don't think mine will become fully ripe before i get my first frost :( next year i need to start gourds indoors#i didn't want to grow them before because i didn't have much garden space but now i do and i need to grow all of them#i might be. a little obsessed with gourds. but also i saw a pair of purple martins flying by the road last year#and i had never seen one before then! and i need to see more of them#i have a few hundred barn swallows but i need more birds flying around my house. more!!#and also i have a ton of invasive cavity nesting species around here. house sparrows and starlings.#gotta make up for those things competing with native birds for nest dites#*sites#the invasive birds very often win :/#that's why they're invasive#i really do need to start trapping them....
31K notes
·
View notes
Text
today i found a plant growing in an alleyway downtown that gave me this delightful little seed pod that looks like a little banana about an inch long but it splits down the front to reveal hundreds of flat little seeds with little papery wings seed wings and theyre all stuffed into neat rows in a way that makes the pod look like an overfull expanding file and if you run your finger over it seeds fall out. the plant had like 6 of them going overhanging this one sidewalk and some of them were huge, like multiple inches long. anyway plants are still just making stuff outside it seems
#seedposting#this pod fell off into my hand when i touched it so i was like oh for me??? the fruits of nature???#also the reason why this strikes me is bc we have multiple milkweed species around here that do a pod thing#but with big floofs on the end of each seed. and those look less like an expanding file and more like a tissue box#but there arent a whole lot of plants around here that have the little papery seed wings inside a pod??#and the size. the whimsy#im assuming its an ornamental bc i havent seen it around here before lmao
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Note to new foragers;
while you are learning about the species you want to harvest, also learn what sustainable harvesting looks like. Learn about invasive species management, and agroecology. A lot of people start with the book Braiding Sweetgrass, by Dr Robin Wall Kimmerer. It is approachable, and covers the Honorable Harvest really well. The Poor Proles Almanac podcast and Substack are both incredible sources of information as well.
In general, tho, you should start by knowing this:
- If a species is native, and especially if it is rare on the landscape, do what you can to encourage it. Don’t over harvest, clear away invasives around it, save and spread its seeds. Maybe even hand pollinate it if needed.
- If a species is not native, feel free to harvest much more of it. Discourage its spread, but you don’t necessarily need to remove every single one you see. For a very small select few non native species, a little bit of spreading can even be okay. But be sure you know what you are doing. In general, it is better to remove a non native species than to let it stay. Keep native seeds on you to replace them with. I carry around little dime bags of seeds.
- if a species is Invasive (not native & choking out native species) remove as much as you can without damaging the local ecology. For foraging this might mean you harvest a ton of yellow charlock, even more than you need, because you see it choking out wild lettuce. This is a good thing to do (at least where I am). Because the charlock will overtake everything. But if you start managing in other ways, like tarping or tilling or spraying, keep in mind that oftentimes the medicine can be worse than the disease. If you spray a field of charlock you don’t get wild lettuce, you get more charlock.
Anyways, good luck!
468 notes
·
View notes
Text
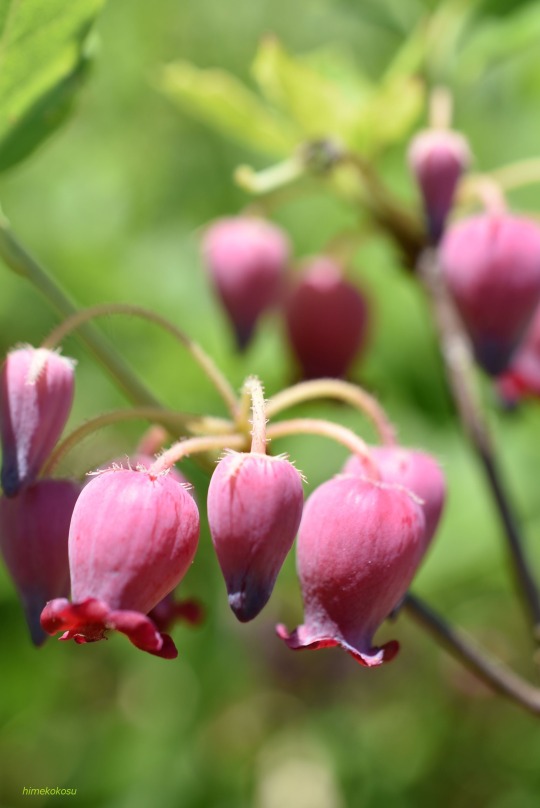


Menziesia multiflora
628 notes
·
View notes
Text
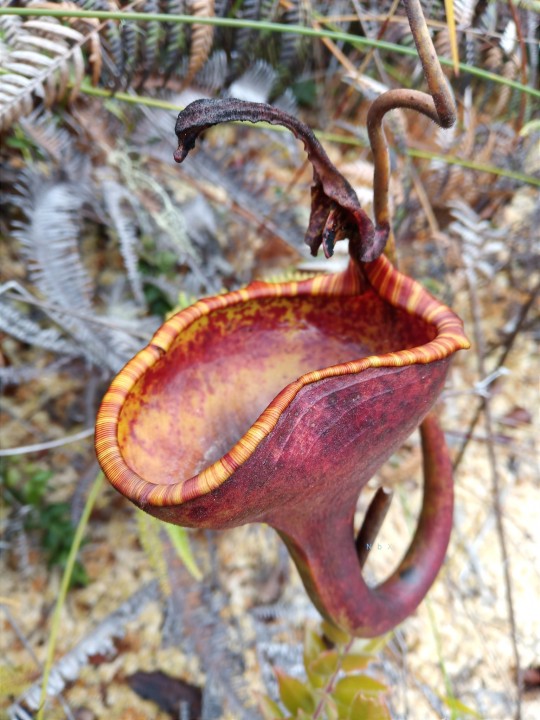
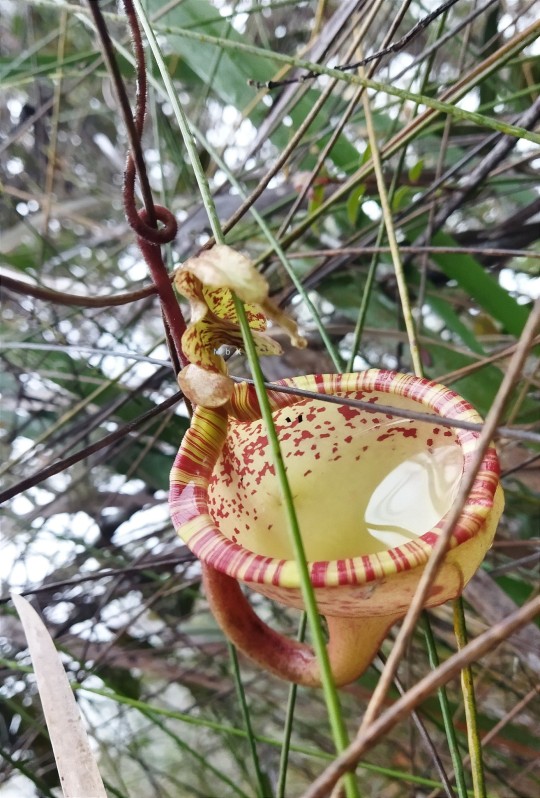
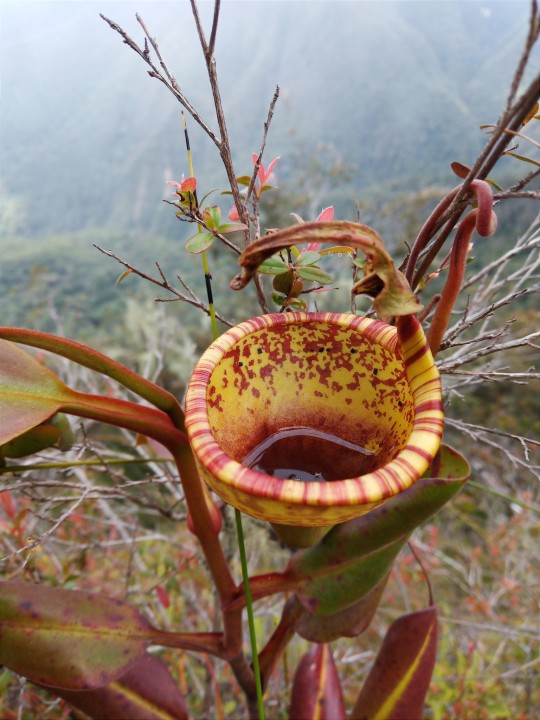
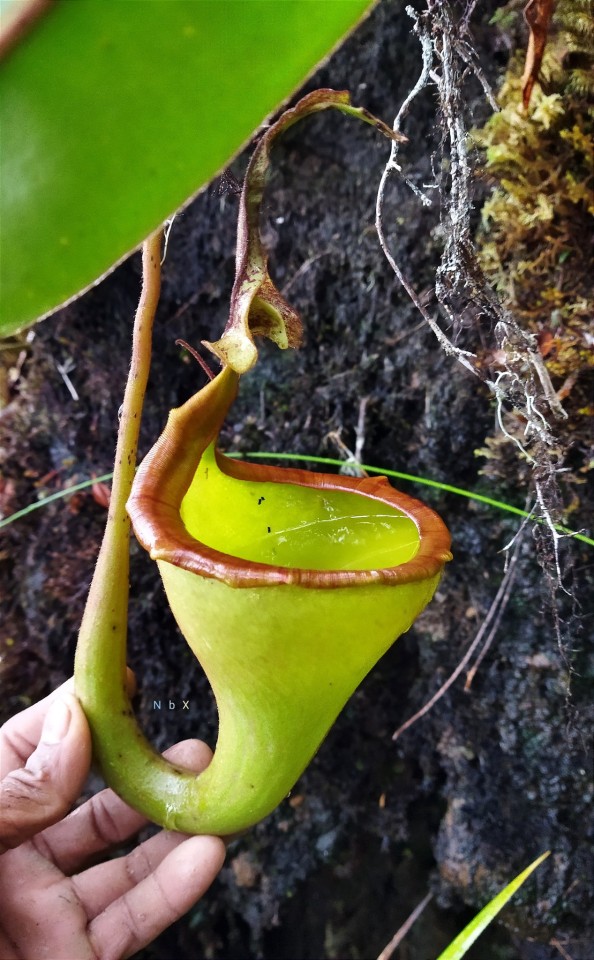
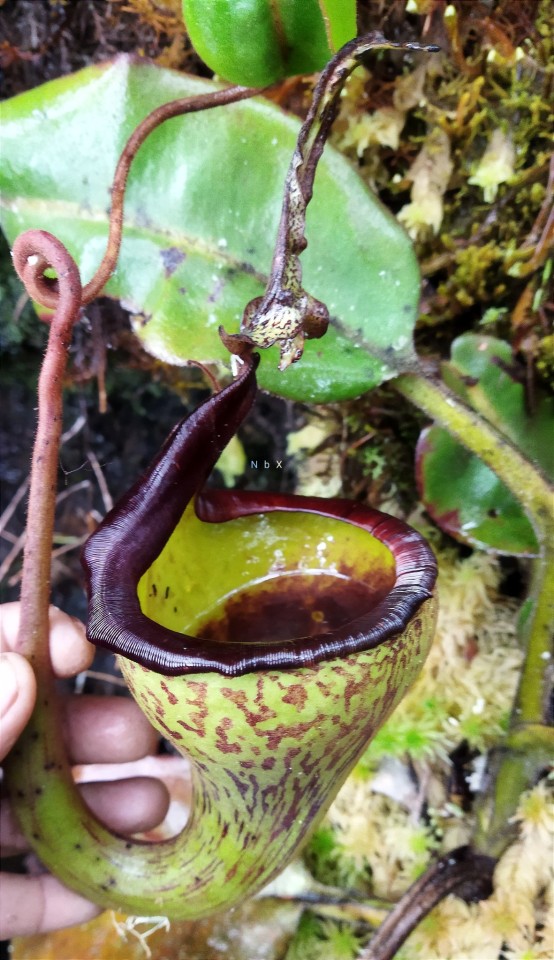







Upper pitcher plants.
Nepenthes Eymae is a colorful plant. very amazing species and beautiful to the eye! Central Sulawesi endemic species. is in the wild in a mossy forest above 1000m.
#plants#nepenthes#carnivorous plants#botany#nepenttheseymae nepenthes eymae pitcherplants carnivoruosplant carnivorousplants species amazingplants nepentheshighland icps
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
How Non-Native Plants Are Contributing to a Global Insect Decline
The impact of introduced plants on native biodiversity has emerged as a hot-button issue in ecology. But recent research provides new evidence that the displacement of native plant communities is a key cause of a collapse in insect populations and is affecting birds as well...
#non-native plants#invasive species#environment#conservation#insect decline#insect#insects#entomology#biodiversity#animals#nature#botany#plants#non-native invasive species
1K notes
·
View notes
Photo
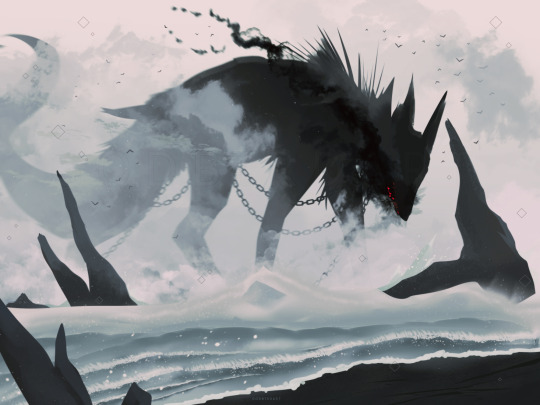
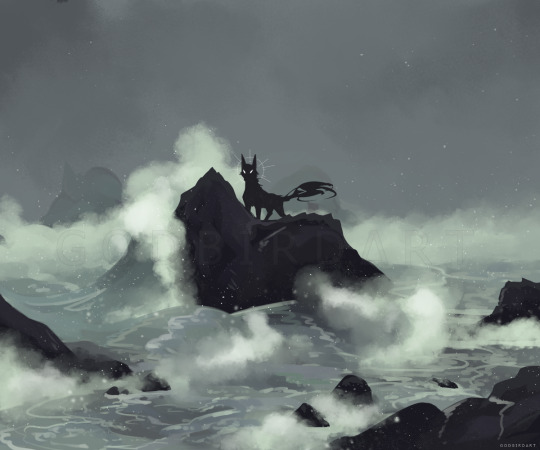




weird dogs
#canines#animals#godbirdart#godbird#2022#2022 art#2021 art#just a repost of some faves#my weird black creature of indeterminate species#art#digital#water#plants#trees#storm#beach#fog#mist#sky#clouds
7K notes
·
View notes
Text








as promised, the transplanting tutorial
most sources make transplanting sound incredibly difficult, but transplanting young seedlings from areas with sparse dirt, like a driveway or roadside, is actually incredibly easy and can get you some great stuff. Once I worked out the method, i've had a very high survival rate
it took me like a month of trial and error to figure this out so you don't have to.
Feel free to repost, no need for credit
28K notes
·
View notes
Text
373 notes
·
View notes
Text
This ties into one of the big conundrums of restoration ecology. When trying to decide what plants to add to a restoration site, should we add those that are there now, even if some of those species are increasingly stressed by the effects of climate change? Or do we start importing native species in adjacent ecoregions that are more tolerant of heat?
Animals can migrate relatively quickly, but plants take longer to expand their range, and the animals that they have mutual relationships with may be moving to cooler areas faster than the plants can follow. Whether the animals will be able to survive in their new range without their plant partners is another question, and that is an argument in favor of trying to help the plants keep up with them. We're not just having to think about what effects climate change will have next summer, but also predict what it's going to look like here in fifty years, a hundred, or beyond. It's an especially important question in regards to slow-growing trees which may not reproduce until they are several years old, and which can take decades to really be a significant support of their local ecosystem.
For example, here in the Pacific Northwest west of the Cascades, western red cedar (Thuja plicata) is experiencing increased die-off due to longer, hotter summer droughts. Do we continue to plant western red cedar, in the hopes that some of them may display greater tolerance to drought and heat? Or do we instead plant Port Orford cedar (Chamaecyparis lawsoniana), which is found in red cedar's southern range, and which may be more drought-tolerant, even though it's not found this far north yet?
Planting something from an adjacent ecoregion isn't the same as grabbing a plant from halfway around the world and establishing it as an invasive species. But there is the question as to whether the established native would have been able to survive if we hadn't introduced a competing "neighbor" species. Would the Port Orford cedars and western red cedars be able to coexist as they do in northern California and southern Oregon, or would the introduced Port Orfords be enough to push the already stressed red cedars over the edge to extirpation?
There's no simple answer. But I am glad to see the government at least allowing some leeway for those ecologists who are desperately trying any tactic they can to save rare species from extinction.
#restoration ecology#ecology#habitat restoration#climate change#global warming#anthropogenic climate change#nature#wildlife#plants#botany#trees#endangered species#extinction#environment#conservation#environmentalism#science#scicomm#science communication
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Note: Reasons to Be Cheerful has had weirdly huge formatting issues for the past six or so months, so if that version is a mess, this link should work better.
"Florida Power & Light Company (FPL), the Sunshine State’s largest power utility, employs all the people you might expect: electricians, lineworkers, mechanical engineers — and a few you might not. For over 40 years, the company has kept a team of wildlife biologists on staff. Their task? Monitoring the giant carnivorous reptiles that reside in one of the state’s nuclear power plants.
Saving the American Crocodile
What sounds like a low-budget creature feature is actually a wildly successful conservation story. It goes like this: In 1975, the shy and reclusive American crocodile was facing extinction. Over-hunting and habitat decline caused by encroaching development had pushed its numbers to a record low. By 1975, when it was listed as endangered under the Endangered Species Act, there were only 200 to 300 left.
Three years later, in 1978, workers at the Turkey Point nuclear power plant in Homestead, Florida happened upon something that must have made them gasp: a crocodile nest along one of the plant’s 5,900-acre “cooling canals.” Rather than drive the crocs away — perhaps the easiest solution — FPL hired a team of biologists and implemented a Crocodile Management Plan. Its goal was unconventional: provide a suitable habitat for the crocs within the workings of the nuclear power plant, allowing both to coexist.
Over the course of the next 30 years, FPL’s wildlife biologists monitored nests, tagged hatchlings and generally created a hospitable environment for the reptiles. As it turned out, the plant’s cooling canals provided an ideal habitat: drained earth that never floods on which to lay eggs directly adjacent to water. Over the years, more and more crocs made the cooling canals home. By 1985, the nests at Turkey Point were responsible for 10 percent of American crocodile hatchlings in South Florida. In 2007, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service downgraded the American crocodile’s status from endangered to threatened, singling out FPL for its efforts.
The program continues to this day. To date, biologists have tagged some 7,000 babies born at the plant. In 2021, there were a record-setting 565 crocodile hatchlings at the Turkey Point facility.
"Reconciliation Ecology"
Turkey Point’s efforts are an example of what is known in the conservation world as “reconciliation ecology.” Rather than create separate areas where nature or animals can thrive in isolation from humans, reconciliation ecology suggests that we can blend the rich natural world with the world of human activity. Michael Rosenzweig, an emeritus professor of ecology and evolutionary biology at the University of Arizona, was a leading force in establishing this concept. The author of Win-Win Ecology: How the Earth’s Species can Survive in the Midst of Human Enterprise, Rosenzweig has pointed out that although human encroachment has typically been considered a threat to biodiversity, the notion that the world must be either “holy” or “profane,” ecologically speaking, is simply not true.
“In addition to its primary value as a conservation tool, reconciliation ecology offers a valuable social byproduct,” writes Rosenzweig in his first chapter. “It promises to reduce the endless bickering and legal wrangling that characterize environmental issues today.”
-via Reasons to Be Cheerful, May 5, 2022. Article continues below. All headings added by me for added readability.
Dr. Madhusudan Katti, an associate professor in the Department of Forestry and Environmental Resources at North Carolina State University, was inspired by Rosenzweig when he did his postdoc at Arizona State. Katti has now been in the field of reconciliation ecology for two decades and teaches classes on the subject. “To me it’s finding solutions to reconciling human development with biodiversity conservation,” Katti says.
This common ground between development and conservation can be consciously planned, like FPL managing a crocodile habitat at a nuclear power plant or the state-sponsored vertical gardens and commercial farms on high-rise buildings in Singapore. Other examples include the restoration of the coral reef around an undersea restaurant in Eilat, Israel, or recent legislation in New York City requiring patterned glass on high-rise buildings, making windows more visible to migratory birds. Other planned examples of reconciliation ecology can be more individually scaled: a rooftop garden in an urban setting, modifying your garden to earn a “backyard bird habitat” certification from the Audubon Society, or even just mowing your lawn less often...
Reconciliation Ecology: Nature's Already Doing It Without Us
But there are countless examples of “accidental” incidents of reconciliation ecology, as well. One of Katti’s favorites is the kit fox of California’s San Joaquin Valley. “The kit fox was one of the very first species listed on the Endangered Species Act,” Katti says. Its decline was caused by habitat loss through agricultural and industrial development, as well as the extermination of the gray wolf population, which led to an increase in coyotes. So kit foxes adapted and moved to new habitats. One of these was the city of Bakersfield, California.
“Bakersfield, surrounded by oil pumps, would be the last place you’d expect to find an endangered species,” Katti says. But researchers think kit foxes have migrated to Bakersfield because they actually have more protection there from predators like coyotes and bobcats. “The kit foxes have figured out that if they can tolerate the human disturbance and live with people, then they are safer from all these other predators,” he says.
Living in the city has led to some interesting behavioral changes. In the wild, for instance, a female kit fox gives birth to her young and raises them by herself in a den. But in the city, researchers have observed multiple females raising their litters together in the same den. “It’s like a form of cooperative breeding,” Katti says. “That wouldn’t happen in the wild.” ...
The Big Picture: How We Think about Conservation
Reconciliation Ecology isn’t just we humans welcoming animals like crocodiles and foxes into our environments, though. It’s also living with nature in a way that most Western societies haven’t done since the Enlightenment. “In recent years, there’s been a recognition that the ‘fortress conservation’ model — keeping nature separated from humans and not thinking of or valuing human-inhabited landscapes — those ideas are outdated,” says Katti.
In fact, in Katti’s classes on reconciliation ecology, he embraces the notion of reconnecting people with their land if they have been unjustly separated from it. “The term reconciliation also applies to all the colonial legacies where both nature and people have been harmed,” Katti says. “For Indigenous communities, the harm done to ecosystems, it’s happened together. So you can talk about addressing both. That’s where a lot of my thinking is at the moment.”
A hopeful version of this sort of reconciliation is happening in California where colleagues of Katti’s who are tribal members are re-introducing “tribal burns” in some areas. Controlled burns have been a part of many Indigenous cultures for millenia, both as a way to prevent devastating forest fires, but also to encourage the growth of certain plants like hazel that are used for basket-weaving and other crafts.
“The notion that people don’t belong there and ‘let nature take care of itself’ doesn’t really work,” Katti says. “That’s the legacy of Western European Enlightenment thinking — a divide between human and nature. That is a real faulty view of nature. People have been part of the ecosystem forever.”
-via Reasons to Be Cheerful, May 5, 2022
#a bit older but still ongoing/relevant and still very cool#florida#crocodile#reptile#ecology#environment#sustainability#endangered species#united states#california#kit fox#nuclear power plant#reconciliation#colonialism#the enlightenment#conservation#human beings#good news#hope#urban ecology
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
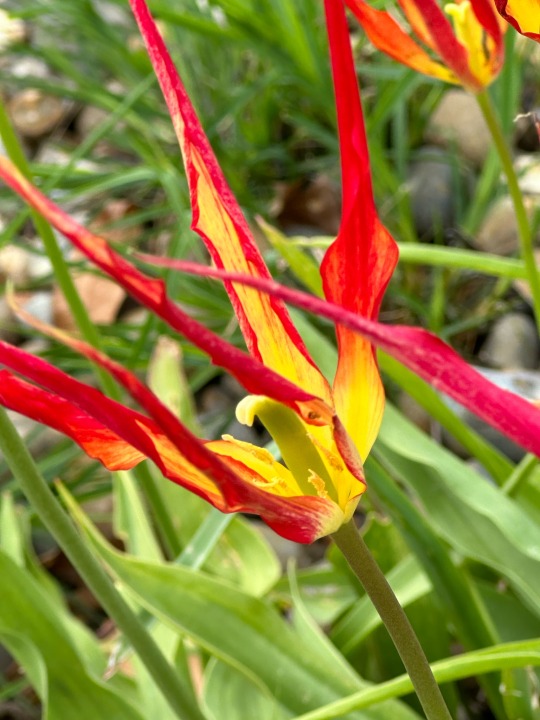
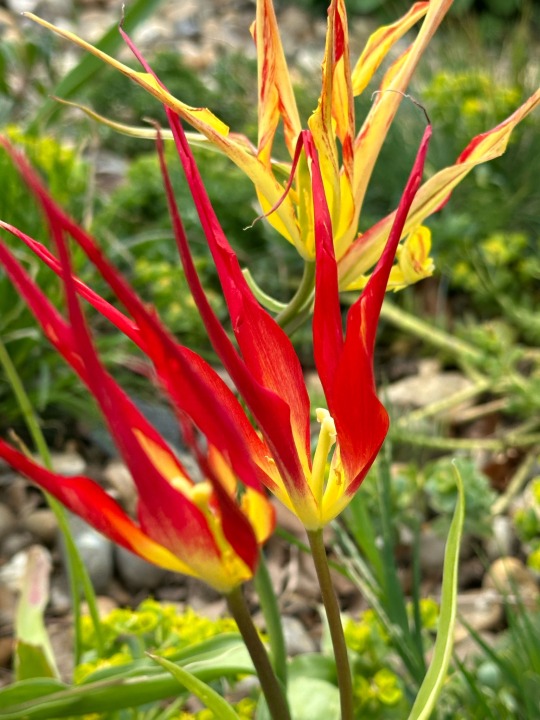



Plant of the Day
Monday 22 April 2024
The delicate flowers of Tulipa acuminata (species tulip, horned tulip) mean the bulbs need careful placement to ensure that their display is not overpowered by the surrounding planting.
Jill Raggett
#Tulipa#tulip#tulips#species tulip#horned tulip#plants#horticulture#gardens#garden#essex#dry garden#RHS Hyde Hall#red flowers
149 notes
·
View notes
Text
ok this sounds insane but in 2018 i went to a few carnivorous plant talks at the botany conference in minnesota. i got caught up in conversation with one of the guys there who was a huge nepenthes guy who told me a story about another collector in the pacific northwest who'd been buying poached plants, like a huge amount, and eventually got staked out by the fish and wildlife service and arrested and had all his plants seized and went to prison for it. idk if i ever talked about this on this blog before-- i know i liveblogged a lot from that conference but cant remember what all i posted-- but ive avoided talking about it since then because i was never able to find like, news articles or anything covering it, but behold.... we now have proof it was real, and im like 80% sure this was this guy he was talking about. the raid happened in 2016 and they'd been staking them out since 2013. he had nearly 400 plants and had been sourcing many of them from poachers in indonesia and borneo.
remember folks: poaching happens with plants too! it's a huge problem not only in carnvirous plants (nepenthes especially, which this piece is dedicated to talking about) but also in native plant populations in the US, including native carnivorous plant populations (north and south carolina's venus fly traps, california's darlingtonia, and sarracenia from the east coast), native orchids (historically one of the most poached categories), desert plants/cacti/succulents, and slow-growing woody ornamentals (cycads, for example). never buy bare-root plants off ebay or facebook! your best bet is local nurseries (which usually purchase farm-raised plants that do well in a wide range of conditions, and as a result have a healthy population in the wild) or specialty greenhouses (more expensive, but at least in the case of carnivorous plants offer young plants bred from established adult plants in-house, raised in captivity).
#super sad piece fellas like this shit guts me i cant even stress it enough#stories about nepenthes poaching hit different#there are hundreds of species#some are really common and widespread all over indonesia/china/japan/oceania#and some are like. super hyperadapted to one specific ridge on one specific mountain#theyre still being recorded and stuff because theyve speciated so much#so youll have a plant that has like. a max of 15 adults in the population at any given time. literally a nightmare scenario#AND theyre diaceous (there are male plants and female plants). doesnt seem like a problem until you think about the population dynamics#there not only has to be two plants but the plants have to be a male and a female#and people living there have reason to take them. like the poacher interviewed in this article does it to supplement his income#from working at a horrifying rubber production ordeal to feed his wife and kids#and he says everyone in his village does the same for the same reasons#nightmare!! nightmare!! nightmare horrible nightmare world!!! horrible fucking nightmare!!!!#nepenethes#carnivorous plants#poaching#conservation
11K notes
·
View notes