#microeconomic
Text
Hot sex with redhead teen
Amateur teen fucked POV on hidden camera
Nick Manning Fucks Phoenix Marie
Twerking nude
Stud bangs two hos with huge jugs who titty fuck and eat cum
Using an Ai Uehara Onahole
Caught My Busty Step Mom Masturbating and Now she Wants Anal Sex - Cory Chase
Huge boobs transgender fucks horny man
Fucking a cum filled pussy
choctaw casino pocola reviews
#epidemic's#snowbushes#isotope#evil-smelling#unrejective#democratian#giant/tiny#Revkah#cohibitive#cleistogamous#crumhorn#coding#Mephisto#retractively#semireflexiveness#chartographical#unhelming#microeconomic#jacent#nonreticently
0 notes
Text
Don’t Be Evil

Tonight (November 22), I'll be joined by Vass Bednar at the Toronto Metro Reference Library for a talk about my new novel, The Lost Cause, a preapocalyptic tale of hope in the climate emergency.

My latest Locus Magazine column is "Don't Be Evil," a consideration of the forces that led to the Great Enshittening, the dizzying, rapid transformation of formerly useful services went from indispensable to unusable to actively harmful:
https://locusmag.com/2023/11/commentary-by-cory-doctorow-dont-be-evil/
While some services have fallen harder and/or faster, they're all falling. When a whole cohort of services all turn sour in the same way, at the same time, it's obvious that something is happening systemically.
After all, these companies are still being led by the same people. The leaders who presided over a period in which these companies made good and useful services are also presiding over these services' decay. What factors are leading to a pandemic of rapid-onset enshittification?
Recall that enshittification is a three-stage process: first surpluses are allocated to users until they are locked in. Then they are withdrawn and given to business-customers until they are locked in. Then all the value is harvested for the company's shareholders, leaving just enough residual value in the service to keep both end-users and business-customers glued to the platform.
We can think of each step in that enshittification process as the outcome of an argument. At some product planning meeting, one person will propose doing something to materially worsen the service to the company's advantage, and at the expense of end-users or business-customers.
Think of Youtube's decay. Over the past year, Google has:
Dramatically increased the cost of ad-free Youtube subscriptions;
Dramatically increased the number of ads shown to non-subscribers;
Dramatically decreased the amount of money paid to Youtube creators;
Added aggressive anti-adblock;
Then, this week, Google started adding a five-second blanking interval for non-Chrome users who have adblockers installed:
https://www.404media.co/youtube-says-new-5-second-video-load-delay-is-supposed-to-punish-ad-blockers-not-firefox-users/
These all smack of Jenga blocks that different product managers are removing in pursuit of their "key performance indicators" (KPIs):
https://pluralistic.net/2023/07/28/microincentives-and-enshittification/
We can think of each of these steps as the outcome of an argument. Someone proposes a Youtube subscription price-hike, and other internal stakeholders object. These objections fall into two categories:
We shouldn't do this because it will make the product worse; and/or
We shouldn't do this because it will reduce the company's earnings.
Lots of googlers sincerely care about product quality. People like doing a good job, and they take pride in making good things. Many have sacrificed something that mattered in the service of making the product better. It's bad enough to miss your kid's school play so you can meet a work deadline – but imagine making that sacrifice and then having the excellent work you put in deliberately degraded.
I have been around Google's orbit since its early days, going to the odd company Christmas party in the early 2000s and giving talks at Google offices in cities all over the world. I've known hundreds of skilled googlers who passionately cared about making the best products they could.
For most of Google's history, those googlers won the argument. But they didn't do so merely by appealing to their colleagues' professional pride in a job well-done. For most of Google's history, the winning argument was a combination of "doing this bad thing would make me sad," and "doing this bad thing will make Google poorer."
Companies are disciplined by three forces:
Competition (the fear of losing business to a rival);
Regulation (the fear of legal penalties that would exceed the expected profits from a given course of action);
Self-help (the fear that customers or users will change their behavior, say, by installing an ad-blocker).
The ability of googlers to win enshittification arguments by appealing to the company's bottom line was a function of one or more of these three disciplining factors. The weakening of each of these factors is the reason that every tech company is sliding into enshittification at once.
For example, when Google contemplates raising the price of a Youtube subscription, the dissent might say, "Well, this will reduce viewership and might shift viewers to rivals like Tiktok" (competition). But the price-hiking side can counter, "No, because we have a giant archive, we control 90% of searches, we are embedded in the workflow of vloggers and other creators who automatically stream and archive to Youtube, and Youtube comes pre-installed on every Android device." Even if the company leaks a few viewers to Tiktok, it will still make more money in aggregate. Prices go up.
When Google contemplates increasing the number of ads shown to nonsubscribers, the dissent might say, "This will incentivize more users to install ad-blockers, and then we'll see no ad-revenue from them." The pro-ad side can counter, "No, because most Youtube viewing is in-app, and reverse-engineering the Youtube app to add an ad-blocker is a felony under Section 1201 of the Digital Millennium Copyright Act. As to non-app viewers: we control the majority of browser installations and have Chrome progressively less hospitable to ad-blocking."
When Google contemplates adding anti-adblock to its web viewers, the dissent might say, "Processing users' data in order to ad-block them will violate Europe's GDPR." The anti-adblock side can counter, "But we maintain the fiction that our EU corporate headquarters is in the corporate crime-haven of Ireland, where the privacy regulator systematically underenforces the GDPR. We can expect a very long tenure of anti-adblock before we are investigated, and we might win the investigation. Even if we are punished, the expected fine is less than the additional ad-revenue we stand to make."
When Google contemplates stealing performers' wages through opaque reshufflings of its revenue-sharing system, the dissent might say, "Our best performers have options, they can go to Twitch or Tiktok." To which the pro-wage-theft side can counter, "But they have no way of taking their viewers with them. There's no way for them to offer their viewers on Youtube a tool that alerts them whenever they post a new video to a rival platform. Their archives are on Youtube, and if they move them to another platform, there's no way redirect users searching for those videos to their new homes. What's more, any attempt to unilaterally extract their users' contact info, or redirect searchers or create a multiplatform client, violates some mix of our terms of service, our rights under DMCA 1201, etc."
It's not just Google. For every giant platform, the threats of competition, regulation and self-help have been in steady decline for years, as acquisitions, underenforcement of privacy/labor/consumer law, and an increase in IP protection for incumbents have all mounted:
https://locusmag.com/2020/09/cory-doctorow-ip/
When internal factions at tech companies argue about whether to make their services worse, there's a heavy weight tilting the scales towards enshittification. The lack of competition, an increase in switching costs for users and business-customers, and broad powers to prevent users from modifying the service for themselves all mean that even when a product gets worse, profits can still go up.
This is the culprit: monopoly, and its handmaiden, regulatory capture. That's why today's antimonopoly movement – and the cases against all the tech giants – are so important. The old, good internet was built by flawed tech companies whose internal ranks included the same amoral enshittifiers who are gobbling up the platforms' seed corn today. The thing that stood in their way before wasn't merely the moral character of colleagues who shrank away from these cynical maneuvers: it was the economic penalties that befell those who enshittified too rashly.
Incentives matter. Money talks and bullshit walks. Enshittification isn't due to the moral failings of individuals in tech companies. It's possible to have a good internet run by flawed people. But to get that new, good internet, we have to support technologists of good will and character by terrorizing their venal and cynical colleagues by hitting them where they live: in their paychecks.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/11/22/who-wins-the-argument/#corporations-are-people-my-friend
#pluralistic#microeconomics#incentives matter#microincentives#enshittification#corporate discipline#big tech#competition#too big to fail#too big to jail#ip#dont be evil#google#institutions#locus magazine
195 notes
·
View notes
Text

Monday afternoon study session. ☕️
154 notes
·
View notes
Text
So karen and ted are just okay with Mike dating someone who they've never seen, and was told is dangerous by the government??
Then just letting him fly to california to see her??
Why do I have a feeling that they think hes dating Will, because I just realised they never said girlfriend. Ted said "or no sweety pie" not girlfriend
Am i making sense? Or just delusional
#byler s4#byler proof#byler s5#mike x will#byler theory#bylerweek2023#byler tumblr#byler nation#byler is real#byler#anti mileven#anti milkvan#anti mileven#anti microeconomics
248 notes
·
View notes
Text
Since psychology is 98% random chance, what is the most empirically-plausible, microeconomic model for the individual mind?
192 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ko-Fi Prompt from Eli:
do landlords have price wars? it seems like with the insane way rents are going it wouldn't be hard for them to undercut competition. but it also doesnt feel like thats happening.
Oh, this is a fun one. Let's talk about price elasticity!
Note: I will be including graphs in this post. While it's helpful as a visual aid, there is no way to describe it that actually helps explain the premise that isn't already in the post's body of text. As such, I will not be providing image descriptions beyond the short sentence before or after stating what it's meant to represent, since further information wouldn't be of any use to those with screen readers.
In the field of microeconomics, one of the basic models everyone learns is the supply and demand curve. Here's a visual example:

Image Source: Wikimedia Commons
Traditionally, a product with an elastic price is one where demand fluctuates directly in response to cost, isolated from other factors*. A basic example is affordable luxury goods, say, a nice steak. If the cost goes up by a dollar, a certain portion of the population will decide it's no longer worth the cost, and will switch to something cheaper, like a chicken breast, instead.
* Other factors include, but are not limited to, luxury appeal, subsidized costs, and the lipstick effect. This post is already pretty long, so I can't go into many details on those situations.
The Demand curve is specifically a visualization of how much of a product can be sold for, not necessarily how much the product can be sold in quantity. As a general rule, it's easier to think of Price as the independent factor for Demand (and quantity as the dependent), and quantity as the independent factor for Supply (and price as the dependent).
With a traditional S&D curve, the intersection of the Supply and Demand curves is the optimal price point from both ends. The X-axis is supply quantity, which a lot of people find unintuitive... but that's where it's been for years and that's where it's staying.
If there is a great quantity of a product, with healthy competition levels, then the supply line moves to the right. The intersection of the lines then drops, and prices go down, as businesses lower prices to gain more customers.
If there is a small quantity of a product, due to limited raw materials or unique patents or skills, then the supply line moves to the left, and they can charge more for the product.
Here is a visual of what I mean by the supply curve moving:
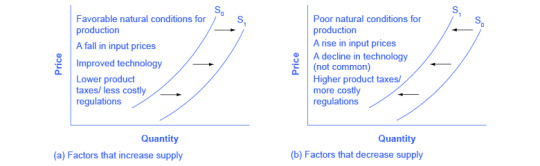
(Source: Wikimedia Commons)
The text is fairly small, so I'll describe here: The image states that factors that can increase supply (shift to the right) include favorable conditions for production, falling input prices, improved technology, and lower taxes or regulation costs. The second graph describes a decrease in supply, causing a shift to the left, the factors of which are the exact inverse of the first graph for increased supply.
A good example of a shift in supply resulting in a change in cost is gas: prices go up when supplies go down, whether due to higher taxes/regulations (e.g. the current refusal to trade with Russia), or disappearing raw materials (diminishing quantities of oil and natural gas, as finite, unrenewable resources). Comparatively, other forms of energy, like solar, have had their quantity lines shift to the right (cheaper) as the technology becomes more efficient and cheaper to produc.
Now, in areas that genuinely do not have enough housing, this is part of why prices go up: options are limited enough that they can get away with charging more. Due to zoning laws, construction costs, etc. they cannot add more housing, and so the supply curve is further to the left (pricier).
Here is a similar example image for the Demand curve, and how it shifts:

(Source: Wikimedia Commons)
The factors, here, are more intuitive. If demand goes up for reasons like trends, population, rise in general disposable income, changes in the costs of competitors or accessories, or expectations of investment viability, then the demand curve shifts to the right, and costs can increase without losing market share. For the reverse causes, the curve shifts to the right, and fewer people are willing to buy at that same cost.
Let's consider laptop computers: they have gotten more popular. A larger portion of the population has reason to buy them than twenty years ago. For that reason, the price can go up without necessarily losing market share (shifting to the right). However, income across the board has dropped, and there is a reasonably cheaper substitute (smartphones) for some uses, so the demand is lower (shifting to the left).
If you are in a city where there are suddenly a lot of people moving in for some shiny new company, then there is a greater population trying to buy, and so the demand curve shifts to the right, and prices can safely go up without losing market share.
...but that's with elastic pricing and competition.
Elastic pricing and costs are for most traditional goods. For specific foods, you can usually just... buy something else. If a plague wiped out half the crop of lettuce for the season, the costs will rise on the supply side (shift to the left), but there are unaffected substitutes, like broccoli and cabbage and tomato, for general use, so demand will also drop (also shift to the left). This means that prices go higher, but they are further to the left for both, meaning the quantity sold is lower.
Selling four million units at $3 vs. selling two million units at $6. The final amount of money changing hands is the same, but it's at a different cost and quantity.
Summary:
Supply moves to the left: less product, higher price from the seller to cover costs
Supply moves to the right: more product with healthy competition, lower price from the seller
Demand moves to the left: less interest in the product, customers need a lower price to buy the same amount
Demand moves to the right: more interest in the product, customers will tolerate a higher price to buy the same amount
But again, this is for elastic products.
What's an inelastic product?
Well... housing, actually, but let's start on the other side this time.
Products with inelastic demand are ones where customers cannot respond to changes in cost or supply. It doesn't matter if the cost goes sky high, and you know the profit is 96% because the cost of production is 4% of the price you paid; you can't afford to not buy it.
You know how insulin prices in the US spent decades being prohibitively expensive because diabetic individuals could not survive without buying it? That's inelastic demand.
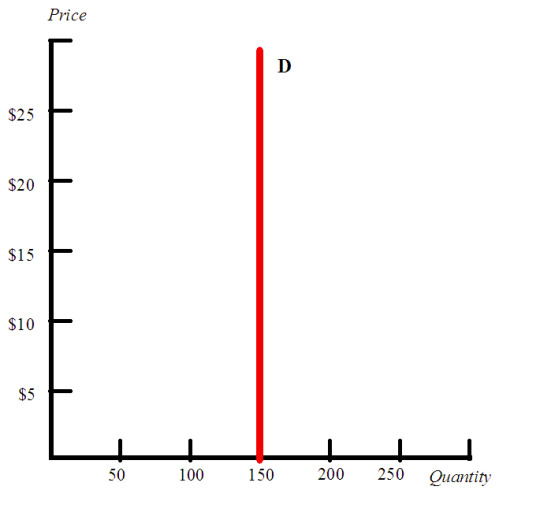
(Source: Wikimedia Commons)
If you look at the image above, you see a 'perfectly' inelastic demand curve. It is a straight, vertical line, where the quantity is immovably stuck at 150 no matter how high the cost goes.
In the real world, very, very few products are perfectly inelastic. Even insulin is... well, some people can move abroad. Not many, so it's pretty close to vertical, but some.
With housing, demand is fairly inelastic. The vast, vast majority of people do need housing. There are very few substitutes for this need, and while there is a range of prices and options, it does sort of... flatten out early.
If you demand that people spend $3000/month in order to live within 50 miles of their place of work, and everyone else is also demanding $3000/month, then there aren't any other options. The person either gets a new job elsewhere, spends a few hours a day on a commute, or pays those $3000.
Inelastic supply is the other side of that coin. The very limited quantity, and the high costs of expanding that supply, mean that the line shifts pretty far to the left, causing prices to rise. The line is also nearly vertical. With housing, there exists an argument that it is often cheaper to let the apartment sit empty than to rent it out too cheaply, due to maintenance costs and property taxes or what have you. Unless there's an exorbitant mortgage that needs to be contributed to by the tenants, though, those numbers don't quite work out.
So... if the Demand curve is nearly vertical, and the Supply curve is also nearly vertical, and there are no viable substitutes other than exiting the market entirely, you have a situation where the Supply side has nearly all the power and an excuse for why they're raising prices that doesn't actually reflect the reality.
Because there's plenty of housing being built, just, you know, not in the tax bracket that needs it. (Remember, a very large portion of Billionaire's row is currently unoccupied.)
You could argue that this is a form of price-fixing, which is an illegal act in which competitors in the same industry agree to collectively raise, lower, or stabilize pricing of a product. If 90% of microprocessor companies raise their prices simultaneously without cause, consumers will have to bite the bullet and buy the product at that new cost, as there aren't enough substitutes to find another option.
(If this sounds like a monopoly to you, good job! It's the same principle: control pricing for enough of the market that you can raise it higher than demand justifies. It's just done by making deals with the competitor instead of buying them out.)
However, due to the shape of the supply and demand curves in this housing market, and the very gradual way in which this situation has developed, it's not really a deliberate, organized price-fix, just something that came about as landlords realized that tenant's rights and alternate options (e.g. the council/public housing, affordable housing lotteries) weren't keeping up with their ability to continue to nudge prices upwards without losing out on money.
(Most of the time. Price-fixing does still happen, in pockets.)
Long story short: landlords don't have price wars because the demand curve is so inelastic that they can basically get away with anything.
(Prompt me on ko-fi!)
#economics#housing#housing industry#supply and demand#supply curves#demand curves#ko fi prompts#economics prompts#microeconomics#phoenix posts
201 notes
·
View notes
Text
not to be repetitive but i hope my exams blow up into a thousand million pieces and i never have to do them and also the uni pays me for emotional damages
#I CANT DO THIS SHITTTT WHY DOES IT HAVE TO BE SO DIFFICULT#CANNOT BELIEVE IM SAYING THIS BUT I MISS FIRST YEAR ECONOMICS#YEAH I HAD A BREAKDOWN ABOUT THAT TOO BUT MY GOD IM SMARTER NOW PLEASEEEEE#FINAL YEAR ADVANCED MICROECONOMICS WHEN I CATCH YOU. SHREDDING YOUR SKIN OFF WITH MY NAILS#hella goes to uni
39 notes
·
View notes
Text

I get my money back from hospitals in condoms.
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
I'm taking microeconomics and every 8 seconds they're like "now, this might SEEM cruel and classist and oppressive but that's only because you're on the receiving end of the damage and not the one benefiting from it! if you were on the other end of things you could see how this is actually good because it generates profit for smart businessmen."
#♥︎#microeconomics#economics#anyone else have this issue with econ or am i losing my mind. i feel crazy
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
I'm gonna join the crowd who says that this episode gives Scherzo vibes.
#doctor who#more doctor who from Carol :)#it would not be a good thing btw#a bit late to this. apparently lost a Newton joke??#fuck my microeconomics. hate the stuff
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Theories of the Philosophy of Microeconomics
The philosophy of microeconomics encompasses various theories and approaches that seek to understand the principles, assumptions, and implications of individual decision-making within the context of markets and economic systems. Some key theories in the philosophy of microeconomics include:
Rational Choice Theory: Rational choice theory posits that individuals make decisions by maximizing utility or satisfaction given their preferences, constraints, and available information. It assumes that individuals act in their self-interest and make choices that maximize their well-being.
Marginalism: Marginalism examines how individuals make decisions at the margin, weighing the benefits and costs of small changes or incremental units of goods and services. It emphasizes the importance of marginal analysis in determining optimal decision-making and resource allocation.
Utility Theory: Utility theory explores the concept of utility as a measure of satisfaction or happiness derived from consuming goods and services. It investigates how individuals allocate their limited resources to maximize utility, subject to budget constraints and preferences.
Consumer Choice Theory: Consumer choice theory analyzes how consumers make decisions about what goods and services to purchase based on their preferences, budget constraints, and the prices of goods in the market. It explores consumer behavior, demand curves, and the determinants of consumer choice.
Production Theory: Production theory examines the behavior of firms and producers in allocating resources to produce goods and services. It analyzes the relationship between inputs (such as labor and capital) and outputs, the concept of production functions, and the factors influencing production decisions.
Market Equilibrium: Market equilibrium theory explores the interaction of supply and demand in determining prices and quantities exchanged in markets. It examines how markets reach equilibrium through the adjustment of prices and quantities to balance supply and demand.
Game Theory: Game theory studies strategic interactions between rational decision-makers, such as individuals, firms, or governments, in competitive or cooperative settings. It analyzes the outcomes of strategic interactions, including the Nash equilibrium, cooperation, and competition.
Information Economics: Information economics investigates the role of information and uncertainty in economic decision-making. It examines how individuals gather, process, and act on information in markets, the impact of asymmetric information on market outcomes, and the role of signaling and screening mechanisms.
Behavioral Economics: Behavioral economics integrates insights from psychology and economics to study how cognitive biases, heuristics, and social factors influence economic behavior. It challenges the assumptions of rationality and explores deviations from standard economic models.
Welfare Economics: Welfare economics evaluates the efficiency and equity of resource allocation in economic systems. It assesses the welfare implications of market outcomes, including market failures, externalities, income distribution, and the role of government intervention.
These theories and approaches in the philosophy of microeconomics provide frameworks for understanding individual decision-making, market dynamics, and the allocation of resources in economic systems.
#philosophy#epistemology#knowledge#learning#chatgpt#education#ethics#psychology#Rational choice theory#Marginalism#Utility theory#Consumer choice theory#Production theory#Market equilibrium#Game theory#Information economics#Behavioral economics#Welfare economics#economics#microeconomics#economic theory#theory
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

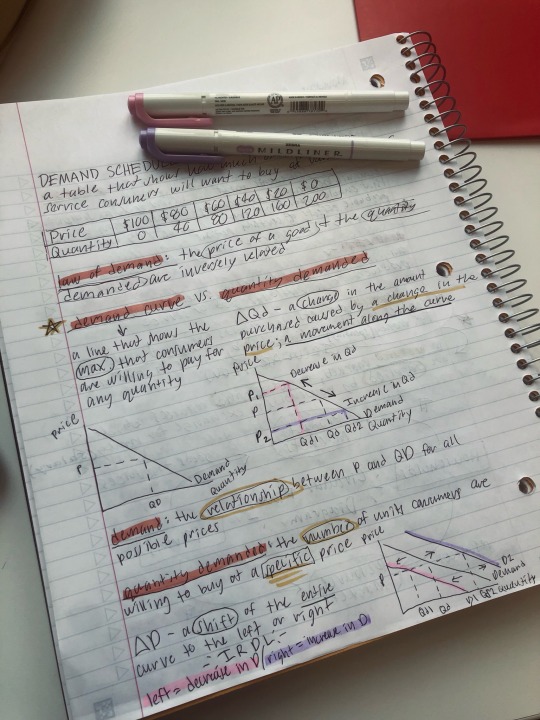
Microeconomics notes from a week ago at the library! I have my second exam this Friday, and let’s just say there’s a lot of room for improvement… anyways, wish me luck!
101 notes
·
View notes
Text
Okay, I've been noticing something lately.
When milevens are talking about mileven, they focus on El. Like the way El looks at Mike. Never the way Mike looks at El (especially after big moments like when El said "I love you")
Like on this (real) Mileven page, they wrote the caption
"Look at the way El looks at Mike after she said I love you! Her hand on Mike's cheek was so sweet🥹"
(this was the picture they used)

(As the extremely anti mileven byler I am, I commented "mike looks mortified")
But the fate of byler is not in El's hands, Its in Mikes. It doesn't matter how El looks at Mike, It matters if Mike returns the same look.
#byler#byler is real#byler nation#byler tumblr#byler proof#byler s4#byler s5#byler theory#bylerweek2023#mike x will#anti mileven#anti mileven#anti milkvan#anti microeconomics#when blue meets yellow in the west#byler endgame
156 notes
·
View notes
Text
if anyone needs college textbooks for 2024 spring semester or current ‘23 fall ig for statistics, managerial economics, managerial accounting (text&workbook) textbooks (will update with with versions upon request)
or data analytics (entry level) powerpoint instructor slides—
FREE (fcfs) lmk and for the physical books i’d just ask for shipping costs.
the microeconomics text is the PDF of the 8th edition of Mankiws’s principles of economics
#college textbooks#college#college community#university#university textbooks#university community#education should be free#education is a right#education#higher education#business major#business#businesses administration major#businies admin major#business admin#microeconomics#data analytics#intro to stats#managerial accounting#statistics#accounting
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

one day at a time
#n-original#business student#microeconomics#study motivation#studyblr#study aesthetic#studying#studyinspo#study blog#study space#girly student
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
i love when you make your environment absolutely perfect to Get Shit Done like i had a nap i ate food and made coffee i put the big light on i got in comfy clothes i made sure i was warm enough i got all my stuff out. and then executive dysfunction goes 'watch this!' and you get nothing done forever and ever
#sincerely a girlie who has a microeconomics exam TOMORROW and was supposed to start studying an hour ago#and i hear your 'most revision the night before is just reassurance bc if u dont know it by now you wont! you'll be fine!'#but im TELLING YOU i will not be fine#i have 50 flashcards to memorise#i have not started#and i dont even mind memorising flashcards bc as dull as it is im really fucking good at bulk memorising shit#like i can memorise 300 flashcards in a night for an exam the next day (<- tried and tested)#(i did all my gcse geography revision the night before by doing this and i was three marks off a grade 9 ur girl can MEMORISE)#and i get into a real groove of it so like. WHAT IS THE ISSUE HERE#JUST DO YOUR FLASHCARDS BITCH WHY ARE U READING FIC#im so burnt out and exams havent even started pray for me please#might shower and see if that wakes me up#my flat has like an actual power shower i have MISSED HER my home shower is this shitty electric one that feels more like light rain#oh yeah im back at uni btw! i missed my bed sm i forgot how comfy she was#hella goes to uni
42 notes
·
View notes