#landscape ecology
Text
For almost 25 years, Bhutan has been working to enhance the wildlife corridors which connect the country's protected areas. These provisions protect tigers, snow leopards, elephants, and drinking water. See how Bhutan is setting an example in our latest digest.
#wildlife corridors#environmental policy#bhutan#landscape ecology#conservation#science communication#scientists on tumblr
54 notes
·
View notes
Text
“For a landscape ecologist, a landscape is made up of a spatial array of patches. Depending on the researcher’s perspective, patches may consist of ecosystems or may simply be areas of habitat for a particular organism. Patches are spread spatially over a landscape in a mosaic. This metaphor reflects how natural systems often are arrayed across landscapes in complex patterns, like an intricate work of art.”
—Environment: The Science Behind The Stories by Jay Withgott and Matthew Laposata
#quotes#environmental science#ecology#landscape ecology#landscape architecture#art#science#science and art#art and science#landscapes#nature#environmental
52 notes
·
View notes
Text
instagram
0 notes
Photo
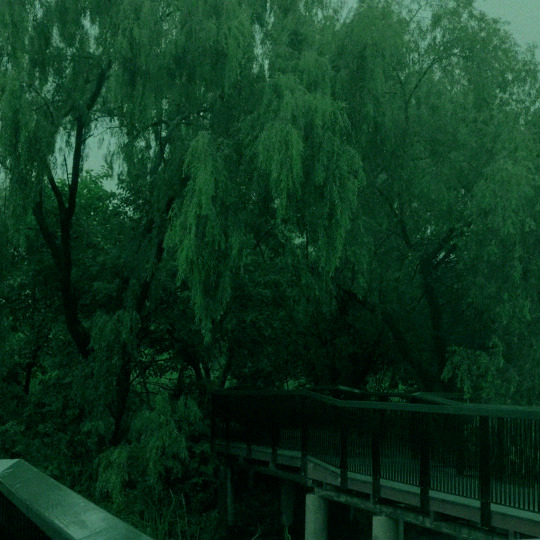
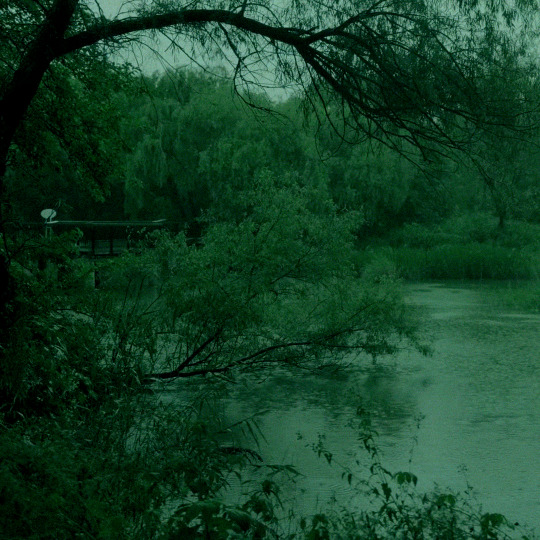



여의도샛강생태공원 / Rainy day in Seoul
#rainy#rainy day#seoul#nature#aesthetic#calm#rain#landscape#south korea#yeouido saetgang ecological park#mine#edit#˗ˋˏ ♡ ˎˊ˗
10K notes
·
View notes
Text
I have an essay brewing in my head constantly about lawns. Which, well, unsurprising, since I post about how I hate lawns all the time, but I think the "lawn" and "landscaping" centered way of thinking about Places Outside is a Bigger Thing that Connects to Other Things
(What isn't? Having ideas about concepts is always like this.)
I will introduce my ideas by a situation where they apply: Sometimes life-forms mimic other life forms. One form of mimicry is called Vavilovian mimicry, where weed species in crops grown by humans evolve over time to be more similar to the crops.
Vavilovian mimicry basically helps weeds survive because the weeds are adapted to the care-taking regimen of the crops, and because the human caretakers of the crop can have a hard time telling them apart, which means they might say "Ehh...I'll wait until it grows up so I can be sure I'm not pulling up my crop."
I think there's something similar at work among flower gardens and landscaping...but it's different.
Regular people don't know the name of every plant that might possibly grow in their flower beds, and they often pull up plants they don't know just because they don't know them. They sometimes say they pull up a plant that "looks weedy" or "looks like a weed."
I think to myself...what does "weedy" look like?
This question collided unexpectedly in my brain with an insight I had about invasive species that I could not explain.
I have to get rid of a lot of Callery pear, wintercreeper, honeysuckle, burningbush, privet, English ivy, and other plants that are invasive where I live. And strangely- many invasive plants look similar in ways they don't share with very many native species. They tend to have small, round or squat, glossy leaves, and they tend to have a very dense growth habit.
I can think of several possible explanations: Maybe these species thrive in North America today because of the loss of controlled burning, but their characteristics look so distinct next to native species because they relate to things that would make a species fire-intolerant? This doesn't seem quite right, since it doesn't predict level of fire-adaptedness in native species.
Another explanation is better: they were selected for these traits by humans for their usefulness in landscaping. Dense growth habit would be useful for creating hedges or ground covers. This is why many invasives were originally planted, right? And small leaves might feel or be perceived as less "messy" when they fall.
But I think this is a clue to something else going on. What does "weedy" look like?
Some plants go on one side of "weeds vs. flowers" and some on the other, and it's almost totally arbitrary...so how do gardeners make the call so decisively?
I think about the commonest "landscaping" plants- Knock Out roses, hostas, petunias, begonias, boxwoods and so on- they share a lot of the characteristics mentioned above. Shiny or at least smooth, typically small and squat leaves, dense and compact growth habit.
Then I think about some of the commonest and most important "weedy" native wildflowers, such as goldenrods, asters, milkweeds, Joe-Pye weed, ironweed, sunflower. They all differ from the above in at least one striking way. Mostly, they have hairy leaves and stems, long and thin leaves, and a tendency to grow up tall before blooming. Milkweed has smooth leaves, but its leaves are long and very big. Hmm...
And I think I can guess where this is coming from.
Landscaping and garden designs often look like this


See how the plants are drawn and arranged to cover a space in two dimensions, mostly not overlapping with each other? This is very easy to plan and design. And those common landscaping plants I mentioned—hostas, Knock Out roses, boxwoods, and so on—are very good at acting just like a two-dimensional representation of them does. Just look, you can see them:
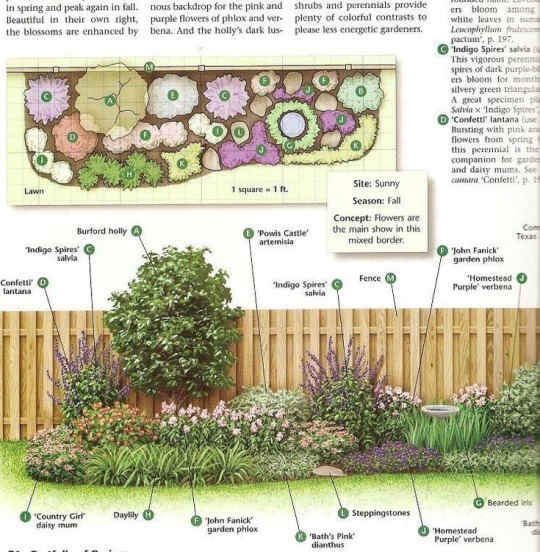
Now look at those important native wildflowers I mentioned:
Goldenrod

Ironweed
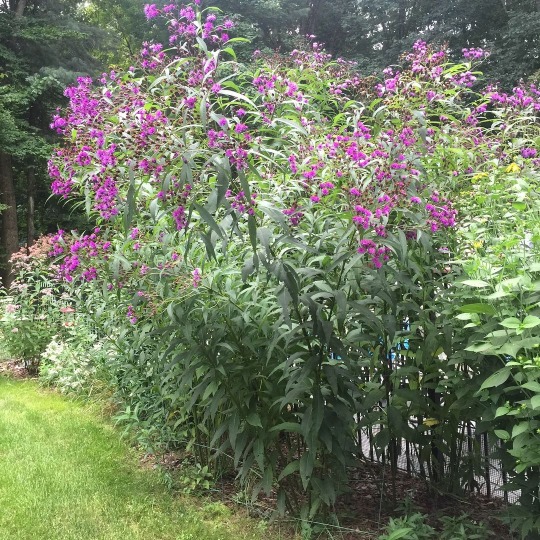

Milkweed
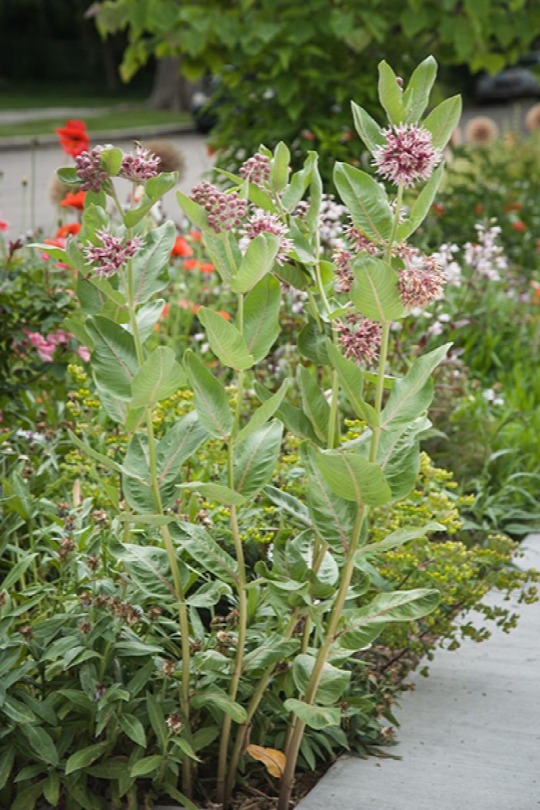

These guys don't fill much space in a horizontal plane, they go straight up. They don't exclude other plants from very much space either. Plants could grow under them and among them. So they're not very good for "filling up" space, and their opener, lankier, less dense shape doesn't do a good job at blocking other plants from growing.
In a garden of North American prairie- or meadow-adapted plants, the plants wouldn't exclude each other and stay within their designated spots because they're evolved to intermix with a great variety of plants.

"Separateness" is a big part of the typical "landscape" aesthetic. These plants are very neatly separate from each other. This is what looks "neat" and well-kept to us...the opposite of "weedy."
This could mean our garden and flower beds are affected by a selective pressure a lot like the Vavilovian mimicry situation. But instead of weeds being selected to look like intentionally grown plants, the intentionally grown plants are being selected to look different from weeds.
The subtle difference makes perfect sense. In a field, the rule is "leave the plant there if you're unsure" because that's your food. In a flower bed, the rule is "get rid of the plant if you're unsure" because having weeds is more aesthetically unacceptable than having blank space.
The point is: Ecology needs to be a big part of gardening and landscaping, because you are DOING ecology. Even if you don't know the evolutionary principles, you're acting them out.
Just like the ineffable preferences of female birds give the males weird elaborate display structures, ineffable aesthetic "senses" that govern our "built" world slowly turn it into something weird.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
I just don't see any enviroment as pristine or free of human influence. I don't see humans as being apart of nature. And I don't see human activity on nature as inmoral or undesirable. Which does not mean I support paving over everything or building farms everywhere. I just think humans build landscapes, it's what they do.
Whenever being hunter-gatherers in cultivated forests, creating rice terraces, building skyscrapers, managing silviculture systems, deforesting to plant soybean monoculture, creating aquaculture in the deep sea, building small fishing towns, or preserving rainforests for tourism, humans are just part of nature. It is our culture that defines what kind of landscapes, what kind of ecosystems, grow around us.
We can either embrace this and build landscapes and ecosystems that will allow us to preserve our planet and recognize the importance of nature to our well-being, or keep the stupid "humans are a plague" way of thinking and keep the sharp dichotomy human/nature, which will only bring us to half-solutions at best.
#cosas mias#ecology#and yes regarding the recent discussion we will carry this to space (because we will go to space) and build landscapes in space#and they will be affected and build on what our culture considers important and what kind of resource use we employ#space is also a part of nature it is and will be the biggest part of nature someday
262 notes
·
View notes
Text
[E]very [interspecies] meeting in fact reminds us that the being we meet is and always shall be strange to us […]. When beings meet there is a distance between, such that in encountering the slug we also encounter something beyond the slug – a multitude of life we cannot sense. [...] So despite shared histories and the close proximity in which slugs and [humans] live, the slug retains a certain darkness as a creature apart; something is held in reserve […]. And so fleeting awareness of the irretrievability of the lives of others intensifies poignancy, such that despite a gulf separating the [human] from other creatures, some connection, however fleeting, is made to something – however strange. Refusing to dismiss the everyday and the banal is an ethical response. […] Slugs are there: sliming, chomping, and oozing around quietly and that should be enough to give them consideration.
[Text by: Franklin Ginn. “Sticky lives: Slugs, detachment and more-than-human ethics in the garden.” Transactions of the Institute of British Geographers, Volume 39, Issue 4. 2013. Bold emphasis added by me.]
---
So, can an insect speak? And if yes, do we understand it? Wittgenstein maintained that ‘if a lion could speak we would not understand him’, by which he implied that we do not share the ‘form of lion-life’ that would make lion language fully transparent to us […]. A similar insight was [...] expressed by [...] [a twentieth-century] honeybee researcher [...]: Beyond the appreciable facts of their life we know but little of the bees. And the closer our acquaintance becomes, the nearer is our ignorance brought to us of the depths of their real existence. But such ignorance is better than the other kind, which is unconscious and satisfied.
[Text by: Eileen Crist. “Can an Insect Speak?: The Case of the Honeybee Dance Language.” Social Studies of Science, Volume 34, Issue 1. 2004. Bold emphasis added.]
---
Animal studies scholarship tends to emphasize animal-human relations, encounters, and similarities. […] Jellyfish and other gelatinous creatures [...], however, float at the far reaches of our ability to construct sturdy interspecies connections [...]. Uexkull’s theory […] insists upon multiple worlds […], a capacious admission that a multitude of other creatures dwell as part of worlds that humans cannot readily or completely access or grasp. Three-quarters of a century later Terry Tempest Williams wonders what it would be like to be a jellyfish. […] [She] writes: “Perhaps this is what moves me most about jellies – their sensory intelligence […] the great hunger that is sent outward through the feathery reach of their tentacles. Imagine the information sought and returned.”
[Text by: Stacy Alaimo. “Jellyfish Science, Jellyfish Aesthetics: Posthuman Reconfigurations of the Sensible”. In: Thinking with Water. 2013. Bold emphasis added.]
---
Although we cannot ‘speak’ with nonhumans in any straightforward way, what we can and more importantly do do is become articulate with them in various ways. [...] If there is a way out of this historical impasse [alienation, climate crisis, global ecological degradation], [for some] it is not to be found in attributing some of ‘our’ qualities to ‘them’. It “would not be a matter of ‘giving speech back’ to animals […]. Perhaps the task is not to seek to compare the dance language of bees […] with human language, the ‘intelligence’ […] of Monarch butterflies with human intelligence, […] but rather (or at least in addition) to find a way of thinking about these ‘remarkable things’ that grants them positive ontological difference in their own right. […] [It] is concerned with what is always a multitude of others rather than a singular other […]; and it is radically nonanthropocentric […].
[Text by: Nick Bingham. “Bees, Butterflies, and Bacteria: Biotechnology and the Politics of Nonhuman Friendship.” Environment and Planning A: Economy and Space, Volume 38, Issue 3. 2006. Bold emphasis added.]
---
Starfish may seem to be still, but longer attention [...] shows them [slowly] moving, changing. [...] Then there are beings [like some insects] that experience hundreds, thousands of generations within a human lifetime. For such beings, the memories, learnings and modes of passing on experience are, it almost goes without saying (yet it must be said as it is so often not), radically different from any human’s in terms of the ways they experience change. The immensity of the alterity is, literally, incomprehensible to humans. We can't know what these beings know. But we can be aware that they have knowledges and experiences beyond us. [...] [W]e should know they live and experience and think beyond us. We should seek respect and be aware of how our lives are entangled […]. It is not abstract, or empty.
[Text by: Bawaka Country et al. “Gathering of the Clouds: Attending to Indigenous understandings of time and climate through songspirals.” Geoforum Volume 108. January 2020. Bold emphasis added.]
557 notes
·
View notes
Text

#ecology#conservation#environment#nature#yards#home and garden#gardens#gardening#landscaping#outdoors#animals#science
233 notes
·
View notes
Text

new thing for new business cards: some lush future Africa, de colon1zed & self determined, where the great green wall has grown thick and steady & date palms & mango trees could maybe share canopies, adapting to the new weather patterns & all hope is not lost
(see more things from me via my newsletter, patreon, or bluesky)
#tumblr why must you destroy the quality#art#illustration#climatechange#afrofuturism#africa#greatgreenwall#reforestation#ecology#solarpunk#antelope#goats#farm#farmlife#painting#concept#herding#design#sahel#sahara#desert#restoration#wildlife#sunset#landscape#sun#star#redgiant#mariah-rose marie
90 notes
·
View notes
Text
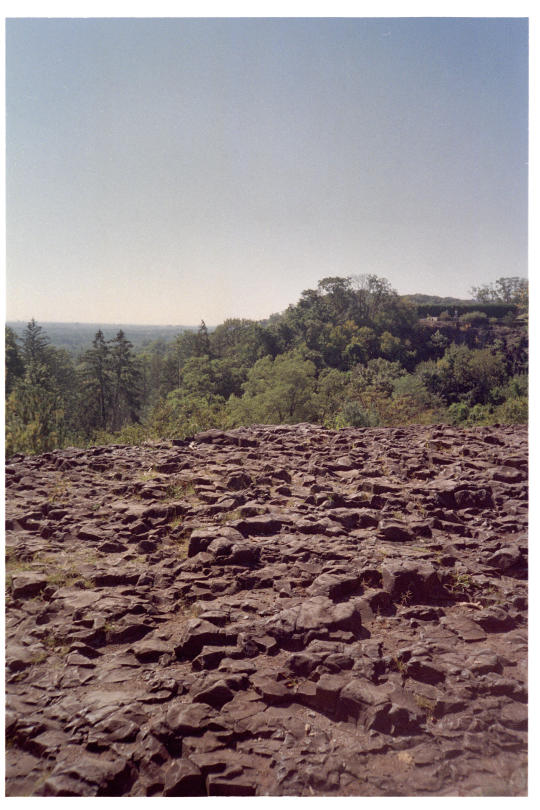


basalt cliffs at mills reservation, montclair, nj - vivitar ps 1-2-3 & 400 film - developed at eliz digital & scanned with minolta dimage dual iii
#35mm#rocks#trees and sky#new jersey#nature#nature aesthetic#film photography#35mm photography#35mm color photography#trees#landscapes#nature photography#mountains#sunlight#lensblr#rock#basalt#geology#minerals#ecology
174 notes
·
View notes
Text


Sylvan lake, Custer State Park, South Dakota.
#sylvan lake#custer state park#south dakota#mine#nature#naturalist#nature photography#photography#ecology#north america#scenery#landscape photography#landscape#lake#geology#state parks
84 notes
·
View notes
Text
In conservation biology we think a lot about spatial configuration - how habitat is fragmented, or how it's connected, or how global patterns like biodiversity are determined.
What if we consider not only geographic space, but also climate space as well? Climate regions can cover the Earth just like geographic regions do, and can be quantified by spatial traits like area and fragmentation.
Come read our latest digest that explores research behind the geography of climate, and how it can be highly useful in explaining why species are found where they are.
#ecology#scientists on tumblr#climate change#habitat connectivity#landscape ecology#sci comm#conservation
22 notes
·
View notes
Text

A lake in Cayambe Coca Ecological Reserve, Ecuador
by Laurence Green
375 notes
·
View notes
Text

#plants#horticulture#botany#landscape architecture#me in all of my landscape/botany-related classes#I do like ornamentals (I really do) but they're not special interest grabby like other things#I go to friends for plant IDs and latin names#they come to me for orchard design and ecological considerations#nd#dungeon meshi
315 notes
·
View notes
Text

Edward Lear A Study of Ferns Civitella (Italy). Oil on green wove paper: 15 × 17 cm (6 × 7 in). October 1842.
#edward lear#art#light academia#forest#beauty#plants#ecology#earth#science#leaves#flowers#botanical#outdoors#oil painting#nature#landscape#19th century#garden#art history#naturecore
92 notes
·
View notes
Text
It would be nice if humanity could reach a point where landscaping like this is not okay. I walk past this area frequently, and they regularly nuke everything with roundup and remove all the detritus. Think of all the arthropods and other wildlife this wasted space could support. I understand having fire buffers around buildings, but this attitude isn’t exclusive to plots close to buildings…

I also understand many native plants can be more difficult to grow, but California poppies (in the Bay Area) are not one of them. I’m sure other regions have similarly easy to grow species. Even a few plants can make a huge difference.
We as a culture need to stop it with the blasé attitude about the destruction of nature, particularly bugs (ie invertebrates). “Kill it with fire” is a shitty and ignorant way to react to a tiny animal that is merely trying to exist. The vast majority of bugs are not out to get you and are, in fact, terrified of you (rightfully so in many cases).
Would you squish a baby bird? Didn’t think so.
#rant#that article yesterday set me off lol#it’s been bothering me for a long time though#ecology#ecological destruction#bugs#don’t squish bugs#sustainable landscaping#plant native#native species#nature#biodiversity#conservation#roundup#stop it
56 notes
·
View notes