#indian space research organization (isro)
Text
Space Technology Opportunity in India

Written By: Jagriti Shahi
Introduction:
Entrepreneurship in space technology in India has been gaining momentum in recent years. The Indian government has been actively promoting the development of the space sector, and private companies are playing an increasingly important role.
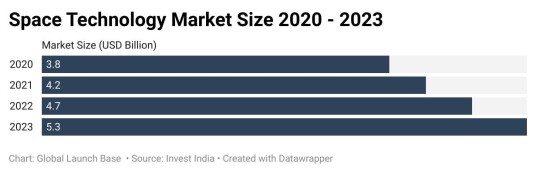
As the nation liberalizes its space sector, a diverse array of players are contributing to the burgeoning space ecosystem. Entrepreneurs are venturing into satellite manufacturing, pushing the boundaries of launch services, delving into space exploration, and exploring innovative solutions for satellite-based communication. The landscape is further enriched by collaborative efforts between private entities, government agencies, and academic institutions, fostering a dynamic environment for research and development.
In this context, it's crucial to explore the challenges and opportunities that define the entrepreneurial spirit in India's space technology sector. Regulatory hurdles, infrastructure development, and the need for sustained investments are among the challenges that entrepreneurs face. However, with increasing investor interest, a robust policy framework, and a commitment to fostering innovation, India's entrepreneurial ventures in space technology are poised to shape the nation's narrative in the cosmic domain. This dynamic interplay of public and private entities is not only propelling India's space capabilities but is also contributing to the global discourse on the commercialization and exploration of space.
Here are some key aspects of entrepreneurship in space technology in India:
Government Initiatives:New Space Policy: The Indian government has introduced policies to encourage private sector participation in space activities. The New Space India Limited (NSIL) was established to promote, commercially exploit, and transfer technologies developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).Liberalization: The government has liberalized the space sector, allowing private companies to undertake a wide range of space-related activities, including satellite launches, space exploration, and satellite communication services. (ISRO) Initiatives: Antrix Corporation: Antrix is the commercial arm of ISRO, and it collaborates with private players for the commercialization of space-related products and services.: SEED is a program initiated by ISRO to promote startups in the space sector by providing them with opportunities for collaboration and technology transfer.: NSIL is a central public sector enterprise (CPSE) under the Department of Space. It plays a crucial role in commercializing space products, technical consultancy services, and transfer of technologies.: ISRO has been actively engaging with startups, providing them access to its facilities, expertise, and technology.: The Department of Space in India oversees the country's space program. It may introduce schemes and programs to support space technology startups and entrepreneurs. (AIM): AIM, a flagship initiative of the NITI Aayog, supports innovation and entrepreneurship in various sectors. It may have programs and funding opportunities that space technology startups can explore. (NIF): NIF supports grassroots innovations and may provide support to startups working on innovative space technologies.
Private Space Companies:Startups: Several startups in India are focusing on various aspects of space technology. Some are involved in satellite manufacturing, launch services, data analytics from space, and more.Launch Services: Companies like Agnikul Cosmos, Skyroot Aerospace, and Pixxel are working on developing small satellite launch vehicles to provide cost-effective and flexible launch options.
Space Exploration and Research: Interplanetary Missions: ISRO has been actively involved in space exploration, and private companies are expressing interest in participating in future interplanetary missions.Research and Development: Private entities are engaging in research and development activities, contributing to advancements in satellite technology, propulsion systems, and other space-related technologies.
Satellite Manufacturing:Private Satellite Manufacturers: Companies like Exseed Space and Bellatrix Aerospace are involved in the manufacturing of satellites, catering to various purposes such as communication, Earth observation, and scientific research.
Communication Services:Telecommunication Satellites: Private companies are exploring opportunities to provide satellite-based communication services. This includes both broadband internet services and other communication solutions.
Funding and Investments:Investor Interest: The space technology sector in India has attracted attention from investors. Funding rounds for space startups have been on the rise, indicating confidence in the potential growth of the industry.
Collaborations and Partnerships:
Industry-Academia Collaboration: Partnerships between private companies, government organizations, and academic institutions are fostering innovation and research in the space sector.
The Indian space technology ecosystem is evolving, and with continued government support, entrepreneurial ventures in space technology are expected to play a crucial role in shaping the future of the Indian space industry.
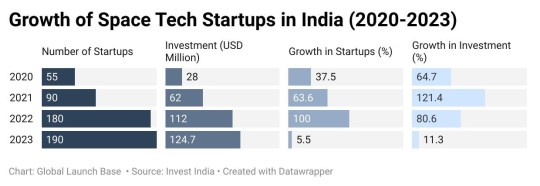
The number of space tech startups in India has witnessed explosive growth, increasing by almost five times in just five years. Investments in the sector have also seen a sharp rise, from $17 million in 2019 to an estimated $124.7 million in 2023.
Commercialization of Space Activities: With India's proven track record in satellite launches and space technology, there is a substantial potential for the commercialization of space activities. The burgeoning demand for satellite-based services, including communication, arth observation, and navigation, opens up opportunities for private entities to actively participate in the space industry. As the cost of space access continues to decrease, private companies can explore ventures such as satellite manufacturing, space tourism, and satellite-based applications, contributing to economic growth and job creation.
International Collaborations: Collaborations with other space-faring nations present a promising avenue for India to augment its space capabilities. Joint ventures, knowledge exchange, and technology transfer can accelerate innovation and enhance the efficiency of space missions. ISRO has already established itself as a reliable partner for international launches, and expanding collaborative efforts can lead to shared resources, reduced costs, and a more diversified approach to space exploration. As India continues to engage in global partnerships, it can leverage collective expertise for ambitious endeavors beyond Earth's orbit.
Innovation in Space Technology: Investments in research and development (R&D) can catapult India into the forefront of space innovation. Emphasis on cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, advanced materials, and propulsion systems can revolutionize space missions. The development of reusable launch vehicles, like the ongoing efforts in creating a Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV), can significantly reduce launch costs, making space exploration more sustainable. Encouraging a culture of innovation, fostering collaboration between academia and industry, and providing incentives for R&D initiatives can fuel breakthroughs in space technology.
Space Applications for Sustainable Development: Leveraging space technology for sustainable development on Earth is an untapped frontier. Utilizing satellite data for precision agriculture, disaster management, environmental monitoring, and resource mapping can contribute to addressing pressing global challenges. By integrating space-based solutions into sectors such as agriculture, healthcare, and urban planning, India can harness the power of space technology for inclusive and sustainable development, bringing tangible benefits to its citizens and contributing to global initiatives.
Expansion of Interplanetary Exploration: Building on the success of Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan), India has the potential to expand its interplanetary exploration efforts. Initiatives for exploring other celestial bodies, such as Venus or asteroids, can contribute to humanity's understanding of the solar system and beyond. A strategic focus on ambitious interplanetary missions can position India as a key player in the broader scientific community and foster international collaboration in the exploration of the cosmos.
Trending Technologies in India's Space Industry:
Nanotechnology: The integration of nanotechnology in space technology has the potential to revolutionize spacecraft design, materials, and instrumentation. Nanosatellites, with their miniaturized components, are becoming increasingly popular for cost-effective and innovative space missions. India can leverage nanotechnology for lightweight yet robust spacecraft, enhancing mission efficiency and scientific capabilities.
Companies: Nano-Tech SpA, Kalva Nanotech
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are playing a pivotal role in data analysis, image processing, and autonomous decision-making in space missions. India can explore AI applications for real-time data interpretation, automated navigation, and predictive maintenance of spacecraft. Incorporating machine learning algorithms into Earth observation data analysis can significantly enhance the understanding of environmental changes.
Companies: Aadyah Aerospace, Blue Sky Analytics
Quantum Computing: Quantum computing holds the promise of solving complex computational problems beyond the capabilities of classical computers. In the space sector, quantum computing can be utilized for optimizing mission trajectories, simulating quantum systems, and enhancing the security of communication channels. India's focus on quantum computing research can contribute to advancements in space-related computations.
Companies: QpiAI, BosonQ
3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: The adoption of 3D printing in space technology can revolutionize the manufacturing process, enabling the production of complex and lightweight structures. India can benefit from 3D printing for rapid prototyping, cost-effective manufacturing of satellite components, and even on-demand production during long-duration space missions.
Companies: Agnikul Cosmos, EOS India
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology offers secure and transparent data management, making it applicable to space-based applications such as satellite communication, data storage, and secure information sharing. By incorporating blockchain, India can enhance the security and integrity of space-related data and transactions.
Companies: SpaceTime Labs, Aryaka Networks
Solar Sail Technology: Solar sails, propelled by the pressure of sunlight, offer a sustainable and efficient means of propulsion for spacecraft. This technology can be harnessed for deep-space exploration, enabling missions to travel vast distances with minimal fuel requirements. India's exploration programs can benefit from research and development in solar sail technology for extended-duration missions.
Companies: Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology (IIST), IIT Bombay - Aerospace Engineering Department
Hyperspectral Imaging: Hyperspectral imaging involves capturing a wide range of wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum. This technology is instrumental in Earth observation, resource mapping, and environmental monitoring. India can explore the integration of hyperspectral imaging in its satellite payloads for enhanced remote sensing capabilities.
Companies: Pixxel, Paras Defence & Space Technologies Ltd
Internet of Things (IoT) for Space: The application of IoT in space technology involves connecting devices and sensors on satellites and spacecraft to gather and transmit data. This interconnected network can facilitate efficient communication, data collection, and collaborative decision-making during space missions. India can explore IoT applications for enhanced space situational awareness and mission coordination.
Companies: Agnikul Cosmos
As India looks to the future, embracing these trending technologies will be crucial for maintaining its competitive edge in space exploration and satellite technology. By actively incorporating these innovations into its space programs, India can not only enhance mission success but also contribute to the global advancement of space technology. Collaborations with research institutions, startups, and the private sector will play a vital role in driving these technological advancements in India's space industry.
Challenges and the Way Forward:
Despite its successes, India's space program faces challenges such as increased competition, budget constraints, and the need for continuous innovation. To overcome these challenges, sustained government support, collaboration with private entities, and a focus on skill development in the space sector are crucial.
Increased Global Competition: The space industry is becoming increasingly competitive with the emergence of new players and the commercialization of space activities. To stay ahead, India must continuously innovate, streamline its processes, and invest in cutting-edge technologies. Developing a robust ecosystem for space startups and fostering public-private partnerships can enhance India's competitiveness in the global space market.
Budget Constraints: Despite commendable achievements, budget constraints pose a challenge for sustaining and expanding India's space endeavors. A consistent and increased allocation of funds to ISRO, along with exploring innovative funding mechanisms, will be crucial. Engaging with the private sector for joint ventures and commercial space activities can help alleviate financial constraints and promote economic sustainability in the long run.
Human Resource Development: The growth of India's space program necessitates a skilled workforce capable of handling complex missions. Investing in education and training programs in collaboration with academic institutions can ensure a steady supply of skilled professionals in fields such as aerospace engineering, astrophysics, and data sciences. This will not only address the current workforce requirements but also fuel future innovations in space technology.
Technological Advancements: Rapid technological advancements globally require India to stay at the forefront of innovation. Embracing emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and advanced propulsion systems will be essential. Establishing research and development centers dedicated to space technology innovation can facilitate the integration of these advancements into future missions.
Space Debris Management: The increasing number of satellites and space missions contribute to the growing issue of space debris. India needs to actively participate in international efforts to address space debris management, adopting sustainable practices in satellite design and end-of-life disposal. Research into debris removal technologies and international collaboration on space traffic management will be pivotal in ensuring the long-term sustainability of space activities.
Climate Change Monitoring: With the rising global concerns about climate change, space technology plays a crucial role in monitoring environmental indicators. India can take a leadership role in developing satellite-based solutions for climate monitoring, disaster response, and sustainable resource management. This requires a dedicated focus on Earth observation satellites, advanced sensors, and data analytics.
Enhanced Space Diplomacy: Strengthening space diplomacy is essential for India to expand its global influence in the space arena. Engaging in collaborative space missions, sharing scientific knowledge, and participating in international forums will enhance India's standing as a responsible space-faring nation. Forming strategic partnerships with countries interested in space exploration can open up new avenues for cooperation and joint missions.
Conclusion:
India's journey in space technology has been nothing short of remarkable, with ISRO consistently pushing the boundaries of innovation. As the nation continues to invest in space exploration, the opportunities for growth, collaboration, and technological advancements are boundless. The future holds exciting possibilities for India's space technology sector, positioning the country as a key player in the global space community.
About Global Launch Base:
Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us.
Contact Info:
Website: www.globallaunchbase.com
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/
Email: [email protected]
#ISRO - Indian Space Research Organization#NewSpace India Limited (NSIL)#SEED(Social Entrepreneurship Empowerment Development)#Atal Innovation Mission Official#National Innovation Foundation - India#Nano-Tech SpA#Kalva Nanotech#AADYAH Aerospace Private Limited#Blue Sky Analytics#QpiAI#BosonQ Psi (BQP)#AgniKul Cosmos#EOS#Spacetime Labs#Aryaka#Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology#Aerospace Engineering Association IIT Bombay#Pixxel#Paras Defence & Space Technologies Ltd.#AgniKul Cosmos hashtag#SpaceTechnologyInIndia hashtag#IndianSpaceProgram hashtag#ISROOpportunities hashtag#SpaceIndustryGrowthIndia hashtag#SpaceResearchOrganizationsIndia hashtag#SatelliteTechnologyOpportunities hashtag#IndianSpaceExploration hashtag#ISROAchievements hashtag#SpaceScienceCareersIndia hashtag#SpaceTechnologyTrends hashtag
0 notes
Text
Chandrayaan-3 अपडेट: ISRO ने घोषणा की, प्रज्ञान रोवर अब 'नींद मोड' में है, और 22 सितंबर को फिर सक्रिय हो सकता है!
Image Credit: ISRO
Chandrayaan-3: चंद्रमा पर Pragyan रोवर ‘नींद मोड’ में, 22 सितंबर को फिर सक्रिय हो सकता है। ISRO के नवाचार से जुड़ें!
भारतीय अंतरिक्ष और अनुसंधान संगठन (ISRO) ने घोषणा की है कि 22 सितंबर 2023 को, विक्रम लैंडर के प्रज्ञान रोवर मॉड्यूल सुनी हवाओं में ‘नींद मोड’ में प्रवेश करेगा। रोवर ने अपने कार्यों को पूरा किया है और अब सुरक्षित रूप से पार्क किया गया है, साथ ही APXS और LIBS…

View On WordPress
#Chandrayaan-3#Chandrayaan-3 News#Indian Space Research Organization#isro#Lunar Mission Update#Lunar Surface#Moon Mission#Pragyan Rover#Sleep Mode#Space Exploration
1 note
·
View note
Text
Aditya L1 Mission - क्यों है एक वरदान
भारत नें Chandrayaan-3 के बाद कल Aditya L1 Mission से सूर्य को नमन की तैयारी है। भारत की स्पेस एजेंसी ISRO के प्रमुख S. Somanath ने कहा कि भारत का यह पहला सौर Mission सूर्य और पृथ्वी के बीच मौजूद L1 Point पर पहुंचने के लिए 125 दिन लेगा। यह Point अपनी धरती से 15 Lakh Kilometer की दूरी पर है। यह धरती से सूरज की दूरी का मात्र 1% है।
Aditya L1 Mission के लिए क्यों खास है L1 Point?
किसी भी ग्रह की…

View On WordPress
#Aditya L1#Aditya L1 mission#Aditya L1 satellite#Astronomical research#Heliosphere#Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO)#ISRO#ISRO missions#Solar missions#Solar Orbiter#Solar research#Solar science#Solar system exploration#Space exploration#Space missions#Space probes#Space science#Space technology#Sun observation#Sun&039;s atmosphere#Sun&039;s corona
0 notes
Text

#Chandrayaan-3#the third lunar mission of the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO)#made a soft landing on the Moon.#World victorious tricolor dear#now the moon is ours🚀🇮🇳#India became the first country in the world to successfully reach the south polar region of the Moon. The landing of Chandrayaan-3 created#today is a proud day for India.#This historic and proud achievement is a symbol of determination#hard work and sacrifice of our scientists.#Congratulations to the countrymen and the entire ISRO team associated with Chandrayaan-3 and best wishes for the future.#ISRO#Chandrayaan3#Chandrayaan3Landing#VikramLander#दीनबंधुसरछोटूरामधाम#JatSewaSangh
1 note
·
View note
Text
The amazing camera aboard ISRO's Chandrayaan-3 that took this amazing moon photo
The Chandrayaan-3 mission, ISRO’s remarkable unmanned lunar endeavour, has gifted us with mesmerising visuals of both the Moon and Earth, enhancing our understanding of these celestial bodies.
Intricate Details Revealed
This awe-inspiring photograph, showcasing intricate lunar craters in great detail, was masterfully taken upon the spacecraft’s entrance into the Moon’s orbit on August 5th. This…

View On WordPress
#celestial photography#Chandrayaan-3#Chandrayaan-3 camera#Chandrayaan-3 instruments#Chandrayaan-3 isro#Chandrayaan-3 moon#chandrayaan-3 spacecraft#India moon mission#Indian Space Research Organization#ISRO#ISRO moon#lunar mission#moon Chandrayaan-3#unmanned lunar mission
0 notes
Text
ISRO Recruitment 2023
ISRO Recruitment 2023 : इंडियन स्पेस रिसर्च ऑर्गेनाइजेशन (इसरो) ने 526 पदों पर नई भर्ती का नोटिफिकेशन जरी किया है l इसरो भर्ती 2023 के लिए ऑनलाइन आवेदन 20 दिसंबर 2022 से 9 जनवरी 2023 तक कर सकते है और आवेदन शुक्ल जमा करवाने की अंतिम तिथि 11 जनवरी 2023 तक रखी गई है l
इसरो भर्ती 2023 के तहत असिस्टेंट, जूनियर पर्सनल असिस्टेंट, अप्पर डिवीज़न क्लर्क, स्टेनोग्राफर, पर्सनल असिस्टेंट सहित कई पदों पर भर्ती…

View On WordPress
#Indian Space Research Organization 2023#Indian Space Research Organization Recruitment 2023#Indian Space Research Organization Vacancy 2023#ISRO Recruitment 2023#ISRO Vacancy 2023#इंडियन स्पेस रिसर्च ऑर्गेनाइजेशन भर्ती 2023#इसरो भर्ती 2023
0 notes
Text
இந்திய விண்வெளி ஆராய்ச்சி நிறுவனத்தின் பின் வரும் பணிகள் நிரப்புவதற்கான அறிவிப்பு வெளியாகியுள்ளன
இந்திய விண்வெளி ஆராய்ச்சி நிறுவனத்தின் பின் வரும் பணிகள் நிரப்புவதற்கான அறிவிப்பு வெளியாகியுள்ளன
#govtjobs #upsc #ssc #currentaffairs #gk #ssccgl #ias #jobs #governmentjobs
இந்திய விண்வெளி ஆராய்ச்சி நிறுவனத்தின் பின் வரும் Assistant (Rajbhasha) பணிகள் நிரப்புவதற்கான அறிவிப்பு வெளியாகியுள்ளன. மத்திய அரசு இந்த அதிகாரப்பூர்வ அறிவிப்பினை வெளியிட்டுள்ளது. இந்திய விண்வெளி ஆராய்ச்சி நிறுவனத்தின் பணிக்கு விண்ணப்பிக்க ஆர்வமுள்ளவர்கள் 08/12/2022 முதல் 28/12/2022க்குல் என்ற இனையத்தில் மூலமாக ஆன்லைன் மூலமாக விண்ணப்பிக்கவும். இப்பணிக்கு விண்ணப்பிக்கும் நபர்கள் விண்ணப்பிக்கும்…

View On WordPress
#india space research organisation#india space research organization#indian research and space organisation#indian space agency#indian space research organisation#indian space research organisation (isro)#indian space research organisation explained#indian space research organisation news#indian space research organisation news today#indian space research organisation upsc#indian space research organization#indian space research organization (isro)#ISRO Recruitment 2022 07 Assistant (Rajbhasha) Posts#space research
0 notes
Text
India launched its first space mission to study the sun on Saturday, less than two weeks after a successful uncrewed landing near the south polar region of the moon.
The Aditya-L1 spacecraft took off on board a satellite launch vehicle from the Sriharikota space center in southern India on a quest to study the sun from a point about 1.5 million kilometers (930,000 miles) from earth, known as L-1.
The spacecraft is equipped with seven payloads to study the sun's corona, chromosphere, photosphere and solar wind, the Indian Space Research Organization said.
After over an hour, the ISRO said the launch was "accomplished successfully."
Continue Reading.
127 notes
·
View notes
Text
Only days after a simular Russian mission failed crashing into the lunar surface, India became only the 4th country in history to land on the moon and the first to land on the South Pole. On August 23, 2023, the ISRO (Indian Space Research Organization) landed the Chandrayaan 3 (Chandrayaan is translated from moon vehichle in Hindi Sanskrit) on the moon to perform experiments on the little known and rough terrained area. (Space Exploration, Real Life Event)

#nerds yearbook#real life event#the moon#august#2023#lunar#space exploration#india#the south pole#isro#chandrayaan3
21 notes
·
View notes
Text

NASA’s LRO Observes Chandrayaan-3 Landing Site
NASA’s LRO – the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter – spacecraft imaged the Chandrayaan-3 landing site on the Moon’s surface.
The ISRO (Indian Space Research Organization) Chandrayaan-3 touched down on the Moon on Aug. 23, 2023. The Chandrayaan-3 landing site is located about 600 kilometers from the Moon’s South Pole.
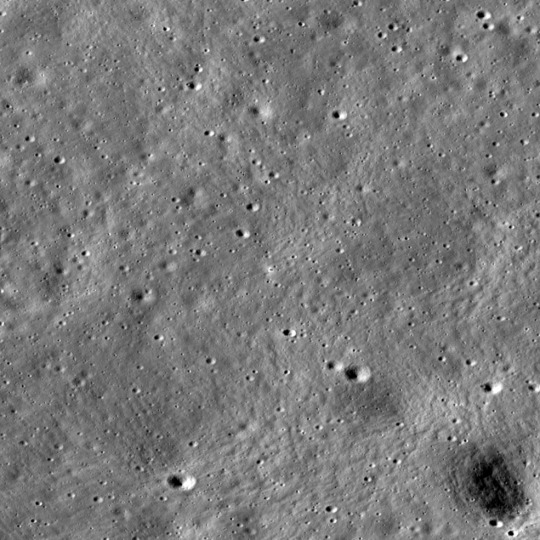

Chandrayaan-3 lander is in the center of the image, its dark shadow is visible against the bright halo surrounding the vehicle. The image is 1,738 meters wide; frame No. M1447750764LR.
Credits: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Arizona State University
The LROC (short for LRO Camera) acquired an oblique view (42-degree slew angle) of the lander four days later. The bright halo around the vehicle resulted from the rocket plume interacting with the fine-grained regolith (soil).
Visit the ISRO gallery of Chandrayaan-3 images.
LRO is managed by NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, for the Science Mission Directorate at the agency’s Headquarters in Washington. Launched on June 18, 2009, LRO has collected a treasure trove of data with its seven powerful instruments, making an invaluable contribution to our knowledge about the Moon. Arizona State University manages and operates LROC.
Banner Image: Chandrayaan-3 lander is in the center of the image, its dark shadow is visible against the bright halo surrounding the vehicle. The image is 1,738 meters wide, frame No. M1447750764LR. Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Arizona State University.
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
India has landed on the Moon!!! The landing is part of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)'s historic Chandrayaan-3 mission.
"'We have achieved soft landing on the moon,'" said ISRO Chairman Shri Somanath. 'Yes, on the moon!'"
"[Indian Prime Minister Narenda Modi] then addressed the ISRO team, speaking in Hindi but adding in English, 'India is now on the moon!'
'The success belongs to all of humanity,' he said. 'And it will help moon missions by other countries in the future. I'm confident that all countries in the world ... can all aspire for the moon and beyond. ... The sky is not the limit!'"
The remote operated lander named Vikram touched down in the south pole region at 6:02pm IST on August 23, 2023. Vikram carried a small but mighty companion, the lunar rover Pragyan (Sanskrit, "wisdom").
Vikram is named after Vikram Sarabhai, PhD, physicist, astronomer, and a major figure in the development of India's space and nuclear programs. Sarabhai served as the first chairman of the ISRO, as well as the driving force behind the organization's creation. Recognizing the need for more coordinated space research in India, Sarabhai urged the Indian government to create INCOSPAR - the committee that eventually formed the ISRO in 1969.
#india moon mission#indian space research organisation#chandrayaan3#ISRO#chandrayaan-3#vikram lander#India moon landing#pragyan rover#Vikram Sarabhai
14 notes
·
View notes
Note
It was a racist ask and Mena’s lukewarm tee-hee guess governments can’t devote all their funds to safeguarding Indian women tucked me off. All the more when she insinuated -you- were the racist for fact-checking that race bait. I’ve noticed a lot of people take cover behind Indian women and the rape problem in India to spew the most vile racist rhetoric and humour about India. Far fewer people approach this problem with the sobriety it required. It’s just a chance to shit on Indian people they pounce on.
I am still weak from the high fever I recently recovered from and I was doing chores now so I am a little dizzy so forgive me if incorrect but when did she insinuate I was being racist? In fact she reblogged my addition.
But for the funding part, it's kinda complicated which I don't think anon (the og one) or anyone using simplistic logic will understand. On the paper, gender equality programs get wayyyyy more funding than space research. But we also know corruption is a huge thing here. But ofc, we can't measure how much money is actually being in effect, so it could be lesser or it could be more. I haven't dug too deep into it. So I think it's kinda hard to verify how much does the government actually prioritize women's welfare over R&D sector in practice. But I get your point.
Organic-homegrown-boyfriend already said that. Anon was stupid because even if the government doesn't care about women, they don't care about a lot about any research sector here either. Dumb to imply they care more about the other when all ISRO missions, including this one, had to be run on tight budget.
It's funny cause Indian MRAs always accuse the Indian government of "favoring" and giving "special treatment" to Indian women, so hearing foreigners say just the opposite and contrasting the two sides is amusing.
And hard agree on the second part. Rape is the only form of misogyny in India people from other countries like to point out. And while it's definitely a problem, I think we should approach the topic with more nuance. The rape rate is high here not simply because Indian men are some unique monsters. But there are number of other conditions. Marital rape being legalized for one. If we criminalize it, I think the number of rapes will go down at least a little bit. And then there's a lack of bathrooms or sex segregated bathrooms in the rural regions. Lack of basic infrastructure like enough street lights. And then the same reasons why rape is an issue in Western countries as well. Law being too lenient towards rapists, fear of reporting due to public smear campaigns and etc. But obviously poverty amplifies a lot of things so there's that. However it's easier to walk down the racist path than to understand why things are this way here.
The gorey kutte will never try analyzing our situation the way they analyze theirs. Double standards. First thing they need to learn is to start viewing us as humans equal to them. How to not be racist beginner volume 1.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Title: Chandrayaan 3: India's Next Giant Leap in Lunar Exploration
Introduction
In the realm of space exploration, India has emerged as a prominent player, making significant strides in recent years. One of the most awaited missions that has captured the world's attention is Chandrayaan 3, India's third lunar mission. Following the successes of Chandrayaan 1 and Chandrayaan 2, this mission promises to take India's lunar exploration endeavors to new heights. In this blog, we will explore the key aspects of Chandrayaan 3 and why it is so exciting for space enthusiasts and scientists alike.
Chandrayaan 3: A Brief Overview
Chandrayaan 3 is the third installment in India's Chandrayaan program, which aims to explore Earth's celestial neighbor, the Moon. The mission follows Chandrayaan 2, which was launched in July 2019 and achieved significant success, despite the Vikram lander's unsuccessful soft landing attempt.
Here are some key features of Chandrayaan 3:
Redefined Goals: Chandrayaan 3 builds upon the previous missions' successes and failures, with a primary focus on achieving a successful soft landing on the Moon's surface. This marks a crucial shift in the mission's objectives, as the previous Chandrayaan missions focused on lunar orbiters and exploring the Moon's surface from afar.
Collaborative Effort: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is collaborating with various international space agencies and organizations for Chandrayaan 3, including NASA. This collaboration opens up opportunities for shared scientific discoveries and technological advancements.
Advanced Technology: Chandrayaan 3 will utilize cutting-edge technology and lessons learned from previous missions to enhance its chances of success. This includes improvements in navigation, communication, and landing systems.
Scientific Goals: While the primary aim is to achieve a successful soft landing, Chandrayaan 3 will also carry scientific instruments to conduct experiments on the Moon's surface, analyze lunar soil samples, and study the Moon's geology and topography.
Why Chandrayaan 3 Matters
Chandrayaan 3 is a mission of paramount importance for several reasons:
National Pride: India has shown tremendous growth in space technology and exploration. Chandrayaan 3 serves as a symbol of national pride and technological prowess, showcasing India's capabilities on the global stage.
Scientific Discovery: The mission is expected to provide invaluable data about the Moon's surface and geology, aiding our understanding of lunar history and the solar system's formation.
International Collaboration: By collaborating with international space agencies, India not only shares the costs and risks but also contributes to the global scientific community. Chandrayaan 3 is part of a larger effort to expand human knowledge beyond Earth.
Inspiration: Chandrayaan 3 inspires a new generation of scientists, engineers, and space enthusiasts in India and around the world. It fosters curiosity and encourages STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) education.
Conclusion
Chandrayaan 3 represents India's unwavering commitment to space exploration and scientific discovery. With its revised goals, international collaborations, and advanced technology, it has the potential to not only achieve a historic soft landing on the Moon but also contribute significantly to our understanding of the lunar surface and the solar system's mysteries.
As we eagerly await the launch of Chandrayaan 3, the world watches with bated breath, hoping for another success story that will leave an indelible mark on the annals of space exploration. This mission reinforces India's status as a rising space power and serves as a testament to the human spirit of exploration and curiosity that knows no bounds.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Space Tech: Private Ventures and Mars Exploration

Space Tech
Beyond intrepid exploration, space technology has advanced to address pressing issues on Earth. It is becoming more and more essential to the effective operation of contemporary societies and their economic growth. Space has the potential to directly affect billions of people’s lives and open up large-scale, highly impactful solutions.
A broad term for satellites, space stations, ground stations, tracking and monitoring centers, downstream analytics and artificial intelligence, software, and other technologies, SpaceTech offers innovative ways to solve global concerns. Satellites increase communication, navigation, and earth observation capacity at low cost even in remote locations. Satellite-based earth observation data is vital, accurate, and reliable for data-driven decision-making by businesses and governments.
The underserved and otherwise unprofitable regions can benefit from high-speed connectivity thanks to the satellites. The application of action plans for intelligent agriculture, resource management (land and water), infrastructure development (urban and rural), climate and weather monitoring, environmental protection (including reducing the risk of disaster), and other purposes can all benefit from the use of satellite data.
Aerospace Innovation
The space industry is predicted to increase in value from USD 360 billion in 2018 to USD 558 billion by 2026 and roughly USD 1 trillion by 2040. Even though the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) is one of the world’s top space agencies and is working on projects like the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (NavIC) and the Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM), India currently only makes up 2%, or USD 7 Bn, of this market value.
One reason could be that the private sector’s contribution to the Indian space industry has primarily consisted of ISRO subcontracting, with ISRO historically handling the crucial value addition activities internally. Because of this, Indian private companies have lagged behind other world leaders in SpaceTech in terms of end-to-end capabilities.
The publication of SpaceCom Policy 2020, Space RS Policy 2020, Geospatial Policy 2021, and other policies, along with the creation of organizations like NewSpace India Ltd (NSIL) and the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Centre (IN–SPACe), have created a national push to expedite the private sector’s involvement in the Indian space area. The Department of Space is also working on a comprehensive Space Act and other policies, including launch vehicle and space exploration policies.
Because of our natural curiosity and desire to understand the universe, space travel has long fascinated people.
Recently, private enterprise and international cooperation have transformed space exploration.
This article will explore the changing face of space exploration and emphasize the importance of international collaboration and private industry.
New Space Technologies
Pioneers of Personal Space Travel
NASA, Roscosmos, and ESA were the only government space agencies allowed to explore space. However, private companies leading space innovation changed everything:
SpaceX since 2002 has resupplied the ISS, developed reusable rocket technology, and prepared to colonize Mars.
Jeff Bezos’ Blue Origin offers professional and recreational suborbital and orbital spaceflight.
Rick Branson’s suborbital space tourism company, Virgin Galactic.
Innovating, competing, and seeking commercial opportunities beyond Earth are redefining space exploration in private space ventures.
Space Exploration Companies
International Space Cooperation
Space exploration requires international cooperation even as private businesses grow:
The Earth-orbiting International Space Station (ISS) is a global collaboration marvel. European, Japanese, Canadian, Russian, and US space agencies participate.
Mars exploration: NASA, ESA, and others work on Curiosity and Mars Sample Return.
The Artemis Accords outlines global cooperation on the Moon and beyond, inviting international partners to lunar exploration.
Global Collaboration and Private Enterprises Benefits
Space exploration benefits from private sector involvement and international cooperation in a number of ways.
Innovation: By bringing in competition and innovation, private endeavors lower costs and advance technology.
Commercialization: Businesses worldwide can take advantage of commercial endeavors to expand their satellite deployment, space tourism, and resource exploitation capabilities.
Shared Resources: Working together, nations can pool resources, exchange knowledge, and take on challenging projects.
Scientific Discovery: Across national boundaries, international cooperation increases the possibility of scientific discovery and exploration.
Difficulties and Things to Think About
Although private and international partnerships present notable benefits, they also present certain challenges.
Regulation: To address new challenges, the framework governing international cooperation and private space endeavors needs to change.
Resource Management: A complex ethical and legal challenge is the responsible use of space resources, such as lunar mining.
Space Debris: Coordinated actions ought to tackle the expanding problem of space debris and environmentally friendly space operations.
Space Travel Prospects
Future space exploration could lead to asteroid mining, planet colonization, and scientific breakthroughs.
Space exploration is entering a new era as private companies and multinational partnerships change the space environment.
Space exploration is more accessible, sustainable, and transformative than ever thanks to private innovation and international collaboration. It shows our willingness to push the limits and our enduring spirit of exploration.
Mars Rover
What is Mars Rover?
A robotic vehicle that investigates the surface of Mars is called a rover. Rovers are long-range, remotely controlled vehicles that gather data and take images while traveling great distances. They have found evidence of water, ancient life, and possible resources on Mars, among many other significant discoveries.
Six Mars rovers have been successful so far:
In 1997, Sojourner became the first rover to set foot on Mars. During 83 days, it investigated the Ares Vallis region.
The twin rovers Spirit (2004) and Opportunity (2004) touched down on Mars in 2004. For many years, they investigated the Gusev Crater and Meridiani Planum, respectively. Opportunity stopped operating in 2018 and Spirit became stuck in 2010.
Gale Crater is presently being explored by Curiosity (2012). It has found evidence of ancient lakes and rivers, among many other significant discoveries.
The Jezero Crater region is being explored in Perseverance (2021). In addition to gathering samples of rock and regolith broken rock and soil for potential return to Earth, it is searching for indications of prehistoric life.
The first Chinese rover to set foot on Mars is Zhurong (2021). It is investigating the area of Utopia Planitia.
An essential component of our Mars exploration are the Mars rovers. They have made significant contributions to our understanding of the Red Planet’s potential for habitability.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#Space Tech#MarsExploration#Ventures#SpaceTech#satellites#AI#Aerospace#NASA#technews#technology#govindhtech
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Chandrayaan-3: India's Next Mission to the Moon

Chandrayaan-3 is an upcoming space mission by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO). Building on the success of its predecessor, Chandrayaan-2, this new mission aims to further explore the lunar surface and expand our understanding of Earth's closest celestial neighbor. In this article, we will delve into the details of Chandrayaan-3, discussing its objectives, key components, and anticipated scientific discoveries. Read More
2 notes
·
View notes