#difference between farming and agriculture
Text
Top Global Trends in Agriculture in 2024 | Eyes For Science

As we step into 2024, the agricultural landscape is evolving at an unprecedented pace, driven by technological advancements, environmental concerns, and shifting consumer preferences. Farmers around the globe are adopting innovative practices to enhance productivity, sustainability, and resilience. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the top Global trends in agriculture that are shaping the industry in 2024. Before that, let us have a glimpse of what agriculture is to start with.
#agriculture trends 2024#global trends in agriculture#Agriculture trends in america#agriculture in india#technology in agriculture#water management in agriculture#development of agriculture#farming information#difference between farming and agriculture#problems in agriculture#types of agriculture#agriculture problems and solutions
0 notes
Text
okay. so.
i'm reading this book The Origins of the Modern World by Robert Marks
and even from the beginning i was getting this weird feeling from it. I'm always really wary of books that are broad overviews of history that claim to explore big theory-of-everything explanations for very broad phenomena, because history is unbelievably complex and there is so much disagreement between historians about everything.
But anyway I come to this section (in the first chapter)

This writer's opinion is that the Americas seemed so abundant when English settlers first arrived because the Native Americans had been mostly killed, and as a result, the wildlife increased greatly in numbers and forests overtook the farms, creating what appeared to be a natural paradise.
I'm immediately suspicious of this paragraph because arguing that the mass death of Native Americans was good for nature seems really contradictory to the research I've explored, on top of being just...disgusting.
But it doesn't sound right in regards to how ecosystems work either. If populations of animals had recently exploded after millennia of being limited by a major predator, it would cause the plants to be overwhelmed by the herbivore populations. The land would be stripped barren and eroded, and soon the animals would be weak and starving.
So I thought to myself, huh, a citation. I will look at the citation and see what it says.
It's a book called Changes in the Land by William Cronon, who seems to be one of the most important and respected guys in his field. I thought, I have to find this book. So I did, I found the book, and spent like an hour reading through it.
And what I discovered, is that Cronon's book directly contradicts what Marks says in the paragraph that cites Cronon?!

So basically this entire book, Changes in the Land, is a detailed exploration of how the arrival of English settlers, the decline of Native American populations, and the slow transition to European farming and land use practices caused increasing degradation to the ecosystem, beginning very early on in colonization.
Changes in the Land quotes a great array of documents from the colonial period where settlers observed the soil becoming depleted, animals disappearing, and the climate itself becoming more hostile even in the 1600's. It's actually a really fascinating book.
Cronon tells us that Native Americans created lush and abundant conditions for wild animals by causing a "mosaic" of habitats, with different areas representing various stages of ecological succession. With this great diversity in habitats, and lots of transitional "edges" between them, the prosperity of the animal life was maximized. This was intentional, and really a type of farming.

The book essentially explains how European settlers couldn't recognize Native American life ways as "agriculture," they thought the land was just supernaturally abundant all by itself because of its inherent nature, and yet almost immediately after settlers came, the abundance of the land degraded and vanished. The settlers cut down vast amounts of trees, which caused erosion, which destroyed the river and stream ecosystems and starved the soil of nutrients. Destruction of forest caused less rain, and more extreme temperatures. It became a vicious cycle where the settlers had to abuse the land more and more just to survive.
The spiral pulled in Native American communities too, forcing them to turn to more exploitative means of survival like the fur trade, (which depleted the beaver population, which caused the decline of beaver ponds, which harmed the whole forest). It describes how the changing ecosystems left Native Americans with no choice but to turn to European practices for survival, which in turn depleted the land even further.
Even I was surprised to learn just how early on environmental disaster set in, and the incredible extent of it. English farming practices literally reshaped the map of New Haven between the 17th and 18th centuries:

To return to Marks, though...Marks' statement in the excerpt, where he says the "abundance" of animals continued throughout the 19th century, is blatantly false according to the source HE CITES.

Deer were becoming scarce in New England by the 1690's. It was so bad by 1718 that deer hunting was forbidden for 3 years at that time, and by 1800, deer were almost extirpated from New England. The book explains on another page that wild turkeys became so rare that a farmer's manual from the time said their domesticated turkeys were from Turkey—settlers had no opportunity to see a wild turkey and no idea they existed.
Marks is supporting his statement using a source entirely dedicated to contradicting the exact thing he's saying! It's unbelievable.
How does this happen? Did Marks just have his own opinion and insert a famous book that seemed to be on the subject as support, without reading it?
I'm thinking now of all the times I've read a book and seen a citation on a statement and unconsciously thought "oh, well it seems there is evidence, so it must be reliable" when actually, something like this was happening. The array of ways misinformation can be propagated and never be found out is terrifying.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
"In response to last year’s record-breaking heat due to El Niño and impacts from climate change, Indigenous Zenù farmers in Colombia are trying to revive the cultivation of traditional climate-resilient seeds and agroecology systems.
One traditional farming system combines farming with fishing: locals fish during the rainy season when water levels are high, and farm during the dry season on the fertile soils left by the receding water.
Locals and ecologists say conflicts over land with surrounding plantation owners, cattle ranchers and mines are also worsening the impacts of the climate crisis.
To protect their land, the Zenù reserve, which is today surrounded by monoculture plantations, was in 2005 declared the first Colombian territory free from GMOs.
...
In the Zenù reserve, issues with the weather, climate or soil are spread by word of mouth between farmers, or on La Positiva 103.0, a community agroecology radio station. And what’s been on every farmer’s mind is last year’s record-breaking heat and droughts. Both of these were charged by the twin impacts of climate change and a newly developing El Niño, a naturally occurring warmer period that last occurred here in 2016, say climate scientists.
Experts from Colombia’s Institute of Hydrology, Meteorology and Environmental Studies say the impacts of El Niño will be felt in Colombia until April 2024, adding to farmers’ concerns. Other scientists forecast June to August may be even hotter than 2023, and the next five years could be the hottest on record. On Jan. 24, President Gustavo Petro said he will declare wildfires a natural disaster, following an increase in forest fires that scientists attribute to the effects of El Niño.
In the face of these changes, Zenù farmers are trying to revive traditional agricultural practices like ancestral seed conservation and a unique agroecology system.

Pictured: Remberto Gil’s house is surrounded by an agroforestry system where turkeys and other animals graze under fruit trees such as maracuyá (Passiflora edulis), papaya (Carica papaya) and banana (Musa acuminata colla). Medicinal herbs like toronjil (Melissa officinalis) and tres bolas (Leonotis nepetifolia), and bushes like ají (Capsicum baccatum), yam and frijol diablito (beans) are part of the undergrowth. Image by Monica Pelliccia for Mongabay.
“Climate change is scary due to the possibility of food scarcity,” says Rodrigo Hernandez, a local authority with the Santa Isabel community. “Our ancestral seeds offer a solution as more resistant to climate change.”
Based on their experience, farmers say their ancestral seed varieties are more resistant to high temperatures compared to the imported varieties and cultivars they currently use. These ancestral varieties have adapted to the region’s ecosystem and require less water, they tell Mongabay. According to a report by local organization Grupo Semillas and development foundation SWISSAID, indigenous corn varieties like blaquito are more resistant to the heat, cariaco tolerates drought easily, and negrito is very resistant to high temperatures.
The Zenù diet still incorporates the traditional diversity of seeds, plant varieties and animals they consume, though they too are threatened by climate change: from fish recipes made from bocachico (Prochilodus magdalenae), and reptiles like the babilla or spectacled caiman (Caiman crocodilus), to different corn varieties to prepare arepas (cornmeal cakes), liquor, cheeses and soups.
“The most important challenge we have now is to save ancient species and involve new generations in ancestral practice,” says Sonia Rocha Marquez, a professor of social sciences at Sinù University in the city of Montería.
...[Despite] land scarcity, Negrete says communities are developing important projects to protect their traditional food systems. Farmers and seed custodians, like Gil, are working with the Association of Organic Agriculture and Livestock Producers (ASPROAL) and their Communitarian Seed House (Casa Comunitaria de Semillas Criollas y Nativas)...

Pictured: Remberto Gil is a seed guardian and farmer who works at the Communitarian Seed House, where the ASPROL association stores 32 seeds of rare or almost extinct species. Image by Monica Pelliccia for Mongabay.
Located near Gil’s house, the seed bank hosts a rainbow of 12 corn varieties, from glistening black to blue to light pink to purple and even white. There are also jars of seeds for local varieties of beans, eggplants, pumpkins and aromatic herbs, some stored in refrigerators. All are ancient varieties shared between local families.
Outside the seed bank is a terrace where chickens and turkeys graze under an agroforestry system for farmers to emulate: local varieties of passion fruit, papaya and banana trees grow above bushes of ají peppers and beans. Traditional medicinal herbs like toronjil or lemon balm (Melissa officinalis) form part of the undergrowth.
Today, 25 families are involved in sharing, storing and commercializing the seeds of 32 rare or almost-extinct varieties.
“When I was a kid, my father brought me to the farm to participate in recovering the land,” says Nilvadys Arrieta, 56, a farmer member of ASPROAL. “Now, I still act with the same collective thinking that moves what we are doing.”
“Working together helps us to save, share more seeds, and sell at fair price [while] avoiding intermediaries and increasing families’ incomes,” Gil says. “Last year, we sold 8 million seeds to organic restaurants in Bogotà and Medellín.”
So far, the 80% of the farmers families living in the Zenù reserve participate in both the agroecology and seed revival projects, he adds."
-via Mongabay, February 6, 2024
#indigenous#ecology#agroforestry#agriculture#traditional food systems#traditional medicine#sustainable agriculture#zenu#indigenous peoples#farming#colombia#indigenous land#traditional knowledge#seeds#corn#sustainability#botany#plant biology#good news#hope#climate action#climate change#climate resilience#agroecology#food sovereignty
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Amazing Digital World
🍀•~ MASTERPOST ~•🍀

•~The beggining~•
In an attempt to do a little experiment. Developers wanted to test Ai's ability to evolve.
They started to create a very basic virtual world. Coding some realms, some biomes, some communities, some special locations, and different types of enemies and villagers. A combination between Minecraft and Stardew Valley.
Caine was like the coder's will inside this world, they coded him to create everything the developers demanded. Once the basics were finished, he had the task to look for errors, bugs, and anything that could harm the proper function of the world, as well as create whatever the creators demanded him to.
The game and its NPCs were specifically coded to be able to evolve. They wanted to see how far the NPCS free will could go, how much they could do. They wanted this virtual reality to feel as real.
This would take a while tho.
The developers had big hopes in this auto-sustained world. But it didn't work as fast as they thought. They left it aside for a while, and the company kept selling with normality. Some eventually forgot about it, but the small world they once created had evolved into a full fleshed out universe.
Entire families of each type of NPCs had formed, a functional economy, and different cultures arose. More importantly, the NPCs had reached the level knowing they lived in a digital world, but they also knew this was where they were supposed to be.
They lived their lives like a regular human being. Everyone expects one particular AI..who unfortunately was never meant to evolve as the others. An AI that till this day, keeps waiting for the coders to give meaning to his existence.
~• The Realms •~
Note: illustrations might be done in the future
The Main Grounds 🎪👣
Human-like creatures made of rubber inhabit what one was the starting point of everything. Most human-like inhabitants are clown themed, wearing colorful combinations and displaying extremely pale skins with iconic make up. Most houses now look like circus tents.
As the starting point of everything, Humanoid Clowns are usually skilled on all kinds of areas, nowadays though they are mostly recognized by their sharp communication abilities.
Feeding habits: Regular Foods and Water
Pomni and Kaufmo inhabit this realm
Woodland Kingdom 🌲🪵
Wood made toys inhabit this prosperous Nation. Although wooden puppets and dolls can be found, the biggest demographic group this realm are Chess-like inhabitants.
Trees on Woodland are abundant since most of this realm is forest surrounded. They provide wood for construction to other realms and are knowledgeable on the matter. Woodland has the widest insect population.
Feeding habits: Wood and Tree Sap
Kinger and Queenie inhabit this realm
The Great Cartoon Plains 🌽🚜
Probably the biggest biome and realm of all. Here cartoonish anthropomorphic animals made out of rubber inhabit the plains. Great weather, excellent soil, and wide terrains, The Great Plains is the hostess of the biggest agricultural production that feeds most realms.
Most families that inhabit this place farm and mine for a living. They provide the raw materials that sustain the rest of the world. They have great resistance and their ATP (Energy) lasts the longest.
Feeding habits: Regular Foods and Water.
Jax inhabits this realm
Raggedy Village 🧸🧵🪡
A village with a welcoming vibe, Raggedy Village is probably one of the safest and calmest realms. Rag dolls, plushies, fabric puppets inhabit this place in big teapot looking houses. They are usually very kind and willing to teach.
Raggedy villagers excel at the refining of cotton and fibers, as well as the art of sewing and designing everything from carpets and curtains to clothes, hair bowties and shoes. Raggedy village is the biggest exporter of clothes and fabric.
Feeding habits: Gossypium and Sweet Tea
Ragatha inhabits this realm
Puzzle City 🧩🎲
Tall, noisy and at times confusing, Puzzle City occupies this place on the list. Wacky and colorful, Puzzle City owns the most abstract and ingenious buildings and transport mechanisms. Their citizens are not any different.
Often called "The Geometrics" citizens of the city are plastic and are usually composed of geometric shapes that can be rearranged. Geometrics are especially good at architectural engineering and design, and are by nature bright in color and personality...with a few exceptions..
Feeding habits: No food is needed for survival
Zooble and Orbsman inhabit this realm
Stone Temples 🎭🎨
Special for being home of NPCS originally designed to be provoked enemies. The Stone temples are clean, polished, resistant and often, artsy. They display beautiful designs and paintings, and with reason.
Often called the porcelains, the inhabitants of this complex are artistic and emotional souls, and excel in every form of art, from painting, sculpting, dancing, music, and theater. Most porcelains have a distinctive physiology: Mask faces with light ribbon bodies.
Feeding habits: Minerals and Gossypium
Gangle inhabits this realm
Candy Island 🍭🍮
The most distant territory, Candy Island feels like a fever dream without a set time period. The name says it all, an island of the size of Australia where everything is made out of every type of candy imagined, including their people.
Lolli citizens, cake fellas, and gummy lads are just a few examples, they are often highly energetic and sweet. Most desserts found in any other realm most likely came from Candy Island.
Feeding habits: Regular desserts and raw sugar
Loolilalu, Gummigoo, Max and Chad inhabit this realm
The Amazing Digital Academia 🪄🔮
A wide academia with a fundamental purpose: Sustain the world they all live in. With the original coders absent, Caine is allowed to grant certain skills to NPCS that seem responsible and acknowledging about the matter
What we might know as coding, for them is magic. Being able to manipulate reality and spawn new creations, new textures, flavors, physics, biomes, was necessary for the expansion of this little world.
Here, students learn everything they need to know in order to maintain and expand this beautiful world. Alongside coding, characters study whatever discipline they want to master.
All characters previously mentioned attend as students and teachers
Uniform Variations:

~• Families and Births •~
Each type of NPC presents a different type of reproduction. No genitalia is present on any of them, but just like in the sims, the game recognizes the baby making process and starts the NPC's corresponding process to spawn a new baby. Different types of NPCS can result in interesting combinations and character designs
Rubber Animals 🐣
Humans and anthropomorphic animals have probably the simplest birth process. Just like in real life, regular pregnancies and Births take place. As stated before, Characters do not possess genitalia, instead the game recognizes certain intimate acts. If both characters desire to have a baby, an immediate fertilization will take place.
Babies are raised by their "biological" families and it is possible to identify the character's ancestry based on code patterns
Chess Pieces ♟️
Chess pieces do not reproduce, but spawn from flowers instead. Each type of piece spawns on its own recurrence, pawns spawn with the most frequency. Knights and Bishops spawn moderately, Queens and Kings spawn with the least frequency. Every 20 years, the new Queen and King must replace the formers.
Each type of piece is raised by its own kind except for Kings and Queens. Kings are raised by bishops, Queens are raised by pawns.
Rag Dolls [coming soon]
Geometrics [coming soon]
Porcelains [coming soon]
❤️ SPECIAL THANKS TO @notnights for helping me with ideas and figuring out a lot of stuff ❤️
#the amazing digital circus#the amazing digital circus au#the amazing digital world#open world au#tadc au
380 notes
·
View notes
Text
As urban populations boom, urban agriculture is increasingly looked to as a local food source and a way to help combat inequitable food access. But little is known about how productive urban agriculture is compared to conventional, rural farming. A new study digs in, finding urban gardeners and hydroponics can meet and sometimes exceed the yields of rural farms.
“Despite its growing popularity, there’s still quite a lot we don’t know about urban agriculture, like whether the yields are similar to conventional agriculture, or even what crops are commonly grown,” says Florian Payen, an environmental scientist at Lancaster University and lead author of the study, published today in AGU’s journal Earth’s Future.
The new study compiles studies on urban agriculture from 53 countries to find out which crops grow well in cities, what growing methods are most effective, and what spaces can be utilized for growing. The researchers find that urban yields for some crops, like cucumbers, tubers and lettuces, are two to four times higher than conventional farming. Many other urban crops studied are produced at similar or higher rates than in rural settings. Cost efficiency remains an open but important question.
Most studies on urban agriculture have focused on green spaces, such as private and community gardens, parks and field growing operations. Payen’s work includes “gray” spaces — places in cities that are already built but could be used for growing, such as rooftops and building facades. In both green and gray spaces, the study examines a suite of crops grown in soils versus hydroponics, horizontal versus vertical farming, and natural versus controlled conditions.
“Surprisingly, there were few differences between overall yields in indoor spaces and outdoor green spaces, but there were clear differences in the suitability of crop types to different gray spaces,” Payen says. Certain crops like lettuces, kale and broccoli are more naturally suited to be grown vertically in indoor spaces than others. “You can’t exactly stack up apple trees in a five- or ten-layer high growth chamber,” he says, “though we did find one study that managed to grow wheat stacked up like that.”
Other crops, like watery vegetables (e.g., tomatoes) and leafy greens, performed well in hydroponic environments. And crops grown in fully controlled environments can be grown throughout the year, allowing harvests to happen more times per year than in open-air environments, which leads to higher annual yields. But scientists will need to keep studying these systems to plan cost-effective agriculture solutions.
The finding that urban agriculture can have similar or greater yields to conventional agriculture “is exactly what we have been waiting for in the urban agriculture research community,” says Erica Dorr, an environmental scientist at AgroParisTech who was not involved in the study.
837 notes
·
View notes
Text
I started off in college as an education major wanting to be a middle school science teacher, but ended up quitting that because of how ableist the major was.
I switched to an agriculture degree because I grew up on a farm, and during 2020 I was constantly at home and convinced myself I could physically do the work, and I completed that degree despite the professors being ableist and morally questionable.
While I was an Ag major, I was working for the geology museum on campus, and decided to get my Masters degree in museum studies. During my studies, I realized how disabled people are constantly left out of deai discussions in the museum field, only ever seen as potential visitors and never potential workers, and so I finished my degree with independent research into how disabled staff are treated.
During my last semester in grad school, I started working as a substitute teacher and realized that my education major professors were wrong; I as a disabled person can totally be a teacher without a problem. My grad school advisor also told me that a lot of myself professionals go back and forth between the school system and museums. So I'm taking the leap to try to become a teacher
I just took my GACE (the Georgia certification test) and passed at a professional level! Once I am hired by a school, I will start taking the remainder of classes that I need to be considered a full fledged teacher
I've literally just made a circle, but the agriculture and museum studies degrees are still a huge help to me as a science educator. Other than space, agriculture perfectly set me up to understand everything required for students to learn and places me in a good spot to introduce an FFA chapter to the school, while my museum studies degree has allowed me to see education from a different perspective than my coworkers in order to more adequately come up with ideas in joint discussions. Additionally, I included disability and deai research in almost everything I did from work to school, and as a disabled person myself, I feel that my understanding of accessibility and empathy for other disabled people has prepared me more for interacting with disabled students in my classes.
Not a single bit of my journey was for naught, and I no longer feel ashamed or regretful towards my agriculture degree. I'm also excited to continue learning and eventually helping others to learn too
#education major#agriculture major#museum studies#museology#study blog#studyblr#ag major#life update#disabled students#disabled studyblr#disabled academia
294 notes
·
View notes
Text
Based on THIS ask
I don’t post on Tumblr often but I felt like getting this out - funnily enough all because of a likely joke response. Ah well. I’ll continue the tradition of making elaborate backstories based on minimal information 💪
Anyway, here’s some background to Jax’s life and upbringing. Call it a headcanon or AU or whatever you feel is best
The purple rabbit individual later known as "Jax" to the circusgoers was born between 1973 and 1982 in Wabash, Indiana, to a Lutheran Protestant family of five, of which he was the middle child of two other brothers whom he got along well with. The family took only a nominal approach to religion to their children in terms of traditions passed down, something that their mother and father would, on occasion, regret doing whenever their sons got into trouble. The small family farm was agricultural in nature, rather than focused on livestock, producing mainly corn as well as carrots and other assorted produce. Due to Wabash’s town-city setting making for easy profit to farmers markets and other retailers, the family were decently well off, as far as single farm households went.
The “corn incident” as it is aptly called, refers to an instance in which the family dog - a Doberman Pinscher named “Bruno” - developed rabies, unbeknownst to the family. Jax and his brothers (ages 15, 17, and 19) stumbled upon the canine after it had killed a stray cat past the fencing. Upon seeing that their beloved pet had gone rabid, the three bolted in different directions through the family cornfield. The dog alternated between the three, causing a warped ironic twist on the game of cat and mouse - in which Jax had to hide from the beloved family dog-turned rabid mongrel, attempting to stifle his breathing over the sound of his pounding heart. For him, few things would terrify him more afterwards.
Though their father was able to regrettably put the dog down with relative ease once his boys eventually scampered out of the vegetative maze, the feeling of helplessness in the thick underbrush of the cornstalks never truly left Jax. Perhaps he developed a fear of mazes, rather than corn; but he never did go back into the cornfield again, much to the teasing of his brothers and chagrin of his folks, who were from then on one pair of hands short on that chore.
#tadc#tadc headcanon#headcanon#farm#tadc jax#jax adopting a thousand mile stare whenever he sees a piece of corn#maybe i’ll write more about this au#or at least it might be an au#regardless if this picks up i mayy just write more tidbits of info about it if people like it#TADC lore#wasteverse
283 notes
·
View notes
Text
food & agriculture in fallout: extrapolation and speculative worldbuilding
Okay, well. This is going to be an extremely long and data heavy post. Bear with me.
I'm going to go into detail about the crops and available food given to us canonically and textually. I'm going to be drawing some real world parallels between the crops we see in Fallout and what we have here. I'll be pulling relevant data from all the games, but the majority focus on this post is going to be about the east coast and Massachusetts in particular because it gives us the opportunity to participate in the agricultural climate of the wasteland.
Is there a point to this? Not really, but I'm pedantic and I take things too seriously.
my sources will be linked in the text throughout. for those of you who want to read about agricultural and growing zones of the continental united states, please follow me under the cut.
Growing zones and real world agriculture
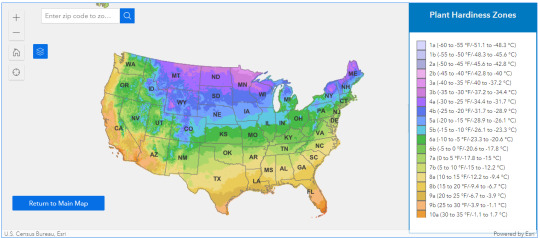
Shown here are the growing zones of the united states, divided into a temperature map of about 19 different regions. It's fairly intuitive to read -- colder temperatures are north and east, while warmer temperatures are south and west. The majority of the Mojave desert sits between 7a to 9a, a temperature range of about 20 degrees. DC and the nearby section of the southeast coast sits between 7a and 8a. The interactive map linked below will tell you where your growing zone sits.
The 2012 USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is the standard by which gardeners and growers can determine which plants are most likely to thrive at a location. The map is based on the average annual minimum winter temperature, divided into 10-degree F zones and further divided into 5-degree F half-zones.
For the moment, we are going to focus on Massachusetts.

Using the temperature above, we can see that the growing zone of Massachusetts is 5a (-20f) at it's very coldest, all the way to 7b, (5f) at it's warmest during winter. Most of what we see in fallout 5 sits in the 6a to 6b zone, which is middle ground during the winter, but cold enough to want to warrant crops that can withstand the frost.
There is a solid 5 month window for planting annual crops, like corn, melons, and gourds like pumpkin. Your perennial crops are limited to fruit trees and possibly grains, depending on the variety and whether or not a perennial variety has been bred.
Cold weather crops include beets, carrots, greens like cabbage, collards, kale, and potatoes. These aren't the types of crops that will survive the winter as much as these are foods that can go in the ground as soon as it is unfrozen enough to be workable. Root vegetables and greens can germinate in soil as cold as 40 degrees Fahrenheit, which provides some leeway with unpredictable frosts and late planting times.
Much of the agricultural landscape of Massachusetts is dependent on the dairy industry, farming cattle, and aquaculture -- fishing and catching shellfish. Those with access to the coasts, fish and shellfish ought to provide protein during lean months.
Why are we talking about this? Well, if we're stepping into the shoes of a subsistence farmer in the fallout universe, we're going to have to take into account climate and ideal planting times for certain crops. It's not wholly important in terms of things like fic writing, unless you happen to be writing about the life and times of wasteland agriculture, in which case, I hope this is helpful! Again, I am pedantic, and this section is to provide a template when considering and discussing other parts of the game and what their specific diet and agricultural landscapes might look like.
Something to keep in mind when thinking about how farms might function in the Mojave, for instance, or if you're doing worldbuilding for a different part of the US.
Crops in the fallout universe
Now that we're familiar with growing zones and why certain crops are planted and when, we're going to apply some speculative worldbuilding to fallout itself. We will be revisiting growing zones when we talk about other climates, but for the moment, we're going to focus on fallout 4.
Now to preface -- I don't think that the food that is given to us in game is wholly representative of the plants or animals that survived the apocalypse. If some managed to mutant and survive, I'm willing to bet others did. I certainly won't deduct any points from anyone who wants to talk about growing cotton, or farming peaches or cherries, and I won't raise any eyebrows if someone includes things like spices into their wasteland cuisine.
In the 210+ years since the bombs fell, I do not think that the majority of the US is a desolate wasteland, but this post is not going to be my beef with the devs about how brown everything is. This beef is about food in particular. However, for sake of ease, I'm mostly just going to focus on the food that is presented to us in game.
There will be some extrapolation and speculation later, but if I do that for everything, then we'll be here all day, and we've all got things to do.
I would also be remiss to mention that agriculture in the US is old. It predates colonialism. The Native Americans cultivated the land long before any European settlers. They practiced a type of crop growing referred to as Three Sisters planting, which utilized corn, pole beans, and squash -- all things that exist in the agricultural landscape of Fallout as we know it.
Corn
I'm not going to say much about corn because there's not a lot to say about it. We all know what corn is. Fallout's corn is visually similar to wild violet, a hybrid corn.

But I am not going to say Fallout's corn is one such variety or another. In the 210 years since the bombs dropped, I imagine corn varietals have been bred and interbred a thousand times, and it is probably it's own unique strain. It's kind of a moot point. Corn is corn. You can do with yellow corn what you can do with wild violet, and whatever special breeds that make up Fallout's corn.
Corn is the third largest plant-based food source in the world. Despite its importance as a major food in many parts of the world, corn is inferior to other cereals in nutritional value. Its protein is of poor quality, and it is deficient in niacin. Diets in which it predominates often result in pellagra (niacin-deficiency disease). Corn is high in dietary fibre and rich in antioxidants.
You can do a shit ton with corn. It's a staple grain. It would not be incongruous with the fallout setting to have settlers making tortillas, cornbread, polenta, grits, tamales, etc. Corn can also be used to make corn whiskey. The husks can be spun into yarn and woven into garments similar to cotton, which I thought was interesting and also solves the problem of where the hell wastelanders are getting their clothes. Corn can be used as livestock feed, especially in the winter when cattle can't graze. While corn is a staple grain of the US, the east coast has minor corn production compared to places like the midwest. Corn is a staple, but it does not consist of the entire diet of your average wastelander.
Carrots
Not going to say much about carrots either. They're carrots. They grow well in colder soil and tend to have a lot of natural sugars. The carrots we're shown in FO4 seem to be a mutated variety different than the "fresh carrot" consumable in FNV, but there's virtually no difference, so I'm not counting it. Make some carrot cake.
Razorgrain
"This species appears to be quite promising. It's a toothy grain that we may be able to grind in order to replace wheat, which is untenable in the Wasteland. We are uncertain how to increase crop yields, which are very unpredictable. Will continue to study."
Razorgrain is our first unique mutated crop in the fallout setting. It most closely resembles a barley or a rye. Both are a fairly hardy species and can grow all across the continental united states; rye can germinate in cold weather temperatures. It wouldn't be outrageous to assume that razorgrain is similar too or a crossbred variation of both rye and barley. I have decided to base the majority of my research assuming it is a barley variant. Barley is also a major crop on the east coast near the Commonwealth, so that would explain why razorgrain is present in FO4 and not in the other games.
Barley requires a mild winter climate and can grow in growing zones 3-8, so it would be viable in Massachusetts. Barley can be milled into flour and it contains gluten; the gluten content of North American wheat and barley tends to be higher to survive the colder climates, so razorgrain would likely be very glutenous. It is also less susceptible to ergot than rye, but barley can still become infected -- and, I am assuming, razorgrain could as well.
Razorgrain fills the nutritional niche of carbohydrates and can be used to make breads, cakes, pastas, etc. It produces darker breads that have an earthier flavor than milled white flour. There has to be some method of actually milling the grain, though, which is an intensive process that can often be dangerous. Grain can also be used to make malted candy, which is our first option for wastelanders with a sweet tooth. Obviously, razorgrain can also be used to make malt or grain alcohol and is probably the source of all the beer you find littered around the wasteland.
Gourds and melons
Gourds and melons are actually a part of the same family, Cucurbita. The category of 'gourd' covers several different kinds of vegetables, including ornamental fruits that shouldn't be eaten. We aren't going to spend a whole lot of time on this one, simply because canon doesn't tell us that much and there's a lot of wiggle room in terms of interpretation.

FO4's model looks the most similar to a pumpkin, but it could be some other squash varietal from the Cucurbita family, which includes watermelon, honey melon, cucumber, squash, zucchini and pumpkin.
Melons is another pretty broad category. Melons and squash are part of the same family, as mentioned above. If we're going visuals again, the model is likely intended to resemble a watermelon. Watermelons grow best in humid and semi-arid environments between 70 and 8- degrees Fahrenheit. It's not impossible for wastelanders to be growing watermelons, but considering the humidity and frequent rainfall in Massachusetts, the melons would be vulnerable to fungal infections.
There isn't a lot of information on what specifically gourds and melons are in the fallout universe, so you could get away with writing in a pretty wide variety. Personally, I lean a little bit towards melons being a muskmelon variety, like cantaloupe or honeydew. Squash fills in some vitamin requirements for the human diet, and can be canned and stored for winter. It tends to be high in vitamin C and magnesium.
The limit to this one seems to be your imagination. Go crazy.
Mutfruit
This wiki claims that the mutfruit (it has a scientific name apparently, malus maata) is a mutated species of apple and crabapple. There are two different wikis about the mutfruit, both distinct. The first is linked above. The second is linked here -- I got most of my information from this second wiki.
There is a handful of "canon" information we can take from this set of wikis.
Priscilla Penske in Vault 81 is attempting to create foods that have increased resistance to radiation. She mentions the mutfruit would do well, but isn't certain how the hybridization would affect the flavor and texture.[5]
This claim is taken directly from the second wiki, but in comparison, it makes no sense. If the mutfruit tree is a product of mutation, then radiation shouldn't really affect it at all. It's survived and propagated to this point, hasn't it? I am disregarding this claim on the basis of being stupid.
Farmers in at Warwick homestead will comment on the fruit's characteristics, such as tasting sweet and being versatile in recipes.[1][2]
The vault dwellers of Vault 81 trade for mutfruit with the outside world, and use it to make special occasion desserts such as pie.[6][7]
If the mutfruit is an apple variant, then it likely has a high sugar content, and it would have to be harvested in the peak of summer or in early fall.
There are fresh apples the be found across the wasteland, implying the existence of apple trees that have been unaffected by the bombs. Personally, I was assuming that the mutfruit was some kind of blackberry, given its appearance as a clustered fruit, or maybe even a type of plum. Regardless, the mutfruit is a fruit, which means that it would preserve well by being jarred or canned, has a high sugar content, and could likely be reduced to form sugar syrups. Like any fruit, it could be used to make alcohol.
Tatos
I want to stop myself from editorializing too much, but goddamn tatos. The crop that makes the least goddamn sense in the fallout universe. The bane of my existence. Let's get into it.
First off, we're given some pretty damning canon facts about tatos:
Tatos are a mutated hybrid of the cross-pollination of the tomato and potato plants.[1] The new consumable looks like a tomato on the outside, but the inside is brown.[2] Commonly cultivated in the Commonwealth, Appalachia and on the Island, its fruit is easy to grow and can keep one from starving, but their taste is described as "disgusting"[2][3][Non-game 1] and resembling "ketchup-flavored cardboard."[1]
According to some old botany texts we found, this appears to be combination of a now extinct plant called a "potato" and another extinct plant called a "tomato." The outside looks like a tomato, but the inside is brown. Tastes as absolutely disgusting as it looks, but will keep you from starving.
Note: This text was written from the perspective of someone who is unaware that both the tomato and the potato are being cultivated elsewhere. The writer also does not mention any sort of DNA test. However, the potato is also found in the Capital Wasteland, and the writer is a scribe in the Brotherhood of Steel, which originated from that area.
Both potatoes and tomatoes are from the nightshade family. They have the same nutrient requirements, and would compete for resources if planted separately but in the same soil. There is a method for planting them together where you splice a tomato stalk onto a potato root, but this is not the same as cross pollination and will not result in what fallout presents as a tato. What will happen is that the roots will grow potatoes and the fruit of the tomato will branch off the stems.
The potato itself is a stem tuber -- high in starch and calorically dense. A stem tuber is an offshoot of the parent plant that will grow beneath the soil as a type of asexual budding reproduction. We all know what a potato is. The tomato is a berry. It's the ovary of a flowering plant -- again, we all know what a tomato is.
I am going to give Fallout a little bit of grace and not comment on how mind bendingly stupid their description of a tato is. The outer skin is a tomato, but the inside is brown and starchy like the potato? I am not going to comment on how it makes little to no biological sense. The starchy tuber is starchy because it's an energy and nutrient storage device. The tomato is the enlarged ovary of a fruit. Why did those things, which are separately very good, combine into one very terrible thing? I don't know. It doesn't make sense. I don't really want to think about it. But these are the facts as they are given to us in game and I suppose I have to live with that. Obligatory "goddamn you todd howard. a pox on your house."
The tato is probably extremely calorically dense. It's specifically mentioned as being easy to grow and it is a better alternative to starving. It's probably grown as a staple crop throughout the planting season. I'm not entirely sure if the tato can produce glycoalkaloids like the potato does (that is, the green sections of the potato that can become poisonous when exposed to light) but if they can, and if stored improperly, it would negatively impact the health of whoever ate them.
I suppose since the taste is so offensive, tatos are better served as a carrier of some other type of food. Fried, mashed, baked -- the purpose of the tato is simply to get calories into your body. Starch can also be turned into alcohol, which I am going to need a lot of after reading the canonical facts of this stupid fucking plant.
Fallout: The Roleplaying Game Rulebook p.158: "A mutated hybrid of the pre-War tomato and potato plants, with the stem and reddish skin of the former and the brownish flesh of the latter. Tatos provide decent nutrition, but taste disgusting. However, they’re relatively easy to grow and thus are a staple of wasteland agriculture and is an ingredient in a variety of recipes."
fucker
"non farmable" crops
You can't cultivate these plants, but again - we're taking what's given to us and interpreting it extremely literally. There is no reason that these crops could not be domesticated and farmed.
Siltbean
Siltbean is likely a type of bushbean, rather than a pole bean. It's squat and low to the ground. Bush beans require little care or attention and you can pick them when you're ready to harvest them. Historically in North America, beans and corn were grown side by side (though those beans were pole beans using the stalks as support). Bush beans require successive plantings since harvests are early.
There's no good allegory for what type of bean this might be. The potato bean (Apios americana) is native to North America and also produces edible tubers, but there's no reason this couldn't be just some other type of bean. No beans that I could find had red/orange pods.

Beans are a good source of both proteins and carbohydrates, and another crop that can store well for the winter.
Tarberry
Tarberry is a little iffy, considering it is farmed by the ghouls at The Slog, but they're the only farm shown capable (or willing?) to farm the berries. Originally, I had assumed that tarberries were a type of mutated cranberry, and I thought the wiki was supporting me in that claim by saying this:
Tarberries are small, dusty orange berries of the tarberry plant. It is a water-grown crop similar to cranberries.
But cranberries themselves are also canon in the world of Fallout. So who knows! There's no canon information presented on the tarberry's characteristics, so it can be treated the same as any other fruit or berry.
Fungus variants
Glowing fungus: Glowing fungus is one of the few real world equivalents we have. It is a Japanese mushroom called Enoki. It is also farmable as shown in FNV at Hell's Motel.

Brain fungus: This is harvestable, but there aren't any "crops" shown as we would consider them. Considering it's benefits as a mentat replacement, then it's likely that there could be a dedicated space for growing it.
Food and Plants mentioned in the text
Potato
Thank god almighty, potatoes are canon in the universe of Fallout. Fresh potatoes are found as consumables in FO3 and FNV but potatoes are also mentioned in the text of FO4:
Mentioned in dialogue -- {Angry} Shut up Jake. If I hear anything out of either of you, you'll both be peeling potatoes for the next year.
I'm taking this as word of god. Potatoes are canon and I don't care what anyone says.
Tomato
Tomatoes are mentioned in the text, but are never actually seen in game. The only hint that this plant survived extinction is this excerpt from the wiki.
Note: As fresh tomatoes and potatoes are seen in the Mojave Wasteland as of 2281, with the potato seen in the Capital Wasteland as of 2277, the claim of either's extinction by 2287 in the Commonwealth Plant Database could be taken to mean local extinction in east coast regions, as opposed to global extinction. This entry may also just be in error.
There's potential for leeway here, but take it as you will!
Fresh apple
We discussed this back up in the mutfruit section of the essay, but the existence of fresh apples implies the existence of non mutated apple trees. They're found in both FO3 and FNV as a consumable item, so the apple tress have either proliferated across the continental united states, or multiple varieties survived the bombs.
Fresh pear
See above. Pears are also naturally high in pectin, which makes them useful for making jams and preserves.
Pinto beans
Pinto beans are a consumable in FNV and is another W in the bean category of the agricultural landscape.
Jalepeno
Look, I'm picking out this one specifically because I need to believe that other spices and peppers exist in the world. Where would we be without her? Nowhere good.
Raw sap
I am going to say that sap collecting is probably where most of the sugars and sweeteners in the wasteland come from. It's relatively easy to tap trees and collect sap, and it only takes a few hours to reduce the sap down into useable syrup.
Wild Blackberry, Lime, Cranberries, as well as Watermelon as being distinct from simply 'melon' are all mentioned in the text. The list of fruits mentioned or found in the games can be found here.
Animal husbandry
Fallout doesn't give us a lot of canonical information on the animal side of farming. The biggest real world agricultural export of Massachusetts is dairy and cattle farming. Chickens are canon in the worldbuilding of fallout as of Far Harbor, but canon feels both restrictive and extremely loose with regards to what animals can be cared for and how.
We aren't going to spend a whole lot of time on this one, only because the information is pretty limited.
Brahmin
There are plenty of brahmin found throughout the landscape of the wasteland. We most commonly see them as either livestock or beasts of burden. Things like milk, cheese, and other dairy products would be common if a farm has access to dairy cows. The investment to raise cows would be enormous for a subsistence farmer. Dairy cows would likely be kept for a number of years, where steers would be raised 12 to 24 months before being slaughtered; they'd likely be grass fed in the summer and corn or grain fed in the winter. Leather and beef would be products, of course, and things like soap and candles can be made from the beef tallow.
Chickens
Chickens are largely easy to keep and care for, producing eggs and necessary proteins. Chickens can provide niacin, filling in the nutritional gap that would be left by a heavy corn based diet. The investment for keeping chickens is lower than raising brahmin, but so is the payoff.
Bighorners
Bighorners are mutated bighorn sheep native to the American Southwest.[1] Humans have since domesticated them for their horns, meat, milk, and hides,[2][3]
Granted, bighorners are only seen in FNV, but I don't think there's any reason they couldn't have migrated east. In the text, it says they're kept for meat and milk, but there's no reason that they shouldn't provide a fleece as well. In the colder climate of Massachusetts, they would find value in wool, which can keep its warmth even when wet. They may be sparse across the commonwealth, but that would make wool and fleece all that much more valuable.
Fish
Yeah, I know. Technically we can't fish in Fallout (and depending on the game you play, you might not even know what a fish is). But aquaculture is huge in Boston, and with access to the coasts, it's completely fair to say that fish, shellfish, and hydroponics is a completely viable source of food in the wasteland. We see dead fish washed up on shore all the time, along with whatever the hell those shark things are. There should be fisheries and fishing towns all along the coasts.
New Vegas and Fallout 3
Consulting our growing zone chart, we can see that much of the southwest sits between 7b to 8b. The winters in the southwest are fairly mild, and while you can get seeds in the ground sooner, the majority of the battle is going to be finding a reliable water source.
The farming we see in New Vegas has one distinct notable inclusion: the NCR sharecropper farm.
The sharecroppers are growing a number of crops, including maize, tobacco, pinto beans, and honey mesquite. Corn can handle hot, arid weather, it's just not commercially grown out west. Barley can also handle hot, arid climates, and razorgrain would be suitable for the western front -- maybe we can assume it's made it's way that far west and is being cultivated alongside corn.
Most of the plants we see in FNV aren't the type we would see typically domesticated for agricultural use, but that doesn't mean people haven't adapted to their surroundings. It makes a lot of sense for locals to have domesticated local plants like prickly pear and banana yucca. There are a number of fresh produce items to be found as consumables, alongside local fruits the local fruits.
Heat-loving plants are best suited for summer production in desert climates. The plant families that fit into the heat-loving category are nightshade or Solanaceae (tomatoes, peppers, eggplant) and squash or Cucurbitaceae (cucumbers, melons, summer and winter squash). Corn and beans also perform best in hot climates.
Most plants CAN handle the heat and climate of the southwest, the issue is just finding a reliable source of water. Somewhere close to Lake Mead or the banks of the Virgin River would be prime real estate for farming, since irrigation could be accomplished without the use of pumps, like the sharecroppers use.
If we look back at the history of agriculture, it's developed along established waterways in almost every ancient civilization because that's what's easiest. There should be thriving communities surrounding the lakes and rivers in the southwest.
Comparatively, DC was formerly a swamp. It's hot and humid in the summer, though the winters are fairly mild. It wouldn't be a stretch to say that farming practices in the Commonwealth don't differ all that much from farming in the Capital Wasteland -- you could even posit that food from the Capital is of better quality ever since the successful activation of Project Purity. Fresh and unirradiated food was growing there before, so it's entirely likely that even more is growing now. YMMV!
Other consumables
We would be here all damn day if I did research onto every single consumable item available across all three games, so this mostly just because I'm covering my bases.
I am going to say that sap collecting is probably where most of the sugars and sweeteners in the wasteland come from. It's relatively easy to tap trees and collect sap, and it only takes a few hours to reduce the sap down into useable syrup.
Look, I'm picking out this one specifically because I need to believe that other spices and peppers exist in the world. Where would we be without her? Nowhere good.
Pre War food
Most shelf-stable foods are safe indefinitely. In fact, canned goods will last for years, as long as the can itself is in good condition (no rust, dents, or swelling). Packaged foods (cereal, pasta, cookies) will be safe past the ‘best by’ date, although they may eventually become stale or develop an off flavor.
The risk with improperly canned good, or damaged canned goods, is botulism. Botulism will straight up kill you. You don't even have to consume that much of it; just a little bit will leave you dead in days. As desperate as I might be for a meal, I'm not going to risk dying because that can of two hundred year old peaches looks really tasty.
If properly sealed and in a dry, ideal environment, I... guess things like cereal and instant food could be okay? But again, with access to fresh grain, sugars, and yes, even potatoes and pasta, why would you want to risk eating InstaMash that's been around since before your great grandmother.
Pre War drinks
Sigh. Okay.
Unless stored extremely, extremely well, most bottled drinks aren't going to last much longer than 9 months. A year, if you're lucky. Exposure to sunlight and improper storage will break down the contents -- the best bottles are brown, then green. Clear glass is the worst because it does nothing to protect the liquid inside.
All the Nuka Cola you find throughout the world is flat, nasty, and will probably make you sick. I don't think that really needs to be pointed out, but there we go. I suppose the soda could probably be reduced to form sugar syrups, but with access to sap syrup and grain malt, I'm not sure why you would be desperate enough to do that.
So what does food look like in Fallout?
If there's one thing I know about humans, it's that humans like to eat. Food is culture, as much as culture and community is built around food. Good food and access to it is paramount to human happiness. All this to say is that food in fallout is whatever you want it to look like.
I can extrapolate and theorize all day long based on what Fallout tells us definitively, but I'm not going to tell you what the culinary landscape in the wasteland looks like. The only point that I will stress is that humans are really, really good at making things appetizing.
The fandom is already so creative when it comes to developing their idea of what food means in the wasteland. It's what's directly inspired me to write up this stupid, long ass post about farming and agriculture.
Obviously this is not a comprehensive list of all the base ingredients you can find in Fallout. I picked the ones I did because of the potential for consistent farming. Wastelanders have had two centuries to develop agricultural practices based around subsistence farming. I am not a subsistence farmer, and I have no idea how wasteland cottagecore would work at the heart of it. Running a farm is extremely labor intensive, and so much of your investment has to be immediately recouped in the form of eating what you harvest.
What a farm is likely to look like will start in the early spring when the ground begins to thaw, and a farmer can plant his cold resistant crops, like green vegetables and razorgrain. Potatos, carrots, and tatos will also weather the spring chill. When it starts to warm up, the more delicate plants like corn, beans, and squash or melons will get planted and tended to.
If your family is lucky enough to have a greenhouse, you can keep crops growing all through the winter and have a surplus for trade and barter, or just to preserve and refill the pantries.
A lot of the investment will have to be immediately recouped. Eggs from the chickens can't be preserved, obviously, but there will be meat from hunted animals, milk from the brahmin, probably an early harvest from the beans and tatos, and whatever else is in the pantry from the previous harvest.
Some of it will be canned or preserved in the forms of jams or jellies (just remember what I said about botulism). Meat from animals that get hunted can be smoked or otherwise preserved. Grain can be milled into flour or eaten whole and unshelled. Even the corn silk can be woven into clothes for the summer.
There really is no limit to what can be done in the end. While a lot of this information was taken from what we're given in the text, there's no rule that says you have to follow it word for word. If you believe something exists out there, then write it! We're all just making shit up as we go along anyway. If you need permission, then here it is. You can do whatever you want. Make up recipes! Go insane. Follow whatever your little foodie heart desires.

#fallout#kal talks#fallout 4#fallout new vegas#fnv#fallout 3#fallout meta#fallout food#fallout headcanons#behold. the agricultural masterpost of my farming headcanons#here she is
765 notes
·
View notes
Text
One of the things I think about a lot is productivity comparisons between conventional and unconventional agriculture. Mostly because that's the first question you get asked when you talk about anything that's outside the norm*, but, on what metric are we measuring? Per acre? Per hour worked? Per cost of input? Are we measuring yields of product or dollars earned?
This question also, to me, rings of fear. Fear of food shortages, which are really a problem of greed & distribution, not the world's capacity to grow food. If we were really worried about calories though, I think we'd at least switch to pastured animals instead of sending so much corn and soy to livestock (for any non-farmers out there, you do not get nearly the calories out of a chicken or pig that you put in- you get much less**). Or we would put more effort into making cities great places to live so we stopped turning farmland into suburbia. Or we would be much more concerned with how to prevent erosion & loss of arable land. But we don't, and we're not.
I also think of the complexity of non- conventional farming, and how instead of it being a return to the past, it actually relies on new information and methods***.
Take the plot of land that I'm working to make into a market garden. It's soil is, from a farmer's perspective, crap. It's gravely, sandy, very little organic matter. If I were to farm it conventionally, I'd basically have till to open the soil and kill weeds, and then provide all of the plant nutrients through fertilizers, which would cause the plants to kick out their symbiotic fungi, leaving them vulnerable to pathogenic fungi, and more dependant on me for water. There would also be bare soil everywhere, increasing evaporation & providing plenty of opportunities for new weeds. My costs would be very high, paying for fertilizers, pesticides, & herbicides, and I would have to water, a lot. It probably wouldn't be at all economically feasible to grow food on this plot using conventional methods.
Now, I look at it and say, I'm going to do no-till. I look at the hard, weedy, depleted soil and there's no way a seed is going to be able to come up through that. But, I'm not just doing no-till, because I'm not looking at it from a conventional mindset and just trading out one practice. I'm doing basically everything different from above.
Instead of tilling, I'm laying down a thick layer of mulch, to shade out the weeds, increase soil organic matter (increasing the amount of water and nutrients the soil can absorb & good on to), and feed the soil ecosystem. By the time spring rolls around, the soil underneath will be much better, but I'll still add more compost in most cases.
Instead of fertilizers I've had to pay for, I'm using mulches that I got for free from my gardening work & composts made for free from restaurant kitchen wastes****. I'm going to use over crops, plants that fix nitrogen and also serve as perennial hosts to beneficial soil fungi, which will also form symbiosis with most of my crops, increasing their resistance to pathogenic fungi while also providing them with increased access to water and soil minerals.
Instead of bare soil, there will be mulches and cover crops every where. Instead of monocrops & pesticides, I'll be intercropping which will help by hosting beneficial native insects that will chow down on aphids and other crop pests.
From this framework, there's an upfront investment of effort and planning, but farming this land now seems feasible.
And the thing is, each of those choices is backed up by research. We know so much more now about soil and nutrient cycling and how it actually works than when conventional ag really got started. We know so much more, and so many practices are new, so growing non-conventionally isn't a step back into the past of how things were grown.
But at the same time, it's not exactly completely information either- other cultures have different ways of growing food crops, and if you broaden your concept of what cultivating plants looks like, there's examples everywhere. We're just studying it now and providing it scientifically.
*and I honestly think that it's a result of the extractive mindframe that comes from being the decendants of colonizers. Just look at the different perspectives between many western foragers ideas and Indigenous peoples' relationship with the land.
** chickens are one of the most efficient, with a feed conversion ratio of 1.6, which means for every 1.6 pounds of food you give them, you can expect the chicken to gain 1 pound (cows are over 4 pounds of feed to pound of live weight, and pigs are 3 to 4ish). That's the whole bird though, counting all the parts we don't eat- guts, feathers, bones, etc. Even so, a pound of chicken food has over 1300 calories, and is about 20% protein for starter/grower, where as a pound of chicken has about 500 calories and about 30% protein (for dark meat, you get fewer calories from white meat). I'm not saying everyone should give up meat, but I am saying that the amount of meat in mainstream diets has increased dramatically, much of it comes from cafos where animals are fed on grains & legumes, and if we're measuring productivity and yield per acre because we're worried about feeding the world, this is a huge factor. Look up how much of the corn & soy crop goes to actually directly feeding people.
*** from a western, colonizing prospective
**** is this a particular boon from my particular circumstances? Yes. But everyone has their own challenges and resources, there is no cookie-cutter solution to all agriculture, everywhere. You have to find the solutions that work for you.
784 notes
·
View notes
Note
This period may be out of your pay grade, but do you happen to know anything about what was going on in Lower Egypt during the Protodynastic Period? There's a fair bit on the main 3 city-states in Upper Egypt, but for the north we have virtually just a handful of names on jugs from Tura and a list of names from the Palermo Stone. Why is Lower Egypt during this period so quiet or enigmatic?
I can't tell you because we don't really know. It's so long ago now that what evidence we do have for it is either in our hands or still below the sands. However, I wouldn't categorise it as either quiet nor enigmatic. It was very likely neither.
What we have here is survivorship bias within the archaeological record. Since Narmer, and to an extent Upper Egypt, won the battles between early Normarchs to unite both halves of Egypt and bring them under one ruler, it is really no surprise that information pertaining to them has survived better than those who perished. The historical record, as we all know, favours the victor when it comes to being recorded in history. We know of Narmer and those cities in Upper Egypt because he won, and therefore the historical record favours them. Lower Egypt, in contrast, well it's rulers lost the battle and more than likely the information on them was destroyed or lost when the country was unified. It wasn't exactly on people's minds to record the names of defeated rulers.
The other element is location. Lower Egypt is the Nile Delta region, an area with a different landscape to that of Upper Egypt. It's wet, it's heavily farmed, and it's occupied by modern Egyptians. This affects things like preservation of organics (more likely to rot in damp conditions), items are destroyed through agriculture, and the continuous settlement of Egyptians in the area means that any information on protodynastic Lower Egypt is likely buried beneath the modern day towns and villages that exist in those areas. This means we cannot access the archaeological record beneath, nor should we unless there is significant cause to do so (see: Pi Ramesses). Of course, we have sites like Memphis and Saqqara which are likely ones that flourished from Protodynastic activity, but these sites were in use for a long time and any excavation is a) going to have to get through the many layers of history before that level was reached (if anything still exists), and b) those sites are not the most hospitable to excavation at times. (wouldn't recommend digging in a sandstorm). Compare this to Upper Egypt, where many of the sites were in drier, less occupied areas, and were continually used by the Egyptians for millennia and you might see why we still know of these sites today.
So, they're not quiet or enigmatic, we just simply don't have the archaeological evidence to say very much about it because it hasn't survived in any meaningful manner thus far for a variety of external factors.
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
Many people, especially USAmericans, are very resistant to knowing the plants and living according to the ways of the plants. They lash out with a mix of arrogance and fear: "Don't you know what bad things would happen if we lived a different way? There is a REASON for living this way. Would you have us go Back—backward to the time without vaccines or antibiotics????"
Ah, yes, the two immutable categories that all proposals for change fit into: Backward Change and Forward Change! Either we must invent a a futuristic, entirely new solution with SCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY that further industrializes and increases the productivity of our world, or we must give up vaccines and antibiotics and become starving illiterate medieval peasants.
Every human practice anywhere on Earth that has declined, stopped, or become displaced by another practice, was clearly objectively worse than whatever replaced it. You see, the only possible reason a way of life could decline or disappear is that it sucked and had it coming anyway!!! Pre-industrial human history is worthless except as a cautionary tale about how miserable we would all be without *checks notes* factories, fossil fuels and colonialism. Obviously!
Anyway, who do you think benefits from the idea that pesticide-dependent, corporate-controlled industrialized monoculture farming liberates us all from spending our short, painful lives as filthy, miserable peasants toiling in the fields?
First of all, I think it's silly to act like farming is a uniquely awful way to live. I can't believe I have to say this, but the awful part of being a medieval peasant was the oppression and poverty, not the fact that harvesting wheat is a lot of work and cows are stinky. Same goes for farm labor in the modern USA: the bad part is that most people working farms are undocumented migrant workers that are getting treated like garbage and who can't complain about it because their boss will rat them out to ICE.
Work is just work. Any work has dignity when the people doing it are paid properly and not being abused. Abuse and human trafficking is rampant in agriculture, but industrialization and consolidation of small farms into gigantic corporate owned farms sure as hell isn't making it better.
Is working on a farm somehow more miserable than working in a factory, a fast food restaurant, or a retail store? Give me a break. "At least I'm not doing physical labor in the sun," you say, at your job where you're forced to stand on concrete for 8 hours and develop chronic pain by age 24.
When you read about small farmers going out of business because of huge corporations, none of them are going "Yay! Now that Giant Corporation has swallowed up all the farms in the area, we can all enjoy the luxurious privileges of the industrial era, like working RETAIL!" What you do see a lot of is farmers bitterly grieving the loss of their way of life.
And also, the fact is, sustainable forms of polyculture farming that create a functional ecosystem made up of many different useful and edible plants are actually way MORE efficient at producing food than a monoculture. The reason we don't do it as much, is that it can't be industrialized where everything is harvested with machines.
Some places folks are starting to get the idea and planting two crops together in alternating rows, letting the mutualistic relationship between plants boost the yields of both, but indigenous people in many parts of the world have been doing this stuff basically forever. I read about a style of agroforestry from Central America that has TWENTY crops all together on the same field.
Our modern system of farming is necessary for feeding the world? Bullshit! Our technology is very powerful and useful, but our harmful monocultures, dangerous pesticides, and wasteful usage of land and resources are making the system very inefficient and severely degrading nature's ability to provide for us.
What is needed, is a SYNTHESIS of the power and insights of technology and science, with the ancient wisdom and knowledge gained by closely and carefully observing Nature. We do not need to reject one, to embrace the other! They should be friends!
Our system thinks land is only used for one thing at a time. Even our science often thinks this way. A corn field has the purpose of producing corn, and no other purpose, so all other plants in the corn must be killed, and it must be a monoculture of only corn.
But this means that the symbiosis between different plants that help each other is destroyed, so we must pollute the earth with fertilizers that wash into bodies of water and cause eutrophication, where algae explode in number and turn the water to green goo. Nature always has variety and diversity with many plants sharing the same space. It supports much more animal life (we are animals!) this way. The Three Sisters" are the perfect example of mutualism between plants being used in an agricultural environment. The planting of corn, beans, and squash together has been traditionally used clear across the North American continent.
And in North America, the weeds we have here are mostly edible plants too. Some of them were even domesticated themselves! Imagine a garden where every weed that pops up is also an edible or otherwise useful crop, and therefore a welcomed friend! So when weeds like Amaranth and Sunflower pop up in your field, that should not be a cause for alarm, but rather the system of symbiosis working as it should.
A field of one single crop is limited in how much it can produce, because one crop fits into a single niche in what should be a whole ecosystem, and worse, it requires artificial inputs to make up for what the rest of the plant community would normally provide. The field with twenty crops does not produce the same amount as the monoculture field divided in twenty ways, but instead produces much more while being a habitat for wild animals, because each plant has its own niche.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Hello darlings! 🏜️
Now that we are well and truly into the 1930s I wanted to give y’all some context about the Darlingtons’ new location. Ultimately, Strangerville is a figment of my imagination, a sims world superimposed into the real world. I did this because I wanted the freedom to draw from different elements of this region’s history and landscape without having to worry about the visual transformation of the actual in-game world.
However, it is very much intended to in a real region of the United States. Specifically, the north west corner of New Mexico, between Albuquerque and Gallup along the newly built Route 66. We’ll see key elements of this in the story time and time again, so if anyone would like more information I’ll leave some maps and context for y’all below the cut:

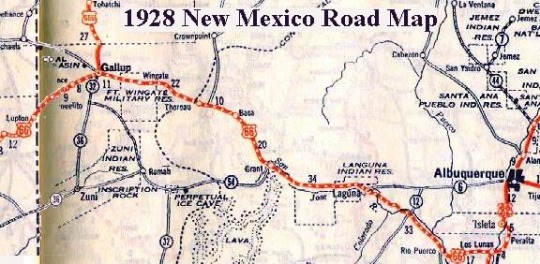
Commissioned in 1926, Route 66 was actually not the first cross country highway system in the U.S.; however it was designed to traverse the flattest and mildest climates so that it could be the most easily traveled. It also followed popular tourist routes from the railroad days and was marketed as an “All American” experience, drawing travelers and families from across the country and leading to its iconic status even today. The first map shows its path as it would have been in 1930, from its start in Chicago to its end in L.A. and the second map is a cutaway of the specific section of the road between Albuquerque and Gallup where Strangerville is meant to be located.
While the cultural significance of Route 66 now perhaps outweighs its era of utility, the Darlingtons are living along the route as it rises to prominence throughout the 1930s into the 1950s. While it was used for utility and leisure travel from its opening, Route 66, particularly between the Dust Bowl states and California, is iconic for its role as “the Mother Route. Perhaps best typified in John Steinbeck’s Grapes of Wrath, this road became one of if not the primary route for people fleeing the plains states during the Dust Bowl. Through their passage it became an American symbol of desperation, poverty, and for some, the hope of a better life.
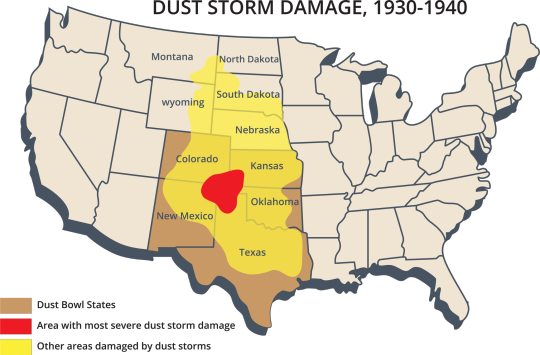
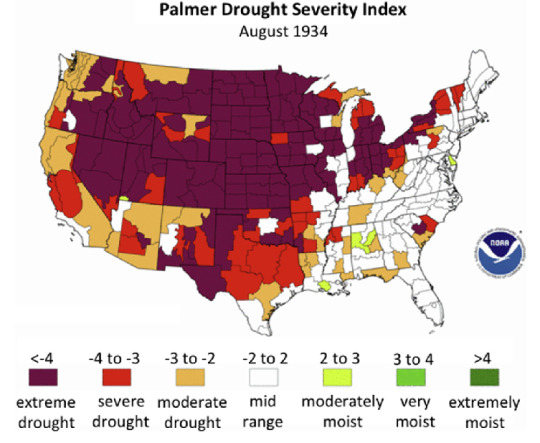
Strangerville is meant to be located at the edge of the Dust Bowl (specifically at the meeting of the brown and yellow zones in the first map toward the leftmost mid-top area of the state of New Mexico). This region would not have suffered the worst conditions (and would have been spared intense dust storms) but it is still close enough to be heavily effected. This is especially true in the early part of the decade, as fear of dust tornados and mass unemployment spreads like wildfire, and explains the intense volatility amongst Strangerville residents who have no way to know just how bad their own situation could get.
For larger context, the Dust Bowl was caused by extenuating weather conditions and poor farming practices. It was an agricultural catastrophe throughout the 1930s that displaced millions of people, and coupled with larger economic factors such as the plummet of crop prices, led to mass homelessness, unemployment, and starvation.
Beginning in 1930 but reaching its zenith in the years 1934 and 1936, vast swaths of the United States experienced record drought and heat. In the second map we can see how widespread drought conditions were. They are of course at their worst in the central Dust Bowl area; however we also see that Strangerville is located in a moderate drought, and in 1936 twelve states recorded their highest temperatures to date.
However, these weather conditions only highlighted underlying farming negligence. After decades of manifest destiny and an influx of settlers with little to no farming knowledge (of which Giorgio falls in line), the land had been woefully over plowed and deprived of nutrients. After the rising farm prices of the 1910s and 1920s met with the crash of 1929, settlers pushed this to an extreme, removing vast swathes of native grasslands and leaving the soil vulnerable to record breaking weather conditions. Without rain or prairie grass, winds ravaged the region, creating dust storms that ravaged the region and ultimately led to hundreds of thousands of abandoned farmland. This collection of photographs shows the scale of dust and desolation better than words can express.
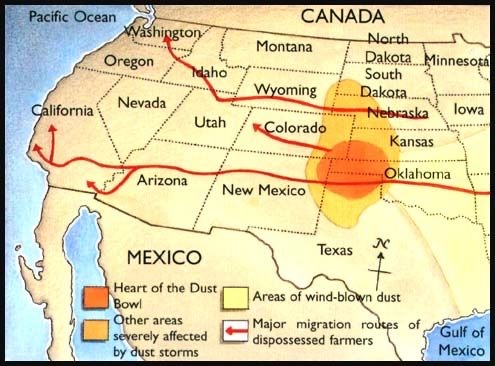

Scholars estimate that somewhere between 2.5 to 3 million people left their homes in the Dust Bowl states. Their stories are notorious, and live in the consciousness of what we now conceptualize as 1930s America. These maps superimpose the path of Route 66 with the Dust Bowl states, highlighting how the two formed a symbiotic relationship and became linked in the American consciousness. Of the millions who fled their homes, approximately 300,000-400,000 eventually settled in California. The number who traversed the mother route looking for work with the hope of a better life is perhaps incalculable.
However, they did not initially receive a warm welcome. As much of the country was also gripped in fear and poverty, migrants, or Okies as they were derogatorily called, were viewed as pariahs, threats, and even harbingers of worse times to come. This, as we now know, is far from the truth. The economy of many small towns along Route 66 fared better than other areas of the Dust Bowl. They became hubs for migrants and businesses alike as gas stations, roadside accommodations, food stalls, and other amenities opened. It provided an alternate means of business for areas that has previously been very rural, and who’s own farms had been gouged by the plummeting crop prices of 1929 as well as the gradual disappearance of herding economies.
As the decade went on and much of the nation began to heal in the New Deal Era, the migrants who passed this stretch of road only made it more legendary. Where they eventually settled they brought stories of Route 66, of a symbolic idea of the American West, of an ocean at the end of the line, of different people and travelers they had met on the way. This coupled with a growing fascination of the “Okie” figure at the end of the decade, perhaps best seen in the celebrated 1940 Hollywood remake of The Grapes of Wrath, as an emblem of American hardship and drive.
Together they fused an iconic idea of an authentic “Americanness” that existed along Route 66, one that was infused with even older ideas of manifest destiny and the “American” cowboy. This is the landscape that the Darlingtons now inhabit, one that they are watching unfold along with us all at the very start of the 1930s.
#sims 4 historical#ts4 decades challenge#ts4 historical#sims 4 decades challenge#the darlingtons#sims 4 legacy#ts4 legacy#sims 4 story#ts4 story#1930s
81 notes
·
View notes
Text
Scientists have uncovered the Amazon’s earliest and largest example of farm-based city-like settlements high in the foothills of the Ecuadorian Andes.
The thousands of mounds, plazas, terraces, roads and agricultural fields — revealed for the first time in their fullest extent by airborne laser scans — necessitate a rethinking of just how complex ancient civilizations of the Amazon may have been, researchers report in the Jan. 12 Science.
Over the last decade or so, the use of light detection and ranging, or lidar, in archaeology has led to significant discoveries in tropical climates, where ancient settlements often lay obscured beneath dense jungle (SN: 12/4/23). In 2018, researchers released scans of remnants of Mayan settlements in Guatemala, followed by Olmec ruins in Mexico in 2021 and Casarabe sites in the Bolivian Amazon in 2022, all which have been revealed to be metropolitan-like settlements filled with complex infrastructure (SN: 9/27/18; SN: 1/6/23; SN: 5/25/22).
“It’s a gold rush scenario, especially for the Americas and the Amazon,” says Christopher Fisher, an archaeologist at Colorado State University in Fort Collins who has scanned sites throughout the Americas but was not involved in the new research. “Scientists are demonstrating conclusively that there were a lot more people in these areas, and that they significantly modified the landscape,” he says. “This is a paradigm shift in our thinking about how extensively people occupied these areas.”
[...]
Beneath the tree canopy was a massive network of roughly 6,000 mounds — once homes and community spaces — clustered into 15 settlements and connected by an intricate road system. The lidar data also revealed that the open spaces between settlements were in fact agricultural fields that had been drained to grow crops such as maize, beans, sweet potatoes and yucca. Within the settlements, the researchers found tiered gardens that would have kept some food closer at hand.
Put together, the results show that the valley wasn’t simply a series of small villages linked by roads, but “an entirely human-engineered landscape” built by skilled urban planners, Rostain says. Dating from several sites suggests the area was inhabited for roughly 2,000 years beginning around 500 B.C. by at least five different cultural groups. A next step will be to calculate how many people might have lived there.
187 notes
·
View notes
Text
HRH Princess Anne talks about her new Rustler 44 yacht and love of sailing in Scotland
Article from Yachting World, published 4th December 2014

Elaine Bunting asks Royal Princess Anne and her husband Vice Admiral Sir Tim Laurence which are their favourite Scottish cruising grounds when they sail their Rustler 44 Ballochbuie.
Scotland is no easy cruising ground. The weather can change quickly. Reaching the more distant islands requires a certain toughness as well as skill, especially if sailing double-handed, as The Princess Royal Princess Anne and her husband Vice Admiral Sir Tim Laurence usually do aboard their new Rustler 44 Ballochbuie. This is ‘black run’ cruising.
Their favourite places are the more remote islands and anchorages. “To be honest, if we get north of Ardnamurchan it suddenly feels different, and if you go north of Skye other boats almost disappear, and although there are some based up at Ullapool and Stornoway, they are rare,” says Princess Anne.
Asked about some of the places they like to visit, they first mention the island of Coll. “We’ve got some friends who live there,” says Sir Tim, adding: “though is not the most hospitable and the anchorages there are a little bit variable.”
“But it is pretty impressive at certain times of the year,” adds Princess Anne, “particularly up at the northern end, the Cairns of Coll. The northern end is rocky and the southern end is a bit more agricultural and there are lots of geese in the winter. Actually, winter is probably more entertaining – you get snipe and woodcock as well.”
At the mention of anchorages, Sir Tim gets up and goes below to Ballochbuie’s navigation table to retrieve a document that runs to several pages of A4 paper. This is a list of all the places he and Princess Anne have been to during their years of sailing the two Rustlers.
It is a very impressive and comprehensive list stretching from Rathlin Island off the north coast of Northern Ireland as far north as Cape Wrath at the north-western tip of Scotland. The scores of anchorages are carefully listed and account for some challenging pilotage and difficult nooks and crannies. But they seem to enjoy exploring new – and preferably out of the way – spots.
“We haven’t kept a record of how many miles we’ve sailed, but we have kept a record of the anchorages,” says Sir Tim, to which the Princess adds: “Every trip we added one anchorage we hadn’t been to before, at least, and usually two or three. Even if you are going over the same ground there are still places to be found, though fish farms are a bit of a menace. There are places we used to anchor in Bloodhound that you can’t get to now.”
The wildlife and sea life are something they both mention. “We see quite a lot of basking sharks, particularly between Coll and Tiree,” says Princess Anne. “Once I lost count at about 25. That was extraordinary.”
Princess Anne recalls: “We had a rough three days on the way from the Sound of Harris down to Lochboisdale [on South Uist] and saw a big pod of dolphins, which was just extraordinary. They were coming at you from the top of the waves. They didn’t quite jump over the top of the boat, but they looked like they were going to.”
Royal favourites
Lewis: the lochs on the east side are great. There are quite a few places to anchor in Loch Roag.
Shiant Islands: we’ve been there a couple of times in Blue Doublet and a couple of times on [the cruise ship] Hebridean Princess with The Queen.

Loch Ewe: we had an interesting time in fog as thick as I’ve ever known it. There is a wonderful garden to see here as well.
Hermitray: there are some nice anchorages in the Sound of Harris, but lots of fish farms around.

Rona: a favourite spot. One of the most sheltered anchorages on the west coast. A very nice man, Bill Cowie, is the warden.
Skye: we’ve been all round Skye. There are lots more places to visit. We’ve only been to 12 anchorages there!

Eriskay: there’s a fantastic little anchorage here. We went there for the first time in Ballochbuie.
Barra: a marvellous place and a wonderful escape from the world.

Vatersay: good shelter in the lee of a sandbar. We anchored near Vatersay in company with Britannia one year.
Canna, Rum, Eigg and Muck: we enjoy visiting all these islands.

Loch Nevis and Loch Awe: both are lovely places.
Loch Moidart: beautiful, but we’ve only been there once. It has quite a scary entrance, not easy in a long-keel boat and you’re always battling the wind to get out.

Mull: Loch Mingary, Bunessan, the Bull Hole and Ardlanish. A beautiful little spot with shelter on the south side of the Ross of Mull. Carsaig is a little notch you wouldn’t think you could get into or get any shelter at all, but there’s a little reef offshore you can tuck behind.
Lismore: the island in Loch Linnhe. Walking there you get the most beautiful views and you can see as far as Ben Nevis.

Loch Feochan: there is a little place right at the entrance that is great.
Garvellach Islands: lovely, but weather- dependent so it has to be very calm.

Loch Craignish: Goat Island is one of the safest anchorages on the west coast of Scotland, as long as you are able to wash off your anchor; it has the stickiest mud.
Jura: we have visited anchorages all round the coast.
Rathlin Island: fascinating, a bit shallow and we bounced off the bottom there.

#sharing this because it’s a favourite of mine 😍🥰#scotland is so magical#i would really like to visit someday#i loved reading about their favourite spots to visit 🥹#i could listen to their sailing stories all day 🥰#princess anne#princess royal#tim laurence#timothy laurence
39 notes
·
View notes
Note
hi, i hope i am not crossing a line, please ignore if this is bad question. i am just curious
in one of your posts u said your caste is karava. this is the first time i am hearing a sinhalese talk about caste (i speak tamil and never really felt confident in my sinhala to make sinhalese friends)
can you explain about the castes or tell me where find information about it
Caste is a fucked up concept across the board, obviously, but Sinhalese castes are different from Tamil Hindu in that they involve the cultural and socio-political organisation of the Sinhalese community, and has no connection to religious scripture.
There are thirteen castes that still exist today. We used to be a chiefly agrarian society, so the majority of Sinhalese are Govigama ("Govi" means farming) and they're the kind of "bourgeoisie" of the social order in that few are above them and anyone else is below them. Those that rank below them are castes like Bathgama and Kinnara (who are meant to be agricultural labourers) Vahampura (something to do with making cinnamon or treacle) Navadanna (artisans, especially makers of jewelry) and Rada (launderers). Radala is the caste of the nobility, and afaik the only one above Govigama. They're all from highlands of Kandy, the last Sinhalese holdout against the Europeans for about 200 years. There's no nobility among the lowlanders (between the Portuguese, Dutch and British, they were either killed, assimilated or fled to Kandy) so the Govigama caste is the highest one everywhere else. This means Govigama used to be the only one that was qualified to join the Theravada Buddhist priesthood* and also receive education and job opportunities as government servants—right up until the mid-20th century, when the karava gentry turned into robber barons under the British Empire's demand for cash crops.
Karava people are the majority inhabitants in the Southern coastal lands, which are predominantly Sinhalese Buddhist, as opposed to the Tamil lands of the Northern coast (Eelam really) and the proliferation of sparsely-populated Muslim communities in the rest of the coastal belt. Karava is called the fisherfolk caste by the rest of country, despite their own strong objections. Caste is reckoned patrilineally. I'm Karava through my Dad and I married into a Karava family. Nearly every Karava person I know insists that we're actually the warrior caste and were given the coastal lands as reward for our service to the king. I'm sure there's a legitimate case to be made for this, (this site keeps being referred to me) but I don't care enough to find out because the Karava insistence that being called fisherfolk is a Govigama conspiracy is incredibly funny. I mean, it could be true, what do I know, but so much of the cope and seethe stem from our lingering inferiority complex and resentment at having been treated as inferior until a few decades ago. After being ground under the Radala and Govigama feet along with the rest for ages beyond record, suddenly us lowlanders were rolling in money from our toddy, coconut and rubber plantations, matching or surpassing the wealth of the nobility. We were chasing off Tamil and Muslim minorities to establish our own lost cultural capitals in Anuradhapura and Pollonnaruwa that predated the Kandyan kingdom and making our own sect of the Buddhist priesthood (Amarapura Nikaya) that would ordain Karava people. The robber baron types also got very chummy with the British colonial administration and were awarded cushy jobs in government over the Govigama, who still disdained industrialization and commerce. (To this day my mother's family looks down on business people no matter how rich. Merchants are considered grasping and untrustworthy.) By the time of Sri Lanka's independence from the British in 1948, we had two varieties of equally rich, snooty, virulently ethnonationalist Sinhalese elites who had gotten ahead by selling us out to the British, but with the highland Radala still believing they were too pure-blooded to mix with the hoi polloi and the lowland Karava resentful at being considered the polloi no matter how hoi they'd become. Post-independence, Sri Lanka's adoption of free education and free state universities saw masses of lowlanders, Karava, Durava and Salagama all, sending their kids to university to attain upwardly mobile careers in engineering, medicine and teaching. "If the boy is Karava he's probably in engineering" is a common joke. It's a clear shift away from our rural agrarian roots into urban sprawl and high socio-economic competition in place of social stratification.
We also have a caste of Untouchables called the Rodiya. In ancient times, you and all your family being stripped of their lands and titles and banished into the Rodi Rahaya was one of the punishments reserved for the noble houses that ran afoul of the monarchy. It condemned your entire lineage forever. This was such a dire fate that some would have favoured execution.
Rodiyas were not permitted to cross a ferry, to draw water at a well, to enter a village, to till land, or learn a trade, as no recognised caste could deal or hold intercourse with a Rodiya [...] They were forced to subsist on alms or such gifts as they might receive for protecting the fields from wild beasts or burying the carcasses of dead cattle; but they were not allowed to come within a fenced field even to beg [...] They were prohibited from wearing a cloth on their heads, and neither men nor women were allowed to cover their bodies above the waist or below the knee. If benighted they dare not lie down in a shed appropriated to other travellers, but hid themselves in caves or deserted watch-huts. Though nominally Buddhists, they were not allowed to go into a temple, and could only pray "standing afar off"
(Source)
Allegations of witchcraft and cannibalism aside, the Rodiyas themselves were known to be a proud folk that considered themselves the pure-blooded descendants of the royalty that were punished this way. Here's a Reddit post that expounds on them more, along with photographs. It seems that the strictures against covering up had fallen away between the turn of the 20th century and the '70s. Not much is known about their current living conditions, but I believe that, like India's own Untouchables and the low caste of Eelam's Tamil Hindus, they must have converted to Christianity to escape the stigma.
Casteism is still somewhat of a problem in the Sinhalese community, but it's lessening every generation. My maternal grandparents weren't entirely happy about my mother marrying my Karava father but conceded because he was an engineer with a stable career. My older cousin had to fight his Karava family to marry his school sweetheart because she was both poor and Bathgama caste (I think "Padu" might be a derogatory name for it). The fact that he succeeded is noteworthy because it would have been a huge scandal in my parents' time. The Radalas are still a bunch of insular dipshits who try to keel over and die if one of them tries to marry out. But many of them are also migrating abroad so Idk if it's too much to hope that they leave the caste shit behind when they assimilate into Western society. It certainly hasn't worked for the Brahmin Indians. But the outlook is better for the rest of us.
*There is no caste system in Buddhism. The Buddha in fact was an egalitarian social reformer who advocated against the Vedic caste system and ordained Untouchables as well as women. So obviously the Theravadin priesthood of Sri Lanka, that bastion of the Buddha's Word, would make sure that only high caste men could ever be ordained. Love the fact that the Karava social revolution just made sure they had their own sect instead of, y'know, pushing for anything more equitable. I always say that if we really want to protect Buddhism we have to abolish the Sinhalese.
#sri lankan culture#casteism#castes#anthropology#south asia#desi tag#sri lanka#sinhalese#govigama#karava#sinhalese culture#society and culture#knee of huss#asks#anon
42 notes
·
View notes
Text
Interpretation/Analysis of Connections between Lan & Yaoshi


Lan - the Aeon of the Hunt
Symbol has a bow (not upright, facing downwards) & arrows
Looks similar to a centaur (like Sagittarius)
Color scheme consists of black, blue, and purple mainly with hints of pink
Yaoshi - the Aeon of the Abundance
Symbol has stalks of wheat
Looks like what a forest spirit might look like
Color scheme consists of green and yellow mostly
Lan & Yaoshi are considered to be enemies & it’s obvious that they’re meant to be opposites of each other almost like foil characters, but it’s interesting how they both complement each other despite their differences
Lan is a destructive Aeon while Yaoshi is considered to be more peaceful, one is followed by death in their wake while the other is followed by life
By setting up this dynamic, it shows the necessity of having both Aeons existing simultaneously
The concepts they represent help curb the other’s more extreme results (for example, Lan’s hyper focus on their revenge pulls in many others who weren’t involved in the destruction of their homeworld, Lan helps create life in light of their violence; Yaoshi on the other hand is an Aeon that can’t allow death or illness as long as they live, which perpetuates immortality, so hunting is what prevents life from going out of control)
They represent the cycle of life & death, which is well-matched by their icons/symbols
A bow and arrows are one of the most common objects to depict a hunter (funny enough when I first saw the symbol, I thought it was supposed to be a deer with antlers but it was only until I noticed the arrows that are more faded in the background that their symbol is actually supposed to be a horizontal bow & arrows 😂 although it’s not supposed to be a deer, it is still good to note that deer are often associated with hunts w/ them being the victims rather than the hunters)
The stalks of wheat that make up Yaoshi’s symbol are often a sign of fertility since grains have been a source of food for many civilizations (farming/agriculture was important for starting out, eventually small groups of people would become civilizations); they can also at times represent resurrection/rebirth since they can grow back as long as there is suitable soil present
Considering the two symbols together, the bow & arrows and the ears of wheat are crucial to the identities that Lan & Yaoshi encompass to the point that they appear in the respective Aeons’ splash art (Lan wields their bow, Yaoshi holds wheat in one of their hands w/ a ring of wheat behind their head); they’re very fitting icons since they’re ancient as well (bows & arrows are one of the oldest forms of weaponry in history, wheat [& grains in general] has been one of the most important sources of food over the course of history)
Another thing to note is the difference between their color themes
Lan’s design utilizes blue & purple which makes them look like they have a nightly aura
Yaoshi’s design uses vibrant green & yellow which makes them look as if they’re part of forests
Now this is just more my own overanalysis but I feel that their color schemes help to establish a connection that presents Lan as the heavens & stars to Yaoshi’s earth
****I didn’t really mean that in shipping terms but I honestly can see it 😂
I love their designs a lot which is why I wanted to look further into their relationship & then I somehow got ideas along the way & fell into a bit of a rabbit hole 😂
****I feel like this thread isn’t finished, I might have to come back to this later; for one thing we’re still in the beginning stages of the game so there’s a lot more that can happen in the future which im very excited for, so I guess this is essentially a WIP (technically I guess all my lore threads are WIPs until the games are done pumping out info about the related topics)
Anyways have my first HSR lore thread ehe
134 notes
·
View notes